Distributed Software Systems
|
|
|
- Raymond Wright
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RMI Programming Distributed Software Systems RMI Programming RMI software Generated by IDL compiler Proxy Behaves like remote object to clients (invoker) Marshals arguments, forwards message to remote object, unmarshals results, returns results to client Skeleton Server side stub; Unmarshals arguments, invokes method, marshals results and sends to sending proxy s method Dispatcher Receives the request message from communication module, passes on the message to the appropriate method in the skeleton Server and Client programs RMI Programming 2 1
2 The role of proxy and skeleton in remote method invocation client object A proxy for B Request server skeleton & dispatcher for B s class remote object B Reply Remote Communication reference module module Communication module Remote reference module RMI Programming 3 RMI Programming Binder Client programs need a means of obtaining a remote object reference Binder is a service that maintains a mapping from textual names to remote object references Servers need to register the services they are exporting with the binder Java RMIregistry, CORBA Naming service Server threads Several choices: thread per object, thread per invocation Remote method invocations must allow for concurrent execution RMI Programming 4 2
3 RMI systems CORBA language independent DCOM - Microsoft Java RMI SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) HTTP is request-reply protocol XML for data representation RMI Programming 5 Java RMI Features Integrated with Java language + libraries Security, write once run anywhere, multithreaded Object orientation Can pass behavior Mobile code Not possible in CORBA, traditional RPC systems Distributed Garbage Collection Remoteness of objects intentionally not transparent RMI Programming 6 3
4 Remote Interfaces, Objects, and Methods Objects become remote by implementing a remote interface A remote interface extends the interface java.rmi.remote Each method of the interface declares java.rmi.remoteexception in its throws clause in addition to any application-specific clauses RMI Programming 7 Creating distributed applications using RMI 1. Define the remote interfaces 2. Implement the remote objects 3. Implement the client (can be done anytime after remote interfaces have been defined) 4. Register the remote object in the name server registry 5. Generate the stub and client using rmic 6. Start the registry 7. Start the server 8. Run the client RMI Programming 8 4
5 Java Remote interfaces Shape and ShapeList import java.rmi.*; import java.util.vector; public interface Shape extends Remote { int getversion() throws RemoteException; GraphicalObject getallstate() throws RemoteException; 1 public interface ShapeList extends Remote { Shape newshape(graphicalobject g) throws RemoteException; 2 Vector allshapes() throws RemoteException; int getversion() throws RemoteException; RMI Programming 9 The Naming class of Java RMIregistry void rebind (String name, Remote obj) This method is used by a server to register the identifier of a remote object by name, as shown in Figure 15.13, line 3. void bind (String name, Remote obj) This method can alternatively be used by a server to register a remote object by name, but if the name is already bound to a remote object reference an exception is thrown. void unbind (String name, Remote obj) This method removes a binding. Remote lookup(string name) This method is used by clients to look up a remote object by name, as shown in Figure line 1. A remote object reference is returned. String [] list() This method returns an array of Strings containing the names bound in the registry. RMI Programming 10 5
6 Java class ShapeListServer with main method import java.rmi.*; public class ShapeListServer{ public static void main(string args[]){ System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager()); try{ ShapeList ashapelist = new ShapeListServant(); 1 Naming.rebind("Shape List", ashapelist ); 2 System.out.println("ShapeList server ready"); catch(exception e) { System.out.println("ShapeList server main " + e.getmessage()); RMI Programming 11 Java class ShapeListServant implements interface ShapeList import java.rmi.*; import java.rmi.server.unicastremoteobject; import java.util.vector; public class ShapeListServant extends UnicastRemoteObject implements ShapeList { private Vector thelist; // contains the list of Shapes 1 private int version; public ShapeListServant()throws RemoteException{... public Shape newshape(graphicalobject g) throws RemoteException { 2 version++; Shape s = new ShapeServant( g, version); 3 thelist.addelement(s); return s; public Vector allshapes()throws RemoteException{... public int getversion() throws RemoteException {... RMI Programming 12 6
7 Java client of ShapeList import java.rmi.*; import java.rmi.server.*; import java.util.vector; public class ShapeListClient{ public static void main(string args[]){ System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager()); ShapeList ashapelist = null; try{ ashapelist = (ShapeList) Naming.lookup("//bruno.ShapeList") ; 1 Vector slist = ashapelist.allshapes(); 2 catch(remoteexception e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage()); catch(exception e) {System.out.println("Client: " + e.getmessage()); RMI Programming 13 Classes supporting Java RMI RemoteObject RemoteServer Activatable UnicastRemoteObject <servant class> RMI Programming 14 7
8 CORBA RMI Programming 15 The main components of the CORBA architecture client implementation repository interface repository server object skeleton adapter client proxy program for A ORB core Request Reply ORB core Servant A or dynamic invocation or dynamic skeleton RMI Programming 16 8
9 IDL interfaces Shape and ShapeList struct Rectangle{ 1 long width; long height; long x; long y; ; struct GraphicalObject{ 2 string type; Rectangle enclosing; boolean isfilled; ; interface Shape { 3 long getversion() ; GraphicalObject getallstate() ; // returns state of the GraphicalObject ; typedef sequence <Shape, 100> All; 4 interface ShapeList { 5 exception FullException{ ; 6 Shape newshape(in GraphicalObject g) raises (FullException); 7 All allshapes(); // returns sequence of remote object references 8 long getversion() ; ; RMI Programming 17 Java interface ShapeList generated by idltojava from CORBA interface ShapeList public interface ShapeList extends org.omg.corba.object { Shape newshape(graphicalobject g) throws ShapeListPackage.FullException; Shape[] allshapes(); int getversion(); RMI Programming 18 9
10 ShapeListServant class of the Java server program for CORBA interface ShapeList import org.omg.corba.*; class ShapeListServant extends _ShapeListImplBase { ORB theorb; private Shape thelist[]; private int version; private static int n=0; public ShapeListServant(ORB orb){ theorb = orb; // initialize the other instance variables public Shape newshape(graphicalobject g) throws ShapeListPackage.FullException { 1 version++; Shape s = new ShapeServant( g, version); if(n >=100) throw new ShapeListPackage.FullException(); thelist[n++] = s; 2 theorb.connect(s); return s; public Shape[] allshapes(){... public int getversion() {... RMI Programming 19 Java class ShapeListServer import org.omg.cosnaming.*; import org.omg.cosnaming.namingcontextpackage.*; import org.omg.corba.*; public class ShapeListServer { public static void main(string args[]) { try{ ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null); 1 ShapeListServant shaperef = new ShapeListServant(orb); 2 orb.connect(shaperef); 3 org.omg.corba.object objref = orb.resolve_initial_references("nameservice"); 4 NamingContext ncref = NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef); NameComponent nc = new NameComponent("ShapeList", ""); 5 NameComponent path[] = {nc; 6 ncref.rebind(path, shaperef); 7 java.lang.object sync = new java.lang.object(); synchronized (sync) { sync.wait(); catch (Exception e) {... RMI Programming 20 10
11 Java client program for CORBA interfaces Shape and ShapeList import org.omg.cosnaming.*; import org.omg.cosnaming.namingcontextpackage.*; import org.omg.corba.*; public class ShapeListClient{ public static void main(string args[]) { try{ ORB orb = ORB.init(args, null); 1 org.omg.corba.object objref = orb.resolve_initial_references("nameservice"); NamingContext ncref = NamingContextHelper.narrow(objRef); NameComponent nc = new NameComponent("ShapeList", ""); NameComponent path [] = { nc ; ShapeList shapelistref = ShapeListHelper.narrow(ncRef.resolve(path)); 2 Shape[] slist = shapelistref.allshapes(); 3 GraphicalObject g = slist[0].getallstate(); 4 catch(org.omg.corba.systemexception e) {... RMI Programming 21 IDL module Whiteboard module Whiteboard { struct Rectangle{... ; struct GraphicalObject {...; interface Shape {...; typedef sequence <Shape, 100> All; interface ShapeList {...; ; RMI Programming 22 11
12 IDL constructed types Type Examples Use sequence typedef sequence <Shape, 100> All; typedef sequence <Shape> All bounded and unbounded sequences of Shapes string array String name; typedef string<8> SmallString; unbounded and bounded sequences of characters Defines a type for a variable-length sequence of elements of a specified IDL type. An upper bound on the length may be specified. Defines a sequences of characters, terminated by the null character. An upper bound on the length may be specified. typedef octet uniqueid[12]; Defines a type for a multi-dimensional typedef GraphicalObject GO[10][8] fixed-length sequence of elements of a specified IDL type. RMI Programming 23 IDL constructed types cont d Type Examples Use record struct GraphicalObject { string type; Rectangle enclosing; boolean isfilled; ; enumerated enum Rand (Exp, Number, Name); union union Exp switch (Rand) { case Exp: string vote; case Number: long n; case Name: string s; ; Defines a type for a record containing a group of related entities. Structs are passed by value in arguments and results. The enumerated type in IDL maps a type name onto a small set of integer values. The IDL discriminated union allows one of a given set of types to be passed as an argument. The header is parameterized by an enum, which specifies which member is in use. RMI Programming 24 12
13 CORBA interoperable object references IOR format IDL interface type nameprotocol and address details Object key interface repository identifier IIOP host domain name port number adapter name object name RMI Programming 25 Naming graph in CORBA Naming Service initial naming context initial naming context initial naming context ShapeList C D B E XX P V R S T Q U RMI Programming 26 13
14 Part of the CORBA Naming Service NamingContext interface in IDL struct NameComponent { string id; string kind; ; typedef sequence <NameComponent> Name; interface NamingContext { void bind (in Name n, in Object obj); binds the given name and remote object reference in my context. void unbind (in Name n); removes an existing binding with the given name. void bind_new_context(in Name n); creates a new naming context and binds it to a given name in my context. Object resolve (in Name n); looks up the name in my context and returns its remote object reference. void list (in unsigned long how_many, out BindingList bl, out BindingIterator bi); returns the names in the bindings in my context. ; RMI Programming 27 14
5.4. Events and notifications
 5.4. Events and notifications Distributed event-based systems extend local event model Allowing multiple objects at diff. locations to be notified of events taking place at an object Two characteristics:
5.4. Events and notifications Distributed event-based systems extend local event model Allowing multiple objects at diff. locations to be notified of events taking place at an object Two characteristics:
Applications. RMI, RPC and events. Request reply protocol External data representation. Operating System
 Figure 5.1 Middleware layer Applications RMI, RPC and events Request reply protocol External data representation Middleware layers Operating System Instructor s Guide for Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg
Figure 5.1 Middleware layer Applications RMI, RPC and events Request reply protocol External data representation Middleware layers Operating System Instructor s Guide for Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg
Modulo II Socket, RMI e Corba
 Modulo II Socket, RMI e Corba Prof. Ismael H F Santos April 05 Prof. Ismael H. F. Santos - ismael@tecgraf.puc-rio.br 1 Ementa Sistemas Distribuídos Cliente-Servidor April 05 Prof. Ismael H. F. Santos -
Modulo II Socket, RMI e Corba Prof. Ismael H F Santos April 05 Prof. Ismael H. F. Santos - ismael@tecgraf.puc-rio.br 1 Ementa Sistemas Distribuídos Cliente-Servidor April 05 Prof. Ismael H. F. Santos -
Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI
 Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI
 Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
The UNIVERSITY of EDINBURGH. SCHOOL of INFORMATICS. CS4/MSc. Distributed Systems. Björn Franke. Room 2414
 The UNIVERSITY of EDINBURGH SCHOOL of INFORMATICS CS4/MSc Distributed Systems Björn Franke bfranke@inf.ed.ac.uk Room 2414 (Lecture 3: Remote Invocation and Distributed Objects, 28th September 2006) 1 Programming
The UNIVERSITY of EDINBURGH SCHOOL of INFORMATICS CS4/MSc Distributed Systems Björn Franke bfranke@inf.ed.ac.uk Room 2414 (Lecture 3: Remote Invocation and Distributed Objects, 28th September 2006) 1 Programming
CORBA CASE STUDY Introduction 20.2 CORBA RMI 20.3 CORBA services 20.4 Summary
 20 CORBA CASE STUDY 20.1 Introduction 20.2 CORBA RMI 20.3 CORBA services 20.4 Summary CORBA is a middeware design that allows application programs to communicate with one another irrespective of their
20 CORBA CASE STUDY 20.1 Introduction 20.2 CORBA RMI 20.3 CORBA services 20.4 Summary CORBA is a middeware design that allows application programs to communicate with one another irrespective of their
Chapter 5 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation
 CSD511 Distributed Systems 分散式系統 Chapter 5 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation 吳俊興 國立高雄大學資訊工程學系 Chapter 5 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Communication between distributed
CSD511 Distributed Systems 分散式系統 Chapter 5 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation 吳俊興 國立高雄大學資訊工程學系 Chapter 5 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Communication between distributed
Distributed Systems. Communication (2) Schedule of Today. Distributed Objects. Distributed Objects and RMI. Corba IDL Example
 1 Overview Distributed Systems Communication (2) Lecture 4 Schedule of Today Remote Object (Method) Invocation Binding Client to an Object Static versus Dynamic Binding Basics MPI, Sockets, Distributed
1 Overview Distributed Systems Communication (2) Lecture 4 Schedule of Today Remote Object (Method) Invocation Binding Client to an Object Static versus Dynamic Binding Basics MPI, Sockets, Distributed
Distributed Systems. Communication (2) Lecture Universität Karlsruhe, System Architecture Group
 Distributed Systems Communication (2) Lecture 4 2003 Universität Karlsruhe, System Architecture Group 1 Overview Schedule of Today Remote Object (Method) Invocation Distributed Objects Binding Client to
Distributed Systems Communication (2) Lecture 4 2003 Universität Karlsruhe, System Architecture Group 1 Overview Schedule of Today Remote Object (Method) Invocation Distributed Objects Binding Client to
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/83/88148270.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [RMI] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L21.1 L21.2 Topics covered in this lecture RMI
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [RMI] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L21.1 L21.2 Topics covered in this lecture RMI
JAVA RMI. Remote Method Invocation
 1 JAVA RMI Remote Method Invocation 2 Overview Java RMI is a mechanism that allows one to invoke a method on an object that exists in another address space. The other address space could be: On the same
1 JAVA RMI Remote Method Invocation 2 Overview Java RMI is a mechanism that allows one to invoke a method on an object that exists in another address space. The other address space could be: On the same
DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS AND REMOTE INVOCATION
 DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS AND REMOTE INVOCATION Introduction This chapter is concerned with programming models for distributed applications... Familiar programming models have been extended to apply to distributed
DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS AND REMOTE INVOCATION Introduction This chapter is concerned with programming models for distributed applications... Familiar programming models have been extended to apply to distributed
6 Distributed Object-Based Systems
 CA464: DISTRIBUTED PROGRAMMING 1 6 Distributed Object-Based Systems 6.1 Architecture Remote distributed objects Data and operations encapsulated in an object Operations implemented as methods grouped into
CA464: DISTRIBUTED PROGRAMMING 1 6 Distributed Object-Based Systems 6.1 Architecture Remote distributed objects Data and operations encapsulated in an object Operations implemented as methods grouped into
RMI: Design & Implementation
 RMI: Design & Implementation Operating Systems RMI 1 Middleware layers Applications, services RMI and RPC request-reply protocol marshalling and external data representation Middleware layers UDP and TCP
RMI: Design & Implementation Operating Systems RMI 1 Middleware layers Applications, services RMI and RPC request-reply protocol marshalling and external data representation Middleware layers UDP and TCP
Remote Method Invocation
 Remote Method Invocation A true distributed computing application interface for Java, written to provide easy access to objects existing on remote virtual machines Provide access to objects existing on
Remote Method Invocation A true distributed computing application interface for Java, written to provide easy access to objects existing on remote virtual machines Provide access to objects existing on
Contents. Java RMI. Java RMI. Java RMI system elements. Example application processes/machines Client machine Process/Application A
 Contents Java RMI G53ACC Chris Greenhalgh Java RMI overview A Java RMI example Overview Walk-through Implementation notes Argument passing File requirements RPC issues and RMI Other problems with RMI 1
Contents Java RMI G53ACC Chris Greenhalgh Java RMI overview A Java RMI example Overview Walk-through Implementation notes Argument passing File requirements RPC issues and RMI Other problems with RMI 1
RPC flow. 4.3 Remote procedure calls IDL. RPC components. Procedure. Program. sum (j,k) int j,k; {return j+k;} i = sum (3,7); Local procedure call
 4.3 Remote procedure calls RPC flow Client process Server process Program i = sum (3,7); Procedure sum (j,k) int j,k; {return j+k; Client stub Program Return Call Unpack Pack result para s Invisible to
4.3 Remote procedure calls RPC flow Client process Server process Program i = sum (3,7); Procedure sum (j,k) int j,k; {return j+k; Client stub Program Return Call Unpack Pack result para s Invisible to
Generic architecture
 Java-RMI Lab Outline Let first builds a simple home-made framework This is useful to understand the main issues We see later how java-rmi works and how it solves the same issues Generic architecture object
Java-RMI Lab Outline Let first builds a simple home-made framework This is useful to understand the main issues We see later how java-rmi works and how it solves the same issues Generic architecture object
Distributed Systems. 5. Remote Method Invocation
 Distributed Systems 5. Remote Method Invocation Werner Nutt 1 Remote Method Invocation 5.1 Communication between Distributed Objects 1. Communication between Distributed Objects 2. RMI 2 Middleware Middleware
Distributed Systems 5. Remote Method Invocation Werner Nutt 1 Remote Method Invocation 5.1 Communication between Distributed Objects 1. Communication between Distributed Objects 2. RMI 2 Middleware Middleware
Java and Distributed Systems
 Java and Distributed Systems Dr. Stephan Fischer GMD-IPSI Dolivostr. 15 D-64293 Darmstadt sfischer@darmstadt.gmd.de Contents Remote Method Invocation Java and CORBA Jini Discussion Java RMI (1) RMI applications:
Java and Distributed Systems Dr. Stephan Fischer GMD-IPSI Dolivostr. 15 D-64293 Darmstadt sfischer@darmstadt.gmd.de Contents Remote Method Invocation Java and CORBA Jini Discussion Java RMI (1) RMI applications:
Object Interaction. Object Interaction. Introduction. Object Interaction vs. RPCs (2)
 Introduction Objective To support interoperability and portability of distributed OO applications by provision of enabling technology Object interaction vs RPC Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) RMI Registry
Introduction Objective To support interoperability and portability of distributed OO applications by provision of enabling technology Object interaction vs RPC Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) RMI Registry
Problems with the specification lead to new specifications, forcing vendors to
 CORBA Distributed object-based system Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) CORBA is a specification of a distributed system. There are no suggestions made about the implementation of the middleware
CORBA Distributed object-based system Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) CORBA is a specification of a distributed system. There are no suggestions made about the implementation of the middleware
Middleware services RT- CORBA. Making an application to CORBA. Distributed objects. Distribution issues, global state, clusters, CORBA, etc
 WEEK 10 Distributed objects Distribution issues, global state, clusters, CORBA, etc Stallings, Chapters 14 & 15 + Appendix B Prev. edition; Chapters 13&14 invokes a method machine proxy OS same interface
WEEK 10 Distributed objects Distribution issues, global state, clusters, CORBA, etc Stallings, Chapters 14 & 15 + Appendix B Prev. edition; Chapters 13&14 invokes a method machine proxy OS same interface
Remote Procedure Call
 Remote Procedure Call Suited for Client-Server structure. Combines aspects of monitors and synchronous message passing: Module (remote object) exports operations, invoked with call. call blocks (delays
Remote Procedure Call Suited for Client-Server structure. Combines aspects of monitors and synchronous message passing: Module (remote object) exports operations, invoked with call. call blocks (delays
Written by: Dave Matuszek
 RMI Remote Method Invocation Written by: Dave Matuszek appeared originally at: http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~matuszek/cit597-2003/ 28-May-07 The network is the computer * Consider the following program organization:
RMI Remote Method Invocation Written by: Dave Matuszek appeared originally at: http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~matuszek/cit597-2003/ 28-May-07 The network is the computer * Consider the following program organization:
Last Class: Network Overview. Today: Distributed Systems
 Last Class: Network Overview =>Processes in a distributed system all communicate via a message exchange. Physical reality: packets Abstraction: messages limited size arbitrary size unordered (sometimes)
Last Class: Network Overview =>Processes in a distributed system all communicate via a message exchange. Physical reality: packets Abstraction: messages limited size arbitrary size unordered (sometimes)
Department of Computer Science & Engineering. M.Tech(CSE)-I Year-II Semester WEB SERVICES AND SERVICE ORIENTED ARCHITECHTURE (B1513) Mr.K.
 Department of Computer Science & Engineering M.Tech(CSE)-I Year-II Semester WEB SERVICES AND SERVICE ORIENTED ARCHITECHTURE (B1513) By Mr.K.Yellaswamy Assistant Professor CMR College of Engineering & Technology,
Department of Computer Science & Engineering M.Tech(CSE)-I Year-II Semester WEB SERVICES AND SERVICE ORIENTED ARCHITECHTURE (B1513) By Mr.K.Yellaswamy Assistant Professor CMR College of Engineering & Technology,
Xx Xx xx CORBA. 4 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed Systems
 Agenda Lecture (10) CORBA Xx Xx xx Dr. Ahmed ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed Systems 2 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed Systems Application Diagram Development
Agenda Lecture (10) CORBA Xx Xx xx Dr. Ahmed ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed Systems 2 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed Systems Application Diagram Development
Chapter 15: Distributed Communication. Sockets Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) Remote Method Invocation (RMI) CORBA Object Registration
 Chapter 15: Distributed Communication Sockets Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) Remote Method Invocation (RMI) CORBA Object Registration Sockets Defined as an endpoint for communcation Concatenation of IP
Chapter 15: Distributed Communication Sockets Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) Remote Method Invocation (RMI) CORBA Object Registration Sockets Defined as an endpoint for communcation Concatenation of IP
RMI. Remote Method Invocation. 16-Dec-16
 RMI Remote Method Invocation 16-Dec-16 The network is the computer Consider the following program organization: method SomeClass call AnotherClass returned object computer 1 computer 2 If the network is
RMI Remote Method Invocation 16-Dec-16 The network is the computer Consider the following program organization: method SomeClass call AnotherClass returned object computer 1 computer 2 If the network is
RMI (Remote Method Invocation) Over the year, there have been 3 different approaches to application development:
 RMI (Remote Method Invocation) History: Over the year, there have been 3 different approaches to application development: 1. the traditional approach. 2. the client / server approach and 3. the component-
RMI (Remote Method Invocation) History: Over the year, there have been 3 different approaches to application development: 1. the traditional approach. 2. the client / server approach and 3. the component-
Distributed Computing
 Distributed Computing Computing on many systems to solve one problem Why? - Combination of cheap processors often more cost-effective than one expensive fast system - Flexibility to add according to needs
Distributed Computing Computing on many systems to solve one problem Why? - Combination of cheap processors often more cost-effective than one expensive fast system - Flexibility to add according to needs
Steps to Demonstrate CORBA Application using Java
 Steps to Demonstrate CORBA Application using Java The CORBA Application composed of three programs a) idl program -:Which contains the declaration of methods to be called by client and defined by the server
Steps to Demonstrate CORBA Application using Java The CORBA Application composed of three programs a) idl program -:Which contains the declaration of methods to be called by client and defined by the server
Verteilte Systeme (Distributed Systems)
 Verteilte Systeme (Distributed Systems) Karl M. Göschka Karl.Goeschka@tuwien.ac.at http://www.infosys.tuwien.ac.at/teaching/courses/ VerteilteSysteme/ Lecture 3: Communication (Part 2) Remote Procedure
Verteilte Systeme (Distributed Systems) Karl M. Göschka Karl.Goeschka@tuwien.ac.at http://www.infosys.tuwien.ac.at/teaching/courses/ VerteilteSysteme/ Lecture 3: Communication (Part 2) Remote Procedure
CORBA COMMON OBJECT REQUEST BROKER ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW OF CORBA, OMG'S OBJECT TECHNOLOGY FOR DISTRIBUTED APPLICATIONS CORBA
 CORBA COMMON OBJECT REQUEST BROKER ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW OF CORBA, OMG'S OBJECT TECHNOLOGY FOR DISTRIBUTED APPLICATIONS Peter R. Egli 1/27 Contents 1. What is CORBA? 2. CORBA Elements 3. The CORBA IDL
CORBA COMMON OBJECT REQUEST BROKER ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW OF CORBA, OMG'S OBJECT TECHNOLOGY FOR DISTRIBUTED APPLICATIONS Peter R. Egli 1/27 Contents 1. What is CORBA? 2. CORBA Elements 3. The CORBA IDL
Remote Objects and RMI
 Outline Remote Objects and RMI Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Distributed/Remote Objects Remote object reference (ROR) Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Case study and example: Java RMI Other issues for objects
Outline Remote Objects and RMI Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Distributed/Remote Objects Remote object reference (ROR) Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Case study and example: Java RMI Other issues for objects
Remote Method Invocation in Java
 Remote Method Invocation in Java Ajay Khatri Senior Assistant Professor,Department IT Acropolis Institute of Technology & Research ajay.acropolis@gmail.com What is RMI RMI is an API that provides a mechanism
Remote Method Invocation in Java Ajay Khatri Senior Assistant Professor,Department IT Acropolis Institute of Technology & Research ajay.acropolis@gmail.com What is RMI RMI is an API that provides a mechanism
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)
 The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) CORBA CORBA is a standard architecture for distributed objects systems CORBA is designed to allow distributed objects to interoperate in a heterogenous
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) CORBA CORBA is a standard architecture for distributed objects systems CORBA is designed to allow distributed objects to interoperate in a heterogenous
Remote Method Invocation
 Remote Method Invocation RMI Dr. Syed Imtiyaz Hassan Assistant Professor, Deptt. of CSE, Jamia Hamdard (Deemed to be University), New Delhi, India. s.imtiyaz@jamiahamdard.ac.in 1 Agenda Introduction Creating
Remote Method Invocation RMI Dr. Syed Imtiyaz Hassan Assistant Professor, Deptt. of CSE, Jamia Hamdard (Deemed to be University), New Delhi, India. s.imtiyaz@jamiahamdard.ac.in 1 Agenda Introduction Creating
03 Remote invocation. Request-reply RPC. Coulouris 5 Birrel_Nelson_84.pdf RMI
 03 Remote invocation Request-reply RPC Coulouris 5 Birrel_Nelson_84.pdf RMI 2/16 Remote Procedure Call Implementation client process Request server process client program client stub procedure Communication
03 Remote invocation Request-reply RPC Coulouris 5 Birrel_Nelson_84.pdf RMI 2/16 Remote Procedure Call Implementation client process Request server process client program client stub procedure Communication
JAVA RMI Java, summer semester
 JAVA RMI Overview Remote Method Invocation usage of remote object objects in a different VM (on the same computer or over the network) as there would be local objects (almost) calls just take longer time
JAVA RMI Overview Remote Method Invocation usage of remote object objects in a different VM (on the same computer or over the network) as there would be local objects (almost) calls just take longer time
CS 5523 Operating Systems: Remote Objects and RMI
 CS 5523 Operating Systems: Remote Objects and RMI Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Thank Dr. Dakai Zhu and Dr. Palden Lama for providing their slides. Outline Distributed/Remote Objects Remote object reference
CS 5523 Operating Systems: Remote Objects and RMI Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Thank Dr. Dakai Zhu and Dr. Palden Lama for providing their slides. Outline Distributed/Remote Objects Remote object reference
Distributed Systems. 02r. Java RMI Programming Tutorial. Paul Krzyzanowski TA: Long Zhao Rutgers University Fall 2017
 Distributed Systems 02r. Java RMI Programming Tutorial Paul Krzyzanowski TA: Long Zhao Rutgers University Fall 2017 1 Java RMI RMI = Remote Method Invocation Allows a method to be invoked that resides
Distributed Systems 02r. Java RMI Programming Tutorial Paul Krzyzanowski TA: Long Zhao Rutgers University Fall 2017 1 Java RMI RMI = Remote Method Invocation Allows a method to be invoked that resides
inside: THE MAGAZINE OF USENIX & SAGE June 2001 Volume 26 Number 3 PROGRAMMING Using CORBA with Java by Prithvi Rao
 THE MAGAZINE OF USENIX & SAGE June 2001 Volume 26 Number 3 inside: PROGRAMMING Using CORBA with Java by Prithvi Rao # & The Advanced Computing Systems Association & The System Administrators Guild using
THE MAGAZINE OF USENIX & SAGE June 2001 Volume 26 Number 3 inside: PROGRAMMING Using CORBA with Java by Prithvi Rao # & The Advanced Computing Systems Association & The System Administrators Guild using
Distributed Object-based Systems CORBA
 Distributed Object-based Systems CORBA Dr. Yong Guan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering & Information Assurance Center Iowa State University Outline for Today s Talk Role of CORBA and need
Distributed Object-based Systems CORBA Dr. Yong Guan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering & Information Assurance Center Iowa State University Outline for Today s Talk Role of CORBA and need
Component-Based Software Engineering
 Component-Based Software Engineering Remote Method Invocation Paul Krause Introduction to RMI Lecture 11 - RMI Simple Example - DivideServer Demo of this example Review a more complex example - StudentEnrollment
Component-Based Software Engineering Remote Method Invocation Paul Krause Introduction to RMI Lecture 11 - RMI Simple Example - DivideServer Demo of this example Review a more complex example - StudentEnrollment
CORBA. CORBA Background. (Common Object Request Broker Architecture)
 CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) CORBA Background CORBA is an architectural framework for distributed object management. Intended to support distributed client-server applications. Developed
CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) CORBA Background CORBA is an architectural framework for distributed object management. Intended to support distributed client-server applications. Developed
S. Monaghan CSEE, University of Essex. September 21, Client Program and Server Program 3
 CSEE University of Essex CE806 - Distributed Computing (2010-11) Laboratory 6 Java IDL (Script/code checked and working in Computer Laboratory 1 on 21/9/2010) S. Monaghan CSEE, University of Essex September
CSEE University of Essex CE806 - Distributed Computing (2010-11) Laboratory 6 Java IDL (Script/code checked and working in Computer Laboratory 1 on 21/9/2010) S. Monaghan CSEE, University of Essex September
Desarrollo de Aplicaciones en Red RMI. Introduction. Considerations. Considerations. RMI architecture
 session Desarrollo de Aplicaciones en Red José Rafael Rojano Cáceres http://www.uv.mx/rrojano RMI Remote Method Invocation Introduction Java RMI let s work calling remote methods. Underneath it works with
session Desarrollo de Aplicaciones en Red José Rafael Rojano Cáceres http://www.uv.mx/rrojano RMI Remote Method Invocation Introduction Java RMI let s work calling remote methods. Underneath it works with
Agent and Object Technology Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Informazione Università degli Studi di Parma. Distributed and Agent Systems RMI
 Agent and Object Technology Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Informazione Università degli Studi di Parma Distributed and Agent Systems RMI Prof. Agostino Poggi What is RMI? Its acronym means Remote
Agent and Object Technology Lab Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Informazione Università degli Studi di Parma Distributed and Agent Systems RMI Prof. Agostino Poggi What is RMI? Its acronym means Remote
2. Java IDL and CORBA
 2. Java IDL and CORBA This lecture was developed by Russ Tront, Instructor, School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University email: tront@sfu.ca Section Table of Contents 32. JAVA IDL AND CORBA POA...
2. Java IDL and CORBA This lecture was developed by Russ Tront, Instructor, School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University email: tront@sfu.ca Section Table of Contents 32. JAVA IDL AND CORBA POA...
Lecture 5: Object Interaction: RMI and RPC
 06-06798 Distributed Systems Lecture 5: Object Interaction: RMI and RPC Distributed Systems 1 Recap Message passing: send, receive synchronous versus asynchronous No global Time types of failure socket
06-06798 Distributed Systems Lecture 5: Object Interaction: RMI and RPC Distributed Systems 1 Recap Message passing: send, receive synchronous versus asynchronous No global Time types of failure socket
Distributed Systems. Distributed Object Systems 2 Java RMI. Java RMI. Example. Applet continued. Applet. slides2.pdf Sep 9,
 Distributed Object Systems 2 Java RMI Piet van Oostrum Distributed Systems What should a distributed system provide? Illusion of one system while running on multiple systems Transparancy Issues Communication,
Distributed Object Systems 2 Java RMI Piet van Oostrum Distributed Systems What should a distributed system provide? Illusion of one system while running on multiple systems Transparancy Issues Communication,
Session plan. sessionx. Desarrollo de Aplicaciones en Red. What s Corba? RPC vs. Corba. Middleware. Middleware task
 sessionx Desarrollo de Aplicaciones en Red José Rafael Rojano Cáceres http://www.uv.mx/rrojano General vision Middleware OMA Corba IDL ORB IIOP Examples Session plan What s Corba? Middleware for Programming
sessionx Desarrollo de Aplicaciones en Red José Rafael Rojano Cáceres http://www.uv.mx/rrojano General vision Middleware OMA Corba IDL ORB IIOP Examples Session plan What s Corba? Middleware for Programming
Introduction & RMI Basics. CS3524 Distributed Systems Lecture 01
 Introduction & RMI Basics CS3524 Distributed Systems Lecture 01 Distributed Information Systems Distributed System: A collection of autonomous computers linked by a network, with software to produce an
Introduction & RMI Basics CS3524 Distributed Systems Lecture 01 Distributed Information Systems Distributed System: A collection of autonomous computers linked by a network, with software to produce an
Interprocess Communication
 1. Foundations and Architecture distributed system architechtures; network interface 2. Time and Global States clocks and concepts of time; event ordering; synchronization; global states 3. Coordination
1. Foundations and Architecture distributed system architechtures; network interface 2. Time and Global States clocks and concepts of time; event ordering; synchronization; global states 3. Coordination
COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS: REMOTE PROCEDURE CALL (RPC)
 COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS: REMOTE PROCEDURE CALL (RPC) 1 2 CONVENTIONAL PROCEDURE CALL (a) (b) Parameter passing in a local procedure call: the stack before the call to read. The stack while the called procedure
COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS: REMOTE PROCEDURE CALL (RPC) 1 2 CONVENTIONAL PROCEDURE CALL (a) (b) Parameter passing in a local procedure call: the stack before the call to read. The stack while the called procedure
RPC and RMI. 2501ICT Nathan
 RPC and RMI 2501ICT Nathan Contents Client/Server revisited RPC Architecture XDR RMI Principles and Operation Case Studies Copyright 2002- René Hexel. 2 Client/Server Revisited Server Accepts commands
RPC and RMI 2501ICT Nathan Contents Client/Server revisited RPC Architecture XDR RMI Principles and Operation Case Studies Copyright 2002- René Hexel. 2 Client/Server Revisited Server Accepts commands
COMP 6231: Distributed System Design
 COMP 6231: Distributed System Design Remote Invocation and RMI Based on Chapters 5, 7 of the text book and the slides from Prof. M.L. Liu, California Polytechnic State University COMP 6231, Fall 2013 Remote
COMP 6231: Distributed System Design Remote Invocation and RMI Based on Chapters 5, 7 of the text book and the slides from Prof. M.L. Liu, California Polytechnic State University COMP 6231, Fall 2013 Remote
RMI Example RMI. CmpE 473 Internet Programming RMI
 CmpE 473 Internet Programming Pınar Yolum pinar.yolum@boun.edu.tr Department of Computer Engineering Boğaziçi University RMI Examples from Advanced Java: Internet Applications, Art Gittleman Remote Method
CmpE 473 Internet Programming Pınar Yolum pinar.yolum@boun.edu.tr Department of Computer Engineering Boğaziçi University RMI Examples from Advanced Java: Internet Applications, Art Gittleman Remote Method
Lecture 06: Distributed Object
 Lecture 06: Distributed Object Distributed Systems Behzad Bordbar School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK Lecture 0? 1 Recap Interprocess communication Synchronous and Asynchronous communication
Lecture 06: Distributed Object Distributed Systems Behzad Bordbar School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK Lecture 0? 1 Recap Interprocess communication Synchronous and Asynchronous communication
IBD Intergiciels et Bases de Données
 IBD Intergiciels et Bases de Données RMI-based distributed systems Fabien Gaud, Fabien.Gaud@inrialpes.fr Overview of lectures and practical work Lectures Introduction to distributed systems and middleware
IBD Intergiciels et Bases de Données RMI-based distributed systems Fabien Gaud, Fabien.Gaud@inrialpes.fr Overview of lectures and practical work Lectures Introduction to distributed systems and middleware
presentation DAD Distributed Applications Development Cristian Toma
 Lecture 8 S4 - Core Distributed Middleware Programming in JEE presentation DAD Distributed Applications Development Cristian Toma D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics www.dice.ase.ro
Lecture 8 S4 - Core Distributed Middleware Programming in JEE presentation DAD Distributed Applications Development Cristian Toma D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics www.dice.ase.ro
Distributed Objects SPL/ SPL 201 / 0 1
 Distributed Objects 1 distributed objects objects which reside on different machines/ network architectures, benefits, drawbacks implementation of a remote object system 2 Why go distributed? large systems
Distributed Objects 1 distributed objects objects which reside on different machines/ network architectures, benefits, drawbacks implementation of a remote object system 2 Why go distributed? large systems
CSci Introduction to Distributed Systems. Communication: RPC In Practice
 CSci 5105 Introduction to Distributed Systems Communication: RPC In Practice Linux RPC Language-neutral RPC Can use Fortran, C, C++ IDL compiler rpgen N to generate all stubs, skeletons (server stub) Example:
CSci 5105 Introduction to Distributed Systems Communication: RPC In Practice Linux RPC Language-neutral RPC Can use Fortran, C, C++ IDL compiler rpgen N to generate all stubs, skeletons (server stub) Example:
JAC444 - Lecture 11. Remote Method Invocation Segment 2 - Develop RMI Application. Jordan Anastasiade Java Programming Language Course
 JAC444 - Lecture 11 Remote Method Invocation Segment 2 - Develop RMI Application 1 Remote Method Invocation In this lesson you will be learning about: Designing RMI application Developing distributed object
JAC444 - Lecture 11 Remote Method Invocation Segment 2 - Develop RMI Application 1 Remote Method Invocation In this lesson you will be learning about: Designing RMI application Developing distributed object
55:182/22C:182. Distributed Application Frameworks Java RMI, CORBA, Web Services (SOAP)
 55:182/22C:182 Distributed Application Frameworks Java RMI, CORBA, Web Services (SOAP) Broker Architecture Example Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Invoking a method which lies in a different address
55:182/22C:182 Distributed Application Frameworks Java RMI, CORBA, Web Services (SOAP) Broker Architecture Example Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Invoking a method which lies in a different address
Remote Method Invocation
 Non-101samples available here: https://github.com/101companies/101repo/tree/master/languages/aspectj/javarmisamples Remote Method Invocation Prof. Dr. Ralf Lämmel Universität Koblenz-Landau Software Languages
Non-101samples available here: https://github.com/101companies/101repo/tree/master/languages/aspectj/javarmisamples Remote Method Invocation Prof. Dr. Ralf Lämmel Universität Koblenz-Landau Software Languages
RMI. (Remote Method Invocation)
 RMI (Remote Method Invocation) Topics What is RMI? Why RMI? Architectural components Serialization & Marshaled Objects Dynamic class loading Code movement Codebase ClassLoader delegation RMI Security Writing
RMI (Remote Method Invocation) Topics What is RMI? Why RMI? Architectural components Serialization & Marshaled Objects Dynamic class loading Code movement Codebase ClassLoader delegation RMI Security Writing
Course Snapshot. The Next Few Classes. Parallel versus Distributed Systems. Distributed Systems. We have covered all the fundamental OS components:
 Course Snapshot The Next Few Classes We have covered all the fundamental OS components: Architecture and OS interactions Processes and threads Synchronization and deadlock Process scheduling Memory management
Course Snapshot The Next Few Classes We have covered all the fundamental OS components: Architecture and OS interactions Processes and threads Synchronization and deadlock Process scheduling Memory management
Outline. EEC-681/781 Distributed Computing Systems. The OSI Network Architecture. Inter-Process Communications (IPC) Lecture 4
 EEC-681/781 Distributed Computing Systems Lecture 4 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org Outline Inter-process communications Computer networks
EEC-681/781 Distributed Computing Systems Lecture 4 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org Outline Inter-process communications Computer networks
Remote Invocation Vladimir Vlassov and Johan Montelius
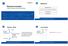 KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Middleware Remote Invocation Vladimir Vlassov and Johan Montelius Application layer Remote invocation / indirect communication Socket layer Network layer ID2201 DISTRIBUTED
KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Middleware Remote Invocation Vladimir Vlassov and Johan Montelius Application layer Remote invocation / indirect communication Socket layer Network layer ID2201 DISTRIBUTED
Chapter 18: CORBA and Jini. Contents
 of 23 27/04/2013 6:07 PM 18.1. CORBA Chapter 18: CORBA and Jini CORBA CORBA to Java Mapping Jini Proxies Simple Example Corba Server in Java Corba Client in Java Jini Service Jini Server and Client Building
of 23 27/04/2013 6:07 PM 18.1. CORBA Chapter 18: CORBA and Jini CORBA CORBA to Java Mapping Jini Proxies Simple Example Corba Server in Java Corba Client in Java Jini Service Jini Server and Client Building
5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach
 5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach Main Points Why distributed objects Distributed Object design points Java RMI Dynamic Code Loading 5.1 What s an Object? An Object is an autonomous entity having
5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach Main Points Why distributed objects Distributed Object design points Java RMI Dynamic Code Loading 5.1 What s an Object? An Object is an autonomous entity having
Course Snapshot. The Next Few Classes
 Course Snapshot We have covered all the fundamental OS components: Architecture and OS interactions Processes and threads Synchronization and deadlock Process scheduling Memory management File systems
Course Snapshot We have covered all the fundamental OS components: Architecture and OS interactions Processes and threads Synchronization and deadlock Process scheduling Memory management File systems
Corba. Distributed Object Systems 5 Corba/Activation/POA. Interaction with ORB. ORB init. Object references. ORB init. slides5.pdf March 10,
 Distributed Object Systems 5 Corba/Activation/POA Piet van Oostrum Mar 11, 2009 Corba Today: Interaction with the ORB Object references Activation Object Adapters Implementation Repository Next time: Naming
Distributed Object Systems 5 Corba/Activation/POA Piet van Oostrum Mar 11, 2009 Corba Today: Interaction with the ORB Object references Activation Object Adapters Implementation Repository Next time: Naming
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation. Programming Models for Distributed Applications
 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Extending Conventional Techniques The remote procedure call model is an extension of the conventional procedure
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Extending Conventional Techniques The remote procedure call model is an extension of the conventional procedure
Chapter 4: Processes. Process Concept. Process State
 Chapter 4: Processes Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Cooperating Processes Interprocess Communication Communication in Client-Server Systems 4.1 Process Concept An operating
Chapter 4: Processes Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Cooperating Processes Interprocess Communication Communication in Client-Server Systems 4.1 Process Concept An operating
DS 2009: middleware. David Evans
 DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
Distributed Systems. 6. Remote Method Invocation. Werner Nutt
 Distributed Systems 6. Remote Method Invocation Werner Nutt 1 Remote Method Invocation 6.1 Communication between Distributed Objects 1. Communication between Distributed Objects 2. Java RMI 3. Dynamic
Distributed Systems 6. Remote Method Invocation Werner Nutt 1 Remote Method Invocation 6.1 Communication between Distributed Objects 1. Communication between Distributed Objects 2. Java RMI 3. Dynamic
Distributed Programming with RMI. Overview CORBA DCOM. Prepared By: Shiba R. Tamrakar
 Distributed Programming with RMI Overview Distributed object computing extends an object-oriented programming system by allowing objects to be distributed across a heterogeneous network, so that each of
Distributed Programming with RMI Overview Distributed object computing extends an object-oriented programming system by allowing objects to be distributed across a heterogeneous network, so that each of
UNIT 4 CORBA 4/2/2013 Middleware 59
 UNIT 4 CORBA 4/2/2013 Middleware 59 CORBA AN OBJECT ORIENTED RPC MECHANISM HELPS TO DEVELOP DISTRIBUTED SYTEMS IN DIFF. PLATFORMS OBJECTS WRITTEN IN DIFF., LANG, CAN BE CALLED BY OBJECTS WRITTEN IN ANOTHER
UNIT 4 CORBA 4/2/2013 Middleware 59 CORBA AN OBJECT ORIENTED RPC MECHANISM HELPS TO DEVELOP DISTRIBUTED SYTEMS IN DIFF. PLATFORMS OBJECTS WRITTEN IN DIFF., LANG, CAN BE CALLED BY OBJECTS WRITTEN IN ANOTHER
Problems with the specification lead to new specifications, forcing vendors to
 CORBA Distributed object-based system Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) CORBA is a specification of a distributed system. There are no suggestions made about the implementation of the middleware
CORBA Distributed object-based system Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) CORBA is a specification of a distributed system. There are no suggestions made about the implementation of the middleware
Questions and Answers. A. RMI allows us to invoke a method of java object that executes on another machine.
 Q.1) What is Remote method invocation (RMI)? A. RMI allows us to invoke a method of java object that executes on another machine. B. RMI allows us to invoke a method of java object that executes on another
Q.1) What is Remote method invocation (RMI)? A. RMI allows us to invoke a method of java object that executes on another machine. B. RMI allows us to invoke a method of java object that executes on another
Info 408 Distributed Applications programming 2 nd semester of Credits: 5 Lecturer: Antoun Yaacoub Ph.D.
 Lebanese University Faculty of Sciences I Master 1 degree Computer Sciences Info 408 Distributed Applications programming 2 nd semester of 2018-2019 Credits: 5 Lecturer: Antoun Yaacoub Ph.D. RMI Serialization
Lebanese University Faculty of Sciences I Master 1 degree Computer Sciences Info 408 Distributed Applications programming 2 nd semester of 2018-2019 Credits: 5 Lecturer: Antoun Yaacoub Ph.D. RMI Serialization
Distributed Objects. Chapter Distributing Objects Overview
 Middleware Architecture with Patterns and Frameworks c 2003-2009, Sacha Krakowiak (version of February 27, 2009-12:58) Creative Commons license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/) Chapter
Middleware Architecture with Patterns and Frameworks c 2003-2009, Sacha Krakowiak (version of February 27, 2009-12:58) Creative Commons license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/) Chapter
Communication Basics, RPC & RMI. CS403/534 Distributed Systems Erkay Savas Sabanci University
 Communication Basics, RPC & RMI CS403/534 Distributed Systems Erkay Savas Sabanci University 1 Communication Models 1. Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Client/Server application 2. Remote Method Invocation
Communication Basics, RPC & RMI CS403/534 Distributed Systems Erkay Savas Sabanci University 1 Communication Models 1. Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Client/Server application 2. Remote Method Invocation
Remote Method Invocation Java RMI & Web-Services
 Remote Method Invocation Java RMI & Web-s CS 4119 - Computer Networks Columbia University - Spring 2003 Alexander V. Konstantinou akonstan@cs.columbia.edu Introduction : Remote Computation Objects encapsulate
Remote Method Invocation Java RMI & Web-s CS 4119 - Computer Networks Columbia University - Spring 2003 Alexander V. Konstantinou akonstan@cs.columbia.edu Introduction : Remote Computation Objects encapsulate
Distributed Systems COMP 212. Lecture 10 Othon Michail
 Distributed Systems COMP 212 Lecture 10 Othon Michail RMI: Remote Method Invocation Allows an object running in one Java virtual machine to invoke methods on an object running in another Java virtual machine.
Distributed Systems COMP 212 Lecture 10 Othon Michail RMI: Remote Method Invocation Allows an object running in one Java virtual machine to invoke methods on an object running in another Java virtual machine.
RMI Case Study. A Typical RMI Application
 RMI Case Study This example taken directly from the Java RMI tutorial http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/rmi/ Editorial note: Please do yourself a favor and work through the tutorial yourself If you
RMI Case Study This example taken directly from the Java RMI tutorial http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/rmi/ Editorial note: Please do yourself a favor and work through the tutorial yourself If you
PROFESSOR: DR.JALILI BY: MAHDI ESHAGHI
 PROFESSOR: DR.JALILI BY: MAHDI ESHAGHI 1 2 Overview Distributed OZ Java RMI CORBA IDL IDL VS C++ CORBA VS RMI 3 Distributed OZ Oz Language Multi paradigm language, strong support for compositionality and
PROFESSOR: DR.JALILI BY: MAHDI ESHAGHI 1 2 Overview Distributed OZ Java RMI CORBA IDL IDL VS C++ CORBA VS RMI 3 Distributed OZ Oz Language Multi paradigm language, strong support for compositionality and
Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation
 Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 Figure 5.1 Middleware layers Applications
Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 Figure 5.1 Middleware layers Applications
Remote Method Invocation Benoît Garbinato
 Remote Method Invocation Benoît Garbinato 1 Fundamental idea (1) Rely on the same programming paradigm for distributed applications as for centralized applications In procedural languages, we will rely
Remote Method Invocation Benoît Garbinato 1 Fundamental idea (1) Rely on the same programming paradigm for distributed applications as for centralized applications In procedural languages, we will rely
Chapter 4 Remote Procedure Calls and Distributed Transactions
 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 4 Remote Procedure Calls and Distributed Transactions Outline
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 4 Remote Procedure Calls and Distributed Transactions Outline
CS193k, Stanford Handout #12. Threads 4 / RMI
 CS193k, Stanford Handout #12 Spring, 99-00 Nick Parlante Threads 4 / RMI Semaphore1 Semaphore1 from last time uses the count in a precise way to know exactly how many threads are waiting. In this way,
CS193k, Stanford Handout #12 Spring, 99-00 Nick Parlante Threads 4 / RMI Semaphore1 Semaphore1 from last time uses the count in a precise way to know exactly how many threads are waiting. In this way,
Communication and Distributed Processing
 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 4 Remote Procedure Calls and Distributed Transactions Outline
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 4 Remote Procedure Calls and Distributed Transactions Outline
Distributed Programming in Java. Distribution (2)
 Distributed Programming in Java Distribution (2) Remote Method Invocation Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Primary design goal for RMI is transparency Should be able to invoke remote objects with same syntax
Distributed Programming in Java Distribution (2) Remote Method Invocation Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Primary design goal for RMI is transparency Should be able to invoke remote objects with same syntax
Activation of remote objects
 Activation of remote objects The Activatable class Prior to the release of Java 2 SDK, an instance of a UnicastRemoteObject could be accessed from a server program that created an instance of the remote
Activation of remote objects The Activatable class Prior to the release of Java 2 SDK, an instance of a UnicastRemoteObject could be accessed from a server program that created an instance of the remote
Message Passing vs. Distributed Objects. 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 1
 Message Passing vs. Distributed Objects 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 1 Distributed Objects M. L. Liu 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 2 Message Passing versus Distributed Objects
Message Passing vs. Distributed Objects 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 1 Distributed Objects M. L. Liu 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 2 Message Passing versus Distributed Objects
