5 R1 The one green in the same place so either of these could be green.
|
|
|
- Beverly Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
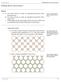
1 Page: 1 of 20 1 R1 Now. Maybe what we should do is write out the cases that work. We wrote out one of them really very clearly here. [R1 takes out some papers.] Right? You did the one here um where you started with um exactly one when it was green and blue in this case, right? 2 Stephanie Um. 3 R1 And all those that had one green, and you said there were four. And then you said the next step was to build all possible towers with two green. All right. And that s what you did here. And you showed how you had to keep it. 4 Stephanie Um hm. 5 R1 The one green in the same place so either of these could be green. 6 Stephanie Um hm. 7 R1 I like that. Okay. So then you said so you multiply by four. What s this? Let s see if I m reading this right. You say multiply four by one and divide by four. 8 Stephanie There s stuff on the back. [R1 turns over each of the papers she is holding.] No, on the other back. 9 R1 On this. Oh. That helps. Now let s see which one am I doing on this? After doing this with all four of the towers we had twelve towers with two green. That you built here. [R1 indicates the towers with two red cubes and two yellow cubes.] 10 Stephanie Um hm. 11 R1 [reading] There were some duplications. Each new tower came in a pair so there was only really six new towers. We took the six new towers and from each one, using the same method, created towers of four high with three green. And that s this stack. [R1 indicates towers on the table.] We created
2 Page: 2 of Stephanie Hm. twelve towers, but like before, there were duplicates. This time they came in groups of three. Here s your groups of three. [R1 indicates the appropriate towers on the table. She continues reading Stephanie s synopsis.] four new towers and we started to see a pattern. And this is 4 x 3 where you wrote the formula looked like this: = 6 Right? Towers 2 four high 13 R1 Four and now this is where maybe it would be helpful to go over again. Let s talk about the formula. Okay? Explain that to us. The four 14 Stephanie Wait. 15 R1 Times three over two equals six. That must be 16 Stephanie For this one, I guess? 17 R1 for 18 Stephanie I uh for this one? With um these. And it would be 19 R1 (inaudible) a number one, two, three, four, five, six. So - - How would that work? 20 Stephanie That was wrong. 21 R1 Is it? Why do you say it s wrong? 22 Stephanie Wouldn t it be um six times two? Because um 23 R1 Well. Think about what you did. Remember you reorganized them. When
3 Page: 3 of Stephanie Um hm. 25 R1 Okay. 26 Stephanie Um hm. R you first had this one here [R1 points to Y.] right? Y Y 27 R1 When you were making two s out of them 28 Stephanie Um hm. 29 R1 Right? - You had you kept this [points to the top red cube of the tower] the same so you had here and here [indicates the top and second positions]. That was one of them, right? 30 Stephanie Yeah. 31 R1 Then you had here and here [the top and third positions]. That was another one. Then you had here and here. [top and bottom positions] That was another one. So you got three, didn t you? 32 Stephanie Yes. 33 R1 You got three. 34 Stephanie Oh. Okay. 35 R1 Right? 36 Stephanie Yeah.
4 Page: 4 of R1 Isn t that right? And the same thing here. This was the same. [points to Y the red cube in the R tower] But you went here and here. [points to the Y Y top and second positions] One. Here and here. [second and third positions] Two. Here and here. [second and bottom positions] Three. 38 Stephanie Yeah. 39 R1 So for each of these four, you got three. 40 Stephanie Yeah. 41 R1 Now, can you predict by looking at this row [pointing to the row of towers four high with one red] that there would be three that would come when you go from one to two? 42 Stephanie Yes. 43 R1 What helps you predict? 44 Stephanie Because there s three places where you can put the second one. 45 R1 Three places. Okay. So - 46 Stephanie Yes. I think it should - 47 R1 Well. Let s write this down, so we can so we don t cause it s easy - 48 Stephanie Alright. 49 R1 It s easy for me when you disassemble it to remember, you know what I m saying,
5 Page: 5 of Stephanie Um hm. 51 R1 what happened before it was assembled. 52 Stephanie So what do you want me to write? 53 R1 So let s think. Well, let s think what makes sense to you? Um. You started with right? four towers 54 Stephanie Four towers. 55 R1 with exactly one red, if you want to say there, right? 56 Stephanie Okay. 57 R1 And you told from each of these, right? 58 Stephanie Um hm. 59 R1 from each one of these 60 Stephanie You can get three. 61 R1 Three. Because there are three positions 62 Stephanie Um hm. 63 R1 to place a red. 64 Stephanie Yes. 65 R1 Isn t that right? So it s - - so you have three positions by four towers. So four is the number of towers. Just happens to be that they re height four. Or is that? 66 Stephanie Oh. No no no. I think what it should ve been is four towers.
6 Page: 6 of R1 Four towers? 68 Stephanie That s what I should ve wrote down. 69 R1 But but well. If the if the towers are height three, would there be four towers? 70 Stephanie No-o. 71 R1 How many would there ve been? 72 Stephanie Two. 73 R1 If it s height three, can you tell me why? 74 Stephanie Because you only have two other places where you can put a red. If it s height 75 R1 Yes, but how many would you start up with if it were height three, where you had one in each position? One red in each position? 76 Stephanie Three. 77 R1 You d start with three. If it was height 78 Stephanie Yeah. It would start with Oh. Like that it would work, but I think it it that what I should ve wrote was four towers. 79 R1 Right, but but if they re four high - 80 Stephanie Yeah. It it really 81 R1 it would be four. If they re three high 82 Stephanie Um hm 83 R1 If they re two high
7 Page: 7 of Stephanie Yeah. It would be two. 85 R1 Does that make sense? 86 Stephanie Yeah. 87 R1 So if they re n high? 88 Stephanie It would be n. 89 R1 Okay. So. So this would be 90 Stephanie It it it still works. 91 R1 Actually it works that it s the number of towers, doesn t it? 92 Stephanie Yeah. 93 R1 It s a way to think about it. So it s you can think of it as the number of towers. 94 Stephanie Um hm. 95 R1 Right. 96 Stephanie Um hm. 97 R1 Cause that always is that way, isn t it? So if the towers are n high, 98 Stephanie It would be n. 99 R1 With exactly one, wouldn t you have anything, you could have cause there are n positions, right? 100 Stephanie Um hm. 101 R1 Okay. So. So. Towers n high, there d be n. That helps me. If they re n
8 Page: 8 of Stephanie n minus one? high, how many positions are there to place that second one? 103 R1 Interesting? So it would be n times n minus one. Why don t we just write that down while we have it in our heads? 104 Stephanie You want me to write n times n minus one? 105 R1 What do you think? Do you want to? If we talk about towers n high, this since we you re doing algebra let s try to connect algebra. 106 Stephanie Do you want me to write For towers n high 107 R1 For towers yeah why not? Let s think about these simple cases and see what we can do with n high. 108 Stephanie For towers n high, um, like, if you re putting 109 R1 If you re moving from what what s the question here? If you re moving from um n things taken one at a time to n things taken two at a time 110 Stephanie Okay. 111 R1 Right? Isn t that right? 112 Stephanie Um hm. [Stephanie is writing down all the information as it is being said.] 113 R1 If you re thinking of selecting those exactly one red 114 Stephanie From 115 R1 to selecting those with exactly two red. 116 Stephanie So if 117 R1 Could you imagine this in your head?
9 Page: 9 of Stephanie Yeah. 119 R1 as we re talking 120 Stephanie Yeah. 121 R1 about this? 122 Stephanie I know what you re saying. 123 R1 That s that s very impressive. I couldn t have done that at your age, Stephanie. 124 Stephanie [chuckles] (inaudible) 125 R1 Could you have, Donna? - - So I m I m not I really if you don t if you can t imagine it, tell me cause I have to think. 126 Stephanie Towers one n at a time [writes this as she speaks] 127 R1 Well, the way um I don t know the way I like to write it 128 Stephanie Okay 129 R1 is this way. [It isn t possible from this tape to see what R1 writes.] But my son tells me you can write it this way. And he told me another way you could write it. - - This way: C n one. Isn t that right? There are three ways you can write it. You have your choice. 130 Stephanie Um. Yeah. 131 R1 This means n high. This means exactly one red. 132 Stephanie Um hm. 133 R1 Right? How many all this tells you that there are n of them and what you are supposed to imagine in your mind these n high towers with
10 Page: 10 of Stephanie Um hm, 135 R1 Right? 136 Stephanie Yeah. 137 R1 One position at n minus one. If you can imagine if you can begin to think like that and imagine these things. 138 Stephanie You want me to write that instead? 139 R1 Well. Any way you it makes sense to you. 140 Stephanie Cause I ll just 141 R1 If you want to start trying 142 Stephanie move from towers 143 R1 to use the notation, this is good practice, you know. 144 Stephanie n n um - one at a time [Stephanie writes.] to n two at a time. Um. It 1 would be n times n minus one. 145 R1 Okay. So n would be 146 Stephanie n would be like the tower like the, the number of towers. 147 R1 Okay. So write that. n is the number total number of towers. 148 Stephanie Okay. Well, it would be 149 R1 So what s n minus one? 150 Stephanie be n times n minus one. Um n be n s the number of towers. Ooooh.
11 Page: 11 of 20 Wait. n s the number of towers in like 151 R1 Do you know what just occurred to me? You can think of n as the number of towers. That s true. That will always work. But it is also the total number of positions. 152 Stephanie Yeah. 153 R1 Alright? So with towers four high, you d have four possible positions. Right? It just so happened 154 Stephanie So. Should I write n being the number of towers and the number of positions? 155 R1 Yeah. I m just trying to think what s useful here. 156 Stephanie Because it the number of towers is useful, but the number of positions is useful when you re talking about n minus one. 157 R1 Maybe so. Yeah. 158 Stephanie Okay. 159 R1 Okay. That s a good idea. 160 Stephanie [Stephanie speaks as she writes.] The position um n minus one being the number of positions minus one? 161 R1 Let s try to think what the n minus one means. The n minus one in this problem is what? 162 Stephanie The n minus one in this problem is? 163 R1 Um hm. 164 Stephanie Is like -
12 Page: 12 of R1 What s n? 166 Stephanie Well, n is this [Stephanie indicates the entire tower.] or 167 R1 What number is it? 168 Stephanie n is four? 169 R1 Four. And so what s n minus one? 170 Stephanie The red, I guess? 171 R1 Well, if n is four Stephanie Yes. 173 R1 We know what n minus one is. 174 Stephanie Oh! It s three. [laughs] 175 R1 That s what happens after a while, by the way. It really is cause you re thinking of something else. Now. Okay. So n is four. n minus one is three. 176 Stephanie is three. 177 R1 But what does it mean in terms of moving from here to here? [Dr. Maher moves from the towers with one red to towers with two reds.] 178 Stephanie That means that you re taking away like well, we re talking about like aren t you talking about like n minus one being like yellow minus space like yellow being like replaced by red? 179 R1 Yeah. Right. That s exactly what I m thinking about. 180 Stephanie So like n minus one would be like this [Stephanie points to the tower of all
13 Page: 13 of 20 R yellow.] being replaced by this [Stephanie indicates Y.] Right? Cause Y Y like it s not taking away R1 Okay. So wait a minute. I thought we were going from here to here. [R1 indicates the towers with one red and then the towers with two reds.] Let s do that one. 182 Stephanie Yeah. Right. 183 R1 Let s go from here to here. 184 Stephanie Alright. 185 R1 R But what we did is, remember this one belonged here. [R1 moves R to Y Y R beside Y.] Y Y 186 Stephanie Um hm. 187 R1 Right? 188 Stephanie Yeah,
14 Page: 14 of R1 190 Stephanie R And then uh this one belonged here [moves the Y ] Y R R And this one [Stephanie moves Y.] R Y 191 R1 This one belonged here. Right? 192 Stephanie Um hm. 193 R1 Okay. So when we moved from one to two, right? 194 Stephanie Um hm. 195 R1 we ended up with three 196 Stephanie Yes. 197 R1 Why three? Because because why? 198 Stephanie Well. If that s n well because we re putting there s three places where you can put it. 199 R1 Right. 200 Stephanie Yeah. 201 R1 Isn t that right? 202 Stephanie Yeah.
15 Page: 15 of R1 So you could put it here. [R1 points to the second position.] You could put it here. [She points to the third position.] 204 Stephanie You could put it there. 205 R1 You could ve put it there. [R1 indicates the bottom position.] 206 Stephanie Um hm. 207 R1 Here, here, or here. So if you have n positions. Right? 208 Stephanie Um hm. 209 R1 And really what you have here n minus one of them are yellow if one is red Stephanie Um hm. 211 R1 Right. Because n minus one plus one is n. 212 Stephanie Um hm. 213 R1 Does that make sense? n minus one plus one 214 Stephanie [laughs] is just n. 215 R1 Isn t that right? 216 Stephanie Yeah. 217 R1 So we have n positions and one red and n minus one yellow. 218 Stephanie Okay. 219 R1 Okay. So n minus one in this case four positions three yellow and of those three positions we could ve put a red.
16 Page: 16 of Stephanie Um hm. 221 R1 And that s where the three came in. The three is the n minus one. 222 Stephanie Okay. 223 R1 Alright. But that could ve happened not just one time. It could have happened [R1 taps the table in front of each of the four towers with one red and three yellows.] 224 Stephanie Four times. 225 R1 four times or n times. 226 Stephanie Okay. So like 227 R1 So it was n times n minus one. 228 Stephanie Um hm. 229 R1 That s how we got twelve. 230 Stephanie Yes. 231 R1 But we got duplicates. 232 Stephanie Yes. 233 R1 Alright. So we know we know we ended up with n, right? 234 Stephanie Um hm. 235 R1 n positions times n minus one how many choices we have for red? 236 Stephanie How many choices do you have for red? You have um I guess n minus one number of choices?
17 Page: 17 of R1 n minus one. Okay. So we have n times n minus one. 238 Stephanie Um hm. 239 R1 If you re writing your formula down. But that s too many. Alright. 240 Stephanie So n times. 241 R1 Four times three is too many. 242 Stephanie Yeah. Divided by um 243 R1 In that case, what did you have to divide by? 244 Stephanie Well, these number of positions. 245 R1 You actually ended up dividing by two. 246 Stephanie Oh. 247 R1 When you found your duplicates. 248 Stephanie Well. Oh. That s right. But I don t know how many R1 Hmmm. That s the part. That s the tricky part. That s the part we haven t really worked out yet. 250 R2 Yeah. 251 Stephanie [in the background] (inaudible) 252 R1 Why do we divide by two. Maybe we don t know that yet. Maybe that s something to keep in the back of our minds as something we re trying to figure out, right? 253 Stephanie Um hm.
18 Page: 18 of R1 But, we know we had to divide by two just by sheer working it out. 255 Stephanie Yes. 256 R1 Isn t that true? 257 Stephanie Yes. 258 R1 Cause you found duplicates. So, so that time it was four times three divided by two. Which is what you wrote here, by the way. 259 Stephanie Yeah. 260 R1 Four, right? 261 Stephanie Yes. 262 R1 Four positions times three 263 Stephanie Um hm. 264 R1 available postions to choose red. 265 Stephanie Um hm. 266 R1 Right? Divided by the number of duplicates. 267 Stephanie Yeah. 268 R1 Let s write down what these mean again so we don t lose track of that. 269 Stephanie Here? 270 R1 So this number the four is like your n the number of positions Stephanie Alright.
19 Page: 19 of R1 or the height of the tower either way. How tall it is. However you want to think 273 Stephanie Okay. Four is [writing] number of positions 274 R1 or height of tower. Right? 275 Stephanie Um hm. - - or height of tower. Um. Three is um the number of spaces you can put a red. 276 R1 Very good. So that s very good. So the spaces available for red. [Stephanie continues to write.] 277 Stephanie And two is cause they came in pairs. 278 R1 Number of duplicates. Right. And that what we we know how we know this is n and we know this is n minus one. [R1 points to the four and the three.] Right? 279 Stephanie Um hm. 280 R1 That s very helpful. But. What is that two? Hmmm Right? 281 R2 That s a tough one (inaudible) 282 R1 I mean I studied probability at college and they told me you had to divide by these numbers Stephanie Um hm. 284 R1 I didn t know why. Did you know why when they just told you to divide by these numbers? No. Don t tell me. I m not going to ask you. But But do you see? That s that s part of the problem. It would be nice to think about, is there a nice explanation that we can see as we generate this that division by two. So let s keep that in back of our minds and go to the next step. Then we ll come to this one.
20 Page: 20 of 20
6 Stephanie Well. It s six, because there s six towers.
 Page: 1 of 10 1 R1 So when we divided by two all this stuff this is the row we ended up with. 2 Stephanie Um hm. 3 R1 Isn t that right? We had a row of six. Alright. Now before doing it see if you can
Page: 1 of 10 1 R1 So when we divided by two all this stuff this is the row we ended up with. 2 Stephanie Um hm. 3 R1 Isn t that right? We had a row of six. Alright. Now before doing it see if you can
1 R1 Right. I mean to keep track. Um. I know that uh do you remember a few years ago um Dr. Davis was in and you were dealing with the Tower of Hanoi?
 Page: 1 of 7 1 R1 Right. I mean to keep track. Um. I know that uh do you remember a few years ago um Dr. Davis was in and you were dealing with the Tower of Hanoi? 2 Stephanie Yes. 3 R1 That was you have
Page: 1 of 7 1 R1 Right. I mean to keep track. Um. I know that uh do you remember a few years ago um Dr. Davis was in and you were dealing with the Tower of Hanoi? 2 Stephanie Yes. 3 R1 That was you have
9 R1 Get another piece of paper. We re going to have fun keeping track of (inaudible). Um How much time do you have? Are you getting tired?
 Page: 1 of 14 1 R1 And this is tell me what this is? 2 Stephanie x times y plus x times y or hm? 3 R1 What are you thinking? 4 Stephanie I don t know. 5 R1 Tell me what you re thinking. 6 Stephanie Well.
Page: 1 of 14 1 R1 And this is tell me what this is? 2 Stephanie x times y plus x times y or hm? 3 R1 What are you thinking? 4 Stephanie I don t know. 5 R1 Tell me what you re thinking. 6 Stephanie Well.
Transcriber(s): Aboelnaga, Eman Verifier(s): Yedman, Madeline Date Transcribed: Fall 2010 Page: 1 of 9
 Page: 1 of 9 0:00 1 R1 The color s not going to show a little bit, but okay. Okay. So, um, a plus b quantity cubed, you said, means Stephanie a plus b times a plus b times a plus b /R1 3 R1 Okay, so you
Page: 1 of 9 0:00 1 R1 The color s not going to show a little bit, but okay. Okay. So, um, a plus b quantity cubed, you said, means Stephanie a plus b times a plus b times a plus b /R1 3 R1 Okay, so you
SPRITES Moving Two At the Same Using Game State
 If you recall our collision detection lesson, you ll likely remember that you couldn t move both sprites at the same time unless you hit a movement key for each at exactly the same time. Why was that?
If you recall our collision detection lesson, you ll likely remember that you couldn t move both sprites at the same time unless you hit a movement key for each at exactly the same time. Why was that?
The name of our class will be Yo. Type that in where it says Class Name. Don t hit the OK button yet.
 Mr G s Java Jive #2: Yo! Our First Program With this handout you ll write your first program, which we ll call Yo. Programs, Classes, and Objects, Oh My! People regularly refer to Java as a language that
Mr G s Java Jive #2: Yo! Our First Program With this handout you ll write your first program, which we ll call Yo. Programs, Classes, and Objects, Oh My! People regularly refer to Java as a language that
Programming and Data Structure
 Programming and Data Structure Dr. P.P.Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture # 09 Problem Decomposition by Recursion - II We will
Programming and Data Structure Dr. P.P.Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture # 09 Problem Decomposition by Recursion - II We will
Post Experiment Interview Questions
 Post Experiment Interview Questions Questions about the Maximum Problem 1. What is this problem statement asking? 2. What is meant by positive integers? 3. What does it mean by the user entering valid
Post Experiment Interview Questions Questions about the Maximum Problem 1. What is this problem statement asking? 2. What is meant by positive integers? 3. What does it mean by the user entering valid
Spam. Time: five years from now Place: England
 Spam Time: five years from now Place: England Oh no! said Joe Turner. When I go on the computer, all I get is spam email that nobody wants. It s all from people who are trying to sell you things. Email
Spam Time: five years from now Place: England Oh no! said Joe Turner. When I go on the computer, all I get is spam email that nobody wants. It s all from people who are trying to sell you things. Email
Section 0.3 The Order of Operations
 Section 0.3 The Contents: Evaluating an Expression Grouping Symbols OPERATIONS The Distributive Property Answers Focus Exercises Let s be reminded of those operations seen thus far in the course: Operation
Section 0.3 The Contents: Evaluating an Expression Grouping Symbols OPERATIONS The Distributive Property Answers Focus Exercises Let s be reminded of those operations seen thus far in the course: Operation
Amber Weyland: [to cameraman] Just hold it there so we can see Mollie.
![Amber Weyland: [to cameraman] Just hold it there so we can see Mollie. Amber Weyland: [to cameraman] Just hold it there so we can see Mollie.](/thumbs/96/128551622.jpg) Interview Transcript Interviewer: Amber Weyland Interviewee: Mollie Hummer Cameraman: Christopher Smith [friend to both] Date: March 22, 2010 Beginning time of interview: 2:30pm End time of interview:
Interview Transcript Interviewer: Amber Weyland Interviewee: Mollie Hummer Cameraman: Christopher Smith [friend to both] Date: March 22, 2010 Beginning time of interview: 2:30pm End time of interview:
Combinatorics Prof. Dr. L. Sunil Chandran Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Combinatorics Prof. Dr. L. Sunil Chandran Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 5 Elementary concepts and basic counting principles So, welcome
Combinatorics Prof. Dr. L. Sunil Chandran Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 5 Elementary concepts and basic counting principles So, welcome
1.7 Limit of a Function
 1.7 Limit of a Function We will discuss the following in this section: 1. Limit Notation 2. Finding a it numerically 3. Right and Left Hand Limits 4. Infinite Limits Consider the following graph Notation:
1.7 Limit of a Function We will discuss the following in this section: 1. Limit Notation 2. Finding a it numerically 3. Right and Left Hand Limits 4. Infinite Limits Consider the following graph Notation:
Trombone players produce different pitches partly by varying the length of a tube.
 Trombone players produce different pitches partly by varying the length of a tube. 7 Variables A variable is a connection between a name and a value.* That sounds simple enough, but some complexities arise
Trombone players produce different pitches partly by varying the length of a tube. 7 Variables A variable is a connection between a name and a value.* That sounds simple enough, but some complexities arise
From video conversation 2. This is a gap fill exercise and can be used as either a quiz/test of
 Teacher s guide to the quizzes/tests available for Unit 4 Quiz 1 Quiz 2 Quiz 3 Quiz 4 From video conversation 1. This is a gap fill exercise and can be used as either a quiz/test of target language acquisition,
Teacher s guide to the quizzes/tests available for Unit 4 Quiz 1 Quiz 2 Quiz 3 Quiz 4 From video conversation 1. This is a gap fill exercise and can be used as either a quiz/test of target language acquisition,
Mr G s Java Jive. #11: Formatting Numbers
 Mr G s Java Jive #11: Formatting Numbers Now that we ve started using double values, we re bound to run into the question of just how many decimal places we want to show. This where we get to deal with
Mr G s Java Jive #11: Formatting Numbers Now that we ve started using double values, we re bound to run into the question of just how many decimal places we want to show. This where we get to deal with
(Refer Slide Time: 06:01)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 28 Applications of DFS Today we are going to be talking about
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 28 Applications of DFS Today we are going to be talking about
MA 1128: Lecture 02 1/22/2018
 MA 1128: Lecture 02 1/22/2018 Exponents Scientific Notation 1 Exponents Exponents are used to indicate how many copies of a number are to be multiplied together. For example, I like to deal with the signs
MA 1128: Lecture 02 1/22/2018 Exponents Scientific Notation 1 Exponents Exponents are used to indicate how many copies of a number are to be multiplied together. For example, I like to deal with the signs
Getting Started. Excerpted from Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners
 Getting Started Excerpted from Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners EARLY ACCESS EDITION Warren D. Sande and Carter Sande MEAP Release: May 2008 Softbound print: November 2008
Getting Started Excerpted from Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners EARLY ACCESS EDITION Warren D. Sande and Carter Sande MEAP Release: May 2008 Softbound print: November 2008
Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners. Chapter 1. by Warren Sande and Carter Sande. Copyright 2009 Manning Publications
 Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners by Warren Sande and Carter Sande Chapter 1 Copyright 2009 Manning Publications brief contents Preface xiii Acknowledgments xix About this
Hello World! Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners by Warren Sande and Carter Sande Chapter 1 Copyright 2009 Manning Publications brief contents Preface xiii Acknowledgments xix About this
Instructor (Mehran Sahami)
 Programming Methodology-Lecture07 Instructor (Mehran Sahami):Alrighty. Welcome back to yet another fun-filled exciting day of CS106a. So a couple quick announcements before we start first announcement,
Programming Methodology-Lecture07 Instructor (Mehran Sahami):Alrighty. Welcome back to yet another fun-filled exciting day of CS106a. So a couple quick announcements before we start first announcement,
Table of Laplace Transforms
 Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
MITOCW ocw f99-lec07_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec07_300k OK, here's linear algebra lecture seven. I've been talking about vector spaces and specially the null space of a matrix and the column space of a matrix. What's in those
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec07_300k OK, here's linear algebra lecture seven. I've been talking about vector spaces and specially the null space of a matrix and the column space of a matrix. What's in those
Instructor (Julie Zelenski)
 ProgrammingAbstractions-Lecture10 Instructor (Julie Zelenski):Hey there. Welcome. Welcome. Welcome. My computer s not quite talking to anything yet here. You guys got an answer for that? Unplug and replug
ProgrammingAbstractions-Lecture10 Instructor (Julie Zelenski):Hey there. Welcome. Welcome. Welcome. My computer s not quite talking to anything yet here. You guys got an answer for that? Unplug and replug
(Refer Slide Time 3:31)
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 5 Logic Simplification In the last lecture we talked about logic functions
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 5 Logic Simplification In the last lecture we talked about logic functions
Here are some of the more basic curves that we ll need to know how to do as well as limits on the parameter if they are required.
 1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
Solution Guide for Chapter 21
 Solution Guide for Chapter 21 Here are the solutions for the Doing the Math exercises in Girls Get Curves! DTM from p. 74-75 2. Find the surface area of a pyramid with slant height 5 in, whose Base is
Solution Guide for Chapter 21 Here are the solutions for the Doing the Math exercises in Girls Get Curves! DTM from p. 74-75 2. Find the surface area of a pyramid with slant height 5 in, whose Base is
IMPORTANT WORDS AND WHAT THEY MEAN
 MOBILE PHONES WHAT IS DATA Data is Internet. It can let you do lots of different things on your phone or tablet. You can send or receive texts, emails or photos, listen to music, watch TV shows, movies
MOBILE PHONES WHAT IS DATA Data is Internet. It can let you do lots of different things on your phone or tablet. You can send or receive texts, emails or photos, listen to music, watch TV shows, movies
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Hey there, I m (name) and today I m gonna talk to you about rate of change and slope.
 Rate and Change of Slope A1711 Activity Introduction Hey there, I m (name) and today I m gonna talk to you about rate of change and slope. Slope is the steepness of a line and is represented by the letter
Rate and Change of Slope A1711 Activity Introduction Hey there, I m (name) and today I m gonna talk to you about rate of change and slope. Slope is the steepness of a line and is represented by the letter
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
 Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Introduction to Counting, Some Basic Principles
 Introduction to Counting, Some Basic Principles These are the class notes for week. Before we begin, let me just say something about the structure of the class notes. I wrote up all of these class notes
Introduction to Counting, Some Basic Principles These are the class notes for week. Before we begin, let me just say something about the structure of the class notes. I wrote up all of these class notes
DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10.
 Ch 3 DECIMALS ~ Notes DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10. Since decimals are special fractions, then all the rules we have already learned for fractions should work for
Ch 3 DECIMALS ~ Notes DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10. Since decimals are special fractions, then all the rules we have already learned for fractions should work for
Text Input and Conditionals
 Text Input and Conditionals Text Input Many programs allow the user to enter information, like a username and password. Python makes taking input from the user seamless with a single line of code: input()
Text Input and Conditionals Text Input Many programs allow the user to enter information, like a username and password. Python makes taking input from the user seamless with a single line of code: input()
Lesson 6-2: Function Operations
 So numbers not only have a life but they have relationships well actually relations. There are special relations we call functions. Functions are relations for which each input has one and only one output.
So numbers not only have a life but they have relationships well actually relations. There are special relations we call functions. Functions are relations for which each input has one and only one output.
Paul's Online Math Notes. Online Notes / Algebra (Notes) / Systems of Equations / Augmented Matricies
 1 of 8 5/17/2011 5:58 PM Paul's Online Math Notes Home Class Notes Extras/Reviews Cheat Sheets & Tables Downloads Algebra Home Preliminaries Chapters Solving Equations and Inequalities Graphing and Functions
1 of 8 5/17/2011 5:58 PM Paul's Online Math Notes Home Class Notes Extras/Reviews Cheat Sheets & Tables Downloads Algebra Home Preliminaries Chapters Solving Equations and Inequalities Graphing and Functions
(Refer Slide Time 6:48)
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 8 Karnaugh Map Minimization using Maxterms We have been taking about
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 8 Karnaugh Map Minimization using Maxterms We have been taking about
The Problem, the Solution and the End FinalPart
 129 11 The Problem, the Solution and the End FinalPart Veni, vidi, vici. Gaius Julius Caesar After lunch, the team was waiting for Al and Bob to show up. They were late. When they finally showed up, John
129 11 The Problem, the Solution and the End FinalPart Veni, vidi, vici. Gaius Julius Caesar After lunch, the team was waiting for Al and Bob to show up. They were late. When they finally showed up, John
(Refer Slide Time: 02.06)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 27 Depth First Search (DFS) Today we are going to be talking
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 27 Depth First Search (DFS) Today we are going to be talking
Filter and PivotTables in Excel
 Filter and PivotTables in Excel FILTERING With filters in Excel you can quickly collapse your spreadsheet to find records meeting specific criteria. A lot of reporters use filter to cut their data down
Filter and PivotTables in Excel FILTERING With filters in Excel you can quickly collapse your spreadsheet to find records meeting specific criteria. A lot of reporters use filter to cut their data down
Intro. Scheme Basics. scm> 5 5. scm>
 Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 20 Priority Queues Today we are going to look at the priority
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 20 Priority Queues Today we are going to look at the priority
Usability Test Report: Requesting Library Material 1
 Usability Test Report: Requesting Library Material 1 Summary Emily Daly and Kate Collins conducted usability testing on the processes of requesting library material. The test was conducted at the temporary
Usability Test Report: Requesting Library Material 1 Summary Emily Daly and Kate Collins conducted usability testing on the processes of requesting library material. The test was conducted at the temporary
Excel Basics: Working with Spreadsheets
 Excel Basics: Working with Spreadsheets E 890 / 1 Unravel the Mysteries of Cells, Rows, Ranges, Formulas and More Spreadsheets are all about numbers: they help us keep track of figures and make calculations.
Excel Basics: Working with Spreadsheets E 890 / 1 Unravel the Mysteries of Cells, Rows, Ranges, Formulas and More Spreadsheets are all about numbers: they help us keep track of figures and make calculations.
Part 1 - Your First algorithm
 California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10A: Accelerated Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2017 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm
California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10A: Accelerated Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2017 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm
Thanks, Peanut! Polygons are simple, closed figures having three or more straight sides. Or are they?
 Angle Sums MA6927 Activity Introduction In Math news today, we re discussing the interior angle sums of polygons. To lead us into this labyrinth of sides and angles is Daaaaaaaaan Anchormann! Direct Instruction
Angle Sums MA6927 Activity Introduction In Math news today, we re discussing the interior angle sums of polygons. To lead us into this labyrinth of sides and angles is Daaaaaaaaan Anchormann! Direct Instruction
Powered by. How did trying to give apples away for free change the world?
 How did trying to give apples away for free change the world? Steve Wozniak can tell you. He put technology in the hands of the people through the invention of the modern personal computer. Leaving college
How did trying to give apples away for free change the world? Steve Wozniak can tell you. He put technology in the hands of the people through the invention of the modern personal computer. Leaving college
Table of Contents. 1. Cover Page 2. Quote 3. Calculated Fields 4. Show Values As 5. Multiple Data Values 6. Enroll Today!
 Table of Contents 1. Cover Page 2. Quote 3. Calculated Fields 4. Show Values As 5. Multiple Data Values 6. Enroll Today! "It is Kind Of fun to do the IMPOSSIBLE" Walt Disney Calculated Fields The purpose
Table of Contents 1. Cover Page 2. Quote 3. Calculated Fields 4. Show Values As 5. Multiple Data Values 6. Enroll Today! "It is Kind Of fun to do the IMPOSSIBLE" Walt Disney Calculated Fields The purpose
Animations involving numbers
 136 Chapter 8 Animations involving numbers 8.1 Model and view The examples of Chapter 6 all compute the next picture in the animation from the previous picture. This turns out to be a rather restrictive
136 Chapter 8 Animations involving numbers 8.1 Model and view The examples of Chapter 6 all compute the next picture in the animation from the previous picture. This turns out to be a rather restrictive
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi.
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 18 Tries Today we are going to be talking about another data
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 18 Tries Today we are going to be talking about another data
C Pointers 2013 Author Riko H i
 http:/cdorm.net/understanding C Pointers 2013 Author Riko H i Copyright 2013 CDorm.net All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form
http:/cdorm.net/understanding C Pointers 2013 Author Riko H i Copyright 2013 CDorm.net All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form
PSoC Academy: How to Create a PSoC BLE Android App Lesson 3: Configure the BLE Component 1
 1 Welcome back. At this point we ve completely configured our schematic. The schematic will define all of the firmware that will run inside of our project. Remember there s two things going on. There will
1 Welcome back. At this point we ve completely configured our schematic. The schematic will define all of the firmware that will run inside of our project. Remember there s two things going on. There will
hp calculators HP 17bII+ Registers / Memory Banks The Stack Registers The Storage Registers
 The Stack Registers The Storage Registers A register is a place where you store information. It is a memory bank where you put information in order to calculate a number or where you want to keep a number
The Stack Registers The Storage Registers A register is a place where you store information. It is a memory bank where you put information in order to calculate a number or where you want to keep a number
CS Introduction to Data Structures How to Parse Arithmetic Expressions
 CS3901 - Introduction to Data Structures How to Parse Arithmetic Expressions Lt Col Joel Young One of the common task required in implementing programming languages, calculators, simulation systems, and
CS3901 - Introduction to Data Structures How to Parse Arithmetic Expressions Lt Col Joel Young One of the common task required in implementing programming languages, calculators, simulation systems, and
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:30)
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 32 Design using Programmable Logic Devices (Refer Slide Time: 00:01:30)
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 32 Design using Programmable Logic Devices (Refer Slide Time: 00:01:30)
Excel for Algebra 1 Lesson 5: The Solver
 Excel for Algebra 1 Lesson 5: The Solver OK, what s The Solver? Speaking very informally, the Solver is like Goal Seek on steroids. It s a lot more powerful, but it s also more challenging to control.
Excel for Algebra 1 Lesson 5: The Solver OK, what s The Solver? Speaking very informally, the Solver is like Goal Seek on steroids. It s a lot more powerful, but it s also more challenging to control.
Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, :52 PM. Part I of Change. The Mechanics. of Change
 Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Part I The Mechanics of Change The Mechanics of Change Chapter01.fm Page 2 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Chapter01.fm Page 3 Monday, August 23, 2004
Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Part I The Mechanics of Change The Mechanics of Change Chapter01.fm Page 2 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Chapter01.fm Page 3 Monday, August 23, 2004
Objective: Use multiplication to calculate volume.
 Lesson 4 Objective: Use multiplication to calculate volume. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (5 minutes) (33 minutes)
Lesson 4 Objective: Use multiplication to calculate volume. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (5 minutes) (33 minutes)
(Refer Slide Time: 01.26)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture # 22 Why Sorting? Today we are going to be looking at sorting.
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture # 22 Why Sorting? Today we are going to be looking at sorting.
Usability Test Report: Bento results interface 1
 Usability Test Report: Bento results interface 1 Summary Emily Daly and Ian Sloat conducted usability testing on the functionality of the Bento results interface. The test was conducted at the temporary
Usability Test Report: Bento results interface 1 Summary Emily Daly and Ian Sloat conducted usability testing on the functionality of the Bento results interface. The test was conducted at the temporary
ICANN Start, Episode 1: Redirection and Wildcarding. Welcome to ICANN Start. This is the show about one issue, five questions:
 Recorded in October, 2009 [Music Intro] ICANN Start, Episode 1: Redirection and Wildcarding Welcome to ICANN Start. This is the show about one issue, five questions: What is it? Why does it matter? Who
Recorded in October, 2009 [Music Intro] ICANN Start, Episode 1: Redirection and Wildcarding Welcome to ICANN Start. This is the show about one issue, five questions: What is it? Why does it matter? Who
Instructor (Jerry Cain)
 ProgrammingParadigms-Lecture27 Instructor (Jerry Cain): cell phone off. Hey, everyone, welcome. I don t have any handouts for you today. You should pretty much be done with all the handouts. Yesterday
ProgrammingParadigms-Lecture27 Instructor (Jerry Cain): cell phone off. Hey, everyone, welcome. I don t have any handouts for you today. You should pretty much be done with all the handouts. Yesterday
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute. Week 02 Module 06 Lecture - 14 Merge Sort: Analysis
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week 02 Module 06 Lecture - 14 Merge Sort: Analysis So, we have seen how to use a divide and conquer strategy, we
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week 02 Module 06 Lecture - 14 Merge Sort: Analysis So, we have seen how to use a divide and conquer strategy, we
Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems]
![Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems] Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems]](/thumbs/77/75726948.jpg) 1 of 9 25/04/2016 13:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems] [Notes] [Practice Calculus III - Notes
1 of 9 25/04/2016 13:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems] [Notes] [Practice Calculus III - Notes
The first thing we ll need is some numbers. I m going to use the set of times and drug concentration levels in a patient s bloodstream given below.
 Graphing in Excel featuring Excel 2007 1 A spreadsheet can be a powerful tool for analyzing and graphing data, but it works completely differently from the graphing calculator that you re used to. If you
Graphing in Excel featuring Excel 2007 1 A spreadsheet can be a powerful tool for analyzing and graphing data, but it works completely differently from the graphing calculator that you re used to. If you
PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between
 MITOCW Lecture 10A [MUSIC PLAYING] PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between all these high-level languages like Lisp and the query
MITOCW Lecture 10A [MUSIC PLAYING] PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between all these high-level languages like Lisp and the query
Arrays/Branching Statements Tutorial:
 Arrays/Branching Statements Tutorial: In the last tutorial, you created a button that, when you clicked on it (the onclick event), changed another image on the page. What if you have a series of pictures
Arrays/Branching Statements Tutorial: In the last tutorial, you created a button that, when you clicked on it (the onclick event), changed another image on the page. What if you have a series of pictures
(Refer Slide Time 04:53)
 Programming and Data Structure Dr.P.P.Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 26 Algorithm Design -1 Having made a preliminary study
Programming and Data Structure Dr.P.P.Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 26 Algorithm Design -1 Having made a preliminary study
Part 1 - Your First algorithm
 California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10: Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2016 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm Flowcharts
California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10: Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2016 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm Flowcharts
So, coming back to this picture where three levels of memory are shown namely cache, primary memory or main memory and back up memory.
 Computer Architecture Prof. Anshul Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 31 Memory Hierarchy: Virtual Memory In the memory hierarchy, after
Computer Architecture Prof. Anshul Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 31 Memory Hierarchy: Virtual Memory In the memory hierarchy, after
Problem Set 12: Service Pack 3
 Not ready reading drive A:... Problem Set 12: Service Pack 3 Problem Set 12: Service Pack 3 Opener 1. a. Use some Zomes to make an equilateral pyramid with a Zomes are sponsored by triangular base. Zoom
Not ready reading drive A:... Problem Set 12: Service Pack 3 Problem Set 12: Service Pack 3 Opener 1. a. Use some Zomes to make an equilateral pyramid with a Zomes are sponsored by triangular base. Zoom
NCAA Instructions Nerdy for Sports
 Home Page / Login 2 Registration 3 Main Menu 4 Making your Picks 5 Editing your Picks 7 View your Picks 8 Double Check your Picks 9 Actual Results 11 Payouts 12 Reports 12 League History 16 Contact Us
Home Page / Login 2 Registration 3 Main Menu 4 Making your Picks 5 Editing your Picks 7 View your Picks 8 Double Check your Picks 9 Actual Results 11 Payouts 12 Reports 12 League History 16 Contact Us
Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008
 Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008 Trackside cameras are a useful and creative way to add visual interest to your route. Rather than just look out the windshield of the locomotive
Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008 Trackside cameras are a useful and creative way to add visual interest to your route. Rather than just look out the windshield of the locomotive
Instructor (Mehran Sahami): All righty. Welcome back to yet another fun-filled, exciting day of CS106A.
 Programming Methodology-Lecture16 Instructor (Mehran Sahami): All righty. Welcome back to yet another fun-filled, exciting day of CS106A. So it s the day before the midterm. This is kind of like, you know,
Programming Methodology-Lecture16 Instructor (Mehran Sahami): All righty. Welcome back to yet another fun-filled, exciting day of CS106A. So it s the day before the midterm. This is kind of like, you know,
Properties and Definitions
 Section 0.1 Contents: Operations Defined Multiplication as an Abbreviation Visualizing Multiplication Commutative Properties Parentheses Associative Properties Identities Zero Product Answers to Exercises
Section 0.1 Contents: Operations Defined Multiplication as an Abbreviation Visualizing Multiplication Commutative Properties Parentheses Associative Properties Identities Zero Product Answers to Exercises
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
MITOCW ocw f99-lec12_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec12_300k This is lecture twelve. OK. We've reached twelve lectures. And this one is more than the others about applications of linear algebra. And I'll confess. When I'm giving you
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec12_300k This is lecture twelve. OK. We've reached twelve lectures. And this one is more than the others about applications of linear algebra. And I'll confess. When I'm giving you
Objective: Find the total volume of solid figures composed of two nonoverlapping
 Lesson 6 Objective: Find the total volume of solid figures composed of two nonoverlapping Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time
Lesson 6 Objective: Find the total volume of solid figures composed of two nonoverlapping Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time
CS 3 Midterm 1 Review
 CS 3 Midterm 1 Review 1. Quick Evaluations Indicate what each of the following would return if typed into STK. If you think it would error, then please write ERROR. If you think that it would loop forever,
CS 3 Midterm 1 Review 1. Quick Evaluations Indicate what each of the following would return if typed into STK. If you think it would error, then please write ERROR. If you think that it would loop forever,
Lab 6 Vectors and functions
 CMSC160 Intro to Algorithmic Design Blaheta Lab 6 Vectors and functions 11 October 2016 The drill for this lab is another part of the Chapter 4 drill. Come to lab on Tuesday either with it completed or
CMSC160 Intro to Algorithmic Design Blaheta Lab 6 Vectors and functions 11 October 2016 The drill for this lab is another part of the Chapter 4 drill. Come to lab on Tuesday either with it completed or
DESIGN YOUR OWN BUSINESS CARDS
 DESIGN YOUR OWN BUSINESS CARDS USING VISTA PRINT FREE CARDS I m sure we ve all seen and probably bought the free business cards from Vista print by now. What most people don t realize is that you can customize
DESIGN YOUR OWN BUSINESS CARDS USING VISTA PRINT FREE CARDS I m sure we ve all seen and probably bought the free business cards from Vista print by now. What most people don t realize is that you can customize
Understanding Recursion
 Understanding Recursion Brian L. Stuart February 23, 2015 It has been suggested that the single most original contribution that the field of Computer Science has made to the tapestry of human intellect
Understanding Recursion Brian L. Stuart February 23, 2015 It has been suggested that the single most original contribution that the field of Computer Science has made to the tapestry of human intellect
Close Your File Template
 In every sale there is always a scenario where I can t get someone to respond. No matter what I do. I can t get an answer from them. When people stop responding I use the Permission To. This is one of
In every sale there is always a scenario where I can t get someone to respond. No matter what I do. I can t get an answer from them. When people stop responding I use the Permission To. This is one of
Win-Back Campaign- Re-Engagement Series
 Win-Back Campaign- Re-Engagement Series At this point the re-engagement campaign has ended, so if the prospect still hasn t responded it s time to turn up the heat. NOTE: In the emails below, everywhere
Win-Back Campaign- Re-Engagement Series At this point the re-engagement campaign has ended, so if the prospect still hasn t responded it s time to turn up the heat. NOTE: In the emails below, everywhere
Fractions and their Equivalent Forms
 Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Fractions Fractions and their Equivalent Forms Little kids use the concept of a fraction long before we ever formalize their knowledge in school. Watching little kids share a candy bar or a bottle of soda
Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques. Marian Small novembre 2017
 Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques Marian Small novembre 2017 Playing with math Uae your linking cubes. Show that the mean of 4, 7 and 7 is 6. Playing with math Uae your linking
Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques Marian Small novembre 2017 Playing with math Uae your linking cubes. Show that the mean of 4, 7 and 7 is 6. Playing with math Uae your linking
Divisibility Rules and Their Explanations
 Divisibility Rules and Their Explanations Increase Your Number Sense These divisibility rules apply to determining the divisibility of a positive integer (1, 2, 3, ) by another positive integer or 0 (although
Divisibility Rules and Their Explanations Increase Your Number Sense These divisibility rules apply to determining the divisibility of a positive integer (1, 2, 3, ) by another positive integer or 0 (although
Solution Guide for Chapter 20
 Solution Guide for Chapter 0 Here are the solutions for the Doing the Math exercises in Girls Get Curves! DTM from p. 351-35. In the diagram SLICE, LC and IE are altitudes of the triangle!sci. L I If SI
Solution Guide for Chapter 0 Here are the solutions for the Doing the Math exercises in Girls Get Curves! DTM from p. 351-35. In the diagram SLICE, LC and IE are altitudes of the triangle!sci. L I If SI
Usability Test Report: get Interface 1
 Usability Test Report: get it@duke Interface 1 Summary Emily Daly, Bendte Fagge, and Candy Guevarra conducted usability testing on the functionality of the get it@duke interface. The test was held outside
Usability Test Report: get it@duke Interface 1 Summary Emily Daly, Bendte Fagge, and Candy Guevarra conducted usability testing on the functionality of the get it@duke interface. The test was held outside
Heuristic Evaluation of igetyou
 Heuristic Evaluation of igetyou 1. Problem i get you is a social platform for people to share their own, or read and respond to others stories, with the goal of creating more understanding about living
Heuristic Evaluation of igetyou 1. Problem i get you is a social platform for people to share their own, or read and respond to others stories, with the goal of creating more understanding about living
VLOOKUP() takes three mandatory parameters and one default/optional parameter:
 Excel Lesson: Table Lookup Functions Topics Covered: VLookup() [Look across] HLookup() [Look down] Lookup() [Look almost anywhere] Related Functions (a list) We will not be examining all forms of these
Excel Lesson: Table Lookup Functions Topics Covered: VLookup() [Look across] HLookup() [Look down] Lookup() [Look almost anywhere] Related Functions (a list) We will not be examining all forms of these
QUICK EXCEL TUTORIAL. The Very Basics
 QUICK EXCEL TUTORIAL The Very Basics You Are Here. Titles & Column Headers Merging Cells Text Alignment When we work on spread sheets we often need to have a title and/or header clearly visible. Merge
QUICK EXCEL TUTORIAL The Very Basics You Are Here. Titles & Column Headers Merging Cells Text Alignment When we work on spread sheets we often need to have a title and/or header clearly visible. Merge
In our first lecture on sets and set theory, we introduced a bunch of new symbols and terminology.
 Guide to and Hi everybody! In our first lecture on sets and set theory, we introduced a bunch of new symbols and terminology. This guide focuses on two of those symbols: and. These symbols represent concepts
Guide to and Hi everybody! In our first lecture on sets and set theory, we introduced a bunch of new symbols and terminology. This guide focuses on two of those symbols: and. These symbols represent concepts
Mark Important Points in Margin. Significant Figures. Determine which digits in a number are significant.
 Knowledge/Understanding: How and why measurements are rounded. Date: How rounding and significant figures relate to precision and uncertainty. When significant figures do not apply. Skills: Determine which
Knowledge/Understanding: How and why measurements are rounded. Date: How rounding and significant figures relate to precision and uncertainty. When significant figures do not apply. Skills: Determine which
Grade 6 Math Circles November 6 & Relations, Functions, and Morphisms
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Relations Let s talk about relations! Grade 6 Math Circles November 6 & 7 2018 Relations, Functions, and
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Relations Let s talk about relations! Grade 6 Math Circles November 6 & 7 2018 Relations, Functions, and
Introduction to Programming
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Programming Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. This method of telling a story is as good today as it was when the King of Hearts prescribed
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Programming Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. This method of telling a story is as good today as it was when the King of Hearts prescribed
Anatomy of a Standard Transcript
 Anatomy of a Standard Transcript Maddie: Hi everyone! Throughout this joint project, Eli, Christina, & I all had to use technical standards to make sure our products met the necessary requirements & specifications,
Anatomy of a Standard Transcript Maddie: Hi everyone! Throughout this joint project, Eli, Christina, & I all had to use technical standards to make sure our products met the necessary requirements & specifications,
Module 10A Lecture - 20 What is a function? Why use functions Example: power (base, n)
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 10A Lecture - 20 What is a function?
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 10A Lecture - 20 What is a function?
Sucuri Webinar Q&A HOW TO IDENTIFY AND FIX A HACKED WORDPRESS WEBSITE. Ben Martin - Remediation Team Lead
 Sucuri Webinar Q&A HOW TO IDENTIFY AND FIX A HACKED WORDPRESS WEBSITE. Ben Martin - Remediation Team Lead 1 Question #1: What is the benefit to spammers for using someone elses UA code and is there a way
Sucuri Webinar Q&A HOW TO IDENTIFY AND FIX A HACKED WORDPRESS WEBSITE. Ben Martin - Remediation Team Lead 1 Question #1: What is the benefit to spammers for using someone elses UA code and is there a way
Yup, left blank on purpose. You can use it to draw whatever you want :-)
 Yup, left blank on purpose. You can use it to draw whatever you want :-) Chapter 1 The task I have assigned myself is not an easy one; teach C.O.F.F.E.E. Not the beverage of course, but the scripting language
Yup, left blank on purpose. You can use it to draw whatever you want :-) Chapter 1 The task I have assigned myself is not an easy one; teach C.O.F.F.E.E. Not the beverage of course, but the scripting language
