Principles of Computer Architecture Processors Lecture 1
|
|
|
- Norma Bradford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Computer Architecture Processors Lecture 1 prof.dr. Dalius Mažeika Dalius.Mazeika@vgtu.lt Room No. L424
2 Lectures and evaluation Scope of the course is 3 ECTS (80 hours) Theory 30 hours (15 lectures) Practice 15 hours (7 lectures) Structure of the final grade - Practice coefficient is Exam coefficient is 0.7
3 Literature W. Stalling. Computer organizations and architecture. 8 th Edition, Pearson, A. S. Tanenbaum, D. J. Wetherall. Computer Networks. Prentice Hall J. F. Kurose, K. W. Ross. Computer Networking. A Top Down Approach. Addison Wesley C. M. Kozierok. The TCP/IP Guide V.Urbanavičius. Kompiuteriai ir jų architektūra. VGTU (
4 Content of the theory course Computer architecture Processors (word, pipes, ISA, ILP, SMP, threads, cores) RAMs (SRAM, DRAM, SDRAM, DDR, CAS, RAS, latency) Cache(L1, L2, L3, Direct mapped, Fully Associative, Set Associative) HDD, SDD, RAID, LUN, file systems File storages (DAS, NAS, SAN, protocols)
5 Content of the theory course Computer networks Network topology, components, main features OSI ir TCP/IP models L2 layer - LAN technologies, IEEE 802.x standard L3 layer, IP protocol (IP v4, IPv6) L4 layer, TCP and UDP protocols WAN technologies Wireless LAN (IEEE x) Routing and protocols (BGP, RIP, OSPF) Application layer (DNS, DHCP, FTP, ICMP, SMTP, etc.)
6 Functional view of the computer Basic functions that a computer performs: Data processing Data storage Data movement Control
7 Structure of the computer
8 von Neumann machine Computer consists of: A main memory, which stores both data and instructions An arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) capable of operating on binary data A control unit, which interprets the instructions in memory and causes them to be executed Input and output (I/O) equipment operated by the control unit
9 Computer components
10 Registers ALU contain storage locations, called registers, defined as follows: Memory buffer register (MBR): Contains a word to be stored in memory or sent to the I/O unit, or is used to receive a word from memory or from the I/O unit. Memory address register (MAR): Specifies the address in memory of the word to be written from or read into the MBR. Instruction register (IR): Contains the 8-bit opcode instruction being executed. Instruction buffer register (IBR): Employed to hold temporarily the right hand instruction from a word in memory. Program counter (PC): Contains the address of the next instructionpair to be fetched from memory. Accumulator (AC) and multiplier quotient (MQ): Employed to hold temporarily operands and results of ALU operations.
11 Principle of the processor Hardware and Software Approaches
12 Operating principles Execution of the program is the main function of the computer. Program consists of serias of instructions and data that are located in main memory. CPU executes instructions. Execution of the program is continual cycles of the instruction fetch and execution.
13 Instruction Instruction is an operation that is executed by processor. -
14 Instructions
15 Instruction cycle An instruction cycle consists of an instruction fetch, followed by zero or more operand fetches, followed by zero or more operand stores, followed by an interrupt check (if interrupts are enabled).
16 Instruction cycle state diagram
17 Example of program exection Program counter (PC) Address of instruction Instruction register (IR) Instruction being executed Accumulator (AC) Temporary storage
18 Interrupts Virtually all computers provide a mechanism by which other modules (I/O, memory) may interrupt the normal processing of the processor. Interrupts are provided primarily as a way to improve processing efficiency.
19 Program Flow
20 Program Timing
21 Sisteminė magistralė
22 Magistralės struktūra Duomenų magistrale vyksta keitimasis duomenimis tarp kompiuterio modulių. Adresų magistrale nurodo duomenų magistralėje esančios informacijos šaltinį ir paskirties įrenginį (destination). Valdymo magistrale kontroliuoja kreiptis (access) į duomenų ir adresų linijas ir šių linijų naudojimą.
23 Registrų sandara Registrų rinkinys funkcionuoja kaip atminties hierarchijos lygmuo, esantis aukščiau už pagrindinę ir spartinančiąją atmintis. CPĮ registrai skirti dviem funkcijoms vykdyti: Vartotojo pasiekiami registrai. Šie registrai leidžia programuotojui, taikant asemblerio programavimo kalbą arba tiesiog per mašininius kodus, sumažinti kreipčių į pagrindinę atmintį skaičių ir optimizuoti šių registrų vartojimą. Valdymo ir būklės registrai. Jie naudojami CPĮ valdymo įrenginio darbui kontroliuoti, o taip pat valdyti operacinių sistemų programų taikomųjų programų vykdymą.
24 Vartotojo pasiekiami registrai Bendrosios paskirties; Duomenų; Adresų Sąlygų kodų. Bendrosios paskirties registrai programuotojo gali būti pritaikyti įvairioms funkcijoms. Duomenų registrai gali būti taikomi tik duomenims saugoti ir niekada netaikomi apskaičiuojant operandų adresus. Adresų registrai patys gali būti realizuojami iš bendrosios paskirties registrų, o gali būti skirti specialiems adresavimo metodams. Sąlygų kodus sudaro tam tikri bitai, kuriais gali operuoti CPĮ techninė įranga, priklausomai nuo vykdomos operacijos rezultato.
25 Valdymo būklės registrai Programos skaitiklis (PS). Saugo sekančios išrenkamos instrukcijos adresą. Instrukcijos registras (IR). Saugo naujausiąją išrinktą instrukciją. Atminties adreso registras (AAR). Saugo atminties ląstelės, iš kurios ką tik buvo perskaityta informacija arba į kurią vyks duomenų rašymas, adresą. Atminties buferio registras (ABR). Saugomas duomenų žodis, kuris bus įrašytas į atmintį arba iš atminties ką tik nuskaitytas.
26 Duomenų srauto diagrama Instrukcija ciklo išrankos metu skaitoma iš atminties. PS registre saugomas sekančios išrenkamos instrukcijos adresas. Šis adresas siunčiamas į AAR ir patalpinamas adresų magistralėje. Valdymo įrenginys organizuoja skaitymą iš atminties. Nuskaitytas rezultatas patalpinamas duomenų magistralėje, kopijuojamas į ABR ir toliau siunčiamas į IR. Tuo tarpu PS turinys didinamas vienetu ir taip gaunamas sekančios instrukcijos adresas.
27 Instrukcijų konvejeris Instrukcijų konvejerizavimas panašus į surinkimo linijos taikymą produkcijos gamyboje. Surinkimo linijos privalumas yra tame, kad surinkimo procesas surinkimo linijoje išskaidomas į etapus ir tame, kad tam tikros gaminio surinkimo procedūros gali būti vykdomos vienu metu. Toks procesas dar vadinamas konvejeriu arba vamzdynu (pipeline), kadangi konvejeryje nauja operacija pradedama viename gale nesulaukus kol kita operacija kitame gale bus užbaigta.
28 Instrukcijų konvejeris Instrukcijos išranka (II). Į buferį nuskaitoma sekanti instrukcija po vykdomos. Instrukcijos dekodavimas (ID). Nustatomi operacijos kodas ir operando specifikatorius. Operando apskaičiavimas (OA). Apskaičiuojamas operando efektyvusis (realusis arba fizinis) adresas. Tai gali būti perkėlimo, registrų netiesioginis adresavimo ir kitų formų adresų apskaičiavimai. Operandų išranka (OI). Operandas arba operandai nuskaitomas iš atminties. Instrukcijos vykdymas (IV). Vykdoma instrukcijoje nurodyta operacija ir išsaugomas jos rezultatas. Operando rašymas (OR). Operacijos rezultatas įrašomas į atmintį.
29 Konvejerio našumas problemos Konvejerio našumą įtakojančius faktorius priimta skirstyti į tris klases: 1) resursų konfliktus (structural hazards); 2) duomenų priklausomumą (data hazards); 3) valdymo nuoseklumo priklausomumą (control hazards). Resursų konfliktai kyla tuomet, kai į tą patį vienintelį resursą kreipiasi ne mažiau kaip dvi komandos. Tokiu atveju viena komanda gali tuo resursu naudotis, o likusios komandos turi laukti, kol resursas bus atlaisvintas ir bus patenkinta kitos komandos paraiška. Jei to tipo resursas turi k egzempliorių (pavyzdžiui, superskaliariniame procesoriuje yra keli to paties tipo funkciniai įtaisai), aišku, kad vienu metu gali būti patenkinta k kreipinių.
30 Konvejerio našumas problemos Duomenų priklausomumas atsiranda dėl to, kad konvejerizuotame procesoriuje pasikeičia gretimų komandų atskirų žingsnių vykdymo nuoseklumas. Tai liečia operandų išrinkimą ir rezultato įrašymą. Pavyzdžiui, vykdoma tokia komandų pora: Komandos Add rezultatas bus įrašytas į registrą R1 fazėje W, o komanda Sub atėminį turi išrinkti iš registro R1 fazėje F, kuri vykdoma dviems ciklais anksčiau. Šis pavyzdys atitinka vadinamąjį tikrąjį duomenų priklausomumą.
31 Valdymo problemos konvejeryje II, OI ir OR etapuose vykdomi kreipiniai į atmintį. Diagramoje numatyta, kad visos šios kreiptys gali vykti vienu metu. Instrukcijos etapų trukmės skirtumai; Sąlygiškojo šakojimosi instrukcija; Tam tikrą neapibrėžtumą taip pat įneša pertrauktys.
32 Klausimai?
JAVA pagrindai Lek. Liudas Drejeris
 JAVA pagrindai Lek. Liudas Drejeris Programa (1) Programa, tai eilė instrukcijų (vadinamų programiniais sakiniais), kurie vykdomi paeiliui, kol gaunamas norimas rezultatas. Programa (2) Programa (2) /*
JAVA pagrindai Lek. Liudas Drejeris Programa (1) Programa, tai eilė instrukcijų (vadinamų programiniais sakiniais), kurie vykdomi paeiliui, kol gaunamas norimas rezultatas. Programa (2) Programa (2) /*
Informacijos apsaugos standartai serija
 Informacijos apsaugos standartai 27000 serija Pareng : Marius Celskis www.isec.lt 2007 m. balandis 12 d. ISO 27000 serija 2 iš 9 Tarptautin standartizacijos organizacija ISO informacijos apsaugos standartizavimui
Informacijos apsaugos standartai 27000 serija Pareng : Marius Celskis www.isec.lt 2007 m. balandis 12 d. ISO 27000 serija 2 iš 9 Tarptautin standartizacijos organizacija ISO informacijos apsaugos standartizavimui
C programavimo kalba. 3 paskaita (Sąlygos ir ciklo operatoriai, funkcija scanf() )
 C programavimo kalba 3 paskaita (Sąlygos ir ciklo operatoriai, funkcija scanf() ) Sąlygos operatorius if - else Sąlygos operatoriai skirti perduoti programos vykdymą vienai ar kitai programos šakai. Operatorius
C programavimo kalba 3 paskaita (Sąlygos ir ciklo operatoriai, funkcija scanf() ) Sąlygos operatorius if - else Sąlygos operatoriai skirti perduoti programos vykdymą vienai ar kitai programos šakai. Operatorius
Atminties technologijos
 Atminties technologijos 3 paskaita RAM (laisvosios kreipties atmintis) Atminties hierarchija Kreipties trukmė Talpa Kompiuterio resursai apibrėžiami pagal lokališkumo principą (laike ir erdvėje), kas leidžia
Atminties technologijos 3 paskaita RAM (laisvosios kreipties atmintis) Atminties hierarchija Kreipties trukmė Talpa Kompiuterio resursai apibrėžiami pagal lokališkumo principą (laike ir erdvėje), kas leidžia
Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 1
 2014.02.02 Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 1 2014.02.02 Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 2 Kaip suprantame masyvą? Pavyzdys: Peteliškių šeima; Gėlių laukas; 2014.02.02 Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 3 Kaip suprasti
2014.02.02 Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 1 2014.02.02 Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 2 Kaip suprantame masyvą? Pavyzdys: Peteliškių šeima; Gėlių laukas; 2014.02.02 Parengė ITMM Artūras Šakalys 3 Kaip suprasti
Chapter One. Introduction to Computer System
 Principles of Programming-I / 131101 Prepared by: Dr. Bahjat Qazzaz -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Chapter One Introduction to Computer System
Principles of Programming-I / 131101 Prepared by: Dr. Bahjat Qazzaz -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Chapter One Introduction to Computer System
El. pašto konfigūravimas
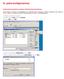 El. pašto konfigūravimas Outlook Express (integruota Windows XP) elektroninio pašto klientas Žemiau pateikta instrukcija, kaip sukonfigūruoti savo elektroninį paštą vartotojams, turintiems elektroninio
El. pašto konfigūravimas Outlook Express (integruota Windows XP) elektroninio pašto klientas Žemiau pateikta instrukcija, kaip sukonfigūruoti savo elektroninį paštą vartotojams, turintiems elektroninio
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 3: von Neumann Architecture von Neumann Architecture Our goal: understand the basics of von Neumann architecture, including memory, control unit
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 3: von Neumann Architecture von Neumann Architecture Our goal: understand the basics of von Neumann architecture, including memory, control unit
Gijos. Gijų modelis Javoje. R.Vaicekauskas, OP, 2017
 Gijos Gijų modelis Javoje R.Vaicekauskas, OP, 2017 1 Turinys Motyvacija Sukūrimas Valdymas Sinchronizacija Susijusios klasės 2 Motyvacija Gijos reikalingos tam, kad išreikšti lygiagretumą vieno proceso
Gijos Gijų modelis Javoje R.Vaicekauskas, OP, 2017 1 Turinys Motyvacija Sukūrimas Valdymas Sinchronizacija Susijusios klasės 2 Motyvacija Gijos reikalingos tam, kad išreikšti lygiagretumą vieno proceso
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 16 Control Unit Operations Rev. 3.2 (2009-10) by Enrico Nardelli 16-1 Execution of the Instruction Cycle It has many elementary phases,
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 16 Control Unit Operations Rev. 3.2 (2009-10) by Enrico Nardelli 16-1 Execution of the Instruction Cycle It has many elementary phases,
Come to the TypeScript
 Come to the TypeScript we have type hinting! Sergej Kurakin Sergej Kurakin Amžius: 36 Dirbu: NFQ Technologies Pareigos: Programuotojas Programuoti pradėjau mokytis 1996 metais. Programuotoju dirbu nuo
Come to the TypeScript we have type hinting! Sergej Kurakin Sergej Kurakin Amžius: 36 Dirbu: NFQ Technologies Pareigos: Programuotojas Programuoti pradėjau mokytis 1996 metais. Programuotoju dirbu nuo
Redis Ma as, greitas, galingas. Specialiai VilniusPHP
 Redis Ma as, greitas, galingas Specialiai VilniusPHP 2013.06.06 Sergej Kurakin Na, Jūs mane jau nekarta matėte, tai nieko nesakysiu apie save. Kaip aš susipa inau! Tai buvo prieš keletą metų! Projektas
Redis Ma as, greitas, galingas Specialiai VilniusPHP 2013.06.06 Sergej Kurakin Na, Jūs mane jau nekarta matėte, tai nieko nesakysiu apie save. Kaip aš susipa inau! Tai buvo prieš keletą metų! Projektas
Computer Networks. Dr. Abdel Ilah ALshbatat Dept. of Communication and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering Tafila Technical University
 Computer Networks Dr. Abdel Ilah ALshbatat Dept. of Communication and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering Tafila Technical University 1 Lecture 0 Course Information Title: Computer Networks 2 Course
Computer Networks Dr. Abdel Ilah ALshbatat Dept. of Communication and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering Tafila Technical University 1 Lecture 0 Course Information Title: Computer Networks 2 Course
AS/A Level Computing Syllabus 2011
 AS/A Level Computing Syllabus 2011 Section 3 - System Software Mechanisms - - Machine Architecture - - Database Theory - - Programming Paradigms - Chapter 3.3 Computer Architectures & Fetch-Execute Cycle
AS/A Level Computing Syllabus 2011 Section 3 - System Software Mechanisms - - Machine Architecture - - Database Theory - - Programming Paradigms - Chapter 3.3 Computer Architectures & Fetch-Execute Cycle
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture. Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function CPU Structure CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Registers
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function CPU Structure CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Registers
KAUNO TECHNOLOGIJOS UNIVERSITETAS
 KAUNO TECHNOLOGIJOS UNIVERSITETAS INFORMATIKOS FAKULTETAS VALDIKLIŲ PROGRAMAVIMAS STANDARTO IEC 61131-3 KALBOMIS Referatas Atliko: Kęstutis Valinčius Kaunas 2011 Turinys 1 Įvadas... 3 2 Struktūriniai elementai...
KAUNO TECHNOLOGIJOS UNIVERSITETAS INFORMATIKOS FAKULTETAS VALDIKLIŲ PROGRAMAVIMAS STANDARTO IEC 61131-3 KALBOMIS Referatas Atliko: Kęstutis Valinčius Kaunas 2011 Turinys 1 Įvadas... 3 2 Struktūriniai elementai...
C++ programavimo kalba. Konstruktorius, destruktorius, klasių metodų modifikatoriai, objektų masyvai (4 paskaita)
 C++ programavimo kalba Konstruktorius, destruktorius, klasių metodų modifikatoriai, objektų masyvai (4 paskaita) Konstruktorius Sukuriant objektą, jo duomenims paprastai turi būti priskiriamos pradinės
C++ programavimo kalba Konstruktorius, destruktorius, klasių metodų modifikatoriai, objektų masyvai (4 paskaita) Konstruktorius Sukuriant objektą, jo duomenims paprastai turi būti priskiriamos pradinės
Outcomes. Lecture 13 - Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) Central Processing UNIT (CPU) or Processor
 Lecture 13 - Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outcomes What is a CPU? How are instructions prepared by the CPU before execution? What registers and operations are involved in this preparation
Lecture 13 - Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outcomes What is a CPU? How are instructions prepared by the CPU before execution? What registers and operations are involved in this preparation
PHP PROGRAMOS EIGOS VYKDYMO VALDYMAS
 PHP PROGRAMOS EIGOS VYKDYMO VALDYMAS Sąlygos sakiniai PHP skriptų vykdymo eigą galite valdyti naudodami sąlygos sakinius. Sąlygos sakiniai tai loginės struktūros, kuriose saugomas kodas, įvykdomas įgyvendinus
PHP PROGRAMOS EIGOS VYKDYMO VALDYMAS Sąlygos sakiniai PHP skriptų vykdymo eigą galite valdyti naudodami sąlygos sakinius. Sąlygos sakiniai tai loginės struktūros, kuriose saugomas kodas, įvykdomas įgyvendinus
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
CPU Structure and Function
 CPU Structure and Function Chapter 12 Lesson 17 Slide 1/36 Processor Organization CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Lesson 17 Slide 2/36 CPU With Systems
CPU Structure and Function Chapter 12 Lesson 17 Slide 1/36 Processor Organization CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Lesson 17 Slide 2/36 CPU With Systems
UNIT- 5. Chapter 12 Processor Structure and Function
 UNIT- 5 Chapter 12 Processor Structure and Function CPU Structure CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data CPU With Systems Bus CPU Internal Structure Registers
UNIT- 5 Chapter 12 Processor Structure and Function CPU Structure CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data CPU With Systems Bus CPU Internal Structure Registers
Computer Architecture and Organization (CS-507)
 Computer Architecture and Organization (CS-507) Muhammad Zeeshan Haider Ali Lecturer ISP. Multan ali.zeeshan04@gmail.com https://zeeshanaliatisp.wordpress.com/ Lecture 4 Basic Computer Function, Instruction
Computer Architecture and Organization (CS-507) Muhammad Zeeshan Haider Ali Lecturer ISP. Multan ali.zeeshan04@gmail.com https://zeeshanaliatisp.wordpress.com/ Lecture 4 Basic Computer Function, Instruction
Kas yra masyvas? Skaičių masyvo A reikšmės: Elementų indeksai (numeriai): Užrašymas Turbo Paskaliu: A[1] A[2] A[3] A[4] A[5]
![Kas yra masyvas? Skaičių masyvo A reikšmės: Elementų indeksai (numeriai): Užrašymas Turbo Paskaliu: A[1] A[2] A[3] A[4] A[5] Kas yra masyvas? Skaičių masyvo A reikšmės: Elementų indeksai (numeriai): Užrašymas Turbo Paskaliu: A[1] A[2] A[3] A[4] A[5]](/thumbs/80/81249842.jpg) Masyvas 2013 1 Vienmatis masyvas Veiksmai su masyvo elementais: reikšmių priskyrimas ir išvedimas, paieška, rikiavimas. Masyvų perdavimas procedūros (funkcijos) parametrais. 2 Kas yra masyvas? Masyvu vadinamas
Masyvas 2013 1 Vienmatis masyvas Veiksmai su masyvo elementais: reikšmių priskyrimas ir išvedimas, paieška, rikiavimas. Masyvų perdavimas procedūros (funkcijos) parametrais. 2 Kas yra masyvas? Masyvu vadinamas
Trumpai-ilga istorija
 Įvadas į Web Services Kas yra Web Service? Kas ką žino??? 70-ieji: Mainframe Trumpai-ilga istorija 80-ieji: Client-Server Istorijos 90-ieji: Web 2000: SOA 2010: Cloud Computing Šaltinis: Sergejus Barinovas,
Įvadas į Web Services Kas yra Web Service? Kas ką žino??? 70-ieji: Mainframe Trumpai-ilga istorija 80-ieji: Client-Server Istorijos 90-ieji: Web 2000: SOA 2010: Cloud Computing Šaltinis: Sergejus Barinovas,
INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO. Architectures for Embedded Computing
 UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 05
UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 05
Polimorfizmas. Lekt. dr. Pijus Kasparaitis m. m. pavasario semestras.
 Polimorfizmas Lekt. dr. Pijus Kasparaitis pkasparaitis@yahoo.com 2009-2010 m. m. pavasario semestras Dar apie paveldėjimą Java kalboje kiekvienas paveldėtos klasės objektas gali būti naudojamas ten, kur
Polimorfizmas Lekt. dr. Pijus Kasparaitis pkasparaitis@yahoo.com 2009-2010 m. m. pavasario semestras Dar apie paveldėjimą Java kalboje kiekvienas paveldėtos klasės objektas gali būti naudojamas ten, kur
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
Struktūrų sintaksė Struktūra tai vienodo arba skirtingo tipo kintamųjų rinkinys. Sintaksė: struct vardas { ; type1 var1; type2 var2;... typen varn; //
 C programavimo kalba 10 paskaita (Struktūros) Struktūrų sintaksė Struktūra tai vienodo arba skirtingo tipo kintamųjų rinkinys. Sintaksė: struct vardas { ; type1 var1; type2 var2;... typen varn; // Gale
C programavimo kalba 10 paskaita (Struktūros) Struktūrų sintaksė Struktūra tai vienodo arba skirtingo tipo kintamųjų rinkinys. Sintaksė: struct vardas { ; type1 var1; type2 var2;... typen varn; // Gale
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - Von Neumann Architecture 2 Two lessons Summary of the traditional computer architecture Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - Von Neumann Architecture 2 Two lessons Summary of the traditional computer architecture Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Chapter 2 Lecture 1 Computer Systems Organization
 Chapter 2 Lecture 1 Computer Systems Organization This chapter provides an introduction to the components Processors: Primary Memory: Secondary Memory: Input/Output: Busses The Central Processing Unit
Chapter 2 Lecture 1 Computer Systems Organization This chapter provides an introduction to the components Processors: Primary Memory: Secondary Memory: Input/Output: Busses The Central Processing Unit
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function Rev. 3.2.1 (2005-06) by Enrico Nardelli 11-1 CPU Functions CPU must: Fetch instructions Decode instructions
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function Rev. 3.2.1 (2005-06) by Enrico Nardelli 11-1 CPU Functions CPU must: Fetch instructions Decode instructions
C programavimo kalba. 5 paskaita (Funkcijos, masyvai)
 C programavimo kalba 5 paskaita (Funkcijos, masyvai) Funkcijų pavyzdys // Skaičių lyginimo programa #include void pmax(int, int); /* prototipas */ int main() {int i, j; for (i = -10; i
C programavimo kalba 5 paskaita (Funkcijos, masyvai) Funkcijų pavyzdys // Skaičių lyginimo programa #include void pmax(int, int); /* prototipas */ int main() {int i, j; for (i = -10; i
CS501_Current Mid term whole paper Solved with references by MASOOM FAIRY
 Total Questions: 6 MCQs: 0 Subjective: 6 Whole Paper is given below: Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) FALCON-A processor bus has 16 lines or is 16-bits wide while that of SRC wide. 8-bits 16-bits 3-bits (Page
Total Questions: 6 MCQs: 0 Subjective: 6 Whole Paper is given below: Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) FALCON-A processor bus has 16 lines or is 16-bits wide while that of SRC wide. 8-bits 16-bits 3-bits (Page
Memory General R0 Registers R1 R2. Input Register 1. Input Register 2. Program Counter. Instruction Register
 CPU Organisation Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory General R0 Registers R1 R2 ALU R3 Output Register Input Register 1 Input Register 2 Internal Bus Address Bus Data Bus Addr. $ 000 001 002 Program Counter
CPU Organisation Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory General R0 Registers R1 R2 ALU R3 Output Register Input Register 1 Input Register 2 Internal Bus Address Bus Data Bus Addr. $ 000 001 002 Program Counter
Computer Architecture
 University of Craiova Faculty of Automation, Computers & Electronics Department of Computers & Information Technology Computer Architecture Elementary Educational Computer (EEC) Cătălina Mancaș catalina.mancas@yahoo.it
University of Craiova Faculty of Automation, Computers & Electronics Department of Computers & Information Technology Computer Architecture Elementary Educational Computer (EEC) Cătălina Mancaș catalina.mancas@yahoo.it
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic
 Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 10 - Computer Arithmetic 1 / 126 1 Motivation 2 Arithmetic and Logic Unit 3 Integer representation
Buferio perpildymo klaida Įvadas, techniniai klausimai
 Buferio perpildymo klaida Įvadas, techniniai klausimai Rolandas Griškevičius rolandas.griskevicius@fm.vgtu.lt MSN: rgrisha@hotmail.com http://fmf.vgtu.lt/~rgriskevicius 2009-10-16 R. Griškevičius, Saugus
Buferio perpildymo klaida Įvadas, techniniai klausimai Rolandas Griškevičius rolandas.griskevicius@fm.vgtu.lt MSN: rgrisha@hotmail.com http://fmf.vgtu.lt/~rgriskevicius 2009-10-16 R. Griškevičius, Saugus
2. Computer Evolution and Performance
 2. Computer Evolution and Performance Spring 2016 Spring 2016 CS430 - Computer Architecture 1 Chapter 2: Computer Evolution and Performance Reading: pp. 16-49 Good Problems to Work: 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.8,
2. Computer Evolution and Performance Spring 2016 Spring 2016 CS430 - Computer Architecture 1 Chapter 2: Computer Evolution and Performance Reading: pp. 16-49 Good Problems to Work: 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.8,
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program --
Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences. Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE
 Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 3401 Assembly Language 4 Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE Objectives: The main objective of this lab is to get you familiarized with MARIE a simple computer
Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 3401 Assembly Language 4 Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE Objectives: The main objective of this lab is to get you familiarized with MARIE a simple computer
06/02/ Local & Metropolitan Area Networks 0. INTRODUCTION. 1. History and Future of TCP/IP ACOE322
 1 Local & Metropolitan Area Networks ACOE322 Lecture 5 TCP/IP Protocol suite and IP addressing 1 0. INTRODUCTION We shall cover in this topic: 1. The relation of TCP/IP with internet and OSI model 2. Internet
1 Local & Metropolitan Area Networks ACOE322 Lecture 5 TCP/IP Protocol suite and IP addressing 1 0. INTRODUCTION We shall cover in this topic: 1. The relation of TCP/IP with internet and OSI model 2. Internet
The Stored Program Computer
 The Stored Program Computer 1 1945: John von Neumann Wrote a report on the stored program concept, known as the First Draft of a Report on EDVAC also Alan Turing Konrad Zuse Eckert & Mauchly The basic
The Stored Program Computer 1 1945: John von Neumann Wrote a report on the stored program concept, known as the First Draft of a Report on EDVAC also Alan Turing Konrad Zuse Eckert & Mauchly The basic
Network Architecture I
 Network Architecture I Degree in: Communications Electronic Engineering Telecommunication Systems Engineering Telecommunication Technologies Engineering Telematics Engineering Universidad de Alcalá 2016/17
Network Architecture I Degree in: Communications Electronic Engineering Telecommunication Systems Engineering Telecommunication Technologies Engineering Telematics Engineering Universidad de Alcalá 2016/17
Faculty of Science and IT Course title. Pre-requisite/corequisite
 Faculty Course number Faculty of Science and IT 022242 Department Course title Computer Science Network Protocols Number of credit hours 3 Pre-requisite/corequisite Computer network Brief course description.
Faculty Course number Faculty of Science and IT 022242 Department Course title Computer Science Network Protocols Number of credit hours 3 Pre-requisite/corequisite Computer network Brief course description.
Apletai (įskiepiai) Lekt. dr. Pijus Kasparaitis m. m. pavasario semestras.
 Apletai (įskiepiai) Lekt. dr. Pijus Kasparaitis pkasparaitis@yahoo.com 2008-2009 m. m. pavasario semestras Java grafinės bibliotekos AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) Swing 2009.04.09 P.Kasparaitis. Objektinis
Apletai (įskiepiai) Lekt. dr. Pijus Kasparaitis pkasparaitis@yahoo.com 2008-2009 m. m. pavasario semestras Java grafinės bibliotekos AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) Swing 2009.04.09 P.Kasparaitis. Objektinis
(Advanced) Computer Organization & Architechture. Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (3 rd Week)
 + (Advanced) Computer Organization & Architechture Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (3 rd Week) + Outline 2. The computer system 2.1 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection 2.2 Cache Memory
+ (Advanced) Computer Organization & Architechture Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (3 rd Week) + Outline 2. The computer system 2.1 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection 2.2 Cache Memory
CPU Structure and Function. Chapter 12, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition
 CPU Structure and Function Chapter 12, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition CPU must: CPU Function Fetch instructions Interpret/decode instructions Fetch data Process data
CPU Structure and Function Chapter 12, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition CPU must: CPU Function Fetch instructions Interpret/decode instructions Fetch data Process data
CSE 473s Introduction to Computer Networks
 CSE 473s Introduction to Computer Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-09/
CSE 473s Introduction to Computer Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-09/
Computer Organization II CMSC 3833 Lecture 33
 Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye, Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye, Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved.
 + William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
+ William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
Where Does The Cpu Store The Address Of The
 Where Does The Cpu Store The Address Of The Next Instruction To Be Fetched The three most important buses are the address, the data, and the control buses. The CPU always knows where to find the next instruction
Where Does The Cpu Store The Address Of The Next Instruction To Be Fetched The three most important buses are the address, the data, and the control buses. The CPU always knows where to find the next instruction
IT4405 Computer Networks (Compulsory)
 IT4405 Computer Networks (Compulsory) INTRODUCTION This course provides a comprehensive insight into the fundamental concepts in data communications, computer network systems and protocols both fixed and
IT4405 Computer Networks (Compulsory) INTRODUCTION This course provides a comprehensive insight into the fundamental concepts in data communications, computer network systems and protocols both fixed and
Elektroninis.lt šakninių sertifikatų diegimas
 Elektroninis.lt šakninių sertifikatų diegimas Ši instrukcija aprašo, kaip į kompiuterį įdiegti šakninius elektroninis.lt sertifikatus. Diegimo darbus galima atlikti turint kompiuterio administratoriaus
Elektroninis.lt šakninių sertifikatų diegimas Ši instrukcija aprašo, kaip į kompiuterį įdiegti šakninius elektroninis.lt sertifikatus. Diegimo darbus galima atlikti turint kompiuterio administratoriaus
Chapter 1 : Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction A Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable, clock driven, register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory,
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction A Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable, clock driven, register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory,
Lecture1: introduction. Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit
 Lecture1: introduction Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit 1 1. History overview Computer systems have conventionally
Lecture1: introduction Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit 1 1. History overview Computer systems have conventionally
SAE5C Computer Organization and Architecture. Unit : I - V
 SAE5C Computer Organization and Architecture Unit : I - V UNIT-I Evolution of Pentium and Power PC Evolution of Computer Components functions Interconnection Bus Basics of PCI Memory:Characteristics,Hierarchy
SAE5C Computer Organization and Architecture Unit : I - V UNIT-I Evolution of Pentium and Power PC Evolution of Computer Components functions Interconnection Bus Basics of PCI Memory:Characteristics,Hierarchy
Chapter 16. Control Unit Operation. Yonsei University
 Chapter 16 Control Unit Operation Contents Micro-Operation Control of the Processor Hardwired Implementation 16-2 Micro-Operations Micro-Operations Micro refers to the fact that each step is very simple
Chapter 16 Control Unit Operation Contents Micro-Operation Control of the Processor Hardwired Implementation 16-2 Micro-Operations Micro-Operations Micro refers to the fact that each step is very simple
The Institution of Engineers - Sri Lanka
 / The Institution of Engineers - Sri Lanka PART III- EXAMINATION 2012 311- COMPUTER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Time Allowed: 3 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This paper contains 8 questions in 5 pages 2.
/ The Institution of Engineers - Sri Lanka PART III- EXAMINATION 2012 311- COMPUTER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Time Allowed: 3 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This paper contains 8 questions in 5 pages 2.
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane. Part A. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane Part A All material copyright 996-06 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th Edition, Global Edition Jim Kurose,
Chapter 4 Network Layer: The Data Plane Part A All material copyright 996-06 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th Edition, Global Edition Jim Kurose,
Chapter 20 - Microprogrammed Control (9 th edition)
 Chapter 20 - Microprogrammed Control (9 th edition) Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 20 - Microprogrammed Control 1 / 47 Table of Contents I 1 Motivation 2 Basic Concepts
Chapter 20 - Microprogrammed Control (9 th edition) Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 20 - Microprogrammed Control 1 / 47 Table of Contents I 1 Motivation 2 Basic Concepts
DUOMENŲ STRUKTŪROS IR ALGORITMAI. Rūšiavimo algoritmai (įterpimo, burbulo, išrinkimo)
 DUOMENŲ STRUKTŪROS IR ALGORITMAI Rūšiavimo algoritmai (įterpimo, burbulo, išrinkimo) Rūšiavimo veiksmas Kasdieniniame gyvenime mes dažnai rūšiuojame: Failus kataloguose Katalogus lokaliame diske Kasdienines
DUOMENŲ STRUKTŪROS IR ALGORITMAI Rūšiavimo algoritmai (įterpimo, burbulo, išrinkimo) Rūšiavimo veiksmas Kasdieniniame gyvenime mes dažnai rūšiuojame: Failus kataloguose Katalogus lokaliame diske Kasdienines
CPU ARCHITECTURE. QUESTION 1 Explain how the width of the data bus and system clock speed affect the performance of a computer system.
 CPU ARCHITECTURE QUESTION 1 Explain how the width of the data bus and system clock speed affect the performance of a computer system. ANSWER 1 Data Bus Width the width of the data bus determines the number
CPU ARCHITECTURE QUESTION 1 Explain how the width of the data bus and system clock speed affect the performance of a computer system. ANSWER 1 Data Bus Width the width of the data bus determines the number
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapters 1 & 3 System Architecture Rev. 3.1.2 (2011-12) by Enrico Nardelli 1&3-1 Le persone che scoprono la potenza e la bellezza di idee di alto
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapters 1 & 3 System Architecture Rev. 3.1.2 (2011-12) by Enrico Nardelli 1&3-1 Le persone che scoprono la potenza e la bellezza di idee di alto
C.P.U Organization. Memory Unit. Central Processing Unit (C.P.U) Input-Output Processor (IOP) Figure (1) Digital Computer Block Diagram
 C.P.U Organization 1.1 Introduction A computer system is sometimes subdivided into two functional entities "Hardware" and "Software". The H/W of the computer consists of all the electronic components and
C.P.U Organization 1.1 Introduction A computer system is sometimes subdivided into two functional entities "Hardware" and "Software". The H/W of the computer consists of all the electronic components and
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model
 Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atananasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atananasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Context and Motivation To better understand a software system, it is mandatory understand two elements: - The computer as a basic building block for the application - The operating
Computer Architecture Context and Motivation To better understand a software system, it is mandatory understand two elements: - The computer as a basic building block for the application - The operating
Micro-programmed Control Ch 15
 Micro-programmed Control Ch 15 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics 1 Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to modify Lots of
Micro-programmed Control Ch 15 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics 1 Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to modify Lots of
Machine Instructions vs. Micro-instructions. Micro-programmed Control Ch 15. Machine Instructions vs. Micro-instructions (2) Hardwired Control (4)
 Micro-programmed Control Ch 15 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics 1 Machine Instructions vs. Micro-instructions Memory execution unit CPU control memory
Micro-programmed Control Ch 15 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics 1 Machine Instructions vs. Micro-instructions Memory execution unit CPU control memory
Micro-programmed Control Ch 15
 Micro-programmed Control Ch 15 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics 1 Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to modify Lots of
Micro-programmed Control Ch 15 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics 1 Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to modify Lots of
EE6364 Advanced Data Networks
 EE 6364 Advanced Data Networks Fall, 2014 Instructor: Dr. David C. Wang Office: Office-Hour: by appointment Mailbox: NH Room 549 E-mail: dwang@exchange.uta.edu Course web site: http://www-ee.uta.edu/online/wang
EE 6364 Advanced Data Networks Fall, 2014 Instructor: Dr. David C. Wang Office: Office-Hour: by appointment Mailbox: NH Room 549 E-mail: dwang@exchange.uta.edu Course web site: http://www-ee.uta.edu/online/wang
Author : Dalbir Singh, Computer Science Deptt. CPU Structure and Functions. 1. Processor Organization
 Author : Dalbir Singh, Computer Science Deptt. CPU Structure and Functions 1. Processor Organization To understand the organization of the CPU, let us consider the requirements placed on the CPU, the things
Author : Dalbir Singh, Computer Science Deptt. CPU Structure and Functions 1. Processor Organization To understand the organization of the CPU, let us consider the requirements placed on the CPU, the things
Paskirstytos atminties lygiagretusis programavimas Įvadas į MPI
 Paskirstytos atminties lygiagretusis programavimas Įvadas į MPI Distributed memory parallel programming Paskirstytos atminties lygiagretieji kompiuteriai Kiekvienas procesorius turi tik savo nuosavą atmintį
Paskirstytos atminties lygiagretusis programavimas Įvadas į MPI Distributed memory parallel programming Paskirstytos atminties lygiagretieji kompiuteriai Kiekvienas procesorius turi tik savo nuosavą atmintį
Summary of Computer Architecture
 Summary of Computer Architecture Summary CHAP 1: INTRODUCTION Structure Top Level Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output
Summary of Computer Architecture Summary CHAP 1: INTRODUCTION Structure Top Level Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output
structural RTL for mov ra, rb Answer:- (Page 164) Virtualians Social Network Prepared by: Irfan Khan
 Solved Subjective Midterm Papers For Preparation of Midterm Exam Two approaches for control unit. Answer:- (Page 150) Additionally, there are two different approaches to the control unit design; it can
Solved Subjective Midterm Papers For Preparation of Midterm Exam Two approaches for control unit. Answer:- (Page 150) Additionally, there are two different approaches to the control unit design; it can
Running Applications
 Running Applications Computer Hardware Central Processing Unit (CPU) CPU PC IR MAR MBR I/O AR I/O BR To exchange data with memory Brain of Computer, controls everything Few registers PC (Program Counter):
Running Applications Computer Hardware Central Processing Unit (CPU) CPU PC IR MAR MBR I/O AR I/O BR To exchange data with memory Brain of Computer, controls everything Few registers PC (Program Counter):
C++ programavimo kalba
 C++ programavimo kalba Šablonai (10 paskaita) Kodėl šablonai (templates)? Programuojant egzistuoja situacijos, kai reikia atlikti tuos pačius veiksmus su skirtingais duomenų tipais (pvz. modulio radimas,
C++ programavimo kalba Šablonai (10 paskaita) Kodėl šablonai (templates)? Programuojant egzistuoja situacijos, kai reikia atlikti tuos pačius veiksmus su skirtingais duomenų tipais (pvz. modulio radimas,
ios Uždara operacinė sistema skirta tik Apple įrenginiams: iphone ipad ipod touch Apple TV
 ios Uždara operacinė sistema skirta tik Apple įrenginiams: iphone ipad ipod touch Apple TV Pagrindas OS X, skirtas ARM įrenginiams Programavimo aplinka: XCode ir Objective-C Programavimo kompiuteris -
ios Uždara operacinė sistema skirta tik Apple įrenginiams: iphone ipad ipod touch Apple TV Pagrindas OS X, skirtas ARM įrenginiams Programavimo aplinka: XCode ir Objective-C Programavimo kompiuteris -
Processing Unit CS206T
 Processing Unit CS206T Microprocessors The density of elements on processor chips continued to rise More and more elements were placed on each chip so that fewer and fewer chips were needed to construct
Processing Unit CS206T Microprocessors The density of elements on processor chips continued to rise More and more elements were placed on each chip so that fewer and fewer chips were needed to construct
ENIAC - background. ENIAC - details. Structure of von Nuemann machine. von Neumann/Turing Computer Architecture
 168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables
168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables
ĮVADAS JVM Java Virtual Machine Java virtualios mašinos (JVM) JVM write once, run everywhere
 ĮVADAS The Java programming language was introduced in 1995 by Sun Microsystems which has since merged into Oracle Corporation. Derived from languages such as C and C++. Pradžioje Java buvo skirta programuoti
ĮVADAS The Java programming language was introduced in 1995 by Sun Microsystems which has since merged into Oracle Corporation. Derived from languages such as C and C++. Pradžioje Java buvo skirta programuoti
On successful completion of this course students should:
 CIT306 Computer Networks Course Name Computer Networks Course Code CIT 306 Course Type Area Elective Course Level Undergraduate AKTS Credit 5 ECTS Course hours per week 3 (Institutional) Practice hours
CIT306 Computer Networks Course Name Computer Networks Course Code CIT 306 Course Type Area Elective Course Level Undergraduate AKTS Credit 5 ECTS Course hours per week 3 (Institutional) Practice hours
CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM CS401 Communication Engineering & Coding Theory Knowledge of communication engineering & coding theory IV
 Course: CS602 Computer Networks PROGRAMME: COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING DEGREE:B. TECH COURSE: Computer Networks SEMESTER: VI CREDITS: 3 COURSECODE: CS602 COURSE TYPE: Theory COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: Communication
Course: CS602 Computer Networks PROGRAMME: COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING DEGREE:B. TECH COURSE: Computer Networks SEMESTER: VI CREDITS: 3 COURSECODE: CS602 COURSE TYPE: Theory COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: Communication
Basics of Microprocessor
 Unit 1 Basics of Microprocessor 1. Microprocessor Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable integrated device that has computing and decision making capability. This semiconductor IC is manufactured
Unit 1 Basics of Microprocessor 1. Microprocessor Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable integrated device that has computing and decision making capability. This semiconductor IC is manufactured
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Guoping Qiu School of Computer Science The University of Nottingham http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~qiu 1 The World of Computers Computers are everywhere Cell phones Game consoles
Computer Systems Architecture Guoping Qiu School of Computer Science The University of Nottingham http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~qiu 1 The World of Computers Computers are everywhere Cell phones Game consoles
Micro-programmed Control Ch 17
 Micro-programmed Control Ch 17 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics Course Summary 1 Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to
Micro-programmed Control Ch 17 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics Course Summary 1 Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527 Computer Networks 1 / 16 Outline 1 Information 2 Broad Overview
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527 Computer Networks 1 / 16 Outline 1 Information 2 Broad Overview
CIT 668: System Architecture. Computer Systems Architecture
 CIT 668: System Architecture Computer Systems Architecture 1. System Components Topics 2. Bandwidth and Latency 3. Processor 4. Memory 5. Storage 6. Network 7. Operating System 8. Performance Implications
CIT 668: System Architecture Computer Systems Architecture 1. System Components Topics 2. Bandwidth and Latency 3. Processor 4. Memory 5. Storage 6. Network 7. Operating System 8. Performance Implications
COSC 243. Computer Architecture 1. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture) Lecture 6 - Computer Architecture 1 1
 COSC 243 Computer Architecture 1 COSC 243 (Computer Architecture) Lecture 6 - Computer Architecture 1 1 Overview Last Lecture Flip flops This Lecture Computers Next Lecture Instruction sets and addressing
COSC 243 Computer Architecture 1 COSC 243 (Computer Architecture) Lecture 6 - Computer Architecture 1 1 Overview Last Lecture Flip flops This Lecture Computers Next Lecture Instruction sets and addressing
Hardwired Control (4) Micro-programmed Control Ch 17. Micro-programmed Control (3) Machine Instructions vs. Micro-instructions
 Micro-programmed Control Ch 17 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics Course Summary Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to modify
Micro-programmed Control Ch 17 Micro-instructions Micro-programmed Control Unit Sequencing Execution Characteristics Course Summary Hardwired Control (4) Complex Fast Difficult to design Difficult to modify
Lecture 5: Computer Organization Instruction Execution. Computer Organization Block Diagram. Components. General Purpose Registers.
 Lecture 5: Computer Organization Instruction Execution Computer Organization Addressing Buses Fetch-Execute Cycle Computer Organization CPU Control Unit U Input Output Memory Components Control Unit fetches
Lecture 5: Computer Organization Instruction Execution Computer Organization Addressing Buses Fetch-Execute Cycle Computer Organization CPU Control Unit U Input Output Memory Components Control Unit fetches
Amadeus On-Line Helpdesk
 Amadeus On-Line Helpdesk Vartotojo instrukcija Skirta kelionių agentūroms Turinys Įžanga... 3 Jungimasis prie Amadeus Helpdesk... 3 Patarimai ir pastabos... 7 Dokumento valdymas 2007 Apsauga Viešas Įmon
Amadeus On-Line Helpdesk Vartotojo instrukcija Skirta kelionių agentūroms Turinys Įžanga... 3 Jungimasis prie Amadeus Helpdesk... 3 Patarimai ir pastabos... 7 Dokumento valdymas 2007 Apsauga Viešas Įmon
Digital System Design Using Verilog. - Processing Unit Design
 Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252 Prof. Mark D. Hill Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252 Prof. Mark D. Hill Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252 Prof. Mark D. Hill Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 4 The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper
CEN 444 Computer networks. Dr. Mohamed Abd-Eldayem
 CEN 444 Computer networks Dr. Mohamed Abd-Eldayem Dr. Mohamed Abd-Eldayem Associate-Professor Dept. of Comp. Engineering College of Computer and Information Sciences (CCIS) King Saud University Email:
CEN 444 Computer networks Dr. Mohamed Abd-Eldayem Dr. Mohamed Abd-Eldayem Associate-Professor Dept. of Comp. Engineering College of Computer and Information Sciences (CCIS) King Saud University Email:
Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer Function
 Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer Function Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 3 - Top Level View 1 / 127 Table of Contents I 1 Introduction 2 Computer Components
Chapter 3 - Top Level View of Computer Function Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 3 - Top Level View 1 / 127 Table of Contents I 1 Introduction 2 Computer Components
Introduction to CPU architecture using the M6800 microprocessor
 Introduction to CPU architecture using the M6800 microprocessor Basics Programs are written in binary object codes which could be understood (after the decoding process) by the designated target CPU. The
Introduction to CPU architecture using the M6800 microprocessor Basics Programs are written in binary object codes which could be understood (after the decoding process) by the designated target CPU. The
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer. Chapter 4 Objectives. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 CPU Basics
 Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
ARM processor organization
 ARM processor organization P. Bakowski bako@ieee.org ARM register bank The register bank,, which stores the processor state. r00 r01 r14 r15 P. Bakowski 2 ARM register bank It has two read ports and one
ARM processor organization P. Bakowski bako@ieee.org ARM register bank The register bank,, which stores the processor state. r00 r01 r14 r15 P. Bakowski 2 ARM register bank It has two read ports and one
