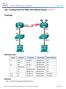
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication
|
|
|
- Kory Richards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally stubby, and not-so-stubby areas. onfigure OSPF authentication. You are responsible for configuring the new network to connect your company s engineering, marketing, and accounting departments, represented by loopback interfaces on each of the three rs. The physical devices have just been installed and connected by serial cables. onfigure multiple-area OSPF to allow full connectivity between all departments. R3 also has a loopback representing a connection to another autonomous system that is not part of OSPF. Note: This lab uses isco 1841 rs with isco IOS Release 12.4(24)T1 and the Advanced IP Services image c1841-advipservicesk9-mz t1.bin. You can use other rs (such as a 2801 or 2811) and isco IOS Software versions if they have comparable capabilities and features. Depending on the r All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 1 of 16
2 NPv6 ROUTE model and isco IOS Software version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab. Required Resources 3 rs (isco 1841 with isco IOS Release 12.4(24)T1 Advanced IP Services or comparable) Serial and console cables Step 1: onfigure addressing and loopbacks. a. Using the addressing scheme in the diagram, apply IP addresses to the serial interfaces on R1, R2, and R3. reate loopbacks on R1, R2, and R3, and address them according to the diagram. Note: Depending on the r models you have, you might need to add clock rates to the DE end of each connection (newer equipment adds this automatically). Verify connectivity across each serial link. R1# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with NTL/Z. R1(config)# interface loopback 1 R1(config-if)# description Engineering Department R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# clockrate R1(config-if)# no shutdown R2# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with NTL/Z. R2(config)# interface loopback 2 R2(config-if)# description Marketing Department R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# clockrate R2(config-if)# no shutdown R3# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with NTL/Z. R3(config)# interface loopback 3 R3(config-if)# description Accounting Department R3(config-if)# ip address R3(config-if)# interface loopback 20 R3(config-if)# description onnection to another AS R3(config-if)# ip address R3(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip address R3(config-if)# no shutdown Step 2: Add interfaces into OSPF. a. reate OSPF process 1 on rs R1 and R2. onfigure the subnet of the serial link between R1 and R2 to be in OSPF area 0 using the network command. Add loopback 1 on R1 and loopback 2 on R2 into OSPF area 0. hange the network type on the loopback interfaces so that they are advertised with the correct subnet. All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 2 of 16
3 NPv6 ROUTE R1(config)# r ospf 1 R1(config-r)# network area 0 R1(config-r)# network area 0 R1(config-r)# exit R1(config)# interface loopback 1 R1(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point R2(config)# r ospf 1 R2(config-r)# network area 0 R2(config-r)# network area 0 R2(config-r)# exit R2(config)# interface loopback 2 R2(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point Note: Another option for adding individual directly connected networks into the OSPF process is to use the ip ospf process-id area area-id interface command that is available with isco IOS version 12.3(11)T and later. b. Verify that both rs have OSPF neighbors using the show ip ospf neighbors command. R1# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/0 R2# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/0 c. Verify that the rs can see each other s loopback with the show ip command. R1# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set O /24 is subnetted, 3 subnets is directly connected, Serial0/0/ [110/65] via , 00:00:10, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback1 R2# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 3 of 16
4 NPv6 ROUTE O /24 is subnetted, 4 subnets is directly connected, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback [110/65] via , 00:00:30, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 d. Add the subnet between R2 and R3 into OSPF area 23 using the network command. Add loopback 3 on R3 into area 23. R2(config)# r ospf 1 R2(config-r)# network area 23 R3(config)# r ospf 1 R3(config-r)# network area 23 R3(config-r)# network area 23 R3(config-r)# exit R3(config)# interface loopback 3 R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point e. Verify that this neighbor relationship comes up using the show ip ospf neighbors command. R2# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/ FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/1 f. If you look at the output of the show ip command on R1, you see a to the R3 loopback. Notice that it is identified as an inter-area. R1# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set O IA O O IA /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets is directly connected, Serial0/0/ [110/129] via , 00:00:28, Serial0/0/ [110/65] via , 00:01:38, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback [110/128] via , 00:01:38, Serial0/0/0 g. Issue the show ip command on R2. Notice that R2 has no inter-area s because R2 is in both areas. It is an ABR, or area border r. R2# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 4 of 16
5 NPv6 ROUTE o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set O O /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets is directly connected, Serial0/0/ [110/65] via , 00:00:50, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback [110/65] via , 00:02:00, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 h. Using a Tcl script, verify connectivity to all interfaces from any r, with the exception of loopback 20 on R3 ( ), which has not yet been configured as part of OSPF. i. Use the following Tcl script to verify that you can ping all addresses in the topology. R1# tclsh R1(tcl)# foreach address { } { ping $address } Step 3: onfigure a stub area. a. Under the OSPF process on R2 and R3, make area 23 the stub area using the area area stub command. The adjacency between the two rs might go down during the transition period, but it should come back up afterwards. R2(config)# r ospf 1 R2(config-r)# area 23 stub R3(config)# r ospf 1 R3(config-r)# area 23 stub b. onfirm that it comes up by using the show ip ospf neighbors command. R2# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/ FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/1 R3# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/1 c. Using the show ip command, you can see that R3 now has a default pointing toward R2. A stub area does not receive any external s. It receives a default and OSPF inter-area s. R3# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 5 of 16
6 NPv6 ROUTE o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets O IA [110/128] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback3 O IA [110/65] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/1 O IA [110/129] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 O*IA /0 [110/65] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/1 d. Look at the output of the show ip ospf command to see what type each area is. R2# show ip ospf Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID Supports only single TOS(TOS0) s Supports opaque LSA Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Supports area transit capability It is an area border r Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs msecs Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs msecs Incremental-SPF disabled Minimum LSA interval 5 secs Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs LSA group pacing timer 240 secs Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs Number of external LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of opaque AS LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of Dbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0 Number of areas in this r is 2. 1 normal 1 stub 0 nssa Number of areas transit capable is 0 External flood list length 0 Area BAKBONE(0) Number of interfaces in this area is 2 Area has no authentication SPF algorithm last executed 00:02: ago SPF algorithm executed 5 times Area ranges are Number of LSA 4. hecksum Sum 0x01A85A Number of opaque link LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of Dbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0 Area 23 Number of interfaces in this area is 1 All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 6 of 16
7 NPv6 ROUTE It is a stub area generates stub default with cost 1 Area has no authentication SPF algorithm last executed 00:01: ago SPF algorithm executed 8 times Area ranges are Number of LSA 6. hecksum Sum 0x Number of opaque link LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of Dbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0 What are the advantages of having a r receive a default rather than a more specific? Why do all rs in a stub area need to know that the area is a stub? Step 4: onfigure a totally stubby area. A modified version of a stubby area is a totally stubby area. A totally stubby area ABR only allows in a single, default from the backbone. To configure a totally stubby area, you only need to change a command at the ABR, R2 in this scenario. Under the r OSPF process, you will enter the area 23 stub no-summary command to replace the existing stub command for area 23. The no-summary option tells the r that this area will not receive summary (inter-area) s. a. To see how this works, issue the show ip command on R3. Notice the inter-area s, in addition to the default generated by R2. R3# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is to network O IA O IA O IA /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets [110/128] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback [110/65] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/ [110/129] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/1 All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 7 of 16
8 NPv6 ROUTE is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 O*IA /0 [110/65] via , 00:00:56, Serial0/0/1 b. Look at the output of the show ip ospf database command on R2 to see which LSAs are in its OSPF database. R2# show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Link count x x0056D x x0057D2 3 Summary Net Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum x x00EFEF x x00093 Router Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Link count x x x x00B762 3 Summary Net Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum x x003BF x x x x00948D x x009E3A c. Enter the stub no-summary command on R2 (the ABR) under the OSPF process. R2(config)# r ospf 1 R2(config-r)# area 23 stub no-summary d. Go back to R3 and issue the show ip command again. Notice that it shows only one incoming from OSPF. R3# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is subnetted, 2 subnets is directly connected, Loopback3 All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 8 of 16
9 NPv6 ROUTE is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 O*IA /0 [110/65] via , 00:00:10, Serial0/0/1 e. Look at the show ip ospf database output to see which s are in area 23. R3# show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Link count x x x x00B762 3 Summary Net Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum x x0039F5 What are the advantages of making an area totally stubby instead of a regular stub area? What are the disadvantages? Why did only the ABR need to know that the area was totally stubby rather than all rs in the area? Step 5: onfigure a not-so-stubby area. Not-so-stubby areas (NSSAs) are similar to regular stub areas, except that they allow s to be redistributed from an ASBR into that area with a special LSA type, which gets converted to a normal external at the ABR. a. hange area 23 into an NSSA. NSSAs are not compatible with stub areas, so the first thing to do is issue the no area 23 stub command on rs R2 and R3. Next, issue the area area nssa command on rs R2 and R3 to change area 23 to an NSSA. To generate an external into the NSSA, use the redistribute connected subnets command on R3. This adds the previously unreachable loopback 20 into OSPF. Be sure to include the subnets keyword; otherwise, only classful networks are redistributed. R2(config)# r ospf 1 R2(config-r)# no area 23 stub R2(config-r)# area 23 nssa R3(config)# r ospf 1 R3(config-r)# no area 23 stub R3(config-r)# area 23 nssa R3(config-r)# redistribute connected subnets All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 9 of 16
10 NPv6 ROUTE b. In the output of the show ip ospf command on R2, notice that area 23 is an NSSA and that R2 is performing the LSA type 7 to type 5 translation. If there are multiple ABRs to an NSSA, the ABR with the highest r ID performs the translation. R2# show ip ospf Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID Supports only single TOS(TOS0) s Supports opaque LSA Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Supports area transit capability It is an area border and autonomous system boundary r Redistributing External Routes from, Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs msecs Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs msecs Incremental-SPF disabled Minimum LSA interval 5 secs Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs LSA group pacing timer 240 secs Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs Number of external LSA 1. hecksum Sum 0x00A2F Number of opaque AS LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of Dbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0 Number of areas in this r is 2. 1 normal 0 stub 1 nssa Number of areas transit capable is 0 External flood list length 0 Area BAKBONE(0) Number of interfaces in this area is 2 Area has no authentication SPF algorithm last executed 00:03: ago SPF algorithm executed 9 times Area ranges are Number of LSA 4. hecksum Sum 0x01A53 Number of opaque link LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of Dbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0 Area 23 Number of interfaces in this area is 1 It is a NSSA area Perform type-7/type-5 LSA translation Area has no authentication SPF algorithm last executed 00:00: ago SPF algorithm executed 16 times Area ranges are Number of LSA 6. hecksum Sum 0x Number of opaque link LSA 0. hecksum Sum 0x Number of Dbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0 c. Look at the show ip output on R2. Notice that the external comes in as type N2 from R3. This is because it is a special NSSA external. R2# show ip All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 10 of 16
11 NPv6 ROUTE odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets O N [110/20] via , 00:00:41, Serial0/0/ /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 O [110/65] via , 00:00:47, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback2 O [110/65] via , 00:03:42, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 d. Look at the show ip output on R1. Notice that the is now a regular E2 external, because R2 has performed the type 7 to type 5 translation. R1# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets O E [110/20] via , 00:01:22, Serial0/0/ /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 O IA [110/129] via , 00:02:06, Serial0/0/0 O [110/65] via , 00:04:22, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback1 O IA [110/128] via , 00:04:22, Serial0/0/0 e. Look at the show ip output on R3. Notice that it no longer has a default in it, but inter-area s are coming in. Note: An NSSA does not have the default injected by the ABR (R2) automatically. It is possible to make the ABR inject the default into the NSSA using the area 23 nssa default-informationoriginate command on R2. R3# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 11 of 16
12 NPv6 ROUTE o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is not set O IA O IA O IA /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets [110/128] via , 00:02:11, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Loopback [110/65] via , 00:02:11, Serial0/0/ [110/129] via , 00:02:11, Serial0/0/ is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 f. Yet another type of area is a totally-stubby NSSA that combines the property of an NSSA area (injecting external routing information into OSPF) with a totally stubby behavior (accepting only default from the backbone). Issue the area 23 nssa no-summary command on R2, similar to converting a stub area into a totally stubby area. R2(config)# r ospf 1 R2(config-r)# area 23 nssa no-summary g. heck the routing table on R3. Notice that the inter-area s have been replaced by a single default. R3# show ip odes: - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is subnetted, 2 subnets is directly connected, Loopback is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 O*IA /0 [110/65] via , 00:00:20, Serial0/0/1 h. On R2, look at the show ip ospf database output to see the various LSA types. R2# show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Link count x x0056D x x005BB 3 Summary Net Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum x x00EFEF x x00093 All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 12 of 16
13 NPv6 ROUTE Router Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Link count x x00B0F x x003FD 3 Summary Net Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum x x00265 Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 23) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Tag x x0076F 0 Type-5 AS External Link States Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# hecksum Tag x x00A2F 0 Where would it be useful to make an area into an NSSA? Step 6: onfigure OSPF interface authentication. For security purposes, you can configure OSPF interfaces to use authentication. a. onfigure the link between R2 and R3 for plaintext authentication. To set up plaintext authentication on an interface, type ip ospf authentication at the interface command prompt. Then set the password to cisco with the ip ospf authentication-key key-string command. R2(config)# interface serial 0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip ospf authentication R2(config-if)# ip ospf authentication-key cisco R3(config)# interface serial 0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip ospf authentication R3(config-if)# ip ospf authentication-key cisco Note: While configuring the authentication, the adjacency might go down if the dead timer expires on one of the rs. The relationship should be reestablished once authentication is configured on both sides. b. Verify the authentication using the show ip ospf interface interface command. R2# show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/1 Serial0/0/1 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /24, Area 23 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, ost: 64 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 13 of 16
14 NPv6 ROUTE Hello due in 00:00:09 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Index 1/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 4 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor ount is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) Simple password authentication enabled c. MD5 authentication encrypts the password for stronger security. onfigure the link between R1 and R2 for MD5 authentication using the ip ospf authentication message-digest interface command. Then set the password to cisco with the ip ospf message-digest-key key_number md5 key-string command. Make sure that the key number is the same on both rs. In this case, use 1 for simplicity. R1(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip ospf authentication message-digest R1(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco R2(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip ospf authentication message-digest R2(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco Note: The MD5 key number works differently than key chains. The r uses the most recently added key for authenticating sent packets. The key number does not have a direct influence on this behavior, that is, if the interface was configured with the MD5 key number 10 and later the key with number 5 was added, the r would use the key number 5 to digitally sign outbound sent packets. If a r having several MD5 keys on an interface detects that at least one of its neighbors has not yet started using the most recently added key, it engages in a simple key migration procedure: it sends each OSPF packet multiple times, with each instance of the packet authenticated by a particular MD5 key configured on the interface, one instance for each key. This ensures a smooth, gradual migration. d. Verify the configuration using the show ip ospf interface interface command. R1# show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, ost: 64 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Index 1/1, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor ount is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0 Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) Message digest authentication enabled Youngest key id is 1 All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 14 of 16
15 NPv6 ROUTE Why is configuring authentication for OSPF, or any routing protocol, a good idea? e. Use the following Tcl script to verify connectivity to all addresses in the topology. R1# tclsh R1(tcl)# foreach address { } { ping $address } All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 15 of 16
16 NPv6 ROUTE Router Interface Summary Table Router Model Ethernet Interface # Fast Ethernet 0 (FA0) 1800 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (FA0/0) 2600 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (FA0/0) 2800 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (FA0/0) Router Interface Summary Ethernet Interface #2 Fast Ethernet 1 (FA1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial Interface #1 Serial 0 (S0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial Interface #2 Serial 1 (S1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Note: To find out how the r is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of r and how many interfaces the r has. Rather than list all combinations of configurations for each r class, this table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific r might contain one. For example, for an ISDN BRI interface, the string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in isco IOS commands to represent the interface. All contents are opyright isco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public Information. Page 16 of 16
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, OSPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization
 NPv6 RUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-3, SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization Topology bjectives Background onfigure multi-area SPF on a r. Verify multi-area behavior. reate an SPF virtual link. Summarize an area.
NPv6 RUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-3, SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization Topology bjectives Background onfigure multi-area SPF on a r. Verify multi-area behavior. reate an SPF virtual link. Summarize an area.
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
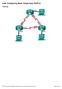 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances
 hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF
 hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv3 Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
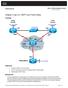 Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Initial Configurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link
 Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
LAB8: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Virtual Link. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
OSPF Virtual Link. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: Requirements. Components Used
 OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: 47866 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest
OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: 47866 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest
The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
 The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability
 OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
A Commands. Send comments to
 This chapter describes the Cisco NX-OS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) commands that begin with A. UCR-555 area authentication (OSPF) area authentication (OSPF) To enable authentication for an Open Shortest
This chapter describes the Cisco NX-OS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) commands that begin with A. UCR-555 area authentication (OSPF) area authentication (OSPF) To enable authentication for an Open Shortest
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv2
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
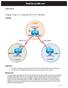 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
 OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
Lab 3.2 Configuring a Basic GRE Tunnel
 Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Creating Multiple OSPF Areas. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. 6-1
 Creating Multiple OSPF Areas 6-1 Issues with Maintaining a Large OSPF Network I am only receiving LSAs, no data. OSPF The SPF is running too often for me to route. OSPF OSPF OSPF OSPF My routing table
Creating Multiple OSPF Areas 6-1 Issues with Maintaining a Large OSPF Network I am only receiving LSAs, no data. OSPF The SPF is running too often for me to route. OSPF OSPF OSPF OSPF My routing table
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF
 Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
Link State. 1 Flooding of link-state information. 5 Routing Table. 3 SPF Algorithm. 2 Building a Topological Database. 4 SPF Tree
 Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA)
 OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) Document ID: 6208 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Is a Type 7 LSA? Configuration Tasks Defining a Not So Stubby Area Defining
OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) Document ID: 6208 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Is a Type 7 LSA? Configuration Tasks Defining a Not So Stubby Area Defining
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature
 OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands
 Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Configuring OSPF with CLI
 OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting OSPF Jono Ladmore 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. Presentation_ID 2 Agenda LSA Details Troubleshooting Commands Common Issues Troubleshooting
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting OSPF Jono Ladmore 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. Presentation_ID 2 Agenda LSA Details Troubleshooting Commands Common Issues Troubleshooting
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 11 Case Study
 bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Configuration and Management of Networks
 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
OSPF. About OSPF. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.4 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 10 Case Study
 Objectives: Use OSPF single area to illustrate basic Link State components and operation. Migrate from EIGRP to OSPF single area. Intro: Trevni Inc. decided to upgrade their routing protocol from EIGRP
Objectives: Use OSPF single area to illustrate basic Link State components and operation. Migrate from EIGRP to OSPF single area. Intro: Trevni Inc. decided to upgrade their routing protocol from EIGRP
Chapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch Topology Objectives Review a basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface. onfigure EIGRP over Frame
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch Topology Objectives Review a basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface. onfigure EIGRP over Frame
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3
 Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
OSPF. OSPF processs can be enabled on 2 levels
 OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS. IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
OSPF Commands: A through Z
 OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
OSPFv3 Commands. address-family (OSPFv3), page 4. authentication (OSPFv3), page 7
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios
 How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios Contents 1. Contents...... 1 2. Introduction...... 2 3. OSPFv3 Basic Configuration...... 3 Commands for basic OSPFv3 configuration... 4 OSPFv3 basic configuration
How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios Contents 1. Contents...... 1 2. Introduction...... 2 3. OSPFv3 Basic Configuration...... 3 Commands for basic OSPFv3 configuration... 4 OSPFv3 basic configuration
OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example
 OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example Document ID: 118879 Contributed by Narra Naukwal, Cisco TAC Engineer. Mar 31, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used
OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example Document ID: 118879 Contributed by Narra Naukwal, Cisco TAC Engineer. Mar 31, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used
OSPFv2 Cryptographic Authentication
 To prevent unauthorized or invalid routing updates in your network, Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) protocol packets must be authenticated. There are two methods of authentication that are
To prevent unauthorized or invalid routing updates in your network, Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) protocol packets must be authenticated. There are two methods of authentication that are
OSPF Commands. adjacency stagger, page 7. authentication-key (OSPF), page 14
 OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
LAB5: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Area Command in Interface Mode for OSPFv2
 This document describes how to enable Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) on a per-interface basis to simplify the configuration of unnumbered interfaces. The ip ospf area command allows you to
This document describes how to enable Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) on a per-interface basis to simplify the configuration of unnumbered interfaces. The ip ospf area command allows you to
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing. Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
OSPF Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
This chapter covers the following subjects:
 This chapter covers the following subjects: Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts OSPF Configuration EIGRP Configuration C H A P T E R 6 OSPF
This chapter covers the following subjects: Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts OSPF Configuration EIGRP Configuration C H A P T E R 6 OSPF
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Last Updated: June 24, 2011
 Configuring OSPF Finding Feature Information Configuring OSPF Last Updated: June 24, 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)
Configuring OSPF Finding Feature Information Configuring OSPF Last Updated: June 24, 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
IP Routing: OSPF Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E
 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION
Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability. Buy Full Product.
 Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
