AP Computer Science. Return values, Math, and double. Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education
|
|
|
- Dale Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP Computer Science Return values, Math, and double
2 Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them If you can t do all of it, pseudocode? What?! You don t remember the distance formula?! 2
3 Java libraries Java comes with lots of goodies Graphics Color Math Learn more from the Application Programming Interface Linked from desktop 3
4 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Description absolute value rounds up rounds down Math.log10(value) logarithm, base 10 Math.max(value1, value2) Math.min(value1, value2) larger of two values smaller of two values Math.pow(base, exp) base to the exp power Math.random() random double between 0 and 1 Math.round(value) Math.sqrt(value) Math.sin(value) Math.cos(value) Math.tan(value) Math.toDegrees(value) Math.toRadians(value) nearest whole number square root sine/cosine/tangent of an angle in radians convert degrees to radians and back Constant Description Math.E Math.PI
5 No output? Simply calling these methods produces no visible result. Math.pow(3, 4); // no output Math method calls use a Java feature called return values that cause them to be treated as expressions. The program runs the method, computes the answer, and then "replaces" the call with its computed result value. Math.pow(3, 4); // no output 81.0; // no output To see the result, we must print it or store it in a variable. double result = Math.pow(3, 4); System.out.println(result); //
6 Return return: To send out a value as the result of a method. The opposite of a parameter: Parameters send information in from the caller to the method. Return values send information out from a method to its caller. A call to the method can be used as part of an expression. -42 Math.abs(-42) main Math.round(2.71) 6
7 Why return and not print? It might seem more useful for the Math methods to print their results rather than returning them. Why don't they? Answer: Returning is more flexible than printing. We can compute several things before printing: double pow1 = Math.pow(3, 4); double pow2 = Math.pow(10, 6); System.out.println("Powers are " + pow1 + " and " + pow2); We can combine the results of many computations: double k = 13 * Math.pow(3, 4) Math.sqrt(17.8); 7
8 Math questions Evaluate the following expressions: Math.abs(-1.23) Math.pow(3, 2) Math.pow(10, -2) Math.sqrt(121.0) - Math.sqrt(256.0) Math.round(Math.PI) + Math.round(Math.E) Math.ceil(6.022) + Math.floor( ) Math.abs(Math.min(-3, -5)) Math.max and Math.min can be used to bound numbers. Consider an int variable named age. What statement would replace negative ages with 0? What statement would cap the maximum age to 40? 8
9 Quirks of real numbers Some Math methods return double or other non-int types. int x = Math.pow(10, 3); // ERROR: incompat. types Some double values print poorly (too many digits). double result = 1.0 / 3.0; System.out.println(result); // The computer represents doubles in an imprecise way. System.out.println( ); Instead of 0.3, the output is
10 Type casting type cast: A conversion from one type to another. To promote an int into a double to get exact division from / To truncate a double from a real number to an integer Syntax: (type) expression Examples: double result = (double) 19 / 5; // 3.8 int result2 = (int) result; // 3 int x = (int) Math.pow(10, 3); //
11 More about type casting Type casting has high precedence and only casts the item immediately next to it. double x = (double) / 2; // 1.0 double y = 1 + (double) 1 / 2; // 1.5 You can use parentheses to force evaluation order. double average = (double) (a + b + c) / 3; A conversion to double can be achieved in other ways. double average = 1.0 * (a + b + c) / 3; 11
12 Interactive Programs with Scanner
13 Interactive programs interactive program: Reads input from the console. While the program runs, it asks the user to type input. The input typed by the user is stored in variables in the code. Can be tricky; users are unpredictable and misbehave. But interactive programs have more interesting behavior. 13
14 Scanner Scanner: An object that can read input from many sources. Communicates with System.in Can also read from files (Ch. 6), web sites, databases, The Scanner class is found in the java.util package. import java.util.*; // so you can use Scanner Constructing a Scanner object to read console input: Scanner name = new Scanner(System.in); Example: Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); 14
15 Scanner methods Method nextint() nextdouble() next() nextline() Description reads an int from the user and returns it reads a double from the user reads a one-word String from the user reads a one-line String from the user Each method waits until the user presses Enter. The value typed by the user is returned. prompt System.out.print("How old are you? "); // int age = console.nextint(); System.out.println("You typed " + age); prompt: A message telling the user what input to type. 15
16 Scanner example import java.util.*; // so that I can use Scanner public class UserInputExample { public static void main(string[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("How old are you? "); int age = console.nextint(); age 29 years 36 } } int years = 65 - age; System.out.println(years + " years until retirement!"); Console (user input underlined): How old are you? years until retirement! 16
17 Scanner example 2 import java.util.*; // so that I can use Scanner public class ScannerMultiply { public static void main(string[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Please type two numbers: "); int num1 = console.nextint(); int num2 = console.nextint(); } } int product = num1 * num2; System.out.println("The product is " + product); Output (user input underlined): Please type two numbers: 8 6 The product is 48 The Scanner can read multiple values from one line. 17
18 Input tokens token: A unit of user input, as read by the Scanner. Tokens are separated by whitespace (spaces, tabs, new lines). How many tokens appear on the following line of input? 23 John Smith 42.0 "Hello world" $2.50 " 19" When a token is not the type you ask for, it crashes. System.out.print("What is your age? "); int age = console.nextint(); Output: What is your age? Zan java.util.inputmismatchexception at java.util.scanner.next(unknown Source) at java.util.scanner.nextint(unknown Source)... 18
19 Scanners as parameters If many methods need to read input, declare a Scanner in main and pass it to the other methods as a parameter. public static void main(string[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); readsum3(console); } // Prompts for 3 numbers and returns their sum. public static int readsum3(scanner console) { System.out.print("Type 3 numbers: "); int num1 = console.nextint(); int num2 = console.nextint(); int num3 = console.nextint(); System.out.println("The sum is " + sum); } 19
AP Computer Science A. Return values
 AP Computer Science A Return values Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them Pseudocode? Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value)
AP Computer Science A Return values Distance between points Write a method that given x and y coordinates for two points prints the distance between them Pseudocode? Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value)
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education 2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value)
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us From this site you can click on the COSC-236
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us From this site you can click on the COSC-236
Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class
 Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class Building Java Programs: A Back to Basic Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. while loops 2 Categories of loops
Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class Building Java Programs: A Back to Basic Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. while loops 2 Categories of loops
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 7: Return values, Math, and casting reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 7: Return values, Math, and casting reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return; doubles and casting reading: 3.2, 4.1 videos: Ch. 3 #2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Finish Car example Lecture outline Returns Java Math library
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return; doubles and casting reading: 3.2, 4.1 videos: Ch. 3 #2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Finish Car example Lecture outline Returns Java Math library
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Description absolute
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Java's Math class Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Description absolute
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Java's Math class Description absolute
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-2: Return values, Math, and double reading: 3.2, 2.1-2.2 Method name Math.abs(value) Math.ceil(value) Math.floor(value) Java's Math class Description absolute
Building Java Programs Chapter 3
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Parameters and Objects Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Redundant recipes Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in a bowl: 4 cups
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Parameters and Objects Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Redundant recipes Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in a bowl: 4 cups
Redundant recipes. Building Java Programs Chapter 3. Parameterized recipe. Redundant figures
 Redundant recipes Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Parameters and Objects Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in a bowl: 4 cups
Redundant recipes Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Parameters and Objects Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in a bowl: 4 cups
Garfield AP CS. User Input, If/Else. Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp!
 Garfield AP CS User Input, If/Else Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp! Warmup Write a method add10 that takes one integer parameter. Your method should return
Garfield AP CS User Input, If/Else Most slides from Building Java Programs. Thanks, Stuart Regesand Marty Stepp! Warmup Write a method add10 that takes one integer parameter. Your method should return
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-1: Scanner; if/else reading: 3.3 3.4, 4.1, 4.5 2 Interactive Programs with Scanner reading: 3.3-3.4 Interactive programs We have written programs that print console
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Animation (sleep and double buffering); Methods with Return; Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf
 Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Topic 12 more if/else, cumulative algorithms, printf "We flew down weekly to meet with IBM, but they thought the way to measure software was the amount of code we wrote, when really the better the software,
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3: Parameters, Return, and Interactive Programs with Scanner 1 Lecture outline console input with Scanner objects input tokens Scanner as a parameter to a method cumulative
Building Java Programs Chapter 3: Parameters, Return, and Interactive Programs with Scanner 1 Lecture outline console input with Scanner objects input tokens Scanner as a parameter to a method cumulative
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Summary of Methods; User Input using Scanner Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Summary of Methods; User Input using Scanner Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin
CSc 110, Spring Lecture 11: return values and math
 CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 11: return values and math Python's Math class Method name math.ceil(value) math.floor(value) math.log(value, base) math.sqrt(value) math.sinh(value) math.cosh(value) math.tanh(value)
CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 11: return values and math Python's Math class Method name math.ceil(value) math.floor(value) math.log(value, base) math.sqrt(value) math.sinh(value) math.cosh(value) math.tanh(value)
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-1: Parameters reading: 3.1 Redundant recipes Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in a bowl: 4 cups flour 1 cup butter 1 cup sugar 2 eggs
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-1: Parameters reading: 3.1 Redundant recipes Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in a bowl: 4 cups flour 1 cup butter 1 cup sugar 2 eggs
AP CS Java Syntax Summary: (version 3)
 : (version 3) CLASSES & METHODS Class & main: public class name { public static void main(string[] args) {... Method creation: public static name(type ,, type
: (version 3) CLASSES & METHODS Class & main: public class name { public static void main(string[] args) {... Method creation: public static name(type ,, type
CSE 373. Data Types and Manipulation; Arrays. slides created by Marty Stepp
 CSE 373 Data Types and Manipulation; Arrays slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/373/ University of Washington, all rights reserved. 1 Numeric data type kind of number memory (bits)
CSE 373 Data Types and Manipulation; Arrays slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/373/ University of Washington, all rights reserved. 1 Numeric data type kind of number memory (bits)
4. Java Project Design, Input Methods
 4-1 4. Java Project Design, Input Methods Review and Preview You should now be fairly comfortable with creating, compiling and running simple Java projects. In this class, we continue learning new Java
4-1 4. Java Project Design, Input Methods Review and Preview You should now be fairly comfortable with creating, compiling and running simple Java projects. In this class, we continue learning new Java
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 10: return values and math
 CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 10: return values and math Python's Math class Method name math.ceil(value) math.floor(value) math.log(value, base) math.sqrt(value) math.sinh(value) math.cosh(value) math.tanh(value)
CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 10: return values and math Python's Math class Method name math.ceil(value) math.floor(value) math.log(value, base) math.sqrt(value) math.sinh(value) math.cosh(value) math.tanh(value)
! definite loop: A loop that executes a known number of times. " The for loops we have seen so far are definite loops. ! We often use language like
 Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( ). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug,
 1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Java Syntax Summary: (version 4)
 : (version 4) CLASSES & METHODS Class & main: public class name { public static void main(string[] args) {... Method creation: public static name(type ,, type
: (version 4) CLASSES & METHODS Class & main: public class name { public static void main(string[] args) {... Method creation: public static name(type ,, type
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Important Java terminology
 1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
Key Concept: all programs can be broken down to a combination of one of the six instructions Assignment Statements can create variables to represent
 Programming 2 Key Concept: all programs can be broken down to a combination of one of the six instructions Assignment Statements can create variables to represent information Input can receive information
Programming 2 Key Concept: all programs can be broken down to a combination of one of the six instructions Assignment Statements can create variables to represent information Input can receive information
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Makeup Spring 2013 / 2014
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Makeup Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Java is. a. case
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Makeup Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Java is. a. case
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
CIS133J. Working with Numbers in Java
 CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
12. Numbers. Java. Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini
 12. Numbers Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Numeric Type Conversions Math Class References Numeric Type Conversions Numeric Data Types (Review) Numeric Type Conversions Consider
12. Numbers Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Numeric Type Conversions Math Class References Numeric Type Conversions Numeric Data Types (Review) Numeric Type Conversions Consider
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4: Conditional Execution 1 loop techniques cumulative sum fencepost loops conditional execution Chapter outline the if statement and the if/else statement relational expressions
Building Java Programs Chapter 4: Conditional Execution 1 loop techniques cumulative sum fencepost loops conditional execution Chapter outline the if statement and the if/else statement relational expressions
The Math Class. Using various math class methods. Formatting the values.
 The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements
 Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Chapter 5 Methods. Modifier returnvaluetype methodname(list of parameters) { // method body; }
 Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions
 Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
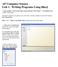 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CS5000: Foundations of Programming. Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University
 CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Mathematical Functions Java provides many useful methods in the Math class for performing common mathematical
CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Mathematical Functions Java provides many useful methods in the Math class for performing common mathematical
Advanced Object Concepts
 Understanding Blocks Blocks - Appears within any class or method, the code between a pair of curly braces Outside block- The first block, begins immediately after the method declaration and ends at the
Understanding Blocks Blocks - Appears within any class or method, the code between a pair of curly braces Outside block- The first block, begins immediately after the method declaration and ends at the
Chapter 4: Control Structures I
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion
 Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Calculations, Formatting and Conversions
 Chapter 5 Calculations, Formatting and Conversions What is in This Chapter? In this chapter we discuss how to do basic math calculations as well as use some readily available Math functions in JAVA. We
Chapter 5 Calculations, Formatting and Conversions What is in This Chapter? In this chapter we discuss how to do basic math calculations as well as use some readily available Math functions in JAVA. We
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O
 STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A7 1 STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O INTRODUCTION: The input and output of a program s data is usually referred to as I/O.
STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A7 1 STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O INTRODUCTION: The input and output of a program s data is usually referred to as I/O.
Data Conversion & Scanner Class
 Data Conversion & Scanner Class Quick review of last lecture August 29, 2007 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2007 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev Numeric Primitive Data Storing
Data Conversion & Scanner Class Quick review of last lecture August 29, 2007 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2007 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev Numeric Primitive Data Storing
Java Foundations: Introduction to Program Design & Data Structures, 4e John Lewis, Peter DePasquale, Joseph Chase Test Bank: Chapter 2
 Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Scanner, Increment/Decrement, Conversion Janyl Jumadinova 17 September, 2018 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 17 September, 2018 1 / 11 Review: Scanner The Scanner class
Computational Expression Scanner, Increment/Decrement, Conversion Janyl Jumadinova 17 September, 2018 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 17 September, 2018 1 / 11 Review: Scanner The Scanner class
AP CS Java Syntax Summary: (version 5)
 : (version 5) CLASSES & METHODS Class & main: public class name { public static void main(string[] args) { statement;... statement; Method creation: public static name(type ,,
: (version 5) CLASSES & METHODS Class & main: public class name { public static void main(string[] args) { statement;... statement; Method creation: public static name(type ,,
Java API: Math, Wrapper Classes, StringBuffer Random Data Quiz2
 Java API: Math, Wrapper Classes, StringBuffer Random Data Quiz2 163 Recap Lessons learned: We can generate documentation from Javadoc We can call any method in a program from any other method in that program
Java API: Math, Wrapper Classes, StringBuffer Random Data Quiz2 163 Recap Lessons learned: We can generate documentation from Javadoc We can call any method in a program from any other method in that program
JAVASCRIPT BASICS. JavaScript Math Functions. The Math functions helps you to perform mathematical tasks
 JavaScript Math Functions Functions The Math functions helps you to perform mathematical tasks in a very way and lot of inbuilt mathematical functions which makes the programmers life easier. Typical example
JavaScript Math Functions Functions The Math functions helps you to perform mathematical tasks in a very way and lot of inbuilt mathematical functions which makes the programmers life easier. Typical example
Chapter 5 Methods. Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk
 Chapter 5 Methods Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that
Chapter 5 Methods Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
Tester vs. Controller. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Compile Time vs. Run Time
 Tester vs. Controller Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG For effective illustrations, code examples will mostly be written in the form of a tester
Tester vs. Controller Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG For effective illustrations, code examples will mostly be written in the form of a tester
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Ninth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods
 Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods Due date for section 001: Monday, February 29 by 10 am Due date for section 002: Wednesday, March 2 by 10 am Purpose: Introduction to writing methods and code re-use.
Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods Due date for section 001: Monday, February 29 by 10 am Due date for section 002: Wednesday, March 2 by 10 am Purpose: Introduction to writing methods and code re-use.
Elementary Programming
 Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Learn ingredients of elementary programming: data types [numbers, characters, strings] literal
Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Learn ingredients of elementary programming: data types [numbers, characters, strings] literal
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-2: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum; reading: 4.2, 4.4-4.5 2 Advanced if/else reading: 4.4-4.5 Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code.
Building Java Programs Chapter 4 Lecture 4-2: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum; reading: 4.2, 4.4-4.5 2 Advanced if/else reading: 4.4-4.5 Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code.
Arrays. Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals
 Arrays Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program
Arrays Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program
Chapter 6 Methods. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Introduction to Java. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
 www.thestudycampus.com Methods Let s imagine an automobile factory. When an automobile is manufactured, it is not made from basic raw materials; it is put together from previously manufactured parts. Some
www.thestudycampus.com Methods Let s imagine an automobile factory. When an automobile is manufactured, it is not made from basic raw materials; it is put together from previously manufactured parts. Some
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us or http://www.class-notes.info or http://www.lecture-notes.tripod.com
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Using Java Classes Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 3 Expression Evaluation and Program Interaction Outline Problem: How do I input data and use it in complicated expressions Creating complicated expressions
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 3 Expression Evaluation and Program Interaction Outline Problem: How do I input data and use it in complicated expressions Creating complicated expressions
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings
 Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Motivations Suppose you need to estimate
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Motivations Suppose you need to estimate
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E
 A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 7 Functions and Randomness 1 Predefined Functions recall: in
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 7 Functions and Randomness 1 Predefined Functions recall: in
Define a method vs. calling a method. Chapter Goals. Contents 1/21/13
 CHAPTER 2 Define a method vs. calling a method Line 3 defines a method called main Line 5 calls a method called println, which is defined in the Java library You will learn later how to define your own
CHAPTER 2 Define a method vs. calling a method Line 3 defines a method called main Line 5 calls a method called println, which is defined in the Java library You will learn later how to define your own
Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S L E C T U R E 8
 Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 8 Math class Math class is a utility class You cannot create an instance of Math All references to constants and methods will use the prefix Math.
Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 8 Math class Math class is a utility class You cannot create an instance of Math All references to constants and methods will use the prefix Math.
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN
 A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 7 Functions and Randomness 1 Predefined Functions recall: in
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 7 Functions and Randomness 1 Predefined Functions recall: in
Computer Programming I - Unit 2 Lecture 1 of 13
 1 of 13 Precedence, Mixed Expressions, Math Methods, and Output Fmatting I. Precedence Rules - der of operations Introduction example: 4 + 2 X 3 =? A) Parenthesis, Division Multiplication (from left to
1 of 13 Precedence, Mixed Expressions, Math Methods, and Output Fmatting I. Precedence Rules - der of operations Introduction example: 4 + 2 X 3 =? A) Parenthesis, Division Multiplication (from left to
int: integers, no fractional part double: floating-point numbers (double precision) 1, -4, 0 0.5, , 4.3E24, 1E-14
 int: integers, no fractional part 1, -4, 0 double: floating-point numbers (double precision) 0.5, -3.11111, 4.3E24, 1E-14 A numeric computation overflows if the result falls outside the range for the number
int: integers, no fractional part 1, -4, 0 double: floating-point numbers (double precision) 0.5, -3.11111, 4.3E24, 1E-14 A numeric computation overflows if the result falls outside the range for the number
Module 4: Characters, Strings, and Mathematical Functions
 Module 4: Characters, Strings, and Mathematical Functions Objectives To solve mathematics problems by using the methods in the Math class ( 4.2). To represent characters using the char type ( 4.3). To
Module 4: Characters, Strings, and Mathematical Functions Objectives To solve mathematics problems by using the methods in the Math class ( 4.2). To represent characters using the char type ( 4.3). To
CISC-124. This week we continued to look at some aspects of Java and how they relate to building reliable software.
 CISC-124 20180129 20180130 20180201 This week we continued to look at some aspects of Java and how they relate to building reliable software. Multi-Dimensional Arrays Like most languages, Java permits
CISC-124 20180129 20180130 20180201 This week we continued to look at some aspects of Java and how they relate to building reliable software. Multi-Dimensional Arrays Like most languages, Java permits
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Reading Input from Text File
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Lab 5 Reading Input from Text File Eng. Mohammed Alokshiya November 2, 2014 The simplest
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Lab 5 Reading Input from Text File Eng. Mohammed Alokshiya November 2, 2014 The simplest
CT 229 Java Syntax Continued
 CT 229 Java Syntax Continued 06/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Due Date for current lab assignment : Oct 8 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment
CT 229 Java Syntax Continued 06/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Due Date for current lab assignment : Oct 8 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment
Big Java. Fifth Edition. Chapter 3 Fundamental Data Types. Cay Horstmann
 Big Java Fifth Edition Cay Horstmann Chapter 3 Fundamental Data Types Chapter Goals To understand integer and floating-point numbers To recognize the limitations of the numeric types To become aware of
Big Java Fifth Edition Cay Horstmann Chapter 3 Fundamental Data Types Chapter Goals To understand integer and floating-point numbers To recognize the limitations of the numeric types To become aware of
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of Java TRUE/FALSE 1. The pair of characters // is used for single line comments. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 29 2. The == characters are a special symbol in Java. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 30
CEN 414 Java Programming
 CEN 414 Java Programming Instructor: H. Esin ÜNAL SPRING 2017 Slides are modified from original slides of Y. Daniel Liang WEEK 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING 2 Computing the Area of a Circle public class ComputeArea
CEN 414 Java Programming Instructor: H. Esin ÜNAL SPRING 2017 Slides are modified from original slides of Y. Daniel Liang WEEK 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING 2 Computing the Area of a Circle public class ComputeArea
double float char In a method: final typename variablename = expression ;
 Chapter 4 Fundamental Data Types The Plan For Today Return Chapter 3 Assignment/Exam Corrections Chapter 4 4.4: Arithmetic Operations and Mathematical Functions 4.5: Calling Static Methods 4.6: Strings
Chapter 4 Fundamental Data Types The Plan For Today Return Chapter 3 Assignment/Exam Corrections Chapter 4 4.4: Arithmetic Operations and Mathematical Functions 4.5: Calling Static Methods 4.6: Strings
A token is a sequence of characters not including any whitespace.
 Scanner A Scanner object reads from an input source (keyboard, file, String, etc) next() returns the next token as a String nextint() returns the next token as an int nextdouble() returns the next token
Scanner A Scanner object reads from an input source (keyboard, file, String, etc) next() returns the next token as a String nextint() returns the next token as an int nextdouble() returns the next token
