EE382M 15: Assignment 2
|
|
|
- Miles Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE382M 15: Assignment 2 Professor: Lizy K. John TA: Jee Ho Ryoo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas, Austin Due: 11:59PM September 28, Introduction The goal of this assignment is to evaluate workloads on real systems using performance monitoring counters (PMCs). You will gain experience working directly with complex vendor provided specifications, in this case, Intel s PMC specification. You will also gain experience using PMCs to evaluate workload performance on real systems. 1.1 Setup and Requirements - You will need access to a Linux machine with the perf utility installed to complete Section 3. Due to the nature of this lab, your machine should be lightly loaded or complete dedicated to you. This lab was written using Ubuntu LTS and perf version While we don t think that a difference in perf version or linux distribution will have a significant impact on this lab, we cannot guarantee success with all possible machine combinations. We will be using the above tools as the gold standard. If you have a doubt as to the suitability of your setup, please ask! - Once you do choose a machine, please use this same machine for all experiments, as we ask for a description of the machine as one of the deliverables. - Some virtual machines (like VMWare player) can virtualize the CPU performance counters. This should be sufficient for this lab if you choose to go down this route. I do not believe that VirtualBox supports counter virtualization however. If youa re not sure, please consult the TA. - To install perf on an Ubuntu machine, execute the following: sudo apt-get install linux-tools-common sudo apt-get install linux-tools generic Different systems will require different packages. 1.2 Deliverables The following deliverables must be completed for this assignment - Problems in Section 2 - Problems in Section 3 - Any scripts used to complete the problems 1
2 - Description of the profiled machine, detailing o CPU [cores/freq/sockets/vendor/model] o [L1/L2/L3] [I/D] cache [size/assoc] o Main Memory Size - HINT: Much can be gleaned from `cat /proc/cpuinfo` and your good friend Google. 2. Performance Monitoring Counters 2.1 Overview For this section, you will read and answer questions about the performance monitoring facilities for Intel processors. Our goal in this endeavor is to exercise your ability to find and interpret information in professional documentation. All major CPU hardware vendors expose performance monitoring counters, mostly for their own debugging and analysis efforts. However, these counters are documented publicly and can be read by anyone with the appropriate hardware. Before we dive too deeply into the high level Linux tools, let us first look at what documentation the CPU vendors provide. It is this documentation that is used by tools such as perf to query the hardware. For this example, let s look at what documentation Intel offers in its Software Developer s Manual. The appropriate section is as follows: architectures-software-developer-vol-3b-part-2-manual.pdf Don t be daunted by the size of this document, it is very modular. Sections 18 and 19 contains documentation for all publically available performance counters, from the Pentium Pro (P6) to Haswell. For this section, your focus will be much more specific. While the x86 instruction set maintains backwards compatibility across microarchitectures, the performance counters can and do change drastically from one generation to another. 2.2 Problems 1. Intel defines architectural performance events as hardware performance counters that do not change across microarchitecture generations. Please list all architectural performance events by name. 2. For the following questions, let s assume we are working with an Intel Core 2 Duo Processor (T7700). a. What architecture Performance Monitoring Version does this processor support? What is the underlying microarchitecture according to the manual? (Be careful here!) b. I need to count L2 cache loads of dirty cache lines for core 0 and not core 1 with all prefetches. What are the Umask Values and Event Numbers? 2
3 c. Let s say I want to count multiply and divide operations for a given workload. Can they both be active at the same time? How can I get around this? (You may not find an answer in the document, so please search Google). d. I have a very specific need to count the number of L2 dirty cache line evictions triggered by all cores including the contribution of hardware prefetches. What are my Umask Values and Event Number in this case? 3. Using Performance Counters for Analysis 3.1 Overview In practice, few people use the MSRs (machine status registers) directly for monitoring the counters (but it s still important to know how it s done!). We use higher level interfaces that abstract that icky complexity away from us. For this lab, we will use the Linux perf tool to extract hardware performance counter information. Take a look through this tutorial: As you can see, there is a lot more that perf can do besides reading PMCs! But for this assignment, we will only focus on this functionality. Pay particular interest to Section 2 on the wiki. To see what performance counters are available on your machine, type `perf list`. The performance counters from the CPU are listed as [Hardware Events] or [Hardware cache events]. Here are a few on my machine: L1-dcache-loads L1-dcache-load-misses L1-dcache-stores L1-dcache-store-misses If I want to see the number of branches and the number of cycles executed during a program, use the following command: perf stat e <events> <program> On my machine the following output is produced from the set of default events running a test program: 2,010,911,722 cycles # GHz 4,001,043,136 instructions # 1.99 insns per cycle 1,000,187,034 branches # M/sec 12,764 branch-misses # 0.00% of all branches seconds time elapsed Using the above tutorial and wiki link, please answer the questions in the following section. 3.2 Problems 3
4 1. I have a program foo that is multithreaded and contains both user space and kernel protected code that I am interested in profiling. Please provide the command line(s) AND identify any post-processing you would need to: a. Collect user-space IPC aggregated across all CPUs. b. Collect kernel branch miss rate on core 2. c. Collect system wide dtlb MPKI. 2. One nice thing about perf is that it allows you program the MSRs directly using what we learned in Section 2.0. This allows you to get at specific features hardware counters not exposed by perf. For this problem, identify a hardware counter on your microarchitecture that is not exposed by perf. Show how you can use perf s raw hardware descriptors to monitor that counter on your system. Give a sample command. 3. Try running perf with as many counters as you can. You will see statistics related to multiplexing. a. How does perf deal with multiplexing the performance counters? Can you think of a better way? (it s ok to look in the literature!) b. How many generic and fixed counters does your microarchitecture have? Cite your source for this. c. What are the rules concerning event assignment to the generic and fixed counters for your microprocessor? 4. In the lab handouts, you will find a program, little_program1, which is compiled from around 10 lines of C. Use perf to analyze the microarchitectural performance of this program. What can you say about this program? Can you make a reasonable guess as to what it is doing? Please include all relevant data to support your argument. NOTE: Yes, I know you can disassemble it and figure this out. Please don t. 5. Compiler optimizations can have a huge impact on program performance. In the lab packet, you will see a simple implementation of the inner product written in C (inner_product.c). Compile this code with O0 and O2 optimization flags. a. How do the branch behavior, cache behavior, IPC, and floating point ops change between the two optimization levels? b. Generate assembly with these optimization flags. What are the major differences that you see in code structure? Do these observations agree with your counter data? 6. In the lab handouts you were provided with a two sample binaries and inputs from the SPEC CPU2006 suite, named program1 and program2. I want you to analyze the microarchitectural performance of these programs. You can run them simply by typing `./program[1/2] program[1/2].in`. NOTE: Try to minimize multiplexing and scaling of the counters by perf. You will need to perform multiple runs. 4
5 a) Please collect and turn the following aggregate statistics for these programs. Show the perf commands issued and any post-processing needed to derive these. Instructions, Cycles, CPI, L1 Miss Rate, LLC MPKI, Branch Miss Rate b) Please collect micro op mixes for these programs. Specifically, I want % Load, % Store, % Branches, %Floating Point, % Other. c) Please create a graphs showing how the following statistics change over the execution of the programs. The x-access should be time, and the y-axis is the statistic. Sample the program counters every 1 second. If you write a script, please include it in the submission along with the raw data and graphs. How do the aggregate statistics for CPI, cache miss rates, and branch miss rates compare with the time-variant statistics? CPI, Load ops, Store ops, Branch ops, L1 Miss Rate, LLC MPKI, Branch Miss Rate d) Using all of these statistics, analyze the performance of these two programs. What can you say about their characteristics? 3.3 Hints and Tips 1. As was previously mentioned, performance counters are attached to the microprocessor generation. It is possible (and highly probable) that you and your friends will have different performance counters on your machines. Don t worry, this assignment should only need the basics that should be available on all vendors/models. But if this assumption proves false, please ask! 2. As you have no doubt noticed, there are many different types of cycles that can be counted. For this assignment, please always use the generic cycles/cpu-cycles counter in perf, not ref-cycles. 4. Submission Instructions 4.1 Submission instructions Your assignment must be compressed in tar.gz format. Please use the following command to tar your submission: % tar zcvf <your last name>-a2.tar.gz <your working directory> There will be a submission link available on the course website, so please submit your tarball by deadline. Your submission directory must have the same directory structure as the template directory structure. Please remove all your temporary and input trace files. You are only required to submit your code and makefile. Make sure that the name of your working directory is named <your last name>-a2. 5
Evaluating Performance Via Profiling
 Performance Engineering of Software Systems September 21, 2010 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.172 Professors Saman Amarasinghe and Charles E. Leiserson Handout 6 Profiling Project 2-1 Evaluating
Performance Engineering of Software Systems September 21, 2010 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.172 Professors Saman Amarasinghe and Charles E. Leiserson Handout 6 Profiling Project 2-1 Evaluating
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 2
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 2 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 21 January 2016 Announcements HW#1 will be posted tomorrow I am handing out
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 2 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 21 January 2016 Announcements HW#1 will be posted tomorrow I am handing out
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 2
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 2 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 4 September 2014 Announcements HW#1 delayed until Tuesday 1 Hardware Performance
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 2 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 4 September 2014 Announcements HW#1 delayed until Tuesday 1 Hardware Performance
Profiling: Understand Your Application
 Profiling: Understand Your Application Michal Merta michal.merta@vsb.cz 1st of March 2018 Agenda Hardware events based sampling Some fundamental bottlenecks Overview of profiling tools perf tools Intel
Profiling: Understand Your Application Michal Merta michal.merta@vsb.cz 1st of March 2018 Agenda Hardware events based sampling Some fundamental bottlenecks Overview of profiling tools perf tools Intel
More on Conjunctive Selection Condition and Branch Prediction
 More on Conjunctive Selection Condition and Branch Prediction CS764 Class Project - Fall Jichuan Chang and Nikhil Gupta {chang,nikhil}@cs.wisc.edu Abstract Traditionally, database applications have focused
More on Conjunctive Selection Condition and Branch Prediction CS764 Class Project - Fall Jichuan Chang and Nikhil Gupta {chang,nikhil}@cs.wisc.edu Abstract Traditionally, database applications have focused
ENCM 501 Winter 2017 Assignment 3 for the Week of January 30
 page 1 of 7 ENCM 501 Winter 2017 Assignment 3 for the Week of January 30 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary January 2017 Assignment instructions and other
page 1 of 7 ENCM 501 Winter 2017 Assignment 3 for the Week of January 30 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary January 2017 Assignment instructions and other
ENCM 501 Winter 2015 Assignment 3 for the Week of February 2
 page 1 of 6 ENCM 501 Winter 2015 Assignment 3 for the Week of February 2 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary January 2015 Assignment instructions and other
page 1 of 6 ENCM 501 Winter 2015 Assignment 3 for the Week of February 2 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary January 2015 Assignment instructions and other
ΕΛΠ 605: Προχωρηµένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών. Εργαστήριο Αρ. 4. Linux Monitoring Utilities (perf,top,mpstat ps, free) and gdb dissasembler, gnuplot
 ΕΛΠ 605: Προχωρηµένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών Εργαστήριο Αρ. 4 Linux Monitoring Utilities (perf,top,mpstat ps, free) and gdb dissasembler, gnuplot Lecturer: Zacharias Hadjilambrou Σελ. 1 Realtime monitoring
ΕΛΠ 605: Προχωρηµένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών Εργαστήριο Αρ. 4 Linux Monitoring Utilities (perf,top,mpstat ps, free) and gdb dissasembler, gnuplot Lecturer: Zacharias Hadjilambrou Σελ. 1 Realtime monitoring
Lab 03 - x86-64: atoi
 CSCI0330 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner Lab 03 - x86-64: atoi Due: October 1, 2017 at 4pm 1 Introduction 1 2 Assignment 1 2.1 Algorithm 2 3 Assembling and Testing 3 3.1 A Text Editor, Makefile, and gdb
CSCI0330 Intro Computer Systems Doeppner Lab 03 - x86-64: atoi Due: October 1, 2017 at 4pm 1 Introduction 1 2 Assignment 1 2.1 Algorithm 2 3 Assembling and Testing 3 3.1 A Text Editor, Makefile, and gdb
CS3350B Computer Architecture CPU Performance and Profiling
 CS3350B Computer Architecture CPU Performance and Profiling Marc Moreno Maza http://www.csd.uwo.ca/~moreno/cs3350_moreno/index.html Department of Computer Science University of Western Ontario, Canada
CS3350B Computer Architecture CPU Performance and Profiling Marc Moreno Maza http://www.csd.uwo.ca/~moreno/cs3350_moreno/index.html Department of Computer Science University of Western Ontario, Canada
CS Programming Languages Fall Homework #2
 CS 345 - Programming Languages Fall 2010 Homework #2 Due: 2pm CDT (in class), September 30, 2010 Collaboration policy This assignment can be done in teams at most two students. Any cheating (e.g., submitting
CS 345 - Programming Languages Fall 2010 Homework #2 Due: 2pm CDT (in class), September 30, 2010 Collaboration policy This assignment can be done in teams at most two students. Any cheating (e.g., submitting
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 23
 ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 23 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 1 December 2015 Don t forget projects Announcements HW8, HW9, and HW10 grades were sent out.
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 23 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 1 December 2015 Don t forget projects Announcements HW8, HW9, and HW10 grades were sent out.
CS155: Computer Security Spring Project #1. Due: Part 1: Thursday, April pm, Part 2: Monday, April pm.
 CS155: Computer Security Spring 2008 Project #1 Due: Part 1: Thursday, April 17-1159 pm, Part 2: Monday, April 21-1159 pm. Goal 1. The goal of this assignment is to gain hands-on experience with the effect
CS155: Computer Security Spring 2008 Project #1 Due: Part 1: Thursday, April 17-1159 pm, Part 2: Monday, April 21-1159 pm. Goal 1. The goal of this assignment is to gain hands-on experience with the effect
EE516: Embedded Software Project 1. Setting Up Environment for Projects
 EE516: Embedded Software Project 1. Setting Up Environment for Projects By Dong Jae Shin 2015. 09. 01. Contents Introduction to Projects of EE516 Tasks Setting Up Environment Virtual Machine Environment
EE516: Embedded Software Project 1. Setting Up Environment for Projects By Dong Jae Shin 2015. 09. 01. Contents Introduction to Projects of EE516 Tasks Setting Up Environment Virtual Machine Environment
PERF performance-counter for Odroid XU3/XU4
 2017/12/07 21:49 1/6 PERF performance-counter for Odroid XU3/XU4 PERF performance-counter for Odroid XU3/XU4 Linux hardware performance measurement using counters, trace-points, software performance counters,
2017/12/07 21:49 1/6 PERF performance-counter for Odroid XU3/XU4 PERF performance-counter for Odroid XU3/XU4 Linux hardware performance measurement using counters, trace-points, software performance counters,
CSC 510 Advanced Operating Systems, Fall 2017
 CSC 510 Advanced Operating Systems, Fall 2017 Dr. Dale E. Parson, Assignment 4, Benchmarking and analyzing a modified Assignment 1 running on System VMs on Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors. This assignment
CSC 510 Advanced Operating Systems, Fall 2017 Dr. Dale E. Parson, Assignment 4, Benchmarking and analyzing a modified Assignment 1 running on System VMs on Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors. This assignment
Operating Systems (234123) Spring 2017 (Homework Wet 1) Homework 1 Wet
 Homework 1 Wet Due Date: 30/4/2017 23:00 Teaching assistant in charge: Yehonatan Buchnik Important: the Q&A for the exercise will take place at a public forum Piazza only. Critical updates about the HW
Homework 1 Wet Due Date: 30/4/2017 23:00 Teaching assistant in charge: Yehonatan Buchnik Important: the Q&A for the exercise will take place at a public forum Piazza only. Critical updates about the HW
Performance Impact of Multithreaded Java Server Applications
 Performance Impact of Multithreaded Java Server Applications Yue Luo, Lizy K. John Laboratory of Computer Architecture ECE Department University of Texas at Austin 1/2/01 1 Outline Motivation VolanoMark
Performance Impact of Multithreaded Java Server Applications Yue Luo, Lizy K. John Laboratory of Computer Architecture ECE Department University of Texas at Austin 1/2/01 1 Outline Motivation VolanoMark
CS155: Computer Security Spring Project #1
 CS155: Computer Security Spring 2018 Project #1 Due: Part 1: Thursday, April 12-11:59pm, Parts 2 and 3: Thursday, April 19-11:59pm. The goal of this assignment is to gain hands-on experience finding vulnerabilities
CS155: Computer Security Spring 2018 Project #1 Due: Part 1: Thursday, April 12-11:59pm, Parts 2 and 3: Thursday, April 19-11:59pm. The goal of this assignment is to gain hands-on experience finding vulnerabilities
Debugging and Profiling
 Debugging and Profiling Dr. Axel Kohlmeyer Senior Scientific Computing Expert Information and Telecommunication Section The Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics http://sites.google.com/site/akohlmey/
Debugging and Profiling Dr. Axel Kohlmeyer Senior Scientific Computing Expert Information and Telecommunication Section The Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics http://sites.google.com/site/akohlmey/
IC220 Slide Set #5B: Performance (Chapter 1: 1.6, )
 Performance IC220 Slide Set #5B: Performance (Chapter 1: 1.6, 1.9-1.11) Measure, Report, and Summarize Make intelligent choices See through the marketing hype Key to understanding underlying organizational
Performance IC220 Slide Set #5B: Performance (Chapter 1: 1.6, 1.9-1.11) Measure, Report, and Summarize Make intelligent choices See through the marketing hype Key to understanding underlying organizational
Introduction to Pintos. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Introduction to Pintos Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Welcome to Pintos! What is Pintos? An instructional operating system Developed
Introduction to Pintos Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Welcome to Pintos! What is Pintos? An instructional operating system Developed
C152 Laboratory Exercise 5
 C152 Laboratory Exercise 5 Professor: Krste Asanovic TA: Scott Beamer Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley April 7, 2009 1 Introduction and goals The
C152 Laboratory Exercise 5 Professor: Krste Asanovic TA: Scott Beamer Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley April 7, 2009 1 Introduction and goals The
C152 Laboratory Exercise 5
 C152 Laboratory Exercise 5 Professor: Krste Asanovic GSI: Henry Cook Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley April 9, 2008 1 Introduction and goals The
C152 Laboratory Exercise 5 Professor: Krste Asanovic GSI: Henry Cook Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley April 9, 2008 1 Introduction and goals The
CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring Project #2
 CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring 2014 Project #2 Part 1 due: 11am CDT, March 25, 2014 Part 2 due: 11am CDT, April 3, 2014 Submission instructions Follow the submission instructions in the
CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring 2014 Project #2 Part 1 due: 11am CDT, March 25, 2014 Part 2 due: 11am CDT, April 3, 2014 Submission instructions Follow the submission instructions in the
Power Struggles: Revisiting the RISC vs. CISC Debate on Contemporary ARM and x86 Architectures
 Power Struggles: Revisiting the RISC vs. CISC Debate on Contemporary ARM and x86 Architectures by Ernily Blern, laikrishnan Menon, and Karthikeyan Sankaralingarn Danilo Dominguez Perez danilo0@iastate.edu
Power Struggles: Revisiting the RISC vs. CISC Debate on Contemporary ARM and x86 Architectures by Ernily Blern, laikrishnan Menon, and Karthikeyan Sankaralingarn Danilo Dominguez Perez danilo0@iastate.edu
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 10
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 10 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 22 February 2018 Announcements HW#5 will be posted, caches Midterm: Thursday
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 10 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 22 February 2018 Announcements HW#5 will be posted, caches Midterm: Thursday
CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring Project #2
 CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring 2017 Project #2 Part 1 due: 11:00, April 3, 2017 Part 2 due: 11:00, April 10, 2017 Submission instructions Follow the submission instructions in the Deliverables
CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring 2017 Project #2 Part 1 due: 11:00, April 3, 2017 Part 2 due: 11:00, April 10, 2017 Submission instructions Follow the submission instructions in the Deliverables
Kernel perf tool user guide
 Kernel perf tool user guide 2017-10-16 Reversion Record Date Rev Change Description Author 2017-10-16 V0.1 Inital Zhang Yongchang 1 / 10 catalog 1 PURPOSE...4 2 TERMINOLOGY...4 3 ENVIRONMENT...4 3.1 HARDWARE
Kernel perf tool user guide 2017-10-16 Reversion Record Date Rev Change Description Author 2017-10-16 V0.1 Inital Zhang Yongchang 1 / 10 catalog 1 PURPOSE...4 2 TERMINOLOGY...4 3 ENVIRONMENT...4 3.1 HARDWARE
C152 Laboratory Exercise 1
 C152 Laboratory Exercise 1 Professor: Krste Asanovic TA: Christopher Celio Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley January 26, 2011 1 Introduction and
C152 Laboratory Exercise 1 Professor: Krste Asanovic TA: Christopher Celio Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley January 26, 2011 1 Introduction and
Registers. Registers
 All computers have some registers visible at the ISA level. They are there to control execution of the program hold temporary results visible at the microarchitecture level, such as the Top Of Stack (TOS)
All computers have some registers visible at the ISA level. They are there to control execution of the program hold temporary results visible at the microarchitecture level, such as the Top Of Stack (TOS)
Distributed: Monday, Nov. 30, Due: Monday, Dec. 7 at midnight
 cs281: Introduction to Computer Systems Project Lab: The Cachelab Simulating a Cache Controler Distributed: Monday, Nov. 30, Due: Monday, Dec. 7 at midnight Introduction This assignment will help you understand
cs281: Introduction to Computer Systems Project Lab: The Cachelab Simulating a Cache Controler Distributed: Monday, Nov. 30, Due: Monday, Dec. 7 at midnight Introduction This assignment will help you understand
Computer Performance. Reread Chapter Quiz on Friday. Study Session Wed Night FB 009, 5pm-6:30pm
 Computer Performance He said, to speed things up we need to squeeze the clock Reread Chapter 1.4-1.9 Quiz on Friday. Study Session Wed Night FB 009, 5pm-6:30pm L15 Computer Performance 1 Why Study Performance?
Computer Performance He said, to speed things up we need to squeeze the clock Reread Chapter 1.4-1.9 Quiz on Friday. Study Session Wed Night FB 009, 5pm-6:30pm L15 Computer Performance 1 Why Study Performance?
MIT OpenCourseWare Multicore Programming Primer, January (IAP) Please use the following citation format:
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, January (IAP) 2007 Please use the following citation format: Phil Sung, 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, January (IAP) 2007.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, January (IAP) 2007 Please use the following citation format: Phil Sung, 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, January (IAP) 2007.
Important Project Dates
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Fall 2002 Handout 4 Project Overview Wednesday, September 4 This is an overview of the course project
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Fall 2002 Handout 4 Project Overview Wednesday, September 4 This is an overview of the course project
COMP 3500 Introduction to Operating Systems Project 5 Virtual Memory Manager
 COMP 3500 Introduction to Operating Systems Project 5 Virtual Memory Manager Points Possible: 100 Submission via Canvas No collaboration among groups. Students in one group should NOT share any project
COMP 3500 Introduction to Operating Systems Project 5 Virtual Memory Manager Points Possible: 100 Submission via Canvas No collaboration among groups. Students in one group should NOT share any project
The Role of Performance
 Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Role of Performance What is performance? A set of metrics that allow us to compare two different hardware
Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Role of Performance What is performance? A set of metrics that allow us to compare two different hardware
Lab 4: Interrupts and Realtime
 Lab 4: Interrupts and Realtime Overview At this point, we have learned the basics of how to write kernel driver module, and we wrote a driver kernel module for the LCD+shift register. Writing kernel driver
Lab 4: Interrupts and Realtime Overview At this point, we have learned the basics of how to write kernel driver module, and we wrote a driver kernel module for the LCD+shift register. Writing kernel driver
Homework 1 CS 642: Information Security
 Homework 1 CS 642: Information Security September 22, 2012 This homework assignment tasks you with understanding vulnerabilities in five target programs. You may (optionally) work with a partner. It is
Homework 1 CS 642: Information Security September 22, 2012 This homework assignment tasks you with understanding vulnerabilities in five target programs. You may (optionally) work with a partner. It is
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 Performance 2005-2-8 John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) TAs: Ted Hong and David Marquardt www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Last Time: Tips
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 Performance 2005-2-8 John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) TAs: Ted Hong and David Marquardt www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Last Time: Tips
SIMD Instructions outside and inside Oracle 12c. Laurent Léturgez 2016
 SIMD Instructions outside and inside Oracle 2c Laurent Léturgez 206 Whoami Oracle Consultant since 200 Former developer (C, Java, perl, PL/SQL) Owner@Premiseo: Data Management on Premise and in the Cloud
SIMD Instructions outside and inside Oracle 2c Laurent Léturgez 206 Whoami Oracle Consultant since 200 Former developer (C, Java, perl, PL/SQL) Owner@Premiseo: Data Management on Premise and in the Cloud
Advanced d Instruction Level Parallelism. Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Advanced d Instruction ti Level Parallelism Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu ILP Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining:
Advanced d Instruction ti Level Parallelism Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu ILP Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining:
Tracing Lustre. New approach to debugging. ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the US Department of Energy
 Tracing Lustre New approach to debugging ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the US Department of Energy Current Lustre debugging tools Utility lctl handles profiling developed long before standard kernel
Tracing Lustre New approach to debugging ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the US Department of Energy Current Lustre debugging tools Utility lctl handles profiling developed long before standard kernel
ECE571: Advanced Microprocessor Design Final Project Spring Officially Due: Friday, 4 May 2018 (Last day of Classes)
 Overview: ECE571: Advanced Microprocessor Design Final Project Spring 2018 Officially Due: Friday, 4 May 2018 (Last day of Classes) Design a project that explores the power, energy, and/or performance
Overview: ECE571: Advanced Microprocessor Design Final Project Spring 2018 Officially Due: Friday, 4 May 2018 (Last day of Classes) Design a project that explores the power, energy, and/or performance
How to Write Fast Numerical Code
 How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Performance Counters and applying the Roofline Model Slides and lecture by Georg Ofenbeck Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Georg Ofenbeck & Daniele Spampinato Read
How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Performance Counters and applying the Roofline Model Slides and lecture by Georg Ofenbeck Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Georg Ofenbeck & Daniele Spampinato Read
Operating Systems and Networks. Lecture 01: Introducing the course and Introduction to OS-part 1 Behzad Bordbar
 Operating Systems and Networks Lecture 01: Introducing the course and Introduction to OS-part 1 Behzad Bordbar 1 Introducing the course Why this module was created? Important First time Both practical
Operating Systems and Networks Lecture 01: Introducing the course and Introduction to OS-part 1 Behzad Bordbar 1 Introducing the course Why this module was created? Important First time Both practical
1.1 For Fun and Profit. 1.2 Common Techniques. My Preferred Techniques
 1 Bug Hunting Bug hunting is the process of finding bugs in software or hardware. In this book, however, the term bug hunting will be used specifically to describe the process of finding security-critical
1 Bug Hunting Bug hunting is the process of finding bugs in software or hardware. In this book, however, the term bug hunting will be used specifically to describe the process of finding security-critical
Cycle Accurate Simulator for TMS320C62x, 8 way VLIW DSP Processor
 Cycle Accurate Simulator for TMS320C62x, 8 way VLIW DSP Processor Vinodh Cuppu, Graduate Student, Electrical Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park For ENEE 646 - Digital Computer Design, Fall
Cycle Accurate Simulator for TMS320C62x, 8 way VLIW DSP Processor Vinodh Cuppu, Graduate Student, Electrical Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park For ENEE 646 - Digital Computer Design, Fall
Systems Programming and Computer Architecture ( ) Exercise Session 01 Data Lab
 Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Exercise Session 01 Data Lab 1 Goal Get familiar with bit level representations, C and Linux Thursday, September 22, 2016 Systems Programming
Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Exercise Session 01 Data Lab 1 Goal Get familiar with bit level representations, C and Linux Thursday, September 22, 2016 Systems Programming
MCS-284, Fall 2018 Cache Lab: Understanding Cache Memories Assigned: Friday, 11/30 Due: Friday, 12/14, by midnight (via Moodle)
 MCS-284, Fall 2018 Cache Lab: Understanding Cache Memories Assigned: Friday, 11/30 Due: Friday, 12/14, by midnight (via Moodle) 1 Logistics This is an individual project. All hand-ins are electronic via
MCS-284, Fall 2018 Cache Lab: Understanding Cache Memories Assigned: Friday, 11/30 Due: Friday, 12/14, by midnight (via Moodle) 1 Logistics This is an individual project. All hand-ins are electronic via
Project #1 Exceptions and Simple System Calls
 Project #1 Exceptions and Simple System Calls Introduction to Operating Systems Assigned: January 21, 2004 CSE421 Due: February 17, 2004 11:59:59 PM The first project is designed to further your understanding
Project #1 Exceptions and Simple System Calls Introduction to Operating Systems Assigned: January 21, 2004 CSE421 Due: February 17, 2004 11:59:59 PM The first project is designed to further your understanding
Assignment 1: Plz Tell Me My Password
 Assignment 1: Plz Tell Me My Password Part I Due: 11:59 pm, September 23, 2013 Part II Due : 11:59 pm, September 27, 2013 1 Introduction The objective of this assignment is to gain experience in: socket
Assignment 1: Plz Tell Me My Password Part I Due: 11:59 pm, September 23, 2013 Part II Due : 11:59 pm, September 27, 2013 1 Introduction The objective of this assignment is to gain experience in: socket
ICS(II), Fall 2017 Cache Lab: Understanding Cache Memories Assigned: Thursday, October 26, 2017 Due: Sunday, November 19, 2017, 11:59PM
 ICS(II), Fall 2017 Cache Lab: Understanding Cache Memories Assigned: Thursday, October 26, 2017 Due: Sunday, November 19, 2017, 11:59PM 1 Logistics This is an individual project. All handins are electronic.
ICS(II), Fall 2017 Cache Lab: Understanding Cache Memories Assigned: Thursday, October 26, 2017 Due: Sunday, November 19, 2017, 11:59PM 1 Logistics This is an individual project. All handins are electronic.
Intel released new technology call P6P
 P6 and IA-64 8086 released on 1978 Pentium release on 1993 8086 has upgrade by Pipeline, Super scalar, Clock frequency, Cache and so on But 8086 has limit, Hard to improve efficiency Intel released new
P6 and IA-64 8086 released on 1978 Pentium release on 1993 8086 has upgrade by Pipeline, Super scalar, Clock frequency, Cache and so on But 8086 has limit, Hard to improve efficiency Intel released new
Introduction. Overview and Getting Started. CS 161 Computer Security Lab 1 Buffer Overflows v.01 Due Date: September 17, 2012 by 11:59pm
 Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Lab 1 Buffer Overflows v.01 Due Date: September 17, 2012 by 11:59pm Introduction In this lab, you will get a hands-on approach to circumventing user permissions
Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Lab 1 Buffer Overflows v.01 Due Date: September 17, 2012 by 11:59pm Introduction In this lab, you will get a hands-on approach to circumventing user permissions
Memory Models. Registers
 Memory Models Most machines have a single linear address space at the ISA level, extending from address 0 up to some maximum, often 2 32 1 bytes or 2 64 1 bytes. Some machines have separate address spaces
Memory Models Most machines have a single linear address space at the ISA level, extending from address 0 up to some maximum, often 2 32 1 bytes or 2 64 1 bytes. Some machines have separate address spaces
M5 simulator system TDT4260 Computer Architecture User documentation
 M5 simulator system TDT4260 Computer Architecture User documentation Last modified: January 20, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Overview............................. 2 1.2 Chapter outlines.........................
M5 simulator system TDT4260 Computer Architecture User documentation Last modified: January 20, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Overview............................. 2 1.2 Chapter outlines.........................
H.J. Lu, Sunil K Pandey. Intel. November, 2018
 H.J. Lu, Sunil K Pandey Intel November, 2018 Issues with Run-time Library on IA Memory, string and math functions in today s glibc are optimized for today s Intel processors: AVX/AVX2/AVX512 FMA It takes
H.J. Lu, Sunil K Pandey Intel November, 2018 Issues with Run-time Library on IA Memory, string and math functions in today s glibc are optimized for today s Intel processors: AVX/AVX2/AVX512 FMA It takes
Homework 2 (r1.1) Due: Part (A) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Part (B) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Part (C) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm
 Second Semester, 2016 17 Homework 2 (r1.1) Due: Part (A) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Part (B) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Part (C) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through
Second Semester, 2016 17 Homework 2 (r1.1) Due: Part (A) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Part (B) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Part (C) -- Apr 2, 2017, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through
CSC D84 Assignment 2 Game Trees and Mini-Max
 0 The Cats Strike Back Due date: Wednesday, Feb. 21, 9am (electronic submission on Mathlab) This assignment can be completed individually, or by a team of 2 students This assignment is worth 10 units toward
0 The Cats Strike Back Due date: Wednesday, Feb. 21, 9am (electronic submission on Mathlab) This assignment can be completed individually, or by a team of 2 students This assignment is worth 10 units toward
Development Environment Embedded Linux Primer Ch 1&2
 Development Environment Embedded Linux Primer Ch 1&2 Topics 1) Systems: Host and Target 2) Host setup 3) Host-Target communication CMPT 433 Slides #3 Dr. B. Fraser 18-05-05 2 18-05-05 1 Host & Target Host
Development Environment Embedded Linux Primer Ch 1&2 Topics 1) Systems: Host and Target 2) Host setup 3) Host-Target communication CMPT 433 Slides #3 Dr. B. Fraser 18-05-05 2 18-05-05 1 Host & Target Host
UChicago CMSC Computer Architecture, Autumn 2018 Lab 5 Extra Credit: Multi-Core and The MESI Cache Coherence Protocol
 UChicago CMSC-22200 Computer Architecture, Autumn 2018 Lab 5 Extra Credit: Multi-Core and The MESI Cache Coherence Protocol Instructor: Prof. Yanjing Li TA: Miao (Tony) He Assigned: Thur., 11/29, 2018
UChicago CMSC-22200 Computer Architecture, Autumn 2018 Lab 5 Extra Credit: Multi-Core and The MESI Cache Coherence Protocol Instructor: Prof. Yanjing Li TA: Miao (Tony) He Assigned: Thur., 11/29, 2018
CS 0449 Project 4: /dev/rps Due: Friday, December 8, 2017, at 11:59pm
 CS 0449 Project 4: /dev/rps Due: Friday, December 8, 2017, at 11:59pm Project Description Standard UNIX and Linux systems come with a few special files like /dev/zero, which returns nothing but zeros when
CS 0449 Project 4: /dev/rps Due: Friday, December 8, 2017, at 11:59pm Project Description Standard UNIX and Linux systems come with a few special files like /dev/zero, which returns nothing but zeros when
Processors, Performance, and Profiling
 Processors, Performance, and Profiling Architecture 101: 5-Stage Pipeline Fetch Decode Execute Memory Write-Back Registers PC FP ALU Memory Architecture 101 1. Fetch instruction from memory. 2. Decode
Processors, Performance, and Profiling Architecture 101: 5-Stage Pipeline Fetch Decode Execute Memory Write-Back Registers PC FP ALU Memory Architecture 101 1. Fetch instruction from memory. 2. Decode
HPC Lab. Session 4: Profiler. Sebastian Rettenberger, Chaulio Ferreira, Michael Bader. November 9, 2015
 HPC Lab Session 4: Profiler Sebastian Rettenberger, Chaulio Ferreira, Michael Bader November 9, 2015 Session 4: Profiler, November 9, 2015 1 Profiler Profiling allows you to learn where your program spent
HPC Lab Session 4: Profiler Sebastian Rettenberger, Chaulio Ferreira, Michael Bader November 9, 2015 Session 4: Profiler, November 9, 2015 1 Profiler Profiling allows you to learn where your program spent
Final Programming Project
 Due Thursday, Dec. 7, at 5:00 pm Logistics This assignment should be completed in groups of 3. This is not optional -- you are not allowed to complete it on your own, or in groups of any other size. I
Due Thursday, Dec. 7, at 5:00 pm Logistics This assignment should be completed in groups of 3. This is not optional -- you are not allowed to complete it on your own, or in groups of any other size. I
Project 2 - Kernel Memory Allocation
 Project 2 - Kernel Memory Allocation EECS 343 - Fall 2014 Important Dates Out: Monday October 13, 2014 Due: Tuesday October 28, 2014 (11:59:59 PM CST) Project Overview The kernel generates and destroys
Project 2 - Kernel Memory Allocation EECS 343 - Fall 2014 Important Dates Out: Monday October 13, 2014 Due: Tuesday October 28, 2014 (11:59:59 PM CST) Project Overview The kernel generates and destroys
C152 Laboratory Exercise 3
 C152 Laboratory Exercise 3 Professor: Krste Asanovic TA: Christopher Celio Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley March 7, 2011 1 Introduction and goals
C152 Laboratory Exercise 3 Professor: Krste Asanovic TA: Christopher Celio Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of California, Berkeley March 7, 2011 1 Introduction and goals
Processor (IV) - advanced ILP. Hwansoo Han
 Processor (IV) - advanced ILP Hwansoo Han Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining: executing multiple instructions in parallel To increase ILP Deeper pipeline Less work per stage shorter clock cycle
Processor (IV) - advanced ILP Hwansoo Han Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining: executing multiple instructions in parallel To increase ILP Deeper pipeline Less work per stage shorter clock cycle
CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall Lecture 3
 CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall 2005 Lecture 3 Pramod V. Argade November 1, 2005 Fall 2005 CSE 141L Course Schedule Lecture # Date Day Lecture Topic Lab Due 1 9/27 Tuesday No Class 2 10/4 Tuesday
CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall 2005 Lecture 3 Pramod V. Argade November 1, 2005 Fall 2005 CSE 141L Course Schedule Lecture # Date Day Lecture Topic Lab Due 1 9/27 Tuesday No Class 2 10/4 Tuesday
CS 2210 Programming Project (Part IV)
 CS 2210 Programming Project (Part IV) April 25, 2018 Code Generation This project is intended to give you experience in writing a code generator as well as bring together the various issues of code generation
CS 2210 Programming Project (Part IV) April 25, 2018 Code Generation This project is intended to give you experience in writing a code generator as well as bring together the various issues of code generation
Superscalar Processors
 Superscalar Processors Superscalar Processor Multiple Independent Instruction Pipelines; each with multiple stages Instruction-Level Parallelism determine dependencies between nearby instructions o input
Superscalar Processors Superscalar Processor Multiple Independent Instruction Pipelines; each with multiple stages Instruction-Level Parallelism determine dependencies between nearby instructions o input
Overview of the ECE Computer Software Curriculum. David O Hallaron Associate Professor of ECE and CS Carnegie Mellon University
 Overview of the ECE Computer Software Curriculum David O Hallaron Associate Professor of ECE and CS Carnegie Mellon University The Fundamental Idea of Abstraction Human beings Applications Software systems
Overview of the ECE Computer Software Curriculum David O Hallaron Associate Professor of ECE and CS Carnegie Mellon University The Fundamental Idea of Abstraction Human beings Applications Software systems
Lesson 2: Using the Performance Console
 Lesson 2 Lesson 2: Using the Performance Console Using the Performance Console 19-13 Windows XP Professional provides two tools for monitoring resource usage: the System Monitor snap-in and the Performance
Lesson 2 Lesson 2: Using the Performance Console Using the Performance Console 19-13 Windows XP Professional provides two tools for monitoring resource usage: the System Monitor snap-in and the Performance
It is academic misconduct to share your work with others in any form including posting it on publicly accessible web sites, such as GitHub.
 p4: Cache Simulator 1. Logistics 1. This project must be done individually. It is academic misconduct to share your work with others in any form including posting it on publicly accessible web sites, such
p4: Cache Simulator 1. Logistics 1. This project must be done individually. It is academic misconduct to share your work with others in any form including posting it on publicly accessible web sites, such
COL862 Programming Assignment-1
 Submitted By: Rajesh Kedia (214CSZ8383) COL862 Programming Assignment-1 Objective: Understand the power and energy behavior of various benchmarks on different types of x86 based systems. We explore a laptop,
Submitted By: Rajesh Kedia (214CSZ8383) COL862 Programming Assignment-1 Objective: Understand the power and energy behavior of various benchmarks on different types of x86 based systems. We explore a laptop,
Microarchitecture Overview. Performance
 Microarchitecture Overview Prof. Scott Rixner Duncan Hall 3028 rixner@rice.edu January 18, 2005 Performance 4 Make operations faster Process improvements Circuit improvements Use more transistors to make
Microarchitecture Overview Prof. Scott Rixner Duncan Hall 3028 rixner@rice.edu January 18, 2005 Performance 4 Make operations faster Process improvements Circuit improvements Use more transistors to make
Microarchitecture Overview. Performance
 Microarchitecture Overview Prof. Scott Rixner Duncan Hall 3028 rixner@rice.edu January 15, 2007 Performance 4 Make operations faster Process improvements Circuit improvements Use more transistors to make
Microarchitecture Overview Prof. Scott Rixner Duncan Hall 3028 rixner@rice.edu January 15, 2007 Performance 4 Make operations faster Process improvements Circuit improvements Use more transistors to make
Real Processors. Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University
 Real Processors Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining: executing multiple instructions in parallel
Real Processors Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining: executing multiple instructions in parallel
Linux Performance Tuning
 Page 1 of 5 close window Print Linux Performance Tuning Getting the most from your Linux investment February March 2007 by Jaqui Lynch This is the first article in a two-part series. The second installment
Page 1 of 5 close window Print Linux Performance Tuning Getting the most from your Linux investment February March 2007 by Jaqui Lynch This is the first article in a two-part series. The second installment
Assignment 6: The Power of Caches
 Assignment 6: The Power of Caches Due by: April 20, 2018 before 10:00 pm Collaboration: Individuals or Registered Pairs (see Piazza). It is mandatory for every student to register on Piazza. Grading: Packaging
Assignment 6: The Power of Caches Due by: April 20, 2018 before 10:00 pm Collaboration: Individuals or Registered Pairs (see Piazza). It is mandatory for every student to register on Piazza. Grading: Packaging
EXPERIMENT 1. FAMILIARITY WITH DEBUG, x86 REGISTERS and MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS
 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARITY WITH DEBUG, x86 REGISTERS and MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS Pre-lab: This lab introduces you to a software tool known as DEBUG. Before the lab session, read the first two sections of chapter
EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARITY WITH DEBUG, x86 REGISTERS and MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS Pre-lab: This lab introduces you to a software tool known as DEBUG. Before the lab session, read the first two sections of chapter
Vectorization Lab Parallel Computing at TACC: Ranger to Stampede Transition
 Vectorization Lab Parallel Computing at TACC: Ranger to Stampede Transition Aaron Birkland Consultant Cornell Center for Advanced Computing December 11, 2012 1 Simple Vectorization This lab serves as an
Vectorization Lab Parallel Computing at TACC: Ranger to Stampede Transition Aaron Birkland Consultant Cornell Center for Advanced Computing December 11, 2012 1 Simple Vectorization This lab serves as an
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures. Computer Abstractions and Technology (4) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI.
 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Computer Abstractions and Technology (4) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Contents 1.7 - End of Chapter 1 Power wall The multicore era
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Computer Abstractions and Technology (4) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Contents 1.7 - End of Chapter 1 Power wall The multicore era
Computer Systems and Networks. ECPE 170 University of the Pacific
 ECPE 170 University of the Pacific Introduction 2 A Modern Computer 3 Applications 4 Application Angry Birds Written in a high level language (Objective C) What resources does Angry Birds need to run?
ECPE 170 University of the Pacific Introduction 2 A Modern Computer 3 Applications 4 Application Angry Birds Written in a high level language (Objective C) What resources does Angry Birds need to run?
Exercise: RISC Programming
 Exercise: RISC Programming Increasing efficiency of a RISC-core with simple instruction extensions 04.04.2016 Michael Gautschi Introduction The exercises in today will be performed on the Pulpino platform
Exercise: RISC Programming Increasing efficiency of a RISC-core with simple instruction extensions 04.04.2016 Michael Gautschi Introduction The exercises in today will be performed on the Pulpino platform
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture. Idea:
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture. Idea:
ECE454, Fall 2014 Homework2: Memory Performance Assigned: Sept 25th, Due: Oct 9th, 11:59PM
 ECE454, Fall 2014 Homework2: Memory Performance Assigned: Sept 25th, Due: Oct 9th, 11:59PM David Lion (david.lion@mail.utoronto.ca) is the TA for this assignment. 1 Introduction After great success with
ECE454, Fall 2014 Homework2: Memory Performance Assigned: Sept 25th, Due: Oct 9th, 11:59PM David Lion (david.lion@mail.utoronto.ca) is the TA for this assignment. 1 Introduction After great success with
/ Cloud Computing. Recitation 5 September 27 th, 2016
 15-319 / 15-619 Cloud Computing Recitation 5 September 27 th, 2016 1 Overview Administrative issues Office Hours, Piazza guidelines Last week s reflection Project 2.1, OLI Unit 2 modules 5 and 6 This week
15-319 / 15-619 Cloud Computing Recitation 5 September 27 th, 2016 1 Overview Administrative issues Office Hours, Piazza guidelines Last week s reflection Project 2.1, OLI Unit 2 modules 5 and 6 This week
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 9
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 9 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 30 September 2014 Announcements Next homework coming soon 1 Bulldozer Paper
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 9 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 30 September 2014 Announcements Next homework coming soon 1 Bulldozer Paper
Buffer Manager: Project 1 Assignment
 Buffer Manager: Project 1 Assignment Due: Feb 11, 2003 Introduction to Database Systems, UC Berkeley Computer Science 186 Spring 2003 1 Overview of Project 1 - Buffer Manager In this project you will add
Buffer Manager: Project 1 Assignment Due: Feb 11, 2003 Introduction to Database Systems, UC Berkeley Computer Science 186 Spring 2003 1 Overview of Project 1 - Buffer Manager In this project you will add
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. - Homework
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Homework Fall 2008 1 st Assignment Rules Each team should deliver Source code (.c,.h and Makefiles files) Please: no.o files and no executables! Documentation (.pdf,.doc,.tex
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Homework Fall 2008 1 st Assignment Rules Each team should deliver Source code (.c,.h and Makefiles files) Please: no.o files and no executables! Documentation (.pdf,.doc,.tex
2 Installing the Software
 INSTALLING 19 2 Installing the Software 2.1 Installation Remember the hour or two of slogging through software installation I promised (or warned) you about in the introduction? Well, it s here. Unless
INSTALLING 19 2 Installing the Software 2.1 Installation Remember the hour or two of slogging through software installation I promised (or warned) you about in the introduction? Well, it s here. Unless
COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs2121 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session 2, 2017 1 Contents Memory models Registers Data types Instructions
COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs2121 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session 2, 2017 1 Contents Memory models Registers Data types Instructions
Programming Standards: You must conform to good programming/documentation standards. Some specifics:
 CS3114 (Spring 2011) PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT #3 Due Thursday, April 7 @ 11:00 PM for 100 points Early bonus date: Wednesday, April 6 @ 11:00 PM for a 10 point bonus Initial Schedule due Thursday, March
CS3114 (Spring 2011) PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT #3 Due Thursday, April 7 @ 11:00 PM for 100 points Early bonus date: Wednesday, April 6 @ 11:00 PM for a 10 point bonus Initial Schedule due Thursday, March
Exercise Session 6 Computer Architecture and Systems Programming
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Exercise Session 6 Computer Architecture and Systems Programming Herbstsemester 2016 Agenda GDB Outlook on assignment 6 GDB The GNU Debugger 3 Debugging..
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Exercise Session 6 Computer Architecture and Systems Programming Herbstsemester 2016 Agenda GDB Outlook on assignment 6 GDB The GNU Debugger 3 Debugging..
Installing VMware Player to Run Ubuntu Linux on a Windows Machine
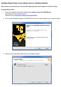 Installing VMware Player to Run Ubuntu Linux on a Windows Machine Check that you are connected to the internet before beginning (open Internet Explorer or Firefox or similar). Installing VMware Player
Installing VMware Player to Run Ubuntu Linux on a Windows Machine Check that you are connected to the internet before beginning (open Internet Explorer or Firefox or similar). Installing VMware Player
CPSC 457: Principles of Operating Systems Assignment 2 due June 9, 2015
 CPSC 457: Principles of Operating Systems Assignment 2 due June 9, 2015 Assignment Objectives This is an individual assignment. You must submit your own work. This assignment has two objectives: (1) reviewing
CPSC 457: Principles of Operating Systems Assignment 2 due June 9, 2015 Assignment Objectives This is an individual assignment. You must submit your own work. This assignment has two objectives: (1) reviewing
Performance. CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming. [K. Bala, A. Bracy, E. Sirer, and H. Weatherspoon]
![Performance. CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming. [K. Bala, A. Bracy, E. Sirer, and H. Weatherspoon] Performance. CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming. [K. Bala, A. Bracy, E. Sirer, and H. Weatherspoon]](/thumbs/93/113797768.jpg) Performance CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming [K. Bala, A. Bracy, E. Sirer, and H. Weatherspoon] Performance Complex question How fast is the processor? How fast your application runs?
Performance CS 3410 Computer System Organization & Programming [K. Bala, A. Bracy, E. Sirer, and H. Weatherspoon] Performance Complex question How fast is the processor? How fast your application runs?
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 9 Performance Dave Patterson. John Lazzaro. www-inst.eecs.berkeley.
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 9 Performance 2004-09-28 Dave Patterson (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson) John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 9 Performance 2004-09-28 Dave Patterson (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson) John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/
