Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
|
|
|
- Willis Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting
2 Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2
3 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked at Layer 2 connectivity To troubleshoot Layer 3 connectivity, you need to have a good understanding of the processes that are involved in routing a packet from a host through multiple routers to the final destination. Lack of network layer connectivity indicates that the problem is at or below network layer. 3
4 Which decisions does Host A make to successfully send a packet destined for Host B to the first hop Router C? What information does it need? Addressing; ARP Cache Which actions does it perform? DHCP Request; Host or GW Address; DNS Query; ARP Request; Layer 2 encapsulation Which decisions does Router C make to successfully send the packet from Host A destined for Host B to the next hop Router D? TTL ICMP Time Exceeded; ; CEF or layer 3; Longest prefix match; Layer 2 Next-hop address; layer 2 encapsulation; Fragmentation Which decisions does Router D make to successfully send the packet from Host A destined for Host B to the next hop Router E? (Same questions) Which decisions does Router E make to successfully send the packet from Host A destined for Host B to its final destination, Host B? (Same questions) Are there any differences in the processes and information required in order to successfully transmit return packets from Host B back to Host A? 4
5 To forward packets, a router combines information from various control plane data structures. The most important of these data structures is the routing table. Other structures include: LSDB or topology table Neighbor table ARP or Frame Relay Map table Unlike switches, which flood unknown frames, routers drop any packet for which they cannot find a matching entry in the routing table. Searches for longest possible prefix match of the destination IP address. Associated with this entry is an egress interface - most cases, a next-hop IP address. 5
6 Troubleshooting EIGRP 6
7 At a high level, each routing protocol consists of the following elements and processes: (RIP is a notable exception to some of these.) Reception of routing information from neighbors: Neighbor relationships Routing protocol data structures: Neighbor table, topology table Route injection or redistribution: Directly connected, dynamic routes, static routes Route selection and installation: Best path, equal cost load balancing, unequal cost load balancing Transmission of routing information to neighbors: Summarization, Broadcast, Multicast, LSAs, Route updates, ACKs 7
8 To diagnose and resolve problems related to EIGRP you must be able to: Apply your knowledge of EIGRP data structures Neighbor table, Topology Table Apply your knowledge of EIGRP processes DUAL, adjacency process, summarization, load balancing Use Cisco IOS commands to gather information from the EIGRP data structures and track the flow of EIGRP routing information Note: As we will see these procedures can be applied to other routing protocols as well. 8
9 R3# show ip eigrp interfaces IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1 Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes Se0/1 1 0/0 60 0/ Se0/0 1 0/ / Se0/2 1 0/0 29 0/ Se0/3 1 0/0 24 0/ R3# EIGRP stores its operational data, configured parameters, and statistics in three main data structures: Interface table: Lists all interfaces that have been enabled for the processing of EIGRP packets Passive interfaces are not listed in this table. 9
10 R3# show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq Type (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Se0/ :17: Se0/ :17: Se0/ :23: Se0/ :24: R3# Neighbor table: Keeps track of all active EIGRP neighbors. Neighbors are added to this table on the reception of hello packets Neighbors are removed when: Hold-time expires Interface goes down or is removed from the interface table 10
11 R3# show ip eigrp topology <output omitted> P /30, 2 successors, FD is via ( / ), Serial0/1 via ( / ), Serial0/0 <output omitted> Feasible distance P /16, 1 successors, FD is via ( /28160), Serial0/2 via ( /28160), Serial0/3 FS if Reported Distance is less than Feasible distance successor feasible successor Topology table: Feasible distance: if this router was the successor. Holds all the routes that were received from neighboring routers, locally injected, or redistributed into EIGRP. EIGRP will select the best path from among the available possible paths EIGRP s best path selection is based on the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL). 11
12 Initial Route Discovery Updated A B Updated EIGRP Neighbor Table Hello, I am Router A. Is anyone there? Hello, I am Router B. EIGRP Neighbor Table Updated EIGRP Topology Table Successor Updated IP Routing Table Here is all my routing information. I m using split horizon. Thanks for the information! That is very nice of you. Here is all my routing information. I m also using split horizon. Thanks for the information! We ve reached convergence. Updated EIGRP Topology Table Successor Updated IP Routing Table 12
13 After the initial updates have been exchanged, routing updates will only be exchanged as a result of changes on the networks. Changes can be caused by changes in connectivity, such as: Loss of a link or neighbor Configuration events 13
14 R2# debug ip routing IP routing debugging is on R2# conf t R2(config)# int fa0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# no shutdown %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up RT: add /24 via , connected metric [0/0] RT: interface FastEthernet0/0 added to routing table debug ip routing: Not specific to EIGRP Displays any changes that are made to the routing table, such as installation or removal of routes. 14
15 debug eigrp packets: Displays the transmission and reception of EIGRP packets. Note: Cisco Press Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) by Diane Teare provides detailed explanation of the output. 15
16 debug ip eigrp: Displays EIGRP routing events, such as updates, queries, and replies sent to or received from neighbors. Focuses on the routing information contained in the packets and the actions that EIGRP takes as a result of the information received. Note: Cisco Press Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) by Diane Teare provides detailed explanation of the output. 16
17 Troubleshooting Example: Routing Problem in an EIGRP Network 17
18 Traffic path unexpectedly goes through BRO2 18
19 ping from BRO1 to CRO1 succeeds, you can conclude that the WAN link is operational at Layers 3 and below 19
20 Two likely reasons why the traffic is routed through router BRO2 instead of directly across the WAN to router CRO1: BRO1 has not learned about the direct route to router CRO1. BRO1 selects the route through router BRO2 as the best route. Let s look at the EIGRP topology table 20
21 The topology table lists all routes that were received, so you can see if the direct route to CRO1 is missing. Note: This command displays all entries in the topology table for this destination, not just feasible successors similar to all-links option. No direct route! Need to determine whether the route was not learned because: A neighbor relationship with CRO1 was never established The relationship was established but the specific route was not exchanged. Good next step is to display the neighbor table 21
22 CRO1 is not listed as a neighbor on router BRO1. Could be one or the other routers is not: Sending Hello packets Ignoring Hello packets Let s look at the EIGRP interfaces to make sure the serial interface is configured for EIGRP. 22
23 Does not list the serial interface of router BRO1. So, even if hello packets are received on the serial interface, router BRO1 does not process them. Two conditions need to be met for an interface to be added to the EIGRP interface table: The interface has to be up and its IP address must match one of the configured network statements. The interface should not be configured as a passive interface. Let s look at the running-config 23
24 Problem with one of the network statements. The statement network matches IP address the IP address of router CRO1 Does not match the serial interface of BRO1 Replaced it with the statement network or some other network statement 24
25 The interface table now lists subinterface Serial 0/0/0.111 in addition to subinterface FastEthernet 0/1.30. This means that EIGRP packets are now processed on interface Serial 0/0/ IP address of router CRO1 ( ) is now listed in the neighbor table on the WAN interface. 25
26 Successor The EIGRP topology table now lists two entries for network /32. Note: BR02 is listed but is not a Feasible Successor (RD is not less than FD) 26
27 show ip route command with network confirms that the path through router CRO1 has been installed in the routing table traceroute command confirms that this path is now used to forward packets to the loopback of CRO1. 27
28 Troubleshooting OSPF 28
29 To diagnose and resolve problems related to OSPF you must be able to: Apply your knowledge of OSPF data structures Apply your knowledge of OSPF processes within an area Apply your knowledge of OSPF processes between areas Use Cisco IOS commands to gather information from the OSPF data structures and track the flow of OSPF routing information 29
30 At a high level, each routing protocol consists of the following elements and processes: (RIP is a notable exception to some of these.) Reception of routing information from neighbors: Neighbor relationships and LSAs Routing protocol data structures: LSDB and SPF Route injection or redistribution: Directly connected, dynamic routes, static routes Route selection and installation: Best path, equal cost load balancing Intra-area, Inter-area and external routes, area types Transmission of routing information to neighbors: Forward to other neighbors Internal routers, ABRs, ASBRs 30
31 R1# show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /30, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 64 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 <output omitted> OSPF stores its operational data, configured parameters, and statistics in four main data structures: Interface table: Lists all interfaces that have been enabled for OSPF. When an interface is configured as a passive interface, it is still listed in the OSPF interface table, but no neighbor relationships are established on this interface. 31
32 R1# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/ FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/0 Neighbor table: Keeps track of all active OSPF neighbors. OSPF goes through a number of states while establishing a neighbor relationship (also known as adjacency) Lists the current state for each individual neighbor 32
33 Link-state database: This is the main data structure that OSPF uses to store all its network topology information. Contains a wealth of network topology information One of the most important data structures to gather information from when troubleshooting OSPF problems. 33
34 R33# show ip route C /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is subnetted, 2 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 O [110/2] via , 00:02:13, FastEthernet0/ /24 is subnetted, 2 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 O [110/2] via , 00:02:23, FastEthernet0/0 O*IA /0 [110/2] via , 00:02:13, FastEthernet0/0 Routing information base: After executing the SPF algorithm, the results of this calculation are stored in the RIB (Routing Information Base). Routes might be added to or deleted from the RIB without the need for a SPF recalculation. From the RIB, OSPF offers its routes to the IP routing table. Note: The collection of best paths is known as the OSPF RIB. There is not a separate physical data structure called the OSPF RIB. Many writings refer to the IP routing table as the RIB to allow it to be distinguished from the FIB that CEF creates. 34
35 R1# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/ FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0/0 Two routers will become neighbors only if the following parameters match in the Hello packets: Hello and dead timers: Use the same Hello and dead time. Broadcast and point-to-point type networks are 10-second Hello and 40- second dead time. OSPF area number: Both consider that link to be in the same area. IP subnet and subnet mask: If they are on the same subnet. The exception to this rule is on a point-to-point link, where the subnet mask is not verified. 35
36 debug ip ospf packet: Displays the transmission and reception of OSPF packets. Only the packet headers are displayed, not the content of the packets. This command is useful to verify if Hellos are sent and received as expected. debug ip ospf events: Displays OSPF events. This includes reception and transmission of Hellos, but also the establishment of neighbor relationships and the reception or transmission of LSAs. This command can also provide clues (mismatched parameters such as timers, area number, etc.) as to why neighbor Hellos might be ignored. debug ip ospf adj: Displays events that are related to the adjacency building See a neighbor relationship transition from one state to the next. Observe possibly the state the relation getting stuck at. debug ip ospf monitor: Monitors when the SPF algorithm is scheduled to run and displays the triggering LSA and a summary of the results after the SPF algorithm has completed. Allows you to discover which LSA was received and triggered an SPF computation. Can easily discover a flapping link. 36
37 Troubleshooting Lab: Routing Problem in an OSPF Network 37
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Configuring EIGRP. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc.
 Configuring EIGRP 4-1 EIGRP Overview 4-2 What Is EIGRP? IPX Routing Protocols IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol Enhanced IGRP IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol IPX Routing Protocols
Configuring EIGRP 4-1 EIGRP Overview 4-2 What Is EIGRP? IPX Routing Protocols IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol Enhanced IGRP IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol IPX Routing Protocols
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 2: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 : Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting. IPv4 Routing Workflow. IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ]
![Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ] Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ]](/thumbs/78/78661316.jpg) Topology & EIGRP Invocation Router-ID is in the EIGRP block Interfaces included at each interface Passive interfaces designated in the EIGRP block The EIGRP block may require a no shutdown R5 ipv6 unicast-routing
Topology & EIGRP Invocation Router-ID is in the EIGRP block Interfaces included at each interface Passive interfaces designated in the EIGRP block The EIGRP block may require a no shutdown R5 ipv6 unicast-routing
Section 6. Implementing EIGRP ICND2
 ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) http:// What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) http:// What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
This chapter covers the following subjects:
 This chapter covers the following subjects: Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts OSPF Configuration EIGRP Configuration C H A P T E R 6 OSPF
This chapter covers the following subjects: Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts OSPF Configuration EIGRP Configuration C H A P T E R 6 OSPF
Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7
 EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Volume 2 Version 1.0 Student Guide Editorial, Production, and Web Services (EPWS): 07.25.07 DISCLAIMER WARRANTY: THIS CONTENT IS BEING PROVIDED AS
ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Volume 2 Version 1.0 Student Guide Editorial, Production, and Web Services (EPWS): 07.25.07 DISCLAIMER WARRANTY: THIS CONTENT IS BEING PROVIDED AS
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Introduction. Lab Diagram
 Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
8. Refer to the exhibit. The ORL router is unable to form a neighbor relationship with the JAX router. What is a possible cause of this problem?
 1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 11 Case Study
 bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.) - packet switching - path selection
 Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features Topology
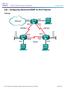 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
RIPv2. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 RIPv2 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7 1 Objectives Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1 s limitations. Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands
RIPv2 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 7 1 Objectives Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1 s limitations. Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com)
 CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com) Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 90 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 642-902 ROUTE Exam Topics Exam Description The Implementing
CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com) Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 90 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 642-902 ROUTE Exam Topics Exam Description The Implementing
Claim desired outcome
 Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Configuration and Management of Networks
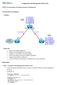 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
NAT Internetworking Standards and Technologies, Computer Engineering, KMITL 2
 EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
CCNP IPSOFTWARE EIGRP ROUTE Lab Manual.
 Lab Manual CCNP ROUTE 300-101 EIGRP Lab - 1 : EIGRP-Basic Configuration Lab - 2 : EIGRP-Metric and Variance Load Sharing Lab - 3 : EIGRP-Summarization Lab - 4 : EIGRP-Query Control Lab - 5 : EIGRP-Authentication
Lab Manual CCNP ROUTE 300-101 EIGRP Lab - 1 : EIGRP-Basic Configuration Lab - 2 : EIGRP-Metric and Variance Load Sharing Lab - 3 : EIGRP-Summarization Lab - 4 : EIGRP-Query Control Lab - 5 : EIGRP-Authentication
EIGRP. About EIGRP. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.7 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
OSPFv2 deep dive. Михайловский Василий Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015
 OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest a (Catalyst 9300 Switches)
 Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1a (Catalyst 9300 Switches) First Published: 2017-06-20 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA
Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1a (Catalyst 9300 Switches) First Published: 2017-06-20 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability. Buy Full Product.
 Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Alcatel-lucent EXAM - 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/4a0-101.html Examskey Alcatel-lucent 4A0-101 exam demo product is
Implementing cisco ip routing
 Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
IPv6 Routing: OSPFv3
 Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
Configuring EIGRP. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
LAB2: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Table of Contents. Cisco Introduction to EIGRP
 Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example
 ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Guidelines and Limitations EIGRP and Failover Configure Network Diagram ASDM
ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Guidelines and Limitations EIGRP and Failover Configure Network Diagram ASDM
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
What Does the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA Error Message Mean?
 What Does the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA Error Message Mean? Document ID: 13676 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information What Causes the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA
What Does the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA Error Message Mean? Document ID: 13676 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information What Causes the EIGRP DUAL 3 SIA
Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]
![Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]](/thumbs/78/78661506.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
Completed Planning Practice Tables
 Appendix F Completed Planning Practice Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-3 Design Review Design Goal The design requires the number of entries in a router s routing table to be reduced. The design calls for the
Appendix F Completed Planning Practice Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-3 Design Review Design Goal The design requires the number of entries in a router s routing table to be reduced. The design calls for the
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS
 Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
IPv6 Routing Protocols
 IPv6 Routing Protocols ISP Workshops Last updated 17 May 2014 1 Initial IPv6 Configuration for Cisco IOS 2 IPv6 Configuration on Cisco IOS p To enable IPv6 the following global commands are required: Router(config)#
IPv6 Routing Protocols ISP Workshops Last updated 17 May 2014 1 Initial IPv6 Configuration for Cisco IOS 2 IPv6 Configuration on Cisco IOS p To enable IPv6 the following global commands are required: Router(config)#
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 10 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 10 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-10-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 10 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 10 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-10-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 10 Exam Answers
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting EIGRP Neale Rowe Presentation_ID 2 Agenda Troubleshooting Common EIGRP Problems Neighbor Stability Stuck-in-Active Routes Troubleshooting
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting EIGRP Neale Rowe Presentation_ID 2 Agenda Troubleshooting Common EIGRP Problems Neighbor Stability Stuck-in-Active Routes Troubleshooting
Understanding IPX EIGRP
 Understanding IPX EIGRP Document ID: 10579 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Information EIGRP Components IPX EIGRP Features IPX EIGRP Internetworking
Understanding IPX EIGRP Document ID: 10579 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Information EIGRP Components IPX EIGRP Features IPX EIGRP Internetworking
Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP
 Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 5.2 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License
Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 5.2 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
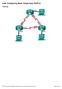 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP
 Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
EXAM Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
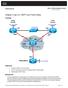 Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Routing Configuration Commands
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
F. Configure a distribute-list on router RTA that allows it to advertise all routes to the spoke routers.
 Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC
Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route Duration: 40 Hours
 COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route 300-101 Duration: 40 Hours CCNP Route Training Day 1: Connecting Remote Locations Principles of Static Routing Configuring an IPv4 Static Route Configuring a Static Default
COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route 300-101 Duration: 40 Hours CCNP Route Training Day 1: Connecting Remote Locations Principles of Static Routing Configuring an IPv4 Static Route Configuring a Static Default
The commands in this appendix are organized in the following sections:
 The commands in this appendix are organized in the following sections: General s Comparison of Configuration File s General Configuration s General Interface Configuration s General IP s IP Configuration
The commands in this appendix are organized in the following sections: General s Comparison of Configuration File s General Configuration s General Interface Configuration s General IP s IP Configuration
Exam Questions 4A0-101
 Exam Questions 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/4a0-101/ 1.When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match in the routing
Exam Questions 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/4a0-101/ 1.When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match in the routing
Chapter 9. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I
 Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP
 CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP EIGRP Initial Configuration Load the task1-1 initial configurations before starting. Task Configure EIGRP on Routers-1, 2, and 4 using the following guidelines: Classic-mode
CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP EIGRP Initial Configuration Load the task1-1 initial configurations before starting. Task Configure EIGRP on Routers-1, 2, and 4 using the following guidelines: Classic-mode
LAB1: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
EIGRP 04/01/2008. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example
 OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example Document ID: 118879 Contributed by Narra Naukwal, Cisco TAC Engineer. Mar 31, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used
OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example Document ID: 118879 Contributed by Narra Naukwal, Cisco TAC Engineer. Mar 31, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min.
 300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training
 REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
Part II. Chapter 3. Determining IP Routes
 Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Inheritence with EIGRP Named mode Route Replication with EIGRP name mode Routing Context
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Inheritence with EIGRP Named mode Route Replication with EIGRP name mode Routing Context
Chapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch Topology Objectives Review a basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface. onfigure EIGRP over Frame
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch Topology Objectives Review a basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface. onfigure EIGRP over Frame
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
