CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE
|
|
|
- Barbra Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos joel.unm.edu Web: Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building (ECE). Room 233 8/21/2017
2 Install Java Development Kit (JDK) Most computers already have the Java Runtime Environment installed. However, to create Java programs, the Java Development Kit is required. Note: the JDK includes a copy of the matching version of the JRE. Download and Install JDK 1.8 2
3 IntelliJ IDE (Integrated Development Environment) IntelliJ Community Edition (free) version Java is a Programming Language. IntelliJ is an Integrated Development Environment. 3
4 Project Default Settings (Code Style) Use to change the code style and other settings that will be used for all new projects created. 4
5 Code Style: IntelliJ File Settings Manage to create custom scheme. 5
6 6 Code Style: Braces
7 7 IntelliJ: Create New Project (1 of 5)
8 IntelliJ: Create New Project (2 of 5) If the Project SDK dropdown does not contain Java 1.8, then the Java JDK has not been correctly installed (see slide 1). 8
9 9 IntelliJ: Create New Project (3 of 5)
10 IntelliJ: Create New Project (4 of 5) This creates a folder in the project root location. For the first half of CS 259, all our projects will use what is called the default package. If you are using a lab computer, select a folder on your USB drive as the root. The default package has a blank Base package. 10
11 IntelliJ: Create New Project (5 of 5) Change project panel to Project Files Notice highlighting of matching braces at curser position. 11
12 12 Application: Add Inputs (Similar to Listing 1.1) 1. import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 5. { 6. public static void main(string[] args) 7. { 8. System.out.println("Hello World"); Filename MUST be Toy.java From IntelliJ Project Files panel, Right-click filename and select: Refactor Rename 9. System.out.println("I want two numbers!"); Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); 12. int n1 = keyboard.nextint(); 13. int n2 = keyboard.nextint(); System.out.println(n1+n2); 16. } 17.}
13 Compile, Run, and the Console 1. System.out.println("Hello World"); 2. System.out.println("I want two numbers!"); Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); 5. int n1 = keyboard.nextint(); //reads characters until 6. int n2 = keyboard.nextint(); System.out.println(n1+n2); 13 Compile and Run User Input
14 Keyword: import 1. import java.util.scanner; public class Toy_1_1 9. { 10. public static void main(string[] args) 11. { 12. System.out.println("Hello World"); 13. Gets the Scanner class from the package (library) java.util. All import statements are placed at the top of the source file. Note: The Java programming language is case-sensitive. 14
15 Keyword: class import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args) In Java, all code is enclosed in a class. 6. { 7. System.out.println("Hello World"); 8. System.out.println("I start with an upper-case want letter. two numbers!"); Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); 11. int The n1 class = keyboard.nextint(); header must be followed by an 12. int n2 open = keyboard.nextint(); curly bracket, {, and ended with a 13. matching close curly bracket, }. 14. System.out.println(n1+n2); 15. } 16.} class header. Class names are your choice but... should All code within those brackets is part of the class.
16 Method Signature import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args) 6. { 7. System.out.println("Hello World"); 8. System.out.println("I Every Java application must want have two a numbers!"); main method. 9. By convention, method names start with a lower- 10. Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); case letter. 11. int n1 = keyboard.nextint(); 12. int A method n2 = keyboard.nextint(); signature must be followed by an 13. opening curly bracket { and a matching closing 14. System.out.println(n1+n2); 15. } 16.} Line 5 is a method signature. curly bracket }. Code within the brackets is part of the method.
17 Keyword: public import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args) 6. { 7. System.out.println("Hello World"); The keyword public means that the class, field (variable), or method is visible to other classes. The outermost class in each Java source file must be public. The main method must be public.
18 Parts of a Method Signature public static void main(string[] args) static Discussed later. The method s argument list must be enclosed in parenthesis: (). main requires one argument : args which is a field of type String[] (an array of String objects). Method's return type (void, int, float, String,...) The return type is not part of the method signature. 18 Public: The method is visible outside the class.
19 Block Structure 1. public class Toy 2. { 3. // Comment inside Toy. 4. public static void main(string[] args) 5. { 6. // Comment inside main which is inside Toy. 7. System.out.println("Hello World"); 8. } 9. } 19 The nesting of curly brackets defines the block structure. Good programming style requires block indentation. In CS-259, we will use exactly two spaces per level.
20 Program Execution Entry Point 1. public class Toy 2. { 3. public static void main(string[] args) 4. { 5. When a Java program runs, code execution starts at main. Every Java application must have at least one class with a main method. It is ok for an application to have more than one class with main. When a user runs a Java application, the user must specify which class contains the main he or she wants to use. 20
21 Method Calls 1. System.out.println("Hello World"); 2. System.out.println("I want two numbers!"); Line 1 Calls the println method of the object System.out with the argument "Hello World". The println method takes a String object for an argument (input). The println method displays its argument in the Java Console and then displays a newline character, '/n'. 21
22 Keyword new: Instantiating a Class Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); Declares a field (with the programmer defined name keyboard) to be of type Scanner. The type Scanner is defined in import java.util.scanner argument list Creates an instance of the Scanner class. 22 The = symbol assigns keyboard to the memory address of the newly created instance of Scanner.
23 Reading User Input from the Keyboard 1. Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); 2. int n1 = keyboard.nextint(); 23 Line 2 does many things: 1) Defines n1 to be a field of type int. 2) Allocates memory for n1. 3) Calls the nextint method of the keyboard instance of Scanner. The nextint method: i. Reads input from the keyboard. ii. Echoes the input to the Console. iii. Tries to convert the user input to an int. iv. Returns the converted input. 4) Assigns the returned int value to n1.
24 End of Statement ; { Start of Block import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args) 6. { 7. System.out.println("Hello World"); 8. System.out.println("I want 2 numbers!"); Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); 11. int n1 = keyboard.nextint(); 12. int n2 = keyboard.nextint(); System.out.println(n1+n2); 15. } 16.}
25 Whitespace: Ignored Between Identifiers 1. System.out.println("Hello World"); System. out. 4. println ( 5. "Life is Good" 6. ); Single statement split across multiple lines. 25
26 Error: Whitespace Within Identifiers One extra space, causes 6 errors!! Tabs on scrollbar are hyperlinks to error locations. IntelliJ s suggestions can sometimes save typing, but often are incorrect.
27 Find and Fix the Syntax Error: # import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args) 6. { 7. System.out.println("Input 2 numbers"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 10. int n1 = keyboard.nextint(); 11. int n2 = keyboard.nextint(); System.out.println(n1+n2); 14. } 15.}
28 Find and Fix the Syntax Error: # import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args) System.out.println("Input 2 numbers"); Scanner bob = new Scanner(System.in); 10. int n1 = bob.nextint(); 11. int n2 = bob.nextint(); System.out.println(n1+n2); 14. } 15.}
29 Find and Fix the Syntax Error: # import java.util.scanner; public class Toy 4. { 5. public static void main(string[] args); 6. { 7. System.out.println("Input 2 numbers"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 10. int n1 = in.nextint(); 11. int n2 = in.nextint(); System.out.println(n1+n2); 14. } 15.}
30 30 Setting IntelliJ to Project Files View
Anatomy of a Java Program: Comments
 CS149 Anatomy of a Java Program: Comments Javadoc comments: /** * Application that converts inches to centimeters. * * @author Alvin Chao * @version 01/21/2014 */ Everything between /** and */ ignored
CS149 Anatomy of a Java Program: Comments Javadoc comments: /** * Application that converts inches to centimeters. * * @author Alvin Chao * @version 01/21/2014 */ Everything between /** and */ ignored
Interpreted vs Compiled. Java Compile. Classes, Objects, and Methods. Hello World 10/6/2016. Python Interpreted. Java Compiled
 Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them.
 Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. Help you get started with Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java Bytecode (binary file)
 Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
The for Loop, Accumulator Variables, Seninel Values, and The Random Class. CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming
 The for Loop, Accumulator Variables, Seninel Values, and The Random Class CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming Review General Form of a switch statement: switch (SwitchExpression) { case CaseExpression1:
The for Loop, Accumulator Variables, Seninel Values, and The Random Class CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming Review General Form of a switch statement: switch (SwitchExpression) { case CaseExpression1:
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Input. Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); String name;
 Reading Resource Input Read chapter 4 (Variables and Constants) in the textbook A Guide to Programming in Java, pages 77 to 82. Key Concepts A stream is a data channel to or from the operating system.
Reading Resource Input Read chapter 4 (Variables and Constants) in the textbook A Guide to Programming in Java, pages 77 to 82. Key Concepts A stream is a data channel to or from the operating system.
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
CS 302: Introduction to Programming
 CS 302: Introduction to Programming Lectures 2-3 CS302 Summer 2012 1 Review What is a computer? What is a computer program? Why do we have high-level programming languages? How does a high-level program
CS 302: Introduction to Programming Lectures 2-3 CS302 Summer 2012 1 Review What is a computer? What is a computer program? Why do we have high-level programming languages? How does a high-level program
Array Basics: Outline. Creating and Accessing Arrays. Creating and Accessing Arrays. Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7)
 Array Basics: Outline Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7) TOPICS Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Programming with Arrays Searching and Sorting Arrays Multi-Dimensional Arrays Static Variables and Constants
Array Basics: Outline Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7) TOPICS Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Programming with Arrays Searching and Sorting Arrays Multi-Dimensional Arrays Static Variables and Constants
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
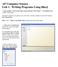 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Object-oriented programming in...
 Programming Languages Week 12 Object-oriented programming in... College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University plan this week intro to Java advantages and disadvantages language
Programming Languages Week 12 Object-oriented programming in... College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University plan this week intro to Java advantages and disadvantages language
Lab # 2. For today s lab:
 1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Console Input and Output Multiple Choice 1) Valid arguments to the System.out object s println method include: (a) Anything with double quotes (b) String variables (c) Variables of type int (d)
Chapter 2 Console Input and Output Multiple Choice 1) Valid arguments to the System.out object s println method include: (a) Anything with double quotes (b) String variables (c) Variables of type int (d)
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Introduction to Java. Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords
 Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
COMP 202 Java in one week
 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lab5. Wooseok Kim
 Lab5 Wooseok Kim wkim3@albany.edu www.cs.albany.edu/~wooseok/201 Question Answer Points 1 A 8 2 A 8 3 E 8 4 D 8 5 20 5 for class 10 for main 5 points for output 6 A 8 7 B 8 8 0 15 9 D 8 10 B 8 Question
Lab5 Wooseok Kim wkim3@albany.edu www.cs.albany.edu/~wooseok/201 Question Answer Points 1 A 8 2 A 8 3 E 8 4 D 8 5 20 5 for class 10 for main 5 points for output 6 A 8 7 B 8 8 0 15 9 D 8 10 B 8 Question
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
I. Variables and Data Type week 3
 I. Variables and Data Type week 3 variable: a named memory (i.e. RAM, which is volatile) location used to store/hold data, which can be changed during program execution in algebra: 3x + 5 = 20, x = 5,
I. Variables and Data Type week 3 variable: a named memory (i.e. RAM, which is volatile) location used to store/hold data, which can be changed during program execution in algebra: 3x + 5 = 20, x = 5,
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise
 COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators
 Page 1 of 6 [Page 56] 2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators A condition is an expression that can be either true or false. This section introduces a simple version of Java's if statement
Page 1 of 6 [Page 56] 2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators A condition is an expression that can be either true or false. This section introduces a simple version of Java's if statement
Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators
 www.thestudycampus.com Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.3 Modifying Your First Java Program 2.4 Displaying
www.thestudycampus.com Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.3 Modifying Your First Java Program 2.4 Displaying
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
First Programs. CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 First Programs CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Output System.out.println( ) prints out something. System.out.println is the first
First Programs CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Output System.out.println( ) prints out something. System.out.println is the first
What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements
 Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Assignment Marking Criteria
 Assignment Marking Criteria Analysis Your analysis documentation must meet the following criteria: All program inputs, processing, and outputs. Each input and output must be given a name and description
Assignment Marking Criteria Analysis Your analysis documentation must meet the following criteria: All program inputs, processing, and outputs. Each input and output must be given a name and description
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming Homework 1 It is due this coming Sunday
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming Homework 1 It is due this coming Sunday
Lecture Notes. System.out.println( Circle radius: + radius + area: + area); radius radius area area value
 Lecture Notes 1. Comments a. /* */ b. // 2. Program Structures a. public class ComputeArea { public static void main(string[ ] args) { // input radius // compute area algorithm // output area Actions to
Lecture Notes 1. Comments a. /* */ b. // 2. Program Structures a. public class ComputeArea { public static void main(string[ ] args) { // input radius // compute area algorithm // output area Actions to
Midterms Save the Dates!
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu (Using the Scanner and String Classes) Anatomy of a Java Program Readings This Week s Reading: Ch 3.1-3.8 (Major conceptual jump
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu (Using the Scanner and String Classes) Anatomy of a Java Program Readings This Week s Reading: Ch 3.1-3.8 (Major conceptual jump
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Review Chapters 1 to 4. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
COMP 202 Java in one week
 COMP 202 Java in one week... Continued CONTENTS: Return to material from previous lecture At-home programming exercises Please Do Ask Questions It's perfectly normal not to understand everything Most of
COMP 202 Java in one week... Continued CONTENTS: Return to material from previous lecture At-home programming exercises Please Do Ask Questions It's perfectly normal not to understand everything Most of
3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS)
 GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION 15 3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS) GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION Checklist: The most recent version of Java SE Development
GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION 15 3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS) GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION Checklist: The most recent version of Java SE Development
CHAPTER 2 Java Fundamentals
 CHAPTER 2 Java Fundamentals Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java Program The print and println Methods, and
CHAPTER 2 Java Fundamentals Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java Program The print and println Methods, and
Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2: Programming Concepts
 Chapter 2: Programming Concepts Objectives Students should Know the steps required to create programs using a programming language and related terminology. Be familiar with the basic structure of a Java
Chapter 2: Programming Concepts Objectives Students should Know the steps required to create programs using a programming language and related terminology. Be familiar with the basic structure of a Java
St. Edmund Preparatory High School Brooklyn, NY
 AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
Getting Started With Java
 Getting Started With Java Sisoft Technologies Pvt Ltd SRC E7, Shipra Riviera Bazar, Gyan Khand-3, Indirapuram, Ghaziabad Website: www.sisoft.in Email:info@sisoft.in Phone: +91-9999-283-283 Java - Overview
Getting Started With Java Sisoft Technologies Pvt Ltd SRC E7, Shipra Riviera Bazar, Gyan Khand-3, Indirapuram, Ghaziabad Website: www.sisoft.in Email:info@sisoft.in Phone: +91-9999-283-283 Java - Overview
Chapter 1 Lab Algorithms, Errors, and Testing
 Chapter 1 Lab Algorithms, Errors, and Testing Lab Objectives Be able to write an algorithm Be able to compile a Java program Be able to execute a Java program using the Sun JDK or a Java IDE Be able to
Chapter 1 Lab Algorithms, Errors, and Testing Lab Objectives Be able to write an algorithm Be able to compile a Java program Be able to execute a Java program using the Sun JDK or a Java IDE Be able to
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion
 Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O
 STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A7 1 STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O INTRODUCTION: The input and output of a program s data is usually referred to as I/O.
STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A7 1 STUDENT LESSON A7 Simple I/O INTRODUCTION: The input and output of a program s data is usually referred to as I/O.
First Programs. CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 First Programs CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Output System.out.println( ) prints out something. System.out.println is the first
First Programs CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Output System.out.println( ) prints out something. System.out.println is the first
AP Computer Science Java Mr. Clausen Program 6A, 6B
 AP Computer Science Java Mr. Clausen Program 6A, 6B Program 6A LastNameFirstNameP6A (Quadratic Formula: 50 points) (Including complex or irrational roots) Write a program that begins by explaining the
AP Computer Science Java Mr. Clausen Program 6A, 6B Program 6A LastNameFirstNameP6A (Quadratic Formula: 50 points) (Including complex or irrational roots) Write a program that begins by explaining the
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Introduction to Java. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
Check out how to use the random number generator (introduced in section 4.11 of the text) to get a number between 1 and 6 to create the simulation.
 Chapter 4 Lab Loops and Files Lab Objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures into Java Be able to write a while loop Be able to write an do-while loop Be able to write a for loop
Chapter 4 Lab Loops and Files Lab Objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures into Java Be able to write a while loop Be able to write an do-while loop Be able to write a for loop
SDKs - Eclipse. SENG 403, Tutorial 2
 SDKs - SENG 403, Tutorial 2 AGENDA - SDK Basics - - How to create Project - How to create a Class - Run Program - Debug Program SDK Basics Software Development Kit is a set of software development tools
SDKs - SENG 403, Tutorial 2 AGENDA - SDK Basics - - How to create Project - How to create a Class - Run Program - Debug Program SDK Basics Software Development Kit is a set of software development tools
IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures
 IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures Module 2.1: Introduction to C# App Programming Xianrong (Shawn) Zheng Spring 2017 1 Outline Introduction Creating a Simple App String Interpolation
IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures Module 2.1: Introduction to C# App Programming Xianrong (Shawn) Zheng Spring 2017 1 Outline Introduction Creating a Simple App String Interpolation
Chapter 2: Java Fundamentals
 Chapter 2: Java Fundamentals Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java
Chapter 2: Java Fundamentals Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java
8/23/2014. Chapter Topics. Chapter Topics (2) Parts of a Java Program. Parts of a Java Program. Analyzing The Example. Chapter 2: Java Fundamentals
 Chapter 2: Java Fundamentals Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java
Chapter 2: Java Fundamentals Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java
Basic Computation. Chapter 2
 Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers and letters. Think of them
Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers and letters. Think of them
CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng. Assignments, Expressions, Operators, Console input & output October 1, 2012
 CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng Assignments, Expressions, Operators, Console input & output October 1, 2012 Instructor: Uma Murthy CSS SKL 161 A Instructor: Joe McCarthy Outline Introduc3on Recap, reminders
CSS 161 Fundamentals of Compu3ng Assignments, Expressions, Operators, Console input & output October 1, 2012 Instructor: Uma Murthy CSS SKL 161 A Instructor: Joe McCarthy Outline Introduc3on Recap, reminders
Software and Programming 1
 Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
First Programs. CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 First Programs CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Output System.out.println( ) prints out something. System.out.println is the first
First Programs CSE 1310 Introduction to Computers and Programming Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Output System.out.println( ) prints out something. System.out.println is the first
Object-Oriented Programming in Java
 CSCI/CMPE 3326 Object-Oriented Programming in Java Class, object, member field and method, final constant, format specifier, file I/O Dongchul Kim Department of Computer Science University of Texas Rio
CSCI/CMPE 3326 Object-Oriented Programming in Java Class, object, member field and method, final constant, format specifier, file I/O Dongchul Kim Department of Computer Science University of Texas Rio
Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 04 Demonstration 1 So, we have learned about how to run Java programs
Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 04 Demonstration 1 So, we have learned about how to run Java programs
Do this by creating on the m: drive (Accessed via start menu link Computer [The m: drive has your login id as name]) the subdirectory CI101.
![Do this by creating on the m: drive (Accessed via start menu link Computer [The m: drive has your login id as name]) the subdirectory CI101. Do this by creating on the m: drive (Accessed via start menu link Computer [The m: drive has your login id as name]) the subdirectory CI101.](/thumbs/78/77153347.jpg) Creating and running a Java program. This tutorial is an introduction to running a computer program written in the computer programming language Java using the BlueJ IDE (Integrated Development Environment).
Creating and running a Java program. This tutorial is an introduction to running a computer program written in the computer programming language Java using the BlueJ IDE (Integrated Development Environment).
Array. Prepared By - Rifat Shahriyar
 Java More Details Array 2 Arrays A group of variables containing values that all have the same type Arrays are fixed length entities In Java, arrays are objects, so they are considered reference types
Java More Details Array 2 Arrays A group of variables containing values that all have the same type Arrays are fixed length entities In Java, arrays are objects, so they are considered reference types
Chapter 4: Loops and Files
 Chapter 4: Loops and Files Chapter Topics Chapter 4 discusses the following main topics: The Increment and Decrement Operators The while Loop Using the while Loop for Input Validation The do-while Loop
Chapter 4: Loops and Files Chapter Topics Chapter 4 discusses the following main topics: The Increment and Decrement Operators The while Loop Using the while Loop for Input Validation The do-while Loop
Using Java Classes Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
S8352: Java From the Very Beginning Part I - Exercises
 S8352: Java From the Very Beginning Part I - Exercises Ex. 1 Hello World This lab uses the Eclipse development environment which provides all of the tools necessary to build, compile and run Java applications.
S8352: Java From the Very Beginning Part I - Exercises Ex. 1 Hello World This lab uses the Eclipse development environment which provides all of the tools necessary to build, compile and run Java applications.
CS11 Java. Fall Lecture 1
 CS11 Java Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! 8 Lectures Slides posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 7-8 Lab Assignments Made available on Mondays Due one week later Monday, 12 noon
CS11 Java Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! 8 Lectures Slides posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 7-8 Lab Assignments Made available on Mondays Due one week later Monday, 12 noon
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 02 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Operators continue if/else statements User input Operators + when used with numeric types (e.g. int,
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 06 / 02 / 2015 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Operators continue if/else statements User input Operators + when used with numeric types (e.g. int,
Lec 3. Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables
 Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Arrays and Lists CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal
 Arrays and Lists CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what an array is Understand how to declare arrays Understand what reference variables are Understand how to pass arrays to methods
Arrays and Lists CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what an array is Understand how to declare arrays Understand what reference variables are Understand how to pass arrays to methods
Basic Computation. Chapter 2
 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers
Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Basic Computation Chapter 2 Outline Variables and Expressions The Class String Keyboard and Screen I/O Documentation and Style Variables Variables store data such as numbers
Week 2: Data and Output
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
Text User Interfaces. Keyboard IO plus
 Text User Interfaces Keyboard IO plus User Interface and Model Model: objects that solve problem at hand. User interface: interacts with user getting input from user giving output to user reporting on
Text User Interfaces Keyboard IO plus User Interface and Model Model: objects that solve problem at hand. User interface: interacts with user getting input from user giving output to user reporting on
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Event-based Programming Misc. Java Operator Precedence Java Formatting
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Event-based Programming Misc. Java Operator Precedence Java Formatting
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
Section 003 Fall CS 170 Exam 1. Name (print): Instructions:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 003 Fall 2012 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 003 Fall 2012 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
Objectives. Problem Solving. Introduction. An overview of object-oriented concepts. Programming and programming languages An introduction to Java
 Introduction Objectives An overview of object-oriented concepts. Programming and programming languages An introduction to Java 1-2 Problem Solving The purpose of writing a program is to solve a problem
Introduction Objectives An overview of object-oriented concepts. Programming and programming languages An introduction to Java 1-2 Problem Solving The purpose of writing a program is to solve a problem
Lecture 02, Fall 2018 Friday September 7
 Anatomy of a class Oliver W. Layton CS231: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 02, Fall 2018 Friday September 7 Follow-up Python is also cross-platform. What s the advantage of Java? It s true: Python
Anatomy of a class Oliver W. Layton CS231: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 02, Fall 2018 Friday September 7 Follow-up Python is also cross-platform. What s the advantage of Java? It s true: Python
Darrell Bethea May 10, MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011
 Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, email me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, email me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
Section 2: Introduction to Java. Historical note
 The only way to learn a new programming language is by writing programs in it. - B. Kernighan & D. Ritchie Section 2: Introduction to Java Objectives: Data Types Characters and Strings Operators and Precedence
The only way to learn a new programming language is by writing programs in it. - B. Kernighan & D. Ritchie Section 2: Introduction to Java Objectives: Data Types Characters and Strings Operators and Precedence
13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition
 SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types
 Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
CS520 Setting Up the Programming Environment for Windows Suresh Kalathur. For Windows users, download the Java8 SDK as shown below.
 CS520 Setting Up the Programming Environment for Windows Suresh Kalathur 1. Java8 SDK Java8 SDK (Windows Users) For Windows users, download the Java8 SDK as shown below. The Java Development Kit (JDK)
CS520 Setting Up the Programming Environment for Windows Suresh Kalathur 1. Java8 SDK Java8 SDK (Windows Users) For Windows users, download the Java8 SDK as shown below. The Java Development Kit (JDK)
Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods
 Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods Due date for section 001: Monday, February 29 by 10 am Due date for section 002: Wednesday, March 2 by 10 am Purpose: Introduction to writing methods and code re-use.
Programming Exercise 7: Static Methods Due date for section 001: Monday, February 29 by 10 am Due date for section 002: Wednesday, March 2 by 10 am Purpose: Introduction to writing methods and code re-use.
M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s
 M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s Objective #1: Call methods. Methods are reusable sections of code that perform actions. Many methods come from classes that are built into the Java language. For
M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s Objective #1: Call methods. Methods are reusable sections of code that perform actions. Many methods come from classes that are built into the Java language. For
! definite loop: A loop that executes a known number of times. " The for loops we have seen so far are definite loops. ! We often use language like
 Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
CHAPTER 7 OBJECTS AND CLASSES
 CHAPTER 7 OBJECTS AND CLASSES OBJECTIVES After completing Objects and Classes, you will be able to: Explain the use of classes in Java for representing structured data. Distinguish between objects and
CHAPTER 7 OBJECTS AND CLASSES OBJECTIVES After completing Objects and Classes, you will be able to: Explain the use of classes in Java for representing structured data. Distinguish between objects and
Chapter Two Bonus Lesson: JavaDoc
 We ve already talked about adding simple comments to your source code. The JDK actually supports more meaningful comments as well. If you add specially-formatted comments, you can then use a tool called
We ve already talked about adding simple comments to your source code. The JDK actually supports more meaningful comments as well. If you add specially-formatted comments, you can then use a tool called
A token is a sequence of characters not including any whitespace.
 Scanner A Scanner object reads from an input source (keyboard, file, String, etc) next() returns the next token as a String nextint() returns the next token as an int nextdouble() returns the next token
Scanner A Scanner object reads from an input source (keyboard, file, String, etc) next() returns the next token as a String nextint() returns the next token as an int nextdouble() returns the next token
Creating a Program in JCreator. JCreator is then used to create our program. But the first step is to create a new file.
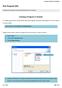 First Program (02) Creating a Java program and understanding the basic concepts. Creating a Program in JCreator It is usually a good idea to create a folder where you re going to save your Java programs.
First Program (02) Creating a Java program and understanding the basic concepts. Creating a Program in JCreator It is usually a good idea to create a folder where you re going to save your Java programs.
Chapter 4: Loops and Files
 Chapter 4: Loops and Files Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 4 discusses the following main topics: The Increment and Decrement
Chapter 4: Loops and Files Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 4 discusses the following main topics: The Increment and Decrement
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Arrays
 WIT COMP1000 Arrays Arrays An array is a list of variables of the same type, that represents a set of related values For example, say you need to keep track of the cost of 1000 items You could declare
WIT COMP1000 Arrays Arrays An array is a list of variables of the same type, that represents a set of related values For example, say you need to keep track of the cost of 1000 items You could declare
Software Installation for CS121
 Software Installation for CS121 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University August 26, 2005 1 Installation of Java J2SE 5 SDK 1. Visit Start Settings Control Panel
Software Installation for CS121 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University August 26, 2005 1 Installation of Java J2SE 5 SDK 1. Visit Start Settings Control Panel
Introduction to Java Applications
 2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
