Deployment of IGRP/EIGRP
|
|
|
- Debra Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 eployment of IGRP/EIGRP Session 2 Presentation_I.scr 1
2 Understanding EIGRP Understanding and deploying EIGRP is like driving a car 3 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP Interaction Query Process eployment Guidelines with EIGRP Summary 4 Presentation_I.scr 2
3 IGRP: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol isco proprietary istance vector roadcast based Utilizes link bandwidth and delay 15 hops is no longer the limit 90 seconds updates (RIP is 30 sec.) Load balance over unequal cost paths 5 IGRP Metrics alculation Metric = [K1 x W + (K2 x W) / (256 - Load) + K3 x elay] x [K5 / (Reliability + K4)] y efault: K1 = 1, K2 = 0, K3 = 1, K4 = K5 = 0 elay is sum of all the delays of the link along the paths elay = elay/10 andwidth is the lowest bandwidth of the link along the paths andwidth = /andwidth 6 Presentation_I.scr 3
4 Problems with RIP and IGRP Slow convergence Not 100% loop free on t support VLSM and discontiguous network Periodic full routing updates RIP has hop count limitation 7 dvantages of EIGRP dvanced distance vector 100% loop free Fast convergence Easy configuration Less network design constraints than OSPF Incremental update Supports VLSM and discontiguous network lassless routing ompatible with existing IGRP network Protocol independent (support IPX and appletalk) 8 Presentation_I.scr 4
5 dvantages of EIGRP Uses multicast instead of broadcast Utilize link bandwidth and delay EIGRP Metric = IGRP Metric x 256 (32 bit Vs. 24 bit) Unequal cost paths load balancing More flexible than OSPF Full support of distribute list Manual summarization can be done in any interface at any router within network 9 EIGRP Packets Hello: Establish neighbor relationships Update: Send routing updates Query: sk neighbors about routing information Reply: Response to query about routing information ck: cknowledgement of a reliable packet 10 Presentation_I.scr 5
6 EIGRP Neighbor Relationship Two routers become neighbors when they see each other s hello packet Hello address = Hellos sent once every five seconds on the following links: roadcast Media: Ethernet, Token Ring, fddi, etc. Point-to-point serial links: PPP, HL, point-topoint frame relay/tm subinterfaces Multipoint circuits with bandwidth greater than T1: ISN PRI, SMS, Frame Relay 11 EIGRP Neighbor Relationship Hellos sent once every 60 seconds on the following links: Multipoint circuits with bandwidth less than T1: ISN RI, Frame Relay, SMS, etc. Neighbor declared dead when no EIGRP packets are received within hold interval Not only Hello can reset the hold timer Hold time by default is three times the hello time 12 Presentation_I.scr 6
7 EIGRP Neighbor Relationship EIGRP will form neighbors even though hello time and hold time don t match EIGRP sources hello packets from primary address of the interface EIGRP will not form neighbor if K-values are mismatched EIGRP will not form neighbor if S numbers are mismatched Passive interface (IGRP vs. EIGRP) 13 iscovering Routes 1 afadjfjorqpoeru Hello I am Router, Who Is on the Link? 14 Presentation_I.scr 7
8 iscovering Routes 1 afadjfjorqpoeru Hello I am Router, Who Is on the Link? Here Is My Routing Information (Unicast) 2 Update afadjfjorqpoeru iscovering Routes 1 afadjfjorqpoeru Hello I am Router, Who Is on the Link? Here Is My Routing Information (Unicast) 2 Update afadjfjorqpoeru afadjfjorqpoeru ck Thanks for the Information! 16 Presentation_I.scr 8
9 afadjfjorqpoeru iscovering Routes 1 afadjfjorqpoeru Hello I am Router, Who Is on the Link? Here Is My Routing Information (Unicast) 2 Update afadjfjorqpoeru Topology Table 3 afadjfjorqpoeru ck Thanks for the Information! 17 iscovering Routes 1 afadjfjorqpoeru Hello I am Router, Who Is on the Link? Here Is My Routing Information (Unicast) 2 Update afadjfjorqpoeru Thanks for the Information! ck Topology Table 5 Here Is My Route Information (Unicast) Update afadjfjorqpoeru Presentation_I.scr 9
10 afadjfjorqpoeru afadjfjorqpoeru iscovering Routes 1 afadjfjorqpoeru Hello I am Router, Who Is on the Link? Here Is My Routing Information (Unicast) 2 Update afadjfjorqpoeru Topology Table 3 5 afadjfjorqpoeru ck Thanks for the Information! Here Is My Route Information (Unicast) Update Thanks for the Information! onverged ck 6 19 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP Interaction Query Process eployment Guidelines with EIGRP Summary 20 Presentation_I.scr 10
11 EIGRP UL iffusing update algorithm Finite-State-Machine Track all routes advertised by neighbors Select loop-free path using a successor and remember any feasible successors If successor lost Use feasible successor If no feasible successor Query neighbors and recompute new successor 21 EIGRP Feasible istance (F) Feasible distance is the minimum distance (metric) along a path to a destination network 22 Presentation_I.scr 11
12 Feasible istance Example (100) H Network 7 (20) (10) G (100) (100) (100) FI E (20) F (10) Topology Table estination 7 7 Feasible istance (F) = =121 Neighbor H = EIGRP Reported istance (R) Reported distance is the distance (metric) towards a destination as advertised by an upstream neighbor Reported distance is the distance reported in the queries, the replies and the updates 24 Presentation_I.scr 12
13 Reported istance Example Network 7 (100) (100) (100) H (20) FI G (10) (100) E (20) F (10) Topology Table estination 7 7 Reported istance (R) 20+10= =21 Neighbor H = EIGRP Feasibility ondition (F) neighbor meets the feasibility condition (F) if the reported distance by the neighbor is smaller than the feasible distance (F) of this router 26 Presentation_I.scr 13
14 EIGRP Successor successor is a neighbor that has met the feasibility condition and has the least cost path towards the destination It is the next hop for forwarding packets Multiple successors are possible (load balancing) 27 EIGRP Feasible Successor (FS) feasible successor is a neighbor whose reported distance (R) is less than the feasible distance (F) 28 Presentation_I.scr 14
15 Successor Example Topology Table is current successor (F = 121) estination (100) (100) (100) H (100) F FI E (20) (20) R Neighbor Router s Routing Table H is the feasible successor (30 < 121) F Network 7 H G (10) (10) 29 Passive, ctive, and Stuck in ctive (SI) Passive routes are routes that have successor information Passive route = Good ctive routes are routes that have lost their successors and no feasible successors are available. The router is actively looking for alternative paths ctive route = ad Stuck in ctive means the neighbor still has not replied to the original query within three minutes Stuck in active = Ugly 30 Presentation_I.scr 15
16 ual lgorithm Local computation When a route is no longer available via the current successor, the router checks its topology table Router can switch from successor to feasible successor without involving other routers in the computation Router stays passive Updates are sent 31 UL: Local omputation #1 (10) #7 121/21 #7 130/30 H H #2 X (100) #8 (20) #3 FI #4 E #5 (100) (20) F (10) #6 (10) G #7 32 Presentation_I.scr 16
17 ual lgorithm iffused omputation When a route is no longer available via its current successor and no feasible successor is available, queries are sent out to neighbors asking about the lost route The route is said to be in active state Neighbors reply to the query if they have information about the lost route. If not, queries are sent out to all of their neighbors. The router sending out the query waits for all of the replies from its neighbors and will make routing decision based on the replies 33 UL: iffused omputation #1 (10) #7 121/21 #7 130/30 H H #2 X X (100) #8 (20) #3 FI #4 E #5 (100) (20) F (10) #6 (10) G #7 34 Presentation_I.scr 17
18 UL Example (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via ost (4/2) (fs) via E ost (4/3) X (a) ost (2) (fd) via ost (2/1) (Successor) via ost (5/3) (2) (2) E E (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/2) (Successor) via ost (4/3) 35 UL Example (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via via E ost (4/3) (a) **TIVE** ost (-1) (fd) via E (q) via ost (5/3) (q) (2) (2) Q Q E E (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/2) (Successor) via ost (4/3) 36 Presentation_I.scr 18
19 UL Example (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via via E (a) **TIVE** ost (-1) (fd) via E (q) via ost (5/3) (2) Q (2) R E E (a) **TIVE** ost (-1) (fd) via via ost (4/3) (q) 37 UL Example (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via via E (a) **TIVE** ost (-1) (fd) via E (q) via ost (5/3) (2) (2) R E E (a) ost (4) (fd) via ost (4/3) (Successor) via 38 Presentation_I.scr 19
20 UL Example (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via via E (2) (2) R E (a) ost (5) (fd) via ost (5/3) (Successor) via E ost (5/4) (Successor) E (a) ost (4) (fd) via ost (4/3) (Successor) via 39 UL Example (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via via E (a) ost (5) (fd) via ost (5/3) (Successor) via E ost (5/4) (Successor) (2) (2) E E (a) ost (4) (fd) via ost (4/3) (Successor) via 40 Presentation_I.scr 20
21 UL Example (Start) (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via ost (4/2) (fs) via E ost (4/3) (a) ost (2) (fd) via ost (2/1) (Successor) via ost (5/3) (2) (2) E E (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/2) (Successor) via ost (4/3) 41 UL Example (End) (a) (a) ost (3) (fd) via ost (3/1) (Successor) via via E (a) ost (5) (fd) via ost (5/3) (Successor) via E ost (5/4) (Successor) (2) (2) E E (a) ost (4) (fd) via ost (4/3) (Successor) via 42 Presentation_I.scr 21
22 EIGRP Reliable Transport Protocol EIGRP reliable packets are packets that requires explicit acknowledgement: Update Query Reply EIGRP unreliable packets are packets that do not require explicit acknowledgement: Hello ck 43 EIGRP Reliable Transport Protocol The router keeps a neighbor list and a retransmission list for every neighbor Each reliable packet (Update, Query, Reply) will be retransmitted when packet is not acked EIGRP transport has window size of one (stop and wait mechanism) Every single reliable packet needs to be acknowledged before the next sequenced packet can be sent 44 Presentation_I.scr 22
23 EIGRP Reliable Transport Protocol With reliable multicast traffic, one must wait to transmit the next reliable multicast packets, until all peers have acknowledged the previous multicast If one or more peers are slow in acknowledging, all other peers suffer from this Solution: The nonacknowledged multicast packet will be retransmitted as a unicast to the slow neighbor 45 EIGRP Reliable Transport Protocol Per neighbor, retransmission limit is 16 Neighbor relationship is reset when retry limit (limit = 16) for reliable packets is reached 46 Presentation_I.scr 23
24 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP Interaction Query Process eployment Guidelines with EIGRP Summary 47 EIGRP Summarization Purpose: Smaller routing tables, smaller updates, query boundary uto summarization: On major network boundaries, networks are summarized to the major networks uto summarization is turned on by default X.X X.X X.X 48 Presentation_I.scr 24
25 EIGRP Summarization Manual summarization onfigurable on per interface basis in any router within network When summarization is configured on an interface, the router immediate creates a route pointing to null zero with administrative distance of five Loop prevention mechanism When the last specific route of the summary goes away, the summary is deleted The minimum metric of the specific routes is used as the metric of the summary route 49 EIGRP Summarization Manual summarization command: ip summary-address eigrp <as number> <address> <mask> /16 S / /16 S0 interface s0 ip address ip summary-address eigrp Presentation_I.scr 25
26 EIGRP Load alancing Routes with equal metric to the minimum metric, will be installed in the routing table (Equal ost Load alancing) There can be up to six entries in the routing table for the same destination (default = 4) ip maximum-paths <1-6> 51 EIGRP Unequal ost Load alancing EIGRP offers unequal cost load balancing feature with the command: Variance <multiplier> Variance command will allow the router to include routes with a metric smaller than multiplier times the minimum metric route for that destination, where multiplier is the number specified by the variance command 52 Presentation_I.scr 26
27 Variance Example E Variance Net X Router E will choose router to get to net X F=20 With variance of 2, router E will also choose router to get to net X Router will not be used to get to net X 53 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP Interaction Query Process eployment Guidelines with EIGRP Summary 54 Presentation_I.scr 27
28 EIGRP and IGRP Interaction dministrative distance vs. routing metrics dministrative distance is used to compare with routes coming from two different routing protocols onnected = 0 Static route = 1 EIGRP summary route = 5 EGP = 20 Internal EIGRP = 90 IGRP = 100 OSPF = 110 RIP = 120 External EIGRP = 170 IGP = EIGRP and IGRP Interaction Metric is used to compare routes coming from the same routing protocol RIP = Hop count EIGRP/IGRP = andwidth and delay OSPF = Link cost 56 Presentation_I.scr 28
29 EIGRP and IGRP Interaction External vs. Internal EIGRP External EIGRP: ny routes being redistributed into an EIGRP process from another routing protocol or EIGRP process is considered as external EIGRP routes dministrative distance = 170 Internal EIGRP: ny routes that originated from its own EIGRP process is considered as internal EIGRP routes dministrative distance = EIGRP and IGRP Interaction To make EIGRP compatible with existing IGRP network with minimum interruption, EIGRP and IGRP with the same process number will be automatically redistributed into each other 58 Presentation_I.scr 29
30 EIGRP and IGRP Interaction Rules for IGRP/EIGRP interaction to avoid routing loops: Internal EIGRP routes preferred over IGRP routes dministrative distance considered (90 vs. 100) External EIGRP routes preferred over IGRP routes on same S number and same scaled route metric dministrative distance not considered 59 EIGRP/IGRP Example IGRP 2 EIGRP 1 FR FR External EIGRP Net X External External EIGRP EIGRP Net Net X External Net X Network X is external EIGRP route Router forwards external EIGRP routes to router and 60 Presentation_I.scr 30
31 EIGRP/IGRP Example (ifferent S) IGRP 2 IGRP Net X FR FR IGRP Net X EIGRP 1 External EIGRP Net X External External EIGRP EIGRP Net Net X External Net X Router and sends IGRP route to router Router sends IGRP network X route back to Router and Router and will choose IGRP route because of lower dministrative distance Result: Router and will take the wrong route to Net X 61 EIGRP/IGRP Example (Same S) IGRP 1 IGRP Net X FR FR IGRP Net X EIGRP 1 External EIGRP Net X External External EIGRP EIGRP Net Net X External Net X Router and will not take administrative distance as decision process if EIGRP and IGRP has the same S Router and still favors external EIGRP routes from router Result: Router and will take correct route to Net X 62 Presentation_I.scr 31
32 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP Interaction Query Process eployment Guidelines with EIGRP Summary 63 EIGRP Query Process EIGRP is dvanced istant Vector. It relies on its neighbor to provide routing information Have You Seen My Sparky? If a route is lost and no feasible successor is available, EIGRP needs to converge fast, its only mechanism for fast convergence is to actively query for the lost route to its neighbors 64 Presentation_I.scr 32
33 EIGRP Query Process Queries are sent out when a route is lost and no feasible successor is available The lost route is now in active state Queries are sent out to all of its neighbors on all interfaces except the interface to the successor If the neighbor does not have the lost route information, queries are sent out to their neighbors 65 EIGRP Query Process The router will have to get LL of the replies from the neighbors before the router calculates the successor information If any neighbor fails to reply the query in three minutes, this route is stuck in active and the router reset the neighbor that fails to reply Solution is to limit query range to be covered later in presentation 66 Presentation_I.scr 33
34 EIGRP Query Range utonomous System oundaries ontrary to popular belief, queries are not bounded by S boundaries. Queries from S 1 will be propagated to S 2 S 2 S 1 X Network X Query for X Reply for X Query for X 67 EIGRP Query Range Summarization point uto or manual summarization is the best way to bound queries Requires a good address allocation scheme 129.x.x.x Reply with Infinity and the Query Stops Here! Summarizes /8 to Query for /24 Query for /24 X / x.x.x 68 Presentation_I.scr 34
35 EIGRP andwidth Utilization EIGRP by default will use up to 50% of the link bandwidth for EIGRP packets This parameter is manually configurable by using the command: ip bandwidth-percent eigrp <S-number> <nnn> Use for greater EIGRP load control 69 andwidth over WN Interfaces andwidth utilization over point-topoint subinterface Frame Relay Treats bandwidth as T1 by default est practice is to manually configure bandwidth as the IR of the PV 70 Presentation_I.scr 35
36 andwidth over WN Interfaces andwidth over multipoint Frame Relay, TM, SMS, and ISN PRI: EIGRP uses the bandwidth on the main interface divided by the number of neighbors on that interface to get the bandwidth information per neighbor 71 andwidth over WN Interfaces Each PV might have different IR, this might create EIGRP packet pacing problem Multipoint interfaces: onvert to point-to-point andwidth configured = (lowest IR x number of PV) ISN PRI: Use ialer Profile (treat as point-to-point link) 72 Presentation_I.scr 36
37 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP Interaction Query Process eployment Guidelines with EIGRP Summary 73 Factors That Influence EIGRP Scalability Keep in mind that EIGRP is not plug and play for large networks Limit EIGRP query range! Quantity of routing information exchanged between peers 74 Presentation_I.scr 37
38 Limiting Updates/Queries Example istribution Layer Remote Sites /24 RTR RTR RTR RTR RTRE 75 Limiting Size/Scope of Updates/Queries Evaluate routing requirements What routes are needed where? Once needs are determined Use summary address Use distribute lists 76 Presentation_I.scr 38
39 Limiting Updates/Queries Example Queries Replies istribution Layer X /24 Remote Sites RTR RTR RTR RTR RTRE 77 Limiting Updates/Queries Summary Remote routers fully involved in convergence Most remotes are never intended to be transit onvergence complicated through lack of information hiding 78 Presentation_I.scr 39
40 Limiting Updates/Queries etter Queries Replies istribution Layer X /24 Remote Sites RTR RTR RTR RTR IP summary-address eigrp on all outbound interfaces to remotes RTRE 79 Limiting Updates/Queries Summary onvergence simplified by adding the summary-address statements Remote routers just reply when queried 80 Presentation_I.scr 40
41 Hierarchy/ddressing Permits maximum information hiding dvertise major net or default route to regions or remotes Provides adequate redundancy 81 EIGRP Scalability EIGRP is a very scalable routing protocol if proper design methods are used: Good allocation of address space Each region should have an unique address space so route summarization is possible Have a tiered network design model (ore, istribution, ccess) 82 Presentation_I.scr 41
42 EIGRP Scalability Proper network resources Sufficient memory on the router Sufficient bandwidth on WN interfaces Proper configuration of the bandwidth statement over WN interfaces, especially over Frame Relay void blind mutual redistribution between two routing protocols or two EIGRP processes 83 Tiered Network esign Summarized Routes Other Regions Other Regions Summarized Routes istribution Layer ore Summarized Routes Other Regions Summarized Routes Other Regions Summarized Routes Summarized Routes ccess Layer 84 Presentation_I.scr 42
43 Nonscalable Network ore Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring ad addressing scheme Subnets are everywhere throughout entire network Queries not bounded 85 Scalable Network ore Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring Token Ring Readdress network Each region has its own block of address Queries bounded by using ip summary-address eigrp command Token Ring 86 Presentation_I.scr 43
44 Summary Query range est way to limit query is through route summarization EIGRP is not plug and play for large networks It s a very scalable protocol with little design requirement Optimizing EIGRP network Limiting query range Route summarization Tiered network design Sufficient network resources 87 Please omplete Your Evaluation Form Session 88 Presentation_I.scr 44
45 89 Presentation_I.scr 45
Configuring EIGRP. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc.
 Configuring EIGRP 4-1 EIGRP Overview 4-2 What Is EIGRP? IPX Routing Protocols IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol Enhanced IGRP IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol IPX Routing Protocols
Configuring EIGRP 4-1 EIGRP Overview 4-2 What Is EIGRP? IPX Routing Protocols IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol Enhanced IGRP IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol IPX Routing Protocols
Section 6. Implementing EIGRP ICND2
 ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
Table of Contents. Cisco Introduction to EIGRP
 Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Routing Fundamentals. What Is Routing? Routing Information. Routing Requirements. Most of the necessary information is contained in the routing table
 Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two
Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
EIGRP Deployment BRKRST , Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Presentation_ID.scr
 EIGRP Deployment 2008 isco Systems, Inc. ll rights reserved. isco Public 2 1 EIGRP EIGRP Operation Topologies and Techniques Managing EIGRP 2008 isco Systems, Inc. ll rights reserved. isco Public 3 EIGRP
EIGRP Deployment 2008 isco Systems, Inc. ll rights reserved. isco Public 2 1 EIGRP EIGRP Operation Topologies and Techniques Managing EIGRP 2008 isco Systems, Inc. ll rights reserved. isco Public 3 EIGRP
Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP
 Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 5.2 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License
Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 5.2 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License
Enhanced IGRP. Chapter Goals. Enhanced IGRP Capabilities and Attributes CHAPTER
 40 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Identify the four key technologies employed by (EIGRP). Understand the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL), and describe how it improves the operational efficiency of EIGRP. Learn
40 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Identify the four key technologies employed by (EIGRP). Understand the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL), and describe how it improves the operational efficiency of EIGRP. Learn
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) http:// What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) http:// What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7
 EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
ITE PC v4.0. Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 1 Objectives Describe the background and history of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). Examine the basic EIGRP configuration commands and
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 1 Objectives Describe the background and history of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). Examine the basic EIGRP configuration commands and
Chapter 2: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 : Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
EIGRP 04/01/2008. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
EIGRP. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9. Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech
 Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
F. Configure a distribute-list on router RTA that allows it to advertise all routes to the spoke routers.
 Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC
Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks
 Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 : The Routing Table: A Closer Look Chapter 9 : EIGRP Chapter
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 : The Routing Table: A Closer Look Chapter 9 : EIGRP Chapter
Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]
![Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]](/thumbs/78/78661506.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
CHAPTER 4: ROUTING DYNAMIC. Routing & Switching
 CHAPTER 4: ROUTING DYNAMIC Routing & Switching CHAPTER4 4.1 Dynamic Routing Protocols 4.2 Distance Vector Dynamic Routing 4.3 RIP and RIPng Routing 4.4 Link-State Dynamic Routing 4.5 The Routing Table
CHAPTER 4: ROUTING DYNAMIC Routing & Switching CHAPTER4 4.1 Dynamic Routing Protocols 4.2 Distance Vector Dynamic Routing 4.3 RIP and RIPng Routing 4.4 Link-State Dynamic Routing 4.5 The Routing Table
Chapter 9. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I
 Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Configuring IP Routing Protocols
 C H A P T E R 1 8 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this
C H A P T E R 1 8 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this
Configuring IP Routing Protocols
 CHAPTER 18 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter,
CHAPTER 18 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter,
Part II. Chapter 3. Determining IP Routes
 Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
Introduction to Routing
 1 Introduction to Routing Session 2 Presentation_ID.scr 1 Agenda Addressing Concepts Routing Protocols Statics and Defaults 3 ISO OSI Reference Model Routing Information Protocol (RIP and RIPv2) L7 L6
1 Introduction to Routing Session 2 Presentation_ID.scr 1 Agenda Addressing Concepts Routing Protocols Statics and Defaults 3 ISO OSI Reference Model Routing Information Protocol (RIP and RIPv2) L7 L6
Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically Routing & Switching The Evolution of Dynamic Routing Protocols Dynamic routing protocols used in networks since the late 1980s Newer versions support the communication based
Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically Routing & Switching The Evolution of Dynamic Routing Protocols Dynamic routing protocols used in networks since the late 1980s Newer versions support the communication based
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
Configuration and Management of Networks
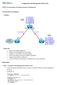 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
Configuring EIGRP. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
EIGRP. About EIGRP. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.7 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
Implementing cisco ip routing
 Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Configuring IP Routing Protocols
 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter, refer to
Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various Internet Protocol (IP) routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter, refer to
Exam : : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Title. Ver :
 Exam : 642-801 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver : 03-22-05 QUESTION 1 A packet that needs to be forwarded arrives on an interface of a router. In order for a router to route data,
Exam : 642-801 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver : 03-22-05 QUESTION 1 A packet that needs to be forwarded arrives on an interface of a router. In order for a router to route data,
NAT Internetworking Standards and Technologies, Computer Engineering, KMITL 2
 EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
Configuring IP Routing Protocols
 C H A P T E R 1 6 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various IP routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter, refer to
C H A P T E R 1 6 Configuring IP Routing Protocols This chapter describes how to configure the various IP routing protocols. For a complete description of the commands listed in this chapter, refer to
Exam Code : Version: Free Demo. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!
 Vendor : Cisco Exam Code : 642-832 Version: Free Demo IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way Cheat-Test.us - The Worldwide Renowned IT Certification Material Provider The safer, easier way to help you
Vendor : Cisco Exam Code : 642-832 Version: Free Demo IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way Cheat-Test.us - The Worldwide Renowned IT Certification Material Provider The safer, easier way to help you
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols V 4.0 RIP, IGRP, EIGRP
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols V 4.0 4.1.1 What are the three distance vector routing protocols? What are the key characteristics of RIP? What are the key characteristics of IGRP?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols V 4.0 4.1.1 What are the three distance vector routing protocols? What are the key characteristics of RIP? What are the key characteristics of IGRP?
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Volume 2 Version 1.0 Student Guide Editorial, Production, and Web Services (EPWS): 07.25.07 DISCLAIMER WARRANTY: THIS CONTENT IS BEING PROVIDED AS
ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Volume 2 Version 1.0 Student Guide Editorial, Production, and Web Services (EPWS): 07.25.07 DISCLAIMER WARRANTY: THIS CONTENT IS BEING PROVIDED AS
Configuring IGRP. The Cisco IGRP Implementation
 Configuring IGRP This chapter describes how to configure the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP). For a complete description of the IGRP commands in this chapter, refer to the IGRP s chapter of the
Configuring IGRP This chapter describes how to configure the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP). For a complete description of the IGRP commands in this chapter, refer to the IGRP s chapter of the
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols
 Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Configuring OSPF in a single area. OSPF overview. Overview. Objectives. To understand how the OSPF protocol works
 Overview onfiguring OSPF in a single area Objectives Terminologies Different topology roadcast multi-access topology Point-to-point topology NM topology Written exercise: OSPF operation onfiguring OSPF
Overview onfiguring OSPF in a single area Objectives Terminologies Different topology roadcast multi-access topology Point-to-point topology NM topology Written exercise: OSPF operation onfiguring OSPF
Distance Vector Routing Protocols
 Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Identify the characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. Describe the network discovery process
Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Identify the characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. Describe the network discovery process
CS 457 Networking and the Internet. Shortest-Path Problem. Dijkstra s Shortest-Path Algorithm 9/29/16. Fall 2016
 9/9/6 S 7 Networking and the Internet Fall 06 Shortest-Path Problem Given: network topology with link costs c(x,y): link cost from node x to node y Infinity if x and y are not direct neighbors ompute:
9/9/6 S 7 Networking and the Internet Fall 06 Shortest-Path Problem Given: network topology with link costs c(x,y): link cost from node x to node y Infinity if x and y are not direct neighbors ompute:
Configuring EIGRP. Finding Feature Information
 The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an enhanced version of the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) developed by Cisco. The convergence properties and the operating efficiency
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an enhanced version of the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) developed by Cisco. The convergence properties and the operating efficiency
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
What Does the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA Error Message Mean?
 What Does the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA Error Message Mean? Document ID: 13676 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information What Causes the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA
What Does the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA Error Message Mean? Document ID: 13676 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information What Causes the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA
LAB15: EIGRP IPv4. LAB 15: Diagram. Disclaimer
 AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
Routing Protocol. RIPv1
 Outline Routing Protocol RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP OSPF o RIPv1, RIPv2 o EIGRP o OSPF 2 3 RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric = hop count Routes with a hop count
Outline Routing Protocol RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP OSPF o RIPv1, RIPv2 o EIGRP o OSPF 2 3 RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric = hop count Routes with a hop count
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
shortcut Tap into learning NOW! Visit for a complete list of Short Cuts. Your Short Cut to Knowledge
 shortcut Your Short Cut to Knowledge The following is an excerpt from a Short Cut published by one of the Pearson Education imprints. Short Cuts are short, concise, PDF documents designed specifically
shortcut Your Short Cut to Knowledge The following is an excerpt from a Short Cut published by one of the Pearson Education imprints. Short Cuts are short, concise, PDF documents designed specifically
EXAM Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Routing Protocols Classification
 Routing Protocols Classification Petr Grygárek rek 1 Classification criteria Internal (IGP) / External (EGP) number of handled routes possibilities of routing politics specification Convergence Time Distance-vector
Routing Protocols Classification Petr Grygárek rek 1 Classification criteria Internal (IGP) / External (EGP) number of handled routes possibilities of routing politics specification Convergence Time Distance-vector
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
ABR (Area Border Router), 206, 216 access, dedicated networks, 23 access layer, three-layer hierarchical design model, 6
 1358_fmi.book Page 460 Thursday, May 27, 2004 2:21 PM A ABR (Area Border Router), 206, 216 access, dedicated networks, 23 access layer, three-layer hierarchical design model, 6 access lists, scalable networks,
1358_fmi.book Page 460 Thursday, May 27, 2004 2:21 PM A ABR (Area Border Router), 206, 216 access, dedicated networks, 23 access layer, three-layer hierarchical design model, 6 access lists, scalable networks,
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP
 Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Designing Large-Scale IP Internetworks
 CHAPTER 3 Designing Large-Scale IP Internetworks This chapter focuses on the following design implications of the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocols,
CHAPTER 3 Designing Large-Scale IP Internetworks This chapter focuses on the following design implications of the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocols,
CCNP IPSOFTWARE EIGRP ROUTE Lab Manual.
 Lab Manual CCNP ROUTE 300-101 EIGRP Lab - 1 : EIGRP-Basic Configuration Lab - 2 : EIGRP-Metric and Variance Load Sharing Lab - 3 : EIGRP-Summarization Lab - 4 : EIGRP-Query Control Lab - 5 : EIGRP-Authentication
Lab Manual CCNP ROUTE 300-101 EIGRP Lab - 1 : EIGRP-Basic Configuration Lab - 2 : EIGRP-Metric and Variance Load Sharing Lab - 3 : EIGRP-Summarization Lab - 4 : EIGRP-Query Control Lab - 5 : EIGRP-Authentication
Claim desired outcome
 Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 3 & 17: Enhanced IGRP
 CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 3 & 17: Enhanced IGRP Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 19 objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: IP Routing Technologies Differentiate
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 3 & 17: Enhanced IGRP Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 19 objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: IP Routing Technologies Differentiate
CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com)
 CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com) Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 90 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 642-902 ROUTE Exam Topics Exam Description The Implementing
CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com) Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 90 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 642-902 ROUTE Exam Topics Exam Description The Implementing
LAB1: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Allows IGRP or Enhanced IGRP exterior routes to be advertised in updates.
 IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Internet Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP). For IGRP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IGRP chapter
IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Internet Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP). For IGRP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IGRP chapter
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks
 Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 : Distance Vector Routing Protocols Chapter 5 : RIP version 1
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 : Distance Vector Routing Protocols Chapter 5 : RIP version 1
Initial Configurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link
 Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
LAB16: Named EIGRP IPv4
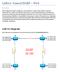 AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Chapter 3. Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols. CCNA2-1 Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-2 Chapter 3 Perspective and Background Dynamic
Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-2 Chapter 3 Perspective and Background Dynamic
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting. IPv4 Routing Workflow. IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing
 Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Understanding IPX EIGRP
 Understanding IPX EIGRP Document ID: 10579 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Information EIGRP Components IPX EIGRP Features IPX EIGRP Internetworking
Understanding IPX EIGRP Document ID: 10579 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Information EIGRP Components IPX EIGRP Features IPX EIGRP Internetworking
Chapter 1 The IP Routing Protocols
 Chapter 1 The IP Routing Protocols 1 This chapter describes routing protocol options for the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. The chapter Routing IP contains all the information you need for configuring IP.
Chapter 1 The IP Routing Protocols 1 This chapter describes routing protocol options for the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. The chapter Routing IP contains all the information you need for configuring IP.
EECS 122, Lecture 16. Link Costs and Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Static Cost Metrics.
 EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
Chapter 5 RIP version 1
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
EIGRP An In-Depth Look At The Protocol
 EIGRP n In-Depth Look t The Protocol RKIPM-2444 Donnie Savage Donald Slice 2 The History and Evolution of EIGRP EIGRP introduction and Feature Roadmap 1990 1993 DUL published to IEEE/CM 1993 EIGRP Shipped
EIGRP n In-Depth Look t The Protocol RKIPM-2444 Donnie Savage Donald Slice 2 The History and Evolution of EIGRP EIGRP introduction and Feature Roadmap 1990 1993 DUL published to IEEE/CM 1993 EIGRP Shipped
EIGRP Features and Operation
 EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name Score Grade Question Answer Question Answer
 CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
Unit 3. EIGRP, Troubleshooting and VoIP
 nit 3 GRP, roubleshooting and VoP VoP elephony ses digitized voice streamed over the internet instead of traditional telephone company lines Requires either a special phone or an adapter for your existing
nit 3 GRP, roubleshooting and VoP VoP elephony ses digitized voice streamed over the internet instead of traditional telephone company lines Requires either a special phone or an adapter for your existing
RIP Version 2. The Classless Brother
 RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
RIP Configuration. RIP Overview. Operation of RIP. Introduction. RIP routing table. RIP timers
 Table of Contents RIP Configuration 1 RIP Overview 1 Operation of RIP 1 Operation of RIP 2 RIP Version 2 RIP Message Format 3 Protocols and Standards 4 Configuring RIP Basic Functions 5 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents RIP Configuration 1 RIP Overview 1 Operation of RIP 1 Operation of RIP 2 RIP Version 2 RIP Message Format 3 Protocols and Standards 4 Configuring RIP Basic Functions 5 Configuration Prerequisites
IP addressing. Overview. IP addressing Issues and solution Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM)
 Overview IP addressing IP addressing Issues and solution Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Written exercise : VLSM calculation Summarisation of routes Classless InterDomain routing (CIDR) Internet registry
Overview IP addressing IP addressing Issues and solution Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Written exercise : VLSM calculation Summarisation of routes Classless InterDomain routing (CIDR) Internet registry
LAB2: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ]
![Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ] Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ]](/thumbs/78/78661316.jpg) Topology & EIGRP Invocation Router-ID is in the EIGRP block Interfaces included at each interface Passive interfaces designated in the EIGRP block The EIGRP block may require a no shutdown R5 ipv6 unicast-routing
Topology & EIGRP Invocation Router-ID is in the EIGRP block Interfaces included at each interface Passive interfaces designated in the EIGRP block The EIGRP block may require a no shutdown R5 ipv6 unicast-routing
Chapter 4: Manipulating Routing
 : Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
: Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
904 ASBRs (Autonomous System Boundary Routers)
 I N D E X A ABRs (Area Border Routers), 292 LSA propagation, 294 Access layer, hierarchical designs, 42 access lists. See also IP access lists BGP-4, 557 controlling terminal access, 51 52 guidelines for
I N D E X A ABRs (Area Border Routers), 292 LSA propagation, 294 Access layer, hierarchical designs, 42 access lists. See also IP access lists BGP-4, 557 controlling terminal access, 51 52 guidelines for
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
Routing, Routing Algorithms & Protocols
 Routing, Routing Algorithms & Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 6 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Circuit-Switched and Packet-Switched WANs 2 Circuit-Switched Networks Older (evolved from telephone networks), a
Routing, Routing Algorithms & Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 6 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Circuit-Switched and Packet-Switched WANs 2 Circuit-Switched Networks Older (evolved from telephone networks), a
Why dynamic route? (1)
 Routing Why dynamic route? (1) Static route is ok only when Network is small There is a single connection point to other network No redundant route 2 Why dynamic route? (2) Dynamic Routing Routers update
Routing Why dynamic route? (1) Static route is ok only when Network is small There is a single connection point to other network No redundant route 2 Why dynamic route? (2) Dynamic Routing Routers update
CCNA IP ROUTING. Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03
 CCNA 640-801 IP ROUTING Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 Routing Basics The term routing is used for taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network.
CCNA 640-801 IP ROUTING Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 Routing Basics The term routing is used for taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network.
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Introduction. Lab Diagram
 Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see a.
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Implementing an EIGRP Solution
 Chapter 3 Implementing an EIGRP Solution This chapter contains the following sections: Dynamic Routing Review EIGRP Features and Function Troubleshooting EIGRP Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 Chapter Summary
Chapter 3 Implementing an EIGRP Solution This chapter contains the following sections: Dynamic Routing Review EIGRP Features and Function Troubleshooting EIGRP Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 Chapter Summary
