Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Example ADTs. Using an Abstract Data Type. Class #08: Linear Data Structures
|
|
|
- Maximillian McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Class #08: Linear Data Structures Software Design III (CS 340): M. Allen, 08 Feb. 16 An ADT defines a kind of computational entity: A set of objects, with possible values A set of operations to perform Abstraction: the ADT does not say how operations are to be performed, exactly, only what they should do Described in terms of its interface How we interact with it, from an external point of view A Java class makes an ADT concrete Instance variables and methods implement the ADT Operations User Interface (visible) Implementation Details (hidden) 2 Example ADTs Primitive type like boolean can be given as an ADT: Values: true and false Operations:!, &&, The ADT for a more complex data structure like a Collection of objects is similar in structure: Values: sets of objects of some particular data-type Operations: ways to add, remove, find, those objects Using an Abstract Data Type Once we have defined the general form of the ADT, we can implement it in any number of ways Client code that uses the ADT should not need to know all the details of how this is actually done Java uses interface to define many ADTs The interface gives the abstract signature of a set of methods: defines the operations of the type in general terms A class that implements the interface will make these operations concrete in some manner We can then write code to use any such class based only on the interface itself, not the concrete implementation 3 4 1
2 The List ADT A list is a sequence of elements E 0, E 1, E 2,, E N-1 Any two elements in the list are related linearly: elements occur before or after one another The Java Collection Framework A built-in library of common ADTs and implementations java.util.collection General operations include the ability to: 1. Check the size of the list 2. Add or remove elements to or from the list 3. Check whether an object exists in the list 4. Iterate (loop) over elements of the list, in order java.util.set java.util.list java.util.queue java.util.linkedlist <class> java.util.arraylist <class> 5 6 Java Collection Interface public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> int size(); boolean isempty(); boolean contains( Object element ); Iterator<E> iterator(); boolean containsall( Collection<?> c ); boolean addall( Collection<? extends E> c ); boolean removeall( Collection<?> c ); boolean retainall( Collection<?> c ); void clear(); Object[] toarray(); <T> T[] toarray( T[] a ); Collection is a sub-interface of another (Iterable, discussed later) 7 Collection Implementation Many of the Collection methods are defined, like the interface itself, in a generic fashion: boolean contains( Object element ); Iterator<E> iterator(); Object[] toarray(); <T> T[] toarray( T[] a ); E: actual type of object the Collection<E> contains T: a type supplied at runtime by input object Remember: when we use a generic type parameter (for the first time) in a method signature, we must declare it before we can use it in that method 8 2
3 Collection Implementation Other methods are given in terms of wildcard types: boolean containsall(collection<?> c); boolean containsall( Collection<?> c ); boolean boolean addall(collection<? Collection<? extends extends E> E> c); c ); boolean removeall(collection<?> c); c ); boolean retainall(collection<?> c); c ); <?>: Any type (usually should conform properly, or may cause runtime type exceptions) <? extends E>: guarantees that method calls only add objects that conform to Collection s type <E> Optional Collection Methods boolean addall( Collection<? extends E> c ); boolean removeall( Collection<?> c ); boolean retainall( Collection<?> c ); void clear(); Collections do not need to fully support destructive interface methods (i.e., those that change the collection from its current state) While these methods must be implemented as part of the interface (as per usual), some of these may simply throw java.lang.unsupportedoperationexception (Note: All of the standard Java Collection classes actually do implement all of these optional methods without exceptions, however.) 9 10 The Iterable/Iterator Interfaces Looping with Iterable/Iterator public interface Iterable<T> Iterator<T> iterator(); Iterable: superinterface of Collection. Every Collection will also be Iterable, and so will have iterator() method. public static <T> void print( Collection<T> coll ) Iterator<T> itr = coll.iterator(); while ( itr.hasnext() ) T item = itr.next(); System.out.println( item ); Basic Iterator starts off before first element of Collection. Each call to next() advances the Iterator onto an actual object (and returns reference) public interface Iterator<T> boolean hasnext(); T next(); default void remove(); Type returned by iterator() method. Also an interface, so whatever is actually returned must implement that interface and its methods. As of Java 8, the remove() method is supplied by default (just throws exception, unless overridden). for ( <Type_Name> <Var_Name> : <Collection_Name> ) <Code that does something to Var_Name> public static <T> void print( Collection<T> coll ) for( T item : coll ) System.out.println( item ); Any Iterable collection allows the for-each loop style. Handy compact notation for any loop that runs over all elements in order, start to end. (Works for arrays, too!)
4 Java List Interface List is a sub-interface of Collection, and therefore implements Iterator, too Iterator and ListIterator public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> // Positional access E get( int index ); E set( int index, E element ); void add( int index, E element ); E remove( int index ); boolean addall( int index, Collection<? extends E> c ); public interface Iterator<T> boolean hasnext(); T next(); default void remove(); ListIterator<T> is a subinterface of Iterator<T>. Extra abilities to add/set objects, move backwards as well as forwards, as well as access the numeric index of any element. // Search int indexof( Object o ); int lastindexof( Object o ); ListIterator<E> listiterator(); ListIterator<E> listiterator( int index ); // Range-view List<E> sublist( int from, int to ); Adds all elements of input c, starting with index, returns true if original changed Two kinds of iterators, with default starting at front of list, other starting from index public interface ListIterator<T> extends Iterator<T> boolean hasprevious(); T previous(); void add( T x ); void set( T newval ); int nextindex(); int previousindex(); Concrete Implementation To make use of the List interface in our programs, we need an actual concrete class that implements it Two basic approaches (with many variations): Direct access (ArrayList): Store elements in an array when we implement the basic List interface Linked access (LinkedList): Store elements in a chain of nodes, not necessarily contiguous, to implement List The java.util.arraylist Class ArrayList data: size: 4 A concrete implementation of the List interface/adt, using an array under the hood, but allowing dynamic re-sizing It has two basic attributes: capacity: the array it uses, with overall holding capacity size: the number of elements currently in the list A single, contiguous block of memory for accessing data
5 Using ArrayList ArrayList<String> teams = new ArrayList<>(); teams.add( "Steelers" ); teams.add( "Giants" ); teams.add( "Packers" ); System.out.println( teams.contains( "Packers" ) ); Iterator<String> iter = teams.iterator(); while ( iter.hasnext() ) System.out.println( iter.next() ); String old = teams.set( 0, "Eagles" ); System.out.println( "Used to contain: " + old ); System.out.println( "Now contains: " + teams.get( 0 ) ); for ( String t : teams ) System.out.println( t ); Iterator-style looping set() method does 2 things: inserts element at given index and returns previously stored element from that position Iterable-style for-each looping 17 This Week Topic: Linear Structures Read: Text, chapter 03 Meetings: as usual Monday Wednesday: 2205 Centennial Friday: Lab, 16/17 Wing Homework 01: due Friday, 15 Feb. (5:00 PM) Office Hours: Wing 210 Tuesday: 3:00 PM 4:00 PM Wednesday: 9:00 AM 10:30 AM Thursday: 2:00 PM 3:00 PM Friday: 9:00 AM 10:30 AM 18 5
Converting Collections to Arrays. A Bad Approach to Array Conversion. A Better Approach to Array Conversion. public Object[] toarray();
![Converting Collections to Arrays. A Bad Approach to Array Conversion. A Better Approach to Array Conversion. public Object[] toarray(); Converting Collections to Arrays. A Bad Approach to Array Conversion. A Better Approach to Array Conversion. public Object[] toarray();](/thumbs/95/123664246.jpg) Converting Collections to Arrays Every Java collection can be converted to an array This is part of the basic Collection interface The most elementary form of this method produces an array of base-type
Converting Collections to Arrays Every Java collection can be converted to an array This is part of the basic Collection interface The most elementary form of this method produces an array of base-type
Java Collections Framework: Interfaces
 Java Collections Framework: Interfaces Introduction to the Java Collections Framework (JCF) The Comparator Interface Revisited The Collection Interface The List Interface The Iterator Interface The ListIterator
Java Collections Framework: Interfaces Introduction to the Java Collections Framework (JCF) The Comparator Interface Revisited The Collection Interface The List Interface The Iterator Interface The ListIterator
Lists. The List ADT. Reading: Textbook Sections
 Lists The List ADT Reading: Textbook Sections 3.1 3.5 List ADT A list is a dynamic ordered tuple of homogeneous elements A o, A 1, A 2,, A N-1 where A i is the i-th element of the list The position of
Lists The List ADT Reading: Textbook Sections 3.1 3.5 List ADT A list is a dynamic ordered tuple of homogeneous elements A o, A 1, A 2,, A N-1 where A i is the i-th element of the list The position of
DM550 / DM857 Introduction to Programming. Peter Schneider-Kamp
 DM550 / DM857 Introduction to Programming Peter Schneider-Kamp petersk@imada.sdu.dk http://imada.sdu.dk/~petersk/dm550/ http://imada.sdu.dk/~petersk/dm857/ ABSTRACT DATATYPES 2 Abstract Datatype (ADT)
DM550 / DM857 Introduction to Programming Peter Schneider-Kamp petersk@imada.sdu.dk http://imada.sdu.dk/~petersk/dm550/ http://imada.sdu.dk/~petersk/dm857/ ABSTRACT DATATYPES 2 Abstract Datatype (ADT)
Abstract data types (again) Announcements. Example ADT an integer bag (next) The Java Collections Framework
 Announcements Abstract data types (again) PS 5 ready Tutoring schedule updated with more hours Today s topic: The Java Collections Framework Reading: Section 7.5 An ADT is a model of a collection of data
Announcements Abstract data types (again) PS 5 ready Tutoring schedule updated with more hours Today s topic: The Java Collections Framework Reading: Section 7.5 An ADT is a model of a collection of data
Class 32: The Java Collections Framework
 Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Class 32: The Java Collections Framework Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward Goals To introduce you to the data structure classes that come
Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Class 32: The Java Collections Framework Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward Goals To introduce you to the data structure classes that come
What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data type that allows us to iterate through the elements of a collection one by one
 Iterators What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data type that allows us to iterate through the elements of a collection one by one 9-2 2-2 What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data
Iterators What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data type that allows us to iterate through the elements of a collection one by one 9-2 2-2 What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data
CMSC 202H. Containers and Iterators
 CMSC 202H Containers and Iterators Container Definition A container is a data structure whose purpose is to hold objects. Most languages support several ways to hold objects Arrays are compiler-supported
CMSC 202H Containers and Iterators Container Definition A container is a data structure whose purpose is to hold objects. Most languages support several ways to hold objects Arrays are compiler-supported
The Java Collections Framework and Lists in Java Parts 1 & 2
 The Java Collections Framework and Lists in Java Parts 1 & 2 Chapter 9 Chapter 6 (6.1-6.2.2) CS 2334 University of Oklahoma Brian F. Veale Groups of Data Data are very important to Software Engineering
The Java Collections Framework and Lists in Java Parts 1 & 2 Chapter 9 Chapter 6 (6.1-6.2.2) CS 2334 University of Oklahoma Brian F. Veale Groups of Data Data are very important to Software Engineering
Introduction to Collections
 Module 3 COLLECTIONS Introduction to Collections > A collection sometimes called a container is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. > Collections are used to store, retrieve,
Module 3 COLLECTIONS Introduction to Collections > A collection sometimes called a container is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. > Collections are used to store, retrieve,
Java Collection Framework
 Java Collection Framework Readings Purpose To provide a working knowledge of the Java Collections framework and iterators. Learning Objectives Understand the structure of the Java Collections framework
Java Collection Framework Readings Purpose To provide a working knowledge of the Java Collections framework and iterators. Learning Objectives Understand the structure of the Java Collections framework
What is the Java Collections Framework?
 1 of 13 What is the Java Collections Framework? To begin with, what is a collection?. I have a collection of comic books. In that collection, I have Tarzan comics, Phantom comics, Superman comics and several
1 of 13 What is the Java Collections Framework? To begin with, what is a collection?. I have a collection of comic books. In that collection, I have Tarzan comics, Phantom comics, Superman comics and several
Java Review: Objects
 Outline Java review Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Interfaces Class Hierarchy, Abstract Classes, Inheritance Invariants Lists ArrayList LinkedList runtime analysis Iterators Java references 1 Exam Preparation
Outline Java review Abstract Data Types (ADTs) Interfaces Class Hierarchy, Abstract Classes, Inheritance Invariants Lists ArrayList LinkedList runtime analysis Iterators Java references 1 Exam Preparation
CONTAİNERS COLLECTİONS
 CONTAİNERS Some programs create too many objects and deal with them. In such a program, it is not feasible to declare a separate variable to hold reference to each of these objects. The proper way of keeping
CONTAİNERS Some programs create too many objects and deal with them. In such a program, it is not feasible to declare a separate variable to hold reference to each of these objects. The proper way of keeping
Vector (Java 2 Platform SE 5.0) Overview Package Class Use Tree Deprecated Index Help
 Overview Package Class Use Tree Deprecated Index Help PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS FRAMES NO FRAMES All Classes SUMMARY: NESTED FIELD CONSTR METHOD DETAIL: FIELD CONSTR METHOD Página 1 de 30 Java TM 2 Platform
Overview Package Class Use Tree Deprecated Index Help PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS FRAMES NO FRAMES All Classes SUMMARY: NESTED FIELD CONSTR METHOD DETAIL: FIELD CONSTR METHOD Página 1 de 30 Java TM 2 Platform
Generic classes & the Java Collections Framework. *Really* Reusable Code
 Generic classes & the Java Collections Framework *Really* Reusable Code First, a bit of history Since Java version 5.0, Java has borrowed a page from C++ and offers a template mechanism, allowing programmers
Generic classes & the Java Collections Framework *Really* Reusable Code First, a bit of history Since Java version 5.0, Java has borrowed a page from C++ and offers a template mechanism, allowing programmers
Iterator and For-Each Loops COMP110 - Lecture 18
 Iterator and For-Each Loops COMP110 - Lecture 18 Announcements PS3 - Paternity Test is out! Game of Thrones: Spoilers vs. No Spoilers Due Sunday at 11:59pm 400 Points - Get started early! Whiteboard Hours
Iterator and For-Each Loops COMP110 - Lecture 18 Announcements PS3 - Paternity Test is out! Game of Thrones: Spoilers vs. No Spoilers Due Sunday at 11:59pm 400 Points - Get started early! Whiteboard Hours
Important Dates. Game State and Tree. Today s topics. Game Tree and Mini-Max. Games and Mini-Max 3/20/14
 MINI-MAX USING TREES AND THE JAVA COLLECTIONS FRAMEWORK Lecture 16 CS2110 Spring 2014 2 Important Dates. April 10 --- A4 due (Connect 4, minimax, trees) April 15 --- A5 due (Exercises on different topics,
MINI-MAX USING TREES AND THE JAVA COLLECTIONS FRAMEWORK Lecture 16 CS2110 Spring 2014 2 Important Dates. April 10 --- A4 due (Connect 4, minimax, trees) April 15 --- A5 due (Exercises on different topics,
Lists and Iterators. CSSE 221 Fundamentals of Software Development Honors Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology
 Lists and Iterators CSSE 221 Fundamentals of Software Development Honors Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Announcements Should be making progress on VectorGraphics. Should have turned in CRC cards,
Lists and Iterators CSSE 221 Fundamentals of Software Development Honors Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Announcements Should be making progress on VectorGraphics. Should have turned in CRC cards,
EECS 2011 M: Fundamentals of Data Structures
 EECS 2011 M: Fundamentals of Data Structures Suprakash Datta Office: LAS 3043 Course page: http://www.eecs.yorku.ca/course/2011m Also on Moodle S. Datta (York Univ.) EECS 2011 W18 1 / 19 Iterators and
EECS 2011 M: Fundamentals of Data Structures Suprakash Datta Office: LAS 3043 Course page: http://www.eecs.yorku.ca/course/2011m Also on Moodle S. Datta (York Univ.) EECS 2011 W18 1 / 19 Iterators and
Lecture 6: ArrayList Implementation
 Lecture 6: ArrayList Implementation CS 62 Fall 2018 Alexandra Papoutsaki & William Devanny 1 Programming Assignment Weak AI/Natural Language Processing: Generate text by building frequency lists based
Lecture 6: ArrayList Implementation CS 62 Fall 2018 Alexandra Papoutsaki & William Devanny 1 Programming Assignment Weak AI/Natural Language Processing: Generate text by building frequency lists based
Section Lists and Sets
 Section 10.2 Lists and Sets IN THE PREVIOUS SECTION, we looked at the general properties of collection classes in Java. In this section, we look at some specific collection classes and how to use them.
Section 10.2 Lists and Sets IN THE PREVIOUS SECTION, we looked at the general properties of collection classes in Java. In this section, we look at some specific collection classes and how to use them.
Review: Object Diagrams for Inheritance. Type Conformance. Inheritance Structures. Car. Vehicle. Truck. Vehicle. conforms to Object
 Review: Diagrams for Inheritance - String makemodel - int mileage + (String, int) Class #3: Inheritance & Polymorphism Software Design II (CS 220): M. Allen, 25 Jan. 18 + (String, int) + void
Review: Diagrams for Inheritance - String makemodel - int mileage + (String, int) Class #3: Inheritance & Polymorphism Software Design II (CS 220): M. Allen, 25 Jan. 18 + (String, int) + void
CS61B Lecture #17. Last modified: Mon Oct 1 13:40: CS61B: Lecture #17 1
 CS61B Lecture #17 Last modified: Mon Oct 1 13:40:29 2018 CS61B: Lecture #17 1 Topics Overview of standard Java Collections classes Iterators, ListIterators Containers and maps in the abstract Amortized
CS61B Lecture #17 Last modified: Mon Oct 1 13:40:29 2018 CS61B: Lecture #17 1 Topics Overview of standard Java Collections classes Iterators, ListIterators Containers and maps in the abstract Amortized
Notes on access restrictions
 Notes on access restrictions A source code file MyClass.java is a compilation unit and can contain at most one public class. Furthermore, if there is a public class in that file, it must be called MyClass.
Notes on access restrictions A source code file MyClass.java is a compilation unit and can contain at most one public class. Furthermore, if there is a public class in that file, it must be called MyClass.
CISC 3115 TY3. C24a: Lists. Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College. 11/15/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College
 CISC 3115 TY3 C24a: Lists Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/15/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Concept of data structure Use data structures List Stack
CISC 3115 TY3 C24a: Lists Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/15/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Concept of data structure Use data structures List Stack
CSE 143 Lecture 14. Interfaces; Abstract Data Types (ADTs) reading: 9.5, 11.1; 16.4
 CSE 143 Lecture 14 Interfaces; Abstract Data Types (ADTs) reading: 9.5, 11.1; 16.4 slides adapted from Marty Stepp and Hélène Martin http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Related classes Consider classes for
CSE 143 Lecture 14 Interfaces; Abstract Data Types (ADTs) reading: 9.5, 11.1; 16.4 slides adapted from Marty Stepp and Hélène Martin http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Related classes Consider classes for
Algorithms. Produced by. Eamonn de Leastar
 Algorithms Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Collections ± Collections Architecture ± Definition ± Architecture ± Interfaces ± Collection ± List ± Set ± Map ± Iterator ± Implementations
Algorithms Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Collections ± Collections Architecture ± Definition ± Architecture ± Interfaces ± Collection ± List ± Set ± Map ± Iterator ± Implementations
} Evaluate the following expressions: 1. int x = 5 / 2 + 2; 2. int x = / 2; 3. int x = 5 / ; 4. double x = 5 / 2.
 Class #10: Understanding Primitives and Assignments Software Design I (CS 120): M. Allen, 19 Sep. 18 Java Arithmetic } Evaluate the following expressions: 1. int x = 5 / 2 + 2; 2. int x = 2 + 5 / 2; 3.
Class #10: Understanding Primitives and Assignments Software Design I (CS 120): M. Allen, 19 Sep. 18 Java Arithmetic } Evaluate the following expressions: 1. int x = 5 / 2 + 2; 2. int x = 2 + 5 / 2; 3.
Lecture 6 Collections
 Lecture 6 Collections Concept A collection is a data structure actually, an object to hold other objects, which let you store and organize objects in useful ways for efficient access Check out the java.util
Lecture 6 Collections Concept A collection is a data structure actually, an object to hold other objects, which let you store and organize objects in useful ways for efficient access Check out the java.util
Case Study: Debugging a Discovered Specification for java.util.arraylist by Using Algebraic Interpretation
 Case Study: Debugging a Discovered Specification for java.util.arraylist by Using Algebraic Interpretation Technical Report CU-CS-970-04 Johannes Henkel and Amer Diwan {henkel,diwan}@cs.colorado.edu February
Case Study: Debugging a Discovered Specification for java.util.arraylist by Using Algebraic Interpretation Technical Report CU-CS-970-04 Johannes Henkel and Amer Diwan {henkel,diwan}@cs.colorado.edu February
Collections and Iterators. Collections
 Collections and Iterators Based on the notes from David Fernandez-Baca and Steve Kautz Based on The Java Tutorial (http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/) Bryn Mawr College CS206 Intro to Data Structures
Collections and Iterators Based on the notes from David Fernandez-Baca and Steve Kautz Based on The Java Tutorial (http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/) Bryn Mawr College CS206 Intro to Data Structures
Lecture Notes Chapter #9 Summery. Inheritance
 Lecture Notes Chapter #9 Summery Inheritance Subclass inherits all members of its superclass except its constructors methods inherited from a superclass can overridden in the subclass o a method overrides
Lecture Notes Chapter #9 Summery Inheritance Subclass inherits all members of its superclass except its constructors methods inherited from a superclass can overridden in the subclass o a method overrides
Taking Stock. IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 7. (A subset of) the Collections Interface. The Java Collections Interfaces
 Taking Stock IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 7 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University January 29, 2007 Last Time Practice Some Sorting Algs
Taking Stock IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 7 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University January 29, 2007 Last Time Practice Some Sorting Algs
Generics Collection Framework
 Generics Collection Framework Sisoft Technologies Pvt Ltd SRC E7, Shipra Riviera Bazar, Gyan Khand-3, Indirapuram, Ghaziabad Website: www.sisoft.in Email:info@sisoft.in Phone: +91-9999-283-283 Generics
Generics Collection Framework Sisoft Technologies Pvt Ltd SRC E7, Shipra Riviera Bazar, Gyan Khand-3, Indirapuram, Ghaziabad Website: www.sisoft.in Email:info@sisoft.in Phone: +91-9999-283-283 Generics
9/16/2010 CS Ananda Gunawardena
 CS 15-121 Ananda Gunawardena A collection (sometimes called a container) is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. Collections are used to store, retrieve and manipulate data,
CS 15-121 Ananda Gunawardena A collection (sometimes called a container) is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. Collections are used to store, retrieve and manipulate data,
CS Ananda Gunawardena
 CS 15-121 Ananda Gunawardena A collection (sometimes called a container) is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. Collections are used to store, retrieve and manipulate data,
CS 15-121 Ananda Gunawardena A collection (sometimes called a container) is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. Collections are used to store, retrieve and manipulate data,
An Interface with Generics
 Generics CSC207 Software Design Generics An Interface with Generics Generics class foo introduces a class with a type parameter T. introduces a type parameter that is required to be
Generics CSC207 Software Design Generics An Interface with Generics Generics class foo introduces a class with a type parameter T. introduces a type parameter that is required to be
CSE 143 Lecture 26. Advanced collection classes. (ADTs; abstract classes; inner classes; generics; iterators) read 11.1, 9.6, ,
 CSE 143 Lecture 26 Advanced collection classes (ADTs; abstract classes; inner classes; generics; iterators) read 11.1, 9.6, 15.3-15.4, 16.4-16.5 slides created by Marty Stepp, adapted by Alyssa Harding
CSE 143 Lecture 26 Advanced collection classes (ADTs; abstract classes; inner classes; generics; iterators) read 11.1, 9.6, 15.3-15.4, 16.4-16.5 slides created by Marty Stepp, adapted by Alyssa Harding
PIC 20A Collections and Data Structures
 PIC 20A Collections and Data Structures Ernest Ryu UCLA Mathematics Last edited: March 14, 2018 Introductory example How do you write a phone book program? Some programmers may yell hash table! and write
PIC 20A Collections and Data Structures Ernest Ryu UCLA Mathematics Last edited: March 14, 2018 Introductory example How do you write a phone book program? Some programmers may yell hash table! and write
Collections class Comparable and Comparator. Slides by Mark Hancock (adapted from notes by Craig Schock)
 Lecture 15 Summary Collections Framework Iterable, Collections List, Set Map Collections class Comparable and Comparator 1 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to use different types of Collections
Lecture 15 Summary Collections Framework Iterable, Collections List, Set Map Collections class Comparable and Comparator 1 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to use different types of Collections
Lecture 15 Summary. Collections Framework. Collections class Comparable and Comparator. Iterable, Collections List, Set Map
 Lecture 15 Summary Collections Framework Iterable, Collections List, Set Map Collections class Comparable and Comparator 1 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to use different types of Collections
Lecture 15 Summary Collections Framework Iterable, Collections List, Set Map Collections class Comparable and Comparator 1 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to use different types of Collections
Abstract Data Types. Data Str. Client Prog. Add. Rem. Find. Show. 01/30/03 Lecture 7 1
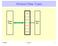 Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/30/03 Lecture 7 1 Linear Lists It is an ordered collection of elements. Lists have items, size or length. Elements may have an index. Main
Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/30/03 Lecture 7 1 Linear Lists It is an ordered collection of elements. Lists have items, size or length. Elements may have an index. Main
Functors. 01/23/03 Lecture 5 1
 Functors A functor is an object with no data and a single method. Functors can be passed as parameters. Since these classes are very small, they are usually implemented as a Nested Class wherever they
Functors A functor is an object with no data and a single method. Functors can be passed as parameters. Since these classes are very small, they are usually implemented as a Nested Class wherever they
List... NOTE We use List as illustrative example of collections Study the others from textbook!
 List... NOTE We use List as illustrative example of collections Study the others from textbook! 25 What is a List? A List is an ordered Collection (sometimes called a sequence) Lists may contain duplicate
List... NOTE We use List as illustrative example of collections Study the others from textbook! 25 What is a List? A List is an ordered Collection (sometimes called a sequence) Lists may contain duplicate
Collections and Maps
 Software and Programming I Collections and Maps Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Outline Array Lists Enhanced for Loop ArrayList and LinkedList Collection Interface Sets and
Software and Programming I Collections and Maps Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Outline Array Lists Enhanced for Loop ArrayList and LinkedList Collection Interface Sets and
DM550 Introduction to Programming part 2. Jan Baumbach.
 DM550 Introduction to Programming part 2 Jan Baumbach jan.baumbach@imada.sdu.dk http://www.baumbachlab.net Sorting Tree Balancing A sorted tree is balanced iff for each node holds: Math.abs(size(node.left)
DM550 Introduction to Programming part 2 Jan Baumbach jan.baumbach@imada.sdu.dk http://www.baumbachlab.net Sorting Tree Balancing A sorted tree is balanced iff for each node holds: Math.abs(size(node.left)
ArrayList. Introduction. java.util.arraylist
 ArrayList Introduction In this article from my free Java 8 course, I will be giving you a basic overview of the Java class java.util.arraylist. I will first explain the meaning of size and capacity of
ArrayList Introduction In this article from my free Java 8 course, I will be giving you a basic overview of the Java class java.util.arraylist. I will first explain the meaning of size and capacity of
Doubly LinkedList is Symmetrical! LinkedList Efficiency. Monday, April 8, 13. insert insert remove remove remove walk
 How Can We Improve the State of Experimental Evaluation in Computer Siene Peter Sweeney IBM Researh, TJ Watson Friday, April 12, 12:00 Kendade 307 1 Doubly LinkedList is Symmetrial! insert insert remove
How Can We Improve the State of Experimental Evaluation in Computer Siene Peter Sweeney IBM Researh, TJ Watson Friday, April 12, 12:00 Kendade 307 1 Doubly LinkedList is Symmetrial! insert insert remove
CMSC 202. Containers
 CMSC 202 Containers Container Definition A container is a data structure whose purpose is to hold objects. Most languages support several ways to hold objects. Arrays are compiler-supported containers.
CMSC 202 Containers Container Definition A container is a data structure whose purpose is to hold objects. Most languages support several ways to hold objects. Arrays are compiler-supported containers.
Collections (Collection Framework) Sang Shin Java Technology Architect Sun Microsystems, Inc.
 Collections (Collection Framework) Sang Shin Java Technology Architect Sun Microsystems, Inc. sang.shin@sun.com www.javapassion.com 2 Disclaimer & Acknowledgments Even though Sang Shin is a full-time employee
Collections (Collection Framework) Sang Shin Java Technology Architect Sun Microsystems, Inc. sang.shin@sun.com www.javapassion.com 2 Disclaimer & Acknowledgments Even though Sang Shin is a full-time employee
Agenda. Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList
 Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList Stack and queues Array-based implementations
Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList Stack and queues Array-based implementations
Abstract Data Types. Data Str. Client Prog. Add. Rem. Find. Show. 01/22/04 Lecture 4 1
 Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/22/04 Lecture 4 1 Containers Powerful tool for programming data structures Provides a library of container classes to hold your objects 2
Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/22/04 Lecture 4 1 Containers Powerful tool for programming data structures Provides a library of container classes to hold your objects 2
Generics. IRS W-9 Form
 Generics IRS W-9 Form Generics Generic class and methods. BNF notation Syntax Non-parametrized class: < class declaration > ::= "class" < identifier > ["extends" < type >] ["implements" < type list >]
Generics IRS W-9 Form Generics Generic class and methods. BNF notation Syntax Non-parametrized class: < class declaration > ::= "class" < identifier > ["extends" < type >] ["implements" < type list >]
CS 151. Exceptions & Javadoc. slides available on course website. Sunday, September 9, 12
 CS 151 Exceptions & Javadoc slides available on course website 1 Announcements Prelab 1 is due now. Please place it in the appropriate (Mon vs. Tues) box. Please attend lab this week. There may be a lecture
CS 151 Exceptions & Javadoc slides available on course website 1 Announcements Prelab 1 is due now. Please place it in the appropriate (Mon vs. Tues) box. Please attend lab this week. There may be a lecture
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 07: Linked Lists and Iterators MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Linked Lists 2 Introduction Linked List Abstract Data Type General Implementation of the ListADT
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 07: Linked Lists and Iterators MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Linked Lists 2 Introduction Linked List Abstract Data Type General Implementation of the ListADT
CS231 - Spring 2017 Linked Lists. ArrayList is an implementation of List based on arrays. LinkedList is an implementation of List based on nodes.
 CS231 - Spring 2017 Linked Lists List o Data structure which stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. o We've already seen two ways that you can store data in lists in Java.
CS231 - Spring 2017 Linked Lists List o Data structure which stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. o We've already seen two ways that you can store data in lists in Java.
package weiss.util; // Fig , pg // Fig 6.16,6.17, pg package weiss.util;
 package weiss.util; // Fig 6.9-10, pg 192-4. public interface Collection extends java.io.serializable int size( ); boolean isempty( ); boolean contains( Object x ); boolean add( Object x ); boolean remove(
package weiss.util; // Fig 6.9-10, pg 192-4. public interface Collection extends java.io.serializable int size( ); boolean isempty( ); boolean contains( Object x ); boolean add( Object x ); boolean remove(
Outline. iterator review iterator implementation the Java foreach statement testing
 Outline iterator review iterator implementation the Java foreach statement testing review: Iterator methods a Java iterator only provides two or three operations: E next(), which returns the next element,
Outline iterator review iterator implementation the Java foreach statement testing review: Iterator methods a Java iterator only provides two or three operations: E next(), which returns the next element,
Tha Java Programming Language
 Tha Java Programming Language Kozsik Tamás (2000-2001) kto@elte.hu http://www.elte.hu/~k to/ III. Arrays, collections and other baseclasses Some of the baseclasses Object String StringBuffer Integer, Double,...
Tha Java Programming Language Kozsik Tamás (2000-2001) kto@elte.hu http://www.elte.hu/~k to/ III. Arrays, collections and other baseclasses Some of the baseclasses Object String StringBuffer Integer, Double,...
Implementing a List in Java. CSC 143 Java. List Interface (review) Just an Illusion? Using an Array to Implement a List CSC
 Implementing a List in Java CSC 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Updated with Java 5.0 Generics Reading: Ch. 13 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked
Implementing a List in Java CSC 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Updated with Java 5.0 Generics Reading: Ch. 13 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked
Agenda. Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList!
 Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList! Stack and queues Array-based implementations
Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList! Stack and queues Array-based implementations
The Collections API. Lecture Objectives. The Collections API. Mark Allen Weiss
 The Collections API Mark Allen Weiss Lecture Objectives To learn how to use the Collections package in Java 1.2. To illustrate features of Java that help (and hurt) the design of the Collections API. Tuesday,
The Collections API Mark Allen Weiss Lecture Objectives To learn how to use the Collections package in Java 1.2. To illustrate features of Java that help (and hurt) the design of the Collections API. Tuesday,
The Java Collections Framework. Chapters 7.5
 The Java s Framework Chapters 7.5 Outline Introduction to the Java s Framework Iterators Interfaces, Classes and Classes of the Java s Framework Outline Introduction to the Java s Framework Iterators Interfaces,
The Java s Framework Chapters 7.5 Outline Introduction to the Java s Framework Iterators Interfaces, Classes and Classes of the Java s Framework Outline Introduction to the Java s Framework Iterators Interfaces,
Generic Programming. *Really* reusable code
 Generic Programming *Really* reusable code First, a bit of history Since Java version 5.0, Java has borrowed a page from C++ and offers a template mechanism, allowing programmers to create data structures
Generic Programming *Really* reusable code First, a bit of history Since Java version 5.0, Java has borrowed a page from C++ and offers a template mechanism, allowing programmers to create data structures
Homework 2: Imperative Due: 5:00 PM, Feb 15, 2019
 CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler Homework 2: Imperative Due: 5:00 PM, Feb 15, 2019 Contents 1 Overview of Generic/Parameterized Types 2 2 Double the Fun with Doubly-Linked Lists
CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler Homework 2: Imperative Due: 5:00 PM, Feb 15, 2019 Contents 1 Overview of Generic/Parameterized Types 2 2 Double the Fun with Doubly-Linked Lists
Lecture 8: Iterators and More Mutation
 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Contents 1 Traversing Lists 1 2 Motivating Iterators 2 3 Writing an Iterator 3 4 Writing Sum with an Iterator 4 Objectives By the end of this
Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Contents 1 Traversing Lists 1 2 Motivating Iterators 2 3 Writing an Iterator 3 4 Writing Sum with an Iterator 4 Objectives By the end of this
Framework in Java 5. DAAD project Joint Course on OOP using Java
 Topic XXX Collections Framework in Java 5 DAAD project Joint Course on OOP using Java Humboldt University Berlin, University of Novi Sad, Polytehnica University of Timisoara, University of Plovdiv, University
Topic XXX Collections Framework in Java 5 DAAD project Joint Course on OOP using Java Humboldt University Berlin, University of Novi Sad, Polytehnica University of Timisoara, University of Plovdiv, University
COMP 250. Lecture 29. interfaces. Nov. 18, 2016
 COMP 250 Lecture 29 interfaces Nov. 18, 2016 1 ADT (abstract data type) ADT s specify a set of operations, and allow us to ignore implementation details. Examples: list stack queue binary search tree priority
COMP 250 Lecture 29 interfaces Nov. 18, 2016 1 ADT (abstract data type) ADT s specify a set of operations, and allow us to ignore implementation details. Examples: list stack queue binary search tree priority
Arrays organize each data element as sequential memory cells each accessed by an index. data data data data data data data data
 1 JAVA PROGRAMMERS GUIDE LESSON 1 File: JGuiGuideL1.doc Date Started: July 10, 2000 Last Update: Jan 2, 2002 Status: proof DICTIONARIES, MAPS AND COLLECTIONS We have classes for Sets, Lists and Maps and
1 JAVA PROGRAMMERS GUIDE LESSON 1 File: JGuiGuideL1.doc Date Started: July 10, 2000 Last Update: Jan 2, 2002 Status: proof DICTIONARIES, MAPS AND COLLECTIONS We have classes for Sets, Lists and Maps and
List ADT. Announcements. The List interface. Implementing the List ADT
 Announcements Tutoring schedule revised Today s topic: ArrayList implementation Reading: Section 7.2 Break around 11:45am List ADT A list is defined as a finite ordered sequence of data items known as
Announcements Tutoring schedule revised Today s topic: ArrayList implementation Reading: Section 7.2 Break around 11:45am List ADT A list is defined as a finite ordered sequence of data items known as
11-1. Collections. CSE 143 Java. Java 2 Collection Interfaces. Goals for Next Several Lectures
 Collections CSE 143 Java Collections Most programs need to store and access collections of data Collections are worth studying because... They are widely useful in programming They provide examples of
Collections CSE 143 Java Collections Most programs need to store and access collections of data Collections are worth studying because... They are widely useful in programming They provide examples of
COMP-202. Generics. COMP Generics, 2013 Jörg Kienzle and others
 COMP-202 Generics Objects and Casting Generics Instantiation Usage ArrayList Iterators Iterator Lecture Outline 2 Objects and Casting All instances of all classes in Java are also of the class Object
COMP-202 Generics Objects and Casting Generics Instantiation Usage ArrayList Iterators Iterator Lecture Outline 2 Objects and Casting All instances of all classes in Java are also of the class Object
+ Abstract Data Types
 Linked Lists Abstract Data Types An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is: a set of values a set of operations Sounds familiar, right? I gave a similar definition for a data structure. Abstract Data Types Abstract
Linked Lists Abstract Data Types An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is: a set of values a set of operations Sounds familiar, right? I gave a similar definition for a data structure. Abstract Data Types Abstract
Topic #9: Collections. Readings and References. Collections. Collection Interface. Java Collections CSE142 A-1
 Topic #9: Collections CSE 413, Autumn 2004 Programming Languages http://www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/413/04au/ If S is a subtype of T, what is S permitted to do with the methods of T? Typing
Topic #9: Collections CSE 413, Autumn 2004 Programming Languages http://www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/413/04au/ If S is a subtype of T, what is S permitted to do with the methods of T? Typing
CS61B Lecture #17. Administrative: Need alternative test time? Make sure you send me mail.
 Administrative: CS61B Lecture #17 Need alternative test time? Make sure you send me mail. Last modified: Fri Oct 18 14:48:51 2013 CS61B: Lecture #17 1 Topics Overview of standard Java Collections classes.
Administrative: CS61B Lecture #17 Need alternative test time? Make sure you send me mail. Last modified: Fri Oct 18 14:48:51 2013 CS61B: Lecture #17 1 Topics Overview of standard Java Collections classes.
DM550 Introduction to Programming part 2. Jan Baumbach.
 DM550 Introduction to Programming part 2 Jan Baumbach jan.baumbach@imada.sdu.dk http://www.baumbachlab.net MULTIVARIATE TREES 2 Multivariate Trees general class of trees nodes can have any number of children
DM550 Introduction to Programming part 2 Jan Baumbach jan.baumbach@imada.sdu.dk http://www.baumbachlab.net MULTIVARIATE TREES 2 Multivariate Trees general class of trees nodes can have any number of children
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 28 April 2, 2014 Generics and CollecCons Midterm 2 is Friday Announcements Towne 100 last names A - L DRLB A1 last names M - Z Review sessions: Tonight!
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 28 April 2, 2014 Generics and CollecCons Midterm 2 is Friday Announcements Towne 100 last names A - L DRLB A1 last names M - Z Review sessions: Tonight!
Topics. CS61B Lecture #17. Collection Structures in java.util. Data Types in the Abstract
 CS61B Lecture #17 Topics Administrative: Need alternative test time? Make sure you send me mail. Overview of standard Java Collections classes. Iterators, ListIterators Containers and maps in the abstract
CS61B Lecture #17 Topics Administrative: Need alternative test time? Make sure you send me mail. Overview of standard Java Collections classes. Iterators, ListIterators Containers and maps in the abstract
Data structure is an organization of information, usually in memory, for better algorithm efficiency.
 Lecture 01 Introduction Wednesday, 29 July 2015 12:59 pm Data structure is an organization of information, usually in memory, for better algorithm efficiency. Abstract data types (ADTs) are a model for
Lecture 01 Introduction Wednesday, 29 July 2015 12:59 pm Data structure is an organization of information, usually in memory, for better algorithm efficiency. Abstract data types (ADTs) are a model for
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 27 Mar 23, 2012 Generics, CollecBons and IteraBon Announcements CIS Course Faire TODAY at 3PM, here HW08 is due on Monday, at 11:59:59pm Midterm 2
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 27 Mar 23, 2012 Generics, CollecBons and IteraBon Announcements CIS Course Faire TODAY at 3PM, here HW08 is due on Monday, at 11:59:59pm Midterm 2
11/2/ Dynamic Data Structures & Generics. Objectives. Array-Based Data Structures: Outline. Harald Gall, Prof. Dr.
 12. Dynamic Data Structures & Generics Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch Objectives! Define and use an instance of ArrayList! Describe general idea
12. Dynamic Data Structures & Generics Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch Objectives! Define and use an instance of ArrayList! Describe general idea
Module 11. Collections and Iterators. Adapted from Absolute Java, Rose Williams, Binghamton University
 Module 11 Collections and Iterators Adapted from Absolute Java, Rose Williams, Binghamton University Parameterized Classes and Generics Beginning with version 5.0, Java allows class and method definitions
Module 11 Collections and Iterators Adapted from Absolute Java, Rose Williams, Binghamton University Parameterized Classes and Generics Beginning with version 5.0, Java allows class and method definitions
JAVA COLLECTION FRAMEWORK & SETS
 JAVA COLLECTION FRAMEWORK & SETS Ch07.4-5 & Ch10.5 Presentation for use with the textbook 1. Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser,
JAVA COLLECTION FRAMEWORK & SETS Ch07.4-5 & Ch10.5 Presentation for use with the textbook 1. Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser,
2. The actual object type stored in an object of type CollectionClassName<E> is specified when the object is created.
 1. Because an ArrayList is an indexed collection, you can access its elements using a subscript. 2. The actual object type stored in an object of type CollectionClassName is specified when the object
1. Because an ArrayList is an indexed collection, you can access its elements using a subscript. 2. The actual object type stored in an object of type CollectionClassName is specified when the object
Week 4, Wednesday (Spring 2015). Dr. Yoder. Sec 051. Page 1 of 5
 CS2852 Exam 1 Name: No note-sheets, calculators, or other study aids on this exam. Write your initials at the top of each page except this one. Read through the whole exam before you get started. Have
CS2852 Exam 1 Name: No note-sheets, calculators, or other study aids on this exam. Write your initials at the top of each page except this one. Read through the whole exam before you get started. Have
Type Parameters: E - the type of elements returned by this iterator Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description
 java.lang Interface Iterable Type Parameters: T - the type of elements returned by the iterator Iterator iterator() Returns an iterator over a set of elements of type T. java.util Interface Iterator
java.lang Interface Iterable Type Parameters: T - the type of elements returned by the iterator Iterator iterator() Returns an iterator over a set of elements of type T. java.util Interface Iterator
[TAP:PMUHE] Stack vs Queue
![[TAP:PMUHE] Stack vs Queue [TAP:PMUHE] Stack vs Queue](/thumbs/84/89362039.jpg) [TAP:PMUHE] Stack vs Queue A Singly Linked List can be used to implement which of the following A. List B. Stack C. Queue D. B and C E. Whatever 1 Administrative Details Midterm and lab scores (4 and 5)
[TAP:PMUHE] Stack vs Queue A Singly Linked List can be used to implement which of the following A. List B. Stack C. Queue D. B and C E. Whatever 1 Administrative Details Midterm and lab scores (4 and 5)
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 8: for Loops, Nested Loops and Arrays Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 8: for Loops, Nested Loops and Arrays Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Review What is the difference between a while loop and an if statement? What is an off-by-one
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 8: for Loops, Nested Loops and Arrays Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Review What is the difference between a while loop and an if statement? What is an off-by-one
Collection Interfaces
 CJ7V2.book Page 85 Wednesday, October 27, 2004 2:32 PM 2 Collections COLLECTION INTERFACES CONCRETE COLLECTIONS THE COLLECTIONS FRAMEWORK ALGORITHMS LEGACY COLLECTIONS Object-oriented programming (OOP)
CJ7V2.book Page 85 Wednesday, October 27, 2004 2:32 PM 2 Collections COLLECTION INTERFACES CONCRETE COLLECTIONS THE COLLECTIONS FRAMEWORK ALGORITHMS LEGACY COLLECTIONS Object-oriented programming (OOP)
JCF: user defined collections
 JCF: user defined collections Bruce Eckel, Thinking in Java, 4th edition, PrenticeHall, New Jersey, cf. http://mindview.net/books/tij4 jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 20-1 Developing of a user-defined
JCF: user defined collections Bruce Eckel, Thinking in Java, 4th edition, PrenticeHall, New Jersey, cf. http://mindview.net/books/tij4 jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 20-1 Developing of a user-defined
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall Office hours:
 CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
List ADT. B/W Confirming Pages
 wu3399_ch8.qxd //7 :37 Page 98 8 List ADT O b j e c t i v e s After you have read and studied this chapter, you should be able to Describe the key features of the List ADT. the List ADT using an array
wu3399_ch8.qxd //7 :37 Page 98 8 List ADT O b j e c t i v e s After you have read and studied this chapter, you should be able to Describe the key features of the List ADT. the List ADT using an array
Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton
 Principles of So3ware Construc9on: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Part 1: Designing classes Design pacerns for reuse (con9nued) and design heuris9cs Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science
Principles of So3ware Construc9on: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Part 1: Designing classes Design pacerns for reuse (con9nued) and design heuris9cs Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science
Two Types of Types. Primitive Types in Java. Using Primitive Variables. Class #07: Java Primitives. Integer types.
 Class #07: Java Primitives Software Design I (CS 120): M. Allen, 13 Sep. 2018 Two Types of Types So far, we have mainly been dealing with objects, like DrawingGizmo, Window, Triangle, that are: 1. Specified
Class #07: Java Primitives Software Design I (CS 120): M. Allen, 13 Sep. 2018 Two Types of Types So far, we have mainly been dealing with objects, like DrawingGizmo, Window, Triangle, that are: 1. Specified
Programmieren II. Polymorphism. Alexander Fraser. June 4, (Based on material from T. Bögel)
 Programmieren II Polymorphism Alexander Fraser fraser@cl.uni-heidelberg.de (Based on material from T. Bögel) June 4, 2014 1 / 50 Outline 1 Recap - Collections 2 Advanced OOP: Polymorphism Polymorphism
Programmieren II Polymorphism Alexander Fraser fraser@cl.uni-heidelberg.de (Based on material from T. Bögel) June 4, 2014 1 / 50 Outline 1 Recap - Collections 2 Advanced OOP: Polymorphism Polymorphism
Lecture 4. The Java Collections Framework
 Lecture 4. The Java s Framework - 1 - Outline Introduction to the Java s Framework Iterators Interfaces, Classes and Classes of the Java s Framework - 2 - Learning Outcomes From this lecture you should
Lecture 4. The Java s Framework - 1 - Outline Introduction to the Java s Framework Iterators Interfaces, Classes and Classes of the Java s Framework - 2 - Learning Outcomes From this lecture you should
Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher
 Principles of So3ware Construc9on: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Part 2: Class-level design Design paderns for reuse, part 2 Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher 1 Administrivia Reading due today:
Principles of So3ware Construc9on: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Part 2: Class-level design Design paderns for reuse, part 2 Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher 1 Administrivia Reading due today:
BlockingArrayQueue.java. Page 1
 1 //BlockingArrayQueue.java 2 //Template blocking queue class, implemented with emulated circular array. 3 //Programmer: Randy Miller 4 //Last modification: April 13, 2015 5 6 7 8 import java.util.arraylist;
1 //BlockingArrayQueue.java 2 //Template blocking queue class, implemented with emulated circular array. 3 //Programmer: Randy Miller 4 //Last modification: April 13, 2015 5 6 7 8 import java.util.arraylist;
Generic Programming Recursive Binary Search SESSION 9. Programming Languages for Objects
 SESSION 9 Programming Languages for Objects Generic Programming Lists and Sets Maps Programming with the Java Collection Framework Writing Generic Classes and Methods Generic Programming.1.1 Recursive
SESSION 9 Programming Languages for Objects Generic Programming Lists and Sets Maps Programming with the Java Collection Framework Writing Generic Classes and Methods Generic Programming.1.1 Recursive
