Chapter 9 RIP Commands
|
|
|
- Crystal Wilkerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 RIP Commands default-metric Defines the global default-metric value that will be assigned to all external routes imported into RIP for redistribution. RIP must be active on the routing switch for this command to be operational. To assign a default metric of 4 to all routes imported as RIP, enter the following: HP9300(config-rip-router)# def 4 Syntax: default-metric <value> Possible values: 1 15 Default value: 1 deny redistribute Defines the route types upon which you do not want to perform RIP redistribution. RIP must be active on the routing switch for this command to be operational. RIP is enabled by default. To deny redistribution on all incoming routes received from the network, enter the following: HP9300(config-rip-router)# deny redis 2 all Syntax: deny redistribute <index> all ospf static address <ip-addr> <ip-mask> [match-metric <value> set-metric <value>] 9-1
2 Command Line Interface Reference Possible values: all ospf static ip address match-metric set-metric apply redistribution to all route types apply redistribution to OSPF routes only apply redistribution to the static route only apply redistribution to a specific network and sub-net address apply redistribution to those routes with a specific metric value; possible values are 1 15 N/A to deny redistribute command end exit filter Moves activity to the privileged EXEC level from any level of the CLI except the user EXEC level. To move to the privileged level, enter the following from any level of the CLI. HP9300(config-rip-router)# end HP9300# Syntax: end Moves activity up one level from the current level. In this case, activity will be moved to the global level. HP9300(config-rip-router)# exit HP9300(config)# Syntax: exit Defines which IP/RIP network numbers the router will learn from the RIP protocol and store in its IP routing table. Once RIP filters are defined, you can assign these filters to individual interfaces with the filter-group command at the Interface Level of CLI. To define an IP/RIP filter, you must first enable RIP on the router using the router rip command to access the RIP Router Level of the CLI. NOTE: A filter defines for inbound routes what routes it will permit to be stored in its IP routing table. For outbound routes, the filter defines what routes are allowed to be advertised through a given interface. You can also specify all routes by using the value, any, instead of specifying a specific route. An IP address and mask define a route. 9-2
3 RIP Commands To define filters with respect to network traffic from , , and , enter the following: HP9300(config-rip-router)# filter 1 permit HP9300(config-rip-router)# filter 2 permit HP9300(config-rip-router)# filter 3 permit HP9300(config-rip-router)# filter 4 deny To enable logging on filter 1 and apply the filter to interface 1/2: HP9300(config-rip-router)# filter 1 deny any any log HP9300(config-rip-router)# int e 1/2 HP9300(config-if-e1000-1/2)# ip rip filter-g in 1 HP9300(config-if-e1000-1/2)# ip rip filter-g out 1 Syntax: filter <filter-num> permit deny <source-ip-addr> any <source-ip-mask> any [log] When the RIP filter causes packets to be denied, the following messages appear in the syslog: 00d00h00m00s:W:rip filter list 1 in V1 denied , 1 packets 00d00h00m00s:W:rip filter list 1 out V1 denied , 1 packets The format of the syslog message is as follows: <time>:w:rip filter list <list-num> <direction> V1 V2 denied <ip-addr>, <num> packets The <list-num> is the ID of the filter list. The <direction> indicates whether the filter was applied to incoming packets or outgoing packets. The value can be one of the following: in out The V1 or V2 value specifies the RIP version (RIPv1 or RIPv2). The <ip-addr> indicates the network number in the denied updates. The <num> indicates how many packets matching the values above were dropped during the five-minute interval represented by the log entry. Possible values: Filter ID: 1 to 64 filter-group Assigns a group of defined RIP filters on either a global or interface basis. Assignments to interfaces are done at the interface level of the CLI. HP9300(config-rip-router)# filter-group out Syntax: filter-group in out <1-64> [<1-64>] Possible values: 1 64 (filter index value) learn-default This feature allows a routing switch to learn and advertise default IP/RIP routes. This command can be applied on a global or interface basis. This example shows the feature enabled at the global level. HP9300(config-rip-router)# learn-default 9-3
4 Command Line Interface Reference Syntax: learn-default neighbor Specifies those routing switches from which a routing switch will receive RIP routes. In the example below, no RIP routes will be learned from any neighbor router. By default, RIP routes will be learned from all neighbors. To configure a routing switch so that no RIP routes are learned from its neighbor routers, enter the following: HP9300(config-rip-router)# neighbor 1 deny any Syntax: neighbor <number> permit deny <ip-addr> any Possible values: 1 64 no Disables other commands. To disable a command, place the word no before the command. permit redistribute quit Allows you to define the route types upon which you want to perform RIP redistribution. To allow (permit) redistribution of all routes received from network , enter the following: HP9300(config-rip-router)# permit redis 1 all Syntax: permit deny redistribute <filter-num> all bgp ospf static <ip-addr> <ip-mask> [match-metric<value> set-metric <value>] Possible values: The all parameter applies redistribution to all route types. The bgp parameter applies redistribution to BGP4 routes only. The ospf parameter applies redistribution to OSPF routes only. The static parameter applies redistribution to the static route only. The <ip-addr> <ip-mask> parameters apply redistribution to the specified network and sub-net address. The match-metric <value> parameter applies redistribution to those routes with a specific metric value; possible values are from The set-metric <value> parameter sets the RIP metric value that will be applied to those routes imported into RIP. Returns you from any level of the CLI to the User EXEC mode. HP9300(config-rip-router)# quit HP9300> Syntax: quit 9-4
5 RIP Commands redistribution show Enables RIP route redistribution on a routing switch. When enabled, RIP will import external routes (OSPF or Static Routes) into the RIP domain. Do this prior to setting up the redistribution table using the permit and deny commands. To enable RIP redistribution on the routing switch, enter the following within the Router RIP Level. HP9300(config-rip-router)# redistribution Syntax: redistribution Default value: disabled Displays a variety of configuration and statistical information about the switch or routing switch. See Show Commands on page update-time Sets the time interval that will exist between the transmission of regular RIP response packets. This parameter is set to 30 seconds by default. RIP must be enabled and active on the routing switch for this command to be operational. To modify the default update time value to 120 seconds, enter the following: HP9300(config-rip-router)# update 120 Syntax: update-time <value> Possible values: 1 1,000 seconds Default value: 30 seconds use-vrrp-path Prevents Backup VRRP routers from advertising route information for the backed up interface, by enabling suppression of the advertisements. To suppress RIP advertisements for a backed up interface, enter the following command on the VRRP Backup router: HP9300(config-rip-router)# use-vrrp-path Syntax: use-vrrp-path write memory Saves the running configuration into the startup-config file. HP9300(config-rip-router)# wr mem Syntax: write memory write terminal Displays the running configuration of the HP switch or routing switch on the terminal screen. NOTE: This command is equivalent to the show running-config command. 9-5
6 Command Line Interface Reference HP9300# wr term Syntax: write terminal 9-6
Chapter 13 RIP Commands
 Chapter 13 RIP Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about IPv4 RIP commands only. For information about IPv6 RIP commands, see IPv6 RIP Commands on page 14-1. default-metric Defines the global
Chapter 13 RIP Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about IPv4 RIP commands only. For information about IPv6 RIP commands, see IPv6 RIP Commands on page 14-1. default-metric Defines the global
Chapter 7 Interface Commands
 Chapter 7 Interface Commands appletalk address Assigns AppleTalk addresses to a seed router. To assign an AppleTalk address of 10.5 to interface 3, module 2, enter the following: HP9300(config)# int e
Chapter 7 Interface Commands appletalk address Assigns AppleTalk addresses to a seed router. To assign an AppleTalk address of 10.5 to interface 3, module 2, enter the following: HP9300(config)# int e
Chapter 12 Configuring IPX
 Chapter 12 Configuring IPX This chapter covers how to configure the IPX protocol on the HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. A summary of all CLI commands noting syntax along
Chapter 12 Configuring IPX This chapter covers how to configure the IPX protocol on the HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. A summary of all CLI commands noting syntax along
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands
 Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 10 IP Access Lists: Standard
 Chapter 10 IP Access Lists: Standard NOTE: This chapter contains information for standard ACLs configured using the ip access-list command. The command manages named and numbered ACLs under the standard
Chapter 10 IP Access Lists: Standard NOTE: This chapter contains information for standard ACLs configured using the ip access-list command. The command manages named and numbered ACLs under the standard
Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands
 Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands NOTE: This chapter describes commands in the BGP configuration level, which is present on HP devices that support IPv4 only. For information about BGP commands and configuration
Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands NOTE: This chapter describes commands in the BGP configuration level, which is present on HP devices that support IPv4 only. For information about BGP commands and configuration
Appendix B Policies and Filters
 Appendix B Policies and Filters NOTE: This appendix does not describe Access Control Lists (ACLs) or IPX SAP ACLs, which are additional methods for filtering packets. See Software-Based IP Access Control
Appendix B Policies and Filters NOTE: This appendix does not describe Access Control Lists (ACLs) or IPX SAP ACLs, which are additional methods for filtering packets. See Software-Based IP Access Control
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF
 Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 20 IPv6 BGP Unicast Address Family Commands
 Chapter 20 IPv6 BGP Unicast Address Family Commands NOTE: The IPv6 BGP unicast address family configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6 and the ProCurve 9408sl Routing Switch
Chapter 20 IPv6 BGP Unicast Address Family Commands NOTE: The IPv6 BGP unicast address family configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6 and the ProCurve 9408sl Routing Switch
Chapter 24 PIM Commands
 Chapter 24 PIM Commands bsr-candidate Configures the Routing Switch as a candidate PIM Sparse Bootstrap Router (BSR). To configure the Routing Switch as a candidate BSR, enter a command such as the following:
Chapter 24 PIM Commands bsr-candidate Configures the Routing Switch as a candidate PIM Sparse Bootstrap Router (BSR). To configure the Routing Switch as a candidate BSR, enter a command such as the following:
Chapter 32 VSRP Commands
 Chapter 32 VSRP Commands activate Activates a VSRP VRID. NOTE: This command is equivalent to the enable command. ProCurveRS(config)# vlan 200 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)# tag ethernet 1/1 to 1/8 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)#
Chapter 32 VSRP Commands activate Activates a VSRP VRID. NOTE: This command is equivalent to the enable command. ProCurveRS(config)# vlan 200 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)# tag ethernet 1/1 to 1/8 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)#
Antonio Cianfrani. Access Control List (ACL) Part I
 Antonio Cianfrani Access Control List (ACL) Part I Index ACL? How to configure Standard ACL Extended ACL Named ACL Limiting the vty access ACL (1/3) Control lists applied to traffic incoming in / outgoing
Antonio Cianfrani Access Control List (ACL) Part I Index ACL? How to configure Standard ACL Extended ACL Named ACL Limiting the vty access ACL (1/3) Control lists applied to traffic incoming in / outgoing
EIGRP Support for Route Map Filtering
 The feature enables Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to interoperate with other protocols to leverage additional routing functionality by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based
The feature enables Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to interoperate with other protocols to leverage additional routing functionality by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based
Chapter 17 Configuring IPX (9300 Series Only)
 Chapter 17 Configuring IPX (9300 Series Only) This chapter describes how to configure the IPX protocol on the ProCurve Routing Switches using the CLI and Web management interface. For information about
Chapter 17 Configuring IPX (9300 Series Only) This chapter describes how to configure the IPX protocol on the ProCurve Routing Switches using the CLI and Web management interface. For information about
Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4
 Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4 This chapter provides details on how to configure Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP4) on HP products using the CLI and the Web management interface. BGP4 is supported on
Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4 This chapter provides details on how to configure Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP4) on HP products using the CLI and the Web management interface. BGP4 is supported on
Chapter 14 Configuring SRP
 Chapter 14 Configuring SRP This chapter describes how to configure the HP ProCurve 9304M, 9308M, or 6308M-SX routing switch to use the Standby Router Protocol (SRP), a proprietary protocol that provides
Chapter 14 Configuring SRP This chapter describes how to configure the HP ProCurve 9304M, 9308M, or 6308M-SX routing switch to use the Standby Router Protocol (SRP), a proprietary protocol that provides
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
Chapter 4 Software-Based IP Access Control Lists (ACLs)
 Chapter 4 Software-Based IP Access Control Lists (ACLs) This chapter describes software-based ACLs, which are ACLs that processed traffic in software or CPU. (This type of ACL was also referred to as flow-based
Chapter 4 Software-Based IP Access Control Lists (ACLs) This chapter describes software-based ACLs, which are ACLs that processed traffic in software or CPU. (This type of ACL was also referred to as flow-based
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface
 Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface The CLI is a text-based interface for configuring and monitoring HP Routing Switches. You can access the CLI can through either a direct serial connection to
Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface The CLI is a text-based interface for configuring and monitoring HP Routing Switches. You can access the CLI can through either a direct serial connection to
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands
 Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands aaa Defines an authentication-method list for access to a switch or routing switch. To configure an access method list, enter a command such as the following: HP9300(config)#
Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands aaa Defines an authentication-method list for access to a switch or routing switch. To configure an access method list, enter a command such as the following: HP9300(config)#
Chapter 10 Configuring SRP
 Chapter 10 Configuring SRP This chapter describes how to configure the HP 9304M, HP 9308M, and HP 6208M-SX routing switches to use the Standby Router Protocol (SRP), a proprietary protocol that provides
Chapter 10 Configuring SRP This chapter describes how to configure the HP 9304M, HP 9308M, and HP 6208M-SX routing switches to use the Standby Router Protocol (SRP), a proprietary protocol that provides
Chapter 3 Command List
 Chapter 3 Command List This chapter lists all the commands in the CLI. The commands are listed in two ways: All commands are listed together in a single alphabetic list. See Complete Command List on page
Chapter 3 Command List This chapter lists all the commands in the CLI. The commands are listed in two ways: All commands are listed together in a single alphabetic list. See Complete Command List on page
BGP Route-Map Continue
 The feature introduces the continue clause to BGP route-map configuration. The continue clause allows for more programmable policy configuration and route filtering and introduces the capability to execute
The feature introduces the continue clause to BGP route-map configuration. The continue clause allows for more programmable policy configuration and route filtering and introduces the capability to execute
Operation Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Lab 6: Access Lists. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/ R1
 Lab 6: Access Lists Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 ----- R1 Fa 0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ----- Se 0/0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 6: Access Lists Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 ----- R1 Fa 0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ----- Se 0/0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
 26 CHAPTER Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way for customers to share bandwidth over an ISP backbone network. A VPN is a collection of sites sharing a common routing table. A customer
26 CHAPTER Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way for customers to share bandwidth over an ISP backbone network. A VPN is a collection of sites sharing a common routing table. A customer
BGP Named Community Lists
 The feature allows the network operator to assign meaningful names to community lists and increases the number of community lists that can be configured. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information
The feature allows the network operator to assign meaningful names to community lists and increases the number of community lists that can be configured. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information
RIP Commands. output-delay, page 32 passive-interface (RIP), page 33 poison-reverse, page 35 receive version, page 37 redistribute (RIP), page 39
 RIP Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). For detailed information about RIP concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
RIP Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). For detailed information about RIP concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
OSPFv3 Route Filtering Using Distribute-List
 The OSPFv3 route filtering using distribute-list feature allows users to filter the incoming routes that are programmed in routing table, and the outgoing routes that are advertised. Finding Feature Information,
The OSPFv3 route filtering using distribute-list feature allows users to filter the incoming routes that are programmed in routing table, and the outgoing routes that are advertised. Finding Feature Information,
Defining Route Maps. Information About Route Maps CHAPTER
 20 CHAPTER This chapter describes route maps and includes the following sections: Information About Route Maps, page 20-1 Licensing Requirements for Route Maps, page 20-3 Guidelines and Limitations, page
20 CHAPTER This chapter describes route maps and includes the following sections: Information About Route Maps, page 20-1 Licensing Requirements for Route Maps, page 20-3 Guidelines and Limitations, page
Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface
 Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface The CLI is a text-based interface for configuring and monitoring ProCurve Routing Switches. You can access the CLI through either a direct serial connection to
Chapter 2 Using the Command Line Interface The CLI is a text-based interface for configuring and monitoring ProCurve Routing Switches. You can access the CLI through either a direct serial connection to
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
BGP Graceful Shutdown
 The feature reduces or eliminates the loss of traffic along a link being shut down for maintenance. Routers always have a valid route available during the convergence process. This feature is used primarily
The feature reduces or eliminates the loss of traffic along a link being shut down for maintenance. Routers always have a valid route available during the convergence process. This feature is used primarily
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
EIGRP Route Tag Enhancements
 The feature enables you to specify and display route tags in dotted-decimal format, filter routes using the route tag value with wildcard mask, and set a default route tag for all internal Enhanced Interior
The feature enables you to specify and display route tags in dotted-decimal format, filter routes using the route tag value with wildcard mask, and set a default route tag for all internal Enhanced Interior
Chapter 4: Manipulating Routing
 : Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
: Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
Route Maps. About Route Maps
 This chapter describes how to configure and customize route-maps, for Cisco ASA. About, on page 1 Guidelines for, on page 3 Define a Route Map, on page 3 Customize a Route Map, on page 3 Example for, on
This chapter describes how to configure and customize route-maps, for Cisco ASA. About, on page 1 Guidelines for, on page 3 Define a Route Map, on page 3 Customize a Route Map, on page 3 Example for, on
Implementing RIP for IPv6
 Implementing RIP for IPv6 This module describes how to configure Routing Information Protocol for IPv6. RIP is a distance-vector routing protocol that uses hop count as a routing metric. RIP is an Interior
Implementing RIP for IPv6 This module describes how to configure Routing Information Protocol for IPv6. RIP is a distance-vector routing protocol that uses hop count as a routing metric. RIP is an Interior
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands
 Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multihoming with BGP and NAT
 Eliminating ISP as a single point of failure www.noction.com Table of Contents Introduction 1. R-NAT Configuration 1.1 NAT Configuration 5. ISPs Routers Configuration 3 15 7 7 5.1 ISP-A Configuration 5.2
Eliminating ISP as a single point of failure www.noction.com Table of Contents Introduction 1. R-NAT Configuration 1.1 NAT Configuration 5. ISPs Routers Configuration 3 15 7 7 5.1 ISP-A Configuration 5.2
BGP Commands: M through N
 match additional-paths advertise-set, on page 3 match as-path, on page 6 match community, on page 8 match extcommunity, on page 10 match local-preference, on page 12 match policy-list, on page 14 match
match additional-paths advertise-set, on page 3 match as-path, on page 6 match community, on page 8 match extcommunity, on page 10 match local-preference, on page 12 match policy-list, on page 14 match
Release Notes for Version of the HP ProCurve Routing Switch 9304M, 9308M,
 Release Notes for Version 05.2.16 of the HP ProCurve Routing Switch 9304M, 9308M, and 6308M-SX, and the HP ProCurve Switch 6208M-SX Operating System These release notes describe: New operating system enhancements
Release Notes for Version 05.2.16 of the HP ProCurve Routing Switch 9304M, 9308M, and 6308M-SX, and the HP ProCurve Switch 6208M-SX Operating System These release notes describe: New operating system enhancements
Seed Metrics and Route Redistribution
 Route Optimization Seed Metrics and Route Redistribution Using Multiple Routing Protocols! Interim during conversion From RIPv1 to EIGRP! Application-specific i ifi protocols One size does not always fit
Route Optimization Seed Metrics and Route Redistribution Using Multiple Routing Protocols! Interim during conversion From RIPv1 to EIGRP! Application-specific i ifi protocols One size does not always fit
Appendix B Command Line Interface Commands
 Appendix B Command Line Interface Commands This chapter provides detailed descriptions of all the CLI commands. A table of contents for all CLI commands, arranged alphabetically by CLI level, is found
Appendix B Command Line Interface Commands This chapter provides detailed descriptions of all the CLI commands. A table of contents for all CLI commands, arranged alphabetically by CLI level, is found
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands
 IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the features that are routing protocol-independent. For configuration information and examples on IP routing
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the features that are routing protocol-independent. For configuration information and examples on IP routing
Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands
 Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands aaa accounting Configures RADIUS or TACACS+ accounting for recording information about user activity and system events. When you configure accounting on an HP device, information
Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands aaa accounting Configures RADIUS or TACACS+ accounting for recording information about user activity and system events. When you configure accounting on an HP device, information
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
Table of Contents Chapter 1 Multicast Routing and Forwarding Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 Multicast Routing and Forwarding Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to Multicast Routing and Forwarding... 1-1 1.1.2 RPF Mechanism... 1-2 1.1.3 Multicast
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 Multicast Routing and Forwarding Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to Multicast Routing and Forwarding... 1-1 1.1.2 RPF Mechanism... 1-2 1.1.3 Multicast
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
Configuring RIP. Information About RIP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure the ASASM to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). This chapter includes
CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure the ASASM to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). This chapter includes
Configuring CDP. Understanding CDP CHAPTER. This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 3560 switch.
 21 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 3560 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
21 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 3560 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
security guide hp procurve routing switches 9304m, 9308m, and 9315m (software release or greater)
 hp procurve security guide hp procurve routing switches 9304m, 9308m, and 9315m (software release 7.6.04 or greater) www.hp.com/go/hpprocurve Security Guide for the HP ProCurve Routing Switches 9304M,
hp procurve security guide hp procurve routing switches 9304m, 9308m, and 9315m (software release 7.6.04 or greater) www.hp.com/go/hpprocurve Security Guide for the HP ProCurve Routing Switches 9304M,
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Chapter 8 Configuring Basic Features
 Chapter 8 Configuring Basic Features This chapter describes how to configure basic, non-protocol features on the HP 9304M, 9308M, and 6308M-SX routing switches, and on the 6208M-SX switch. A summary of
Chapter 8 Configuring Basic Features This chapter describes how to configure basic, non-protocol features on the HP 9304M, 9308M, and 6308M-SX routing switches, and on the 6208M-SX switch. A summary of
RIP Configuration. RIP Overview. Operation of RIP. Introduction. RIP routing table. RIP timers
 Table of Contents RIP Configuration 1 RIP Overview 1 Operation of RIP 1 Operation of RIP 2 RIP Version 2 RIP Message Format 3 Protocols and Standards 4 Configuring RIP Basic Functions 5 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents RIP Configuration 1 RIP Overview 1 Operation of RIP 1 Operation of RIP 2 RIP Version 2 RIP Message Format 3 Protocols and Standards 4 Configuring RIP Basic Functions 5 Configuration Prerequisites
Configuring VRF-lite CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 36 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way for customers to share bandwidth over an ISP backbone network. A VPN is a collection of sites sharing a common routing table. A customer
CHAPTER 36 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way for customers to share bandwidth over an ISP backbone network. A VPN is a collection of sites sharing a common routing table. A customer
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Redistribution & Layer 3 Path Control. Route Redistribution Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Redistribution & Layer 3 Path Control http:// Route Redistribution Overview Process of exchanging reachability information between routing domains e.g. OSPF to EIGRP
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Redistribution & Layer 3 Path Control http:// Route Redistribution Overview Process of exchanging reachability information between routing domains e.g. OSPF to EIGRP
IP Routing: RIP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: RIP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 11, 2013 Last Modified: January 11, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: RIP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 11, 2013 Last Modified: January 11, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Chapter 12 Configuring AppleTalk
 Chapter 12 Configuring AppleTalk This chapter describes how to configure AppleTalk on HP 9304M, HP 9308M, and HP 6208M-SX routing switches using the CLI and the Web management interface. The routing switches
Chapter 12 Configuring AppleTalk This chapter describes how to configure AppleTalk on HP 9304M, HP 9308M, and HP 6208M-SX routing switches using the CLI and the Web management interface. The routing switches
DE-CIX Academy: BGP Introduction. Notice of Liability. BGP Configuration Examples. Network Diagram for all examples. Links and Examples
 Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols
 Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Chapter 7 Routing Protocols Nonroutable Protocols In the early days of networking, networks were small collections of computers linked together For the purposes of sharing information and expensive peripherals
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) Course Overview
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) Course Overview This course will teach students about building a simple network, establishing internet connectivity, managing network device security,
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) Course Overview This course will teach students about building a simple network, establishing internet connectivity, managing network device security,
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
BGP Cost Community. Prerequisites for the BGP Cost Community Feature
 The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
A Commands. Send comments to
 This chapter describes the Cisco NX-OS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) commands that begin with A. UCR-555 area authentication (OSPF) area authentication (OSPF) To enable authentication for an Open Shortest
This chapter describes the Cisco NX-OS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) commands that begin with A. UCR-555 area authentication (OSPF) area authentication (OSPF) To enable authentication for an Open Shortest
Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features Topology
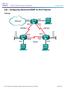 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Configuring BGP. Cisco s BGP Implementation
 Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF
 hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
Section 6.2, IP Routing. Section 6.4, IP/VPN Policy. Section 6.5, IP Quality of Service. Section 6.6, The BANDIT as Firewall
 Chapter 6 IP Routing and IPX Routing This chapter discusses IP routing, IP/VPN Policy, and related features in the BANDIT products. It also discusses IPX routing. See the following sections: Section 6.2,
Chapter 6 IP Routing and IPX Routing This chapter discusses IP routing, IP/VPN Policy, and related features in the BANDIT products. It also discusses IPX routing. See the following sections: Section 6.2,
BGP Address-Family (IPv4/IPv6) Configuration Mode Commands
 BGP Address-Family (IPv4/IPv6) Configuration Mode Commands The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Address-Family (IPv4/IPv6) Configuration Mode is used to configure the IPv4 and IPv6 address family information.
BGP Address-Family (IPv4/IPv6) Configuration Mode Commands The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Address-Family (IPv4/IPv6) Configuration Mode is used to configure the IPv4 and IPv6 address family information.
Multihoming Techniques. bdnog8 May 4 8, 2018 Jashore, Bangladesh.
 Multihoming Techniques bdnog8 May 4 8, 2018 Jashore, Bangladesh. 2 ISP Hierarchy Default free zone Internet Routers that have explicit routes to every network on the Internet Regional /Access Providers
Multihoming Techniques bdnog8 May 4 8, 2018 Jashore, Bangladesh. 2 ISP Hierarchy Default free zone Internet Routers that have explicit routes to every network on the Internet Regional /Access Providers
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
Configuring IP Summary Address for RIPv2
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About IP Summary Address for RIPv2, page 1 How to Configure IP Summary Address for RIPv2, page 3 Configuring Examples for IP Summary Address for RIPv2, page
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About IP Summary Address for RIPv2, page 1 How to Configure IP Summary Address for RIPv2, page 3 Configuring Examples for IP Summary Address for RIPv2, page
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
Configuring IPv6 ACLs
 CHAPTER 37 When the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch is running the metro IP access image, you can filter IP Version 6 (IPv6) traffic by creating IPv6 access control lists (ACLs) and applying them
CHAPTER 37 When the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch is running the metro IP access image, you can filter IP Version 6 (IPv6) traffic by creating IPv6 access control lists (ACLs) and applying them
Configuring EIGRP. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
Routing Configuration Commands
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
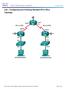 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Active Inactive Deleted Static
 a1#show frame-relay pvc PVC Statistics for interface Serial0/0/0 (Frame Relay DTE) Active Inactive Deleted Static Local 1 0 0 0 Switched 0 0 0 0 Unused 3 0 0 0 DLCI = 100, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS
a1#show frame-relay pvc PVC Statistics for interface Serial0/0/0 (Frame Relay DTE) Active Inactive Deleted Static Local 1 0 0 0 Switched 0 0 0 0 Unused 3 0 0 0 DLCI = 100, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS
IPv6 Routing: RIP for IPv6
 IPv6 Routing Information Protocol (RIP) functions the same and offers the same benefits as IPv4 RIP. RIP enhancements for IPv6, detailed in RFC 2080, include support for IPv6 addresses and prefixes and
IPv6 Routing Information Protocol (RIP) functions the same and offers the same benefits as IPv4 RIP. RIP enhancements for IPv6, detailed in RFC 2080, include support for IPv6 addresses and prefixes and
Table of Contents. 2 Static Route Configuration Commands 2-1 Static Route Configuration Commands 2-1 delete static-routes all 2-1 ip route-static 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 display ip routing-table 1-1 display ip routing-table acl 1-3 display ip routing-table ip-address 1-5 display ip routing-table
Table of Contents 1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 display ip routing-table 1-1 display ip routing-table acl 1-3 display ip routing-table ip-address 1-5 display ip routing-table
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series
 HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series MCE Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-2896 Software version: Release2207 Document version: 6W100-20121130 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series MCE Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-2896 Software version: Release2207 Document version: 6W100-20121130 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development
RIPv2. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 RIPv2 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7 1 Objectives Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1 s limitations. Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands
RIPv2 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7 1 Objectives Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1 s limitations. Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands
NOTES: Software Update Notice: Mini-GBIC ports: Flash Images: SNMP: Devices Without Redundant Management:
 Release Notes Version 08.0.01c Operating System for the ProCurve 9304M, 9308M, and 9315M Routing Switches with Redundant Management (M2, M4, EP, and T-Flow), June 2006 Software release 08.0.01c is the
Release Notes Version 08.0.01c Operating System for the ProCurve 9304M, 9308M, and 9315M Routing Switches with Redundant Management (M2, M4, EP, and T-Flow), June 2006 Software release 08.0.01c is the
InterAS Option B. Information About InterAS. InterAS and ASBR
 This chapter explains the different InterAS option B configuration options. The available options are InterAS option B, InterAS option B (with RFC 3107), and InterAS option B lite. The InterAS option B
This chapter explains the different InterAS option B configuration options. The available options are InterAS option B, InterAS option B (with RFC 3107), and InterAS option B lite. The InterAS option B
Chapter 6 Reading Organizer
 Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
FiberstoreOS BGP Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS BGP Command Line Reference Contents 1 BGP Commands...1 1.1 address-family...1 1.2 aggregate-address...2 1.3 bgp always-compare-med... 2 1.4 bgp bestpath as-path ignore...3 1.5 bgp bestpath
FiberstoreOS BGP Command Line Reference Contents 1 BGP Commands...1 1.1 address-family...1 1.2 aggregate-address...2 1.3 bgp always-compare-med... 2 1.4 bgp bestpath as-path ignore...3 1.5 bgp bestpath
Multi-VRF Support. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Multi-VRF Support
 The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
Chapter 5 Privileged EXEC Commands
 Chapter 5 Privileged EXEC Commands 10gig copy Upgrades the Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) on a 10 Gigabit Ethernet module. Syntax: 10gig copy tftp [module ] tftp parameter
Chapter 5 Privileged EXEC Commands 10gig copy Upgrades the Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) on a 10 Gigabit Ethernet module. Syntax: 10gig copy tftp [module ] tftp parameter
