DDR Routing Commands
|
|
|
- Ellen West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DDR Routing Commands This section describes the function and displays the syntax of each dial-on-demand routing (DDR) command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding chapter of the Router Products Command Reference publication. [no] backup delay {enable-delay never} {disable-delay never} To define how much time should elapse before a secondary line status changes after a primary line status has changed, use the backup delay interface configuration command. To return to the default, which means as soon as the primary fails, the secondary is immediately brought up without delay, use the no backup delay command. enable-delay disable-delay never Number of seconds that elapse after the primary line goes down before the router activates the secondary line. The default is 0 seconds. Number of seconds that elapse after the primary line goes up before the router deactivates the secondary line. The default is 0 seconds. Prevents the secondary line from being activated or deactivated. [no] backup interface interface number To configure the serial interface as a secondary or dial backup line, use the backup interface interface configuration command. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command. interface number Type of interface. It must be serial. Serial port to be set as the secondary line. 118
2 [no] backup load {enable-threshold never} {disable-load never} To set traffic load threshold for dial backup service, use the backup load interface configuration command. To return to the default value, use the no form of this command. enable-threshold disable-load never Percentage of the primary line s available bandwidth. Percentage of the primary line s available bandwidth. Sets the secondary line to never be activated due to traffic load. [no] chat-script script-name expect-send Use the chat-script global configuration command to create a script that will place a call over a modem. Use the no form of the command to disable the specified chat script. script-name expect-send Name of the chat script. Content of the chat script. dialer enable-timeout seconds no dialer enable-timeout Use the dialer enable-timeout interface configuration command to set the length of time an interface stays down after a call has completed or failed before it is available to dial again. Use the no form of this command to reset the enable timeout value to the default. seconds Time in seconds that the router waits before the next call can occur on the specific interface. Acceptable values are positive, nonzero integers. The default is 15 seconds. 119
3 dialer fast-idle seconds no dialer fast-idle Use the dialer fast-idle interface configuration command to specify the amount of time that a line for which there is contention will stay idle before the line is disconnected and the competing call is placed. Use the no form of this command to return to the default value. seconds Idle time, in seconds, that must occur on an interface before the line is disconnected. Acceptable values are positive, nonzero integers. The default is 20 seconds. dialer-group group-number no dialer-group To control access, use the dialer-group interface configuration command. To remove an interface from the specified dialer access group, use the no form of this command. group-number Number of the dialer access group to which the specific interface belongs. This access group is defined using the dialer-list command. Acceptable values are nonzero, positive integers between 1 and 10. dialer idle-timeout seconds no dialer idle-timeout Use the dialer idle-timeout interface configuration command to specify the idle time before the line is disconnected. Use the no form of this command to reset the idle timeout to the default value. seconds Idle time, in seconds, that must occur on an interface before the line is disconnected. Acceptable values are positive, nonzero integers. The default is 120 seconds. DDR Routing Commands 120
4 dialer in-band [no-parity odd-parity] no dialer in-band Use the dialer in-band interface configuration command to specify that DDR is to be supported. Use the no form of this command to disable dial-on-demand routing for the interface. no-parity odd-parity (Optional) Indicates that no parity is to be applied to the dialer string that is sent out to the modem on synchronous interfaces. (Optional) Indicates that the dialed number has odd parity (7-bit ASCII characters with the eighth bit the parity bit) on synchronous interfaces. [no] dialer-list dialer-group list access-list-number Use the dialer-list list global configuration command to group access lists. Use the no form of this command to disable automatic dialing. dialer-group access-list-number Specifies the number of a dialer access group identified in any dialer-group interface configuration command. Specifies the access list number specified in any IP service access point or Novell IPX access lists, including Novell IPX extended Service Advertisement Protocol (SAP) access lists, and bridging type. See the supported access list types and numbers table in the Router Products Command Reference publication for the supported access list types and numbers. 121
5 [no] dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name {permit deny} Use the dialer-list protocol global configuration command to control automatic dialing by a protocol name. Use the no form of this command to disable automatic dialing. dialer-group protocol-name permit deny Number of a dialer access group identified in any dialer access group interface configuration command. One of the supported protocols as listed in the supported protocols for DDR access lists table in the Router Products Command Reference publication. (Optional) Permits access to an entire protocol. (Optional) Denies access to an entire protocol. dialer load-threshold load no dialer load-threshold To configure bandwidth on demand by setting the maximum load before the dialer places another call to a destination, use the dialer load-threshold interface configuration command. To disable the setting, use the no form of the command. load Interface load beyond which the dialer will initiate another call to the destination. This argument is a number between 1 and 255. DDR Routing Commands 122
6 [no] dialer map protocol next-hop-address [modem-script modem-regexp] [system-script system-regexp] dial-string [:isdn-subaddress] [no] dialer map protocol next-hop-address [modem-script modem-regexp] [system-script system-regexp] name hostname dial-string [:isdn-subaddress] Use the dialer map interface configuration command to configure a serial interface to call one or multiple sites. Use the first form of the dialer map command to place a call to a single site on an asynchronous line for which a modem script has not been assigned or a system script must be specified, or to multiple sites on a single line, multiple lines, or a dialer rotary group. Use the second form of the dialer map command to place a call to multiple sites and to authenticate calls from multiple sites. To delete a particular dialer map entry, use a no form of this command. protocol next-hop-address modem-script modem-regexp system-script system-regexp name hostname Name of the protocol. Protocol address used to match against addresses to which packets are destined. (Optional) Indicates the modem script to be used for the connection (for asynchronous interfaces). (Optional) Regular expression to which a modem script will be matched (for asynchronous interfaces). (Optional) Indicates the system script to be used for the connection (for asynchronous interfaces). (Optional) Regular expression to which a system script will be matched for asynchronous interfaces). (Optional) Indicates the remote system with which the local router communicates. (Optional) Name of the remote device (usually the host name). 123
7 dial-string :isdn-subaddress Telephone number sent to the dialing device when it sees packets with the specified next-hop-address that matches the access lists defined. (Optional) Subaddress number used for ISDN multipoint connections. [no] dialer map protocol next-hop-address name hostname Use the dialer map name interface configuration command to configure a dialer rotary group to receive and take advantage of caller identification using CHAP. Use the no form of this command to delete a particular dialer map entry. protocol next-hop-address hostname Name of the protocol. Protocol address used to match against addresses to which packets are destined. Name of the remote device (usually the host name). [no] dialer map protocol next-hop-address speed speed Use the dialer map speed interface configuration command to set the dialer speed. Use the no form of this command to return to the default speed. protocol next-hop-address speed Name of the protocol. Protocol address used to match against addresses to which packets are destined. Dialer speed. It can be either 56 (for 56 kbps) or 64 (for 64 kbps). The default is 64 kbps. DDR Routing Commands 124
8 dialer rotary-group number Use the dialer rotary-group interface configuration command to include an interface in a dialer rotary group. number Number of the dialer interface in whose rotary group you want this interface included. An integer that you select that indicates the dialer rotary group; defined by the interface dialer command. A number from 0 to 255. dialer string dial-string no dialer string Use the dialer string interface configuration command to specify the string (telephone number) to be called for interfaces calling a single site. Use the no form of this command to delete the dialer string specified for the interface. dial-string String of characters to be sent to a DCE. dialer wait-for-carrier-time seconds no dialer wait-for-carrier-time Use the dialer wait-for-carrier-time interface configuration command to specify how long to wait for a carrier. Use the no form of this command to reset the carrier wait time value to the default. seconds Number of seconds that the interface waits for the carrier to come up when a call is placed. Acceptable values are positive, nonzero integers. The default is 30 seconds. encapsulation ppp Use the encapsulation ppp interface configuration command to configure Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) encapsulation. 125
9 interface dialer number Use the interface dialer global configuration command to define a dialer rotary group. number Number of the dialer rotary group. It can be number in the range 0 through 255. modem chat-script regexp Use the modem chat-script line configuration command for asynchronous lines to set a regular expression for a script on a modem line. regexp Regular expression to be used to select a chat script. The chat script name will be matched to regexp. [no] ppp authentication chap Use the ppp authentication chap interface configuration command to enable Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) on a serial interface. Use the no form of this command to disable this feature. [no] ppp authentication pap To enable Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) on a serial interface, use the ppp authentication pap interface configuration command. To disable this encapsulation, use the no form of this command. show dialer [interface interface unit] Use the show dialer EXEC command to obtain a general diagnostic display for serial interfaces configured for DDR. interface interface unit (Optional) Information for the interface specified by the arguments interface and unit is to be displayed. (Optional) Interface and unit identifiers. DDR Routing Commands 126
10 username name password secret Use the username command to specify the password to be used in Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) caller identification and Password Authentication Protocol (PAP). name password secret Host name, server name, user ID, or command name. Possibly an encrypted password for this username. For CHAP authentication: specifies the secret for the local router or the remote device. The secret is encrypted when it is stored on the local router. This prevents the secret from being stolen. The secret can consist of any string of up to 11 printable ASCII characters. There is no limit to the number of username/password combinations that can be specified, allowing any number of remote devices to be authenticated. 127
Number of seconds that elapse after the primary line goes down before the router activates the secondary line. The default is 0 seconds.
 This chapter describes the function and displays the syntax of each dialon-demand routing command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding chapter of the Router
This chapter describes the function and displays the syntax of each dialon-demand routing command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding chapter of the Router
Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing This chapter describes how to configure your communication server for dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. For a complete description of the
C H A P T E R 7 Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing This chapter describes how to configure your communication server for dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. For a complete description of the
Configuring Legacy DDR Hubs
 Configuring Legacy DDR Hubs This chapter describes how to configure legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) on interfaces functioning as the hub in a hub-and-spoke network topology. It includes the following
Configuring Legacy DDR Hubs This chapter describes how to configure legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) on interfaces functioning as the hub in a hub-and-spoke network topology. It includes the following
Configuring PPP Callback
 Configuring PPP Callback This chapter describes how to configure PPP callback for dial-on-demand routing (DDR). It includes the following main sections: PPP Callback for DDR Overview How to Configure PPP
Configuring PPP Callback This chapter describes how to configure PPP callback for dial-on-demand routing (DDR). It includes the following main sections: PPP Callback for DDR Overview How to Configure PPP
Configuring X.25 on ISDN Using AO/DI
 Configuring X.25 on ISDN Using AO/DI The chapter describes how to configure the X.25 on ISDN using the Always On/Dynamic ISDN (AO/DI) feature. It includes the following main sections: AO/DI Overview How
Configuring X.25 on ISDN Using AO/DI The chapter describes how to configure the X.25 on ISDN using the Always On/Dynamic ISDN (AO/DI) feature. It includes the following main sections: AO/DI Overview How
Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites
 Case Study 1 Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: Asynchronous
Case Study 1 Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: Asynchronous
Evaluating Backup Interfaces, Floating Static Routes, and Dialer Watch for DDR Backup
 Evaluating Backup Interfaces, Floating Static Routes, and Dialer Watch for DDR Backup Document ID: 10213 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configurations Backup
Evaluating Backup Interfaces, Floating Static Routes, and Dialer Watch for DDR Backup Document ID: 10213 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configurations Backup
Using ISDN Effectively
 CHAPTER 21 Using ISDN Effectively in Multiprotocol Networks As telephone companies make Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) services available, ISDN is becoming an increasingly popular way of connecting
CHAPTER 21 Using ISDN Effectively in Multiprotocol Networks As telephone companies make Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) services available, ISDN is becoming an increasingly popular way of connecting
Completing an ISDN BRI Call. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13-1
 Completing an ISDN BRI Call 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks:? Describe the components that make up ISDN connectivity?
Completing an ISDN BRI Call 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks:? Describe the components that make up ISDN connectivity?
ROUTER COMMANDS. BANNER: Config# banner motd # TYPE MESSAGE HERE # - # can be substituted for any character, must start and finish the message
 ROUTER COMMANDS TERMINAL CONTROLS: Config# terminal editing - allows for enhanced editing commands Config# terminal monitor - shows output on telnet session Config# terminal ip netmask-format hexadecimal
ROUTER COMMANDS TERMINAL CONTROLS: Config# terminal editing - allows for enhanced editing commands Config# terminal monitor - shows output on telnet session Config# terminal ip netmask-format hexadecimal
Service Managed Gateway TM. Configuring a V90 Modem on an SMG
 Service Managed Gateway TM Configuring a V90 Modem on an SMG Issue 2.1 Date 18 August 2010 Table of contents 1 About this document... 3 1.1 Scope... 3 1.2 Readership... 3 1.3 More information... 3 1.3.1
Service Managed Gateway TM Configuring a V90 Modem on an SMG Issue 2.1 Date 18 August 2010 Table of contents 1 About this document... 3 1.1 Scope... 3 1.2 Readership... 3 1.3 More information... 3 1.3.1
PPPoE Client DDR Idle-Timer
 The feature supports the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client, but also keeps original functionality
The feature supports the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client, but also keeps original functionality
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts
 Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles
 Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles Document ID: 10219 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Are Dialer Profiles Right for You?
Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles Document ID: 10219 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Are Dialer Profiles Right for You?
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 350-025
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 350-025
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms
 1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms Feature History Release 12.2(2)XB Description This feature was introduced. The 1- and 2-port V.90 modem WAN interface
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms Feature History Release 12.2(2)XB Description This feature was introduced. The 1- and 2-port V.90 modem WAN interface
Configuring BACP. Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Configuration Guide DC-667
 This chapter describes how to configure the Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol (BACP), described in RFC 2125. It includes the following main sections: BACP Overview How to Configure BACP Monitoring
This chapter describes how to configure the Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol (BACP), described in RFC 2125. It includes the following main sections: BACP Overview How to Configure BACP Monitoring
Terminal Services Commands translate lat
 translate lat translate lat To translate a connection request to another protocol connection type when receiving a local-area transport (LAT) request, use the translate lat command in global configuration
translate lat translate lat To translate a connection request to another protocol connection type when receiving a local-area transport (LAT) request, use the translate lat command in global configuration
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode
 How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
Exam : Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial. Version : DEMO
 Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Version : DEMO 1. What command is used to set the length of time a non-isdn interface stays down after a call has been completed or has failed and before
Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Version : DEMO 1. What command is used to set the length of time a non-isdn interface stays down after a call has been completed or has failed and before
HP VSR1000 Virtual Services Router
 HP VSR1000 Virtual Services Router Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-6023 Software version: VSR1000_HP-CMW710-R0202-X64 Document version: 6W100-20140418 Legal and notice information
HP VSR1000 Virtual Services Router Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-6023 Software version: VSR1000_HP-CMW710-R0202-X64 Document version: 6W100-20140418 Legal and notice information
PPP Configuration Options
 PPP Configuration Options 1 PPP Configuration Options PPP can be configured to support various functions including: Authentication using either PAP or CHAP Compression using either Stacker or Predictor
PPP Configuration Options 1 PPP Configuration Options PPP can be configured to support various functions including: Authentication using either PAP or CHAP Compression using either Stacker or Predictor
Cisco 2- and 4-Port ISDN BRI S/T Network Interface Modules
 Data Sheet Cisco 2- and 4-Port ISDN BRI S/T Network Interface Modules Integrated Services Routers 2- and 4-Port ISDN BRI S/T Network Interface Modules Data Sheet Product overview The Cisco 4000 Series
Data Sheet Cisco 2- and 4-Port ISDN BRI S/T Network Interface Modules Integrated Services Routers 2- and 4-Port ISDN BRI S/T Network Interface Modules Data Sheet Product overview The Cisco 4000 Series
Table of Contents 1 PPP Configuration Commands PPPoE Configuration Commands 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1-1 link-protocol ppp 1-2 mtu 1-2 ppp account-statistics enable 1-3 ppp authentication-mode 1-3
Table of Contents 1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 PPP Configuration Commands 1-1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1-1 link-protocol ppp 1-2 mtu 1-2 ppp account-statistics enable 1-3 ppp authentication-mode 1-3
Configuring a GSM (3G) modem on a GW2040 Series Router
 Configuring a GSM (3G) modem on a GW2040 Series Router Issue 1.5 Date 10 May 2012 Table of contents 1 About this document... 3 1.1 Scope... 3 1.2 Readership... 3 1.3 More information... 3 1.3.1 Assigned
Configuring a GSM (3G) modem on a GW2040 Series Router Issue 1.5 Date 10 May 2012 Table of contents 1 About this document... 3 1.1 Scope... 3 1.2 Readership... 3 1.3 More information... 3 1.3.1 Assigned
Passwords and Privileges Commands
 Passwords and Privileges Commands This chapter describes the commands used to establish password protection and configure privilege levels. Password protection lets you restrict access to a network or
Passwords and Privileges Commands This chapter describes the commands used to establish password protection and configure privilege levels. Password protection lets you restrict access to a network or
Configuring TACACS. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Configuring TACACS
 TACACS+ is a security application that provides centralized validation of users attempting to gain access to a router or network access server. TACACS+ provides detailed accounting information and flexible
TACACS+ is a security application that provides centralized validation of users attempting to gain access to a router or network access server. TACACS+ provides detailed accounting information and flexible
Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6
 Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6, page 1 Information
Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6, page 1 Information
Lab Configuring PPP Callback
 Lab 3.7.3 Configuring PPP Callback Objective In this lab, the student will configure a Cisco router for PPP callback over an asynchronous connection. Scenario Step 1 The International Travel Agency has
Lab 3.7.3 Configuring PPP Callback Objective In this lab, the student will configure a Cisco router for PPP callback over an asynchronous connection. Scenario Step 1 The International Travel Agency has
Cisco - Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable
 1 of 5 6/12/2001 1:43 PM Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable Contents Introduction Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshooting the Configuration
1 of 5 6/12/2001 1:43 PM Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable Contents Introduction Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshooting the Configuration
PPP configuration commands
 Contents PPP configuration commands 1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1 ip pool 1 link-protocol ppp 2 ppp authentication-mode 2 ppp chap password 4 ppp chap user 5 ppp ipcp remote-address forced 5 ppp pap local-user
Contents PPP configuration commands 1 ip address ppp-negotiate 1 ip pool 1 link-protocol ppp 2 ppp authentication-mode 2 ppp chap password 4 ppp chap user 5 ppp ipcp remote-address forced 5 ppp pap local-user
WHITE PAPERS from the files of Networking Unlimited, Inc. Using Dial-on-Demand Routing to Trigger Backup Links on Cisco Routers
 WHITE PAPERS from the files of Networking Unlimited, Inc. WebQuery@NetworkingUnlimited.com 14 Dogwood Lane, Tenafly, NJ 07670 Phone: +1 201 568-7810 FAX: +1 201 568-7269 Using Dial-on-Demand Routing to
WHITE PAPERS from the files of Networking Unlimited, Inc. WebQuery@NetworkingUnlimited.com 14 Dogwood Lane, Tenafly, NJ 07670 Phone: +1 201 568-7810 FAX: +1 201 568-7269 Using Dial-on-Demand Routing to
Vendor-Proprietary Attribute
 RADIUS s The IETF draft standard for RADIUS specifies a method for communicating vendor-proprietary information between the network access server and the RADIUS server. However, some vendors have extended
RADIUS s The IETF draft standard for RADIUS specifies a method for communicating vendor-proprietary information between the network access server and the RADIUS server. However, some vendors have extended
Connections, addressing and common configuration rules.
 Lab #1 r9-1 s2 e1 3/11 VLAN_21 BGP AS 100 s1 3/1 e0 s0 e0 3/2 s1 VLAN_22 BGP AS 200 r1 r2 Ring 4 r4 s0/1 r3 to0/0 s0/0 s0 s1 OSPF Area 33 to0 e0/0 e0 OSPF Area 4 3/4 b0/0 3/3 VLAN_14 VLAN_13 403 304 c15
Lab #1 r9-1 s2 e1 3/11 VLAN_21 BGP AS 100 s1 3/1 e0 s0 e0 3/2 s1 VLAN_22 BGP AS 200 r1 r2 Ring 4 r4 s0/1 r3 to0/0 s0/0 s0 s1 OSPF Area 33 to0 e0/0 e0 OSPF Area 4 3/4 b0/0 3/3 VLAN_14 VLAN_13 403 304 c15
BRI commonly used as a backup connection. Can support any Layer 3 protocol. Connections. Wide-Area Network Technologies
 804 BCRAN Quick Reference Sheets BCRAN Quick Reference Sheets Wide-Area Network Technologies WAN Technologies Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Cell relay technology One physical interface can support many
804 BCRAN Quick Reference Sheets BCRAN Quick Reference Sheets Wide-Area Network Technologies WAN Technologies Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Cell relay technology One physical interface can support many
Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
 CHAPTER 4 The Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-POTS and Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-ISDN routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address
CHAPTER 4 The Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-POTS and Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-ISDN routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address
Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN
 Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN Cisco IOS software offers two solutions to send virtual asynchronous traffic over ISDN: Using International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication
Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN Cisco IOS software offers two solutions to send virtual asynchronous traffic over ISDN: Using International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication
Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
 CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
PPPoE Client DDR Idle Timer
 The feature supports the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client, but also keeps original functionality
The feature supports the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client, but also keeps original functionality
Configuring Snapshot Routing
 Configuring Snapshot Routing This chapter describes how to configure snapshot routing. It includes the following main sections: Snapshot Routing Overview How to Configure Snapshot Routing Monitoring and
Configuring Snapshot Routing This chapter describes how to configure snapshot routing. It includes the following main sections: Snapshot Routing Overview How to Configure Snapshot Routing Monitoring and
aaa max-sessions maximum-number-of-sessions The default value for aaa max-sessions command is platform dependent. Release 15.0(1)M.
 aaa max-sessions aaa max-sessions To set the maximum number of simultaneous authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) connections permitted for a user, use the aaa max-sessions command in global
aaa max-sessions aaa max-sessions To set the maximum number of simultaneous authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) connections permitted for a user, use the aaa max-sessions command in global
Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server
 Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server Document ID: 10384 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Network Diagram General AAA Configuration Enabling AAA Specifying
Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server Document ID: 10384 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Network Diagram General AAA Configuration Enabling AAA Specifying
RADIUS Vendor-Specific Attributes and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Attribute Values
 RADIUS s and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Values The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft standard specifies a method for communicating vendor-specific information between the network access server
RADIUS s and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Values The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft standard specifies a method for communicating vendor-specific information between the network access server
Dial Solutions C H A P T E R
 C H A P T E R 3 Dial Solutions This chapter shows you how to configure and use the following network security features: 3-1: Modems Cisco routers and access servers can use internal or external modems
C H A P T E R 3 Dial Solutions This chapter shows you how to configure and use the following network security features: 3-1: Modems Cisco routers and access servers can use internal or external modems
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP
 Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
CCNA 4 - Final Exam Answers
 CCNA 4 - Final Exam Answers 1 Which of the following describes the roles of devices in a WAN? (Choose three.) *** A CSU/DSU terminates a digital local loop. A modem terminates a digital local loop. A CSU/DSU
CCNA 4 - Final Exam Answers 1 Which of the following describes the roles of devices in a WAN? (Choose three.) *** A CSU/DSU terminates a digital local loop. A modem terminates a digital local loop. A CSU/DSU
RADIUS Vendor-Specific Attributes (VSA) and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Attribute Values
 RADIUS Vendor-Specific Attributes (VSA) and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Attribute Values First Published: September 23, 2005 Last Updated: August 18, 2010 The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft standard
RADIUS Vendor-Specific Attributes (VSA) and RADIUS Disconnect-Cause Attribute Values First Published: September 23, 2005 Last Updated: August 18, 2010 The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft standard
We have looked at how and why one router dials another using ISDN. Just as important is knowing what keeps the link up once it is dialed.
 ISDN Technologies From the CCNA to the CCIE, ISDN is one of the most important technologies you'll work with. It's also very common in the field; ISDN is frequently used as a backup connection in case
ISDN Technologies From the CCNA to the CCIE, ISDN is one of the most important technologies you'll work with. It's also very common in the field; ISDN is frequently used as a backup connection in case
Configuring Authorization
 Configuring Authorization AAA authorization enables you to limit the services available to a user. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user
Configuring Authorization AAA authorization enables you to limit the services available to a user. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user
HP MSR Router Series. Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide(V7)
 HP MSR Router Series Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: 5998-6465 Software version: CMW710-R0106 Document version: 6PW101-20140807 Legal and notice information Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard
HP MSR Router Series Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: 5998-6465 Software version: CMW710-R0106 Document version: 6PW101-20140807 Legal and notice information Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard
CiscoWorks Windows Features 2-1
 CHAPTER 2 CiscoWorks Windows Features CiscoWorks Windows is a suite of integrated PC-based network configuration and diagnostic tools for small to medium-sized networks or remote workgroups. This chapter
CHAPTER 2 CiscoWorks Windows Features CiscoWorks Windows is a suite of integrated PC-based network configuration and diagnostic tools for small to medium-sized networks or remote workgroups. This chapter
Access Service Security
 CHAPTER 4 Access Service Security The access service security paradigm presented in this guide uses the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) facility: Authentication requires dial-in users
CHAPTER 4 Access Service Security The access service security paradigm presented in this guide uses the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) facility: Authentication requires dial-in users
POINT TO POINT DATALINK PROTOCOLS. ETI 2506 Telecommunication Systems Monday, 7 November 2016
 POINT TO POINT DATALINK PROTOCOLS ETI 2506 Telecommunication Systems Monday, 7 November 2016 TELECOMMUNICATION SYLLABUS Principles of Telecom (IP Telephony and IP TV) - Key Issues to remember PPP Frame
POINT TO POINT DATALINK PROTOCOLS ETI 2506 Telecommunication Systems Monday, 7 November 2016 TELECOMMUNICATION SYLLABUS Principles of Telecom (IP Telephony and IP TV) - Key Issues to remember PPP Frame
User Guide IP Connect CSD
 The contents of this document are subject to revision without notice due to continued progress in methodology, design and manufacturing. Wireless Maingate AB shall have no liability for any error or damages
The contents of this document are subject to revision without notice due to continued progress in methodology, design and manufacturing. Wireless Maingate AB shall have no liability for any error or damages
Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
 This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 819, Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco
This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 819, Cisco 860, Cisco 880, and Cisco
Configuring Link Fragmentation and Interleaving for Multilink PPP
 Configuring Link Fragmentation and Interleaving for Multilink PPP The Cisco IOS Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) feature uses Multilink PPP (MLP). MLP provides a method of splitting, recombining,
Configuring Link Fragmentation and Interleaving for Multilink PPP The Cisco IOS Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) feature uses Multilink PPP (MLP). MLP provides a method of splitting, recombining,
RADIUS Vendor-Proprietary Attributes
 RADIUS Vendor-Proprietary Attributes Last Updated: January 17, 2012 The IETF draft standard for RADIUS specifies a method for communicating vendor-proprietary information between the network access server
RADIUS Vendor-Proprietary Attributes Last Updated: January 17, 2012 The IETF draft standard for RADIUS specifies a method for communicating vendor-proprietary information between the network access server
Configuring the CSS as a Client of a TACACS+ Server
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring the CSS as a Client of a TACACS+ Server The Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS+) protocol provides access control for routers, network access servers (NAS),
CHAPTER 4 Configuring the CSS as a Client of a TACACS+ Server The Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS+) protocol provides access control for routers, network access servers (NAS),
Using an ADTRAN Terminal Adapter with Cisco Routers
 Using an ADTRAN Terminal Adapter with Cisco Routers Document ID: 28080 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dialing Method V.25 or V.25bis Dialing DTR Dialing Keypad
Using an ADTRAN Terminal Adapter with Cisco Routers Document ID: 28080 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dialing Method V.25 or V.25bis Dialing DTR Dialing Keypad
PT Activity 5.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Connections, addressing and common configuration rules.
 Lab #2 r9-1 r7 Lab 2 BGP AS 100 VLAN_21 r5 e1 3/11 fa0/0.25 fa0/0.15 3/6 2/1 2/1 VLAN_25 VLAN_15 IGRP AS 5 OSPF Area 5 BGP AS 65005 ISDN 3/1 504 Frame-Relay OSPF Area 0 VLAN_22 604 EIGRP AS 6 r9-0 OSPF
Lab #2 r9-1 r7 Lab 2 BGP AS 100 VLAN_21 r5 e1 3/11 fa0/0.25 fa0/0.15 3/6 2/1 2/1 VLAN_25 VLAN_15 IGRP AS 5 OSPF Area 5 BGP AS 65005 ISDN 3/1 504 Frame-Relay OSPF Area 0 VLAN_22 604 EIGRP AS 6 r9-0 OSPF
SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands
 CHAPTER 15 SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands SLIP and PPP define methods of sending Internet Protocol (IP) packets over standard EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial lines with minimum line speeds of 1200
CHAPTER 15 SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands SLIP and PPP define methods of sending Internet Protocol (IP) packets over standard EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial lines with minimum line speeds of 1200
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
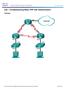 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
HP MSR Router Series. Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide(V7)
 HP MSR Router Series Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: 5998-7721b Software version: CMW710-R0304 Document version: 6PW104-20150914 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
HP MSR Router Series Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: 5998-7721b Software version: CMW710-R0304 Document version: 6PW104-20150914 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
HPE FlexNetwork MSR Router Series
 HPE FlexNetwork MSR Router Series Comware 7 Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guides Part number: 5998-8783 Software version: CMW710-E0407 Document version: 6W100-20160526 Copyright 2016 Hewlett Packard
HPE FlexNetwork MSR Router Series Comware 7 Layer 2 - WAN Access Configuration Guides Part number: 5998-8783 Software version: CMW710-E0407 Document version: 6W100-20160526 Copyright 2016 Hewlett Packard
RADIUS Commands. Cisco IOS Security Command Reference SR
 RADIUS Commands This chapter describes the commands used to configure RADIUS. RADIUS is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation,
RADIUS Commands This chapter describes the commands used to configure RADIUS. RADIUS is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation,
Universal Port Resource Pooling for Voice and Data Services
 Universal Port Resource Pooling for Voice and Data Services Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB1 12.2(11)T Description This feature was introduced on the Cisco AS5350 and AS5400. This feature was
Universal Port Resource Pooling for Voice and Data Services Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB1 12.2(11)T Description This feature was introduced on the Cisco AS5350 and AS5400. This feature was
Autosense for ATM PVCs and MUX SNAP Encapsulation
 Autosense for ATM PVCs and MUX SNAP Encapsulation The PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATM PVCs feature enables a router to distinguish between incoming PPP over ATM (PPPoA) and PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) over
Autosense for ATM PVCs and MUX SNAP Encapsulation The PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATM PVCs feature enables a router to distinguish between incoming PPP over ATM (PPPoA) and PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) over
Lab Configuring ISDN PRI
 Lab 4.9.4 Configuring ISDN PRI Objective In this lab, the student will configure ISDN BRI on the remote site routers and ISDN PRI on the central site router. Scenario Step 1 The International Travel Agency
Lab 4.9.4 Configuring ISDN PRI Objective In this lab, the student will configure ISDN BRI on the remote site routers and ISDN PRI on the central site router. Scenario Step 1 The International Travel Agency
H3C MSR Series Routers
 H3C MSR Series Routers Layer 2 - WAN Command Reference(V7) Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Software version: MSR-CMW710-R0007 Document version: 6W100-20140320 Copyright 2014, Hangzhou
H3C MSR Series Routers Layer 2 - WAN Command Reference(V7) Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com Software version: MSR-CMW710-R0007 Document version: 6W100-20140320 Copyright 2014, Hangzhou
IP Routing: ODR Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15M&T
 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION
Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION
Basic Configuration D. Contents
 451-0084D Contents Overview...5 IP/PPP Protocols...7 IP/PPP (IPCP) Features...7 IPX /IPXCP Protocols...10 CCL Scripts... 27 Protocols and Features... 28 Automatic Protocol Detection (APD)... 30 APD Notes...30
451-0084D Contents Overview...5 IP/PPP Protocols...7 IP/PPP (IPCP) Features...7 IPX /IPXCP Protocols...10 CCL Scripts... 27 Protocols and Features... 28 Automatic Protocol Detection (APD)... 30 APD Notes...30
Operation Manual Security. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 802.1x Configuration... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 802.1x Standard Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 802.1x System Architecture... 1-1 1.1.3 802.1x Authentication
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 802.1x Configuration... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 802.1x Standard Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 802.1x System Architecture... 1-1 1.1.3 802.1x Authentication
Configuring RADIUS. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for RADIUS
 The RADIUS security system is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS clients run on Cisco devices and send authentication
The RADIUS security system is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS clients run on Cisco devices and send authentication
RADIUS Configuration. Overview. Introduction to RADIUS. Client/Server Model
 Table of Contents RADIUS Configuration 1 Overview 1 Introduction to RADIUS 1 Client/Server Model 1 Security and Authentication Mechanisms 2 Basic Message Exchange Process of RADIUS 2 RADIUS Packet Format
Table of Contents RADIUS Configuration 1 Overview 1 Introduction to RADIUS 1 Client/Server Model 1 Security and Authentication Mechanisms 2 Basic Message Exchange Process of RADIUS 2 RADIUS Packet Format
Tactical Software requires that Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(9) or later be installed on the NAS to interoperate with DialOut/EZ.
 Products & Services Using Dialout/EZ with a Cisco Access Server Document ID: 23241 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Installation and Configuration Installing
Products & Services Using Dialout/EZ with a Cisco Access Server Document ID: 23241 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Installation and Configuration Installing
Table of Contents X Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-2 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-3 EAP over LAN 1-4 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-2 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-3 EAP over LAN 1-4 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
Configuration File Management Commands
 This chapter provides detailed descriptions of commands used to manage configuration files in Cisco IOS Release 12.2. Configuration files contain the set of commands used to customize the function of the
This chapter provides detailed descriptions of commands used to manage configuration files in Cisco IOS Release 12.2. Configuration files contain the set of commands used to customize the function of the
PPP. Point-to-Point Protocol
 PPP Point-to-Point Protocol 1 Introduction One of the most common types of WAN connection is the point-to-point connection. Point-to-point connections are used to connect LANs to service provider WANs,
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol 1 Introduction One of the most common types of WAN connection is the point-to-point connection. Point-to-point connections are used to connect LANs to service provider WANs,
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Enchilada Solutions
 Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Copyright Statement. Trademarks. Limited Warranty. Copyright 1997 D-Link Corporation
 Copyright Statement Trademarks Limited Warranty Copyright 1997 D-Link Corporation No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative such as translation,
Copyright Statement Trademarks Limited Warranty Copyright 1997 D-Link Corporation No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative such as translation,
Using the Command Line Interface
 CHAPTER 2 Using the Command Line Interface 2.1 Commonly Used Commands This section documents the Cisco Broadband Operating System (CBOS) commands and command arguments that manage the Cisco 67x. CBOS runs
CHAPTER 2 Using the Command Line Interface 2.1 Commonly Used Commands This section documents the Cisco Broadband Operating System (CBOS) commands and command arguments that manage the Cisco 67x. CBOS runs
A device that bridges the wireless link on one side to the wired network on the other.
 GLOSSARY A Access point Analog Channel ARP ATM ATO A device that bridges the wireless link on one side to the wired network on the other. A circuit-switched communication path intended to carry 3.1 KHz
GLOSSARY A Access point Analog Channel ARP ATM ATO A device that bridges the wireless link on one side to the wired network on the other. A circuit-switched communication path intended to carry 3.1 KHz
Configuring the PPPoE Client
 CHAPTER 72 This section describes how to configure the PPPoE client provided with the ASA. It includes the following topics: PPPoE Client Overview, page 72-1 Username and Password, page 72-2 Enabling PPPoE,
CHAPTER 72 This section describes how to configure the PPPoE client provided with the ASA. It includes the following topics: PPPoE Client Overview, page 72-1 Username and Password, page 72-2 Enabling PPPoE,
Table of Contents X Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-1 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-2 EAP over LAN 1-3 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
Table of Contents 1 802.1X Configuration 1-1 802.1X Overview 1-1 Architecture of 802.1X 1-1 Authentication Modes of 802.1X 1-2 Basic Concepts of 802.1X 1-2 EAP over LAN 1-3 EAP over RADIUS 1-5 802.1X Authentication
Operation Manual 802.1x. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Architecture of 802.1x... 1-1 1.1.2 Operation of 802.1x... 1-3 1.1.3 EAP Encapsulation over LANs... 1-4 1.1.4 EAP Encapsulation
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 802.1x Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Architecture of 802.1x... 1-1 1.1.2 Operation of 802.1x... 1-3 1.1.3 EAP Encapsulation over LANs... 1-4 1.1.4 EAP Encapsulation
This document is a tutorial related to the Router Emulator which is available at:
 Introduction This document is a tutorial related to the Router Emulator which is available at: http://www.dcs.napier.ac.uk/~bill/router.html A demo is also available at: http://www.dcs.napier.ac.uk/~bill/router_demo.htm
Introduction This document is a tutorial related to the Router Emulator which is available at: http://www.dcs.napier.ac.uk/~bill/router.html A demo is also available at: http://www.dcs.napier.ac.uk/~bill/router_demo.htm
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
 CHAPTER 19 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Virtual private network is defined as customer connectivity deployed on a shared infrastructure with the same policies as a private network. The shared infrastructure
CHAPTER 19 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Virtual private network is defined as customer connectivity deployed on a shared infrastructure with the same policies as a private network. The shared infrastructure
Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
 This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 860 and Cisco 880
This chapter provides an overview of Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address translation (NAT) that can be configured on the Cisco 860 and Cisco 880
Configuring Accounting
 The AAA Accounting feature allows the services that users are accessing and the amount of network resources that users are consuming to be tracked. When AAA Accounting is enabled, the network access server
The AAA Accounting feature allows the services that users are accessing and the amount of network resources that users are consuming to be tracked. When AAA Accounting is enabled, the network access server
Configuring Virtual Profiles
 Configuring Virtual Profiles This chapter describes how to configure virtual profiles for use with virtual access interfaces. It includes the following main sections: Virtual Profiles Overview How Virtual
Configuring Virtual Profiles This chapter describes how to configure virtual profiles for use with virtual access interfaces. It includes the following main sections: Virtual Profiles Overview How Virtual
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (A)
 CCNA 4 - Final Exam (A) 1. A network administrator is asked to design a system to allow simultaneous access to the Internet for 250 users. The ISP for this network can only supply five public IPs. What
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (A) 1. A network administrator is asked to design a system to allow simultaneous access to the Internet for 250 users. The ISP for this network can only supply five public IPs. What
Configuring DNS Sticky
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to configure a GSS to support Domain Name System (DNS) stickiness to answer requests received from client D-proxies. The GSS supports DNS sticky both locally and globally
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to configure a GSS to support Domain Name System (DNS) stickiness to answer requests received from client D-proxies. The GSS supports DNS sticky both locally and globally
Configuring Accounting
 The AAA Accounting feature allows the services that users are accessing and the amount of network resources that users are consuming to be tracked. When AAA Accounting is enabled, the network access server
The AAA Accounting feature allows the services that users are accessing and the amount of network resources that users are consuming to be tracked. When AAA Accounting is enabled, the network access server
Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists)
 Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists) Feature History Release Modification Cisco IOS For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This chapter
Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists) Feature History Release Modification Cisco IOS For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This chapter
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Chapter 8. User Authentication
 Chapter 8. User Authentication This chapter describes how NetDefendOS implements user authentication. Overview, page 220 Authentication Setup, page 221 8.1. Overview In situations where individual users
Chapter 8. User Authentication This chapter describes how NetDefendOS implements user authentication. Overview, page 220 Authentication Setup, page 221 8.1. Overview In situations where individual users
PPP over Frame Relay
 The feature allows a router to establish end-to-end Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) sessions over Frame Relay. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information
The feature allows a router to establish end-to-end Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) sessions over Frame Relay. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information
Introduction Overview of L2TP Support for L2TP Configuration Examples Simple Dial-In System...
 Chapter 27 Layer Two Tun unnelli lling Protocol (L2TP) Introduction... 27-2 Overview of L2TP... 27-2 Support for L2TP... 27-3 Configuration... 27-6 Simple Dial-In System... 27-6 Two-Way Communications
Chapter 27 Layer Two Tun unnelli lling Protocol (L2TP) Introduction... 27-2 Overview of L2TP... 27-2 Support for L2TP... 27-3 Configuration... 27-6 Simple Dial-In System... 27-6 Two-Way Communications
