Darrell Bethea May 10, MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011
|
|
|
- Arnold Frederick Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1
2 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
3 Hardware and Memory Programs and Compiling Your first program
4 Need to know basics of a computer If you want to cook, you should know basic ingredients and understand how food is prepared. Understand what your program is doing Talk intelligently about computers 5
5 Hardware - physical machine CPU, Memory Software - programs that give instructions to the computer Windows XP, Google Chrome, Games, Eclipse 6
6 CPU (Central Processing Unit) - the Brain GHz Number of billions of instructions per second I.e, how fast the computer is Dual Core - multiple processing units per CPU 7
7 Holds data for the computer How much the Brain can remember Main Memory Memory computer uses for intermediate calculations (program you are running) Disappears when you shut down your computer Secondary Memory Disk drives, CDs, Flash drives Exists until you delete it 8
8 Your main memory 2 gigabytes of RAM (Meter - unit of distance) Bytes - unit of data Kilobyte = 1 thousand bytes Megabyte = 1 million bytes Gigabyte = 1 billion bytes 9
9 Smallest addressable unit of memory Both main memory and auxiliary memory are measured in bits 1 byte = 8 bits Bit = 0 or 1 (on or off) Language of the computer is bits byte of 8 bits 10
10 Set of instructions for a CPU to follow Also known as software. You will be writing programs We will look at one soon Hard for humans to write bits directly 11
11 Your Program High-level language (human readable) Compiler Machine Language (Bits) Low-level language (computer readable) 12
12 What are the two kinds of memory in a computer? What is software? What is the difference between a machinelanguage program and a high-level language program? 13
13 import java.util.*; public class FirstProgram { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello out there."); System.out.println("I will add two number for you."); System.out.println("Enter two whole numbers on a line:"); int n1, n2; Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); n1 = keyboard.nextint(); n2 = keyboard.nextint(); } } System.out.println("The sum of those two numbers is"); System.out.println(n1 + n2); 14
14 import java.util.*; Package = Library of classes Java.util is a package Different libraries give different information Physics Library = Newtonian Physics Music Library = your itunes collection java.util. = Allows you to read data from keyboard 15
15 Begin the Program public class FirstProgram { public static void main(string[] args) { Begin a program named FirstProgram Program names should make sense Another name for this program could be AddTwoNumbers You should always capitalize the first letter of each word in your program name 16
16 System.out.println("Hello out there."); System.out.println("I will add two numbers for you."); System.out.println("Enter two whole numbers on a line:"); Write what is in quotes to screen 17
17 Class - Category of Objects E.g., Stapler Object - A specific member of that category E.g., My red Swingline Method - Actions performed by objects E.g., Staple pages, load staples, fix jam, etc. 18
18 myredswingline.fixjam(); Object ramses.eatgrass(); System.out.println( Hi ); Method Invoke Method 19
19 int n1, n2; Variable - store piece of data n1 - store integer n2 - store integer 20
20 Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); Class Object Not always System.in Create object (keyboard) of Scanner class Stapler myredswingline = new Stapler(); 21
21 Object n1 = keyboard.nextint(); Invoke/Call Method Read an integer from the keyboard and store it in n1 22
22 System.out.println("The sum of those two numbers is"): System.out.println(n1 + n2); Add n1 and n2 Print the sum to the screen 23
23 import java.util.*; public class FirstProgram { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello out there."); System.out.println("I will add two number for you."); System.out.println("Enter two whole numbers on a line:"); int n1, n2; Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); n1 = keyboard.nextint(); n2 = keyboard.nextint(); } } System.out.println("The sum of those two numbers is"); System.out.println(n1 + n2); 24
24 Hello out there. I will add two numbers for you. Enter two whole numbers on a line: Input by user The sum of those two numbers is 42
25 Before Tomorrow Eclipse Your first java program Download and Install Eclipse before lab (see webpage) Go through the Eclipse Tutorial on your own Get the textbook! Read
COMP Computer Basics. Yi Hong May 13, 2015
 COMP 110-001 Computer Basics Yi Hong May 13, 2015 Today Hardware and memory Programs and compiling Your first program 2 Before Programming Need to know basics of a computer Understand what your program
COMP 110-001 Computer Basics Yi Hong May 13, 2015 Today Hardware and memory Programs and compiling Your first program 2 Before Programming Need to know basics of a computer Understand what your program
St. Edmund Preparatory High School Brooklyn, NY
 AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
Introduction to Computers and Java. Objectives. Outline. Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich.
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Darrell Bethea May 25, 2011
 Darrell Bethea May 25, 2011 Yesterdays slides updated Midterm on tomorrow in SN014 Closed books, no notes, no computer Program 3 due Tuesday 2 3 A whirlwind tour of almost everything we have covered so
Darrell Bethea May 25, 2011 Yesterdays slides updated Midterm on tomorrow in SN014 Closed books, no notes, no computer Program 3 due Tuesday 2 3 A whirlwind tour of almost everything we have covered so
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java. Objectives. Outline. Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich.
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Input. Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); String name;
 Reading Resource Input Read chapter 4 (Variables and Constants) in the textbook A Guide to Programming in Java, pages 77 to 82. Key Concepts A stream is a data channel to or from the operating system.
Reading Resource Input Read chapter 4 (Variables and Constants) in the textbook A Guide to Programming in Java, pages 77 to 82. Key Concepts A stream is a data channel to or from the operating system.
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics 1 Computer Basics Computer system: hardware + software Hardware: the physical components Software: the instructions that
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics 1 Computer Basics Computer system: hardware + software Hardware: the physical components Software: the instructions that
Chapter 1. Introduction to Computers and Programming. M hiwa ahmad aziz
 . Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming www.raparinweb.com M hiwa ahmad aziz 1 Ch 1 - Introduction to Computers and Programming Hardware Terminology Main Memory Auxiliary Memory Drives Writing
. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming www.raparinweb.com M hiwa ahmad aziz 1 Ch 1 - Introduction to Computers and Programming Hardware Terminology Main Memory Auxiliary Memory Drives Writing
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers the Java programming language Example program Hardware and Software Computer systems
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers the Java programming language Example program Hardware and Software Computer systems
What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements
 Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE
 CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
CS 101 Spring 2007 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
Lab Determining Data Storage Capacity
 Lab 1.3.2 Determining Data Storage Capacity Objectives Determine the amount of RAM (in MB) installed in a PC. Determine the size of the hard disk drive (in GB) installed in a PC. Determine the used and
Lab 1.3.2 Determining Data Storage Capacity Objectives Determine the amount of RAM (in MB) installed in a PC. Determine the size of the hard disk drive (in GB) installed in a PC. Determine the used and
Introduction. Arizona State University 1
 Introduction CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 1 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Introduction CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 1 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Loops. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
! Learn how to think like a computer scientist. ! Learn problem solving. ! Read and write code. ! Understand object oriented programming
 1 TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE AND PROGRAMMING Topic 1 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia
1 TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE AND PROGRAMMING Topic 1 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview of the Java programming
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview of the Java programming
Over and Over Again GEEN163
 Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise
 COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
Chapter 1: Why Program? Computers and Programming. Why Program?
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
Chapter. Focus of the Course. Object-Oriented Software Development. program design, implementation, and testing
 Introduction 1 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Focus of the Course Object-Oriented Software Development
Introduction 1 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Focus of the Course Object-Oriented Software Development
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Anatomy of a Java Program: Comments
 CS149 Anatomy of a Java Program: Comments Javadoc comments: /** * Application that converts inches to centimeters. * * @author Alvin Chao * @version 01/21/2014 */ Everything between /** and */ ignored
CS149 Anatomy of a Java Program: Comments Javadoc comments: /** * Application that converts inches to centimeters. * * @author Alvin Chao * @version 01/21/2014 */ Everything between /** and */ ignored
Chapter 5 Lab Methods
 Chapter 5 Lab Methods Lab Objectives Be able to write methods Be able to call methods Be able to write javadoc comments Be able to create HTML documentation using the javadoc utility Introduction Methods
Chapter 5 Lab Methods Lab Objectives Be able to write methods Be able to call methods Be able to write javadoc comments Be able to create HTML documentation using the javadoc utility Introduction Methods
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java
 CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Intro to CSC116 Instructors Course Instructor:
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Intro to CSC116 Instructors Course Instructor:
4. If the following Java statements are executed, what will be displayed?
 Chapter 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. To compile a program named First, use the following command a. java First.java b. javac First c. javac First.java d. compile First.javac 2. A Java program must have at least
Chapter 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. To compile a program named First, use the following command a. java First.java b. javac First c. javac First.java d. compile First.javac 2. A Java program must have at least
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview computer hardware and software Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview the java
Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview computer hardware and software Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview the java
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
Gaddis: Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects, 6/e
 Chapter 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which one of the following would contain the translated Java byte code for a program named Demo? a. Demo.java b. Demo.code c. Demo.class d. Demo.byte 2. To compile a program
Chapter 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which one of the following would contain the translated Java byte code for a program named Demo? a. Demo.java b. Demo.code c. Demo.class d. Demo.byte 2. To compile a program
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java
 CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Intro to CSC116 Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Course Instructor: Instructors
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Intro to CSC116 Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Course Instructor: Instructors
Class List. Java Must Have. Class Goals. Class Goals. Schedule
 Class List Accelerated Introduction to CS Using Java 5 2004 Illinois Institute of Technology Schedule CS -201-071 M 06:25-09:05PM Rice Campus - Wheaton Room RI 148 LAB W 06:25-09:05PM CS -201-392 MW 06:25-09:05PM
Class List Accelerated Introduction to CS Using Java 5 2004 Illinois Institute of Technology Schedule CS -201-071 M 06:25-09:05PM Rice Campus - Wheaton Room RI 148 LAB W 06:25-09:05PM CS -201-392 MW 06:25-09:05PM
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
Tutorial 1 CSC 201. Java Programming Concepts عؾادئماظربجمةمبادؿكدامماجلاصا
 Tutorial 1 CSC 201 Java Programming Concepts عؾادئماظربجمةمبادؿكدامماجلاصا م- م- م- م- م- Chapter 1 1. What is Java? 2. Why Learn Java? a. Java Is Platform Independent b. Java is Easy to learn 3. Programming
Tutorial 1 CSC 201 Java Programming Concepts عؾادئماظربجمةمبادؿكدامماجلاصا م- م- م- م- م- Chapter 1 1. What is Java? 2. Why Learn Java? a. Java Is Platform Independent b. Java is Easy to learn 3. Programming
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them.
 Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures 3e (Gaddis and Muganda) Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals
 Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures 3e (Gaddis and Muganda) Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) Which one of the following would contain the
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures 3e (Gaddis and Muganda) Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) Which one of the following would contain the
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
What two elements are usually present for calculating a total of a series of numbers?
 Dec. 12 Running Totals and Sentinel Values What is a running total? What is an accumulator? What is a sentinel? What two elements are usually present for calculating a total of a series of numbers? Running
Dec. 12 Running Totals and Sentinel Values What is a running total? What is an accumulator? What is a sentinel? What two elements are usually present for calculating a total of a series of numbers? Running
Example Program. public class ComputeArea {
 COMMENTS While most people think of computer programs as a tool for telling computers what to do, programs are actually much more than that. Computer programs are written in human readable language for
COMMENTS While most people think of computer programs as a tool for telling computers what to do, programs are actually much more than that. Computer programs are written in human readable language for
System Unit Components Chapter2
 System Unit Components Chapter2 ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2013 The System Unit What is the system unit? Case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data Sometimes called the chassis
System Unit Components Chapter2 ITBIS105 IS-IT-UOB 2013 The System Unit What is the system unit? Case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data Sometimes called the chassis
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
Lec 3. Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables
 Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 3* * 3 17 % 9-20 % (26 / 7) "2"
 CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 1. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate its value in the right hand column. Be sure to show a constant
CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 1. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate its value in the right hand column. Be sure to show a constant
ITERATION WEEK 4: EXMAPLES IN CLASS
 Monday Section 2 import java.util.scanner; public class W4MSection2 { ITERATION WEEK 4: EXMAPLES IN CLASS public static void main(string[] args) { Scanner input1 = new Scanner (System.in); int CircleCenterX
Monday Section 2 import java.util.scanner; public class W4MSection2 { ITERATION WEEK 4: EXMAPLES IN CLASS public static void main(string[] args) { Scanner input1 = new Scanner (System.in); int CircleCenterX
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
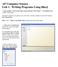 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CompSci 125 Lecture 02
 Assignments CompSci 125 Lecture 02 Java and Java Programming with Eclipse! Homework:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/compsci-125-homework! hw1 due Jan 28 (MW), 29 (TuTh)! Programming:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/cs125-programming-assignments!
Assignments CompSci 125 Lecture 02 Java and Java Programming with Eclipse! Homework:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/compsci-125-homework! hw1 due Jan 28 (MW), 29 (TuTh)! Programming:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/cs125-programming-assignments!
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types
 Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Chapter 1: Why Program? Main Hardware Component Categories 8/23/2014. Main Hardware Component Categories: Why Program?
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Software and Programming 1
 Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Full file at
 Gaddis: Starting Out with Java: Early Objects, 4/e Test Bank 1 Chapter 2 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the
Gaddis: Starting Out with Java: Early Objects, 4/e Test Bank 1 Chapter 2 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1. Name SOLUTION
 CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
9/11/08 (c) 2008 Matthew J. Rutherford Class (c) 2008 Matthew J. Rutherford Class
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 ISBN 0136130887 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved 7 Hardware and Software
1 2 3 4 5 6 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 ISBN 0136130887 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved 7 Hardware and Software
Chapter 5 Lab Methods
 Chapter 5 Lab Methods Lab Objectives Be able to write methods Be able to call methods Be able to write javadoc comments Be able to create HTML documentation for our Java class using javadoc Introduction
Chapter 5 Lab Methods Lab Objectives Be able to write methods Be able to call methods Be able to write javadoc comments Be able to create HTML documentation for our Java class using javadoc Introduction
COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction. CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics
 COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics Last Class Solving many little problems to avoid thinking about too much at once! A tiny
COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics Last Class Solving many little problems to avoid thinking about too much at once! A tiny
CHAPTER 5 VARIABLES AND OTHER BASIC ELEMENTS IN JAVA PROGRAMS
 These are sample pages from Kari Laitinen s book "A Natural Introduction to Computer Programming with Java". For more information, please visit http://www.naturalprogramming.com/javabook.html CHAPTER 5
These are sample pages from Kari Laitinen s book "A Natural Introduction to Computer Programming with Java". For more information, please visit http://www.naturalprogramming.com/javabook.html CHAPTER 5
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions
 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University January 15, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 1 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data
Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 Department of Computer Science College of Engineering Boise State University January 15, 2015 Chapter 2: Data and Expressions CS 121 1 / 1 Chapter 2 Part 1: Data
Tutorials. Tutorial every Friday at 11:30 AM in Toldo 204 * discuss the next lab assignment
 60-212 subir@cs.uwindsor.ca Phone # 253-3000 Ext. 2999 web site for course www.cs.uwindsor.ca/60-212 Dr. Subir Bandyopadhayay Website has detailed rules and regulations All assignments and labs will be
60-212 subir@cs.uwindsor.ca Phone # 253-3000 Ext. 2999 web site for course www.cs.uwindsor.ca/60-212 Dr. Subir Bandyopadhayay Website has detailed rules and regulations All assignments and labs will be
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics: Why Program? Computer Systems: Hardware and
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics: Why Program? Computer Systems: Hardware and
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
Data Structures Lecture 1
 Fall 2018 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 1 A brief review of Java programming Popularity of Programming Languages
Fall 2018 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 1 A brief review of Java programming Popularity of Programming Languages
10/3/2018 Programming Data Structures. Casting: upcasting, downcasting Debugging again! Yay! Exception Handling
 10/3/2018 Programming Data Structures Casting: upcasting, downcasting Debugging again! Yay! Exception Handling 1 If you need more time on the take-home assignment, email me today or tomorrow. Oct. 3 or
10/3/2018 Programming Data Structures Casting: upcasting, downcasting Debugging again! Yay! Exception Handling 1 If you need more time on the take-home assignment, email me today or tomorrow. Oct. 3 or
Java Assignment 3: Loop Practice Ver 3.0 Last Updated: 12/1/2015 8:57 AM
 Java Assignment 3: Loop Practice Ver 3.0 Last Updated: 12/1/2015 8:57 AM Let s get some practice creating programs that repeat commands inside of a loop in order to accomplish a particular task. You may
Java Assignment 3: Loop Practice Ver 3.0 Last Updated: 12/1/2015 8:57 AM Let s get some practice creating programs that repeat commands inside of a loop in order to accomplish a particular task. You may
CS 177 Recitation. Week 1 Intro to Java
 CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Objectives overview computer hardware and software introduce program design and object-oriented programming overview the Java programming language
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Objectives overview computer hardware and software introduce program design and object-oriented programming overview the Java programming language
1. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter? Also, discuss Java s method.
 Name: Write all of your responses on these exam pages. 1 Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter? Also, discuss Java s method. 2. Java is a platform-independent
Name: Write all of your responses on these exam pages. 1 Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter? Also, discuss Java s method. 2. Java is a platform-independent
13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition
 SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
Arrays and Lists CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal
 Arrays and Lists CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what an array is Understand how to declare arrays Understand what reference variables are Understand how to pass arrays to methods
Arrays and Lists CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what an array is Understand how to declare arrays Understand what reference variables are Understand how to pass arrays to methods
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java
 CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Schedule Computing Environment AFS (Andrew File System) Linux/Unix Commands Helpful Tricks Computers First Java
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Schedule Computing Environment AFS (Andrew File System) Linux/Unix Commands Helpful Tricks Computers First Java
CS 101 Fall 2005 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 This exam is open text book but closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts (in particular, the final two questions are worth substantially more than any
This exam is open text book but closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts (in particular, the final two questions are worth substantially more than any
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
! definite loop: A loop that executes a known number of times. " The for loops we have seen so far are definite loops. ! We often use language like
 Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Indefinite loops while loop! indefinite loop: A loop where it is not obvious in advance how many times it will execute.! We often use language like " "Keep looping as long as or while this condition is
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Chapter 6 Lab Classes and Objects
 Gaddis_516907_Java 4/10/07 2:10 PM Page 51 Chapter 6 Lab Classes and Objects Objectives Be able to declare a new class Be able to write a constructor Be able to write instance methods that return a value
Gaddis_516907_Java 4/10/07 2:10 PM Page 51 Chapter 6 Lab Classes and Objects Objectives Be able to declare a new class Be able to write a constructor Be able to write instance methods that return a value
Lesson 10: Quiz #1 and Getting User Input (W03D2)
 Lesson 10: Quiz #1 and Getting User Input (W03D2) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro September 1, 2015 1 / 13 Do Now: Prep GitHub Repo for PS #1 You ll need to submit the 5.2 solution on the paper form
Lesson 10: Quiz #1 and Getting User Input (W03D2) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro September 1, 2015 1 / 13 Do Now: Prep GitHub Repo for PS #1 You ll need to submit the 5.2 solution on the paper form
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
Computer Training for Newcomers
 Computer Training for Newcomers Lesson 1 Introduction to Computers PREPARED FOR: PREPARED BY: REVISED BY: THE IMMIGRATION CENTRE DIANE FROESE & SHELLEY MALO ELMER BALDONADO DATE: MAY 2010 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Computer Training for Newcomers Lesson 1 Introduction to Computers PREPARED FOR: PREPARED BY: REVISED BY: THE IMMIGRATION CENTRE DIANE FROESE & SHELLEY MALO ELMER BALDONADO DATE: MAY 2010 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Electricity: Voltage. Gate: A signal enters the gate at a certain voltage. The gate performs operations on it, and sends it out was a new signal.
 Hardware CSCE 101 Electricity: Voltage Gate: A signal enters the gate at a certain voltage. The gate performs operations on it, and sends it out was a new signal. The signals voltage will either be between
Hardware CSCE 101 Electricity: Voltage Gate: A signal enters the gate at a certain voltage. The gate performs operations on it, and sends it out was a new signal. The signals voltage will either be between
Computer Basics 1/24/13. Computer Organization. Computer systems consist of hardware and software.
 Hardware and Software Computer Basics TOPICS Computer Organization Data Representation Program Execution Computer Languages Computer systems consist of hardware and software. Hardware includes the tangible
Hardware and Software Computer Basics TOPICS Computer Organization Data Representation Program Execution Computer Languages Computer systems consist of hardware and software. Hardware includes the tangible
COMP 202 Java in one week
 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
Loops. Eng. Mohammed Abdualal. Islamic University of Gaza. Faculty of Engineering. Computer Engineering Department
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 6 Loops
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 6 Loops
Lab Activity Plan. John Dalbey CPE /30/2013
 John Dalbey CPE 13-5 9/3/213 Lab Activity Plan Purpose The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate the performance impacts of autoboxing in Java. The textbook describes how Java will automatically convert
John Dalbey CPE 13-5 9/3/213 Lab Activity Plan Purpose The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate the performance impacts of autoboxing in Java. The textbook describes how Java will automatically convert
CSCI 1103: Introduction
 CSCI 1103: Introduction Chris Kauffman Last Updated: Wed Sep 13 10:43:47 CDT 2017 1 Logistics Reading Eck Ch 1 Available online: http://math.hws.edu/javanotes/ Reading ahead is encouraged Goals Basic Model
CSCI 1103: Introduction Chris Kauffman Last Updated: Wed Sep 13 10:43:47 CDT 2017 1 Logistics Reading Eck Ch 1 Available online: http://math.hws.edu/javanotes/ Reading ahead is encouraged Goals Basic Model
Chapter Two. Hardware Basics: Inside the Box
 Chapter Two Hardware Basics: Inside the Box After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Explain general terms how computers store and manipulate information. Describe the basic structure of a computer
Chapter Two Hardware Basics: Inside the Box After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Explain general terms how computers store and manipulate information. Describe the basic structure of a computer
Welcome to Solving Problems with Computers I
 Welcome to Solving Problems with Computers I CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #1 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Image from agorolabs on slideshare.com A Word About Registration
Welcome to Solving Problems with Computers I CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #1 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Image from agorolabs on slideshare.com A Word About Registration
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
C Sc 227 Project 1: Three Main Methods
 C Sc 227 Project 1: Three Main Methods Collaboration Solo! Complete all four programs by yourself. Turnin: Print programs 1, 2, and 3 (Welcome.java not needed), staple them together (or lose points) and
C Sc 227 Project 1: Three Main Methods Collaboration Solo! Complete all four programs by yourself. Turnin: Print programs 1, 2, and 3 (Welcome.java not needed), staple them together (or lose points) and
Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S L E C T U R E 8
 Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 8 Math class Math class is a utility class You cannot create an instance of Math All references to constants and methods will use the prefix Math.
Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 8 Math class Math class is a utility class You cannot create an instance of Math All references to constants and methods will use the prefix Math.
BASICS.
 BASICS http://www.flickr.com/photos/oskay/472097903/ CSCI 135 - Fundamentals of Computer Science I 2 Outline Computer Basics Programs and Languages Introduction to the Eclipse IDE Our First Program Comments
BASICS http://www.flickr.com/photos/oskay/472097903/ CSCI 135 - Fundamentals of Computer Science I 2 Outline Computer Basics Programs and Languages Introduction to the Eclipse IDE Our First Program Comments
CIS260 Summer Exam 1 First Name Last Name: 2) is the brain of a computer. 2) A) Memory B) Hardware C) Disk D) CPU
 CIS260 Summer 2012 - Exam 1 First Name Last Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) is the physical aspect of the computer that can
CIS260 Summer 2012 - Exam 1 First Name Last Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) is the physical aspect of the computer that can
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion
 Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
Chapter 4: Conditionals and Recursion Think Java: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist 5.1.2 by Allen B. Downey Agenda The modulus operator Random Number Generation Conditional Execution Alternative
CS 101 Fall 2006 Midterm 1 Name: ID:
 You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
