RIP. Table of Contents. General Information. Summary. Specifications
|
|
|
- Tracy Walker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents General Setup Interfaces Networks Neighbors Routes General Information Summary Specifications Page 1 of 8
2 Packages required: routing License required: level3 Home menu level: /routing rip Standards and Technologies: RIPv1, RIPv2 Hardware usage: Not significant Related Documents id est /ip route print Additional Documents General Setup redistribute-static (yes no; default: no) - specifies whether to redistribute static routes to neighbour routers or not redistribute-connected (yes no; default: no) - specifies whether to redistribute connected routes to neighbour routers or not redistribute-ospf (yes no; default: no) - specifies whether to redistribute routes learned via OSPF protocol to neighbour routers or not redistribute-bgp (yes no; default: no) - specifies whether to redistribute routes learned via bgp protocol to neighbour routers or not metric-static (integer; default: 1) - specifies metric (the number of hops) for the static routes metric-connected (integer; default: 1) - specifies metric (the number of hops) for the connected routes Page 2 of 8
3 metric-ospf (integer; default: 1) - specifies metric (the number of hops) for the routes learned via OSPF protocol metric-bgp (integer; default: 1) - specifies metric (the number of hops) for the routes learned via BGP protocol update-timer (time; default: 30s) - specifies frequency of RIP updates timeout-timer (time; default: 3m) - specifies time interval after which the route is considered invalid garbage-timer (time; default: 2m) - specifies time interval after which the invalid route will be dropped from neighbor router table redistribute 1 set redistribute-connected=yes print redistribute-static: no redistribute-connected: yes redistribute-ospf: no redistribute-bgp: no metric-static: 1 metric-connected: 1 metric-ospf: 1 metric-bgp: 1 update-timer: 30s timeout-timer: 3m garbage-timer: 2m Interfaces Home menu level: /routing rip interface interface (name; default: all) - interface on which RIP runs all - sets defaults for interfaces not having any specific settings send (v1 v1-2 v2; default: v2) - specifies RIP protocol update versions to distribute receive (v1 v1-2 v2; default: v2) - specifies RIP protocol update versions the router will be able to receive Page 3 of 8
4 authentication (none simple md5; default: none) - specifies authentication method to use for RIP messages none - no authentication performed simple - plain text authentication md5 - Keyed Message Digest 5 authentication authentication-key (text; default: "") - specifies authentication key for RIP messages prefix-list-in (name; default: "") - name of the filtering prefix list for received routes prefix-list-out (name; default: "") - name of the filtering prefix list for advertised routes ether1 plout interface add interface=ether1 \ \... prefix-list-out=plout interface print Flags: I - inactive 0 interface=ether1 receive=v2 send=v2 authentication=none authentication-key="" prefix-list-in=plout prefix-list-out=none Networks Home menu level: /routing rip network address (IP address/mask; default: /0) - specifies the network on which RIP will run. Only directly connected networks of the router may be specified netmask (IP address; default: ) - specifies the network part of the address (if it is not specified in the address argument) netmask /32 Page 4 of 8
5 /24 routing rip network> add address= /24 routing rip network> print # ADDRESS /24 Neighbors address (IP address; default: ) - IP address of neighboring router neighbor add address= neighbor print Flags: I - inactive # ADDRESS Routes Home menu level: /routing rip route dst-address (read-only: IP address/mask) - network address and netmask of destination gateway (read-only: IP address) - last gateway on the route to destination metric (read-only: integer) - distance vector length to the destination network from (IP address) - specifies the IP address of the router from which the route was received Page 5 of 8
6 routing rip route> print Flags: S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, C - connect, B - bgp 0 O dst-address= /32 gateway= metric=1 from= R dst-address= /29 gateway= metric=2 from= R dst-address= /28 gateway= metric=2 from= [admin@mikrotik] routing rip route> Application s [admin@mikrotik] > interface print Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic, R - running # NAME TYPE MTU 0 R ether1 ether R ether2 ether 1500 [admin@mikrotik] > ip address print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE / ether / ether2 [admin@mikrotik] > ip route print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, J - rejected, C - connect, S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, B - bgp # DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE 0 DC /24 r ether2 1 DC /24 r ether1 [admin@mikrotik] > set redistribute-connected=yes print redistribute-static: no redistribute-connected: yes redistribute-ospf: no redistribute-bgp: no metric-static: 1 metric-connected: 1 metric-ospf: 1 metric-bgp: 1 update-timer: 30s timeout-timer: 3m garbage-timer: 2m [admin@mikrotik] routing rip network> add address= /2 [admin@mikrotik] routing rip network> print # ADDRESS /24 [admin@mikrotik] routing rip network> Page 6 of 8
7 route print Flags: S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, C - connect, B - bgp 0 R dst-address= /0 gateway= metric=2 from= C dst-address= /24 gateway= metric=1 from= C dst-address= /24 gateway= metric=1 from= R dst-address= /24 gateway= metric=1 from= R dst-address= /24 gateway= metric=1 from= [MikroTik] routing rip> /ip route print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, J - rejected, C - connect, S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, B - bgp # DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE 0 R /0 r ether1 1 R /24 r ether1 2 R /24 r ether1 3 DC /24 r ether2 4 DC /24 r ether1 Cisco#show running-config... interface Ethernet0 ip address no ip directed-broadcast! interface Serial1 ip address ip directed-broadcast! router rip version 2 redistribute connected redistribute static network network ! ip classless!... Cisco#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, * - candidate default U - per-user static route, o - ODR Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Ethernet0 R /24 [120/1] via , 00:00:19, Ethernet /30 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Serial1 R /24 [120/1] via , 00:00:05, Serial1 R* /0 [120/1] via , 00:00:05, Serial1 Page 7 of 8
8 Cisco# Page 8 of 8
Distance vector Routing protocols. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1
 Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
Distance vector Routing protocols 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9-1 IP Routing Configuration Tasks Router configuration Select routing protocols Specify networks or interfaces RIP Network 172.16.0.0 IGRP,
Network Layer Week 5. Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White Office : 324
 Network Layer Week 5 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 1 Network Layer Network Layer Protocols Common Network Layer Protocols Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
Network Layer Week 5 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 1 Network Layer Network Layer Protocols Common Network Layer Protocols Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
MOXA C101 Synchronous Interface
 MOXA C101 Synchronous Interface Document revision 1.1 (Fri Mar 05 08:15:42 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related
MOXA C101 Synchronous Interface Document revision 1.1 (Fri Mar 05 08:15:42 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network design. Identify several ways to classify
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Antonio Cianfrani. Routing Protocols
 Antonio Cianfrani Routing Protocols Routing protocols A routing protocol provides a communication channel among routers to exchange reachability information about networks Routing tables are properly configured
Antonio Cianfrani Routing Protocols Routing protocols A routing protocol provides a communication channel among routers to exchange reachability information about networks Routing tables are properly configured
LAB11: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB11: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB11: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Route Redistribution 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1of 38
 1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Adapted from the Synchronization example in g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html
 Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
MOXA C101 Synchronous Interface
 MOXA C101 Synchronous Interface Document revision 1.3 (February 6, 2008, 2:58 GMT) This document applies to V3.0 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Additional
MOXA C101 Synchronous Interface Document revision 1.3 (February 6, 2008, 2:58 GMT) This document applies to V3.0 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Additional
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB
 INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
INTERNET TEACHING LAB: Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) LAB Overview In this lab, we will explore some common interior gateway protocols - RIP version 1 (Routing Information Protocol) - OSPF (Open Shortest
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
LAB12: OSPF IPv6. OSPF: Redistribution. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB12: OSPF IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB12: OSPF IPv6 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
The most simple way to accelerate a Router is at 9.8 m/sec/sec.
 Routing Introduction Direct vs. Indirect Delivery Static vs. Dynamic Routing Distance Vector vs. Link State (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 The most simple way to accelerate a Router is at 9.8 m/sec/sec. Seen
Routing Introduction Direct vs. Indirect Delivery Static vs. Dynamic Routing Distance Vector vs. Link State (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 The most simple way to accelerate a Router is at 9.8 m/sec/sec. Seen
Routing Protocols and
 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocol Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 3 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocol Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 3 1 Objectives Describe the role of dynamic routing protocols and place these protocols in the context of modern network
Initial Configurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link
 Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
RIP Configuration. RIP Overview. Operation of RIP. Introduction. RIP routing table. RIP timers
 Table of Contents RIP Configuration 1 RIP Overview 1 Operation of RIP 1 Operation of RIP 2 RIP Version 2 RIP Message Format 3 Protocols and Standards 4 Configuring RIP Basic Functions 5 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents RIP Configuration 1 RIP Overview 1 Operation of RIP 1 Operation of RIP 2 RIP Version 2 RIP Message Format 3 Protocols and Standards 4 Configuring RIP Basic Functions 5 Configuration Prerequisites
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
shortcut Tap into learning NOW! Visit for a complete list of Short Cuts. Your Short Cut to Knowledge
 shortcut Your Short Cut to Knowledge The following is an excerpt from a Short Cut published by one of the Pearson Education imprints. Short Cuts are short, concise, PDF documents designed specifically
shortcut Your Short Cut to Knowledge The following is an excerpt from a Short Cut published by one of the Pearson Education imprints. Short Cuts are short, concise, PDF documents designed specifically
ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect
 ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Problem: Packets Destined for a Disconnected
ASA Has High CPU Usage Due to a Traffic Loop When VPN Clients Disconnect Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Problem: Packets Destined for a Disconnected
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 Case Study
 Objectives: Consolidate routing table reading skills. Introduce the idea of more than 1 routing protocol running into the same router. Explain the use of routes to Null0 interface. Intro: Connex Inc. is
Objectives: Consolidate routing table reading skills. Introduce the idea of more than 1 routing protocol running into the same router. Explain the use of routes to Null0 interface. Intro: Connex Inc. is
Configuring RIP. Information About RIP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure the ASASM to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). This chapter includes
CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure the ASASM to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). This chapter includes
LAB8: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB8: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
EIGRP Lab / lo1. .1 lo / /30
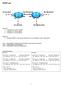 EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands
 IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the features that are routing protocol-independent. For configuration information and examples on IP routing
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the features that are routing protocol-independent. For configuration information and examples on IP routing
RIP Version 2. The Classless Brother
 RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Lab Configuring Static NAT
 Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
LAB5: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Lecture (03) RIP. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee. Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2016, Practical App. Networks II
 Lecture (03) RIP By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2016, Practical App. Networks II Dynamic Routing Protocol Overview Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths
Lecture (03) RIP By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2016, Practical App. Networks II Dynamic Routing Protocol Overview Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths
Routing Fundamentals. What Is Routing? Routing Information. Routing Requirements. Most of the necessary information is contained in the routing table
 Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two
Routing Fundamentals What Is Routing? Routing is the process of forwarding an item from one location to another Routers forward traffic to a logical destination in a computer network Routers perform two
Chapter 3. Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols. CCNA2-1 Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-2 Chapter 3 Perspective and Background Dynamic
Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols CCNA2-2 Chapter 3 Perspective and Background Dynamic
FSOS IP Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands... 7 1.1 ip address...7 1.2 ip icmp error-interval... 9 1.3 ip redirects...10 1.4 ip unreachables...11 1.5 ip verify unicast
FSOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands... 7 1.1 ip address...7 1.2 ip icmp error-interval... 9 1.3 ip redirects...10 1.4 ip unreachables...11 1.5 ip verify unicast
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
 OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
Chapter 5 RIP version 1
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Table of Contents. 2 Static Route Configuration Commands 2-1 Static Route Configuration Commands 2-1 delete static-routes all 2-1 ip route-static 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 display ip routing-table 1-1 display ip routing-table acl 1-3 display ip routing-table ip-address 1-5 display ip routing-table
Table of Contents 1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 display ip routing-table 1-1 display ip routing-table acl 1-3 display ip routing-table ip-address 1-5 display ip routing-table
Configuring EIGRP. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example
 FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Basic Idea. Routing. Example. Routing by the Network
 Basic Idea Routing Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Basic Idea Routing Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Routing by the Network
 Routing Basic Idea Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
Routing Basic Idea Routing table at each router/gateway When IP packet comes, destination address checked with routing table to find next hop address Questions: Route by host or by network? Routing table:
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands...6 1.1 ip address...6 1.2 ip icmp error-interval...7 1.3 ip redirects... 8 1.4 ip unreachables...9 1.5 ip verify unicast
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands...6 1.1 ip address...6 1.2 ip icmp error-interval...7 1.3 ip redirects... 8 1.4 ip unreachables...9 1.5 ip verify unicast
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols
 Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
RIP Commands. output-delay, page 32 passive-interface (RIP), page 33 poison-reverse, page 35 receive version, page 37 redistribute (RIP), page 39
 RIP Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). For detailed information about RIP concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
RIP Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). For detailed information about RIP concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
EIGRP. About EIGRP. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.7 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
LAB15: EIGRP IPv4. LAB 15: Diagram. Disclaimer
 AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
Terminal Console. Table of Contents. General Information. Summary. Specifications. Related Documents. Summary Specifications
 Terminal Console Document revision NaN (Tue Apr 20 16:17:53 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents Summary Specifications Related Documents Common Console Functions
Terminal Console Document revision NaN (Tue Apr 20 16:17:53 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents Summary Specifications Related Documents Common Console Functions
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
Command Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 delete static-routes all... 1-1 1.1.2 ip route-static...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 delete static-routes all... 1-1 1.1.2 ip route-static...
Routing Information Protocol
 Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 18.2, 2018/11/21 13:11:09) Friday, November 23, 2018 Karst Koymans (UvA)
Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 18.2, 2018/11/21 13:11:09) Friday, November 23, 2018 Karst Koymans (UvA)
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 11 Case Study
 bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
DMVPN Topology. Page1
 DMVPN DMVPN Topology Page1 LAB 2: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN: Task 1: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN Process Step 1 In the configuration mode of router configure EIGRP over DMVPN by following command: R1:
DMVPN DMVPN Topology Page1 LAB 2: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN: Task 1: Configure EIGRP over DMVPN Process Step 1 In the configuration mode of router configure EIGRP over DMVPN by following command: R1:
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Operation Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
RealCiscoLAB.com. Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
Routing Information Protocol. A simple distance vector scheme
 Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme RIP version 1 RFC 1058 Charles Hedrick, Rutgers University, 1988 Based on Bellman-Ford distance vector Also used as ARPANET routing protocol
Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme RIP version 1 RFC 1058 Charles Hedrick, Rutgers University, 1988 Based on Bellman-Ford distance vector Also used as ARPANET routing protocol
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Routing Protocols of IGP. Koji OKAMURA Kyushu University, Japan
 Routing Protocols of IGP Koji OKAMURA Kyushu University, Japan Routing Protocol AS (Autonomous System) Is operated autonomous in the organization. 6bit IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) Routing Control inside
Routing Protocols of IGP Koji OKAMURA Kyushu University, Japan Routing Protocol AS (Autonomous System) Is operated autonomous in the organization. 6bit IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) Routing Control inside
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Information About Routing
 19 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the adaptive security appliance, and the routing protocols that are supported. The chapter includes the following sections:,
19 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the adaptive security appliance, and the routing protocols that are supported. The chapter includes the following sections:,
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Configuration and Management of Networks
 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
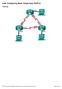 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Distance Vector Routing Protocols
 Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Identify the characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. Describe the network discovery process
Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 4 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Identify the characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. Describe the network discovery process
2008 NDP Lectures 7 th Semester
 2008 NDP Lectures 7 th Semester Neeli R. Prasad, Associate Professor Head of Wireless Security and Sensor Networks Group Networking and Security Aalborg University Niels Jernes Vej 12, 9220 Aalborg East,
2008 NDP Lectures 7 th Semester Neeli R. Prasad, Associate Professor Head of Wireless Security and Sensor Networks Group Networking and Security Aalborg University Niels Jernes Vej 12, 9220 Aalborg East,
Configuring Network Access to the GGSN
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
Draft Manuscript Draft M. Manuscript Draft Ma. t Manuscript Draft Manu. ipt Draft Manuscript Dra. anuscript Draft Manuscri
 M aft Ma CHAPTER 5 ript Dra RIP Version 1 Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the functions, characteristics, and operation
M aft Ma CHAPTER 5 ript Dra RIP Version 1 Objectives aft Ma Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the functions, characteristics, and operation
LAB8: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Virtual Link. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Routing Information Protocol. RIP application. RIP version 1
 Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/01 13:00:45) Friday, March 3, 2017 RIP version 1 Origin and
Routing Information Protocol A simple distance vector scheme Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/01 13:00:45) Friday, March 3, 2017 RIP version 1 Origin and
Routing Overview. Information About Routing CHAPTER
 21 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About
21 CHAPTER This chapter describes underlying concepts of how routing behaves within the ASA, and the routing protocols that are supported. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About
LAB2: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
