CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
|
|
|
- Ashlie Maud Bryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [RPC & DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey XDR Standard serialization format: Uses big-endian, IEEE 754 for floating point, 4-byte words Where does it get implemented? How does RPC serialize complex objects? How does RPC handle dynamic allocations? What if two languages have different unsupported functions like lambda expressions? L20.1 L20.2 Topics covered in this lecture RPC Distributed Objects Synchronous and Asynchronous RPC Wait for result Client Synchronous Server Client Call local procedure Time Asynchronous Accept request Server Call local procedure L20.3 L20.4 Programming with interfaces GENERATION OF STUBS IN RPC/DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS Most modern languages provide means to organize program as a set of modules Modules can communicate with each other via invocations or direct access to variables To control possible interactions An explicit interface is defined for each module L20.5 L20.6 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.1
2 Interface Specifies methods/procedures and variables that can be accessed from other modules Modules are implemented so that all information about them are hidden, except for What was announced via its interface Implementation can also change so long as the interface does not In a distributed setting, interfaces become even more critical Programmers are only concerned with abstraction offered by the service and not implementation details Natural support for software evolution Implementations can change so long as the interface (external view) does not change Programmers also need not be aware of the programming language used by remote object CORBA L20.7 L20.8 Generation of client and server stubs Interface is usually specified by means of an interface definition language (IDL) IDL is compiled into a client and server stub Distributed Objects: CORBA early 1990s, RMI mid-late 90s RPC based on distributed objects with an inheritance mechanism Create, invoke or destroy remote objects, and interact with them as if they are local Data sent over network: References: class, object and method Method arguments L20.9 L20.10 Distributed Objects in CORBA defined using the Interface Definition Language Web Services in a sense borrowed some of these concepts CLIENT IDL Stub Object Implementation IDL Skeleton Object Implementation IDL Skeleton Used XML to describe services: Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Defined methods and arguments to them Added another feature/problem Generation of WSDL from actual implementation. OBJECT REQUEST BROKER (ORB) OBJECT REQUEST BROKER (ORB 2) GIOP/IIOP General Inter-ORB Protocol/Internet Inter-Orb Protocol L20.11 L20.12 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.2
3 RPC style communications: Disadvantages Access transparency is at the expense of flexibility Receiver needs to execute when the sender is sending something Communications in RPC are usually synchronous Client is blocked until request is processed DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS (LETS TRY TO DO THIS IN JAVA) L20.13 L20.14 The JRE and bytecodes The Java runtime environment is based upon a virtual machine that Interprets, verifies, and executes classes in the form of platform-independent bytecode ClassLoader Java API includes mechanisms to: Load class definitions in their bytecode form Integrate them into the JRE so that instances of classes can be constructed and used When your Java files are compiled? A similar mechanism is used when import statements are encountered Referenced classes are loaded in bytecode format n Using the CLASSPATH variable to locate classes L20.15 L20.16 Distributed Objects vs The ClassLoader Distributed Objects (based on CORBA, RMI, etc.) Create object on one host; allow process on another host to invoke methods on that object ClassLoader Read bytecodes making up a class definition; create an object within its own process Essential requirements for a distributed object system Create or invoke objects on remote host/process To create a remote object? Reference a class Provide constructor arguments for the class Receive a reference to the created object n Used to invoke methods on the object L20.17 L20.18 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.3
4 Creating an object once the name of a class is known String classname;... Class targetclass= Class.forName(className); Object createdobj = targetclass.newinstance(); Methods: How to retrieve and invoke String methodname = getname ; Class targetclass = Class.forName( a.b.myclass ); java.lang.reflect.method targetmethod; targetmethod = targetclass.getdeclaredmethod(methodname, null); targetmethod.invoke(); L20.19 L20.20 A truly open system for distributed objects will DISTRIBUTED OBJECT MODEL Allow clients to access objects regardless of details such as: Hardware platform Implementation Language Java RMI Java specific but platform-independent CORBA Language & platform independent L20.21 L20.22 The object model Programs are composed of interacting objects Each object has data and a set of methods Objects communicate with each other by invoking their methods Passing arguments Receiving results In a distributed object setting, object s data is accessible only via its methods Objects are accessed via object references In Java, a variable that appears to hold an object? Holds a reference to that object Object references are first-class values Can be assigned to variables, passed as arguments, and returned as results L20.23 L20.24 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.4
5 Distributed Objects Object-based programs are logically partitioned Physical distribution of objects is a natural extension A remote object and its interface Remote Object Architectural styles Client-Server is the most popular one But there could be other ones n Replication for fault tolerance, performance and availability Remote interface m1 m2 m3 Data Implementation of methods m4 m5 m6 L20.25 L20.26 Exceptions in distributed objects Remote invocations may fail for several reasons Process containing remote object crashed or is too busy to reply Invocation or result message may be lost Remote method invocations should be able to raise exceptions E.g. timeouts, problems during method execution Remote object references need to unique over space and time Internet Address Port Number time Object Number 32-bits 32-bits 32-bits 32-bits Interface of Remote Object L20.27 L20.28 Remote method invocation Communication Module Object A CLIENT Proxy for B Request Reply SERVER Skeleton + Dispatcher for B s class Remote object B IMPLEMENTING REMOTE METHOD INVOCATIONS Remote reference module L20.29 L20.30 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.5
6 Remote reference module Creates remote object references Translates between local and remote object references The remote reference module in each process maintains a remote object table An entry for all remote objects held by process E.g. in our figure, table in server records remote Object B An entry for each local proxy E.g. proxy for B will be in a table at the client L20.31 L20.32 Actions of the remote reference module When a remote object is passed as an argument or result for the first time? The module creates a remote object reference Add this reference to the remote object table The server remote object Lives in the server process Instance of class that provides the body of a remote object Eventually handles remote requests passed by the corresponding skeleton When a remote object arrives in a reply or request message? Reference module is asked for the corresponding local object reference n Refers either to a proxy or a remote object L20.33 L20.34 The Proxy [1/3] Role is to make a remote method invocation transparent to clients Behave like a local object to the invoker Instead of executing an invocation, the proxy forwards invocation in a message to a remote object The Proxy [2/3] Hides details of : 1 Remote object references 2 Marshaling & unmarshaling 3 Sending & receiving of messages from the client There is one proxy for each remote object for which the process holds a remote object reference L20.35 L20.36 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.6
7 The Proxy [3/3] The class of a proxy implements the methods in the remote interface of the remote object Ensures remote invocations are suitable for the remote object Each method of the proxy marshals several things into a request message: A reference to the target object Its operationid Arguments After the request the proxy awaits a reply, unmarshals it, and returns results to the invoker Dispatcher A server has one dispatcher and one skeleton for each remote class representing a remote object Dispatcher receives request messages from the communications modules Uses the operationid to select the appropriate method in the skeleton n Passes on request message The dispatcher and the proxy use the same allocation of operationids to methods of the remote interface L20.37 L20.38 Skeleton The class of a remote object has a skeleton Implements methods in the remote interface Skeleton method unmarshals arguments in the request message Invokes corresponding method in the server remote object Wait for invocation to complete Marshals results Include exceptions in a reply to the sender proxy s method Generation of classes for proxies, dispatchers, and skeletons These are generated automatically by an interface compiler Based on the remote interface L20.39 L20.40 Dynamic Invocation: Alternative to proxies Proxy is generated from an interface definition Then compiled statically n Sometimes this is not enough What if a client program receives a remote reference to an object that was not available at compile time? We need another way to invoke the object Dynamic Invocation Dynamic invocation The remote object reference includes information about the interface of the remote object The names of methods and types of arguments are needed to make the invocation L20.41 L20.42 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.7
8 Server program Contains classes for the dispatchers and skeletons Implementations of classes of all server remote objects Server remote objects also created in response to requests from clients Factory methods Remote object interfaces cannot include constructors Remote server objects cannot be created by remote invocation on constructors Remote server objects are created either in: The initialization section Methods in a remote interface designed for that purpose n Also called factory methods L20.43 L20.44 The binder Server threads Client programs need a way to obtain a remote object reference For at least one of the remote objects held by server A binder is separate service that maintains a table with a mapping of textual names to remote object references Used by: Servers: Register their remote objects by name Clients: Lookup remote objects When an object executes a remote method invocation? Execution may lead to further invocations of methods in other remote objects Avoid situations where execution of a remote invocation delays execution of another Servers generally allocate a separate thread for the execution of each remote invocation L20.45 L20.46 The contents of this slide-set are based on the following references Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design. George Coulouris, Jean Dollimore, Tim Kindberg, Gordon Blair. 5th Edition. Addison Wesley. ISBN: [Chapter 5] Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms. Andrew S. Tanenbaum and Maarten Van Steen. 2nd Edition. Prentice Hall. ISBN: / Java Distributed Computing. Jim Farley. O Reilly. ISBN L20.47 SLIDES CREATED BY: SHRIDEEP PALLICKARA L20.8
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/83/88148270.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [RMI] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L21.1 L21.2 Topics covered in this lecture RMI
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [RMI] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L21.1 L21.2 Topics covered in this lecture RMI
CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey
![CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey](/thumbs/77/76235814.jpg) CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L23.1 Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey
CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L23.1 Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/92/108913314.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [THREADS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shuffle less/shuffle better Which actions?
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [THREADS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shuffle less/shuffle better Which actions?
CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/86/93658701.jpg) CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Yes. But what really is a second? 1 second ==time for a cesium 133 atom
CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Yes. But what really is a second? 1 second ==time for a cesium 133 atom
Lecture 5: Object Interaction: RMI and RPC
 06-06798 Distributed Systems Lecture 5: Object Interaction: RMI and RPC Distributed Systems 1 Recap Message passing: send, receive synchronous versus asynchronous No global Time types of failure socket
06-06798 Distributed Systems Lecture 5: Object Interaction: RMI and RPC Distributed Systems 1 Recap Message passing: send, receive synchronous versus asynchronous No global Time types of failure socket
CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/89/97640828.jpg) CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [ELECTION ALGORITHMS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Does a process
CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [ELECTION ALGORITHMS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Does a process
Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation
 Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 Figure 5.1 Middleware layers Applications
Chapter 5: Distributed objects and remote invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 Figure 5.1 Middleware layers Applications
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/89/100180686.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [LOGICAL CLOCKS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey What happens in a cluster when 2 machines
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [LOGICAL CLOCKS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey What happens in a cluster when 2 machines
Lecture 06: Distributed Object
 Lecture 06: Distributed Object Distributed Systems Behzad Bordbar School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK Lecture 0? 1 Recap Interprocess communication Synchronous and Asynchronous communication
Lecture 06: Distributed Object Distributed Systems Behzad Bordbar School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK Lecture 0? 1 Recap Interprocess communication Synchronous and Asynchronous communication
Unit 7: RPC and Indirect Communication
 SR (Systèmes Répartis) Unit 7: RPC and Indirect Communication François Taïani Outline n Remote Procedure Call è First Class RPC è Second Class RPC (RMI) n Indirect Communication è Group Communication è
SR (Systèmes Répartis) Unit 7: RPC and Indirect Communication François Taïani Outline n Remote Procedure Call è First Class RPC è Second Class RPC (RMI) n Indirect Communication è Group Communication è
Distributed Systems Lecture 2 1. External Data Representation and Marshalling (Sec. 4.3) Request reply protocol (failure modes) (Sec. 4.
 Distributed Systems Lecture 2 1 Today s Topics External Data Representation and Marshalling (Sec. 4.3) Request reply protocol (failure modes) (Sec. 4.4) Distributed Objects and Remote Invocations (5.1)
Distributed Systems Lecture 2 1 Today s Topics External Data Representation and Marshalling (Sec. 4.3) Request reply protocol (failure modes) (Sec. 4.4) Distributed Objects and Remote Invocations (5.1)
Structured communication (Remote invocation)
 Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Structured communication (Remote invocation) Nov 8th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Structured communication (Remote invocation) Nov 8th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/95/125142682.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [P2P SYSTEMS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Byzantine failures vs malicious nodes
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [P2P SYSTEMS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Byzantine failures vs malicious nodes
Middleware and Interprocess Communication
 Middleware and Interprocess Communication Reading Coulouris (5 th Edition): 41 4.1, 42 4.2, 46 4.6 Tanenbaum (2 nd Edition): 4.3 Spring 2015 CS432: Distributed Systems 2 Middleware Outline Introduction
Middleware and Interprocess Communication Reading Coulouris (5 th Edition): 41 4.1, 42 4.2, 46 4.6 Tanenbaum (2 nd Edition): 4.3 Spring 2015 CS432: Distributed Systems 2 Middleware Outline Introduction
CHAPTER - 4 REMOTE COMMUNICATION
 CHAPTER - 4 REMOTE COMMUNICATION Topics Introduction to Remote Communication Remote Procedural Call Basics RPC Implementation RPC Communication Other RPC Issues Case Study: Sun RPC Remote invocation Basics
CHAPTER - 4 REMOTE COMMUNICATION Topics Introduction to Remote Communication Remote Procedural Call Basics RPC Implementation RPC Communication Other RPC Issues Case Study: Sun RPC Remote invocation Basics
DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS AND REMOTE INVOCATION
 DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS AND REMOTE INVOCATION Introduction This chapter is concerned with programming models for distributed applications... Familiar programming models have been extended to apply to distributed
DISTRIBUTED OBJECTS AND REMOTE INVOCATION Introduction This chapter is concerned with programming models for distributed applications... Familiar programming models have been extended to apply to distributed
Distributed Information Processing
 Distributed Information Processing 5 th Lecture Eom, Hyeonsang ( 엄현상 ) Department of Computer Science & Engineering Seoul National University Copyrights 2017 Eom, Hyeonsang All Rights Reserved Outline
Distributed Information Processing 5 th Lecture Eom, Hyeonsang ( 엄현상 ) Department of Computer Science & Engineering Seoul National University Copyrights 2017 Eom, Hyeonsang All Rights Reserved Outline
Java RMI Middleware Project
 Java RMI Middleware Project Nathan Balon CIS 578 Advanced Operating Systems December 7, 2004 Introduction The semester project was to implement a middleware similar to Java RMI or CORBA. The purpose of
Java RMI Middleware Project Nathan Balon CIS 578 Advanced Operating Systems December 7, 2004 Introduction The semester project was to implement a middleware similar to Java RMI or CORBA. The purpose of
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/80/81272615.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [MESSAGING SYSTEMS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Distributed Servers Security risks
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [MESSAGING SYSTEMS] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Distributed Servers Security risks
Chapter 10 DISTRIBUTED OBJECT-BASED SYSTEMS
 DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 10 DISTRIBUTED OBJECT-BASED SYSTEMS Distributed Objects Figure 10-1. Common organization of a remote
DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 10 DISTRIBUTED OBJECT-BASED SYSTEMS Distributed Objects Figure 10-1. Common organization of a remote
MODELS OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS
 Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-1 Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-2 MODELS OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Basic Elements 1. Architectural Models 2. Interaction Models Resources in a distributed system are shared between
Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-1 Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-2 MODELS OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Basic Elements 1. Architectural Models 2. Interaction Models Resources in a distributed system are shared between
Introduction & RMI Basics. CS3524 Distributed Systems Lecture 01
 Introduction & RMI Basics CS3524 Distributed Systems Lecture 01 Distributed Information Systems Distributed System: A collection of autonomous computers linked by a network, with software to produce an
Introduction & RMI Basics CS3524 Distributed Systems Lecture 01 Distributed Information Systems Distributed System: A collection of autonomous computers linked by a network, with software to produce an
03 Remote invoaction. Request-reply RPC. Coulouris 5 Birrel_Nelson_84.pdf RMI
 03 Remote invoaction Request-reply RPC Coulouris 5 Birrel_Nelson_84.pdf RMI 2/23 Remote invocation Mechanisms for process communication on a Built on top of interprocess communication primitives Lower
03 Remote invoaction Request-reply RPC Coulouris 5 Birrel_Nelson_84.pdf RMI 2/23 Remote invocation Mechanisms for process communication on a Built on top of interprocess communication primitives Lower
Chapter 5 Remote Invocation. Gandeva Bayu Satrya, ST., MT. Telematics Labz. Informatics Department Telkom
 Chapter 5 Remote Invocation Gandeva Bayu Satrya, ST., MT. Telematics Labz. Informatics Department Telkom University @2014 Outline Today Chapter 5 Remote Invocation. Chapter 6 Indirect Communication. Request-Reply
Chapter 5 Remote Invocation Gandeva Bayu Satrya, ST., MT. Telematics Labz. Informatics Department Telkom University @2014 Outline Today Chapter 5 Remote Invocation. Chapter 6 Indirect Communication. Request-Reply
Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey
 CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED COORDINATION/MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L22.1 Frequently asked questions from the previous
CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED COORDINATION/MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L22.1 Frequently asked questions from the previous
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation. Programming Models for Distributed Applications
 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Extending Conventional Techniques The remote procedure call model is an extension of the conventional procedure
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Extending Conventional Techniques The remote procedure call model is an extension of the conventional procedure
CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS455: Introduction to Distributed Systems [Spring 2018] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/90/101789192.jpg) Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED COORDINATION/MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University
Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [DISTRIBUTED COORDINATION/MUTUAL EXCLUSION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University
Introduction to Distributed Systems. Fabienne Boyer, LIG,
 Introduction to Distributed Systems Fabienne Boyer, LIG, fabienne.boyer@imag.fr What is a distributed system? Set of software components Running in separate address spaces Communicating through a network
Introduction to Distributed Systems Fabienne Boyer, LIG, fabienne.boyer@imag.fr What is a distributed system? Set of software components Running in separate address spaces Communicating through a network
MODELS OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS
 Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-1 Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-2 MODELS OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Basic Elements 1. Architectural Models 2. Interaction Models Resources in a distributed system are shared between
Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-1 Distributed Systems Fö 2/3-2 MODELS OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Basic Elements 1. Architectural Models 2. Interaction Models Resources in a distributed system are shared between
Remote Invocation. Today. Next time. l Overlay networks and P2P. l Request-reply, RPC, RMI
 Remote Invocation Today l Request-reply, RPC, RMI Next time l Overlay networks and P2P Types of communication " Persistent or transient Persistent A submitted message is stored until delivered Transient
Remote Invocation Today l Request-reply, RPC, RMI Next time l Overlay networks and P2P Types of communication " Persistent or transient Persistent A submitted message is stored until delivered Transient
COMMUNICATION IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS
 Distributed Systems Fö 3-1 Distributed Systems Fö 3-2 COMMUNICATION IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Communication Models and their Layered Implementation 1. Communication System: Layered Implementation 2. Network
Distributed Systems Fö 3-1 Distributed Systems Fö 3-2 COMMUNICATION IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Communication Models and their Layered Implementation 1. Communication System: Layered Implementation 2. Network
Interprocess Communication
 Interprocess Communication Tanenbaum & Van Steen, Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms, 2e, (c) 2007 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-239227-5 Introduction Applications, services
Interprocess Communication Tanenbaum & Van Steen, Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms, 2e, (c) 2007 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-239227-5 Introduction Applications, services
Chapter 4 Communication
 DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 4 Communication Layered Protocols (1) Figure 4-1. Layers, interfaces, and protocols in the OSI
DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 4 Communication Layered Protocols (1) Figure 4-1. Layers, interfaces, and protocols in the OSI
Distributed Systems. 5. Remote Method Invocation
 Distributed Systems 5. Remote Method Invocation Werner Nutt 1 Remote Method Invocation 5.1 Communication between Distributed Objects 1. Communication between Distributed Objects 2. RMI 2 Middleware Middleware
Distributed Systems 5. Remote Method Invocation Werner Nutt 1 Remote Method Invocation 5.1 Communication between Distributed Objects 1. Communication between Distributed Objects 2. RMI 2 Middleware Middleware
SAI/ST course Distributed Systems
 SAI/ST course Distributed Systems 2013, Sep. 26 Oct 01 Lecture 3: Communication Agenda Overview Concepts Organization in layers IPC primitives Direct communication Indirect communication R.H. Mak 27-9-2013
SAI/ST course Distributed Systems 2013, Sep. 26 Oct 01 Lecture 3: Communication Agenda Overview Concepts Organization in layers IPC primitives Direct communication Indirect communication R.H. Mak 27-9-2013
Distributed Systems. The main method of distributed object communication is with remote method invocation
 Distributed Systems Unit III Syllabus:Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation: Introduction, Communication between Distributed Objects- Object Model, Distributed Object Modal, Design Issues for RMI,
Distributed Systems Unit III Syllabus:Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation: Introduction, Communication between Distributed Objects- Object Model, Distributed Object Modal, Design Issues for RMI,
Operating System Support
 Operating System Support Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Adopted from Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 1 Learning Objectives Know what a modern
Operating System Support Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Adopted from Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 4, Addison-Wesley 2005 1 Learning Objectives Know what a modern
Slides for Chapter 5: Remote Invocation
 Slides for Chapter 5: Remote Invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore, Kindberg and Blair Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 5, Addison-Wesley 2012 Text extensions to slides David E. Bakken,
Slides for Chapter 5: Remote Invocation From Coulouris, Dollimore, Kindberg and Blair Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design Edition 5, Addison-Wesley 2012 Text extensions to slides David E. Bakken,
Implementing Remote Procedure Calls*
 Overview Implementing Remote Procedure Calls* Birrell, A. D. and Nelson, B. J. Brief introduction RPC issues Implementation Examples Current RPC implementations Presented by Emil Constantinescu Review
Overview Implementing Remote Procedure Calls* Birrell, A. D. and Nelson, B. J. Brief introduction RPC issues Implementation Examples Current RPC implementations Presented by Emil Constantinescu Review
Distributed Object-Based Systems The WWW Architecture Web Services Handout 11 Part(a) EECS 591 Farnam Jahanian University of Michigan.
 Distributed Object-Based Systems The WWW Architecture Web Services Handout 11 Part(a) EECS 591 Farnam Jahanian University of Michigan Reading List Remote Object Invocation -- Tanenbaum Chapter 2.3 CORBA
Distributed Object-Based Systems The WWW Architecture Web Services Handout 11 Part(a) EECS 591 Farnam Jahanian University of Michigan Reading List Remote Object Invocation -- Tanenbaum Chapter 2.3 CORBA
Today: Distributed Objects. Distributed Objects
 Today: Distributed Objects Case study: EJBs (Enterprise Java Beans) Case study: CORBA Lecture 23, page 1 Distributed Objects Figure 10-1. Common organization of a remote object with client-side proxy.
Today: Distributed Objects Case study: EJBs (Enterprise Java Beans) Case study: CORBA Lecture 23, page 1 Distributed Objects Figure 10-1. Common organization of a remote object with client-side proxy.
CS370: Operating Systems [Spring 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS370: Operating Systems [Spring 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS370: Operating Systems [Spring 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/83/87505258.jpg) Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 370: OPERATING SYSTEMS [MEMORY MANAGEMENT] Matrices in Banker s algorithm Max, need, allocated Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado
Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 370: OPERATING SYSTEMS [MEMORY MANAGEMENT] Matrices in Banker s algorithm Max, need, allocated Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado
RMI: Design & Implementation
 RMI: Design & Implementation Operating Systems RMI 1 Middleware layers Applications, services RMI and RPC request-reply protocol marshalling and external data representation Middleware layers UDP and TCP
RMI: Design & Implementation Operating Systems RMI 1 Middleware layers Applications, services RMI and RPC request-reply protocol marshalling and external data representation Middleware layers UDP and TCP
Object-Oriented Distributed Technology
 Objects Objects in Distributed Systems Requirements of Multi-User Applications Reading: Coulouris: Distributed Systems, Chapter 5 Object-Oriented Languages Object Identity object identifiers (OIDs) OIDs
Objects Objects in Distributed Systems Requirements of Multi-User Applications Reading: Coulouris: Distributed Systems, Chapter 5 Object-Oriented Languages Object Identity object identifiers (OIDs) OIDs
Outline. EEC-681/781 Distributed Computing Systems. The OSI Network Architecture. Inter-Process Communications (IPC) Lecture 4
 EEC-681/781 Distributed Computing Systems Lecture 4 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org Outline Inter-process communications Computer networks
EEC-681/781 Distributed Computing Systems Lecture 4 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org Outline Inter-process communications Computer networks
Module 3 - Distributed Objects & Remote Invocation
 Module 3 - Distributed Objects & Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Extension of the conventional procedure call model Allows client programs
Module 3 - Distributed Objects & Remote Invocation Programming Models for Distributed Applications Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Extension of the conventional procedure call model Allows client programs
Chapter 1: Distributed Systems: What is a distributed system? Fall 2013
 Chapter 1: Distributed Systems: What is a distributed system? Fall 2013 Course Goals and Content n Distributed systems and their: n Basic concepts n Main issues, problems, and solutions n Structured and
Chapter 1: Distributed Systems: What is a distributed system? Fall 2013 Course Goals and Content n Distributed systems and their: n Basic concepts n Main issues, problems, and solutions n Structured and
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/89/98876845.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [REPLICATION & CONSISTENCY] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L25.1 L25.2 Topics covered
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [REPLICATION & CONSISTENCY] Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L25.1 L25.2 Topics covered
Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI
 Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI
 Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Prof. Dr. Claudia Müller-Birn Institute for Computer Science, Networked Information Systems Distributed object component middleware I - Java RMI Nov 15th, 2011 Netzprogrammierung (Algorithmen und Programmierung
Module 1 - Distributed System Architectures & Models
 Module 1 - Distributed System Architectures & Models System Architecture Defines the structure of the system components identified functions of each component defined interrelationships and interactions
Module 1 - Distributed System Architectures & Models System Architecture Defines the structure of the system components identified functions of each component defined interrelationships and interactions
Lecture 5: RMI etc. Servant. Java Remote Method Invocation Invocation Semantics Distributed Events CDK: Chapter 5 TVS: Section 8.3
 Lecture 5: RMI etc. Java Remote Method Invocation Invocation Semantics Distributed Events CDK: Chapter 5 TVS: Section 8.3 CDK Figure 5.7 The role of proxy and skeleton in remote method invocation client
Lecture 5: RMI etc. Java Remote Method Invocation Invocation Semantics Distributed Events CDK: Chapter 5 TVS: Section 8.3 CDK Figure 5.7 The role of proxy and skeleton in remote method invocation client
Distributed Systems. Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV RWTH Aachen. Organisation. Classification of the lecture. Literature
 Organisation Distributed Systems Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV RWTH Aachen Prof. Dr. Otto Spaniol Dipl.-Inform. Dirk Thißen Exercises about all 14 days Wednesday, 15.30 17.00 Room AH III, RWTH Aachen Teacher-centred
Organisation Distributed Systems Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV RWTH Aachen Prof. Dr. Otto Spaniol Dipl.-Inform. Dirk Thißen Exercises about all 14 days Wednesday, 15.30 17.00 Room AH III, RWTH Aachen Teacher-centred
MTAT Enterprise System Integration. Lecture 2: Middleware & Web Services
 MTAT.03.229 Enterprise System Integration Lecture 2: Middleware & Web Services Luciano García-Bañuelos Slides by Prof. M. Dumas Overall view 2 Enterprise Java 2 Entity classes (Data layer) 3 Enterprise
MTAT.03.229 Enterprise System Integration Lecture 2: Middleware & Web Services Luciano García-Bañuelos Slides by Prof. M. Dumas Overall view 2 Enterprise Java 2 Entity classes (Data layer) 3 Enterprise
Distributed Systems Theory 4. Remote Procedure Call. October 17, 2008
 Distributed Systems Theory 4. Remote Procedure Call October 17, 2008 Client-server model vs. RPC Client-server: building everything around I/O all communication built in send/receive distributed computing
Distributed Systems Theory 4. Remote Procedure Call October 17, 2008 Client-server model vs. RPC Client-server: building everything around I/O all communication built in send/receive distributed computing
Advanced Topics in Operating Systems
 Advanced Topics in Operating Systems MSc in Computer Science UNYT-UoG Dr. Marenglen Biba 8-9-10 January 2010 Lesson 10 01: Introduction 02: Architectures 03: Processes 04: Communication 05: Naming 06:
Advanced Topics in Operating Systems MSc in Computer Science UNYT-UoG Dr. Marenglen Biba 8-9-10 January 2010 Lesson 10 01: Introduction 02: Architectures 03: Processes 04: Communication 05: Naming 06:
5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach
 5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach Main Points Why distributed objects Distributed Object design points Java RMI Dynamic Code Loading 5.1 What s an Object? An Object is an autonomous entity having
5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach Main Points Why distributed objects Distributed Object design points Java RMI Dynamic Code Loading 5.1 What s an Object? An Object is an autonomous entity having
Distributed Systems COMP 212. Lecture 1 Othon Michail
 Distributed Systems COMP 212 Lecture 1 Othon Michail Course Information Lecturer: Othon Michail Office 2.14 Holt Building http://csc.liv.ac.uk/~michailo/teaching/comp2 12 Structure 30 Lectures + 10 lab
Distributed Systems COMP 212 Lecture 1 Othon Michail Course Information Lecturer: Othon Michail Office 2.14 Holt Building http://csc.liv.ac.uk/~michailo/teaching/comp2 12 Structure 30 Lectures + 10 lab
COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS: REMOTE PROCEDURE CALL (RPC)
 COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS: REMOTE PROCEDURE CALL (RPC) 1 2 CONVENTIONAL PROCEDURE CALL (a) (b) Parameter passing in a local procedure call: the stack before the call to read. The stack while the called procedure
COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS: REMOTE PROCEDURE CALL (RPC) 1 2 CONVENTIONAL PROCEDURE CALL (a) (b) Parameter passing in a local procedure call: the stack before the call to read. The stack while the called procedure
DS 2009: middleware. David Evans
 DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
Object Interaction. Object Interaction. Introduction. Object Interaction vs. RPCs (2)
 Introduction Objective To support interoperability and portability of distributed OO applications by provision of enabling technology Object interaction vs RPC Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) RMI Registry
Introduction Objective To support interoperability and portability of distributed OO applications by provision of enabling technology Object interaction vs RPC Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) RMI Registry
Communication. Distributed Systems Santa Clara University 2016
 Communication Distributed Systems Santa Clara University 2016 Protocol Stack Each layer has its own protocol Can make changes at one layer without changing layers above or below Use well defined interfaces
Communication Distributed Systems Santa Clara University 2016 Protocol Stack Each layer has its own protocol Can make changes at one layer without changing layers above or below Use well defined interfaces
Today CSCI Communication. Communication in Distributed Systems. Communication in Distributed Systems. Remote Procedure Calls (RPC)
 Today CSCI 5105 Communication in Distributed Systems Overview Types Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) Instructor: Abhishek Chandra 2 Communication How do program modules/processes communicate on a single machine?
Today CSCI 5105 Communication in Distributed Systems Overview Types Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) Instructor: Abhishek Chandra 2 Communication How do program modules/processes communicate on a single machine?
CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture)
 CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) René de Vries (rgv@cs.ru.nl) Based on slides by M.L. Liu 1 Overview Introduction / context Genealogical of CORBA CORBA architecture Implementations Corba
CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) René de Vries (rgv@cs.ru.nl) Based on slides by M.L. Liu 1 Overview Introduction / context Genealogical of CORBA CORBA architecture Implementations Corba
Broker Pattern. Teemu Koponen
 Broker Pattern Teemu Koponen tkoponen@iki.fi Broker Pattern Context and problem Solution Implementation Conclusions Comments & discussion Example Application Stock Exchange Trader 1 Stock Exchange 1 Trader
Broker Pattern Teemu Koponen tkoponen@iki.fi Broker Pattern Context and problem Solution Implementation Conclusions Comments & discussion Example Application Stock Exchange Trader 1 Stock Exchange 1 Trader
Message Passing vs. Distributed Objects. 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 1
 Message Passing vs. Distributed Objects 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 1 Distributed Objects M. L. Liu 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 2 Message Passing versus Distributed Objects
Message Passing vs. Distributed Objects 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 1 Distributed Objects M. L. Liu 5/15/2009 Distributed Computing, M. L. Liu 2 Message Passing versus Distributed Objects
Distributed Systems. Lehrstuhl für Informatik 4. RWTH Aachen. Organization. Literature. Classification of the lecture
 Organization Distributed Systems RWTH Aachen Dr. Dirk Thißen Prof. Dr. Otto Spaniol 1 Exercises about all 14 days Room AH 5, RWTH Aachen Teacher-centered exercises Contact Dirk Thißen, Room 4226 (Building
Organization Distributed Systems RWTH Aachen Dr. Dirk Thißen Prof. Dr. Otto Spaniol 1 Exercises about all 14 days Room AH 5, RWTH Aachen Teacher-centered exercises Contact Dirk Thißen, Room 4226 (Building
CAS 703 Software Design
 Dr. Ridha Khedri Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University Canada L8S 4L7, Hamilton, Ontario Acknowledgments: Material based on Software by Tao et al. (Chapters 9 and 10) (SOA) 1 Interaction
Dr. Ridha Khedri Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University Canada L8S 4L7, Hamilton, Ontario Acknowledgments: Material based on Software by Tao et al. (Chapters 9 and 10) (SOA) 1 Interaction
Distributed Objects. Object-Oriented Application Development
 Distributed s -Oriented Application Development Procedural (non-object oriented) development Data: variables Behavior: procedures, subroutines, functions Languages: C, COBOL, Pascal Structured Programming
Distributed s -Oriented Application Development Procedural (non-object oriented) development Data: variables Behavior: procedures, subroutines, functions Languages: C, COBOL, Pascal Structured Programming
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Ministry of Higher Education College of Computer & Information Sciences Majmaah University. Course Profile
 Kingdom Saudi Arabia Ministry Higher Education College Computer & Information Sciences Majmaah University Course Prile Course Name:- Course Code:- CEN 449 Academic Year:- 1434-1435(2013-2014) Semester
Kingdom Saudi Arabia Ministry Higher Education College Computer & Information Sciences Majmaah University Course Prile Course Name:- Course Code:- CEN 449 Academic Year:- 1434-1435(2013-2014) Semester
Remote Invocation. 1. Introduction 2. Remote Method Invocation (RMI) 3. RMI Invocation Semantics
 Remote Invocation Nicola Dragoni Embedded Systems Engineering DTU Informatics 1. Introduction 2. Remote Method Invocation (RMI) 3. RMI Invocation Semantics From the First Lecture (Architectural Models)...
Remote Invocation Nicola Dragoni Embedded Systems Engineering DTU Informatics 1. Introduction 2. Remote Method Invocation (RMI) 3. RMI Invocation Semantics From the First Lecture (Architectural Models)...
Remote Invocation. Today. Next time. l Indirect communication. l Request-reply, RPC, RMI
 Remote Invocation Today l Request-reply, RPC, RMI Next time l Indirect communication Data representation and marshalling Processes information kept as data structures but sent in msgs as sequence of bytes
Remote Invocation Today l Request-reply, RPC, RMI Next time l Indirect communication Data representation and marshalling Processes information kept as data structures but sent in msgs as sequence of bytes
Operating Systems. 18. Remote Procedure Calls. Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Spring /20/ Paul Krzyzanowski
 Operating Systems 18. Remote Procedure Calls Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2015 4/20/2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Remote Procedure Calls 2 Problems with the sockets API The sockets
Operating Systems 18. Remote Procedure Calls Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2015 4/20/2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Remote Procedure Calls 2 Problems with the sockets API The sockets
Distributed Systems Course. a.o. Univ.-Prof. Dr. Harald Kosch
 Distributed Systems Course a.o. Univ.-Prof. Dr. Harald Kosch Topics Introduction Advantages, Disadvantages, Hard/Soft Concepts Network / Distributed Operating Systems Basics of Communication Models (Client/Server,
Distributed Systems Course a.o. Univ.-Prof. Dr. Harald Kosch Topics Introduction Advantages, Disadvantages, Hard/Soft Concepts Network / Distributed Operating Systems Basics of Communication Models (Client/Server,
Software Paradigms (Lesson 10) Selected Topics in Software Architecture
 Software Paradigms (Lesson 10) Selected Topics in Software Architecture Table of Contents 1 World-Wide-Web... 2 1.1 Basic Architectural Solution... 2 1.2 Designing WWW Applications... 7 2 CORBA... 11 2.1
Software Paradigms (Lesson 10) Selected Topics in Software Architecture Table of Contents 1 World-Wide-Web... 2 1.1 Basic Architectural Solution... 2 1.2 Designing WWW Applications... 7 2 CORBA... 11 2.1
C 1. Recap: Finger Table. CSE 486/586 Distributed Systems Remote Procedure Call. Chord: Node Joins and Leaves. Recall? Socket API
 Recap: Finger Table Finding a using fingers CSE 486/586 Distributed Systems Remote Procedure Call Steve Ko Computer Sciences and Engineering University at Buffalo N102" 86 + 2 4! N86" 20 +
Recap: Finger Table Finding a using fingers CSE 486/586 Distributed Systems Remote Procedure Call Steve Ko Computer Sciences and Engineering University at Buffalo N102" 86 + 2 4! N86" 20 +
Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms. Distributed Object-Based Systems. Remote distributed objects. Remote distributed objects
 Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms Maarten van Steen VU Amsterdam, Dept. Computer Science steen@cs.vu.nl Chapter 10: Version: December 10, 2012 1 / 22 10.1 Architecture 10.1 Architecture Remote
Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms Maarten van Steen VU Amsterdam, Dept. Computer Science steen@cs.vu.nl Chapter 10: Version: December 10, 2012 1 / 22 10.1 Architecture 10.1 Architecture Remote
RPC and RMI. 2501ICT Nathan
 RPC and RMI 2501ICT Nathan Contents Client/Server revisited RPC Architecture XDR RMI Principles and Operation Case Studies Copyright 2002- René Hexel. 2 Client/Server Revisited Server Accepts commands
RPC and RMI 2501ICT Nathan Contents Client/Server revisited RPC Architecture XDR RMI Principles and Operation Case Studies Copyright 2002- René Hexel. 2 Client/Server Revisited Server Accepts commands
Two Phase Commit Protocol. Distributed Systems. Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) Network & Distributed Operating Systems. Network OS.
 A distributed system is... Distributed Systems "one on which I cannot get any work done because some machine I have never heard of has crashed". Loosely-coupled network connection could be different OSs,
A distributed system is... Distributed Systems "one on which I cannot get any work done because some machine I have never heard of has crashed". Loosely-coupled network connection could be different OSs,
Distributed Systems. Definitions. Why Build Distributed Systems? Operating Systems - Overview. Operating Systems - Overview
 Distributed Systems Joseph Spring School of Computer Science Distributed Systems and Security Areas for Discussion Definitions Operating Systems Overview Challenges Heterogeneity Limitations and 2 Definitions
Distributed Systems Joseph Spring School of Computer Science Distributed Systems and Security Areas for Discussion Definitions Operating Systems Overview Challenges Heterogeneity Limitations and 2 Definitions
CSci Introduction to Distributed Systems. Communication: RPC
 CSci 5105 Introduction to Distributed Systems Communication: RPC Today Remote Procedure Call Chapter 4 TVS Last Time Architectural styles RPC generally mandates client-server but not always Interprocess
CSci 5105 Introduction to Distributed Systems Communication: RPC Today Remote Procedure Call Chapter 4 TVS Last Time Architectural styles RPC generally mandates client-server but not always Interprocess
Remote Invocation Vladimir Vlassov and Johan Montelius
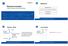 KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Middleware Remote Invocation Vladimir Vlassov and Johan Montelius Application layer Remote invocation / indirect communication Socket layer Network layer ID2201 DISTRIBUTED
KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Middleware Remote Invocation Vladimir Vlassov and Johan Montelius Application layer Remote invocation / indirect communication Socket layer Network layer ID2201 DISTRIBUTED
Last Class: RPCs. Today:
 Last Class: RPCs RPCs make distributed computations look like local computations Issues: Parameter passing Binding Failure handling Lecture 4, page 1 Today: Case Study: Sun RPC Lightweight RPCs Remote
Last Class: RPCs RPCs make distributed computations look like local computations Issues: Parameter passing Binding Failure handling Lecture 4, page 1 Today: Case Study: Sun RPC Lightweight RPCs Remote
Chapter 5: Remote Invocation. Copyright 2015 Prof. Amr El-Kadi
 Chapter 5: Remote Invocation Outline Introduction Request-Reply Protocol Remote Procedure Call Remote Method Invocation This chapter (and Chapter 6) Applications Remote invocation, indirect communication
Chapter 5: Remote Invocation Outline Introduction Request-Reply Protocol Remote Procedure Call Remote Method Invocation This chapter (and Chapter 6) Applications Remote invocation, indirect communication
Distributed Information Systems
 Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models For Distributed Applications Objectives RPC and RMI. Remote invocation semantics. Implementation of RMI. References DSCD: Chapter 5 Conventional
Distributed Objects and Remote Invocation Programming Models For Distributed Applications Objectives RPC and RMI. Remote invocation semantics. Implementation of RMI. References DSCD: Chapter 5 Conventional
Middleware. Adapted from Alonso, Casati, Kuno, Machiraju Web Services Springer 2004
 Middleware Adapted from Alonso, Casati, Kuno, Machiraju Web Services Springer 2004 Outline Web Services Goals Where do they come from? Understanding middleware Middleware as infrastructure Communication
Middleware Adapted from Alonso, Casati, Kuno, Machiraju Web Services Springer 2004 Outline Web Services Goals Where do they come from? Understanding middleware Middleware as infrastructure Communication
Module 7 - Replication
 Module 7 - Replication Replication Why replicate? Reliability Avoid single points of failure Performance Scalability in numbers and geographic area Why not replicate? Replication transparency Consistency
Module 7 - Replication Replication Why replicate? Reliability Avoid single points of failure Performance Scalability in numbers and geographic area Why not replicate? Replication transparency Consistency
416 Distributed Systems. RPC Day 2 Jan 11, 2017
 416 Distributed Systems RPC Day 2 Jan 11, 2017 1 Last class Finish networks review Fate sharing End-to-end principle UDP versus TCP; blocking sockets IP thin waist, smart end-hosts, dumb (stateless) network
416 Distributed Systems RPC Day 2 Jan 11, 2017 1 Last class Finish networks review Fate sharing End-to-end principle UDP versus TCP; blocking sockets IP thin waist, smart end-hosts, dumb (stateless) network
CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring Lecture 22: Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
 CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring 2002 Lecture 22: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) 22.0 Main Point Send/receive One vs. two-way communication Remote Procedure
CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring 2002 Lecture 22: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) 22.0 Main Point Send/receive One vs. two-way communication Remote Procedure
02 - Distributed Systems
 02 - Distributed Systems Definition Coulouris 1 (Dis)advantages Coulouris 2 Challenges Saltzer_84.pdf Models Physical Architectural Fundamental 2/58 Definition Distributed Systems Distributed System is
02 - Distributed Systems Definition Coulouris 1 (Dis)advantages Coulouris 2 Challenges Saltzer_84.pdf Models Physical Architectural Fundamental 2/58 Definition Distributed Systems Distributed System is
A Report on RMI and RPC Submitted by Sudharshan Reddy B
 A Report on RMI and RPC Submitted by Sudharshan Reddy B Abstract: This report mainly explains the RMI and RPC technologies. In the first part of the paper the RMI technology is briefly explained and in
A Report on RMI and RPC Submitted by Sudharshan Reddy B Abstract: This report mainly explains the RMI and RPC technologies. In the first part of the paper the RMI technology is briefly explained and in
02 - Distributed Systems
 02 - Distributed Systems Definition Coulouris 1 (Dis)advantages Coulouris 2 Challenges Saltzer_84.pdf Models Physical Architectural Fundamental 2/60 Definition Distributed Systems Distributed System is
02 - Distributed Systems Definition Coulouris 1 (Dis)advantages Coulouris 2 Challenges Saltzer_84.pdf Models Physical Architectural Fundamental 2/60 Definition Distributed Systems Distributed System is
Remote Procedure Calls
 CS 5450 Remote Procedure Calls Vitaly Shmatikov Abstractions Abstractions for communication TCP masks some of the pain of communicating over unreliable IP Abstractions for computation Goal: programming
CS 5450 Remote Procedure Calls Vitaly Shmatikov Abstractions Abstractions for communication TCP masks some of the pain of communicating over unreliable IP Abstractions for computation Goal: programming
Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems. Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid. Computer Science Department Virginia Tech
 Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia Tech Communication (Based on Ch2 in Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms, 1/E or Ch4 in 2/E)
Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia Tech Communication (Based on Ch2 in Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms, 1/E or Ch4 in 2/E)
Distributed Systems COMP 212. Lecture 1 Othon Michail
 Distributed Systems COMP 212 Lecture 1 Othon Michail Course Information Lecturer: Othon Michail Office 2.14 Holt Building http://csc.liv.ac.uk/~michailo/teaching/comp2 12 Structure 30 Lectures + 10 lab
Distributed Systems COMP 212 Lecture 1 Othon Michail Course Information Lecturer: Othon Michail Office 2.14 Holt Building http://csc.liv.ac.uk/~michailo/teaching/comp2 12 Structure 30 Lectures + 10 lab
CS655: Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems [Fall 2013] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS655: Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems [Fall 2013] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS655: Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems [Fall 2013] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/89/100104790.jpg) Topics covered in this lecture CS 655: ADVANCED TOPICS IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [INTRODUCTION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Course outline Grading Policy Critical reviews
Topics covered in this lecture CS 655: ADVANCED TOPICS IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [INTRODUCTION] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Course outline Grading Policy Critical reviews
Distributed Systems 8. Remote Procedure Calls
 Distributed Systems 8. Remote Procedure Calls Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 10/1/2012 1 Problems with the sockets API The sockets interface forces a read/write mechanism Programming is often easier
Distributed Systems 8. Remote Procedure Calls Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 10/1/2012 1 Problems with the sockets API The sockets interface forces a read/write mechanism Programming is often easier
Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey
 CS 370: OPERATING SYSTEMS [MEMORY MANAGEMENT] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L20.1 Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Virtual addresses L20.2 SLIDES
CS 370: OPERATING SYSTEMS [MEMORY MANAGEMENT] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University L20.1 Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Virtual addresses L20.2 SLIDES
Distributed Systems Concepts Design 5th Edition Solutions
 Distributed Systems Concepts Design 5th Edition Solutions DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS CONCEPTS DESIGN 5TH EDITION SOLUTIONS PDF - Are you looking for distributed systems concepts design 5th edition solutions Books?
Distributed Systems Concepts Design 5th Edition Solutions DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS CONCEPTS DESIGN 5TH EDITION SOLUTIONS PDF - Are you looking for distributed systems concepts design 5th edition solutions Books?
Distributed Systems Concepts Design 4th Edition
 DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS CONCEPTS DESIGN 4TH EDITION PDF - Are you looking for distributed systems concepts design 4th edition Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time distributed systems concepts design
DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS CONCEPTS DESIGN 4TH EDITION PDF - Are you looking for distributed systems concepts design 4th edition Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time distributed systems concepts design
