The Nervous Shapes Example
|
|
|
- Joan Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Nervous Shapes Example This Example is taken from Dr. King s Java book 1
2 11.6 Abstract Classes Some classes are purely artificial, created solely so that subclasses can take advantage of inheritance. The Vehicle class was created for convenience in the real world, there are no generic vehicles, only specific types of vehicles. The same reasoning applies to the Account class: banks offer only specific kinds of accounts. In Java, artificial classes like Vehicle and Account are called abstract classes. 2
3 Characteristics of Abstract Classes The declaration of an abstract class must include the word abstract, which is usually placed just before the word class. Some of the methods in an abstract class may be abstract methods. An abstract method is a dummy method that has no body: public abstract double doublevalue(); It is illegal to create an instance of an abstract class. 3
4 Uses of Abstract Classes Abstract classes are useful only as starting points for defining subclasses. They often arise from bottom-up design, where the strategy is to first identify which classes are needed and then look for ways to factor out whatever those classes have in common. The result is an abstract class that can be extended to create the classes that are actually needed. 4
5 Example: A Shape Class Suppose that the need arises for a series of classes that represent specific geometric shapes, such as Circle and Rectangle. These classes have much in common, so work can be saved by first creating a generic Shape class. No Shape objects will ever be created. Instead, the Shape class will serve solely as a starting point for defining more-specific shape classes. 5
6 Example: A Shape Class Shape will have instance variables representing the properties that are common to all shapes: Location (a pair of x and y coordinates) Color (a Color object) Every shape will also have a width and a height. It might not be a good idea for the Shape class to have width and height variables, which would force all subclasses to inherit these variables. Some subclasses, such as Circle, won t need these variables. 6
7 Example: A Shape Class Shape will have instance methods representing the behaviors that are common to all shapes: draw move getx, gety, getcolor, getwidth, getheight setcolor The draw, getheight, and getwidth methods will have to be abstract they can t be written without knowing what kind of shape is involved. 7
8 Shape.java // Represents a geometric shape that can be displayed in a // graphics context import java.awt.*; public abstract class Shape { // Instance variables private int x; private int y; private Color color; // Constructor protected Shape(int x, int y, Color color) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.color = color; 8
9 // Abstract methods public abstract void draw(graphics g); public abstract int getheight(); public abstract int getwidth(); // Other instance methods public Color getcolor() { return color; public int getx() { return x; public int gety() { return y; 9
10 public void move(int dx, int dy) { x += dx; y += dy; public void setcolor(color color) { this.color = color; 10
11 The Circle Class The Circle class will need a diameter instance variable. Circle will need to override the abstract methods that were inherited from the Shape class: draw, getheight, and getwidth. 11
12 Circle.java // Represents a circle that can be displayed in a graphics // context import java.awt.*; public class Circle extends Shape { // Instance variables private int diameter; // Constructor public Circle(int x, int y, Color color, int diameter) { super(x, y, color); this.diameter = diameter; 12
13 // Instance methods public void draw(graphics g) { g.setcolor(getcolor()); g.filloval(getx(), gety(), diameter, diameter); public int getheight() { return diameter; public int getwidth() { return diameter; 13
14 The Rectangle Class The Rectangle class will need width and height instance variables. Like the Circle class, Rectangle will need to override the draw, getheight, and getwidth methods. 14
15 Rectangle.java // Represents a rectangle that can be displayed in a graphics // context import java.awt.*; public class Rectangle extends Shape { // Instance variables private int width; private int height; // Constructor public Rectangle(int x, int y, Color color, int width, int height) { super(x, y, color); this.width = width; this.height = height; 15
16 // Instance methods public void draw(graphics g) { g.setcolor(getcolor()); g.fillrect(getx(), gety(), width, height); public int getheight() { return height; public int getwidth() { return width; 16
17 11.9 Case Study: Nervous Shapes The NervousShapes program will create a frame containing a random mixture of circles and rectangles with random colors, sizes, and positions. After a brief delay, the shapes will be moved to slightly different positions, with the direction of motion for each shape chosen randomly. 17
18 Program Behavior The new x coordinate for each shape will either be the same as the old x coordinate, one pixel smaller, or one pixel larger. The new y coordinate will be computed in a similar manner. The size of the frame s drawing area will be fixed at 200 pixels by 200 pixels. The number of shapes displayed will be 50. The delay time the interval between animation cycles will be 10 milliseconds. 18
19 Program Behavior 19
20 Design of the NervousShapes Program The program will consist of three steps: 1. Create a frame labeled Nervous Shapes. 2. Create 50 random Circle and Rectangle objects. 3. Display the shapes within an animation loop. Each step will be done by a helper method. The helper methods will be named createwindow, createshapes, and animateshapes. createwindow is easy to write. 20
21 The createshapes Method createshapes will need a shapes array in which to store the 50 shapes that it creates. Because animateshapes will also need access to the shapes array, it will be a class variable. shapes will be declared as an array of Shape objects so that it can store both Circle objects and Rectangle objects. 21
22 The createshapes Method createshapes will execute the following steps 50 times: 1. Select a color in which each component is a random number between 0 and Decide whether the new shape will be a circle or a rectangle. 3. If it s a circle, choose a random diameter between 10 and 20, choose a random position, create a Circle object, and store it in the shapes array. If it s a rectangle, choose a random width and height between 10 and 20, choose a random position, create a Rectangle object, and store it in the shapes array. 22
23 The animateshapes Method animateshapes will consist of an infinite loop that repeats the following steps: 1. Clear the frame s drawing area. 2. Move each shape in the shapes array to a new position and display it. The new x coordinate for each shape will be the same as the old one, one pixel smaller, or one pixel larger; the new y coordinate is computed in a similar fashion. A move is not performed if it would cause any part of the shape to go outside the frame s drawing area. 3. Call repaint to update the screen. 4. Pause briefly. 23
24 The animateshapes Method To display element i of the shapes array, animateshapes will call the draw method: shapes[i].draw(g); Thanks to dynamic binding, there s no need to test whether shapes[i] is a Circle object or a Rectangle object before calling draw. 24
25 The generaterandomint Method One more helper is needed: generaterandomint, which returns an integer chosen randomly from a specified range of integers. 25
26 NervousShapes.java // Program name: NervousShapes // Author: K. N. King // Written: // // Displays a frame containing a random mixture of circles // and rectangles with random colors, sizes, and positions. // The shapes periodically change position, with the // direction of motion chosen randomly for each shape. The // new x coordinate for each shape will either be the same // as the old x coordinate, one pixel smaller, or one pixel // larger; the new y coordinate will be computed in a // similar manner. Shapes will be constrained so that they // do not move outside the drawing area. import java.awt.*; import jpb.*; 26
27 public class NervousShapes { // Constants private static final int DELAY = 10; // Animation delay (milliseconds) private static final int MAX_SIZE = 20; // Maximum width and height of a shape private static final int MIN_SIZE = 10; // Minimum width and height of a shape private static final int NUM_SHAPES = 50; // Number of shapes private static final int WINDOW_SIZE = 200; // Width and height of drawable portion of frame // Class variables private static DrawableFrame df; // Frame in which shapes are displayed private static Graphics g; // Graphics context for frame private static Shape shapes[] = new Shape[NUM_SHAPES]; // Array of shapes 27
28 public static void main(string[] args) { createwindow(); createshapes(); animateshapes(); 28
29 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // NAME: createwindow // BEHAVIOR: Creates a frame labeled "Nervous Shapes", // displays the frame, and sets the size of // the frame (using the WINDOW_SIZE class // variable). Assigns the frame to the df // class variable, and assigns the frame's // graphics context to the g class variable. // PARAMETERS: None // RETURNS: Nothing /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// private static void createwindow() { // Create a frame labeled "Nervous Shapes" and set its // size df = new DrawableFrame("Nervous Shapes"); df.show(); df.setsize(window_size, WINDOW_SIZE); // Get the frame's graphics context g = df.getgraphicscontext(); 29
30 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // NAME: createshapes // BEHAVIOR: Creates enough Circle and Rectangle objects // to fill the shapes array. Each shape has a // random color, size, and position. The height // and width of each shape must lie between // MIN_SIZE and MAX_SIZE (inclusive). The // position is chosen so that the shape is // completely within the drawing area. // PARAMETERS: None // RETURNS: Nothing /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// private static void createshapes() { for (int i = 0; i < shapes.length; i++) { // Select a random color int red = generaterandomint(0, 255); int green = generaterandomint(0, 255); int blue = generaterandomint(0, 255); Color color = new Color(red, green, blue); 30
31 // Decide whether to create a circle or a rectangle if (Math.random() < 0.5) { // Generate a circle with a random size and position int diameter = generaterandomint(min_size, MAX_SIZE); int x = generaterandomint(0, WINDOW_SIZE - diameter); int y = generaterandomint(0, WINDOW_SIZE - diameter); shapes[i] = new Circle(x, y, color, diameter); else { // Generate a rectangle with a random size and // position int width = generaterandomint(min_size, MAX_SIZE); int height = generaterandomint(min_size, MAX_SIZE); int x = generaterandomint(0, WINDOW_SIZE - width); int y = generaterandomint(0, WINDOW_SIZE - height); shapes[i] = new Rectangle(x, y, color, width, height); 31
32 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // NAME: animateshapes // BEHAVIOR: Establishes an infinite loop in which the // shapes are animated. During each loop // iteration, the drawing area is cleared and // the shapes are then drawn at new positions. // The new x and y coordinates for each shape // will either be the same as the old ones, // one pixel smaller, or one pixel larger. A // shape is not moved if doing so would cause // any portion of the shape to go outside the // drawing area. At the end of each animation // cycle, there is a brief pause, which is // controlled by the delay constant. // PARAMETERS: None // RETURNS: Nothing /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// private static void animateshapes() { while (true) { // Clear drawing area g.setcolor(color.white); g.fillrect(0, 0, WINDOW_SIZE - 1, WINDOW_SIZE - 1); 32
33 for (int i = 0; i < shapes.length; i++) { // Change the x coordinate for shape i int dx = generaterandomint(-1, +1); int newx = shapes[i].getx() + dx; if (newx >= 0 && newx + shapes[i].getwidth() < WINDOW_SIZE) shapes[i].move(dx, 0); // Change the y coordinate for shape i int dy = generaterandomint(-1, +1); int newy = shapes[i].gety() + dy; if (newy >= 0 && newy + shapes[i].getheight() < WINDOW_SIZE) shapes[i].move(0, dy); // Draw shape i at its new position shapes[i].draw(g); // Call repaint to update the screen df.repaint(); 33
34 // Pause briefly try { Thread.sleep(DELAY); catch (InterruptedException e) { /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // NAME: generaterandomint // BEHAVIOR: Generates a random integer within a // specified range. // PARAMETERS: min - the lower bound of the range // max - the upper bound of the range // RETURNS: A random integer that is greater than or // equal to min and less than or equal to max /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// private static int generaterandomint(int min, int max) { return (int) ((max - min + 1) * Math.random()) + min; 34
35 Demo Source code is in your D2L account 35
On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle
 Berner Fachhochschule Engineering and Information Technology On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle Prof. Dr. Eric Dubuis Berner Fachhochschule, Engineering and Information Technology @ Biel Course
Berner Fachhochschule Engineering and Information Technology On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle Prof. Dr. Eric Dubuis Berner Fachhochschule, Engineering and Information Technology @ Biel Course
Polymorphism: Interfaces and Iteration. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Polymorphism: Interfaces and Iteration Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline A shape object hierarchy Classes that extend Versus classes that implements Java interfaces How Java handles multiple-inheritance
Polymorphism: Interfaces and Iteration Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline A shape object hierarchy Classes that extend Versus classes that implements Java interfaces How Java handles multiple-inheritance
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle
 On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle Prof. Dr. Eric Dubuis Berner Fachhochschule, @ Biel Course "UML and Design Patterns" of module "Software Engineering and Design", version March 2008 BFH/TI/Software
On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle Prof. Dr. Eric Dubuis Berner Fachhochschule, @ Biel Course "UML and Design Patterns" of module "Software Engineering and Design", version March 2008 BFH/TI/Software
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004
 First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: JSP Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: JSP Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
Interfaces and itera-on. CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen
 Interfaces and itera-on CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Overview A shape object hierarchy Classes that extend Versus classes that implements Java interfaces How Java handles
Interfaces and itera-on CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Overview A shape object hierarchy Classes that extend Versus classes that implements Java interfaces How Java handles
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004
 First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: Standard Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: Standard Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
Chapter 6: Inheritance
 Chapter 6: Inheritance EECS 1030 moodle.yorku.ca State of an object final int WIDTH = 3; final int HEIGTH = 4; final int WEIGHT = 80; GoldenRectangle rectangle = new GoldenRectangle(WIDTH, HEIGHT, WEIGHT);
Chapter 6: Inheritance EECS 1030 moodle.yorku.ca State of an object final int WIDTH = 3; final int HEIGTH = 4; final int WEIGHT = 80; GoldenRectangle rectangle = new GoldenRectangle(WIDTH, HEIGHT, WEIGHT);
Objects and Classes (1)
 Objects and Classes (1) Reading: Classes (interface, implementation, garbage collection) http://moodle.cs.man.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=81 Interface Examples Creating and using objects of existing classes
Objects and Classes (1) Reading: Classes (interface, implementation, garbage collection) http://moodle.cs.man.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=81 Interface Examples Creating and using objects of existing classes
ICS 4U. Introduction to Programming in Java. Chapter 10 Notes
 ICS 4U Introduction to Programming in Java Chapter 10 Notes Classes and Inheritance In Java all programs are classes, but not all classes are programs. A standalone application is a class that contains
ICS 4U Introduction to Programming in Java Chapter 10 Notes Classes and Inheritance In Java all programs are classes, but not all classes are programs. A standalone application is a class that contains
Chapter 21- Using Generics Case Study: Geometric Bunch. Class: Driver. package csu.matos; import java.util.arraylist; public class Driver {
 Chapter 21- Using Generics Case Study: Geometric Bunch In this example a class called GeometricBunch is made to wrap around a list of GeometricObjects. Circle and Rectangle are subclasses of GeometricObject.
Chapter 21- Using Generics Case Study: Geometric Bunch In this example a class called GeometricBunch is made to wrap around a list of GeometricObjects. Circle and Rectangle are subclasses of GeometricObject.
COMP 401 Fall Recitation 6: Inheritance
 COMP 401 Fall 2017 Recitation 6: Inheritance Agenda Brief Review of Inheritance Examples of extending existing classes Exercises and Quiz 2 High-level Classes are Abstract Data Types We can define a set
COMP 401 Fall 2017 Recitation 6: Inheritance Agenda Brief Review of Inheritance Examples of extending existing classes Exercises and Quiz 2 High-level Classes are Abstract Data Types We can define a set
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Spring Semester, ENCE 688R: Midterm Exam: 1 1/2 Hours, Open Book and Open Notes
 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Spring Semester, 2013 ENCE 688R: Midterm Exam: 1 1/2 Hours, Open Book and Open Notes Name : Question Points Score 1 30 2 30 3 40 Total 100 1 Question
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Spring Semester, 2013 ENCE 688R: Midterm Exam: 1 1/2 Hours, Open Book and Open Notes Name : Question Points Score 1 30 2 30 3 40 Total 100 1 Question
8359 Object-oriented Programming with Java, Part 2. Stephen Pipes IBM Hursley Park Labs, United Kingdom
 8359 Object-oriented Programming with Java, Part 2 Stephen Pipes IBM Hursley Park Labs, United Kingdom Dallas 2003 Intro to Java recap Classes are like user-defined types Objects are like variables of
8359 Object-oriented Programming with Java, Part 2 Stephen Pipes IBM Hursley Park Labs, United Kingdom Dallas 2003 Intro to Java recap Classes are like user-defined types Objects are like variables of
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2)
 Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
1B1b Inheritance. Inheritance. Agenda. Subclass and Superclass. Superclass. Generalisation & Specialisation. Shapes and Squares. 1B1b Lecture Slides
 1B1b Inheritance Agenda Introduction to inheritance. How Java supports inheritance. Inheritance is a key feature of object-oriented oriented programming. 1 2 Inheritance Models the kind-of or specialisation-of
1B1b Inheritance Agenda Introduction to inheritance. How Java supports inheritance. Inheritance is a key feature of object-oriented oriented programming. 1 2 Inheritance Models the kind-of or specialisation-of
INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Inheritance Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket Extremely common in modern OOP languages Managing
INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Inheritance Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket Extremely common in modern OOP languages Managing
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap. Inheritance & Polymorphism 1
 Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Outline. Inheritance. Abstract Classes Interfaces. Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism.
 Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 26 March 26, 2015 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch Chapter 24 public interface Displaceable { public int getx(); public int gety(); public void move
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 26 March 26, 2015 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch Chapter 24 public interface Displaceable { public int getx(); public int gety(); public void move
Inheritance and objects
 Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket
Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket
TWO-DIMENSIONAL FIGURES
 TWO-DIMENSIONAL FIGURES Two-dimensional (D) figures can be rendered by a graphics context. Here are the Graphics methods for drawing draw common figures: java.awt.graphics Methods to Draw Lines, Rectangles
TWO-DIMENSIONAL FIGURES Two-dimensional (D) figures can be rendered by a graphics context. Here are the Graphics methods for drawing draw common figures: java.awt.graphics Methods to Draw Lines, Rectangles
Final Exam May 21, 2003
 1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Final Exam May 21, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have three hours to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Final Exam May 21, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have three hours to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need
Extending Classes (contd.) (Chapter 15) Questions:
 Extending Classes (contd.) (Chapter 15) Questions: 1 1. The following C++ program compiles without any problems. When run, it even prints out the hello called for in line (B) of main. But subsequently
Extending Classes (contd.) (Chapter 15) Questions: 1 1. The following C++ program compiles without any problems. When run, it even prints out the hello called for in line (B) of main. But subsequently
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
OBJECT ORİENTATİON ENCAPSULATİON
 OBJECT ORİENTATİON Software development can be seen as a modeling activity. The first step in the software development is the modeling of the problem we are trying to solve and building the conceptual
OBJECT ORİENTATİON Software development can be seen as a modeling activity. The first step in the software development is the modeling of the problem we are trying to solve and building the conceptual
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
CS 120 Fall 2008 Practice Final Exam v1.0m. Name: Model Solution. True/False Section, 20 points: 10 true/false, 2 points each
 CS 120 Fall 2008 Practice Final Exam v1.0m Name: Model Solution True/False Section, 20 points: 10 true/false, 2 points each Multiple Choice Section, 32 points: 8 multiple choice, 4 points each Code Tracing
CS 120 Fall 2008 Practice Final Exam v1.0m Name: Model Solution True/False Section, 20 points: 10 true/false, 2 points each Multiple Choice Section, 32 points: 8 multiple choice, 4 points each Code Tracing
Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects
 Unit 5, Part 1 Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Types of Decomposition When writing a program, it's important
Unit 5, Part 1 Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Types of Decomposition When writing a program, it's important
RECITATION 4. Casting and graphics (with ObjectEditor)
 RECITATION 4 Casting and graphics (with ObjectEditor) CASTING Changing the type of one variable into another type Cast a variable by adding the new type in parentheses before the variable Example: int
RECITATION 4 Casting and graphics (with ObjectEditor) CASTING Changing the type of one variable into another type Cast a variable by adding the new type in parentheses before the variable Example: int
Java and OOP. Part 3 Extending classes. OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1
 Java and OOP Part 3 Extending classes OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1 Inheritance Suppose we want a version of an existing class, which is slightly different from it. We want to avoid starting again
Java and OOP Part 3 Extending classes OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1 Inheritance Suppose we want a version of an existing class, which is slightly different from it. We want to avoid starting again
Abstract Class. Lecture 21. Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof
 Abstract Class Lecture 21 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Abstract Class Abstract class is a class with one or more abstract methods. The abstract method Method signature without implementation
Abstract Class Lecture 21 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Abstract Class Abstract class is a class with one or more abstract methods. The abstract method Method signature without implementation
CS 3331 Advanced Object-Oriented Programming Exam 1
 1 Fall 2015 (Thursday, October 22) Name: CS 3331 Advanced Object-Oriented Programming Exam 1 This test has 13 questions and pages numbered 1 through 9. Reminders This test is closed-notes and closed-book.
1 Fall 2015 (Thursday, October 22) Name: CS 3331 Advanced Object-Oriented Programming Exam 1 This test has 13 questions and pages numbered 1 through 9. Reminders This test is closed-notes and closed-book.
Abstract Classes. Abstract Classes a and Interfaces. Class Shape Hierarchy. Problem AND Requirements. Abstract Classes.
 a and Interfaces Class Shape Hierarchy Consider the following class hierarchy Shape Circle Square Problem AND Requirements Suppose that in order to exploit polymorphism, we specify that 2-D objects must
a and Interfaces Class Shape Hierarchy Consider the following class hierarchy Shape Circle Square Problem AND Requirements Suppose that in order to exploit polymorphism, we specify that 2-D objects must
Reusing Classes. Hendrik Speleers
 Hendrik Speleers Overview Composition Inheritance Polymorphism Method overloading vs. overriding Visibility of variables and methods Specification of a contract Abstract classes, interfaces Software development
Hendrik Speleers Overview Composition Inheritance Polymorphism Method overloading vs. overriding Visibility of variables and methods Specification of a contract Abstract classes, interfaces Software development
CS170 Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 2
 CS170 Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 2 03/25/2009 Name: Solution You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed book and closednotes exam, and you are not to use any other resource than
CS170 Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 2 03/25/2009 Name: Solution You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed book and closednotes exam, and you are not to use any other resource than
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Interface Abstract data types Version of January 26, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are meant
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Interface Abstract data types Version of January 26, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are meant
+ Inheritance. Sometimes we need to create new more specialized types that are similar to types we have already created.
 + Inheritance + Inheritance Classes that we design in Java can be used to model some concept in our program. For example: Pokemon a = new Pokemon(); Pokemon b = new Pokemon() Sometimes we need to create
+ Inheritance + Inheritance Classes that we design in Java can be used to model some concept in our program. For example: Pokemon a = new Pokemon(); Pokemon b = new Pokemon() Sometimes we need to create
CSE 8B Programming Assignments Spring Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3:
 PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT 3: Read Savitch: Chapter 7 Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3: ShapeP3.java PointP3.java CircleP3.java RectangleP3.java TriangleP3.java
PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT 3: Read Savitch: Chapter 7 Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3: ShapeP3.java PointP3.java CircleP3.java RectangleP3.java TriangleP3.java
Topic 9 More Graphics. Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from
 Topic 9 More Graphics Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ Clicker Question What happens if a graphics object is used to draw a shape that exceeds the
Topic 9 More Graphics Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ Clicker Question What happens if a graphics object is used to draw a shape that exceeds the
Programming in the Large II: Objects and Classes (Part 2)
 Programming in the Large II: Objects and Classes (Part 2) 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen
Programming in the Large II: Objects and Classes (Part 2) 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen
Classes. Integer Division. Thursday, October 23, March 13, 2008
 Classes March 13, 2008 1 Integer Division private static final int FACE_SIZE = HEAD_SIZE * (4/5); WARNING! FACE_SIZE is not 80% of the HEAD_SIZE! 4 and 5 are integers 4 / 5 is integer division and results
Classes March 13, 2008 1 Integer Division private static final int FACE_SIZE = HEAD_SIZE * (4/5); WARNING! FACE_SIZE is not 80% of the HEAD_SIZE! 4 and 5 are integers 4 / 5 is integer division and results
IST311. Advanced Issues in OOP: Inheritance and Polymorphism
 IST311 Advanced Issues in OOP: Inheritance and Polymorphism IST311/602 Cleveland State University Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Introduction to Java Programming: Comprehensive Version, Eighth Edition
IST311 Advanced Issues in OOP: Inheritance and Polymorphism IST311/602 Cleveland State University Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Introduction to Java Programming: Comprehensive Version, Eighth Edition
22. Inheritance. Java. Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini
 22. Inheritance Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Superclasses and Subclasses Using the super Keyword Overriding Methods The Object Class References Inheritance Object-oriented programming
22. Inheritance Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Superclasses and Subclasses Using the super Keyword Overriding Methods The Object Class References Inheritance Object-oriented programming
CSE wi Final Exam 3/12/18. Name UW ID#
 Name UW ID# There are 13 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Name UW ID# There are 13 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism
 COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism Ibrahim Albluwi Composition A GuitarString has a RingBuffer. A MarkovModel has a Symbol Table. A Symbol Table has a Binary
COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism Ibrahim Albluwi Composition A GuitarString has a RingBuffer. A MarkovModel has a Symbol Table. A Symbol Table has a Binary
24. Inheritance. Java. Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini
 24. Inheritance Java Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Superclasses and Subclasses Using the super Keyword Overriding Methods The Object Class References Superclasses and Subclasses Inheritance
24. Inheritance Java Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Superclasses and Subclasses Using the super Keyword Overriding Methods The Object Class References Superclasses and Subclasses Inheritance
CSC 160 LAB 8-1 DIGITAL PICTURE FRAME. 1. Introduction
 CSC 160 LAB 8-1 DIGITAL PICTURE FRAME PROFESSOR GODFREY MUGANDA DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 1. Introduction Download and unzip the images folder from the course website. The folder contains 28 images
CSC 160 LAB 8-1 DIGITAL PICTURE FRAME PROFESSOR GODFREY MUGANDA DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 1. Introduction Download and unzip the images folder from the course website. The folder contains 28 images
Produced by. Design Patterns. MSc in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Design Patterns MSc in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
Design Patterns MSc in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1
 Name: CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1 Directions: Test is closed book, closed notes. Answer every question; write solutions in spaces provided. Use backs of pages for scratch work. Good
Name: CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1 Directions: Test is closed book, closed notes. Answer every question; write solutions in spaces provided. Use backs of pages for scratch work. Good
PowerPoint Slides. Object-Oriented Design Using JAVA. Chapter 2. by Dale Skrien
 PowerPoint Slides Object-Oriented Design Using JAVA by Dale Skrien Chapter 2 Object-oriented Programming Divides the program into a set of communicating objects Encapsulates in an object all the behavior
PowerPoint Slides Object-Oriented Design Using JAVA by Dale Skrien Chapter 2 Object-oriented Programming Divides the program into a set of communicating objects Encapsulates in an object all the behavior
Assignment 2. Application Development
 Application Development Assignment 2 Content Application Development Day 2 Lecture The lecture covers the key language elements of the Java programming language. You are introduced to numerical data and
Application Development Assignment 2 Content Application Development Day 2 Lecture The lecture covers the key language elements of the Java programming language. You are introduced to numerical data and
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario
 More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
Animation Part 2: MoveableShape interface & Multithreading
 Animation Part 2: MoveableShape interface & Multithreading MoveableShape Interface In the previous example, an image was drawn, then redrawn in another location Since the actions described above can apply
Animation Part 2: MoveableShape interface & Multithreading MoveableShape Interface In the previous example, an image was drawn, then redrawn in another location Since the actions described above can apply
Overview. ITI Introduction to Computing II. Interface 1. Problem 1. Problem 1: Array sorting. Problem 1: Array sorting. Problem 1: Array sorting
 Overview ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Rafael Falcon and Marcel Turcotte (with contributions from R. Holte) Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Ottawa Interface Abstract
Overview ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Rafael Falcon and Marcel Turcotte (with contributions from R. Holte) Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Ottawa Interface Abstract
The AWT Package, Graphics- Introduction to Images
 Richard G Baldwin (512) 223-4758, baldwin@austin.cc.tx.us, http://www2.austin.cc.tx.us/baldwin/ The AWT Package, Graphics- Introduction to Images Java Programming, Lecture Notes # 170, Revised 09/23/98.
Richard G Baldwin (512) 223-4758, baldwin@austin.cc.tx.us, http://www2.austin.cc.tx.us/baldwin/ The AWT Package, Graphics- Introduction to Images Java Programming, Lecture Notes # 170, Revised 09/23/98.
CIS 120 Midterm II March 31, 2017 SOLUTIONS
 CIS 120 Midterm II March 31, 2017 SOLUTIONS 1 1. OCaml and Java (14 points) Check one box for each part. a. The following OCaml function will terminate by exhausting stack space if called as loop 10: let
CIS 120 Midterm II March 31, 2017 SOLUTIONS 1 1. OCaml and Java (14 points) Check one box for each part. a. The following OCaml function will terminate by exhausting stack space if called as loop 10: let
AShape.java Sun Jan 21 22:32: /** * Abstract strategy to compute the area of a geometrical shape. Dung X. Nguyen * * Copyright
 AShape.java Sun Jan 21 22:32:31 2001 1 Abstract strategy to compute the area of a geometrical shape. @author Dung X. Nguyen Copyright 1999 by Dung X. Nguyen - All rights reserved. Modifications by Alan
AShape.java Sun Jan 21 22:32:31 2001 1 Abstract strategy to compute the area of a geometrical shape. @author Dung X. Nguyen Copyright 1999 by Dung X. Nguyen - All rights reserved. Modifications by Alan
COMP200 INHERITANCE. OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed
 1 1 COMP200 INHERITANCE OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Inheritance Derive new classes (subclass) from existing ones (superclass). Only the Object class (java.lang) has no superclass Every
1 1 COMP200 INHERITANCE OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Inheritance Derive new classes (subclass) from existing ones (superclass). Only the Object class (java.lang) has no superclass Every
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2014 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Java OO (Object Orientation) 2 Python and Matlab have objects and classes. Strong-typing nature of
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2014 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Java OO (Object Orientation) 2 Python and Matlab have objects and classes. Strong-typing nature of
G Programming Languages - Fall 2012
 G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 12 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last lecture Modules Outline Classes Encapsulation and Inheritance Initialization and Finalization Dynamic
G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 12 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last lecture Modules Outline Classes Encapsulation and Inheritance Initialization and Finalization Dynamic
Inheritance and objects
 Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Pu8ng similar objects in the same bucket Extremely
Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Pu8ng similar objects in the same bucket Extremely
CSE wi Final Exam 3/12/18 Sample Solution
 Question 1. (8 points, 2 each) Equality. Recall that there are several different notions of object equality that we ve encountered this quarter. In particular, we have the following three: Reference equality:
Question 1. (8 points, 2 each) Equality. Recall that there are several different notions of object equality that we ve encountered this quarter. In particular, we have the following three: Reference equality:
public class SomeClass OtherClass SomeInterface { }
 CMP 326 Final Fall 2015 Name: There is a blank page at the end of the exam if you need more room to answer a question. 1) (10 pts) Fill in the blanks to specify the missing keywords or definitions. public
CMP 326 Final Fall 2015 Name: There is a blank page at the end of the exam if you need more room to answer a question. 1) (10 pts) Fill in the blanks to specify the missing keywords or definitions. public
1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4'
 Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 25 November 1, 2017 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch (Chapter 24) Announcements HW7: Chat Client Available Soon Due: Tuesday, November 14 th at 11:59pm
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 25 November 1, 2017 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch (Chapter 24) Announcements HW7: Chat Client Available Soon Due: Tuesday, November 14 th at 11:59pm
CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OBJECT-ORIENTED
CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OBJECT-ORIENTED
Using Graphics. Building Java Programs Supplement 3G
 Using Graphics Building Java Programs Supplement 3G Introduction So far, you have learned how to: output to the console break classes/programs into static methods store and use data with variables write
Using Graphics Building Java Programs Supplement 3G Introduction So far, you have learned how to: output to the console break classes/programs into static methods store and use data with variables write
Exercice G09 (v3) File: Shape.java Project: G09-MiniDraw_v3 1GGE
 Exercice G09 (v3) File: Shape.java Project: G09-MiniDraw_v3 1GGE public class Shape private Point from; private Point to; private Color color; public Shape(int px1, int py1, int px2, int py2, Color pcolor)
Exercice G09 (v3) File: Shape.java Project: G09-MiniDraw_v3 1GGE public class Shape private Point from; private Point to; private Color color; public Shape(int px1, int py1, int px2, int py2, Color pcolor)
CSE 143 Au04 Midterm 1 Page 1 of 9
 CSE 143 Au04 Midterm 1 Page 1 of 9 Question 1. (4 points) When we re modifying Java code, some of the things we do will change the coupling between the class we re working on and other classes that it
CSE 143 Au04 Midterm 1 Page 1 of 9 Question 1. (4 points) When we re modifying Java code, some of the things we do will change the coupling between the class we re working on and other classes that it
Reviewing OO Concepts
 Reviewing OO Concepts Users want to draw circles onto the display canvas. public class Circle { // more code here SWEN-261 Introduc2on to So3ware Engineering Department of So3ware Engineering Rochester
Reviewing OO Concepts Users want to draw circles onto the display canvas. public class Circle { // more code here SWEN-261 Introduc2on to So3ware Engineering Department of So3ware Engineering Rochester
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Spring Semester, ENCE 688R: Midterm Exam: 1 1/2 Hours, Open Book and Open Notes
 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Spring Semester, 2016 ENCE 688R: Midterm Exam: 1 1/2 Hours, Open Book and Open Notes Name : Question Points Score 1 30 2 40 3 30 Total 100 1 Question
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Spring Semester, 2016 ENCE 688R: Midterm Exam: 1 1/2 Hours, Open Book and Open Notes Name : Question Points Score 1 30 2 40 3 30 Total 100 1 Question
CS100B: Prelim 3 Solutions November 16, :30 PM 9:00 PM
 CS100B: Prelim 3 Solutions November 16, 1999 7:30 PM 9:00 PM (Print your name) Statement of integrity: I did not break the rules of academic integrity on this exam: (Signature) (Student ID) Sections 10
CS100B: Prelim 3 Solutions November 16, 1999 7:30 PM 9:00 PM (Print your name) Statement of integrity: I did not break the rules of academic integrity on this exam: (Signature) (Student ID) Sections 10
COMP 249: Object Oriented Programming II. Tutorial 2: Intro to Inheritance
 COMP 249: Object Oriented Programming II Tutorial 2: Intro to Inheritance 1 Overriding Methods Consider the following two classes: public Dog { public void bark() {... public void wagtail() {... public
COMP 249: Object Oriented Programming II Tutorial 2: Intro to Inheritance 1 Overriding Methods Consider the following two classes: public Dog { public void bark() {... public void wagtail() {... public
CISC 3115 TY3. C09a: Inheritance. Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College. 9/20/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College
 CISC 3115 TY3 C09a: Inheritance Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 9/20/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Inheritance Superclass/supertype, subclass/subtype
CISC 3115 TY3 C09a: Inheritance Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 9/20/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Inheritance Superclass/supertype, subclass/subtype
About This Lecture. Data Abstraction - Interfaces and Implementations. Outline. Object Concepts. Object Class, Protocol and State.
 Revised 01/09/05 About This Lecture Slide # 2 Data Abstraction - Interfaces and Implementations In this lecture we will learn how Java objects and classes can be used to build abstract data types. CMPUT
Revised 01/09/05 About This Lecture Slide # 2 Data Abstraction - Interfaces and Implementations In this lecture we will learn how Java objects and classes can be used to build abstract data types. CMPUT
Agenda. Objects and classes Encapsulation and information hiding Documentation Packages
 Preliminaries II 1 Agenda Objects and classes Encapsulation and information hiding Documentation Packages Inheritance Polymorphism Implementation of inheritance in Java Abstract classes Interfaces Generics
Preliminaries II 1 Agenda Objects and classes Encapsulation and information hiding Documentation Packages Inheritance Polymorphism Implementation of inheritance in Java Abstract classes Interfaces Generics
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Supplement 3G: Graphics 1 drawing 2D graphics Chapter outline DrawingPanel and Graphics objects drawing and filling shapes coordinate system colors drawing with loops drawing with
Building Java Programs Supplement 3G: Graphics 1 drawing 2D graphics Chapter outline DrawingPanel and Graphics objects drawing and filling shapes coordinate system colors drawing with loops drawing with
Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava, Book 2 CMS available. Visit course webpage, click Links, then
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava, Book 2 CMS available. Visit course webpage, click Links, then
Inheritance (cont.) Inheritance. Hierarchy of Classes. Inheritance (cont.)
 Inheritance Inheritance (cont.) Object oriented systems allow new classes to be defined in terms of a previously defined class. All variables and methods of the previously defined class, called superclass,
Inheritance Inheritance (cont.) Object oriented systems allow new classes to be defined in terms of a previously defined class. All variables and methods of the previously defined class, called superclass,
Chapter 3: Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Chapter 3: Inheritance and Polymorphism Overview Inheritance is when a child class, or a subclass, inherits, or gets, all the data (properties) and methods from the parent class, or superclass. Just like
Chapter 3: Inheritance and Polymorphism Overview Inheritance is when a child class, or a subclass, inherits, or gets, all the data (properties) and methods from the parent class, or superclass. Just like
IS-A / HAS-A. I IS-A Teacher and I HAS-A Laptop
 IS-A / HAS-A I IS-A Teacher and I HAS-A Laptop 1 Corresponding Book Sections Pearson Custom Computer Science: Chapter 1, Sections 9, 12 2 IS-A A class has an IS-A relationship to a class type if it is
IS-A / HAS-A I IS-A Teacher and I HAS-A Laptop 1 Corresponding Book Sections Pearson Custom Computer Science: Chapter 1, Sections 9, 12 2 IS-A A class has an IS-A relationship to a class type if it is
Inheritance (Deitel chapter 9)
 Inheritance (Deitel chapter 9) 1 2 Plan Introduction Superclasses and Subclasses protected Members Constructors and Finalizers in Subclasses Software Engineering with Inheritance 3 Introduction Inheritance
Inheritance (Deitel chapter 9) 1 2 Plan Introduction Superclasses and Subclasses protected Members Constructors and Finalizers in Subclasses Software Engineering with Inheritance 3 Introduction Inheritance
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Graphics reading: Supplement 3G videos: Ch. 3G #1-2 Objects (briefly) object: An entity that contains data and behavior. data: Variables inside the object. behavior: Methods inside
Building Java Programs Graphics reading: Supplement 3G videos: Ch. 3G #1-2 Objects (briefly) object: An entity that contains data and behavior. data: Variables inside the object. behavior: Methods inside
Programming via Java Subclasses
 Programming via Java Subclasses Every class in Java is built from another Java class. The new class is called a subclass of the other class from which it is built. A subclass inherits all the instance
Programming via Java Subclasses Every class in Java is built from another Java class. The new class is called a subclass of the other class from which it is built. A subclass inherits all the instance
AP CS Unit 11: Graphics and Events
 AP CS Unit 11: Graphics and Events This packet shows how to create programs with a graphical interface in a way that is consistent with the approach used in the Elevens program. Copy the following two
AP CS Unit 11: Graphics and Events This packet shows how to create programs with a graphical interface in a way that is consistent with the approach used in the Elevens program. Copy the following two
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Graphics reading: Supplement 3G videos: Ch. 3G #1-2 Objects (briefly) object: An entity that contains data and behavior. data: variables inside the object behavior: methods inside
Building Java Programs Graphics reading: Supplement 3G videos: Ch. 3G #1-2 Objects (briefly) object: An entity that contains data and behavior. data: variables inside the object behavior: methods inside
Inheritance Systems. Merchandise. Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress 9.1.1
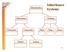 Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava 2 CMS. Visit course webpage, click Links, then CMS for 2110.
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava 2 CMS. Visit course webpage, click Links, then CMS for 2110.
COMP 249: Object Oriented Programming II. Tutorial 11: Generics
 COMP 249: Object Oriented Programming II Tutorial 11: Generics What are generics and why use them? Generics enable types (Classes and interfaces) to be parameters when defining classes, interfaces and
COMP 249: Object Oriented Programming II Tutorial 11: Generics What are generics and why use them? Generics enable types (Classes and interfaces) to be parameters when defining classes, interfaces and
Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011
 Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE COURSE CODE TIME DEPARTMENT LECTURER : JAVA PROGRAMMING : PROG1114 : 2 1/2 HOURS : COMPUTER SCIENCE : LIM PEI GEOK Student
Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE COURSE CODE TIME DEPARTMENT LECTURER : JAVA PROGRAMMING : PROG1114 : 2 1/2 HOURS : COMPUTER SCIENCE : LIM PEI GEOK Student
Objectives. INHERITANCE - Part 1. Using inheritance to promote software reusability. OOP Major Capabilities. When using Inheritance?
 INHERITANCE - Part 1 OOP Major Capabilities Introduction Basic Concepts and Syntax Protected Members Constructors and Destructors Under Inheritance Multiple Inheritance Common Programming Errors encapsulation
INHERITANCE - Part 1 OOP Major Capabilities Introduction Basic Concepts and Syntax Protected Members Constructors and Destructors Under Inheritance Multiple Inheritance Common Programming Errors encapsulation
Constructor. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Constructor Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design these classes so to avoid redundancy? The
Constructor Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design these classes so to avoid redundancy? The
INHERITANCE - Part 1. CSC 330 OO Software Design 1
 INHERITANCE - Part 1 Introduction Basic Concepts and Syntax Protected Members Constructors and Destructors Under Inheritance Multiple Inheritance Common Programming Errors CSC 330 OO Software Design 1
INHERITANCE - Part 1 Introduction Basic Concepts and Syntax Protected Members Constructors and Destructors Under Inheritance Multiple Inheritance Common Programming Errors CSC 330 OO Software Design 1
INHERITANCE - Part 1. CSC 330 OO Software Design 1
 INHERITANCE - Part 1 Introduction Basic Concepts and Syntax Protected Members Constructors and Destructors Under Inheritance Multiple Inheritance Common Programming Errors CSC 330 OO Software Design 1
INHERITANCE - Part 1 Introduction Basic Concepts and Syntax Protected Members Constructors and Destructors Under Inheritance Multiple Inheritance Common Programming Errors CSC 330 OO Software Design 1
CSC 102 Lecture Notes Week 1 Introduction to the Course Introduction to Jav a
 CSC102-S010-L1 Page 1 I. Relevant reading. A. Horstmann chapters 1-6 B. Writeups for Labs 1 and 2 C. Various cited material in writeups CSC 102 Lecture Notes Week 1 Introduction to the Course Introduction
CSC102-S010-L1 Page 1 I. Relevant reading. A. Horstmann chapters 1-6 B. Writeups for Labs 1 and 2 C. Various cited material in writeups CSC 102 Lecture Notes Week 1 Introduction to the Course Introduction
Object-Oriented Programming
 Abstract classes Object-Oriented Programming Outline Abstract classes Abstract methods Design pattern: Template method Dynamic & static binding Upcasting & Downcasting Readings: HFJ: Ch. 8. GT: Ch. 8.
Abstract classes Object-Oriented Programming Outline Abstract classes Abstract methods Design pattern: Template method Dynamic & static binding Upcasting & Downcasting Readings: HFJ: Ch. 8. GT: Ch. 8.
