Bluetooth implementation frameworks
|
|
|
- Laurence Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bluetooth implementation frameworks HARMATNÉ MEDVE Anna Department of Information Systems University of Veszprém, Veszprém, Hungary Institute of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering H-8200 Veszprém, Egyetem u. 10. HUNGARY Abstract: - This paper will represent an SDL implementation of Bluetooth mobile system s protocol stack. This implementation is part of a research and development of validation protocol system s implementation. The final goal is to develop a method for protocol implementation frameworks using design patterns of Protocol Systems in SDL. This work represents common problems and solutions for specification, design and implementation of communication protocols, furthermore it also gives a prototype implementation framework for Bluetooth s usage models. Key-Words: - Protocol,Bluetooth, Reverse Engineering, Design Pattern, SDL. 1 Introduction The large size, currency and real-time nature of mobile communication systems represent a set of difficulties when generating a good specification. The software to be developed must be flexible and portable enough to be employed into different environments and different platforms for different customer segments. The usage of formal methods makes the quick implementation of complex systems possible. The SDL [1,2,3] is a standard language for specification and description of communicating systems. SDL currently has a dual role as a specification and also an implementation language. Most of commercial tools [4] have more functionality, including automatic code generation, simulation and validation. These are the main advantages of system modelling by SDL and it opens new possibilities for formal analysis of design. SDL provides the mechanisms to copye with large number of communicating processes, and there are SDL tools that give necessary features so that they can be used as protocol implementation frameworks By using the domain specific patterns it is possible to describe structures and interactions of the systems. The detected SDL patterns could help in a run-time analysis of SDL models. SDL patterns have particular context while conventional design patterns are specified by an independent design language a mostly natural language based description pattern. The language of SDL patterns is the SDL itself, SDL patterns are defined in terms of SDL syntax. Protocol systems offer a multitude variety of services on different networks with a number of service options. They can be described by the SDL patterns - presented in Section 2.1. It is becoming very valuable to understand, maintain and re-engineer SDL models. An object-oriented analysis method needs to be integrated into SDL, the SOMT method (SDL-oriented Object Modelling Technique) [7]. As the name indicates, the method is essentially the adaptation of OMT to the requirements given by the special application area of distributed, reactive, real-time systems together with the usage of SDL for the design. The Problem Formulation includes three main parts: section 2.1 Patterns for Protocol System Architecture and SDL patterns contains background information about communication protocols and their patterns [5,6], and we point out how it is possible to create an implementation framework of protocols by SDL. The section 2.2. gives an introduction to the context of Bluetooth usage models. Section 2.3 is The Bluetooth implementation framework. Section 3.1is an application of them by producing a Bluetooth SDL pattern for the context presented in section 2.2. Finally in the Conclusion we will relate to the possibilities offered by SDL-2000 to enrich actual patterns + The lecture was made under research contract OTKA
2 2 Problem Formulation 2.1 Patterns for Protocol System Architecture and SDL patterns Protocol systems offer a multitude variety of services on different networks with a number of service options. The protocol systems are organized as series of subsystems, often called protocol layers or protocol entities. Conceptually different functions are separated into different layers and implemented separately. Figure 1 describes two protocol systems communicating with each other via physical connection. Protocol entities communicate with each other by sending messages. Protocol stacks are connected by means of using psyhical connection, which represents the network. The entities in the same stack are connected to each other via message paths, they carry the messages within the system. Protocol entities are connected to their peer entities using virtual message paths, the messages outside the system are sent on them. Peer communication is virtual as the messages sent to peer entities are actually sent using the interface provided by the lower protocol entity. The common general parts and relations in different protocols can be identified and described as design patterns [5]. In figure 2 we will represent three important patterns for protocol system architecture, which can be considered as architectural patterns and can be used in protocol-engineering.[6] The Protocol System pattern - as shown in Figure 2 - specifies the components of a system, responsibilities and interconnections of components and the system environment. The Protocol Entity pattern represents one protocol layer, the Protocol Behavior pattern contains the active parts of a protocol entity. Fig 2: Patterns for protocol system architecture The Protocol Architecture patterns components mapped in SDL its the following: 1. Figure Protocol system elements The behaviour of a protocol is specified only in terms of protocol messages answering the question how protocol entities within a system communicate with each other. Communication of an entity can be connectionoriented and/or connectionless. A connection-oriented communication consists of connection establishment phase, message excange phase and disconnection phase. A connectionless communication is a simple message exchange by Request-Response couple or only Request. Research [6] on several existing protocol implementations contains the elements shown in figure 1. The same high-level model can be found in several protocol frameworks, including SDL [2]. Fig 3: Protocol Architecture pattern in SDL An SDL block type forms a Protocol Entity pattern : it represents a protocol layer or sublayer. Protocol Entity has to have communication accesswith other entities in the same system and with entities in peer systems. It manages possible multiple concurrent communication session, stores internal states and other information. Storage contains all information of a Protocol Entity. The behaviour of a block can be derived from the behaviour of its processes. The Peer Interface functionality is implemented in the process interaction
3 part by processes and signal routes. The Protocol Entity serves multiple requests and at the same time dinamically created and destroyed SDL process instances, too. An SDL process type models a Protocol Behaviour pattern. The Protocol Behaviour element handles protocol functionality by the Communication Manager (creates, controls and closes sessions) the Communication Session (handles communication between peer entities) and Peer Interface elements of patterns (modeled by process instance and interactions between processes). These protocol features always have to be implemented. The reusable components are defined as SDL types. The SDL package consists of libraries that are used for making reusable SDL components available in protocol systems. In this passage I introduced my researches on correspondence between the elements of protocol system patterns and the elements of SDL. For us this research proves that if we improve protocol implementation with SDL development tools, it is not necessary to construct the whole description of protocol analysis neither in pattern language nor in UML for the requirements of re-use theory. We can construct SDL protocol patterns by means of applying the SOMT [7] method and Telelogic Tau TM library modules in SDL development environment. SDL package may be used in the implementation of SDL frameworks. The packages are libraries that are used for making reusable SDL components available in different systems. 2.2 Bluetooth network usage models Bluetooth is the name of a new short-range radio link technology developed by SIG (Bluetooth Special Interest Group), the standard is opened and the specification is downloadable from the SIG web site [8]. It helps to connect portable or fixed devices without cables. The Bluetooth radio module operates in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz ISM band using 79 or 23 channels with FHSS (Frequency Hop Spread Spectrum) scheme for avoiding interference from other signals in this band. The transmission works at 1 Mbps at a distance of 10 or 100 meters. A link can be ACL (asynchronous connectionless) for data transfer or SCO (Synchronous connectionoriented) for voice transfer. The standard supports both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections as well. The system follows master-slave pattern, but the master can collect more slaves (max. 7) to a piconet. A group of piconets in which the connections between different piconets are called scatternet. This network can mix heterogeneous applications, devices and usage models. Fig 4: The Bluetooth protocol stack and profiles The SIG has defined these protocols in the specification and determined some basic profiles for Bluetooth. A profile is (one or more) vertical slice in the protocol stack describing the mandatory protocols and parameter ranges for different user scenarios. The used protocols are application-dependent, but the base Bluetooth protocols (Bluetooth Radio, Baseband, LMP, L2CAP, SDP) are used in every cases - except audio transfer.[4] There are four general profiles determined by covering the common user scenarios. (Figure 4.) The Generic Access Profile (GAP) handles discovery and connection establishment between unconnected devices. The second defined profile is the Service Discovery Application Profile (SDAP). It is responsible for searching for specific or general services in the range of the Bluetooth unit. SDAP re-uses parts of the GAP. The Serial Port Profile (SPP) emulates serial ports on two devices and connects them with Bluetooth. It is used in the case of dial-up network, fax, headset or LAN access. This profile re-uses the pattern of GAP, too. Finally the Generic Object Exchange Profile (GOEP) defines the protocols needed for applications using object exchange. This kind of profile can be File Transfer Profile, Object Push Profile or Synchronization Profile. GOEP uses GAP and SPP, so protocol engineers, who work out protocol stacks for object exchanging Bluetooth devices, can re-use GAP and SPP implementations. In practice, for every usage model there is one or more adaptable profile. There are situations where the tasks are similar to each other, the used protocols are the same even in a different manner. In these cases it is practical to use one of the achievements of the object oriented protocol technology: reusing profiles. The L2CAP protocol layer handles the various packages arriving from different applications and includes the protocol-multiplexing function the effect of which is the increasing number of use-cases of Bluetooth.
4 In the Bluetooth usage models there are several possible applications over L2CAP to communicate with each other. Such applications can be over the different LANs (wired or wireless [9]) based on IP protocol, over the object exchanging protocols based on OBEX, the telephone, fax or point-to-point modem just like the simple audio transfer. Thanks to L2CAP these applications can communicate with each other in every variation. The formal realization of these cases only needs to work out the different application scenes. If we want to use the same upper layer protocol to describe a part of a communicating situation, we can reuse the earlier predefined protocol s package. 2.3 The Bluetooth implementation framework A framework is a reusable design of a complete system (or part of it) that is represented by a set of abstract classes and the way of their interaction [5] The Bluetooth implementation framework is a set of SDL packages for protocol system patterns. In section 3 I will ilustrate the L2CAP protocol entity description. SDL package containes the static and dynamic parts of protocol entity specification and their data descriptions. For pattern construction the data definitions are needed (ASN.1), because ASN.1 data-type definitions and inheritances are needed so that we can re-use the patterns by means of redefining SDL sorts. For example in figure 5 one can see that protocol L2CAP executes multiplexing in all network models. The multiplexing function, the segmentation and reassembly (SAR) operation are implinks in the same way as the PDU s data type definition is in ASN.1 [11] using CHOICE type. initiated by the master of piko network. The following status occur during system operation on the grounds of specification: Closed: status of both master and slave position is possible, the connection is closed W4_L2CAP_Connect_Rsp: after having transmitted the master s respond sign to the slave referring to the question of connection setting, the master is waiting for the slave s answer W4_L2CA_Connect_Rsp: this status is only peculiar to slave, having introduced the connection setting request, it is waiting for its respond Config: this status can be taken up by both the master and the slave following a successful connection setting or during the communication intended to promote agreement on channel particulars Open: this status is capable of being taken up by both parties for the sake of successful communication flow following the determination of channels W4_L2CAP_Disconnect_Rsp: the master gets here after having sent its disconnection request to the slave and is waiting for the slave s respond W4_L2CA_Disconnect_Rsp: after having received the disconnection request from the master, the slave informs its higher layer about this fact and shifts to this status waiting for the respond of the layer situated above The service primitives (request, indication, response and confirmation) are signalled by L2CA_, while the PDU-s are completed with P ( protocol ) as, can be see in figure 7. During the analysis MSC s scenarios [10] are needed for solving the timing problem and for the differentiating illustration of possible application cases (figure 6). Fig 5: BNEP with an Ethernet payload sent using L2CAP multiplexing and SAR 3 Problem Solution 3.1 Presenting the Bluetooth L2CAP protocol analysis and formal description using L2CAP pattern Protocol analysis, defining system requirements The structure, process and division of communication take place on the basis of master-slave relationship Fig 6: In the basic configuration process the devices exchange Maximal Transmission Unit information With the help of all the status being distinguishable in the specification, service primitives and PDUs I drew a
5 state-flow graph (Figure 7) in which the operation of both the slave and the master are described at the same time. use L2CAP; system L2CAP 1(1) SP_LinkCfm P_LinkRsp SP_LinkRsp, err UP1 SP_LinkReq, err, ERTX, SP_Data G1 L2CAP_Ini:L2CAP G2 PC P_LinkReq, P_Data G2 UP2 L2CAP_Resp:L2CAP G1 SP_LinkInd, SP_Data The block of the initiator s L2CAP protocol. It communicates with the upper layer protocols via channel UP1 and with the responder unit via the peer channel (PC). The block of the responder s L2CAP protocol. It communicates with the upper layer protocols via channel UP2 and with the initiator unit via the peer channel. Fig 9: A part of protocol L2CAP system-level description, which illustrates the members taking part in communication Fig 7: state-flow graph of L2CAP layer of Bluetooth Preparation of formal description of protocol L2CAP SDL description is structured hierarchically. On the highest level we can find the system-level description with the illustration of communicating parties, namely the L2CAP layer of the two Bluetooth objects, the signs used by them, and channels functioning on the basis of FIFO theory between objects carrying out informationexchange. The two parties L2CAP layer and the signals can be derived from the pattern described in the package (Figure 8). On the following hierarchy-level I will indicate the process interactions of block-level description breaking further down the L2CAP layers of master and slave. It also shows the inner development of the element, the included functional units (processes) and their communication channels, the signs used for information exchange. Let s take a look at the block diagram of L2CAP_Resp as an example: SC block L2CAP_Resp 1(1) P_LinkRsp SR2 P_LinkReq, P_Data G2 L2CAP_RespPR:L2CAP G1 SP_LinkRsp, err UPR2 SP_LinkInd, SP_Data UP2 package L2CAP 2(3) P_LinkReq= L2CAP_ConnectReq, L2CAP_ConfigReq, L2CAP_DisconnectReq; SP_LinkReq= L2CA_ConnectReq, L2CA_ConfigReq, L2CA_DisconnectReq; SP_LinkInd= L2CA_ConnectInd, L2CA_ConfigInd, L2CA_DisconnectInd; L2CAP SP_LinkCfm= L2CA_ConnectCfm, L2CA_ConnectCfmPnd, L2CA_ConnectCfmNeg, L2CA_ConfigCfm, L2CA_ConfigCfmPnd, L2CA_ConfigCfmNeg, L2CA_DisconnectCfm; P_LinkRsp= L2CAP_ConnectRsp, L2CAP_ConnectRspPnd, L2CAP_ConnectRspNeg, L2CAP_ConfigRsp, L2CAP_ConfigRspPnd, L2CAP_ConfigRspNeg, L2CAP_DisconnectRsp; err= LP_QoSViolationInd, RTX; Fig 8: A part of protocol L2CAP package P_Data= L2CAP_DataRead, L2CAP_DataWrite; SP_Data= L2CA_DataRead, L2CA_DataWrite; SP_LinkRsp= L2CA_ConnectRsp, L2CA_ConnectRspPnd, L2CA_ConnectRspNeg, L2CA_ConfigRsp, L2CA_ConfigRspPnd, L2CA_ConfigRspNeg, L2CA_DiconnectRsp; Reusing that we can implement those elements only once (in the package patterns). In our case Figure 9 perfectly demonstrates the two system-level elements (master = L2CAP_Ini, slave = L2CAP_Resp), the PDUs used in communication between them, and the communication channels. It is the process of the responder s L2CAP layer. The functions requested by the initiator are accepted by this process. Fig 10: L2CAP protocol block-level description particulars The Figure 10 sufficiently indicates that the block contains only one single process. One can easily observe the sign channels (SR2,UPR2) used in communication, their connections to the channels illustrated on systemlevel, and the type and character of signs transmitted by them. Every process is manifested as a separate finite state machine that communicates with the other and thus they build up the actual system. The full-scale description capacity of SDL provides opportunity for defining processes, illustrating its structures with the help of which the stages and flow of operation can also be illustrated. I demonstrate the inner operation of L2CAP layers on this level (receiving and sending signs, actions and status shifts) and the way of realising services in the form os these layer particulars. And now let s have a look at such details of protocol SDL-description (see Figure 11)
6 p ro c e s s L 2 C A P _ R e s p P r 1 (4) L 2 C A P _ D i s c o n n e c t R e q D C L n,p Integer; T I M E R t ; W 4 _ L 2 C A _ C o n n e c t _ R s p L 2 C A _ C o n n e c t R s p reset(t) L 2 C A _ D i s c o n n e c t I n d n : = 1 set(now+p,t) W 4 _ L 2 C A _ D i s c o n n e c t _ R s p L 2 C A P _ C o n n e c t R s p L 2 C A _ C o n f i g I n d set(now+p,t) C o n f i g L 2 C A P _ C o n f i g R e q Fig 11: Particulars of L2CAP protocol process-level description The highlighted part illustrates the possibilities of the slave originated from W4_L2CA_Connect_Rsp starting status. As long as it gets L2CAP_DisconnectReq disconnection requesting PDU from the master, it informs the higher layer with the help of L2CA_DisconnectInd service primitive about the situation and after setting the timer it shifts to W4_L2CA_Disconnect_Rsp status preceding disconnection. The description is similar in the case of receiving accepted connection response from the higher layer. The total L2CAP_RespPr process description continues on several other pages. It is necessary to similarly provide similarly the description of L2CAP_Ini block and its process and thus we get the total formal description of protocol. In the case of difficult systems we make differences between hierarchy-levels for the sake of better understanding of dividing block-levels into new block-levels. Paying attention to functionality in the field of illustration we have the opportunity of utilising userfriendly illustration by means of carefully thought arrangement with the help of SDL even in the case of huge systems. 4 Conclusion We could see in the foregoing that the planning of Bluetooth network usage models offers the use of design patterns and the application of reuse theories. Finding models in protocol development may even take place in the phase of requirement-analysis due to the structured and documented protocol standards. In recent years protocol standardisers have more often used the wellknown formal languages as unambiguous transmitting languages, namely SDL, MSC, and ASN.1. It is rather the verification of implementation that is the semantics of languages and their adequate application in planning methods. Recent development of SDL approves that the engineering of any real-time system can be realised in SDL. The main power ever of protocol engineering derives from its basis: the role of protocol specification mixed with prevailing OO techniques ensures unique and economical planning of protocol life-cycle elements. However, the role of implementation and verification has been increasing due to the fact that by using formal languages the analysis is not a usual OMT technology analysis any longer. One way of facilitating prevention is creating SDL packages with the application of pattern-based programming and applying the OO characteristics and specification of SDL. The SDL-2000 offers new possibilities with the introduction of agent type. Actions (that can be granted on system-level), definable variables and several block instances are such powers that reinforce pattern-based planning and with their help even new protocol patterns can be introduced. References: [1] ITU-T Recommendation Z.100 (11/99), Specification and Description Language (SDL) Supplement 1 to Z.100 (05/97): SDL+ Methodology. Update for SDL-2000 in progress. ITU-T, [2] Jan Elsberger, Dieter Hogrefe and Armadeo Sarma, SDL Formal Object-oriented Language for Communicating Systems, Prentice Hall, 1997 [3] Zoubir Mammeri, SDL modélisation de protocoles et systèmes réactifs, Hermes Science, 2000 [4] [5] Frank Buschmann, Regine Meunier, Hans Rohnert, Peter Sommerlad, Michael Stal Pattern-Oriented Software Architecture, Volume 1: A System of Patterns, John Wiley&Sons, 1996 [6] Juha Pärssinen and Markku Turunen, Patterns for Protocol System Architecture In PloP 2000 Proceedings, /proceedings/parssinen/parssinen.pdf, iuc.edu/~plop, 2000 [7] Telelogic Tau TM 4.1 User s Manual Guidelines, Telelogic AB, 2000 [8] SIG, Specification on the Bluetooth System V.1.1, Vol. 1 and 2, [9] Tibor Dulai, Anna Harmatné Medve, Bluetooth - One of the Best WPAN Solutions for Bridging PAN and Wider Networks?, 14th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems,Workshop on Real-Time LANs in the Internet Age., June 19-21, 2002, 6_rtlia.pdf, Vienna, 2002 [10] ITU-T Recommendation Z.120, (11/99) Message Sequence Chart (MSC) Geneva,1999. [11] ASN.1 Informational Site,
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
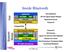 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology
 SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Bluetooth PCI Adapter
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Installation...2 2.1 Software Installation...2 2.1.1 Installation on Windows 95/98/ME/2000/XP...2 2.1.2 Installation on Windows NT...3 2.1.3 Installation on Linux...3
Table of Contents 1 Introduction...2 2 Installation...2 2.1 Software Installation...2 2.1.1 Installation on Windows 95/98/ME/2000/XP...2 2.1.2 Installation on Windows NT...3 2.1.3 Installation on Linux...3
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Universal Communication Component on Symbian Series60 Platform
 Universal Communication Component on Symbian Series60 Platform Róbert Kereskényi, Bertalan Forstner, Hassan Charaf Department of Automation and Applied Informatics Budapest University of Technology and
Universal Communication Component on Symbian Series60 Platform Róbert Kereskényi, Bertalan Forstner, Hassan Charaf Department of Automation and Applied Informatics Budapest University of Technology and
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU
 Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING
 A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
BlueSerial. Bluetooth Serial RS232 Port Adapters. User Manual HANTZ + PARTNER. The Upgrade Company!
 Bluetooth Serial RS232 Port Adapters User Manual HANTZ + PARTNER The Upgrade Company! www.hantz.com Deutschland: Tel.: 0761 / 59 21 00 Fax: 0761 / 58 52 28 Schweiz: Tel.: 061 / 27 311-31 Fax: 061 / 27
Bluetooth Serial RS232 Port Adapters User Manual HANTZ + PARTNER The Upgrade Company! www.hantz.com Deutschland: Tel.: 0761 / 59 21 00 Fax: 0761 / 58 52 28 Schweiz: Tel.: 061 / 27 311-31 Fax: 061 / 27
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
WIRELESS LANs: THE DECT APPROACH
 WIRELESS LANs: THE DECT APPROACH Anthony Lo Centre for Wireless Communications National University of Singapore 20 Science Park Road #02-34/37 TeleTech Park Singapore Science Park II Singapore 117674 Email:
WIRELESS LANs: THE DECT APPROACH Anthony Lo Centre for Wireless Communications National University of Singapore 20 Science Park Road #02-34/37 TeleTech Park Singapore Science Park II Singapore 117674 Email:
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Development of a Service Discovery Architecture for. Christian Schwingenschlögl, Anton Heigl
 Development of a Service Discovery Architecture for the Bluetooth Radio System Christian Schwingenschlögl, Anton Heigl Technische Universität München (TUM), Institute of Communication Networks Arcisstr.
Development of a Service Discovery Architecture for the Bluetooth Radio System Christian Schwingenschlögl, Anton Heigl Technische Universität München (TUM), Institute of Communication Networks Arcisstr.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
CALIFORNIA SOFTWARE LABS
 CALIFORNIA SOFTWARE LABS R E A L I Z E Y O U R I D E A S California Software Labs 6800 Koll Center Parkway, Suite 100 Pleasanton CA 94566, USA. Phone (925) 249 3000 Fax (925) 426 2556 info@cswl.com http://www.cswl.com
CALIFORNIA SOFTWARE LABS R E A L I Z E Y O U R I D E A S California Software Labs 6800 Koll Center Parkway, Suite 100 Pleasanton CA 94566, USA. Phone (925) 249 3000 Fax (925) 426 2556 info@cswl.com http://www.cswl.com
Bluetooth Information Exchange Network
 Bluetooth Information Exchange Network Xiaoning (Linda) Liu A thesis submitted to AUT University In partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Engineering (ME) October 2008 School
Bluetooth Information Exchange Network Xiaoning (Linda) Liu A thesis submitted to AUT University In partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Engineering (ME) October 2008 School
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
DIAL-UP NETWORKING PROFILE
 Part K:7 DIAL-UP NETWORKING PROFILE This profile defines the requirements for Bluetooth devices necessary for the support of the Dial-up Networking use case. The requirements are expressed in terms of
Part K:7 DIAL-UP NETWORKING PROFILE This profile defines the requirements for Bluetooth devices necessary for the support of the Dial-up Networking use case. The requirements are expressed in terms of
TELEPHONY CONTROL PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION
 Part F:3 TELEPHONY CONTROL PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION TCS Binary This document describes the Bluetooth Telephony Control protocol Specification Binary (TCS Binary), using a bit-oriented protocol. This protocol
Part F:3 TELEPHONY CONTROL PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION TCS Binary This document describes the Bluetooth Telephony Control protocol Specification Binary (TCS Binary), using a bit-oriented protocol. This protocol
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY
 Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Rab Nawaz Jadoon (Assistant Professor) Department of Computer Science COMSATS University, Abbottabad, Pakistan
 Rab Nawaz Jadoon (Assistant Professor) Department of Computer Science COMSATS University, Abbottabad, Pakistan rabnawaz@ciit.net.pk 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 History... 3 1.2 Bluetooth
Rab Nawaz Jadoon (Assistant Professor) Department of Computer Science COMSATS University, Abbottabad, Pakistan rabnawaz@ciit.net.pk 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 History... 3 1.2 Bluetooth
T : Protocol Design
 T-110.300: Protocol Design Protocol Design Theory Methods Protocol Engineering Process (PEP) Timo.Kyntaja@vtt.fi 1 (154) Motivation Telecom systems engineering is a huge industry networks, terminals, services
T-110.300: Protocol Design Protocol Design Theory Methods Protocol Engineering Process (PEP) Timo.Kyntaja@vtt.fi 1 (154) Motivation Telecom systems engineering is a huge industry networks, terminals, services
Bluetooth hotspots: Extending the reach of Bluetooth by seamlessly transporting Bluetooth communications over IP Networks
 Bluetooth hotspots: Extending the reach of Bluetooth by seamlessly transporting Bluetooth communications over IP Networks David Mackie and Peter Clayton Department of Computer Science Rhodes University,
Bluetooth hotspots: Extending the reach of Bluetooth by seamlessly transporting Bluetooth communications over IP Networks David Mackie and Peter Clayton Department of Computer Science Rhodes University,
Introducing Bluetooth
 Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Bluetooth PC Card from IBM
 Bluetooth PC Card from IBM Installation and User s Guide IBM 19K4260 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read Appendix E, Product warranties and notices on page E-1. First
Bluetooth PC Card from IBM Installation and User s Guide IBM 19K4260 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read Appendix E, Product warranties and notices on page E-1. First
BLUETOOTH PAN and external IP networks
 BLUETOOTH PAN and external IP networks 1 Tore E. ]j1jnvik, 2Paal Engelstad & 2 Do van Thanh 1. Unik - University of Oslo - Norway - tlf: +47 90199176 - torejoen@iji.uio.no 2. Telenor R&D - Norway - tif:
BLUETOOTH PAN and external IP networks 1 Tore E. ]j1jnvik, 2Paal Engelstad & 2 Do van Thanh 1. Unik - University of Oslo - Norway - tlf: +47 90199176 - torejoen@iji.uio.no 2. Telenor R&D - Norway - tif:
CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING
 Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Pattern Language for Architecture of Protocol Systems
 Pattern Language for Architecture of Protocol Systems Juha Pärssinen, Markku Turunen Introduction This paper presents the pattern language for architecture of communication protocols. This is a pattern
Pattern Language for Architecture of Protocol Systems Juha Pärssinen, Markku Turunen Introduction This paper presents the pattern language for architecture of communication protocols. This is a pattern
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth
 Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Bhopal, , India 3 M.Tech Scholor,Department Of Computer Science, BIST Bhopal. Bhopal, , India
 Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
1 Introduction to. Languages and Notations. Chapter
 1 Introduction to Languages and Notations This chapter begins with a brief introduction to SDL; the language, its history, its main concepts and application areas. Next follows an introduction to the MSC
1 Introduction to Languages and Notations This chapter begins with a brief introduction to SDL; the language, its history, its main concepts and application areas. Next follows an introduction to the MSC
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth
 Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Image acquisition and Communication
 Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Bluetooth in Mobile Devices
 Bluetooth in Mobile Devices Vidar Rinne Mälardalen University School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Computer Science: Game Development vre03001@student.mdh.se Abstract The basic idea of Bluetooth
Bluetooth in Mobile Devices Vidar Rinne Mälardalen University School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Computer Science: Game Development vre03001@student.mdh.se Abstract The basic idea of Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY. Flavia Martelli
 Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology
 Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
EC Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank
 EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a. worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the
 Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
MavBlue: A Bluetooth Development Kit for Undergraduate and Graduate Research and Education
 MavBlue: A Bluetooth Development Kit for Undergraduate and Graduate Research and Education Steven V. Case Department of Computer and Information Sciences Minnesota State University Mankato steven.case@mnsu.edu
MavBlue: A Bluetooth Development Kit for Undergraduate and Graduate Research and Education Steven V. Case Department of Computer and Information Sciences Minnesota State University Mankato steven.case@mnsu.edu
PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin
 Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Collaborative Middleware for Bluetooth-based ad-hoc Wireless Networks on Symbian OS
 6th WSEAS International Conference on E-ACTIVITIES, Tenerife, Spain, December 14-16, 2007 304 Collaborative iddleware for Bluetooth-based ad-hoc Wireless Networks on Symbian OS FENG GAO, ARTIN HOPE Informatics
6th WSEAS International Conference on E-ACTIVITIES, Tenerife, Spain, December 14-16, 2007 304 Collaborative iddleware for Bluetooth-based ad-hoc Wireless Networks on Symbian OS FENG GAO, ARTIN HOPE Informatics
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Wireless LAN. Access Point. Provides network connectivity over wireless media
 LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
IrDA INTEROPERABILITY
 Part F:2 IrDA INTEROPERABILITY The IrOBEX protocol is utilized by the Bluetooth technology. In Bluetooth, OBEX offers same features for applications as within the IrDA protocol hierarchy and enabling the
Part F:2 IrDA INTEROPERABILITY The IrOBEX protocol is utilized by the Bluetooth technology. In Bluetooth, OBEX offers same features for applications as within the IrDA protocol hierarchy and enabling the
Inside Bluetooth Low Energy
 Inside Bluetooth Low Energy Naresh Gupta BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface Acknowledgments Foreword xix xxiii xxv Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction to Wireless Communication 1 1.2 Data Rates
Inside Bluetooth Low Energy Naresh Gupta BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface Acknowledgments Foreword xix xxiii xxv Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction to Wireless Communication 1 1.2 Data Rates
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF IEEE WIRELESS-LAN AND BLUETOOTH PICONET RANGE INTERFERENCE
 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF IEEE 802.11 WIRELESS-LAN AND BLUETOOTH PICONET RANGE INTERFERENCE Patrick O. Bobbie and Abdul-Lateef Yussiff School of Computing and Software Engineering Southern Polytechnic
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF IEEE 802.11 WIRELESS-LAN AND BLUETOOTH PICONET RANGE INTERFERENCE Patrick O. Bobbie and Abdul-Lateef Yussiff School of Computing and Software Engineering Southern Polytechnic
Computer Network : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan
 Computer Network : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapter3: OSI Reference Model: Network Software: Network
Computer Network : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapter3: OSI Reference Model: Network Software: Network
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 Shaila Kharde,, 2013; Volume 1(8): 969-978 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK UNDER WATER EMBEDDED BLUETOOTH DATA
Shaila Kharde,, 2013; Volume 1(8): 969-978 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK UNDER WATER EMBEDDED BLUETOOTH DATA
OBJECT-ORIENTED MODELING AND DESIGN. Introduction
 OBJECT-ORIENTED MODELING AND DESIGN Introduction Contents: Introduction. Course Relevance Learning Outcomes Overview of the syllabus Introduction to Object Orientation Introduction Object Oriented Approach
OBJECT-ORIENTED MODELING AND DESIGN Introduction Contents: Introduction. Course Relevance Learning Outcomes Overview of the syllabus Introduction to Object Orientation Introduction Object Oriented Approach
Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference
 Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be
 IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
3.0. Manual and. Application note. USB Adapter
 3.0 USB Adapter Manual and Application note Index INTRODUCTION 1 CHAPTER 1 Package 2 Features 2 Bluetooth profile support 2 Drivers support 3 CHAPTER 2 Setup for Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP 4 CHAPTER 3 Application
3.0 USB Adapter Manual and Application note Index INTRODUCTION 1 CHAPTER 1 Package 2 Features 2 Bluetooth profile support 2 Drivers support 3 CHAPTER 2 Setup for Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP 4 CHAPTER 3 Application
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for informatikk. Monitoring Bluetooth network topology. Cand Scient Thesis. Fredrik Borg
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for informatikk Monitoring Bluetooth network topology Cand Scient Thesis Fredrik Borg February 1, 2002 II Foreword This thesis is a part of my cand.scient. degree in Communication
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for informatikk Monitoring Bluetooth network topology Cand Scient Thesis Fredrik Borg February 1, 2002 II Foreword This thesis is a part of my cand.scient. degree in Communication
A Study of Wireless Compressed Digitalaudio
 A Study of Wireless Compressed Digital Transmission Andreas Floros 1, Marios Koutroubas 2, Nicolas-Alexander Tatlas 2 and John Mourjopoulos 2 1 ATMEL Hellas S.A., Patras Science Park, Platani, 26 500 Patras,
A Study of Wireless Compressed Digital Transmission Andreas Floros 1, Marios Koutroubas 2, Nicolas-Alexander Tatlas 2 and John Mourjopoulos 2 1 ATMEL Hellas S.A., Patras Science Park, Platani, 26 500 Patras,
Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society
 Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society Martin Sauter Nortel Networks, Germany John Wiley Si Sons, Ltd Contents Preface List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xi xiii xix
Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society Martin Sauter Nortel Networks, Germany John Wiley Si Sons, Ltd Contents Preface List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xi xiii xix
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
