Lock-free Programming
|
|
|
- Kerrie Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lock-free Programming Nathaniel Wesley Filardo April 10, 2006
2 Outline Motivation Lock-Free Linked List Insertion Lock-Free Linked List Deletion Some real algorithms?
3 Motivation Review of atomic primitives Locks can be expensive
4 Review of atomic primitives ˆ XCHG (ptr, val) atomically: ˆ old val = *ptr ˆ *ptr = val ˆ return old val ˆ CAS (ptr, expect, new) atomically: ˆ if ( *ptr!= expect ) return *ptr; ˆ else return XCHG (ptr, new); ˆ Note that CAS is no harder - it s a read and a write; the logic is free (it s on the chip).
5 Locks can be expensive ˆ Consider XCHG style locks which use while( xchg( &locked, LOCKED ) == LOCKED ) as their core operation. ˆ Each xchg flushes the processor pipeline... ˆ We could spend a long time here waiting or yielding... ˆ This implies we ll have very high latency on contention...
6 Lock-Free Linked List Insertion Lock-Free Linked List Node Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Successful case Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Race case
7 Lock-Free Linked List Node ˆ Node definition is simple: void* data void* next
8 Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Successful case Setup A next C next B next ˆ Some thread constructs the bottom node B; wishes to place it between the two above, A and C.
9 Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Successful case First step A next C next B next ˆ Thread points B node s next into list at C.
10 Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Successful case First step A next C set by CAS B next next ˆ CAS used to point previous node A to new node B. ˆ... ˆ So wait, what s the cleverness?
11 Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Race case First step B next A next D next C next ˆ Two threads point their respective nodes B and C into list at D ˆ Both of them try to CAS the previous node s (A s) next pointer...
12 Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Race case One thread goes B next CAS A C next next D next ˆ One of the two goes (here the thread owning B won)...
13 Insertion into a Lock-free Linked List: Race case And the other... B next CAS A CAS fail! C next next D next ˆ And the other (owning C)... ˆ But the expect value doesn t match, so the linked list structure is OK. ˆ So this thread tries again and does the same dance...
14 That s great! ˆ Yes, if we want an insert-and-read only list, then it s fine! ˆ How many datastructures are like that?
15 Deletion is easy? ˆ Can we just prune the node? ˆ Given B next A next ˆ Can t we just transition via CAS to C next B next A next C next ˆ Yes, but can we reclaim that memory?
16 Deletion is easy? Continued ˆ Can t we just transition via CAS to B next A next C next ˆ There might be another thread touching the upper node (B)! ˆ Can t touch that memory at all! ˆ In particular, can t free() it!
17 Compromise? ˆ So, for a deleted node (often logically deleted node )... ˆ Let s just leave it detatched from the list, marking it somehow as deleted. B INVALID A next C next ˆ Other threads will fail their operations and restart. ˆ We might have a free list of available nodes, even... ˆ Some real-world implementations do this, leaving as an exercise to syncrhonize all threads to delete the the list and free list when everybody s done.
18 Compromise? Now reusing that memory... ˆ We might have a somewhat complex case of a sorted list 1 next 6 next 5 next
19 Compromise? Now reusing that memory... ˆ Thread X trying to insert 3 after 1 races against somebody deleting 5. ˆ So we now have 1 next 6 next 3 next 5 INVALID ˆ There is a deleted node ( 5, bottom right) that was the next of 1 when thread X started running
20 Compromise? Now reusing that memory (part 2) ˆ Thread Y now reclaims deleted node, pushes in 2 and points to 6. ˆ Trying for a sorted list with 1 next 6 next 3 next 2 next ˆ Thread X still trying to insert 3 after 1. Been preempted for a while ˆ Anybody see the problem yet?
21 Compromise? Now reusing that memory (part 3) ˆ Thread Y now inserts the reclaimed node where it belongs! (using CAS, of course) ˆ Trying for a sorted list with 1 next 6 next 3 next 2 next ˆ Thread X still trying to insert 3 after 1. Been preempted for a while ˆ The dotted line indicates what X expects to see! ˆ How about now?
22 Compromise? Now reusing that memory (part 4) ˆ Thread X wakes up, and the CAS works (!) giving instead 1 next 6 next 3 next 2 next
23 Compromise? Earth-Shattering KABOOM! Figure: There was supposed to be an... [mar()]
24 Compromise? Woah, what just happened? 1 next 6 next 3 next 2 next ˆ But, but, but... {1, 3, 2, 6} isn t sorted! ˆ This is called The ABA problem: the pointer changed meaning but we didn t notice.
25 Full fledged deletion & reclaim OK, so how do we actually do this? ˆ It turns out that we need a more sophisticated delete function. Look at [Fomitchev and Ruppert(2004)] or [Michael(2002a)] (or others) for more details. ˆ Generation counters are a simple way to solve ABA (usually requires use of CASn - acts on n words at once; much slower than CAS) ˆ But that doesn t solve memory reclaim - for these we need more sophisticated algorithms (which also solve ABA for us): ˆ Hazard Pointers ( Safe Memory Reclaimation or just SMR ) [Michael(2002b)] and [Michael(2004)] ˆ Wait-free reference counters [Sundell(2005)]
26 Some real algorithms? ˆ [Fomitchev and Ruppert(2004)] gives a simple, non-reclaimable lock-free linked/skip-list algorithm. ˆ [Michael(2002a)] specifies a CAS-based lock-free list-based sets and hash tables using SMR as a refinement of the above. ˆ Their performance figures are worth looking at. Summary: fine-grained locks (lock per node) show linear-time increase with # threads, their algorithm shows essentially constant time!
27 Marvin the martian, URL Marvin%20Martian%201.jpg. M. Fomitchev and E. Ruppert, PODC pp (2004), URL michael/podc-2002.pdf. M. M. Michael, SPAA pp (2002a), URL \&type=pdf\&coll=GUIDE\&dl=ACM\&CFID= \&CFTOKEN= M. M. Michael, PODC pp (2002b), URL podc-2002.pdf.
28 M. M. Michael, IEEECS pp (2004), URL podc-2002.pdf. H. Sundell (IEEE, 2005), /05, URL ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/9722/30685/ pdf?tp=\&arnumber= \&isnumber= Wikipedia, Lock-free and wait-free algorithms (2006a), URL and_wait-free_algorithms. Wikipedia, Non-blocking synchronization (2006b), URL synchronization.
29 Acknowledgements ˆ Dave Eckhardt (de0u) and Bruce Maggs (bmm) for moral support and big-picture guidance ˆ Jess Mink (jmink), Matt Brewer (mbrewer), and Mister Wright (mrwright) for being victims of beta versions of this lecture.
Program Graph. Lecture 25: Parallelism & Concurrency. Performance. What does it mean?
 Program Graph Lecture 25: Parallelism & Concurrency CS 62 Fall 2015 Kim Bruce & Michael Bannister Some slides based on those from Dan Grossman, U. of Washington Program using fork and join can be seen
Program Graph Lecture 25: Parallelism & Concurrency CS 62 Fall 2015 Kim Bruce & Michael Bannister Some slides based on those from Dan Grossman, U. of Washington Program using fork and join can be seen
Concurrent Preliminaries
 Concurrent Preliminaries Sagi Katorza Tel Aviv University 09/12/2014 1 Outline Hardware infrastructure Hardware primitives Mutual exclusion Work sharing and termination detection Concurrent data structures
Concurrent Preliminaries Sagi Katorza Tel Aviv University 09/12/2014 1 Outline Hardware infrastructure Hardware primitives Mutual exclusion Work sharing and termination detection Concurrent data structures
Marwan Burelle. Parallel and Concurrent Programming
 marwan.burelle@lse.epita.fr http://wiki-prog.infoprepa.epita.fr Outline 1 2 Solutions Overview 1 Sharing Data First, always try to apply the following mantra: Don t share data! When non-scalar data are
marwan.burelle@lse.epita.fr http://wiki-prog.infoprepa.epita.fr Outline 1 2 Solutions Overview 1 Sharing Data First, always try to apply the following mantra: Don t share data! When non-scalar data are
Fine-grained synchronization & lock-free programming
 Lecture 17: Fine-grained synchronization & lock-free programming Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming CMU 15-418/15-618, Spring 2016 Tunes Minnie the Moocher Robbie Williams (Swings Both Ways)
Lecture 17: Fine-grained synchronization & lock-free programming Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming CMU 15-418/15-618, Spring 2016 Tunes Minnie the Moocher Robbie Williams (Swings Both Ways)
CS4961 Parallel Programming. Lecture 12: Advanced Synchronization (Pthreads) 10/4/11. Administrative. Mary Hall October 4, 2011
 CS4961 Parallel Programming Lecture 12: Advanced Synchronization (Pthreads) Mary Hall October 4, 2011 Administrative Thursday s class Meet in WEB L130 to go over programming assignment Midterm on Thursday
CS4961 Parallel Programming Lecture 12: Advanced Synchronization (Pthreads) Mary Hall October 4, 2011 Administrative Thursday s class Meet in WEB L130 to go over programming assignment Midterm on Thursday
Lecture 10: Avoiding Locks
 Lecture 10: Avoiding Locks CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown (with thanks to Paul McKenney) Locking: A necessary evil? Locks are an easy to understand solution to critical section problem Protect
Lecture 10: Avoiding Locks CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown (with thanks to Paul McKenney) Locking: A necessary evil? Locks are an easy to understand solution to critical section problem Protect
Last Time. Think carefully about whether you use a heap Look carefully for stack overflow Especially when you have multiple threads
 Last Time Cost of nearly full resources RAM is limited Think carefully about whether you use a heap Look carefully for stack overflow Especially when you have multiple threads Embedded C Extensions for
Last Time Cost of nearly full resources RAM is limited Think carefully about whether you use a heap Look carefully for stack overflow Especially when you have multiple threads Embedded C Extensions for
Lock-Free and Practical Doubly Linked List-Based Deques using Single-Word Compare-And-Swap
 Lock-Free and Practical Doubly Linked List-Based Deques using Single-Word Compare-And-Swap Håkan Sundell Philippas Tsigas OPODIS 2004: The 8th International Conference on Principles of Distributed Systems
Lock-Free and Practical Doubly Linked List-Based Deques using Single-Word Compare-And-Swap Håkan Sundell Philippas Tsigas OPODIS 2004: The 8th International Conference on Principles of Distributed Systems
LOCKLESS ALGORITHMS. Lockless Algorithms. CAS based algorithms stack order linked list
 Lockless Algorithms CAS based algorithms stack order linked list CS4021/4521 2017 jones@scss.tcd.ie School of Computer Science and Statistics, Trinity College Dublin 2-Jan-18 1 Obstruction, Lock and Wait
Lockless Algorithms CAS based algorithms stack order linked list CS4021/4521 2017 jones@scss.tcd.ie School of Computer Science and Statistics, Trinity College Dublin 2-Jan-18 1 Obstruction, Lock and Wait
Cache Coherence and Atomic Operations in Hardware
 Cache Coherence and Atomic Operations in Hardware Previously, we introduced multi-core parallelism. Today we ll look at 2 things: 1. Cache coherence 2. Instruction support for synchronization. And some
Cache Coherence and Atomic Operations in Hardware Previously, we introduced multi-core parallelism. Today we ll look at 2 things: 1. Cache coherence 2. Instruction support for synchronization. And some
Learning from Bad Examples. CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 25 11/18/2014
 Learning from Bad Examples CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 25 11/18/2014 1 Goals Demonstrate techniques to design for shared mutability Build on an example where multiple threads
Learning from Bad Examples CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 25 11/18/2014 1 Goals Demonstrate techniques to design for shared mutability Build on an example where multiple threads
Lecture 8: September 30
 CMPSCI 377 Operating Systems Fall 2013 Lecture 8: September 30 Lecturer: Prashant Shenoy Scribe: Armand Halbert 8.1 Semaphores A semaphore is a more generalized form of a lock that can be used to regulate
CMPSCI 377 Operating Systems Fall 2013 Lecture 8: September 30 Lecturer: Prashant Shenoy Scribe: Armand Halbert 8.1 Semaphores A semaphore is a more generalized form of a lock that can be used to regulate
Håkan Sundell University College of Borås Parallel Scalable Solutions AB
 Brushing the Locks out of the Fur: A Lock-Free Work Stealing Library Based on Wool Håkan Sundell University College of Borås Parallel Scalable Solutions AB Philippas Tsigas Chalmers University of Technology
Brushing the Locks out of the Fur: A Lock-Free Work Stealing Library Based on Wool Håkan Sundell University College of Borås Parallel Scalable Solutions AB Philippas Tsigas Chalmers University of Technology
Lecture #7: Implementing Mutual Exclusion
 Lecture #7: Implementing Mutual Exclusion Review -- 1 min Solution #3 to too much milk works, but it is really unsatisfactory: 1) Really complicated even for this simple example, hard to convince yourself
Lecture #7: Implementing Mutual Exclusion Review -- 1 min Solution #3 to too much milk works, but it is really unsatisfactory: 1) Really complicated even for this simple example, hard to convince yourself
NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY. Tim Harris, 31 October 2012
 NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY Tim Harris, 31 October 2012 Lecture 6 Linearizability Lock-free progress properties Queues Reducing contention Explicit memory management Linearizability
NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY Tim Harris, 31 October 2012 Lecture 6 Linearizability Lock-free progress properties Queues Reducing contention Explicit memory management Linearizability
Order Is A Lie. Are you sure you know how your code runs?
 Order Is A Lie Are you sure you know how your code runs? Order in code is not respected by Compilers Processors (out-of-order execution) SMP Cache Management Understanding execution order in a multithreaded
Order Is A Lie Are you sure you know how your code runs? Order in code is not respected by Compilers Processors (out-of-order execution) SMP Cache Management Understanding execution order in a multithreaded
EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems
 EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems Winter 2018 Harsha V. Madhyastha Monitors vs. Semaphores Monitors: Custom user-defined conditions Developer must control access to variables Semaphores: Access
EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems Winter 2018 Harsha V. Madhyastha Monitors vs. Semaphores Monitors: Custom user-defined conditions Developer must control access to variables Semaphores: Access
Other consistency models
 Last time: Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) Lecture 25: Synchronization primitives Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) CPU 0 CPU 1 CPU 2 CPU 3 Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012
Last time: Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) Lecture 25: Synchronization primitives Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) CPU 0 CPU 1 CPU 2 CPU 3 Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012
Programmazione di sistemi multicore
 Programmazione di sistemi multicore A.A. 2015-2016 LECTURE 12 IRENE FINOCCHI http://wwwusers.di.uniroma1.it/~finocchi/ Shared-memory concurrency & mutual exclusion TASK PARALLELISM AND OVERLAPPING MEMORY
Programmazione di sistemi multicore A.A. 2015-2016 LECTURE 12 IRENE FINOCCHI http://wwwusers.di.uniroma1.it/~finocchi/ Shared-memory concurrency & mutual exclusion TASK PARALLELISM AND OVERLAPPING MEMORY
Fine-grained synchronization & lock-free data structures
 Lecture 19: Fine-grained synchronization & lock-free data structures Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Redo Exam statistics Example: a sorted linked list struct Node { int value; Node* next;
Lecture 19: Fine-grained synchronization & lock-free data structures Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Redo Exam statistics Example: a sorted linked list struct Node { int value; Node* next;
3. Concurrency Control for Transactions Part One
 3. Concurrency Control for Transactions Part One CSEP 545 Transaction Processing Philip A. Bernstein Copyright 2012 Philip A. Bernstein 1/11/2012 1 Outline 1. A Simple System Model 2. Serializability Theory
3. Concurrency Control for Transactions Part One CSEP 545 Transaction Processing Philip A. Bernstein Copyright 2012 Philip A. Bernstein 1/11/2012 1 Outline 1. A Simple System Model 2. Serializability Theory
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter Lecture 7 Synchronization. Steve Gribble. Synchronization. Threads cooperate in multithreaded programs
 CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2005 Lecture 7 Synchronization Steve Gribble Synchronization Threads cooperate in multithreaded programs to share resources, access shared data structures e.g., threads
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2005 Lecture 7 Synchronization Steve Gribble Synchronization Threads cooperate in multithreaded programs to share resources, access shared data structures e.g., threads
NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY. Tim Harris, 17 November 2017
 NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY Tim Harris, 17 November 2017 Lecture 7 Linearizability Lock-free progress properties Hashtables and skip-lists Queues Reducing contention Explicit
NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY Tim Harris, 17 November 2017 Lecture 7 Linearizability Lock-free progress properties Hashtables and skip-lists Queues Reducing contention Explicit
Part 1 Fine-grained Operations
 Part 1 Fine-grained Operations As we learned on Monday, CMPXCHG can be used to implement other primitives, such as TestAndSet. int CMPXCHG (int* loc, int oldval, int newval) { ATOMIC(); int old_reg_val
Part 1 Fine-grained Operations As we learned on Monday, CMPXCHG can be used to implement other primitives, such as TestAndSet. int CMPXCHG (int* loc, int oldval, int newval) { ATOMIC(); int old_reg_val
Efficient and Reliable Lock-Free Memory Reclamation Based on Reference Counting
 Efficient and Reliable Lock-Free Memory Reclamation d on Reference ounting nders Gidenstam, Marina Papatriantafilou, Håkan Sundell and Philippas Tsigas Distributed omputing and Systems group, Department
Efficient and Reliable Lock-Free Memory Reclamation d on Reference ounting nders Gidenstam, Marina Papatriantafilou, Håkan Sundell and Philippas Tsigas Distributed omputing and Systems group, Department
Locking: A necessary evil? Lecture 10: Avoiding Locks. Priority Inversion. Deadlock
 Locking: necessary evil? Lecture 10: voiding Locks CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 ngela Demke Brown (with thanks to Paul McKenney) Locks are an easy to understand solution to critical section problem Protect shared
Locking: necessary evil? Lecture 10: voiding Locks CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 ngela Demke Brown (with thanks to Paul McKenney) Locks are an easy to understand solution to critical section problem Protect shared
15 418/618 Project Final Report Concurrent Lock free BST
 15 418/618 Project Final Report Concurrent Lock free BST Names: Swapnil Pimpale, Romit Kudtarkar AndrewID: spimpale, rkudtark 1.0 SUMMARY We implemented two concurrent binary search trees (BSTs): a fine
15 418/618 Project Final Report Concurrent Lock free BST Names: Swapnil Pimpale, Romit Kudtarkar AndrewID: spimpale, rkudtark 1.0 SUMMARY We implemented two concurrent binary search trees (BSTs): a fine
Tom Hart, University of Toronto Paul E. McKenney, IBM Beaverton Angela Demke Brown, University of Toronto
 Making Lockless Synchronization Fast: Performance Implications of Memory Reclamation Tom Hart, University of Toronto Paul E. McKenney, IBM Beaverton Angela Demke Brown, University of Toronto Outline Motivation
Making Lockless Synchronization Fast: Performance Implications of Memory Reclamation Tom Hart, University of Toronto Paul E. McKenney, IBM Beaverton Angela Demke Brown, University of Toronto Outline Motivation
G52CON: Concepts of Concurrency
 G52CON: Concepts of Concurrency Lecture 4: Atomic Actions Natasha Alechina School of Computer Science nza@cs.nott.ac.uk Outline of the lecture process execution fine-grained atomic actions using fine-grained
G52CON: Concepts of Concurrency Lecture 4: Atomic Actions Natasha Alechina School of Computer Science nza@cs.nott.ac.uk Outline of the lecture process execution fine-grained atomic actions using fine-grained
Administrivia. p. 1/20
 p. 1/20 Administrivia Please say your name if you answer a question today If we don t have a photo of you yet, stay after class If you didn t get test email, let us know p. 2/20 Program A int flag1 = 0,
p. 1/20 Administrivia Please say your name if you answer a question today If we don t have a photo of you yet, stay after class If you didn t get test email, let us know p. 2/20 Program A int flag1 = 0,
CS 241 Honors Concurrent Data Structures
 CS 241 Honors Concurrent Data Structures Bhuvan Venkatesh University of Illinois Urbana Champaign March 27, 2018 CS 241 Course Staff (UIUC) Lock Free Data Structures March 27, 2018 1 / 43 What to go over
CS 241 Honors Concurrent Data Structures Bhuvan Venkatesh University of Illinois Urbana Champaign March 27, 2018 CS 241 Course Staff (UIUC) Lock Free Data Structures March 27, 2018 1 / 43 What to go over
Lecture 5: Synchronization w/locks
 Lecture 5: Synchronization w/locks CSE 120: Principles of Operating Systems Alex C. Snoeren Lab 1 Due 10/19 Threads Are Made to Share Global variables and static objects are shared Stored in the static
Lecture 5: Synchronization w/locks CSE 120: Principles of Operating Systems Alex C. Snoeren Lab 1 Due 10/19 Threads Are Made to Share Global variables and static objects are shared Stored in the static
Scalable Locking. Adam Belay
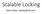 Scalable Locking Adam Belay Problem: Locks can ruin performance 12 finds/sec 9 6 Locking overhead dominates 3 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Cores Problem: Locks can ruin performance the locks
Scalable Locking Adam Belay Problem: Locks can ruin performance 12 finds/sec 9 6 Locking overhead dominates 3 0 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 Cores Problem: Locks can ruin performance the locks
The Java Memory Model
 The Java Memory Model The meaning of concurrency in Java Bartosz Milewski Plan of the talk Motivating example Sequential consistency Data races The DRF guarantee Causality Out-of-thin-air guarantee Implementation
The Java Memory Model The meaning of concurrency in Java Bartosz Milewski Plan of the talk Motivating example Sequential consistency Data races The DRF guarantee Causality Out-of-thin-air guarantee Implementation
Summary: Issues / Open Questions:
 Summary: The paper introduces Transitional Locking II (TL2), a Software Transactional Memory (STM) algorithm, which tries to overcomes most of the safety and performance issues of former STM implementations.
Summary: The paper introduces Transitional Locking II (TL2), a Software Transactional Memory (STM) algorithm, which tries to overcomes most of the safety and performance issues of former STM implementations.
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions
 CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter Lecture 7 Synchronization. Hank Levy 412 Sieg Hall
 CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2003 Lecture 7 Synchronization Hank Levy Levy@cs.washington.edu 412 Sieg Hall Synchronization Threads cooperate in multithreaded programs to share resources, access shared
CSE 451: Operating Systems Winter 2003 Lecture 7 Synchronization Hank Levy Levy@cs.washington.edu 412 Sieg Hall Synchronization Threads cooperate in multithreaded programs to share resources, access shared
Multiprocessor Support
 CSC 256/456: Operating Systems Multiprocessor Support John Criswell University of Rochester 1 Outline Multiprocessor hardware Types of multi-processor workloads Operating system issues Where to run the
CSC 256/456: Operating Systems Multiprocessor Support John Criswell University of Rochester 1 Outline Multiprocessor hardware Types of multi-processor workloads Operating system issues Where to run the
CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring Lecture 15: Caching: Demand Paged Virtual Memory
 CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring 2003 Lecture 15: Caching: Demand Paged Virtual Memory 15.0 Main Points: Concept of paging to disk Replacement policies
CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring 2003 Lecture 15: Caching: Demand Paged Virtual Memory 15.0 Main Points: Concept of paging to disk Replacement policies
FINE-GRAINED SYNCHRONIZATION. Operating Systems Engineering. Sleep & Wakeup [chapter #5] 15-Jun-14. in the previous lecture.
![FINE-GRAINED SYNCHRONIZATION. Operating Systems Engineering. Sleep & Wakeup [chapter #5] 15-Jun-14. in the previous lecture. FINE-GRAINED SYNCHRONIZATION. Operating Systems Engineering. Sleep & Wakeup [chapter #5] 15-Jun-14. in the previous lecture.](/thumbs/82/85844943.jpg) Operating Systems Engineering Sleep & Wakeup [chapter #5] By Dan Tsafrir, 2014-04-02 1 in the previous lecture. When critical section is very short FINE-GRAINED SYNCHRONIZATION 2 1 in this lecture. When
Operating Systems Engineering Sleep & Wakeup [chapter #5] By Dan Tsafrir, 2014-04-02 1 in the previous lecture. When critical section is very short FINE-GRAINED SYNCHRONIZATION 2 1 in this lecture. When
Fast and Lock-Free Concurrent Priority Queues for Multi-Thread Systems
 Fast and Lock-Free Concurrent Priority Queues for Multi-Thread Systems Håkan Sundell Philippas Tsigas Outline Synchronization Methods Priority Queues Concurrent Priority Queues Lock-Free Algorithm: Problems
Fast and Lock-Free Concurrent Priority Queues for Multi-Thread Systems Håkan Sundell Philippas Tsigas Outline Synchronization Methods Priority Queues Concurrent Priority Queues Lock-Free Algorithm: Problems
Concurrent Programming Lecture 10
 Concurrent Programming Lecture 10 25th September 2003 Monitors & P/V Notion of a process being not runnable : implicit in much of what we have said about P/V and monitors is the notion that a process may
Concurrent Programming Lecture 10 25th September 2003 Monitors & P/V Notion of a process being not runnable : implicit in much of what we have said about P/V and monitors is the notion that a process may
ATOMIC COMMITMENT Or: How to Implement Distributed Transactions in Sharded Databases
 ATOMIC COMMITMENT Or: How to Implement Distributed Transactions in Sharded Databases We talked about transactions and how to implement them in a single-node database. We ll now start looking into how to
ATOMIC COMMITMENT Or: How to Implement Distributed Transactions in Sharded Databases We talked about transactions and how to implement them in a single-node database. We ll now start looking into how to
Ext3/4 file systems. Don Porter CSE 506
 Ext3/4 file systems Don Porter CSE 506 Logical Diagram Binary Formats Memory Allocators System Calls Threads User Today s Lecture Kernel RCU File System Networking Sync Memory Management Device Drivers
Ext3/4 file systems Don Porter CSE 506 Logical Diagram Binary Formats Memory Allocators System Calls Threads User Today s Lecture Kernel RCU File System Networking Sync Memory Management Device Drivers
Control Hazards. Prediction
 Control Hazards The nub of the problem: In what pipeline stage does the processor fetch the next instruction? If that instruction is a conditional branch, when does the processor know whether the conditional
Control Hazards The nub of the problem: In what pipeline stage does the processor fetch the next instruction? If that instruction is a conditional branch, when does the processor know whether the conditional
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #5 May 2th, 2013 Professor Krste Asanović Name: <ANSWER KEY>
 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #5 May 2th, 2013 Professor Krste Asanović Name: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 15 pages Notes: Not all questions are
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #5 May 2th, 2013 Professor Krste Asanović Name: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 15 pages Notes: Not all questions are
Page Replacement. (and other virtual memory policies) Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 27, 2018
 Page Replacement (and other virtual memory policies) Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 27, 2018 Today s Goals Making virtual memory virtual : incorporating disk backing. Explore page replacement policies
Page Replacement (and other virtual memory policies) Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 27, 2018 Today s Goals Making virtual memory virtual : incorporating disk backing. Explore page replacement policies
CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 23: Programming with Locks and Critical Sections. Tyler Robison Summer 2010
 CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 23: Programming with Locks and Critical Sections Tyler Robison Summer 2010 1 Concurrency: where are we Done: The semantics of locks Locks in Java Using locks for mutual
CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 23: Programming with Locks and Critical Sections Tyler Robison Summer 2010 1 Concurrency: where are we Done: The semantics of locks Locks in Java Using locks for mutual
CS 220: Introduction to Parallel Computing. Introduction to CUDA. Lecture 28
 CS 220: Introduction to Parallel Computing Introduction to CUDA Lecture 28 Today s Schedule Project 4 Read-Write Locks Introduction to CUDA 5/2/18 CS 220: Parallel Computing 2 Today s Schedule Project
CS 220: Introduction to Parallel Computing Introduction to CUDA Lecture 28 Today s Schedule Project 4 Read-Write Locks Introduction to CUDA 5/2/18 CS 220: Parallel Computing 2 Today s Schedule Project
Lecture 9: Multiprocessor OSs & Synchronization. CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown
 Lecture 9: Multiprocessor OSs & Synchronization CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown The Problem Coordinated management of shared resources Resources may be accessed by multiple threads Need to control
Lecture 9: Multiprocessor OSs & Synchronization CSC 469H1F Fall 2006 Angela Demke Brown The Problem Coordinated management of shared resources Resources may be accessed by multiple threads Need to control
A Sophomoric Introduction to Shared-Memory Parallelism and Concurrency Lecture 5 Programming with Locks and Critical Sections
 A Sophomoric Introduction to Shared-Memory Parallelism and Concurrency Lecture 5 Programming with Locks and Critical Sections Dan Grossman Last Updated: May 2012 For more information, see http://www.cs.washington.edu/homes/djg/teachingmaterials/
A Sophomoric Introduction to Shared-Memory Parallelism and Concurrency Lecture 5 Programming with Locks and Critical Sections Dan Grossman Last Updated: May 2012 For more information, see http://www.cs.washington.edu/homes/djg/teachingmaterials/
Linux kernel synchronization. Don Porter CSE 506
 Linux kernel synchronization Don Porter CSE 506 The old days Early/simple OSes (like JOS): No need for synchronization All kernel requests wait until completion even disk requests Heavily restrict when
Linux kernel synchronization Don Porter CSE 506 The old days Early/simple OSes (like JOS): No need for synchronization All kernel requests wait until completion even disk requests Heavily restrict when
Linux kernel synchronization
 Linux kernel synchronization Don Porter CSE 56 Memory Management Logical Diagram Binary Memory Formats Allocators Threads Today s Lecture Synchronization System Calls RCU in the kernel File System Networking
Linux kernel synchronization Don Porter CSE 56 Memory Management Logical Diagram Binary Memory Formats Allocators Threads Today s Lecture Synchronization System Calls RCU in the kernel File System Networking
Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Written Assignment 3
 Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Written Assignment 3 50 points total. Due Monday, July 17 at the start of class. Problem 1: Message Passing (6 pts) A. (3 pts) You and your friend liked the
Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Written Assignment 3 50 points total. Due Monday, July 17 at the start of class. Problem 1: Message Passing (6 pts) A. (3 pts) You and your friend liked the
Lecture 21: Transactional Memory. Topics: consistency model recap, introduction to transactional memory
 Lecture 21: Transactional Memory Topics: consistency model recap, introduction to transactional memory 1 Example Programs Initially, A = B = 0 P1 P2 A = 1 B = 1 if (B == 0) if (A == 0) critical section
Lecture 21: Transactional Memory Topics: consistency model recap, introduction to transactional memory 1 Example Programs Initially, A = B = 0 P1 P2 A = 1 B = 1 if (B == 0) if (A == 0) critical section
Transactionalizing Legacy Code: An Experience Report Using GCC and Memcached. Trilok Vyas, Yujie Liu, and Michael Spear Lehigh University
 Transactionalizing Legacy Code: An Experience Report Using GCC and Memcached Trilok Vyas, Yujie Liu, and Michael Spear Lehigh University 1 High-Level Overview Much work toward standardizing TM in C++ Draft
Transactionalizing Legacy Code: An Experience Report Using GCC and Memcached Trilok Vyas, Yujie Liu, and Michael Spear Lehigh University 1 High-Level Overview Much work toward standardizing TM in C++ Draft
Rsyslog: going up from 40K messages per second to 250K. Rainer Gerhards
 Rsyslog: going up from 40K messages per second to 250K Rainer Gerhards What's in it for you? Bad news: will not teach you to make your kernel component five times faster Perspective user-space application
Rsyslog: going up from 40K messages per second to 250K Rainer Gerhards What's in it for you? Bad news: will not teach you to make your kernel component five times faster Perspective user-space application
Multiprocessor Synchronization
 Multiprocessor Synchronization Material in this lecture in Henessey and Patterson, Chapter 8 pgs. 694-708 Some material from David Patterson s slides for CS 252 at Berkeley 1 Multiprogramming and Multiprocessing
Multiprocessor Synchronization Material in this lecture in Henessey and Patterson, Chapter 8 pgs. 694-708 Some material from David Patterson s slides for CS 252 at Berkeley 1 Multiprogramming and Multiprocessing
MULTITHREADING AND SYNCHRONIZATION. CS124 Operating Systems Fall , Lecture 10
 MULTITHREADING AND SYNCHRONIZATION CS124 Operating Systems Fall 2017-2018, Lecture 10 2 Critical Sections Race conditions can be avoided by preventing multiple control paths from accessing shared state
MULTITHREADING AND SYNCHRONIZATION CS124 Operating Systems Fall 2017-2018, Lecture 10 2 Critical Sections Race conditions can be avoided by preventing multiple control paths from accessing shared state
Readers-Writers Problem. Implementing shared locks. shared locks (continued) Review: Test-and-set spinlock. Review: Test-and-set on alpha
 Readers-Writers Problem Implementing shared locks Multiple threads may access data - Readers will only observe, not modify data - Writers will change the data Goal: allow multiple readers or one single
Readers-Writers Problem Implementing shared locks Multiple threads may access data - Readers will only observe, not modify data - Writers will change the data Goal: allow multiple readers or one single
CS510 Advanced Topics in Concurrency. Jonathan Walpole
 CS510 Advanced Topics in Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Threads Cannot Be Implemented as a Library Reasoning About Programs What are the valid outcomes for this program? Is it valid for both r1 and r2 to
CS510 Advanced Topics in Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Threads Cannot Be Implemented as a Library Reasoning About Programs What are the valid outcomes for this program? Is it valid for both r1 and r2 to
CPS 310 midterm exam #1, 2/19/2016
 CPS 310 midterm exam #1, 2/19/2016 Your name please: NetID: Answer all questions. Please attempt to confine your answers to the boxes provided. For the execution tracing problem (P3) you may wish to use
CPS 310 midterm exam #1, 2/19/2016 Your name please: NetID: Answer all questions. Please attempt to confine your answers to the boxes provided. For the execution tracing problem (P3) you may wish to use
(Refer Slide Time: 1:26)
 Information Security-3 Prof. V Kamakoti Department of Computer science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Basics of Unix and Network Administration Operating Systems Introduction Mod01,
Information Security-3 Prof. V Kamakoti Department of Computer science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Basics of Unix and Network Administration Operating Systems Introduction Mod01,
230 Million Tweets per day
 Tweets per day Queries per day Indexing latency Avg. query response time Earlybird - Realtime Search @twitter Michael Busch @michibusch michael@twitter.com buschmi@apache.org Earlybird - Realtime Search
Tweets per day Queries per day Indexing latency Avg. query response time Earlybird - Realtime Search @twitter Michael Busch @michibusch michael@twitter.com buschmi@apache.org Earlybird - Realtime Search
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems
 CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2018 Lecture 15: Multicore Geoffrey M. Voelker Multicore Operating Systems We have generally discussed operating systems concepts independent of the number
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2018 Lecture 15: Multicore Geoffrey M. Voelker Multicore Operating Systems We have generally discussed operating systems concepts independent of the number
A Sophomoric Introduction to Shared-Memory Parallelism and Concurrency Lecture 4 Shared-Memory Concurrency & Mutual Exclusion
 A Sophomoric Introduction to Shared-Memory Parallelism and Concurrency Lecture 4 Shared-Memory Concurrency & Mutual Exclusion Dan Grossman Last Updated: August 2010 For more information, see http://www.cs.washington.edu/homes/djg/teachingmaterials/
A Sophomoric Introduction to Shared-Memory Parallelism and Concurrency Lecture 4 Shared-Memory Concurrency & Mutual Exclusion Dan Grossman Last Updated: August 2010 For more information, see http://www.cs.washington.edu/homes/djg/teachingmaterials/
Split-Ordered Lists: Lock-Free Extensible Hash Tables. Pierre LaBorde
 1 Split-Ordered Lists: Lock-Free Extensible Hash Tables Pierre LaBorde Nir Shavit 2 Tel-Aviv University, Israel Ph.D. from Hebrew University Professor at School of Computer Science at Tel-Aviv University
1 Split-Ordered Lists: Lock-Free Extensible Hash Tables Pierre LaBorde Nir Shavit 2 Tel-Aviv University, Israel Ph.D. from Hebrew University Professor at School of Computer Science at Tel-Aviv University
Implementing Mutual Exclusion. Sarah Diesburg Operating Systems CS 3430
 Implementing Mutual Exclusion Sarah Diesburg Operating Systems CS 3430 From the Previous Lecture The too much milk example shows that writing concurrent programs directly with load and store instructions
Implementing Mutual Exclusion Sarah Diesburg Operating Systems CS 3430 From the Previous Lecture The too much milk example shows that writing concurrent programs directly with load and store instructions
Need for synchronization: If threads comprise parts of our software systems, then they must communicate.
 Thread communication and synchronization There are two main aspects to Outline for Lecture 19 multithreaded programming in Java: I. Thread synchronization. thread lifecycle, and thread synchronization.
Thread communication and synchronization There are two main aspects to Outline for Lecture 19 multithreaded programming in Java: I. Thread synchronization. thread lifecycle, and thread synchronization.
CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 22: Shared-Memory Concurrency and Mutual Exclusion. Tyler Robison Summer 2010
 CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 22: Shared-Memory Concurrency and Mutual Exclusion Tyler Robison Summer 2010 1 Toward sharing resources (memory) So far we ve looked at parallel algorithms using fork-join
CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 22: Shared-Memory Concurrency and Mutual Exclusion Tyler Robison Summer 2010 1 Toward sharing resources (memory) So far we ve looked at parallel algorithms using fork-join
Threads and Too Much Milk! CS439: Principles of Computer Systems January 31, 2018
 Threads and Too Much Milk! CS439: Principles of Computer Systems January 31, 2018 Last Time CPU Scheduling discussed the possible policies the scheduler may use to choose the next process (or thread!)
Threads and Too Much Milk! CS439: Principles of Computer Systems January 31, 2018 Last Time CPU Scheduling discussed the possible policies the scheduler may use to choose the next process (or thread!)
NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY. Tim Harris, 21 November 2014
 NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY Tim Harris, 21 November 2014 Lecture 7 Linearizability Lock-free progress properties Queues Reducing contention Explicit memory management Linearizability
NON-BLOCKING DATA STRUCTURES AND TRANSACTIONAL MEMORY Tim Harris, 21 November 2014 Lecture 7 Linearizability Lock-free progress properties Queues Reducing contention Explicit memory management Linearizability
An Almost Non- Blocking Stack
 An Almost Non- Blocking Stack Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice Motivation Update data structures
An Almost Non- Blocking Stack Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice Motivation Update data structures
Problem Set 2. CS347: Operating Systems
 CS347: Operating Systems Problem Set 2 1. Consider a clinic with one doctor and a very large waiting room (of infinite capacity). Any patient entering the clinic will wait in the waiting room until the
CS347: Operating Systems Problem Set 2 1. Consider a clinic with one doctor and a very large waiting room (of infinite capacity). Any patient entering the clinic will wait in the waiting room until the
CSE380 - Operating Systems
 CSE380 - Operating Systems Notes for Lecture 17-11/10/05 Matt Blaze, Micah Sherr (some examples by Insup Lee) Implementing File Systems We ve looked at the user view of file systems names, directory structure,
CSE380 - Operating Systems Notes for Lecture 17-11/10/05 Matt Blaze, Micah Sherr (some examples by Insup Lee) Implementing File Systems We ve looked at the user view of file systems names, directory structure,
What is the Race Condition? And what is its solution? What is a critical section? And what is the critical section problem?
 What is the Race Condition? And what is its solution? Race Condition: Where several processes access and manipulate the same data concurrently and the outcome of the execution depends on the particular
What is the Race Condition? And what is its solution? Race Condition: Where several processes access and manipulate the same data concurrently and the outcome of the execution depends on the particular
Cache-Aware Lock-Free Queues for Multiple Producers/Consumers and Weak Memory Consistency
 Cache-Aware Lock-Free Queues for Multiple Producers/Consumers and Weak Memory Consistency Anders Gidenstam Håkan Sundell Philippas Tsigas School of business and informatics University of Borås Distributed
Cache-Aware Lock-Free Queues for Multiple Producers/Consumers and Weak Memory Consistency Anders Gidenstam Håkan Sundell Philippas Tsigas School of business and informatics University of Borås Distributed
EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems
 EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems Winter 2018 Baris Kasikci Slides by: Harsha V. Madhyastha Use of CVs in Project 1 Incorrect use of condition variables: while (cond) { } cv.signal() cv.wait()
EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems Winter 2018 Baris Kasikci Slides by: Harsha V. Madhyastha Use of CVs in Project 1 Incorrect use of condition variables: while (cond) { } cv.signal() cv.wait()
Multiprocessors and Locking
 Types of Multiprocessors (MPs) Uniform memory-access (UMA) MP Access to all memory occurs at the same speed for all processors. Multiprocessors and Locking COMP9242 2008/S2 Week 12 Part 1 Non-uniform memory-access
Types of Multiprocessors (MPs) Uniform memory-access (UMA) MP Access to all memory occurs at the same speed for all processors. Multiprocessors and Locking COMP9242 2008/S2 Week 12 Part 1 Non-uniform memory-access
Introduction to Embedded Systems. Lab Logistics
 Introduction to Embedded Systems CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: lab logistics interrupt synchronization reentrant code 1 CS 5780 Lab Logistics Lab2 Status Wed: 3/11 teams have completed their
Introduction to Embedded Systems CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: lab logistics interrupt synchronization reentrant code 1 CS 5780 Lab Logistics Lab2 Status Wed: 3/11 teams have completed their
Multiprocessors II: CC-NUMA DSM. CC-NUMA for Large Systems
 Multiprocessors II: CC-NUMA DSM DSM cache coherence the hardware stuff Today s topics: what happens when we lose snooping new issues: global vs. local cache line state enter the directory issues of increasing
Multiprocessors II: CC-NUMA DSM DSM cache coherence the hardware stuff Today s topics: what happens when we lose snooping new issues: global vs. local cache line state enter the directory issues of increasing
Midterm Exam Solutions and Grading Guidelines March 3, 1999 CS162 Operating Systems
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 1999 Anthony D. Joseph Midterm Exam Solutions and Grading Guidelines March 3, 1999 CS162 Operating Systems
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 1999 Anthony D. Joseph Midterm Exam Solutions and Grading Guidelines March 3, 1999 CS162 Operating Systems
Mutex Implementation
 COS 318: Operating Systems Mutex Implementation Jaswinder Pal Singh Computer Science Department Princeton University (http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cos318/) Revisit Mutual Exclusion (Mutex) u Critical
COS 318: Operating Systems Mutex Implementation Jaswinder Pal Singh Computer Science Department Princeton University (http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cos318/) Revisit Mutual Exclusion (Mutex) u Critical
[537] Locks. Tyler Harter
![[537] Locks. Tyler Harter [537] Locks. Tyler Harter](/thumbs/75/72450143.jpg) [537] Locks Tyler Harter Review: Threads+Locks CPU 1 CPU 2 running thread 1 running thread 2 RAM PageDir A PageDir B CPU 1 CPU 2 running thread 1 running thread 2 RAM PageDir A PageDir B Virt Mem (PageDir
[537] Locks Tyler Harter Review: Threads+Locks CPU 1 CPU 2 running thread 1 running thread 2 RAM PageDir A PageDir B CPU 1 CPU 2 running thread 1 running thread 2 RAM PageDir A PageDir B Virt Mem (PageDir
Characterizing the Performance and Energy Efficiency of Lock-Free Data Structures
 Characterizing the Performance and Energy Efficiency of Lock-Free Data Structures Nicholas Hunt Paramjit Singh Sandhu Luis Ceze University of Washington {nhunt,paramsan,luisceze}@cs.washington.edu Abstract
Characterizing the Performance and Energy Efficiency of Lock-Free Data Structures Nicholas Hunt Paramjit Singh Sandhu Luis Ceze University of Washington {nhunt,paramsan,luisceze}@cs.washington.edu Abstract
Today: Segmentation. Last Class: Paging. Costs of Using The TLB. The Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB)
 Last Class: Paging Process generates virtual addresses from 0 to Max. OS divides the process onto pages; manages a page table for every process; and manages the pages in memory Hardware maps from virtual
Last Class: Paging Process generates virtual addresses from 0 to Max. OS divides the process onto pages; manages a page table for every process; and manages the pages in memory Hardware maps from virtual
Non-blocking Array-based Algorithms for Stacks and Queues. Niloufar Shafiei
 Non-blocking Array-based Algorithms for Stacks and Queues Niloufar Shafiei Outline Introduction Concurrent stacks and queues Contributions New algorithms New algorithms using bounded counter values Correctness
Non-blocking Array-based Algorithms for Stacks and Queues Niloufar Shafiei Outline Introduction Concurrent stacks and queues Contributions New algorithms New algorithms using bounded counter values Correctness
CS 111. Operating Systems Peter Reiher
 Operating System Principles: Mutual Exclusion and Asynchronous Completion Operating Systems Peter Reiher Page 1 Outline Mutual Exclusion Asynchronous Completions Page 2 Mutual Exclusion Critical sections
Operating System Principles: Mutual Exclusion and Asynchronous Completion Operating Systems Peter Reiher Page 1 Outline Mutual Exclusion Asynchronous Completions Page 2 Mutual Exclusion Critical sections
Exploring mtcp based Single-Threaded and Multi-Threaded Web Server Design
 Exploring mtcp based Single-Threaded and Multi-Threaded Web Server Design A Thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Technology by Pijush Chakraborty (153050015)
Exploring mtcp based Single-Threaded and Multi-Threaded Web Server Design A Thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Technology by Pijush Chakraborty (153050015)
G Programming Languages - Fall 2012
 G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 4 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops Adding Invariants Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter
G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 4 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops Adding Invariants Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter
Control Hazards. Branch Prediction
 Control Hazards The nub of the problem: In what pipeline stage does the processor fetch the next instruction? If that instruction is a conditional branch, when does the processor know whether the conditional
Control Hazards The nub of the problem: In what pipeline stage does the processor fetch the next instruction? If that instruction is a conditional branch, when does the processor know whether the conditional
Progress Guarantees When Composing Lock-Free Objects
 Progress Guarantees When Composing Lock-Free Objects Nhan Nguyen Dang and Philippas Tsigas Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Gothenburg, Sweden {nhann,tsigas}@chalmers.se
Progress Guarantees When Composing Lock-Free Objects Nhan Nguyen Dang and Philippas Tsigas Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Gothenburg, Sweden {nhann,tsigas}@chalmers.se
Timers 1 / 46. Jiffies. Potent and Evil Magic
 Timers 1 / 46 Jiffies Each timer tick, a variable called jiffies is incremented It is thus (roughly) the number of HZ since system boot A 32-bit counter incremented at 1000 Hz wraps around in about 50
Timers 1 / 46 Jiffies Each timer tick, a variable called jiffies is incremented It is thus (roughly) the number of HZ since system boot A 32-bit counter incremented at 1000 Hz wraps around in about 50
Proving liveness. Alexey Gotsman IMDEA Software Institute
 Proving liveness Alexey Gotsman IMDEA Software Institute Safety properties Ensure bad things don t happen: - the program will not commit a memory safety fault - it will not release a lock it does not hold
Proving liveness Alexey Gotsman IMDEA Software Institute Safety properties Ensure bad things don t happen: - the program will not commit a memory safety fault - it will not release a lock it does not hold
Kernel Scalability. Adam Belay
 Kernel Scalability Adam Belay Motivation Modern CPUs are predominantly multicore Applications rely heavily on kernel for networking, filesystem, etc. If kernel can t scale across many
Kernel Scalability Adam Belay Motivation Modern CPUs are predominantly multicore Applications rely heavily on kernel for networking, filesystem, etc. If kernel can t scale across many
Review: Easy Piece 1
 CS 537 Lecture 10 Threads Michael Swift 10/9/17 2004-2007 Ed Lazowska, Hank Levy, Andrea and Remzi Arpaci-Dussea, Michael Swift 1 Review: Easy Piece 1 Virtualization CPU Memory Context Switch Schedulers
CS 537 Lecture 10 Threads Michael Swift 10/9/17 2004-2007 Ed Lazowska, Hank Levy, Andrea and Remzi Arpaci-Dussea, Michael Swift 1 Review: Easy Piece 1 Virtualization CPU Memory Context Switch Schedulers
Verifying Concurrent Programs
 Verifying Concurrent Programs Daniel Kroening 8 May 1 June 01 Outline Shared-Variable Concurrency Predicate Abstraction for Concurrent Programs Boolean Programs with Bounded Replication Boolean Programs
Verifying Concurrent Programs Daniel Kroening 8 May 1 June 01 Outline Shared-Variable Concurrency Predicate Abstraction for Concurrent Programs Boolean Programs with Bounded Replication Boolean Programs
Page 1. Goals for Today" Atomic Read-Modify-Write instructions" Examples of Read-Modify-Write "
 Goals for Today" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 5 Semaphores, Conditional Variables" Atomic instruction sequence Continue with Synchronization Abstractions Semaphores, Monitors
Goals for Today" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 5 Semaphores, Conditional Variables" Atomic instruction sequence Continue with Synchronization Abstractions Semaphores, Monitors
ò Very reliable, best-of-breed traditional file system design ò Much like the JOS file system you are building now
 Ext2 review Very reliable, best-of-breed traditional file system design Ext3/4 file systems Don Porter CSE 506 Much like the JOS file system you are building now Fixed location super blocks A few direct
Ext2 review Very reliable, best-of-breed traditional file system design Ext3/4 file systems Don Porter CSE 506 Much like the JOS file system you are building now Fixed location super blocks A few direct
Questions answered in this lecture: CS 537 Lecture 19 Threads and Cooperation. What s in a process? Organizing a Process
 Questions answered in this lecture: CS 537 Lecture 19 Threads and Cooperation Why are threads useful? How does one use POSIX pthreads? Michael Swift 1 2 What s in a process? Organizing a Process A process
Questions answered in this lecture: CS 537 Lecture 19 Threads and Cooperation Why are threads useful? How does one use POSIX pthreads? Michael Swift 1 2 What s in a process? Organizing a Process A process
