LESSON 5 SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
|
|
|
- Clinton Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LESSON 5 SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
2 License for Use Information The following lessons and workbooks are open and publicly available under the following terms and conditions of ISECOM: All works in the Hacker Highschool project are provided for non-commercial use with elementary school students, junior high school students, and high school students whether in a public institution, private institution, or a part of home-schooling. These materials may not be reproduced for sale in any form. The provision of any class, course, training, or camp with these materials for which a fee is charged is expressly forbidden without a license including college classes, university classes, trade-school classes, summer or computer camps, and similar. To purchase a license, visit the LICENSE section of the Hacker Highschool web page at The HHS Project is a learning tool and as with any learning tool, the instruction is the influence of the instructor and not the tool. ISECOM cannot accept responsibility for how any information herein is applied or abused. The HHS Project is an open community effort and if you find value in this project, we do ask you support us through the purchase of a license, a donation, or sponsorship. All works copyright ISECOM,
3 Table of Contents License for Use Information... 2 Contributors Introduction Identifying a Server Identifying the Owner of a Domain Identifying the IP address of a Domain Identifying Services Ping and TraceRoute Banner Grabbing Identifying Services from Ports and Protocols System Fingerprinting Scanning Remote Computers... 9 Further Reading
4 Contributors Chuck Truett, ISECOM Marta Barceló, ISECOM Kim Truett, ISECOM Pete Herzog, ISECOM 4
5 5.0 Introduction It is obvious that someone who sits down at the keyboard of your computer can gather information about it, including the operating system and the programs that are running, but it is also possible for someone to use a network connection to gather information about a remote computer. This lesson will describe some of the ways in which that information can be gathered. Knowing how this information is gathered will help you to ensure that your local computer is safe from these activities. 5
6 5.1 Identifying a Server There are a number of useful sources on the Web which will allow you to collect information about domain names and IP addresses Identifying the Owner of a Domain The first step in identifying a remote system is to look at the domain name or IP address. Using a Whois lookup, you can discover valuable information, including the identity of the owner of a domain and contact information, which may include addresses and phone numbers. Note that there are now a number of domain name registrars, and not all whois databases contain information for all domains. You may have to look at more that one whois database to find information on the domain that you are investigating Identifying the IP address of a Domain There are a number of ways to determine the IP address of a domain. The address may be contained in the whois information or you may have to use a DNS or Domain Name Service lookup. (A web search engine will provide a number of resources for discovering IP addresses from domain names.) Once you have the IP address, you can access the records of the various members of the Number Resource Organization ( or to gain information about how IP addresses are distributed. IP numbers are assigned to service providers and networks in large groups, and knowing which group an IP address is contained in, and who has the rights to that group, can be very useful. This can help you determine information about the server or service provider that a website uses. Exercises: Pick a valid domain name and use a Whois lookup to find out who owns that domain. dominio ( -> isecom.org +Go -> Whois Lookup) What other information is available? When was the domain created? When will it expire? When was it last updated? Find the IP address for this domain name. Using the whois lookups for the various members of the Number Resource Organization determine who this IP address has been assigned to. (Start with the page, which also links to the other members of the NRO.) What is the range of the other numbers that have also been registered to this entity? 5.2 Identifying Services Once you have established the owner and the IP address of a domain, then you can start to look for information about the server to which that domain refers Ping and TraceRoute Now that you know who owns the domain, and who the IP number has been assigned to, you can check to see if the server that the website is on is actually active. The ping command will tell you if there is actually a computer associated with that domain or IP. The command ping domain or ping ipaddress 6
7 will tell you if there is an active computer at that address. If the output of the ping command indicates that the packets sent were received, then you can assume that the server is active. Another command, tracert (in Windows) or traceroute (in Linux) will show you the steps that information takes as it travels from your computer to the remote computer. Tracing the route that the packets take will sometimes give you additional information about the computers in the network with the computer that is the target of your trace. For example, computers will similar IP addresses will often be part of the same network. Exercises: Ping a valid website or IP address (ping or ping ). If you get a successful response, ping the next IP address. Did this produce a successful response? Use tracert or traceroute to trace the route from your local computer to the IP address that you used in the previous exercise. How many steps does it take? Do any of the listed computers have similar IP addresses? Banner Grabbing The next step in identifying a remote system is to try to connect using telnet and FTP. The server programs for these services display text messages called banners. A banner may state clearly and precisely what server program is running. For example, when you connect to an anonymous FTP server, you might get the following message: Connected to anon.server. 220 ProFTPD Server (Welcome... ) User (anon.server:(none)): While the number 220 is an FTP code which indicates that the server is ready for a new user, the text message ProFTPD Server identifies the FTP server program that is running on the remote computer. Using a web search engine, you can learn what operating system the program runs on and other details about its requirements, capabilities, limitations, and flaws. The primary flaw in the use of banner grabbing to gather information about a system is that clever system administrators can spoof banners. A banner that reads NoneOfYourBusiness Server is obviously misleading, but a Unix system with a banner that reads WS_FTP Server (a Windows-based FTP server) is going to complicate any intelligence gathering that may be done Identifying Services from Ports and Protocols You can also determine what programs are running on a system by looking at what ports are open and what protocols are in use. Start by looking at your own local computer. Go to a command line or shell prompt and run the netstat program using the -a (or all) switch: netstat -a The computer will display a list of open ports and some of the services that are using those ports: Active Connections 7
8 Proto Local Address Foreign Address State TCP YourComputer:microsoft-ds YourComputer:0 LISTENING TCP YourComputer:1025 YourComputer:0 LISTENING TCP YourComputer:1030 YourComputer:0 LISTENING TCP YourComputer:5000 YourComputer:0 LISTENING TCP YourComputer:netbios-ssn YourComputer:0 LISTENING TCP YourComputer: :http TIME_WAIT UDP YourComputer:microsoft-ds *:* UDP YourComputer:isakmp *:* UDP YourComputer:1027 *:* UDP YourComputer:1034 *:* UDP YourComputer:1036 *:* UDP YourComputer:ntp *:* UDP YourComputer:netbios-ns *:* UDP YourComputer:netbios-dgm *:* From this you can see many of the programs and services that are running on your local computer many of which you don't even realize are running. Another program, called fport, provides information similar to that which netstat does, but it also details which programs are using the open ports and protocols. (Fport is available for free download from Another program, called nmap (for network mapper), will more thoroughly probe your computer for open ports. When nmap is run, it will display a list of open ports and the services or protocols that use those ports. It may also be able to determine what operating system your computer is using. For example, if you run nmap on your local computer, you might see the following output: Port State Service 22/tcp open ssh 68/tcp open dhcpclient 139/tcp open netbios-ssn 445/tcp open microsoft-ds Device type: general purpose Running: Linux 2.4X 2.5.X OS details: Linux Kernel Uptime days (since Sat Jul 4 12:15: ) Nmap is available on your Hacker Highschool or L. A. S. cd. It is also available for download from Exercises: Run netstat on your local computer, using the -a switch. netstat -a 8
9 What ports are open? Using a web search engine, can you match these ports with the services that run on them? (This would be a good exercise to try at home, also, to see if your computer is running unnecessary and potentially dangerous services, such as FTP and telnet.) Run nmap, using the -ss (for SYN Stealth scan), and -O (for guess operating system) switches and the IP address as the target. nmap -ss -O The IP address specifies the local host, or your local computer. (Note: this is different from the IP address that other computers on the internet use to communicate with yours; on any machine, the IP address refers to the local computer) What open ports does nmap find? What services and programs are using these ports? Try running nmap while you have a web browser or telnet client open. Does this change the results? 5.3 System Fingerprinting Now that you know how to identify a server and how to scan for open ports and use this information to determine what services are running, you can put this information together to fingerprint a remote system, establishing the most likely operating system and services that the remote computer is running Scanning Remote Computers Using an IP address or a domain name other than as an argument for nmap allows you to scan for open ports on remote computers. It doesn't mean that there will be open ports, or that you will find them, but it does allow you to try. For example, imagine that you have been receiving a large amount of spam s, and you want to discover information about the person who is sending you these s. Looking at the headers of one of the s, you see that many of the s have originated from the same IP address: (see Lesson 9: Security for more details on reading e- mail headers). A whois lookup shows you that the address is part of a block assigned to a large ISP, but gives you no information regarding this particular IP address. If you then use nmap to scan the computer at that address, you get the following results: nmap -ss -O Starting nmap 3.50 ( ) at :13 Eastern Daylight Time Interesting ports on : (The 1632 ports scanned but not shown below are in state: closed) PORT STATE SERVICE 21/tcp open ftp 22/tcp open ssh 23/tcp open telnet 25/tcp open smtp 80/tcp open http 9
10 110/tcp open pop3 113/tcp open auth 135/tcp 136/tcp 137/tcp 138/tcp 139/tcp filtered msrpc filtered profile filtered netbios-ns filtered netbios-dgm filtered netbios-ssn 143/tcp open imap 144/tcp open news 161/tcp filtered snmp 306/tcp open unknown 443/tcp open https 445/tcp filtered microsoft-ds 513/tcp open login 514/tcp open shell No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see TCP/IP fingerprint: SInfo(V=3.50%P=i686-pc-windows-windows%D=7/3%Time=40E74EC0%O=21%C=1) TSeq(Class=TR%IPID=RD%TS=1000HZ) T1(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=FFFF%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNWNNT) T2(Resp=N) T3(Resp=N) T4(Resp=N) T5(Resp=Y%DF=N%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=) T6(Resp=N) T7(Resp=N) Uptime days (since Thu Jul 01 23:23: ) Nmap run completed -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in seconds The ports marked as filtered are well-known as potentially vulnerable to attack, so it is not a surprise to find them listed as filtered. What is most interesting is that ports 21, 22 and 23 for ftp, ssh and telnet are all listed as open. The last thing that nmap does is to try to identify the operating system that is running on the scanned computer. In this instance, the tests that nmap runs are inconclusive, however, since nmap does show that ftp and telnet services are both running, you can attempt to connect through each of those to see if there is a banner that will be broadcast. When you connect through FTP you see a banner that says: 10
11 220 ftp316.pair.com NcFTPd Server (licensed copy) ready. When you then connect through telnet, the computer displays a banner which says FreeBSD/i386 (ttyp7) A quick web search tells you that NcFTPd is a Unix program and that FreeBSD is a Unix-type operating system, so it is likely that the server is running a version of FreeBSD as its operating system. You can't be certain that this is accurate (banners can be spoofed), but you can accept this as a reasonable guess. So, by using nmap, along with FTP and telnet, you have determined that the server which has been sending you spam runs a Unix-type operating system probably FreeBSD and is set up to send and receive a large variety of information, through a number of services including FTP, telnet, http, smtp and pop3. 11
12 Further Reading Nmap: More on Nmap: oom= Fport: =/resources/proddesc/fport.htm A number of site detailing ports and the services that use them: Various DNS lookups: Ping: 12
LESSON 3 PORTS AND PROTOCOLS
 LESSON 3 PORTS AND PROTOCOLS License for Use Information The following lessons and workbooks are open and publicly available under the following terms and conditions of ISECOM: All works in the Hacker
LESSON 3 PORTS AND PROTOCOLS License for Use Information The following lessons and workbooks are open and publicly available under the following terms and conditions of ISECOM: All works in the Hacker
Scanning. Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III. Reading Assignment. Unit Lesson UNIT III STUDY GUIDE
 UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Recall the terms port scanning, network scanning, and vulnerability scanning. 2.
UNIT III STUDY GUIDE Course Learning Outcomes for Unit III Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Recall the terms port scanning, network scanning, and vulnerability scanning. 2.
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense
 Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 2 TCP/IP Concepts Review Last modified 1-11-17 Objectives Describe the TCP/IP protocol stack Explain the basic concepts of IP addressing Explain the
Hands-On Ethical Hacking and Network Defense Chapter 2 TCP/IP Concepts Review Last modified 1-11-17 Objectives Describe the TCP/IP protocol stack Explain the basic concepts of IP addressing Explain the
Penetration Testing with Kali Linux
 Penetration Testing with Kali Linux PWK Copyright Offensive Security Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 11 All rights reserved to Offensive Security No part of this publication, in whole or in part, may
Penetration Testing with Kali Linux PWK Copyright Offensive Security Ltd. All rights reserved. Page 1 of 11 All rights reserved to Offensive Security No part of this publication, in whole or in part, may
INF5290 Ethical Hacking. Lecture 3: Network reconnaissance, port scanning. Universitetet i Oslo Laszlo Erdödi
 INF5290 Ethical Hacking Lecture 3: Network reconnaissance, port scanning Universitetet i Oslo Laszlo Erdödi Lecture Overview Identifying hosts in a network Identifying services on a host What are the typical
INF5290 Ethical Hacking Lecture 3: Network reconnaissance, port scanning Universitetet i Oslo Laszlo Erdödi Lecture Overview Identifying hosts in a network Identifying services on a host What are the typical
SE 4C03 Winter Final Examination Answer Key. Instructor: William M. Farmer
 SE 4C03 Winter 2003 Final Examination Answer Key Instructor: William M. Farmer (1) [2 pts.] Both the source and destination IP addresses are used to route IP datagrams. Is this statement true or false?
SE 4C03 Winter 2003 Final Examination Answer Key Instructor: William M. Farmer (1) [2 pts.] Both the source and destination IP addresses are used to route IP datagrams. Is this statement true or false?
TCP/IP Fundamentals. Introduction. Practice Practice : Name. Date Period
 Name Date Period TCP/IP Fundamentals Introduction For the Network+ Certification exam, you should be able to identify the class of an IP address, an APIPA IP address, and a private IP address as well as
Name Date Period TCP/IP Fundamentals Introduction For the Network+ Certification exam, you should be able to identify the class of an IP address, an APIPA IP address, and a private IP address as well as
ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. No matter what medium connects computers on a network copper wires, fiber-optic cables, or a wireless setup the same protocol must be
ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. No matter what medium connects computers on a network copper wires, fiber-optic cables, or a wireless setup the same protocol must be
Nsauditor White Paper. Abstract
 Nsauditor White Paper NSASOFT LLC. http://www.nsauditor.com E-mail: info@nsauditor.com Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples herein
Nsauditor White Paper NSASOFT LLC. http://www.nsauditor.com E-mail: info@nsauditor.com Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples herein
Network Forensics Prefix Hijacking Theory Prefix Hijacking Forensics Concluding Remarks. Network Forensics:
 Network Forensics: Network OS Fingerprinting Prefix Hijacking Analysis Scott Hand September 30 th, 2011 Outline 1 Network Forensics Introduction OS Fingerprinting 2 Prefix Hijacking Theory BGP Background
Network Forensics: Network OS Fingerprinting Prefix Hijacking Analysis Scott Hand September 30 th, 2011 Outline 1 Network Forensics Introduction OS Fingerprinting 2 Prefix Hijacking Theory BGP Background
Starting Nmap 6.40 ( ) at :54 Pacific Daylight Time Nmap scan report for mass_dns: warning: Unable to
 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2016-06-12 12:54 Pacific Daylight Time Nmap scan report for 172.30.0.7 mass_dns: warning: Unable to determine any DNS servers. Reverse DNS is disabled. Try using
Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2016-06-12 12:54 Pacific Daylight Time Nmap scan report for 172.30.0.7 mass_dns: warning: Unable to determine any DNS servers. Reverse DNS is disabled. Try using
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems
 CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting CIT 480: Securing Computer
CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Scanning CIT 480: Securing Computer Systems Slide #1 Topics 1. Port Scanning 2. Stealth Scanning 3. Version Identification 4. OS Fingerprinting CIT 480: Securing Computer
Network+ Guide to Networks, Seventh Edition Chapter 2, Solutions
 Network+ Guide to Networks, Seventh Edition Chapter 2, Solutions Review Questions 1. Which part of a MAC address is unique to each manufacturer? A. The network identifier B. The OUI C. The device identifier
Network+ Guide to Networks, Seventh Edition Chapter 2, Solutions Review Questions 1. Which part of a MAC address is unique to each manufacturer? A. The network identifier B. The OUI C. The device identifier
Layered Networking and Port Scanning
 Layered Networking and Port Scanning David Malone 22nd June 2004 1 IP Header IP a way to phrase information so it gets from one computer to another. IPv4 Header: Version Head Len ToS Total Length 4 bit
Layered Networking and Port Scanning David Malone 22nd June 2004 1 IP Header IP a way to phrase information so it gets from one computer to another. IPv4 Header: Version Head Len ToS Total Length 4 bit
TCP, UDP Ports, and ICMP Message Types1
 Appendix A APPENDIX A TCP, UDP Ports, and ICMP Message Types1 I list useful TCP, UDP ports, and ICMP message types in this appendix. A comprehensive list of registered TCP and UDP services may be found
Appendix A APPENDIX A TCP, UDP Ports, and ICMP Message Types1 I list useful TCP, UDP ports, and ICMP message types in this appendix. A comprehensive list of registered TCP and UDP services may be found
LESSON 5 SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
 LESSON 5 SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION WARNING The Hacker Highschool Project is a learning tool and as with any learning tool there are dangers. Some lessons if abused may result in physical injury. Some additional
LESSON 5 SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION WARNING The Hacker Highschool Project is a learning tool and as with any learning tool there are dangers. Some lessons if abused may result in physical injury. Some additional
Certified Vulnerability Assessor
 Certified Vulnerability Assessor COURSE BENEFITS Course Title:Certified Vulnerability Assessor Duration: 3Day Language: English Class Format Options: Instructor-led classroom Live Online Training Prerequisites:
Certified Vulnerability Assessor COURSE BENEFITS Course Title:Certified Vulnerability Assessor Duration: 3Day Language: English Class Format Options: Instructor-led classroom Live Online Training Prerequisites:
n Given a scenario, analyze and interpret output from n A SPAN has the ability to copy network traffic passing n Capacity planning for traffic
 Chapter Objectives n Understand how to use appropriate software tools to assess the security posture of an organization Chapter #7: Technologies and Tools n Given a scenario, analyze and interpret output
Chapter Objectives n Understand how to use appropriate software tools to assess the security posture of an organization Chapter #7: Technologies and Tools n Given a scenario, analyze and interpret output
Basics of executing a penetration test
 Basics of executing a penetration test 25.04.2013, WrUT BAITSE guest lecture Bernhards Blumbergs, CERT.LV Outline Reconnaissance and footprinting Scanning and enumeration System exploitation Outline Reconnaisance
Basics of executing a penetration test 25.04.2013, WrUT BAITSE guest lecture Bernhards Blumbergs, CERT.LV Outline Reconnaissance and footprinting Scanning and enumeration System exploitation Outline Reconnaisance
Term 2 Grade 12 -Project Task 2 Teachers Guidelines Ethical Hacking Picture 1 Picture 2
 Term 2 Grade 12 -Project Task 2 Teachers Guidelines Ethical Hacking Picture 1 PRESENTATION Picture 2 Page 1 of 11 PROJECT TASK 2 INTRODUCTION The educational system has databases full of personal information
Term 2 Grade 12 -Project Task 2 Teachers Guidelines Ethical Hacking Picture 1 PRESENTATION Picture 2 Page 1 of 11 PROJECT TASK 2 INTRODUCTION The educational system has databases full of personal information
Introduction to TCP/IP
 Introduction to TCP/IP Properties and characteristics of TCP/IP IPv4 IPv6 Public vs private vs APIPA/link local Static vs dynamic Client-side DNS settings Client-side DHCP Subnet mask vs CIDR Gateway TCP/IP
Introduction to TCP/IP Properties and characteristics of TCP/IP IPv4 IPv6 Public vs private vs APIPA/link local Static vs dynamic Client-side DNS settings Client-side DHCP Subnet mask vs CIDR Gateway TCP/IP
TCP/IP Filtering. Main TCP/IP Filtering Dialog Box. Route Filters Button. Packet Filters Button CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 Main Dialog Box To access this dialog box (Figure 11-1), select Global/Filtering/ from the Device View. Figure 11-1 Main Configuration Dialog Box Route Filters Button This button brings up a
CHAPTER 11 Main Dialog Box To access this dialog box (Figure 11-1), select Global/Filtering/ from the Device View. Figure 11-1 Main Configuration Dialog Box Route Filters Button This button brings up a
Scanning. Scanning. Goals Useful Tools. The Basics NMAP. Scanning 1 / 34
 Goals Useful s 1 / 34 Goals Useful s Suppose you re an attacker You want to attack a site How do you proceed? 2 / 34 Goals Goals Useful s Find an interesting (or vulnerable) machine Find a vulnerable service
Goals Useful s 1 / 34 Goals Useful s Suppose you re an attacker You want to attack a site How do you proceed? 2 / 34 Goals Goals Useful s Find an interesting (or vulnerable) machine Find a vulnerable service
Windows Insecurity. Penetrated. v0.11
 Windows Insecurity Penetrated v0.11 1 Copyright (c) 2004 ADRIAN PASTOR. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version
Windows Insecurity Penetrated v0.11 1 Copyright (c) 2004 ADRIAN PASTOR. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version
Session 16 Windows 7 Professional DNS & Active Directory
 Session 16 Windows 7 Professional DNS & Active Directory Fall 2011 ITE153 Operating Systems 1 Session 16 Windows 7 Professional Configuring TCP/IP Addressing & Name Resolution Fall 2011 ITE153 Operating
Session 16 Windows 7 Professional DNS & Active Directory Fall 2011 ITE153 Operating Systems 1 Session 16 Windows 7 Professional Configuring TCP/IP Addressing & Name Resolution Fall 2011 ITE153 Operating
AN TOÀN LỚP 4: TCP/IP ATTACKS NGUYEN HONG SON PTITHCM
 1 AN TOÀN LỚP 4: TCP/IP ATTACKS NGUYEN HONG SON PTITHCM 2 Introduction (1/2) TCP provides a full duplex reliable stream connection between two end points A connection is uniquely defined by the quadruple
1 AN TOÀN LỚP 4: TCP/IP ATTACKS NGUYEN HONG SON PTITHCM 2 Introduction (1/2) TCP provides a full duplex reliable stream connection between two end points A connection is uniquely defined by the quadruple
Computer Network Vulnerabilities
 Computer Network Vulnerabilities Objectives Explain how routers are used to protect networks Describe firewall technology Describe intrusion detection systems Describe honeypots Routers Routers are like
Computer Network Vulnerabilities Objectives Explain how routers are used to protect networks Describe firewall technology Describe intrusion detection systems Describe honeypots Routers Routers are like
1/18/13. Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition. Objectives. Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Paper solution Subject: Computer Networks (TE Computer pattern) Marks : 30 Date: 5/2/2015
 Paper solution Subject: Computer Networks (TE Computer- 2012 pattern) Marks : 30 Date: 5/2/2015 Q1 a) What is difference between persistent and non persistent HTTP? Also Explain HTTP message format. [6]
Paper solution Subject: Computer Networks (TE Computer- 2012 pattern) Marks : 30 Date: 5/2/2015 Q1 a) What is difference between persistent and non persistent HTTP? Also Explain HTTP message format. [6]
Features of Netcat. Abstract. Keywords. I. Introduction. II. History. Jeffrey Kurcz School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 Features of Netcat Jeffrey Kurcz School of Computer Science University of Windsor kurcz@uwindsor.ca Abstract This paper discusses the many uses that Netcat can perform for many different tasks that need
Features of Netcat Jeffrey Kurcz School of Computer Science University of Windsor kurcz@uwindsor.ca Abstract This paper discusses the many uses that Netcat can perform for many different tasks that need
IK2206 Internet Security and Privacy Firewall & IP Tables
 IK2206 Internet Security and Privacy Firewall & IP Tables Group Assignment Following persons were members of group C and authors of this report: Name: Christoph Moser Mail: chmo@kth.se P-Nr: 850923-T513
IK2206 Internet Security and Privacy Firewall & IP Tables Group Assignment Following persons were members of group C and authors of this report: Name: Christoph Moser Mail: chmo@kth.se P-Nr: 850923-T513
ECE435: Network Engineering Homework 5 TCP. Due: Thursday, 18 October 2018, 3:30pm
 ECE435: Network Engineering Homework 5 TCP Due: Thursday, 18 October 2018, 3:30pm Submission Directions: For this homework short answers will suffice. To submit, create a document with your answers (text,
ECE435: Network Engineering Homework 5 TCP Due: Thursday, 18 October 2018, 3:30pm Submission Directions: For this homework short answers will suffice. To submit, create a document with your answers (text,
Sam Spade 1.14 Open Source Security Tool by Steve Atkins
 CS 413 Spring 2005 Max Konovalov Sam Spade 1.14 Open Source Security Tool by Steve Atkins University of Alaska Anchorage Department of Mathematical Sciences This paper describes Sam Spade 1.14 open source
CS 413 Spring 2005 Max Konovalov Sam Spade 1.14 Open Source Security Tool by Steve Atkins University of Alaska Anchorage Department of Mathematical Sciences This paper describes Sam Spade 1.14 open source
CSC 574 Computer and Network Security. TCP/IP Security
 CSC 574 Computer and Network Security TCP/IP Security Alexandros Kapravelos kapravelos@ncsu.edu (Derived from slides by Will Enck and Micah Sherr) Network Stack, yet again Application Transport Network
CSC 574 Computer and Network Security TCP/IP Security Alexandros Kapravelos kapravelos@ncsu.edu (Derived from slides by Will Enck and Micah Sherr) Network Stack, yet again Application Transport Network
Ethical Hacking Basics Course
 Ethical Hacking Basics Course By : Mohammad Askar @Mohammadaskar2 Module 3 Information Gathering. Definition of Information Gathering Information Gathering means the proccess to collecting data and information
Ethical Hacking Basics Course By : Mohammad Askar @Mohammadaskar2 Module 3 Information Gathering. Definition of Information Gathering Information Gathering means the proccess to collecting data and information
Nessus Scan Report. Hosts Summary (Executive) Hosts Summary (Executive) Mon, 15 May :27:44 EDT
 Nessus Scan Report Mon, 15 May 2017 15:27:44 EDT Table Of Contents Hosts Summary (Executive) 192.168.168.134 Hosts Summary (Executive) [-] Collapse All [+] Expand All 192.168.168.134 Summary Critical High
Nessus Scan Report Mon, 15 May 2017 15:27:44 EDT Table Of Contents Hosts Summary (Executive) 192.168.168.134 Hosts Summary (Executive) [-] Collapse All [+] Expand All 192.168.168.134 Summary Critical High
Fundamentals of Computer Networking AE6382
 Computer networks are an integral part of the modern computing infrastructure The local network (LAN) is usually Ethernet LAN s are inter-connected with other LAN s in a hierarchical fashion eventually
Computer networks are an integral part of the modern computing infrastructure The local network (LAN) is usually Ethernet LAN s are inter-connected with other LAN s in a hierarchical fashion eventually
Lab 2: Creating Secure Architectures
 Lab 2: Creating Secure Architectures A Challenge Our challenge is to setup MyBank Incorp, where each of you will be allocated a network and hosts to configure and get on-line (Figure 1). For this you will
Lab 2: Creating Secure Architectures A Challenge Our challenge is to setup MyBank Incorp, where each of you will be allocated a network and hosts to configure and get on-line (Figure 1). For this you will
Port Mirroring in CounterACT. CounterACT Technical Note
 Table of Contents About Port Mirroring and the Packet Engine... 3 Information Based on Specific Protocols... 4 ARP... 4 DHCP... 5 HTTP... 6 NetBIOS... 7 TCP/UDP... 7 Endpoint Lifecycle... 8 Active Endpoint
Table of Contents About Port Mirroring and the Packet Engine... 3 Information Based on Specific Protocols... 4 ARP... 4 DHCP... 5 HTTP... 6 NetBIOS... 7 TCP/UDP... 7 Endpoint Lifecycle... 8 Active Endpoint
Firewall Identification: Banner Grabbing
 Honey POt Firewall Identification: Banner Grabbing Banners are messages sent out by network services during the connection to the service. Banners announce which service is running on the system. Banner
Honey POt Firewall Identification: Banner Grabbing Banners are messages sent out by network services during the connection to the service. Banners announce which service is running on the system. Banner
Extended ACL Configuration Mode Commands
 Extended ACL Configuration Mode Commands To create and modify extended access lists on a WAAS device for controlling access to interfaces or applications, use the ip access-list extended global configuration
Extended ACL Configuration Mode Commands To create and modify extended access lists on a WAAS device for controlling access to interfaces or applications, use the ip access-list extended global configuration
Computer Forensics: Investigating Network Intrusions and Cyber Crime, 2nd Edition. Chapter 3 Investigating Web Attacks
 Computer Forensics: Investigating Network Intrusions and Cyber Crime, 2nd Edition Chapter 3 Investigating Web Attacks Objectives After completing this chapter, you should be able to: Recognize the indications
Computer Forensics: Investigating Network Intrusions and Cyber Crime, 2nd Edition Chapter 3 Investigating Web Attacks Objectives After completing this chapter, you should be able to: Recognize the indications
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals. Chapter 03 Application Functionality and Protocols
 CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 03 Application Functionality and Protocols Updated: 27/04/2008 1 3.1 Applications: The Interface Between Human and Networks Applications provide the means
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 03 Application Functionality and Protocols Updated: 27/04/2008 1 3.1 Applications: The Interface Between Human and Networks Applications provide the means
Debian/GNU Linux Networking
 Debian/GNU Linux Networking Basics of the Networking Károly Erdei October 15, 2014 Károly Erdei Debian/GNU Linux Networking 1/41 Agenda 1 Networks 2 Ethernet 3 Internet Protocol 4 TCP 5 DHCP 6 Check Network
Debian/GNU Linux Networking Basics of the Networking Károly Erdei October 15, 2014 Károly Erdei Debian/GNU Linux Networking 1/41 Agenda 1 Networks 2 Ethernet 3 Internet Protocol 4 TCP 5 DHCP 6 Check Network
Computer and Network Security
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 8 Announcements Plan for Today: Networks: TCP Firewalls Midterm 1: One week from Today! 2/17/2009 In class, short answer, multiple choice,
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 8 Announcements Plan for Today: Networks: TCP Firewalls Midterm 1: One week from Today! 2/17/2009 In class, short answer, multiple choice,
Firewall Simulation COMP620
 Firewall Simulation COMP620 Firewall Simulation The simulation allows participants to configure their own simulated firewalls using Cisco-like syntax. Participants can take benign or malicious actions
Firewall Simulation COMP620 Firewall Simulation The simulation allows participants to configure their own simulated firewalls using Cisco-like syntax. Participants can take benign or malicious actions
2.1 A Primer on Network Sniffing Reconstructing TCP Streams Reconstructing Fragmented Packets 14
 Index 1 Executive Summary 4 1 Introduction 6 2 NIDS Concepts 8 2.1 A Primer on Network Sniffing 9 2.2 NIDS Placement 11 2.3 Logging 12 2.4 Reconstructing TCP Streams 13 2.5 Reconstructing Fragmented Packets
Index 1 Executive Summary 4 1 Introduction 6 2 NIDS Concepts 8 2.1 A Primer on Network Sniffing 9 2.2 NIDS Placement 11 2.3 Logging 12 2.4 Reconstructing TCP Streams 13 2.5 Reconstructing Fragmented Packets
Overview. Computer Network Lab, SS Security. Type of attacks. Firewalls. Protocols. Packet filter
 Computer Network Lab 2017 Fachgebiet Technische Informatik, Joachim Zumbrägel Overview Security Type of attacks Firewalls Protocols Packet filter 1 Security Security means, protect information (during
Computer Network Lab 2017 Fachgebiet Technische Informatik, Joachim Zumbrägel Overview Security Type of attacks Firewalls Protocols Packet filter 1 Security Security means, protect information (during
DESCRIPTION OF TYPICAL NETWORK SERVICES ON SERVERS
 DESCRIPTION OF TYPICAL NETWORK SERVICES ON SERVERS Before you start Objectives: Familiarize yourself with the services such as File and Print, WWW, FTP, E- mail, Faxing, Remote Access, DHCP, DNS and WINS.
DESCRIPTION OF TYPICAL NETWORK SERVICES ON SERVERS Before you start Objectives: Familiarize yourself with the services such as File and Print, WWW, FTP, E- mail, Faxing, Remote Access, DHCP, DNS and WINS.
Lab 1: Creating Secure Architectures (Revision)
 Lab 1: Creating Secure Architectures (Revision) A Challenge Our challenge is to setup MyBank Incorp, where each of you will be allocated a network and hosts to configure and get on-line (Figure 1). For
Lab 1: Creating Secure Architectures (Revision) A Challenge Our challenge is to setup MyBank Incorp, where each of you will be allocated a network and hosts to configure and get on-line (Figure 1). For
Netcat Scanning to Backdoors
 Netcat Scanning to Backdoors Security & Privacy on the Internet (03-60-467) Fall 2009 Submitted to Dr. A.K. Aggarwal Submitted By Jeffrey Kurcz School of Computer Science University of Windsor CONTENTS
Netcat Scanning to Backdoors Security & Privacy on the Internet (03-60-467) Fall 2009 Submitted to Dr. A.K. Aggarwal Submitted By Jeffrey Kurcz School of Computer Science University of Windsor CONTENTS
Software Engineering 4C03 Answer Key
 Software Engineering 4C03 Answer Key DAY CLASS Dr. William M. Farmer DURATION OF EXAMINATION: 2 Hours MCMASTER UNIVERSITY FINAL EXAMINATION April 2002 (1) [2 pts.] Conventional encryption cannot be used
Software Engineering 4C03 Answer Key DAY CLASS Dr. William M. Farmer DURATION OF EXAMINATION: 2 Hours MCMASTER UNIVERSITY FINAL EXAMINATION April 2002 (1) [2 pts.] Conventional encryption cannot be used
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals. Chapter 3 Application Layer Functionality and Protocols
 CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 3 Application Layer Functionality and Protocols Application Layer Functionality and Protocols Applications: The Interface Between the Networks Horny/Coufal
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals Chapter 3 Application Layer Functionality and Protocols Application Layer Functionality and Protocols Applications: The Interface Between the Networks Horny/Coufal
Networking Notes. Common Internet Speeds. Online Speed Test myspeed.visualware.com
 Networking Notes Common Internet Speeds Dial Up 56 kbs 1000kbs = 1 mbs (1 user capacity) DSL 1.5 mbs (1 channel 10 user capacity) T1 1.5 mbs (24 channel 500 user capacity) Scalable Ethernet (Adjustable
Networking Notes Common Internet Speeds Dial Up 56 kbs 1000kbs = 1 mbs (1 user capacity) DSL 1.5 mbs (1 channel 10 user capacity) T1 1.5 mbs (24 channel 500 user capacity) Scalable Ethernet (Adjustable
TCP /IP Fundamentals Mr. Cantu
 TCP /IP Fundamentals Mr. Cantu OSI Model and TCP/IP Model Comparison TCP / IP Protocols (Application Layer) The TCP/IP subprotocols listed in this layer are services that support a number of network functions:
TCP /IP Fundamentals Mr. Cantu OSI Model and TCP/IP Model Comparison TCP / IP Protocols (Application Layer) The TCP/IP subprotocols listed in this layer are services that support a number of network functions:
Project 4: Penetration Test
 Project description Project 4: Penetration Test April 28, 2014 Bing Hao The learning objective of this project is to gain hands on experiences with the usage and functionality of Nmap, Neussus and Metsploit.
Project description Project 4: Penetration Test April 28, 2014 Bing Hao The learning objective of this project is to gain hands on experiences with the usage and functionality of Nmap, Neussus and Metsploit.
General Network Troubleshooting
 Overview Contents This document outlines some basic network troubleshooting techniques that can be used to test network connectivity. They are useful when troubleshooting issues with Crystal Enterprise
Overview Contents This document outlines some basic network troubleshooting techniques that can be used to test network connectivity. They are useful when troubleshooting issues with Crystal Enterprise
Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition. Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Network+ Guide to Networks 5 th Edition Chapter 10 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Understand methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Exam Questions SY0-401
 Exam Questions SY0-401 CompTIA Security+ Certification https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/sy0-401/ 1. A company has implemented PPTP as a VPN solution. Which of the following ports would need to be opened
Exam Questions SY0-401 CompTIA Security+ Certification https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/sy0-401/ 1. A company has implemented PPTP as a VPN solution. Which of the following ports would need to be opened
Objectives. Connecting with Computer Science 2
 Objectives Learn what the Internet really is Become familiar with the architecture of the Internet Become familiar with Internet-related protocols Understand how the TCP/IP protocols relate to the Internet
Objectives Learn what the Internet really is Become familiar with the architecture of the Internet Become familiar with Internet-related protocols Understand how the TCP/IP protocols relate to the Internet
Chapter 2. Switch Concepts and Configuration. Part II
 Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part II CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Configuring Switch Security MAC Address Flooding Passwords Spoofing Attacks Console Security Tools
Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part II CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Configuring Switch Security MAC Address Flooding Passwords Spoofing Attacks Console Security Tools
Module 19 : Threats in Network What makes a Network Vulnerable?
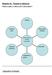 Module 19 : Threats in Network What makes a Network Vulnerable? Sharing Unknown path Many points of attack What makes a network vulnerable? Unknown perimeter Anonymity Complexity of system Categories of
Module 19 : Threats in Network What makes a Network Vulnerable? Sharing Unknown path Many points of attack What makes a network vulnerable? Unknown perimeter Anonymity Complexity of system Categories of
The ACK and NACK of Programming
 NFJS Software Symposium Series 2012 The ACK and NACK of Programming Ken Sipe About Speaker http://kensipe.blogspot.com/ http://del.icio.us/kensipe twitter: @kensipe ken.sipe@gmail.com Developer: Embedded,
NFJS Software Symposium Series 2012 The ACK and NACK of Programming Ken Sipe About Speaker http://kensipe.blogspot.com/ http://del.icio.us/kensipe twitter: @kensipe ken.sipe@gmail.com Developer: Embedded,
Global Information Assurance Certification Paper
 Global Information Assurance Certification Paper Copyright SANS Institute Author Retains Full Rights This paper is taken from the GIAC directory of certified professionals. Reposting is not permited without
Global Information Assurance Certification Paper Copyright SANS Institute Author Retains Full Rights This paper is taken from the GIAC directory of certified professionals. Reposting is not permited without
Layer 4: UDP, TCP, and others. based on Chapter 9 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers
 Layer 4: UDP, TCP, and others based on Chapter 9 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers Concepts application set transport set High-level, "Application Set" protocols deal only with how handled
Layer 4: UDP, TCP, and others based on Chapter 9 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers Concepts application set transport set High-level, "Application Set" protocols deal only with how handled
Configure Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Service Settings on a Switch
 Configure Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Service Settings on a Switch Objective Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are transportation
Configure Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Service Settings on a Switch Objective Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are transportation
Incident Response Tools
 Incident Response Tools James Madison University Dept. of Computer Science June 13, 2013 1 Introduction Being successfully attacked is inevitable. A determined hacker WILL be able to penetrate your network.
Incident Response Tools James Madison University Dept. of Computer Science June 13, 2013 1 Introduction Being successfully attacked is inevitable. A determined hacker WILL be able to penetrate your network.
Snort Rules Classification and Interpretation
 Snort Rules Classification and Interpretation Pop2 Rules: Class Type Attempted Admin(SID: 1934, 284,285) GEN:SID 1:1934 Message POP2 FOLD overflow attempt Summary This event is generated when an attempt
Snort Rules Classification and Interpretation Pop2 Rules: Class Type Attempted Admin(SID: 1934, 284,285) GEN:SID 1:1934 Message POP2 FOLD overflow attempt Summary This event is generated when an attempt
Curso: Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures
 Curso: Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures Module 1: Introduction to Ethical Hacking Who is a Hacker? Essential Terminologies Effects of Hacking Effects of Hacking on Business Elements of Information Security
Curso: Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures Module 1: Introduction to Ethical Hacking Who is a Hacker? Essential Terminologies Effects of Hacking Effects of Hacking on Business Elements of Information Security
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 9 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 9 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Describe methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 9 In-Depth TCP/IP Networking Objectives Describe methods of network design unique to TCP/IP networks, including subnetting, CIDR, and address translation
Information for Domain Admin & Web Admin. Version v 2.0
 Information for Domain Admin & Web Admin Version v 2.0 Copyright 2008 Precise-ITC, Inc. All rights reserved. Information for Domain Admin and Web Admin.doc v2.0 2008 Precise-ITC, Inc. All rights reserved
Information for Domain Admin & Web Admin Version v 2.0 Copyright 2008 Precise-ITC, Inc. All rights reserved. Information for Domain Admin and Web Admin.doc v2.0 2008 Precise-ITC, Inc. All rights reserved
On Assessing the Impact of Ports Scanning on the Target Infrastructure
 2018 On Assessing the Impact of Ports Scanning on the Target Infrastructure Dr Mahdi Aiash 4/24/2018 1. Introduction A port scan is a method for determining which ports on a network are open. As ports
2018 On Assessing the Impact of Ports Scanning on the Target Infrastructure Dr Mahdi Aiash 4/24/2018 1. Introduction A port scan is a method for determining which ports on a network are open. As ports
HP ArcSight Port and Protocol Information
 Important Notice HP ArcSight Port and Protocol Information The information (data) contained on all sheets of this document constitutes confidential information of Hewlett- Packard Company or its affiliates
Important Notice HP ArcSight Port and Protocol Information The information (data) contained on all sheets of this document constitutes confidential information of Hewlett- Packard Company or its affiliates
Using Ethereal As A Tool For Network Security Mentor: Mr. Christopher Edwards Team Members: Jerome Mitchell, Anthony Anderson, and Napoleon Paxton
 Using Ethereal As A Tool For Network Security Mentor: Mr. Christopher Edwards Team Members: Jerome Mitchell, Anthony Anderson, and Napoleon Paxton Abstract The Office of Navel Research Network Team actively
Using Ethereal As A Tool For Network Security Mentor: Mr. Christopher Edwards Team Members: Jerome Mitchell, Anthony Anderson, and Napoleon Paxton Abstract The Office of Navel Research Network Team actively
Practical network security. How hackers do it. Warning. Outline. How hackers do it : Scan Exploit Sniff How to secure?
 Practical network security How hackers do it. 1 3 Outline Warning How hackers do it : Scan Exploit Sniff How to secure? Using the tools presented here is ILLEGAL! It is STRICTLY FORBIDDEN to use these
Practical network security How hackers do it. 1 3 Outline Warning How hackers do it : Scan Exploit Sniff How to secure? Using the tools presented here is ILLEGAL! It is STRICTLY FORBIDDEN to use these
Computer Networks. More on Standards & Protocols Quality of Service. Week 10. College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University
 Computer Networks More on Standards & Protocols Quality of Service Week 10 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Introduction to Protocols l A protocol is a set of rules
Computer Networks More on Standards & Protocols Quality of Service Week 10 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Introduction to Protocols l A protocol is a set of rules
The Swiss Army Knife netcat
 The Swiss Army Knife netcat Lab Objectives In this lab, you will perform the following six labs: Lab 1 Use Netcat for Port Scanning Lab 2 Use Netcat for Banner Grabbing Lab 3 Use Netcat to Transfer Files
The Swiss Army Knife netcat Lab Objectives In this lab, you will perform the following six labs: Lab 1 Use Netcat for Port Scanning Lab 2 Use Netcat for Banner Grabbing Lab 3 Use Netcat to Transfer Files
Week Date Teaching Attended 5 Feb 2013 Lab 7: Snort IDS Rule Development
 Weekly Tasks Week 5 Rich Macfarlane 2013 Week Date Teaching Attended 5 Feb 2013 Lab 7: Snort IDS Rule Development Aim: The aim of these labs are to further investigate the Snort, network IDS, and methods
Weekly Tasks Week 5 Rich Macfarlane 2013 Week Date Teaching Attended 5 Feb 2013 Lab 7: Snort IDS Rule Development Aim: The aim of these labs are to further investigate the Snort, network IDS, and methods
CN Assignment I. 1. With an example explain how cookies are used in e-commerce application to improve the performance.
 CN Assignment I 1. With an example explain how cookies are used in e-commerce application to improve the performance. In an e-commerce application, when the user sends a login form to the server, the server
CN Assignment I 1. With an example explain how cookies are used in e-commerce application to improve the performance. In an e-commerce application, when the user sends a login form to the server, the server
Wireshark: Are You Under Attack? Kyle Feuz School of Computing
 Wireshark: Are You Under Attack? Kyle Feuz School of Computing Introduction Download Wireshark and capture files https://www.wireshark.org/download.html http://icarus.cs.weber.edu/~kfeuz/downloads/sai
Wireshark: Are You Under Attack? Kyle Feuz School of Computing Introduction Download Wireshark and capture files https://www.wireshark.org/download.html http://icarus.cs.weber.edu/~kfeuz/downloads/sai
When does it work? Packet Sniffers. INFO Lecture 8. Content 24/03/2009
 Packet Sniffers INFO 404 - Lecture 8 24/03/2009 nfoukia@infoscience.otago.ac.nz Definition Sniffer Capabilities How does it work? When does it work? Preventing Sniffing Detection of Sniffing References
Packet Sniffers INFO 404 - Lecture 8 24/03/2009 nfoukia@infoscience.otago.ac.nz Definition Sniffer Capabilities How does it work? When does it work? Preventing Sniffing Detection of Sniffing References
GCIH. GIAC Certified Incident Handler.
 GIAC GCIH GIAC Certified Incident Handler TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/gcih.html Examskey GIAC GCIH exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This GIAC GCIH demo also
GIAC GCIH GIAC Certified Incident Handler TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/gcih.html Examskey GIAC GCIH exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This GIAC GCIH demo also
TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL. ETI 2506 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, 7 November 2016
 TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL ETI 2506 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, 7 November 2016 ETI 2506 - TELECOMMUNICATION SYLLABUS Principles of Telecom (IP Telephony and IP TV) - Key Issues to remember 1.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL ETI 2506 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, 7 November 2016 ETI 2506 - TELECOMMUNICATION SYLLABUS Principles of Telecom (IP Telephony and IP TV) - Key Issues to remember 1.
8/19/2010. Computer Forensics Network forensics. Data sources. Monitoring
 Computer Forensics Network forensics Thomas Mundt thm@informatik.uni-rostock.de Data sources Assessment Monitoring Monitoring Software Logs and Log Analysis Incident Analysis External Assessment Hackers
Computer Forensics Network forensics Thomas Mundt thm@informatik.uni-rostock.de Data sources Assessment Monitoring Monitoring Software Logs and Log Analysis Incident Analysis External Assessment Hackers
Hands-On Activity. Firewall Simulation. Simulated Network. Firewall Simulation 3/19/2010. On Friday, February 26, we will be meeting in
 Hands-On Activity Firewall Simulation COMP620 On Friday, February 26, we will be meeting in the Graham 212 lab to participate in a firewall configuration simulation. This simulator was written by Dr. Williams
Hands-On Activity Firewall Simulation COMP620 On Friday, February 26, we will be meeting in the Graham 212 lab to participate in a firewall configuration simulation. This simulator was written by Dr. Williams
Evaluating Website Security with Penetration Testing Methodology
 Evaluating Website Security with Penetration Testing Methodology D. Menoski, P. Mitrevski and T. Dimovski St. Clement of Ohrid University in Bitola/Faculty of Technical Sciences, Bitola, Republic of Macedonia
Evaluating Website Security with Penetration Testing Methodology D. Menoski, P. Mitrevski and T. Dimovski St. Clement of Ohrid University in Bitola/Faculty of Technical Sciences, Bitola, Republic of Macedonia
System Programming. Introduction to computer networks
 Content : by Dr. B. Boufama School of Computer Science University of Windsor Instructor: Dr. A. Habed adlane@cs.uwindsor.ca http://cs.uwindsor.ca/ adlane/60-256 Content Content 1 Introduction to Computer
Content : by Dr. B. Boufama School of Computer Science University of Windsor Instructor: Dr. A. Habed adlane@cs.uwindsor.ca http://cs.uwindsor.ca/ adlane/60-256 Content Content 1 Introduction to Computer
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Java and Socket Communication
 CS 351 Design of Large Programs Java and Socket Communication Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel@unm.edu 4/6/2017 Transmission Control Protocol The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Java and Socket Communication Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel@unm.edu 4/6/2017 Transmission Control Protocol The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of
Internet Applications II
 Internet Applications II รศ.ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม Asso. Prof. Anan Phonphoem, Ph.D. anan.p@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~anan Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand 1 Application
Internet Applications II รศ.ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม Asso. Prof. Anan Phonphoem, Ph.D. anan.p@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~anan Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand 1 Application
Networking and Health Information Exchange: ISO Open System Interconnection (OSI)
 Networking and Health Information Exchange: ISO Open System Interconnection (OSI) Lecture 4 Audio Transcript Slide 1 Welcome to Networking and Health Information Exchange, ISO Open System Interconnection
Networking and Health Information Exchange: ISO Open System Interconnection (OSI) Lecture 4 Audio Transcript Slide 1 Welcome to Networking and Health Information Exchange, ISO Open System Interconnection
SECURITY+ LAB SERIES. Lab 3: Protocols and Default Network Ports Connecting to a Remote System
 SECURITY+ LAB SERIES Lab 3: Protocols and Default Network Ports Connecting to a Remote System Document Version: 2015-09-24 otherwise noted, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported
SECURITY+ LAB SERIES Lab 3: Protocols and Default Network Ports Connecting to a Remote System Document Version: 2015-09-24 otherwise noted, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported
LECTURE WK4 NETWORKING
 LECTURE WK4 NETWORKING Workbook and Quiz Workbook o Due in WK5 o Must hand in a hard copy to the tutor as well as an online submission Quiz o In the practical class o 30mins to complete the quiz o Short,
LECTURE WK4 NETWORKING Workbook and Quiz Workbook o Due in WK5 o Must hand in a hard copy to the tutor as well as an online submission Quiz o In the practical class o 30mins to complete the quiz o Short,
General Terms Node - File Permissions - file permissions file
 CIS 375 General Terms Node - A networked computing device that takes a protocol address andcan initiate and respond to communication from other networked devices that employ similar protocols. File Permissions
CIS 375 General Terms Node - A networked computing device that takes a protocol address andcan initiate and respond to communication from other networked devices that employ similar protocols. File Permissions
OSI Model with Protocols. Layer Name PDU Address Protocols Device
 NetEss Name: Networking Essentials Prof. CHIN OSI Model with Protocols Layer Name PDU Address Protocols Device 7 Application Data FTP, SSH, Telnet, SMTP, DNS TFTP,HTTP, POP3, IMAP, HTTPS 6 Presentation
NetEss Name: Networking Essentials Prof. CHIN OSI Model with Protocols Layer Name PDU Address Protocols Device 7 Application Data FTP, SSH, Telnet, SMTP, DNS TFTP,HTTP, POP3, IMAP, HTTPS 6 Presentation
Penetration Testing and Fuzzing. John Slankas
 Penetration Testing and Fuzzing John Slankas jbslanka@ncsu.edu Course Slides adapted from OWASP Testing Guide v4 CSC 515 Software Security Penetration Testing aka Ethical Hacking Art of testing a running
Penetration Testing and Fuzzing John Slankas jbslanka@ncsu.edu Course Slides adapted from OWASP Testing Guide v4 CSC 515 Software Security Penetration Testing aka Ethical Hacking Art of testing a running
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 10: The Application Layer
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 10: The Application Layer Frank Schneemann 10.0.1.1 Introduction 10.0.1.2 Activity - Application Investigation 10.1.1.1 OSI and TCP/IP Models Revisited The application
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 10: The Application Layer Frank Schneemann 10.0.1.1 Introduction 10.0.1.2 Activity - Application Investigation 10.1.1.1 OSI and TCP/IP Models Revisited The application
CE Advanced Network Security Honeypots
 CE 817 - Advanced Network Security Honeypots Lecture 12 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially obtained
CE 817 - Advanced Network Security Honeypots Lecture 12 Mehdi Kharrazi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Acknowledgments: Some of the slides are fully or partially obtained
TCP/IP Attack Lab. 1 Lab Overview. 2 Lab Environment. 2.1 Environment Setup. SEED Labs TCP/IP Attack Lab 1
 SEED Labs TCP/IP Attack Lab 1 TCP/IP Attack Lab Copyright c 2006-2016 Wenliang Du, Syracuse University. The development of this document was partially funded by the National Science Foundation under Award
SEED Labs TCP/IP Attack Lab 1 TCP/IP Attack Lab Copyright c 2006-2016 Wenliang Du, Syracuse University. The development of this document was partially funded by the National Science Foundation under Award
Network Security. Kitisak Jirawannakool Electronics Government Agency (public organisation)
 1 Network Security Kitisak Jirawannakool Electronics Government Agency (public organisation) A Brief History of the World 2 OSI Model vs TCP/IP suite 3 TFTP & SMTP 4 ICMP 5 NAT/PAT 6 ARP/RARP 7 DHCP 8
1 Network Security Kitisak Jirawannakool Electronics Government Agency (public organisation) A Brief History of the World 2 OSI Model vs TCP/IP suite 3 TFTP & SMTP 4 ICMP 5 NAT/PAT 6 ARP/RARP 7 DHCP 8
HP Sygate Security Agent 4.0 User Guide
 HP Sygate Security Agent 4.0 User Guide Documentation Build 1004 Published: May 1, 2005 Copyright Information Copyright 2003-2005 by Sygate Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document
HP Sygate Security Agent 4.0 User Guide Documentation Build 1004 Published: May 1, 2005 Copyright Information Copyright 2003-2005 by Sygate Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document
