Start Active-HDL. Create a new workspace TUTORIAL #1 CREATING AND SIMULATING SIMPLE SCHEMATICS
|
|
|
- Marilynn Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
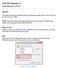
1 Introduction to Active-HDL TUTORIAL #1 CREATING AND SIMULATING SIMPLE SCHEMATICS This tutorial will introduce the tools and techniques necessary to design a basic schematic. The goal of this tutorial is to familiarize you with Active-HDL and to help you complete your assignment. After finishing this tutorial you will know how to: Start Active-HDL. Create a new workspace and design Add and remove files to and from a design. Place parts in a schematic design from the built-in library. Use wires in a schematic design. Run a basic simulation. Debug a schematic design. Even though this tutorial will show you all you need to know to do basic designs and complete the assignment, you should experiment with Active-HDL on your own. You will find that there are many tools and options that have been left out of this tutorial for the sake of simplicity. By experimenting with these tools on your own, you will become more proficient with Active-HDL, and you may find different methods to achieve the same design goal that better suit your style. Start Active-HDL First, start Active-HDL by double-clicking the icon located on your desktop. If the icon is not present then go to Start and select Active-HDL 6.3 under the Programs menu. NOTE: If you already have a Workspace you can skip to Create a New Design Create a new workspace A workspace holds your designs, and each design may consist of many files (i.e. schematics, Verilog source code, etc). When you open Active-HDL, you will be presented with the Getting Started window. Once you have created other workspaces, they will appear in the field at the center of the Getting Started window. The More button allows you to browse for existing workspaces. 1. Select the Create new workspace option. This opens the New Workspace window: - 1 -
2 Figure 1 2. Enter a descriptive name into the Type the workspace name field. 3. Change the workspace directory by entering it in the Select the location of the workspace folder field, or use the Browse button to select the new directory (we recommend you use your student drive). 4. Select the Add New Design to Workspace check box if it is not already checked. 5. Your New Workspace window should look like Figure 2. If so, click the OK button, and continue. Figure 2-2 -
3 Create a design If you just completed creating a workspace and if you check the box Add New Design to Workspace in the New Workspace Wizard the New Design Wizard will automatically start. Otherwise you will need to select a new design from the File menu. Figure 3 The New Design Wizard walks you through creating a design. A design can consist of one or more Verilog modules, schematics, and other design files. A workspace, as mentioned earlier, can contain one or more designs. You can add more designs later by selecting File/New/Design in the menu bar. For now, we will add the first design to the workspace by following the steps provided on the following pages. 1. Click the Create an empty design and Add Design to Current Workspace radio buttons. Then click the Next button. Figure 4 2. Find the Block Diagram Configuration field and select the Default HDL Language option. Leave the Synthesis tool field and the Implementation tool field blank since we will not be synthesizing yet. Your New Design Wizard window should look like Figure 5. If so, then click the Next button
4 Figure 5 3. In the Type the design name field, type a name for your new design. The name must contain only letters, numbers, and underscores ( _ ), and cannot start with a number (i.e. 4bitadder is invalid, however four_bit_adder is valid). Use descriptive names that do not match file names, other design names, or workspace names. By default, the design directory is under the workspace directory, and the name of the default working library of the design is the same as the design name. Leave these default values alone. Warning: the directory path should not contain any spaces in it. Your window should now look like Figure 6 with a MORE descriptive name than combo_logic
5 Figure 6 4. Double check your file name and location, then click the Next button. 5. Make sure that your design name is correct and the design directory is correct in the window that follows (not shown). If not, click the Back button to make any changes, or click the Finish button to create the design. Add a Block Diagram (schematic) file At this point your screen should look like Figure 7 (shown on the following page). The frame on the left is called the Design Browser and lists all of the components in your design. The frame on the bottom is the Console and is where status and error messages are printed. If these frames are not open, or if you have closed them by accident, you can open them by going to View in the menu bar. In the center of the screen is the main window where you will draw your schematics. When your design is first opened, the Design Flow Manager opens in this window. We won t be using this tool during this tutorial. At the top of this window is the Standard toolbar. Finally, notice the tab at the bottom left side of the main window. As you create schematics and other components in your design, you can use the tabs at the bottom of this window to make the corresponding file active in the main window
6 Figure 7 1. Double-click the Add New File option in the Design Browser (Figure 8). This will open the Add New File window. Figure 8 2. Click the Wizards tab in the Add New File window. Select the Block Diagram Wizard icon, and then click the OK button (Figure 9)
7 Figure 9 3. In the New Source File Wizard, make sure that the box is checked next to the Add the generated file to the design option. Click the Next button. Note: this window is not shown. 4. Select the Verilog option, and click the Next button (see Figure 10). Figure In the Type the name of the source file to create field, enter the name of your schematic design. Use descriptive names. Do not us the same name that you named your design or workspace. Also, do not use a different name for the module; leave this field blank. Active-HDL will use the source files name for the module by default. Click the Next button. (See Figure 11) - 7 -
8 Figure This window is where you add your input and output ports. You do not have to add any ports at this point in the design process; however, adding the ports now will save time. If you choose not to add any, click Finish and skip steps To add ports, click the New button. Choose whether you want an input or output port by clicking the desired radio button located under the Port Direction heading. 8. In the Name field, type the name of the port. 9. We will only be using 1-bit ports, so ignore the Array Indexes fields for now. Your screen should look like Figure 12. If so, then click the Finish button. Figure 12 The wizard generates a schematic that is empty except for any ports you specified in the design process (see Figure 13). Notice this schematic file has been added to the design in the Design Browser on the left. Schematic files in Active-HDL are called Block Diagram - 8 -
9 files and have an extension of.bde. The question mark means the file has not been compiled yet, which we will get to later. Also, new toolbars have been added below the standard tool bar, which are used to edit block diagrams. Figure 13 At some point, you may wish to detach files from your design, or delete them completely. You can do any of those tasks by simply right clicking the file in the Design Browser and selecting the Remove option from the pop-up menu. You will then be asked if you want to detach the file (remove it from the design without deleting it completely) or delete the file. Obviously there is a lot more that you can and may want to do to manage your files, but for now just get comfortable with these basic steps towards file management. Place parts into your schematic design Now you are ready to build your gate logic. The steps below will teach you how to add basic gates to your schematic and how to add single bit input and output terminals, in case you decided not to do so in the design wizard process, or you realized that you are missing some terminals (Note: this tutorial uses the icons in the toolbars and other shortcuts to access most of the tools in Active-HDL; however, all the commands accessed from the toolbars can be found in the menu as well). Additionally, you will need to know how to move and delete gates to clean up your design s appearance. Figure 14 is the final version of the schematic you will be drawing. Your final design should look similar*
10 Figure 14 *Some of the components you use may differ in appearance from the components shown in this tutorial. 1. You are required to use the components located in the standard class library. Do not use built-in symbols. Therefore, you need to add the symbols for the components in the standard class library to the symbols toolbox using the Library Manager. Open the Library Manager by clicking the Library Manger icon in the toolbar (Figure 15). Figure Locate the lib370 library in the left frame of the main window, and right click it (Figure 16). 3. Select the Add to Symbols Toolbox option
11 Figure Close the Library Manger by clicking its icon in the toolbar, or select File/Close. 5. Open the Symbols Toolbox by clicking the Symbols Toolbox icon in the toolbar (Figure 17). Figure
12 6. Click the plus symbol to the left of the lib370 option to expand the list. Scroll down the to find the desired part from the list, or type in the name of the part in the field at the top of the Symbols Toolbox to search the list. 7. Click on the parts name in the list and notice that its symbol appears at the bottom of the Symbols Toolbox. 8. Add the part to your schematic by dragging the symbol from the Symbols Toolbox into your design. Figure Active-HDL uses the standard Windows user-interface to select, move, and copy items in the schematic (i.e. drag, Ctrl-drag for copying multiple parts, Ctrl-z for undo, etc.). Figure 19 is an example of Ctrl-drag. Figure (Skip steps 6-8 if you added your terminals in the New Block Diagram Wizard) To add a terminal click the drop down arrow next to the Terminal icon in the toolbar (or click Diagram/Terminal in the menu bar). Click the Input or Output option in the expansion menu
13 Figure Click in the schematic where you want the terminal. 12. Notice that you can continue to click and add multiple terminals. To stop adding terminals, press the Esc key. Note: The Esc key is very useful to get out of just about any process (i.e. drawing wires, placing components, etc). Moving gates and terminals is as easy as clicking and dragging the part to the new location. Additionally, the arrow keys are very useful for moving components precisely where you need them in the schematic. To delete parts, simply click the part to be deleted (when properly selected, the part will be outlined in a red box), and then press the Delete key. In addition to moving and deleting gates, you may want to rotate and flip gates. Step 1: Select the part by clicking on it. Step 2: Then right click on the part. Step 3: In the pop-up menu, select the Mirror or Rotate options. Using wires in Active-HDL This part of the tutorial will show you how to make connections using wires, how to move the wires, how to name wires, and how to delete wires. 1. Click on the Wire icon in the toolbar (see Figure 21). Figure Now click anywhere in the schematic and drag your mouse to the point in the schematic where you want the wire to end. Clicking on a port or terminal will connect an end of the wire to that port or terminal, clicking on another wire will create a junction, clicking on an empty space in the schematic will create an anchor or bend in the wire at that point, and double-clicking an empty space in the schematic will create an end to the wire at that point. 3. When you are done placing wires, go back to select mode by pressing the Esc key or clicking the Select Mode button in the toolbar
14 Removing wires: 1. Select the wire by clicking on it (the selected wire will turn red). 2. Press the Delete key. Figure 22 Moving wires: 1. Click and drag on the wire or part of the wire to be moved. 2. Drag your mouse to the new location and release the button. Naming wires: 1. Double-click the wire segment you wish to label. This opens the Wire Properties window (Figure 23). 2. In the Segment field under the General tab, type the name. 3. Click OK. Figure
15 Connections to terminals can be made by wire or by name. By wire connections connect terminals by a wire. If a wire and a terminal have the same name, they are connected by name. Lots of wires can be confusing and named connections are used to make easy to read schematics. Figure 24 is an example of both methods. Also, the final schematic version of the full adder presented earlier (Figure 14) shows how to create an easy to read schematic using connections by name. Figure 24 ** Complete your schematic so it looks like Figure 14 ** Checking, saving, and compiling your design At this point you should have a schematic with gates and terminals connected using wires. However, your file in the Design Browser is still preceded by a question mark. Before you can run simulations you need to compile your design, at which point the question mark will become a green check mark if all is well, or a red x if there are errors. 1. Always save your files first. To do this, click the Save icon in the toolbar, or press Ctrl-S with the file s tab active in the main window. Remember to save early and often throughout the design process. 2. Active-HDL provides a Check Diagram tool. This tool will verify that the components are connected properly by printing the results into the Design Rule Check report (DRC). To open this report, go to the Console and double-click the line that states, Double click on this line to view the log (see Figure 27 in the DRC section). The DRC report is explained later in this tutorial. Always use the Check Diagram tool prior to compiling by clicking the Diagram/Check Diagram option in the menu bar (see Figure 25)
16 Figure After you have checked your diagram and resolved any errors or warnings, click the Compile icon in the Standard toolbar. See the DRC Report (immediately following this section) and the debugging section, which follows the Simulation section, for examples on how to locate and debug errors in your design. The Console window will display the results of the compilation. When compiling a schematic, the console will generally compile successfully even if there are gates and/or terminals that are not connected (in some cases, warnings will be issued for unconnected ports). Therefore, just because a schematic compiles does not mean that it will do what you intended it to do during simulations. This is the reason you need to check your diagram prior to compiling. Figure 26 (next page) shows a successful compilation even though there are terminals and ports unconnected
17 Figure 26 DRC Report When you run the check diagram tool, a DRC report file is created. Open this file by going to the DRC line in the Console and double-click the appropriate line (see Figure 27). This file will list any errors or warnings your design might contain, such as unconnected ports, mislabeled wires and/or terminals, and other connection related errors/warnings. Each error/warning in the report is a hyperlink that will take you to the problematic component in your design. Figure 27 shows an example of a DRC report file for a schematic with an error and some warnings
18 Figure 27 Simulating a design To ensure that your design functions as you intend, you need to simulate it. This portion of the tutorial will show you how to set the top-level, how to open a waveform, how to add signals to a waveform, and how to use stimulators. Important: close all open waveforms from previous simulations, if any, prior to running a new simulation. 1. Before you can simulate a design, you must set the top-level. Since designs can be composed of multiple files or layers, we need to tell Active-HDL which file is our top-level. After you compiled your block diagram file, two files were created: a Verilog file, and a module. Expand your block diagram file list by clicking the plus symbol next to the file name in the Design browser. Continue to expand the list until you see the module, which is proceeded by an M icon. Note: the following design entities are valid choices when setting the top-level: a configuration [ C icon], a module [ M icon], or an EDIF cell [ D icon]. 2. Right click the module. 3. Select the Set as Top-Level option. If you do not set the top-level, Active-HDL will ask you to do so when you attempt to initialize a simulation
19 Figure Select Initialize Simulation under Simulation in the menu bar. Figure
20 After selecting Initialize Simulation, notice in Figure 30 that the Structures tab is opened in the Design Browser. Figure Click the New Waveform icon in the Standard toolbar. Figure Click the file name in the top window in the Design Browser under the Structures tab. Notice in Figure 32 how the signals and wires (Nets) appear in the bottom window of the Design Browser
21 Figure Add the signals to the waveform by dragging the signals one by one into the left side of the waveform. A faster method of adding signals to the waveform is to select the signals using the Shift or Ctrl keys. Now you may drag them as described above into the waveform. You can also right-click on a selected signal, and click the Add to waveform option in the pop-up menu as shown in Figure 33. Figure To simulate a design, we have to provide values for the input signals. Active- HDL provides Stimulators to drive input signals in a waveform. In the left half of the waveform window, right click on the input signal you wish to stimulate
22 Figure Click the Stimulators option in the pop-up menu. Figure The Stimulators window will pop up with the Signals tab active. The large arrow points to a list of stimulators, and your signal is shown on the left side of the window in the signals field. The Type list shows the different stimulator options: choose the Clock option. See Using Stimulators at the end of this tutorial to learn about some of the other options. Figure With the Stimulators window still opened, you can set additional signals by clicking the signals in the left side of the waveform. Once you have added all three input signals (i.e. A, B, and CI), choose a clock period of 10 ns for A by entering the time in second box from the left at the top of the window (see Figure 37). Click the Apply button
23 Figure Select clocks with periods of 20 ns, and 40 ns for the other inputs. 13. When you are finished applying your stimulators, click the Close button. At this point, you are ready to run the simulation using the waveform and stimulators. 1. The Run For field located in the Standard toolbar controls how long to run the simulation. You may change this by using the up and down arrows to the right of the field, or you may type in a time. Figure Click the Run For button in the Standard toolbar Figure To restart the simulation, click the Restart button in the Standard toolbar. Figure 40 Note: if you make changes to the waveform by changing stimulators or adding/removing signals, you need to restart the simulation. Similarly, any changes in the file mean the file needs to be saved and recompiled prior to restarting the simulation. To end a simulation, simply click Simulation/End Simulation in the menu bar. Figure 41 is an example of a simulation using the steps provided in this tutorial
24 Figure 41 Now that you have ran a simulation and created a waveform, you should save that waveform. With the waveform tab active, press Ctrl-s to save, or right-click the tab and select save. Remember to use descriptive names. A good naming convention is <design name>_wv. This is the naming convention that will be used in the next assignment. For example, the waveform below would be saved as full_adder_wv. Figure 42 You may have several waveforms for the same design. This is very useful in comparing different signal values and methods of driving the input signals. However, you should close all waveforms when you are done to avoid confusing signals when simulating other designs. You should experiment with the different methods available and save the results in separate waveforms for comparison; however, this is optional
25 Debugging a design We will walk through a simple, yet common, scenario with a schematic that contains errors and warnings. Some of these problems can be pinpointed and solved by simply running a check diagram and reviewing the DRC. However, the DRC cannot find and report your logic errors. What do you do if you have checked your design, compiled successfully, and when you run your simulation, your results are flawed? The techniques below will show you how to use the tools provided by Active-HDL to trouble-shoot your design, and fix some of the most common mistakes. We used Figure 43 in the following steps to demonstrate the debugging process*. Figure 43 *This schematic was designed using parts from the Built-in library. Therefore, there are no gate delays. 1. First, we saved, and checked our design. When checking the schematic shown in Figure 43, Active-HDL generated the DRC report shown below
26 Figure Clicking on the first line took us to the broken connection on the 3-input OR gate. The part in question was highlighted in a red box (not shown here). Therefore, we simply reestablished the connection by dragging the hanging wire to the 3-input OR gate port (shown fixed in Figure 45). 3. The second warning showed that net C was without a source. Again, we clicked this hyperlink, and it took us to our schematic and highlighted the wire named C in red (see Figure 45). The connection looked fine, but notice that we have no terminals by the name of C. The terminal we wanted to connect from was CI. This kind of mistake is common when using naming connections, and Active- HDL is good at alerting us to this mistake. Figure After we had corrected the first two warnings, we clicked on the third. This hyperlink took us to our schematic and highlighted the segment that was broken earlier, but we had already fixed it in the second step. This could have meant there
27 was another problem with this segment, or the problem was that this broken connection had raised two errors involving the two gates. At this point, we saved the file, and ran the check diagram tool again. Figure 46 shows the results of this DRC report, and according to Active-HDL all was well. Figure Now we compiled the design, and it compiled successfully. Therefore, we initialized a simulation, added the signals to a waveform, provided clock stimulators for the signals, and simulated the design. Figure 47 shows the results of this simulation. When comparing the waveform to the expected results (we used a truth table), everything looked fine until we got to the 10 to 15 ns period. The sum should have been 1 and the carryout should have been 0, but both were 1. This showed us that there was a logic error. Figure With the simulation still initialized, we went back to our schematic design by clicking the design s tab in the main window. 7. Then, we restarted the simulation. Since we were using clocks of 10 ns, 20 ns, and 40 ns, we knew that the first problem arose at 10 ns. Therefore, we entered 10 ns in the Run For field in the toolbar, and ran the simulation with the schematic open. 8. The sum waveform showed that the sum was correct. Therefore, we focused on the carryout logic. When running a simulation, there are boxes next to each input and output signal in the schematic that display their values throughout the simulation. A green box means the signal is low (0), a red box means the signal is high (1), a yellow box (z) means the signal is unconnected, and a blue box (x) means the signal is unknown. We noticed that after running the simulation for 10 ns that the box next to the carryout output terminal was red (see Figure 48 on the next page). Using the mouse-over feature, we traced the signal from the carryout terminal all the way back to the input signals
28 9. Since the carryout is determined by the 3-input OR gate, we knew that the outputs of each of the AND gates and the OR gate should have been 0. As we mouse over each of the outputs, we notice a 1 at the output of the OR gate. Figure Next, we needed to verify that the inputs were correct. By rolling the mouse over the two inputs to the OR gate, we verified that the inputs were indeed correct. Since the signal B was a 1 and the signal C was a 0, the only way that we could have produced a 0 for the output was with an AND gate. Therefore, our logic was flawed and we needed to change this OR gate to an AND gate. As you can see, logic errors like this one are undetectable by Active-HDL, and you will need to use this technique or techniques of your own to pinpoint these errors. 11. We replaced the part by right-clicking it, and selecting the Replace Symbol option and selected a 2-input AND gate from the pop-up menu. Then we connected the symbol, saved the file, ran check diagram, and compiled it while making sure to fix any new bugs we may have created while fixing the old bugs. This is a simplified example of what you may encounter in your design process. However, the techniques described above can be applied in the same way to larger, more complicated designs. You need to know how to debug your designs using a simulation as well as the DRC report. Even if you do not run into any problems with this assignment, you may need to use these techniques in the more complex upcoming assignments
29 Using Stimulators (other than a clock) This section will describe two of the available stimulators that you may use in your simulations other than the Clock option you used above. Value: The value option allows you to set a value of a signal to 1, 0, z (high impedance), or x (unknown). For this tutorial choose either 1 or 0 by following the steps below. 1. With the Stimulators window open and a signal selected, click the Value option in the list. 2. Select the desired value from the Force value field (see Figure 49 on the next page). Figure Click Apply, and repeat the steps above for other signals. When you are finished, click the Close button
30 Formula: 1. With the Stimulators window open and a signal selected, click the Formula option in the list. 2. In the Enter formula field, enter the value (1 or 0) followed by a space and the time at which to assert this value. For example, the following formula will cause a signal to start out at 1, then change to 0 at 10 us and back to 1 at 20 us: 1 0 us, 0 10 us, 1 20 us (see Figure 50). Figure Alternatively, you can let Active-HDL create the formula for you by entering the desired value and time offset in the fields provided. You are allowed three sets of these values, then you can choose to repeat the sequence by entering a time in the repeat above sequence every field. Once you have set your formula click the Apply button. 4. To set formulas for more signals simply add the signals and repeat the above steps. When you are finished, click the Close button. Concluding Remarks This completes the first tutorial for Active-HDL. Remember that this tutorial has only scratched the surface of the capabilities of this program. We strongly recommend you practice using the techniques described within this tutorial while experimenting with and exploring other methods and techniques that Active-HDL offers. You may want to try the Verilog tutorial that comes with Active-HDL as well. Don t be discouraged if you do not understand what all of the tools are used for or the concepts the tutorial covers that have not yet been covered in class. By spending time with this tool and experimenting, you will save time by being better prepared for the more complicated upcoming assignments
TUTORIAL #2 HIERARCHICAL DESIGNS AND TEST FIXTURES
 Introduction to Active-HDL TUTORIAL #2 HIERARCHICAL DESIGNS AND TEST FIXTURES This tutorial will use the 1-bit full adder you designed in Tutorial #1 to construct larger adders. This will introduce the
Introduction to Active-HDL TUTORIAL #2 HIERARCHICAL DESIGNS AND TEST FIXTURES This tutorial will use the 1-bit full adder you designed in Tutorial #1 to construct larger adders. This will introduce the
CSE370 TUTORIAL 3 - INTRODUCTION TO USING VERILOG IN ACTIVE-HDL
 Introduction to Active-HDL CSE370 TUTORIAL 3 - INTRODUCTION TO USING VERILOG IN ACTIVE-HDL Objectives In this tutorial, you will learn how to write an alternate version of the full adder using Verilog,
Introduction to Active-HDL CSE370 TUTORIAL 3 - INTRODUCTION TO USING VERILOG IN ACTIVE-HDL Objectives In this tutorial, you will learn how to write an alternate version of the full adder using Verilog,
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS SCHOOL OF COMPUTER & COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING EKT 124 LABORATORY MODULE INTRODUCTION TO QUARTUS II DESIGN SOFTWARE : INTRODUCTION TO QUARTUS II DESIGN SOFTWARE OBJECTIVES To
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS SCHOOL OF COMPUTER & COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING EKT 124 LABORATORY MODULE INTRODUCTION TO QUARTUS II DESIGN SOFTWARE : INTRODUCTION TO QUARTUS II DESIGN SOFTWARE OBJECTIVES To
Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Code
 Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Code (Version 15) 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow
Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Code (Version 15) 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow
and 32 bit for 32 bit. If you don t pay attention to this, there will be unexpected behavior in the ISE software and thing may not work properly!
 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. EECS 150 Spring 2000
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2000 Lab 1 Introduction to Xilinx Design Software 1 Objectives In this
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2000 Lab 1 Introduction to Xilinx Design Software 1 Objectives In this
NOTE: This tutorial contains many large illustrations. Page breaks have been added to keep images on the same page as the step that they represent.
 CSE 352 Tutorial # 4 Synthesizing onto an FPGA Objectives This tutorial will walk you through the steps of implementing a design made in Active-HDL onto the Altera Cyclone II FPGA NOTE: This tutorial contains
CSE 352 Tutorial # 4 Synthesizing onto an FPGA Objectives This tutorial will walk you through the steps of implementing a design made in Active-HDL onto the Altera Cyclone II FPGA NOTE: This tutorial contains
Active-HDL. Getting Started
 Active-HDL Getting Started Active-HDL is an integrated environment designed for development of VHDL designs. The core of the system is a VHDL simulator. Along with debugging and design entry tools, it
Active-HDL Getting Started Active-HDL is an integrated environment designed for development of VHDL designs. The core of the system is a VHDL simulator. Along with debugging and design entry tools, it
EE261 Computer Project 1: Using Mentor Graphics for Digital Simulation
 EE261 Computer Project 1: Using Mentor Graphics for Digital Simulation Introduction In this project, you will begin to explore the digital simulation tools of the Mentor Graphics package available on the
EE261 Computer Project 1: Using Mentor Graphics for Digital Simulation Introduction In this project, you will begin to explore the digital simulation tools of the Mentor Graphics package available on the
SCHEMATIC DESIGN IN QUARTUS
 SCHEMATIC DESIGN IN QUARTUS Consider the design of a three-bit prime number detector. Figure 1 shows the block diagram and truth table. The inputs are binary signals A, B, and C while the output is binary
SCHEMATIC DESIGN IN QUARTUS Consider the design of a three-bit prime number detector. Figure 1 shows the block diagram and truth table. The inputs are binary signals A, B, and C while the output is binary
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Fall 2000 Original Lab By: J.Wawrzynek and N. Weaver Edited by B. Choi, R.
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Fall 2000 Original Lab By: J.Wawrzynek and N. Weaver Edited by B. Choi, R.
Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4
 Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Implement a function using
Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Implement a function using
Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Schematic Designs
 Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Schematic Designs (Version 15) 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD
Tutorial on Quartus II Introduction Using Schematic Designs (Version 15) 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD
Contents. Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2 Page 1 of 14
 Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2 Page 1 of 14 Contents Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2...2 B.1 Getting Started...2 B.1.1 Preparing a Folder for the Project...2 B.1.2 Starting Quartus II...2 B.1.3 Creating
Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2 Page 1 of 14 Contents Appendix B HDL Entry Tutorial 2...2 B.1 Getting Started...2 B.1.1 Preparing a Folder for the Project...2 B.1.2 Starting Quartus II...2 B.1.3 Creating
Xilinx Tutorial Basic Walk-through
 Introduction to Digital Logic Design with FPGA s: Digital logic circuits form the basis of all digital electronic devices. FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array) are large programmable digital electronic
Introduction to Digital Logic Design with FPGA s: Digital logic circuits form the basis of all digital electronic devices. FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array) are large programmable digital electronic
Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Design
 Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Design This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus R II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented
Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Design This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus R II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented
Introduction to Computer Engineering (E114)
 Introduction to Computer Engineering (E114) Lab 1: Full Adder Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for
Introduction to Computer Engineering (E114) Lab 1: Full Adder Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for
Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for single transistor analysis. Based on existing schematic entry tutorial developed for ECE410
 Cadence Analog Tutorial 1: Schematic Entry and Transistor Characterization Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for
Cadence Analog Tutorial 1: Schematic Entry and Transistor Characterization Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for
Easy Windows Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files
 Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Page 1 of 11 Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Task 1: Opening Folders Folders contain files, programs, or other
Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Page 1 of 11 Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Task 1: Opening Folders Folders contain files, programs, or other
Code::Blocks Student Manual
 Code::Blocks Student Manual Lawrence Goetz, Network Administrator Yedidyah Langsam, Professor and Theodore Raphan, Distinguished Professor Dept. of Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College of
Code::Blocks Student Manual Lawrence Goetz, Network Administrator Yedidyah Langsam, Professor and Theodore Raphan, Distinguished Professor Dept. of Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College of
University of Florida EEL 3701 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Madison Emas, TA Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Revision 1 5-Jun-17
 Page 1/14 Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate and two inverters under the Quartus environment. Upon completion
Page 1/14 Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate and two inverters under the Quartus environment. Upon completion
Step 1: Downloading the source files
 Introduction: In this lab and in the remainder of the ELEC 2607 labs, you will be using the Xilinx ISE to enter and simulate the designs for your circuits. In labs 3 and 4, you will use ISE to compile
Introduction: In this lab and in the remainder of the ELEC 2607 labs, you will be using the Xilinx ISE to enter and simulate the designs for your circuits. In labs 3 and 4, you will use ISE to compile
ANADOLU UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING. EEM Digital Systems II
 ANADOLU UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 334 - Digital Systems II LAB 1 - INTRODUCTION TO XILINX ISE SOFTWARE AND FPGA 1. PURPOSE In this lab, after you learn to use
ANADOLU UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 334 - Digital Systems II LAB 1 - INTRODUCTION TO XILINX ISE SOFTWARE AND FPGA 1. PURPOSE In this lab, after you learn to use
ECSE-323 Digital System Design. Lab #1 Using the Altera Quartus II Software Fall 2008
 1 ECSE-323 Digital System Design Lab #1 Using the Altera Quartus II Software Fall 2008 2 Introduction. In this lab you will learn the basics of the Altera Quartus II FPGA design software through following
1 ECSE-323 Digital System Design Lab #1 Using the Altera Quartus II Software Fall 2008 2 Introduction. In this lab you will learn the basics of the Altera Quartus II FPGA design software through following
Lesson 1: Getting Familiar with Microsoft Word 2007 for Windows
 Lesson 1: Getting Familiar with Microsoft Word 2007 for Windows Microsoft Word is a word processing software package. You can use it to type letters, reports, and other documents. This tutorial teaches
Lesson 1: Getting Familiar with Microsoft Word 2007 for Windows Microsoft Word is a word processing software package. You can use it to type letters, reports, and other documents. This tutorial teaches
Tutorial on Simulation using Aldec Active-HDL Ver 1.0
 Tutorial on Simulation using Aldec Active-HDL Ver 1.0 by Shashi Karanam Introduction Active- HDL is an integrated environment designed for development of VHDL designs. The core of the system is a VHDL
Tutorial on Simulation using Aldec Active-HDL Ver 1.0 by Shashi Karanam Introduction Active- HDL is an integrated environment designed for development of VHDL designs. The core of the system is a VHDL
Altera Quartus II Tutorial ECE 552
 Altera Quartus II Tutorial ECE 552 Quartus II by Altera is a PLD Design Software which is suitable for high-density Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) designs, low-cost FPGA designs, and Complex Programmable
Altera Quartus II Tutorial ECE 552 Quartus II by Altera is a PLD Design Software which is suitable for high-density Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) designs, low-cost FPGA designs, and Complex Programmable
ELEC 4200 Lab#0 Tutorial
 1 ELEC 4200 Lab#0 Tutorial Objectives(1) In this Lab exercise, we will design and implement a 2-to-1 multiplexer (MUX), using Xilinx Vivado tools to create a VHDL model of the design, verify the model,
1 ELEC 4200 Lab#0 Tutorial Objectives(1) In this Lab exercise, we will design and implement a 2-to-1 multiplexer (MUX), using Xilinx Vivado tools to create a VHDL model of the design, verify the model,
Module 3: Working with C/C++
 Module 3: Working with C/C++ Objective Learn basic Eclipse concepts: Perspectives, Views, Learn how to use Eclipse to manage a remote project Learn how to use Eclipse to develop C programs Learn how to
Module 3: Working with C/C++ Objective Learn basic Eclipse concepts: Perspectives, Views, Learn how to use Eclipse to manage a remote project Learn how to use Eclipse to develop C programs Learn how to
Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers
 Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers 1) Open Corel Draw. Create a blank 8.5 x 11 Document. 2) Go to the Import option and browse to the Graphics 1 > Lessons folder 3) Find the Cell
Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers 1) Open Corel Draw. Create a blank 8.5 x 11 Document. 2) Go to the Import option and browse to the Graphics 1 > Lessons folder 3) Find the Cell
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group.
 Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Aug. 2003 update and edit A. Mason add intro/revision/contents
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Aug. 2003 update and edit A. Mason add intro/revision/contents
Creating a PCB Design with OrCAD PCB Editor
 Creating a PCB Design with OrCAD PCB Editor This guide is focused on learning how to create a PCB (Printed Circuit board) design. The guide will make use of the PCB Flow menu that is part of this workshop
Creating a PCB Design with OrCAD PCB Editor This guide is focused on learning how to create a PCB (Printed Circuit board) design. The guide will make use of the PCB Flow menu that is part of this workshop
EET2141 Project 2: Binary Adder Using Xilinx 7.1i Due Friday April 25
 EET2141 Project 2: Binary Adder Using Xilinx 7.1i Due Friday April 25 Introduction This Xilinx project introduces the characteristics of the ripple carry adder. From the last project, you learned that
EET2141 Project 2: Binary Adder Using Xilinx 7.1i Due Friday April 25 Introduction This Xilinx project introduces the characteristics of the ripple carry adder. From the last project, you learned that
ekaizen Lessons Table of Contents 1. ebook Basics 1 2. Create a new ebook Make Changes to the ebook Populate the ebook 41
 Table of Contents 1. ebook Basics 1 2. Create a new ebook 20 3. Make Changes to the ebook 31 4. Populate the ebook 41 5. Share the ebook 63 ekaizen 1 2 1 1 3 4 2 2 5 The ebook is a tabbed electronic book
Table of Contents 1. ebook Basics 1 2. Create a new ebook 20 3. Make Changes to the ebook 31 4. Populate the ebook 41 5. Share the ebook 63 ekaizen 1 2 1 1 3 4 2 2 5 The ebook is a tabbed electronic book
Getting Started with Xilinx WebPack 13.1
 Getting Started with Xilinx WebPack 13.1 B. Ackland June 2011 (Adapted from S. Tewksbury notes WebPack 7.1) This tutorial is designed to help you to become familiar with the operation of the WebPack software
Getting Started with Xilinx WebPack 13.1 B. Ackland June 2011 (Adapted from S. Tewksbury notes WebPack 7.1) This tutorial is designed to help you to become familiar with the operation of the WebPack software
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL. Introduction. Projects. Design Entry
 EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial
 Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Quartus II Introduction Using Schematic Design
 Quartus II Introduction Using Schematic Design This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus R II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented
Quartus II Introduction Using Schematic Design This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus R II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented
Unit 12. Electronic Spreadsheets - Microsoft Excel. Desired Outcomes
 Unit 12 Electronic Spreadsheets - Microsoft Excel Desired Outcomes Student understands Excel workbooks and worksheets Student can navigate in an Excel workbook and worksheet Student can use toolbars and
Unit 12 Electronic Spreadsheets - Microsoft Excel Desired Outcomes Student understands Excel workbooks and worksheets Student can navigate in an Excel workbook and worksheet Student can use toolbars and
LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC GATE AND ITS BEHAVIOUR
 LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC GATE AND ITS BEHAVIOUR OBJECTIVE 1. To verify the operation of OR, AND, INVERTER gates 2. To implement the operation of NAND and NOR gate 3. To construct a simple combinational
LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC GATE AND ITS BEHAVIOUR OBJECTIVE 1. To verify the operation of OR, AND, INVERTER gates 2. To implement the operation of NAND and NOR gate 3. To construct a simple combinational
How to Get Started. Figure 3
 Tutorial PSpice How to Get Started To start a simulation, begin by going to the Start button on the Windows toolbar, then select Engineering Tools, then OrCAD Demo. From now on the document menu selection
Tutorial PSpice How to Get Started To start a simulation, begin by going to the Start button on the Windows toolbar, then select Engineering Tools, then OrCAD Demo. From now on the document menu selection
Xilinx Schematic Entry Tutorial
 Overview Xilinx Schematic Entry Tutorial Xilinx ISE Schematic Entry & Modelsim Simulation What is circuit simulation and why is it important? Complex designs, short design cycle Simultaneous system design
Overview Xilinx Schematic Entry Tutorial Xilinx ISE Schematic Entry & Modelsim Simulation What is circuit simulation and why is it important? Complex designs, short design cycle Simultaneous system design
Engineering 1630 Fall Simulating XC9572XL s on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board
 Engineering 1630 Fall 2016 Simulating XC9572XL s on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board You will use the Aldec Active-HDL software for the required timing simulation of the XC9572XL CPLD programmable logic chips
Engineering 1630 Fall 2016 Simulating XC9572XL s on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board You will use the Aldec Active-HDL software for the required timing simulation of the XC9572XL CPLD programmable logic chips
University of Florida EEL 3701 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Revision 0 12-Jun-16
 Page 1/14 Quartus Tutorial with Basic Graphical Gate Entry and Simulation Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate
Page 1/14 Quartus Tutorial with Basic Graphical Gate Entry and Simulation Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate
Name EGR 2131 Lab #6 Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits
 Name EGR 2131 Lab #6 Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits Equipment and Components Quartus software and Altera DE2-115 board PART 1: Number Representation in Microsoft Calculator. First, let s
Name EGR 2131 Lab #6 Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits Equipment and Components Quartus software and Altera DE2-115 board PART 1: Number Representation in Microsoft Calculator. First, let s
Code::Blocks Student Manual
 Code::Blocks Student Manual Lawrence Goetz, Network Administrator Yedidyah Langsam, Professor and Theodore Raphan, Distinguished Professor Dept. of Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College of
Code::Blocks Student Manual Lawrence Goetz, Network Administrator Yedidyah Langsam, Professor and Theodore Raphan, Distinguished Professor Dept. of Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College of
Lecture 5: Aldec Active-HDL Simulator
 Lecture 5: Aldec Active-HDL Simulator 1. Objective The objective of this tutorial is to introduce you to Aldec s Active-HDL 9.1 Student Edition simulator by performing the following tasks on a 4-bit adder
Lecture 5: Aldec Active-HDL Simulator 1. Objective The objective of this tutorial is to introduce you to Aldec s Active-HDL 9.1 Student Edition simulator by performing the following tasks on a 4-bit adder
VeriLogger Tutorial: Basic Verilog Simulation
 VeriLogger Tutorial: Basic Verilog Simulation This tutorial demonstrates the basic simulation features of VeriLogger Pro. It teaches you how to create and manage a project and how to build, simulate, and
VeriLogger Tutorial: Basic Verilog Simulation This tutorial demonstrates the basic simulation features of VeriLogger Pro. It teaches you how to create and manage a project and how to build, simulate, and
The QuickCalc BASIC User Interface
 The QuickCalc BASIC User Interface Running programs in the Windows Graphic User Interface (GUI) mode. The GUI mode is far superior to running in the CONSOLE mode. The most-used functions are on buttons,
The QuickCalc BASIC User Interface Running programs in the Windows Graphic User Interface (GUI) mode. The GUI mode is far superior to running in the CONSOLE mode. The most-used functions are on buttons,
Verilog Design Entry, Synthesis, and Behavioral Simulation
 ------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
NVU Web Authoring System
 NVU Web Authoring System http://www.nvu.com/index.php Table of Contents Using Nvu as Your Web Page Authoring System: Getting Started Opening a page, saving, and previewing your work...3 Formatting the
NVU Web Authoring System http://www.nvu.com/index.php Table of Contents Using Nvu as Your Web Page Authoring System: Getting Started Opening a page, saving, and previewing your work...3 Formatting the
E85: Digital Design and Computer Engineering Lab 2: FPGA Tools and Combinatorial Logic Design
 E85: Digital Design and Computer Engineering Lab 2: FPGA Tools and Combinatorial Logic Design Objective The purpose of this lab is to learn to use Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) tools to simulate
E85: Digital Design and Computer Engineering Lab 2: FPGA Tools and Combinatorial Logic Design Objective The purpose of this lab is to learn to use Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) tools to simulate
Interface. 2. Interface Adobe InDesign CS2 H O T
 2. Interface Adobe InDesign CS2 H O T 2 Interface The Welcome Screen Interface Overview The Toolbox Toolbox Fly-Out Menus InDesign Palettes Collapsing and Grouping Palettes Moving and Resizing Docked or
2. Interface Adobe InDesign CS2 H O T 2 Interface The Welcome Screen Interface Overview The Toolbox Toolbox Fly-Out Menus InDesign Palettes Collapsing and Grouping Palettes Moving and Resizing Docked or
Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Designs. 1 Introduction. For Quartus II 12.0
 Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Designs For Quartus II 12.0 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for
Quartus II Introduction Using Verilog Designs For Quartus II 12.0 1 Introduction This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II CAD system. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for
The first time you open Word
 Microsoft Word 2010 The first time you open Word When you open Word, you see two things, or main parts: The ribbon, which sits above the document, and includes a set of buttons and commands that you use
Microsoft Word 2010 The first time you open Word When you open Word, you see two things, or main parts: The ribbon, which sits above the document, and includes a set of buttons and commands that you use
EMT1250 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT. EXPERIMENT # 6: Quartus II Tutorial and Practice. Name: Date:
 EXPERIMENT # 6: Quartus II Tutorial and Practice Name: Date: Equipment/Parts Needed: Quartus II R Web Edition V9.1 SP2 software by Altera Corporation USB drive to save your files Objective: Learn how to
EXPERIMENT # 6: Quartus II Tutorial and Practice Name: Date: Equipment/Parts Needed: Quartus II R Web Edition V9.1 SP2 software by Altera Corporation USB drive to save your files Objective: Learn how to
1. Introduction EE108A. Lab 1: Combinational Logic: Extension of the Tic Tac Toe Game
 EE108A Lab 1: Combinational Logic: Extension of the Tic Tac Toe Game 1. Introduction Objective This lab is designed to familiarize you with the process of designing, verifying, and implementing a combinational
EE108A Lab 1: Combinational Logic: Extension of the Tic Tac Toe Game 1. Introduction Objective This lab is designed to familiarize you with the process of designing, verifying, and implementing a combinational
Microsoft Word. An alternative to following these steps are to double click on the Microsoft Word Icon on the desktop.
 Microsoft Word To access this Lesson Plan on-line, open up the library website www.bellevillelibrary.com and go to the tab that reads Adults. Scroll down and click on FREE Computer Lessons. On this page
Microsoft Word To access this Lesson Plan on-line, open up the library website www.bellevillelibrary.com and go to the tab that reads Adults. Scroll down and click on FREE Computer Lessons. On this page
Word 2016 Advanced. North American Edition SAMPLE
 Word 2016 Advanced Word 2016 Advanced North American Edition WORD 2016 ADVANCED Page 2 2015 Cheltenham Group Pty. Ltd. All trademarks acknowledged. E&OE. No part of this document may be copied without
Word 2016 Advanced Word 2016 Advanced North American Edition WORD 2016 ADVANCED Page 2 2015 Cheltenham Group Pty. Ltd. All trademarks acknowledged. E&OE. No part of this document may be copied without
Advanced Copy Pro 9.0 Plugin User Guide
 Advanced Copy Pro 9.0 Plugin User Guide UPDATED ON 6/26/2018 PlanSwift Authored by: Dave Hansen 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Purchasing and Installation... 4 Purchasing Plugins... 4 Installation and
Advanced Copy Pro 9.0 Plugin User Guide UPDATED ON 6/26/2018 PlanSwift Authored by: Dave Hansen 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Purchasing and Installation... 4 Purchasing Plugins... 4 Installation and
Creating a new CDC policy using the Database Administration Console
 Creating a new CDC policy using the Database Administration Console When you start Progress Developer Studio for OpenEdge for the first time, you need to specify a workspace location. A workspace is a
Creating a new CDC policy using the Database Administration Console When you start Progress Developer Studio for OpenEdge for the first time, you need to specify a workspace location. A workspace is a
Basic Software Maintenance. Ham Station Ultra Software Package
 1 Carl Skip Glover, Jr. K1SPG Custom Software & Hardware Solutions 4 Valley of Industry Boscawen, NH 03303 (603) 369-7015 Email: pctech.skip@gmail.com Email: k1spg@arrl.net Basic Software Maintenance Ham
1 Carl Skip Glover, Jr. K1SPG Custom Software & Hardware Solutions 4 Valley of Industry Boscawen, NH 03303 (603) 369-7015 Email: pctech.skip@gmail.com Email: k1spg@arrl.net Basic Software Maintenance Ham
Introduction to Simulation of VHDL Designs Using ModelSim Graphical Waveform Editor. 1 Introduction. For Quartus Prime 16.1
 Introduction to Simulation of VHDL Designs Using ModelSim Graphical Waveform Editor For Quartus Prime 16.1 1 Introduction This tutorial provides an introduction to simulation of logic circuits using the
Introduction to Simulation of VHDL Designs Using ModelSim Graphical Waveform Editor For Quartus Prime 16.1 1 Introduction This tutorial provides an introduction to simulation of logic circuits using the
Quartus II Tutorial. September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0
 Quartus II Tutorial September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with Modelsim, and downloading
Quartus II Tutorial September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with Modelsim, and downloading
An Introductory Guide to SpecTRM
 An Introductory Guide to SpecTRM SpecTRM (pronounced spectrum and standing for Specification Tools and Requirements Methodology) is a toolset to support the specification and development of safe systems
An Introductory Guide to SpecTRM SpecTRM (pronounced spectrum and standing for Specification Tools and Requirements Methodology) is a toolset to support the specification and development of safe systems
FPGA Introductory Tutorial: Part 1
 FPGA Introductory Tutorial: Part 1 This tutorial is designed to assist in learning the basics of the Altera Quartus II v9.0 software. Part 1 of the tutorial will cover the basics of creating a Project,
FPGA Introductory Tutorial: Part 1 This tutorial is designed to assist in learning the basics of the Altera Quartus II v9.0 software. Part 1 of the tutorial will cover the basics of creating a Project,
VLSI Lab Tutorial 1. Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction
 VLSI Lab Tutorial 1 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of the first lab tutorial is to help you become familiar with the schematic editor, Virtuoso Schematic
VLSI Lab Tutorial 1 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of the first lab tutorial is to help you become familiar with the schematic editor, Virtuoso Schematic
Using Microsoft Word. Tables
 Using Microsoft Word are a useful way of arranging information on a page. In their simplest form, tables can be used to place information in lists. More complex tables can be used to arrange graphics on
Using Microsoft Word are a useful way of arranging information on a page. In their simplest form, tables can be used to place information in lists. More complex tables can be used to arrange graphics on
Getting Started (1.8.7) 9/2/2009
 2 Getting Started For the examples in this section, Microsoft Windows and Java will be used. However, much of the information applies to other operating systems and supported languages for which you have
2 Getting Started For the examples in this section, Microsoft Windows and Java will be used. However, much of the information applies to other operating systems and supported languages for which you have
eproduct Designer A Simple Design and Simulation Tutorial
 eproduct Designer A Simple Design and Simulation Tutorial Written by Bahram Dahi Fall 2003 Updated Spring 2007 Dashboard Project management tool 1. In the main window, click on the File menu and select
eproduct Designer A Simple Design and Simulation Tutorial Written by Bahram Dahi Fall 2003 Updated Spring 2007 Dashboard Project management tool 1. In the main window, click on the File menu and select
For additional information, please consult the Read-Me and Help documentation or contact Electro-Voice or Dynacord technical support.
 Quick Start Guide Hello, and welcome to IRIS-Net software. We want you to get the most from your IRIS-Net projects and encourage you to explore the additional Read-Me and Help documentation provided with
Quick Start Guide Hello, and welcome to IRIS-Net software. We want you to get the most from your IRIS-Net projects and encourage you to explore the additional Read-Me and Help documentation provided with
SolidWorks 2½D Parts
 SolidWorks 2½D Parts IDeATe Laser Micro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part In this lab, you ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select
SolidWorks 2½D Parts IDeATe Laser Micro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part In this lab, you ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select
The Fundamentals. Document Basics
 3 The Fundamentals Opening a Program... 3 Similarities in All Programs... 3 It's On Now What?...4 Making things easier to see.. 4 Adjusting Text Size.....4 My Computer. 4 Control Panel... 5 Accessibility
3 The Fundamentals Opening a Program... 3 Similarities in All Programs... 3 It's On Now What?...4 Making things easier to see.. 4 Adjusting Text Size.....4 My Computer. 4 Control Panel... 5 Accessibility
Tutorial 3: Using the Waveform Viewer Introduces the basics of using the waveform viewer. Read Tutorial SIMPLIS Tutorials SIMPLIS provide a range of t
 Tutorials Introductory Tutorials These tutorials are designed to give new users a basic understanding of how to use SIMetrix and SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. Tutorial 1: Getting Started Guides you through getting
Tutorials Introductory Tutorials These tutorials are designed to give new users a basic understanding of how to use SIMetrix and SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. Tutorial 1: Getting Started Guides you through getting
EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007
 EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn USING MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Opening Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Features Keyboard Review Pointer Shapes
EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn USING MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Opening Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Features Keyboard Review Pointer Shapes
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015
 EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 Creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC Early and Often... 2 1.2 Create N active and connect the transistors... 3 1.3 Vias...
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 Creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC Early and Often... 2 1.2 Create N active and connect the transistors... 3 1.3 Vias...
Getting Started Guide. Chapter 3 Using Styles and Templates
 Getting Started Guide Chapter 3 Using Styles and Templates Copyright This document is Copyright 2005 2009 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You may distribute it and/or modify
Getting Started Guide Chapter 3 Using Styles and Templates Copyright This document is Copyright 2005 2009 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You may distribute it and/or modify
EE 231 Fall Lab 1: Introduction to Verilog HDL and Altera IDE
 Lab 1: Introduction to Verilog HDL and Altera IDE Introduction In this lab you will design simple circuits by programming the Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). At the end of the lab you should be able
Lab 1: Introduction to Verilog HDL and Altera IDE Introduction In this lab you will design simple circuits by programming the Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). At the end of the lab you should be able
Tutorial for Altera DE1 and Quartus II
 Tutorial for Altera DE1 and Quartus II Qin-Zhong Ye December, 2013 This tutorial teaches you the basic steps to use Quartus II version 13.0 to program Altera s FPGA, Cyclone II EP2C20 on the Development
Tutorial for Altera DE1 and Quartus II Qin-Zhong Ye December, 2013 This tutorial teaches you the basic steps to use Quartus II version 13.0 to program Altera s FPGA, Cyclone II EP2C20 on the Development
Working with Mailbox Manager
 Working with Mailbox Manager A user guide for Mailbox Manager supporting the Message Storage Server component of the Avaya S3400 Message Server Mailbox Manager Version 5.0 February 2003 Copyright 2003
Working with Mailbox Manager A user guide for Mailbox Manager supporting the Message Storage Server component of the Avaya S3400 Message Server Mailbox Manager Version 5.0 February 2003 Copyright 2003
Introduction to IBM Rational HATS For IBM System i (5250)
 Introduction to IBM Rational HATS For IBM System i (5250) Introduction to IBM Rational HATS 1 Lab instructions This lab teaches you how to use IBM Rational HATS to create a Web application capable of transforming
Introduction to IBM Rational HATS For IBM System i (5250) Introduction to IBM Rational HATS 1 Lab instructions This lab teaches you how to use IBM Rational HATS to create a Web application capable of transforming
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION. GIS Software Solutions. Getting Started. With MapLogic Layout Manager
 MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
Lab 1 Modular Design and Testbench Simulation ENGIN 341 Advanced Digital Design University of Massachusetts Boston
 Lab 1 Modular Design and Testbench Simulation ENGIN 341 Advanced Digital Design University of Massachusetts Boston Introduction This lab introduces the concept of modular design by guiding you through
Lab 1 Modular Design and Testbench Simulation ENGIN 341 Advanced Digital Design University of Massachusetts Boston Introduction This lab introduces the concept of modular design by guiding you through
OU EDUCATE TRAINING MANUAL
 OU EDUCATE TRAINING MANUAL OmniUpdate Web Content Management System El Camino College Staff Development 310-660-3868 Course Topics: Section 1: OU Educate Overview and Login Section 2: The OmniUpdate Interface
OU EDUCATE TRAINING MANUAL OmniUpdate Web Content Management System El Camino College Staff Development 310-660-3868 Course Topics: Section 1: OU Educate Overview and Login Section 2: The OmniUpdate Interface
Turns your Wallbox into a Complete Jukebox
 JukeMP3 Wallbox Controller Turns your Wallbox into a Complete Jukebox JukeMP3 Features: 1. The JukeMP3 kit includes everything you need to turn your wallbox into a complete jukebox, except speakers and
JukeMP3 Wallbox Controller Turns your Wallbox into a Complete Jukebox JukeMP3 Features: 1. The JukeMP3 kit includes everything you need to turn your wallbox into a complete jukebox, except speakers and
Introduction. About this tutorial. How to use this tutorial
 Basic Entry & not About this tutorial This tutorial consists of an introduction to creating simple circuits on an FPGA using a variety of methods. There are two ways to create the circuit: using or by
Basic Entry & not About this tutorial This tutorial consists of an introduction to creating simple circuits on an FPGA using a variety of methods. There are two ways to create the circuit: using or by
Using the ispxpga Floorplanner
 Using the ispxpga Floorplanner Table of Contents USING THE ISPXPGA FLOORPLANNER...3 Task 1: Open the Design...4 Task 2: Open a Floorplanner Design File...5 Task 3: Tour the Graphical User Interface - The
Using the ispxpga Floorplanner Table of Contents USING THE ISPXPGA FLOORPLANNER...3 Task 1: Open the Design...4 Task 2: Open a Floorplanner Design File...5 Task 3: Tour the Graphical User Interface - The
2 Getting Started. Getting Started (v1.8.6) 3/5/2007
 2 Getting Started Java will be used in the examples in this section; however, the information applies to all supported languages for which you have installed a compiler (e.g., Ada, C, C++, Java) unless
2 Getting Started Java will be used in the examples in this section; however, the information applies to all supported languages for which you have installed a compiler (e.g., Ada, C, C++, Java) unless
Netlist Viewer User's Guide
 Netlist Viewer User's Guide 1 Netlist Viewer User's Guide Table Of Contents Viewing Your Netlist...3 Starting NetlistViewer...3 NetlistViewer...4 Navigation...6 Menu Commands...7 Starting MultiView Navigator...9
Netlist Viewer User's Guide 1 Netlist Viewer User's Guide Table Of Contents Viewing Your Netlist...3 Starting NetlistViewer...3 NetlistViewer...4 Navigation...6 Menu Commands...7 Starting MultiView Navigator...9
Function. Description
 Function Check In Get / Checkout Description Checking in a file uploads the file from the user s hard drive into the vault and creates a new file version with any changes to the file that have been saved.
Function Check In Get / Checkout Description Checking in a file uploads the file from the user s hard drive into the vault and creates a new file version with any changes to the file that have been saved.
RTL Design and IP Generation Tutorial. PlanAhead Design Tool
 RTL Design and IP Generation Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the "Materials") is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products.
RTL Design and IP Generation Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the "Materials") is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products.
To practice combinational logic on Logisim and Xilinx ISE tools. ...
 ENGG1203: Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering Second Semester, 2017 18 Lab 1 Objective: To practice combinational logic on Logisim and Xilinx ISE tools. 1 Find your lab partner You will
ENGG1203: Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering Second Semester, 2017 18 Lab 1 Objective: To practice combinational logic on Logisim and Xilinx ISE tools. 1 Find your lab partner You will
Revision: February 27, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 Xilinx ISE WebPACK Schematic Capture Tutorial Revision: February 27, 2010 215 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview This tutorial provides instruction for using the Xilinx
Xilinx ISE WebPACK Schematic Capture Tutorial Revision: February 27, 2010 215 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview This tutorial provides instruction for using the Xilinx
IT Essentials v6.0 Windows 10 Software Labs
 IT Essentials v6.0 Windows 10 Software Labs 5.2.1.7 Install Windows 10... 1 5.2.1.10 Check for Updates in Windows 10... 10 5.2.4.7 Create a Partition in Windows 10... 16 6.1.1.5 Task Manager in Windows
IT Essentials v6.0 Windows 10 Software Labs 5.2.1.7 Install Windows 10... 1 5.2.1.10 Check for Updates in Windows 10... 10 5.2.4.7 Create a Partition in Windows 10... 16 6.1.1.5 Task Manager in Windows
PSpice Tutorial. Physics 160 Spring 2006
 PSpice Tutorial This is a tutorial designed to guide you through the simulation assignment included in the first homework set. You may either use the program as installed in the lab, or you may install
PSpice Tutorial This is a tutorial designed to guide you through the simulation assignment included in the first homework set. You may either use the program as installed in the lab, or you may install
1 Introduction 2. 2 Background 3. 3 Getting Started 4. 4 Starting a New Project 6. 5 Design Entry Using VHDL Code 13
 Quartus Prime Introduction Using VHDL Designs For Quartus Prime 17.0 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Background 3 3 Getting Started 4 3.1 Quartus Prime Online Help................................................................................................
Quartus Prime Introduction Using VHDL Designs For Quartus Prime 17.0 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Background 3 3 Getting Started 4 3.1 Quartus Prime Online Help................................................................................................
Electronic Portfolios in the Classroom
 Electronic Portfolios in the Classroom What are portfolios? Electronic Portfolios are a creative means of organizing, summarizing, and sharing artifacts, information, and ideas about teaching and/or learning,
Electronic Portfolios in the Classroom What are portfolios? Electronic Portfolios are a creative means of organizing, summarizing, and sharing artifacts, information, and ideas about teaching and/or learning,
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b
 SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2010
 EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2010 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn USING MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Opening Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Features Keyboard Review Pointer Shapes
EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2010 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn USING MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Opening Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Features Keyboard Review Pointer Shapes
