Location-based Services in Ubiquitous Computing Environments
|
|
|
- Madison May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Location-based Services in Ubiquitous Computing Environments National Institute of Informatics
2 Outline 1. Motivation 2. Approach 3. Design and Implementation 4. Applications 5. Conclusion
3 Location-based Services Context-aware services: location-based information services personalized information services For example Location-dependent advertising Tourist navigation information Regional/local personalized portals
4 Existing Approaches Context-aware services on portable computing devices: User moves with computing devices equipped with poitioning systems. e.g. Cooltown (HP) and NEXUS (Stuttgart University) Context-aware services in smart spaces: A space is equipped with tracking systems and services can be provided at computers near the locations of users. e.g. Sentient Computing (Cambridge University) and EasyLiving (Microsoft Research) The two approaches aim at the same goals but are posed as polar opposites. A unified framework for integrating the two approaches is
5 Problems Several problems in existing location-based services: A ubiquitous computing environment consists of various computing devices, e.g. mobile and embedded computers. Ubiquitous computing devices have limited resources so that they can support only their initial services. Existing services are designed dependently on particular vendors s. PDA with GPS public terminal PDA public terminal embedded computer embedded computer PDA
6 Positioning Sensors and Tracking Sensors Two types of location-sensing systems: Tracking s e.g., RFID s and computer vision systems RFID RFID RFID Positioning s e.g., GPS and wireless LAN RF-transmitter () RF-based Location Sensor RF- (reader) The framework supports various s, including RFID s, and hides differences between sensing systems.
7 Requirements Adaptability Services can adapt not only their contents but also their locations according to changes in the positions of people and physical objects. Modularity Services must be modular and reusable independently of the underlying systems as much as possible. Application-neutral Various and multiple services can be supported. Generality A unified approach for integrating the following settings: stationary computers and mobile computers stationary s and mobile s tracking s and positioning s
8 Approach A framework for building and managing location-based and personalized services in ubiquitous computing environments. It supports services for annotating and supporting people, things, and places. Each service is implemented as a mobile agent. Each service can be spatially bound to people, objects, and places and dynamically deployed at proper computers. The framework seamlessly supports stationary and mobile computing devices, and tracking and positioning s, The framework enables most existing mobile agent platforms, including non Java-based platforms, to migrate their mobile agents according to the locations of physical entities or places.
9 Dynamically Deployable Services Services are implemented within mobile agents and can migrate to computing devices according to the locations of the physical entities that they are bound to. step 1: suspension of execution mobile agent state code step 2: migration state code mobile agent network step 3: resumption of execution mobile agent state code Mobile agent-based service providers are self-contained and mobile software units. They can be deployed at and continue its execution at the destination only while they are needed. They can be locally executed without network latency and conserve the limited resources of computing devices.
10 Spatial Links between Physical Entities or Places and Services All application-specific services cannot monitor the underlying systems, including location-s. It is complex and difficult for services to adapt their contents and locations according to results measured by the s. The framework introduce a simple policy for the deployment of service provider mobile agents. It migrates services bound to physical entities or places to computers near the current location of the physical entities or places. To interact with users locally, services do not have to handle their own positions, because they can be automatically deployed at devices near the users by the framework.
11 Architecture The framework can monitor the location of each and instruct the mobile agents that is bound to the to migrate to proper computers in the region that contains the. Location Information Server: A location-aware directory service for mobile agents according to the locations of entities in physical world Agent Host: A computer for executing and migrating mobile agents. Service Provider Agent (Mobile Agent): A service-provider and virtual counterpart of physical entity or place.
12 Location Information Server Each LIS can run on a stationary or mobile computer and be coordinated with other LISs in a peer-to-peer manner. Management of more than one locating sensing system e.g. tracking s and positioning s Discovery of agent hosts and service provider agents Context-aware deployment of mobile agents. Location Information Server Location Information Server database event handler abstraction layer network manager database event handler abstraction layer network manager locating locating peer-to-peer connection locating
13 Tag Resolution Each LIS has a database for information about agent hosts and service provider agents. When an LIS detects a new entity or, the LIS searches information about the entity or from its database. agent host Location Information Server database RF-? RF- movement locating RF- place locating non-agent host region 1 region 2 Each may be bound to an agent host or non-agent host.
14 Service Deployment When an LIS can multicast a query about a newly visiting RFID (i.e. physical entity or place), other LISs process Case 1:If the is attached with an entity or place, other LISs search agents bound to the and then inform the agents about candidate agent hosts. Case 2:If the is attached with an agent host, other LISs or the agent host returns its profile to the LIS. Case 3:Otherwise the is unknown Location Information Server the visiting host s profile query network manager place-bound agent s requirement navigation movement agent host migration agent host place-bound agent
15 Agent Host Each agent host is a stationary or mobile computing device attached with an RFID. It provides a mobile agent platform for executing and migrating agents to other agent hosts through a TCP connection. Userbound Agent Placebound Agent API MobileSpaces:Mobile Agent Runtime System Java VM OS Hardware command Proxy Agent Agent host Network Manager query message about the identifier of the agent host s query message about unknown reply message with its network address
16 Service Provider Agent Since application-specific services are encapsulated within agents, the framework is independent of any applications. Each mobile agent can registry the identifier of its and the host requirements written in CC/PP. class TaggedAgent extends Agent implements Serializable { void go(url url) throws NoSuchHostException {... } void duplicate() throws IllegalAccessException {... } void destroy() {... } void settagidentifier(tagidentifier tid) {... } void setagentprofile(agentprofile apf) {... } URL getcurrenthost() {... } boolean isconformablehost(hostprofile hfs) {... }... } Please refer to the Appendix of the paper for detail information on programming interfaces for service provider agents.
17 Location-Aware Services (the first linkage) A moving entity is attached with an RFID and agent hosts and RFID s are stationary in places. Step 1 agent host agent host moving entity Step 1: An RFID in a place detects the of a moving entity. Step 2 agent host migration agent host Step 2: An agent bound to the entity migrates to an agent host in the same place.
18 Follow-Me Services Navigation system for patient in a hospital: User navigating agents are bound to particular partients. Agents are automatically migrated to the nearest computer from the current positions of users. START user camera wall-mounted display user assistant agent computer camera camera computer user assistant agent GOAL
19 Location-Aware Services (the second linkage) A moving entity carries an agent host and a place is equipped with a stationary RFID. Step 1 agent host Step 1: An RFID in a place detects the of an agent host. moving agent host agent host Step 2 agent host migration agent host Step 2: An agent bound to the place migrate to the visiting agent host.
20 Step 1 Location-aware Universal Controller for Appliances A desktop-lamp bound agent communicates with X10-based servers to switch the desktop-lamp on or off. The agent can migrate to a PDA near from the desktoplamp. agent host PDA desktop-lamp bound agent A PDA comes in the region that contains the desktop-lamp. desktop-lamp bound agent PDA Step 2
21 Location-aware Universal Controller for Appliances When a PDA enters in the area that contains a desktop-lamp, the agent bound to the lamp migrates to the PDA.
22 Location-Aware Services (the third linkage) A moving entity carries an agent host and an RFID-based positioning and a place is attached with an RFID. Step 1 Step 1: A moving detects the of a place. moving and agent host agent host Step 2 migration agent host Step 2: An agent bound to the place migrate to the visiting agent host. agent host
23 User Navigation System A location-based navigation on a Tablet-PC equipped with a positioning the s coverage area tablet PC (agent host + LIS) the s coverage area tablet PC (agent the s host + LIS) coverage area tablet PC (agent host + LIS) positionbound migration positionbound migration
24 Why the framework is not based on web-service Mobile agent-based services have several advanes in comparison with web-services. Ubiquitous computing devices are often connected through wireless networks. Mobile agents can be executed even when their source hosts are disconnected from a network. Web-services assume that networks are connected and reliable anytime. Ubiquitous computing services are often managed without any servers. Mobile agent runtime systems can exchange agents with other systems in a peer-to-peer manner. Web-services are essentially managed and operated by servers. Ubiquitous computing environments must support proactive services rather than request-and-response-based services. Mobile agents are autonomous and programmable entities. Web-services are based on request-and-response paradigm
25 Conclusion A framework for building and managing location-aware services. It binds service provider agents with physical entities and places. It dynamically deploys agents to computers whose capabilities can satisfy the requirements of the agents and which are near the location of the entities and places. The framework can spatially bridge between physical world and cyber-space with mobile agents. Cyberspace 1 Link counterpart agent counterpart agent counterpart agent movement counterpart agent Cyberspace 2 Physical World 1 movement Physical World 2
26 Future Work Several new results will appear in upcoming papers: Other linkages between physical entity and agents[ieee MDM 04] Dynamic aggregation of computing devices [IEEE PerCom 04] Specification for migration policies of services [IEEE ICDCS 04] Rapid development and testing for network/location-aware software [IEEE Trans. Software Engineering vol. 29, no. 12, 2003] Future issues: Enhancement of privacy and security mechanism Inter-service provider agents communication Adaptive mechanisms for resource-dependent services More applications
Middleware for Ubiquitous Computing
 Middleware for Ubiquitous Computing Software Testing for Mobile Computing National Institute of Informatics Ichiro Satoh Abstract When a portable computing device is moved into and attached to a new local
Middleware for Ubiquitous Computing Software Testing for Mobile Computing National Institute of Informatics Ichiro Satoh Abstract When a portable computing device is moved into and attached to a new local
A Location Model for Ambient Intelligence
 A Location Model for Ambient Intelligence National Institute of Informatics, Japan Email: ichiro@nii.ac.jp Outline 1. Motivation 2. Approach 3. Location Model 4. Design and Implementation 5. Applications
A Location Model for Ambient Intelligence National Institute of Informatics, Japan Email: ichiro@nii.ac.jp Outline 1. Motivation 2. Approach 3. Location Model 4. Design and Implementation 5. Applications
A World Model for Smart Spaces
 A World Model for Smart Spaces Ichiro Satoh National Institute of Informatics 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan E-mail: ichiro@nii.ac.jp Abstract. A world model for ubiquitous computing
A World Model for Smart Spaces Ichiro Satoh National Institute of Informatics 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan E-mail: ichiro@nii.ac.jp Abstract. A world model for ubiquitous computing
SpatialAgents: integrating user mobility and program mobility in ubiquitous computing environments
 WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2003; 3:411 423 (DOI: 10.1002/wcm.126) SpatialAgents: integrating user mobility and program mobility in ubiquitous computing environments
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2003; 3:411 423 (DOI: 10.1002/wcm.126) SpatialAgents: integrating user mobility and program mobility in ubiquitous computing environments
Dynamic Federation of Partitioned Applications in Ubiquitous Computing Environments
 Dynamic Federation of Partitioned pplications in Ubiquitous Computing Environments Ichiro Satoh National Institute of Informatics 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan E-mail: ichiro@nii.ac.jp
Dynamic Federation of Partitioned pplications in Ubiquitous Computing Environments Ichiro Satoh National Institute of Informatics 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan E-mail: ichiro@nii.ac.jp
Virtual Sensors: Abstracting Data from Physical Sensors
 Virtual Sensors: Abstracting Data from Physical Sensors Sanem Kabadayı, Adam Pridgen, and Christine Julien Mobile and Pervasive Computing Group The University of Texas at Austin June 26, 2006 Overview
Virtual Sensors: Abstracting Data from Physical Sensors Sanem Kabadayı, Adam Pridgen, and Christine Julien Mobile and Pervasive Computing Group The University of Texas at Austin June 26, 2006 Overview
VXLAN Overview: Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches
 White Paper VXLAN Overview: Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches What You Will Learn Traditional network segmentation has been provided by VLANs that are standardized under the IEEE 802.1Q group. VLANs provide
White Paper VXLAN Overview: Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches What You Will Learn Traditional network segmentation has been provided by VLANs that are standardized under the IEEE 802.1Q group. VLANs provide
Service-Oriented Computing in Recomposable Embedded Systems
 Service-Oriented Computing in Recomposable Embedded Systems Autonomous + Backend Support Yinong Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering http://www.public.asu.edu/~ychen10/ 2 Motivation Embedded
Service-Oriented Computing in Recomposable Embedded Systems Autonomous + Backend Support Yinong Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering http://www.public.asu.edu/~ychen10/ 2 Motivation Embedded
Introduction to Mobile Ubiquitous Computing Systems
 CPET 565 Mobile Computing Systems CPET/ITC 499 Mobile Computing Lecture 1 Introduction to Mobile Ubiquitous Computing Systems Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor Spring 2016 A Specialty Course Purdue University
CPET 565 Mobile Computing Systems CPET/ITC 499 Mobile Computing Lecture 1 Introduction to Mobile Ubiquitous Computing Systems Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor Spring 2016 A Specialty Course Purdue University
Network Processing of Mobile Agents, by Mobile Agents, for Mobile Agents
 Network Processing of Mobile Agents, by Mobile Agents, for Mobile Agents Ichiro Satoh National Institute of Informatics / Japan Science and Technology Corporation 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
Network Processing of Mobile Agents, by Mobile Agents, for Mobile Agents Ichiro Satoh National Institute of Informatics / Japan Science and Technology Corporation 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
FlexiNet 2.1 Roundup. Richard Hayton ANSA Consortium
 FlexiNet 2.1 Roundup Richard Hayton FlexiNet 2.1 Statistics 118,000 lines of Java 80,000 words 47 Code Fragments 87 Figures Code Architecture Document What does it contain? Core Framework binding, naming,
FlexiNet 2.1 Roundup Richard Hayton FlexiNet 2.1 Statistics 118,000 lines of Java 80,000 words 47 Code Fragments 87 Figures Code Architecture Document What does it contain? Core Framework binding, naming,
A Mobile Agent-Based Framework for Active Networks. Ichiro Satoh
 A Mobile -Based Framework for Active Networks Ichiro Satoh Department of Information Sciences, Ochanomizu University 2-1-1 Otsuka Bunkyo-ku Tokyo 112-8610, Japan E-mail: ichiro@is.ocha.ac.jp IEEE Systems,
A Mobile -Based Framework for Active Networks Ichiro Satoh Department of Information Sciences, Ochanomizu University 2-1-1 Otsuka Bunkyo-ku Tokyo 112-8610, Japan E-mail: ichiro@is.ocha.ac.jp IEEE Systems,
An IoT-Aware Architecture for Smart
 An IoT-Aware Architecture for Smart Healthcare System Presented By: Amnah Allboani Abstract Smart hospital system (SHS) relies on complementary technologies specifically RFID, WSN, and smart mobile, interoperating
An IoT-Aware Architecture for Smart Healthcare System Presented By: Amnah Allboani Abstract Smart hospital system (SHS) relies on complementary technologies specifically RFID, WSN, and smart mobile, interoperating
(9A05803) WEB SERVICES (ELECTIVE - III)
 1 UNIT III (9A05803) WEB SERVICES (ELECTIVE - III) Web services Architecture: web services architecture and its characteristics, core building blocks of web services, standards and technologies available
1 UNIT III (9A05803) WEB SERVICES (ELECTIVE - III) Web services Architecture: web services architecture and its characteristics, core building blocks of web services, standards and technologies available
Einführung in die Erweiterte Realität
 Einführung in die Erweiterte Realität - 7. Context Toolkit - Gudrun Klinker Dec. 2, 2003 Literature Anind K. Dey, Gregory D. Abowd, and Danieal Salber, A Conceptual Framework and a Toolkit for Supporting
Einführung in die Erweiterte Realität - 7. Context Toolkit - Gudrun Klinker Dec. 2, 2003 Literature Anind K. Dey, Gregory D. Abowd, and Danieal Salber, A Conceptual Framework and a Toolkit for Supporting
Tracking Indoors. Pervasive Computing MIT SMA 5508 Spring 2006 Larry. Rudolph
 Tracking Indoors Pervasive Computing MIT 6.883 SMA 5508 Spring 2006 Larry 1 Rudolph Location of what? Objects Static, Moveable, or Mobile Frequency of movement: door, desk, laptop Dumb or Networked People
Tracking Indoors Pervasive Computing MIT 6.883 SMA 5508 Spring 2006 Larry 1 Rudolph Location of what? Objects Static, Moveable, or Mobile Frequency of movement: door, desk, laptop Dumb or Networked People
Context Aware Computing
 CPET 565/CPET 499 Mobile Computing Systems Context Aware Computing Lecture 7 Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Technology Purdue University Fort Wayne Campus 1 Context-Aware
CPET 565/CPET 499 Mobile Computing Systems Context Aware Computing Lecture 7 Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Technology Purdue University Fort Wayne Campus 1 Context-Aware
ATP: Autonomous Transport Protocol
 ATP: Autonomous Transport Protocol Tamer Elsayed,, Mohamed Hussein, Moustafa Youssef,, Tamer Nadeem, Adel Youssef and Liviu Iftode Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, USA Tracking in
ATP: Autonomous Transport Protocol Tamer Elsayed,, Mohamed Hussein, Moustafa Youssef,, Tamer Nadeem, Adel Youssef and Liviu Iftode Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, USA Tracking in
PROCE55 Mobile: Web API App. Web API. https://www.rijksmuseum.nl/api/...
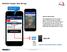 PROCE55 Mobile: Web API App PROCE55 Mobile with Test Web API App Web API App Example This example shows how to access a typical Web API using your mobile phone via Internet. The returned data is in JSON
PROCE55 Mobile: Web API App PROCE55 Mobile with Test Web API App Web API App Example This example shows how to access a typical Web API using your mobile phone via Internet. The returned data is in JSON
A Framework for Building Reusable Mobile Agents for Network Management
 A Framework for Building Reusable Mobile Agents for Network Management Ichiro Satoh Λ National Institute of Informatics / Japan Science and Technology Corporation 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
A Framework for Building Reusable Mobile Agents for Network Management Ichiro Satoh Λ National Institute of Informatics / Japan Science and Technology Corporation 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
Ch 1. Mobile Adaptive Computing
 Ch 1. Mobile Adaptive Computing What is Mobile Computing Mobile computing? Distributed system Wireless communications Mobility of communications devices Difference between mobile computing and mobile communications?
Ch 1. Mobile Adaptive Computing What is Mobile Computing Mobile computing? Distributed system Wireless communications Mobility of communications devices Difference between mobile computing and mobile communications?
The Role of a Context Service in a System that aims at integrating the Digital with the Real World
 The Role of a Context Service in a System that aims at integrating the Digital with the Real World Dagstuhl Seminar Ubiquitous Computing, 09.09.2001 Fritz Hohl (hohl@sony.de) Telecommunication Research
The Role of a Context Service in a System that aims at integrating the Digital with the Real World Dagstuhl Seminar Ubiquitous Computing, 09.09.2001 Fritz Hohl (hohl@sony.de) Telecommunication Research
Agent-Environment for Small Mobile Devices
 -Environment for Small Mobile Devices Thomas Strang and Melanie Meyer {firstname.lastname}@dlr.de German Aerospace Center (DLR), Site Oberpfaffenhofen Institute of Communications and Navigation (KN-S)
-Environment for Small Mobile Devices Thomas Strang and Melanie Meyer {firstname.lastname}@dlr.de German Aerospace Center (DLR), Site Oberpfaffenhofen Institute of Communications and Navigation (KN-S)
Distributed Systems Question Bank UNIT 1 Chapter 1 1. Define distributed systems. What are the significant issues of the distributed systems?
 UNIT 1 Chapter 1 1. Define distributed systems. What are the significant issues of the distributed systems? 2. What are different application domains of distributed systems? Explain. 3. Discuss the different
UNIT 1 Chapter 1 1. Define distributed systems. What are the significant issues of the distributed systems? 2. What are different application domains of distributed systems? Explain. 3. Discuss the different
JXTA for J2ME Extending the Reach of Wireless With JXTA Technology
 JXTA for J2ME Extending the Reach of Wireless With JXTA Technology Akhil Arora Carl Haywood Kuldip Singh Pabla Sun Microsystems, Inc. 901 San Antonio Road Palo Alto, CA 94303 USA 650 960-1300 The Wireless
JXTA for J2ME Extending the Reach of Wireless With JXTA Technology Akhil Arora Carl Haywood Kuldip Singh Pabla Sun Microsystems, Inc. 901 San Antonio Road Palo Alto, CA 94303 USA 650 960-1300 The Wireless
SWE 760 Lecture 1: Introduction to Analysis & Design of Real-Time Embedded Systems
 SWE 760 Lecture 1: Introduction to Analysis & Design of Real-Time Embedded Systems Hassan Gomaa References: H. Gomaa, Chapters 1, 2, 3 - Real-Time Software Design for Embedded Systems, Cambridge University
SWE 760 Lecture 1: Introduction to Analysis & Design of Real-Time Embedded Systems Hassan Gomaa References: H. Gomaa, Chapters 1, 2, 3 - Real-Time Software Design for Embedded Systems, Cambridge University
Mobile Computing (3C05) Outline. Introduction
 Mobile Computing (3C05) Boris Vilidnitsky March 2005 1 Outline Introduction Current situation in mobile computing Problems Middleware current solutions New approaches GPS Paradigms for mobile computing
Mobile Computing (3C05) Boris Vilidnitsky March 2005 1 Outline Introduction Current situation in mobile computing Problems Middleware current solutions New approaches GPS Paradigms for mobile computing
McAfee Product Entitlement Definitions
 McAfee Product Entitlement Definitions Corporate Headquarters 2821 Mission College Blvd. Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA Application Server CPU CPU Core Database Database Instance Entity File Submission Daily
McAfee Product Entitlement Definitions Corporate Headquarters 2821 Mission College Blvd. Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA Application Server CPU CPU Core Database Database Instance Entity File Submission Daily
Modeling Context-Aware Behavior by Interpreted ECA Rules
 Modeling Context-Aware Behavior by Interpreted ECA Rules Wolfgang Beer 1, Volker Christian 1, Alois Ferscha 1, and Lars Mehrmann 2 1 Johannes Kepler University Linz, Department for Practical Informatics,
Modeling Context-Aware Behavior by Interpreted ECA Rules Wolfgang Beer 1, Volker Christian 1, Alois Ferscha 1, and Lars Mehrmann 2 1 Johannes Kepler University Linz, Department for Practical Informatics,
Mobile Computing Introduction
 Mobile Computing Introduction UNIT - 1 Prepared By:- NITIN PANDYA Assistant Professor, SVBIT. What is Mobile Computing 2 NTIIN PANDYA 3 NTIIN PANDYA Definitions Mobile Computing What is mobile computing?
Mobile Computing Introduction UNIT - 1 Prepared By:- NITIN PANDYA Assistant Professor, SVBIT. What is Mobile Computing 2 NTIIN PANDYA 3 NTIIN PANDYA Definitions Mobile Computing What is mobile computing?
Distributed and Cloud Computing
 Distributed and Cloud Computing K. Hwang, G. Fox and J. Dongarra Chapter 9: Ubiquitous Clouds and The Internet of Things (suggested for use in 5 lectures in 250 minutes) Prepared by Kai Hwang University
Distributed and Cloud Computing K. Hwang, G. Fox and J. Dongarra Chapter 9: Ubiquitous Clouds and The Internet of Things (suggested for use in 5 lectures in 250 minutes) Prepared by Kai Hwang University
Context-Awareness and Adaptation in Distributed Event-Based Systems
 Context-Awareness and Adaptation in Distributed Event-Based Systems Eduardo S. Barrenechea, Paulo S. C. Alencar, Rolando Blanco, Don Cowan David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo
Context-Awareness and Adaptation in Distributed Event-Based Systems Eduardo S. Barrenechea, Paulo S. C. Alencar, Rolando Blanco, Don Cowan David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo
ICT-SHOK Project Proposal: PROFI
 ICT-SHOK Project Proposal: PROFI Full Title: Proactive Future Internet: Smart Semantic Middleware Overlay Architecture for Declarative Networking ICT-SHOK Programme: Future Internet Project duration: 2+2
ICT-SHOK Project Proposal: PROFI Full Title: Proactive Future Internet: Smart Semantic Middleware Overlay Architecture for Declarative Networking ICT-SHOK Programme: Future Internet Project duration: 2+2
Introduction to Distributed Systems
 Introduction to Distributed Systems Other matters: review of the Bakery Algorithm: why can t we simply keep track of the last ticket taken and the next ticvket to be called? Ref: [Coulouris&al Ch 1, 2]
Introduction to Distributed Systems Other matters: review of the Bakery Algorithm: why can t we simply keep track of the last ticket taken and the next ticvket to be called? Ref: [Coulouris&al Ch 1, 2]
Mobility and Media. How mobile computing is evolving at HP. Mark Smith Mobile and Media Systems Lab Hewlett Packard Laboratories
 Mobility and Media How mobile computing is evolving at HP Mark Smith (msmith@hpl.hp.com) Mobile and Media Systems Lab Hewlett Packard Laboratories 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
Mobility and Media How mobile computing is evolving at HP Mark Smith (msmith@hpl.hp.com) Mobile and Media Systems Lab Hewlett Packard Laboratories 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
Wireless Transmission and Mobility
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Wireless Transmission and Mobility Modulation, MAC and IPv6" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Modulation" Digital modulation! digital data is translated into an
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Wireless Transmission and Mobility Modulation, MAC and IPv6" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Modulation" Digital modulation! digital data is translated into an
Computing Technologies
 Computing Technologies Computing CPU, Memory, Communication Ubiquitous everywhere indefinite number of times Not really possible or desirable more than in traditional computing so widespread that unnoticed
Computing Technologies Computing CPU, Memory, Communication Ubiquitous everywhere indefinite number of times Not really possible or desirable more than in traditional computing so widespread that unnoticed
Context-Aware Actors. Outline
 Context-Aware Actors Anne H. H. Ngu Department of Computer Science Texas State University-San Macos 02/8/2011 Ngu-TxState Outline Why Context-Aware Actor? Context-Aware Scientific Workflow System - Architecture
Context-Aware Actors Anne H. H. Ngu Department of Computer Science Texas State University-San Macos 02/8/2011 Ngu-TxState Outline Why Context-Aware Actor? Context-Aware Scientific Workflow System - Architecture
Realizing the Promise of SANs
 Business without interruption. Realizing the Promise of SANs Bill North Director, Storage Network Programs Strategic Initiatives Group VERITAS Software Education Committee Chairman Storage Network Industry
Business without interruption. Realizing the Promise of SANs Bill North Director, Storage Network Programs Strategic Initiatives Group VERITAS Software Education Committee Chairman Storage Network Industry
Mobile IP Overview. Based on IP so any media that can support IP can also support Mobile IP
 Introduction: Mobile IP Overview An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet
Introduction: Mobile IP Overview An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet
Introduction. Distributed Systems IT332
 Introduction Distributed Systems IT332 2 Outline Definition of A Distributed System Goals of Distributed Systems Types of Distributed Systems 3 Definition of A Distributed System A distributed systems
Introduction Distributed Systems IT332 2 Outline Definition of A Distributed System Goals of Distributed Systems Types of Distributed Systems 3 Definition of A Distributed System A distributed systems
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept COE 540 Computer Networks Term 121 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-420 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@kfupm.edu.sa 9/1/2012 Dr. Ashraf
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept COE 540 Computer Networks Term 121 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-420 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@kfupm.edu.sa 9/1/2012 Dr. Ashraf
universaal Architecture and The Resource Discovery
 universaal Architecture and The Resource Discovery Michele Girolami ISTI-CNR Wireless Network Lab. Departimento di Informatica Università Pisa 1 Outline 1. Ambient Intelligence and AAL 2. The universaal
universaal Architecture and The Resource Discovery Michele Girolami ISTI-CNR Wireless Network Lab. Departimento di Informatica Università Pisa 1 Outline 1. Ambient Intelligence and AAL 2. The universaal
Lesson 8 Internet Connected Smart Home Services And Monitoring. Chapter-12 L08: "Internet of Things ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Lesson 8 Internet Connected Smart Home Services And Monitoring 1 Internet Connected Smart Home Services And Monitoring Smart home services Home lighting control Control and monitoring of appliances Security
Lesson 8 Internet Connected Smart Home Services And Monitoring 1 Internet Connected Smart Home Services And Monitoring Smart home services Home lighting control Control and monitoring of appliances Security
(i) Fixed, portable or mobile computing devices -- categorized on the basis of their mobility and portability,
 Remote Procedure Calls Based Middleware Design for Ubiquitous Computing Environment Sunil Kumar Nandal*, Yogesh Chaba* *Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, Hisar E-mail:- nandal_sunil@yahoo.com,yogeshchaba@yahoo.com
Remote Procedure Calls Based Middleware Design for Ubiquitous Computing Environment Sunil Kumar Nandal*, Yogesh Chaba* *Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, Hisar E-mail:- nandal_sunil@yahoo.com,yogeshchaba@yahoo.com
Outline. CS5984 Mobile Computing. Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid, CS5984. Wireless Sensor Networks 1/2. Wireless Sensor Networks 2/2
 CS5984 Mobile Computing Outline : a Survey Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia Tech An Introduction to 1 2 1/2 Advances in micro-electro-mechanical systems technology, wireless communications,
CS5984 Mobile Computing Outline : a Survey Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia Tech An Introduction to 1 2 1/2 Advances in micro-electro-mechanical systems technology, wireless communications,
Distributed Systems Architectures. Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 12 Slide 1
 Distributed Systems Architectures Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 12 Slide 1 Objectives To explain the advantages and disadvantages of different distributed systems architectures
Distributed Systems Architectures Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 12 Slide 1 Objectives To explain the advantages and disadvantages of different distributed systems architectures
Policy-Based Context-Management for Mobile Solutions
 Policy-Based Context-Management for Mobile Solutions Caroline Funk 1,Björn Schiemann 2 1 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Oettingenstraße 67, 80538 München caroline.funk@nm.ifi.lmu.de 2 Siemens AG,
Policy-Based Context-Management for Mobile Solutions Caroline Funk 1,Björn Schiemann 2 1 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Oettingenstraße 67, 80538 München caroline.funk@nm.ifi.lmu.de 2 Siemens AG,
Agilla/Agimone: Middleware for Sensor Networks
 Agilla/Agimone: Middleware for Sensor Networks Motivation Existing sensor network software lacks flexibility Entire network runs just one application Cannot adapt to changes in the environment the network
Agilla/Agimone: Middleware for Sensor Networks Motivation Existing sensor network software lacks flexibility Entire network runs just one application Cannot adapt to changes in the environment the network
ForeScout Extended Module for MaaS360
 Version 1.8 Table of Contents About MaaS360 Integration... 4 Additional ForeScout MDM Documentation... 4 About this Module... 4 How it Works... 5 Continuous Query Refresh... 5 Offsite Device Management...
Version 1.8 Table of Contents About MaaS360 Integration... 4 Additional ForeScout MDM Documentation... 4 About this Module... 4 How it Works... 5 Continuous Query Refresh... 5 Offsite Device Management...
A c t i v e w o r k s p a c e f o r e x t e r n a l d a t a a g g r e g a t i o n a n d S e a r c h. 1
 A c t i v e w o r k s p a c e f o r e x t e r n a l d a t a a g g r e g a t i o n a n d S e a r c h B a l a K a n t h i www.intelizign.com 1 Active workspace can search and visualize PLM data better! Problems:
A c t i v e w o r k s p a c e f o r e x t e r n a l d a t a a g g r e g a t i o n a n d S e a r c h B a l a K a n t h i www.intelizign.com 1 Active workspace can search and visualize PLM data better! Problems:
MOBILE COMPUTING (Common to Computer Science & Engineering and Information Technology)
 Code No: R41054 R10 Set No. 1 1 a) Explain functional architecture of GSM. [8] b) Write and explain novel applications of Mobile Computing. [7] 2 a) Explain in detail about IEEE 802.11 MAC Data frames.
Code No: R41054 R10 Set No. 1 1 a) Explain functional architecture of GSM. [8] b) Write and explain novel applications of Mobile Computing. [7] 2 a) Explain in detail about IEEE 802.11 MAC Data frames.
Offline Location Based Services Using Android OS Implemented In Smartphone and Beagleboard Xm
 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal Published By: Oriental Scientific Publishing Co., India. www.computerscijournal.org ISSN:
ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal Published By: Oriental Scientific Publishing Co., India. www.computerscijournal.org ISSN:
Introduction. The Safe-T Solution
 Secure Application Access Product Brief Contents Introduction 2 The Safe-T Solution 3 How It Works 3 Capabilities 4 Benefits 5 Feature List 6 6 Introduction As the world becomes much more digital and global,
Secure Application Access Product Brief Contents Introduction 2 The Safe-T Solution 3 How It Works 3 Capabilities 4 Benefits 5 Feature List 6 6 Introduction As the world becomes much more digital and global,
Universal Communication Component on Symbian Series60 Platform
 Universal Communication Component on Symbian Series60 Platform Róbert Kereskényi, Bertalan Forstner, Hassan Charaf Department of Automation and Applied Informatics Budapest University of Technology and
Universal Communication Component on Symbian Series60 Platform Róbert Kereskényi, Bertalan Forstner, Hassan Charaf Department of Automation and Applied Informatics Budapest University of Technology and
Internet Protocols Fall Lectures Inter-domain routing, mobility support, multicast routing Andreas Terzis
 Internet Protocols Fall 2006 Lectures 11-12 Inter-domain routing, mobility support, multicast routing Andreas Terzis Outline Inter-domain Internet Routing BGP Routing for mobile nodes Multicast routing
Internet Protocols Fall 2006 Lectures 11-12 Inter-domain routing, mobility support, multicast routing Andreas Terzis Outline Inter-domain Internet Routing BGP Routing for mobile nodes Multicast routing
Mobile Edge Computing
 Mobile Edge Computing 기술동향 Sung-Yeon Kim, Ph.D. Sung-Yeon.Kim@InterDigital.com 1 Outline Mobile Edge Computing Overview Mobile Edge Computing Architecture Mobile Edge Computing Application Mobile Edge
Mobile Edge Computing 기술동향 Sung-Yeon Kim, Ph.D. Sung-Yeon.Kim@InterDigital.com 1 Outline Mobile Edge Computing Overview Mobile Edge Computing Architecture Mobile Edge Computing Application Mobile Edge
Year, pier University Nikos Migas PhD student 2 Supervisors: School of Computing, Na MARIAN
 MARIAN Mobile Agents for Routing In Ad-hoc Networks Nikos Migas PhD student 2 nd Year, School of Computing, Napier University n.migas@napier.ac.uk Supervisors: W.Buchanan, K.McArtney Introduction MARIAN
MARIAN Mobile Agents for Routing In Ad-hoc Networks Nikos Migas PhD student 2 nd Year, School of Computing, Napier University n.migas@napier.ac.uk Supervisors: W.Buchanan, K.McArtney Introduction MARIAN
Customer Guide to Cisco JTAPI- BiB Integrations. March
 Customer Guide to Cisco JTAPI- BiB Integrations March 2017 www.incontact.com Introduction Customer Guide to Cisco JTAPI-BiB Integrations Version: This guide should be used with NICE Uptivity (formerly
Customer Guide to Cisco JTAPI- BiB Integrations March 2017 www.incontact.com Introduction Customer Guide to Cisco JTAPI-BiB Integrations Version: This guide should be used with NICE Uptivity (formerly
CounterACT DHCP Classifier Plugin
 CounterACT DHCP Classifier Plugin Version 2.0.7 and Above Table of Contents About the CounterACT DHCP Classifier Plugin... 3 What to Do... 3 Requirements... 4 Install the Plugin... 4 Concepts, Components,
CounterACT DHCP Classifier Plugin Version 2.0.7 and Above Table of Contents About the CounterACT DHCP Classifier Plugin... 3 What to Do... 3 Requirements... 4 Install the Plugin... 4 Concepts, Components,
CrossMount MediaTek White Paper April2015
 MediaTek White Paper April2015 2015 MediaTek Inc. Technology Introducing is a new MediaTek technology that simplifies hardware and software resource sharing between different consumer devices. Designed
MediaTek White Paper April2015 2015 MediaTek Inc. Technology Introducing is a new MediaTek technology that simplifies hardware and software resource sharing between different consumer devices. Designed
IEEE C /26. IEEE Working Group on Mobile Broadband Wireless Access <http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/802/20/>
 2003-03-09 IEEE C802.20-03/26 Project Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.20 Working Group on Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Architectural Attributes of an IP-based
2003-03-09 IEEE C802.20-03/26 Project Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.20 Working Group on Mobile Broadband Wireless Access Architectural Attributes of an IP-based
Browsing the World in the Sensors Continuum. Franco Zambonelli. Motivations. all our everyday objects all our everyday environments
 Browsing the World in the Sensors Continuum Agents and Franco Zambonelli Agents and Motivations Agents and n Computer-based systems and sensors will be soon embedded in everywhere all our everyday objects
Browsing the World in the Sensors Continuum Agents and Franco Zambonelli Agents and Motivations Agents and n Computer-based systems and sensors will be soon embedded in everywhere all our everyday objects
Project: IEEE P Task Group for Wireless Smart Sensors
 Project: IEEE P1451.5 Task Group for Wireless Smart Sensors Title: [Industrial Sensing Applications] Date Submitted: [23 Sep, 2002] Source: [Kenneth D. Cornett] Company: [Motorola, Inc.] Address: [8000
Project: IEEE P1451.5 Task Group for Wireless Smart Sensors Title: [Industrial Sensing Applications] Date Submitted: [23 Sep, 2002] Source: [Kenneth D. Cornett] Company: [Motorola, Inc.] Address: [8000
A Ubiquitous Web Services Framework for Interoperability in Pervasive Environments
 A Ubiquitous Web Services Framework for Interoperability in Pervasive Environments Hyung-Jun Yim and Kyu-Chul Lee * Dept. of Computer Engineering, Chungnam National University 220 Gung-Dong, Yuseong-Gu,
A Ubiquitous Web Services Framework for Interoperability in Pervasive Environments Hyung-Jun Yim and Kyu-Chul Lee * Dept. of Computer Engineering, Chungnam National University 220 Gung-Dong, Yuseong-Gu,
DS 2009: middleware. David Evans
 DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
DS 2009: middleware David Evans de239@cl.cam.ac.uk What is middleware? distributed applications middleware remote calls, method invocations, messages,... OS comms. interface sockets, IP,... layer between
Foreword xxiii Preface xxvii IPv6 Rationale and Features
 Contents Foreword Preface xxiii xxvii 1 IPv6 Rationale and Features 1 1.1 Internet Growth 1 1.1.1 IPv4 Addressing 1 1.1.2 IPv4 Address Space Utilization 3 1.1.3 Network Address Translation 5 1.1.4 HTTP
Contents Foreword Preface xxiii xxvii 1 IPv6 Rationale and Features 1 1.1 Internet Growth 1 1.1.1 IPv4 Addressing 1 1.1.2 IPv4 Address Space Utilization 3 1.1.3 Network Address Translation 5 1.1.4 HTTP
one.world Towards a System Architecture for Pervasive Computing
 Towards a System Architecture for Pervasive Computing Robert Grimm, Janet Davis, Ben Hendrickson, Eric Lemar, Tom Anderson, Brian Bershad, Gaetano Borriello, David Wetherall University of Washington Vision
Towards a System Architecture for Pervasive Computing Robert Grimm, Janet Davis, Ben Hendrickson, Eric Lemar, Tom Anderson, Brian Bershad, Gaetano Borriello, David Wetherall University of Washington Vision
Chapter 5 INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE AGENT
 Chapter 5 INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE AGENT 135 Chapter 5 Introductions to Mobile Agent 5.1 Mobile agents What is an agent? In fact a software program is containing an intelligence to help users and take action
Chapter 5 INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE AGENT 135 Chapter 5 Introductions to Mobile Agent 5.1 Mobile agents What is an agent? In fact a software program is containing an intelligence to help users and take action
Galaxy TabPro S Guidance for Custom OS installation
 Galaxy TabPro S Guidance for Custom OS installation Contents Galaxy TabPro S Guidance for Custom OS installation... 1 Pre-conditions for Customers Deployment Scenario... 2 Support for PXE boot... 2 Details...
Galaxy TabPro S Guidance for Custom OS installation Contents Galaxy TabPro S Guidance for Custom OS installation... 1 Pre-conditions for Customers Deployment Scenario... 2 Support for PXE boot... 2 Details...
Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services
 Q&A Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services Q. What are Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services? A. Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services are a modular security service that extends the Cisco
Q&A Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services Q. What are Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services? A. Cisco ASA Next-Generation Firewall Services are a modular security service that extends the Cisco
Internet ITS. ITABASHI, Tatsuo Leader, Network Platform SIG Internet ITS Consortium (IIC)
 Internet ITS ITABASHI, Tatsuo Leader, Network Platform SIG Internet ITS Consortium (IIC) TOC 1. Introduction 2. IIC 3. SIG 4. NW Platform SIG 5. Approaches 6. FY2005 1. Introduction 1.1 Mobile e-commerce
Internet ITS ITABASHI, Tatsuo Leader, Network Platform SIG Internet ITS Consortium (IIC) TOC 1. Introduction 2. IIC 3. SIG 4. NW Platform SIG 5. Approaches 6. FY2005 1. Introduction 1.1 Mobile e-commerce
WhamTech SmartData Fabric Healthcare Configurable FHIR REST APIs
 WhamTech SmartData Fabric Healthcare Configurable FHIR REST APIs March 2017 (Best viewed in slideshow mode) Revision 1.2 Copyright 2017 WhamTech, Inc. 1 Challenges facing interoperability in healthcare
WhamTech SmartData Fabric Healthcare Configurable FHIR REST APIs March 2017 (Best viewed in slideshow mode) Revision 1.2 Copyright 2017 WhamTech, Inc. 1 Challenges facing interoperability in healthcare
UML Robotics: SUBTLE MURI. Dan Brooks, Abe Shultz, Holly Yanco University of Massachusetts Lowell
 UML Robotics: SUBTLE MURI Dan Brooks, Abe Shultz, Holly Yanco University of Massachusetts Lowell Funded by the Army Research Office SUBTLE Pipeline Parsing, Semantics, Pragmatics Parsing Separates parts
UML Robotics: SUBTLE MURI Dan Brooks, Abe Shultz, Holly Yanco University of Massachusetts Lowell Funded by the Army Research Office SUBTLE Pipeline Parsing, Semantics, Pragmatics Parsing Separates parts
Evaluation of Electronic Guidebook Mobile Web Resources
 Evaluation of Electronic Guidebook Mobile Web Resources Executive Summary The Electronic Guidebook research project began in 1998 at The Exploratorium, an interactive science museum in San Francisco, in
Evaluation of Electronic Guidebook Mobile Web Resources Executive Summary The Electronic Guidebook research project began in 1998 at The Exploratorium, an interactive science museum in San Francisco, in
An Introduction to the Intelligent IoT Integrator (I3)
 An Introduction to the Intelligent IoT Integrator (I3) Bhaskar Krishnamachari Professor of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Director, Center for Cyber-Physical Systems and the Internet of Things
An Introduction to the Intelligent IoT Integrator (I3) Bhaskar Krishnamachari Professor of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Director, Center for Cyber-Physical Systems and the Internet of Things
DOE Award number: Name of recipient: Project Title: Principal investigator: Date of Report: Period covered by the report:
 Progress Report DOE Award number: DE-SC0004909 Name of recipient: University of Massachusetts, Dartmouth Project Title: Coordinated Multi-layer Multi-domain Optical Network (COMMON) for Large- Scale Science
Progress Report DOE Award number: DE-SC0004909 Name of recipient: University of Massachusetts, Dartmouth Project Title: Coordinated Multi-layer Multi-domain Optical Network (COMMON) for Large- Scale Science
ALPR to Milestone Integration. User Ma
 C2P ALPR ALPR to Milestone Integration User Ma Page 1 Contents Overview... 3 Introduction... 3 Critical features include:... 4 Installation... 5 Figure 1... 5 Pre-install requirements... 6 Installation
C2P ALPR ALPR to Milestone Integration User Ma Page 1 Contents Overview... 3 Introduction... 3 Critical features include:... 4 Installation... 5 Figure 1... 5 Pre-install requirements... 6 Installation
5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach
 5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach Main Points Why distributed objects Distributed Object design points Java RMI Dynamic Code Loading 5.1 What s an Object? An Object is an autonomous entity having
5 Distributed Objects: The Java Approach Main Points Why distributed objects Distributed Object design points Java RMI Dynamic Code Loading 5.1 What s an Object? An Object is an autonomous entity having
Web Services for Geospatial Mobile AR
 Web Services for Geospatial Mobile AR Introduction Christine Perey PEREY Research & Consulting cperey@perey.com Many popular mobile applications already use the smartphone s built-in sensors and receivers
Web Services for Geospatial Mobile AR Introduction Christine Perey PEREY Research & Consulting cperey@perey.com Many popular mobile applications already use the smartphone s built-in sensors and receivers
CSE 535 Mobile Computing. An Overview of Mobile Computing: Part I Motivation and Challenges
 CSE 535 Mobile Computing An Overview of Mobile Computing: Part I Motivation and Challenges Georgios Varsamopoulos School of Computing and Informatics Arizona State University 2 Mobile Computing The need
CSE 535 Mobile Computing An Overview of Mobile Computing: Part I Motivation and Challenges Georgios Varsamopoulos School of Computing and Informatics Arizona State University 2 Mobile Computing The need
Contents. UBWALL, ubiquitous wall changes an ordinary wall into the smart ambience
 14 Oct. 2005 UBWALL, ubiquitous wall changes an ordinary wall into the smart ambience Minoru Sekiguchi FUJITSU LABORATORIES LTD. Contents Introduction What is UBWALL? Simple Demo Sample Scenario Discussion
14 Oct. 2005 UBWALL, ubiquitous wall changes an ordinary wall into the smart ambience Minoru Sekiguchi FUJITSU LABORATORIES LTD. Contents Introduction What is UBWALL? Simple Demo Sample Scenario Discussion
Prottoy: A Middleware for Sentient Environment
 Prottoy: A Middleware for Sentient Environment Fahim Kawsar, Kaori Fujinami and Tatsuo Nakajima Department of Computer Science, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan. {fahim,fujinami, tatsuo}@dcl.info.waseda.ac.jp
Prottoy: A Middleware for Sentient Environment Fahim Kawsar, Kaori Fujinami and Tatsuo Nakajima Department of Computer Science, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan. {fahim,fujinami, tatsuo}@dcl.info.waseda.ac.jp
Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms
 Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms Chapter 01 (version September 5, 2007) Maarten van Steen Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Faculty of Science Dept. Mathematics and Computer Science Room R4.20.
Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms Chapter 01 (version September 5, 2007) Maarten van Steen Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Faculty of Science Dept. Mathematics and Computer Science Room R4.20.
Chapter 12 Network Protocols
 Chapter 12 Network Protocols 1 Outline Protocol: Set of defined rules to allow communication between entities Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Transmission Control Protocol/Internetworking Protocol (TCP/IP)
Chapter 12 Network Protocols 1 Outline Protocol: Set of defined rules to allow communication between entities Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Transmission Control Protocol/Internetworking Protocol (TCP/IP)
The RUNES Middleware System
 The Middleware System The EU Project Paolo Costa, Luca Mottola, Gian Pietro Picco Dip. Di Elettronica ed Informazione Politecnico di Milano Geoff Coulson Department of Computing Lancaster University Cecilia
The Middleware System The EU Project Paolo Costa, Luca Mottola, Gian Pietro Picco Dip. Di Elettronica ed Informazione Politecnico di Milano Geoff Coulson Department of Computing Lancaster University Cecilia
ForeScout CounterACT. Configuration Guide. Version 1.8
 ForeScout CounterACT Network Module: Wireless Plugin Version 1.8 Table of Contents About the Wireless Plugin... 4 Wireless Network Access Device Terminology... 6 How It Works... 6 About WLAN Controller/Lightweight
ForeScout CounterACT Network Module: Wireless Plugin Version 1.8 Table of Contents About the Wireless Plugin... 4 Wireless Network Access Device Terminology... 6 How It Works... 6 About WLAN Controller/Lightweight
Smart Call Home Deploying thetransport Gateway on Cisco Unified Computing System and Red Hat Linux
 Deployment Guide Smart Call Home Deploying thetransport Gateway on Cisco Unified Computing System and Red Hat Linux Deployment Guide For further information, questions and comments please contact ask-smart-services@cisco.com
Deployment Guide Smart Call Home Deploying thetransport Gateway on Cisco Unified Computing System and Red Hat Linux Deployment Guide For further information, questions and comments please contact ask-smart-services@cisco.com
Cisco Service Advertisement Framework Deployment Guide
 Cisco Service Advertisement Framework Deployment Guide What You Will Learn Cisco Service Advertisement Framework (SAF) is a network-based, scalable, bandwidth-efficient approach to service advertisement
Cisco Service Advertisement Framework Deployment Guide What You Will Learn Cisco Service Advertisement Framework (SAF) is a network-based, scalable, bandwidth-efficient approach to service advertisement
SOFTWARE TESTING FOR WIRELESS MOBILE COMPUTING ICHIRO SATOH, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF INFORMATICS
 APPLICATIONS AND SERVICES FOR THE B3G/4G ERA SOFTWARE TESTING FOR WIRELESS MOBILE COMPUTING ICHIRO SATOH, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF INFORMATICS N B LAN Control C LA To construct correct software to run in
APPLICATIONS AND SERVICES FOR THE B3G/4G ERA SOFTWARE TESTING FOR WIRELESS MOBILE COMPUTING ICHIRO SATOH, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF INFORMATICS N B LAN Control C LA To construct correct software to run in
Distributed Embedded Systems with AmbiComp
 Motivation Hardware Software Eclipse Plugin Conclusion Distributed Embedded Systems with AmbiComp Johannes Eickhold jeick@so.in.tum.de Self-Organizing Systems Group Faculty of Informatics TU Munich June
Motivation Hardware Software Eclipse Plugin Conclusion Distributed Embedded Systems with AmbiComp Johannes Eickhold jeick@so.in.tum.de Self-Organizing Systems Group Faculty of Informatics TU Munich June
KillTest *KIJGT 3WCNKV[ $GVVGT 5GTXKEG Q&A NZZV ]]] QORRZKYZ IUS =K ULLKX LXKK [VJGZK YKX\OIK LUX UTK _KGX
![KillTest *KIJGT 3WCNKV[ $GVVGT 5GTXKEG Q&A NZZV ]]] QORRZKYZ IUS =K ULLKX LXKK [VJGZK YKX\OIK LUX UTK _KGX KillTest *KIJGT 3WCNKV[ $GVVGT 5GTXKEG Q&A NZZV ]]] QORRZKYZ IUS =K ULLKX LXKK [VJGZK YKX\OIK LUX UTK _KGX](/thumbs/95/125553791.jpg) KillTest Q&A Exam : 70-401 Title : MS System Center Configuration Manager2007, Configuring Version : Demo 1 / 7 1.You have a System Center Configuration Manager 2007 environment. A new branch office needs
KillTest Q&A Exam : 70-401 Title : MS System Center Configuration Manager2007, Configuring Version : Demo 1 / 7 1.You have a System Center Configuration Manager 2007 environment. A new branch office needs
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 0B0-105 Title : BEA8.1 Certified Architect:Enterprise Architecture Vendors
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 0B0-105 Title : BEA8.1 Certified Architect:Enterprise Architecture Vendors
Managing and Securing Computer Networks. Guy Leduc. Chapter 2: Software-Defined Networks (SDN) Chapter 2. Chapter goals:
 Managing and Securing Computer Networks Guy Leduc Chapter 2: Software-Defined Networks (SDN) Mainly based on: Computer Networks and Internets, 6 th Edition Douglas E. Comer Pearson Education, 2015 (Chapter
Managing and Securing Computer Networks Guy Leduc Chapter 2: Software-Defined Networks (SDN) Mainly based on: Computer Networks and Internets, 6 th Edition Douglas E. Comer Pearson Education, 2015 (Chapter
Ad Hoc Networks - Applications and System Design
 Ad Hoc Networks - Applications and System Design Prof Sanjay Srivastava DA-IICT, Gandhinagar Modelling and Analysis Group of NeTworks (MAGNeT) Two day workshop on Ad Hoc Networks: Design, Applications,
Ad Hoc Networks - Applications and System Design Prof Sanjay Srivastava DA-IICT, Gandhinagar Modelling and Analysis Group of NeTworks (MAGNeT) Two day workshop on Ad Hoc Networks: Design, Applications,
Panel 1 Service Platform and Network Infrastructure for Ubiquitous Services
 Panel 1 Platform and Network Infrastructure for Ubiquitous s Wolfgang Kellerer DoCoMo Euro-Labs Munich, Germany WWRF WG2 ( Architecture) Vice Chair DoCoMo Communications Landsberger Str. 312 80687 Munich
Panel 1 Platform and Network Infrastructure for Ubiquitous s Wolfgang Kellerer DoCoMo Euro-Labs Munich, Germany WWRF WG2 ( Architecture) Vice Chair DoCoMo Communications Landsberger Str. 312 80687 Munich
Cisco Virtual Networking Solution for OpenStack
 Data Sheet Cisco Virtual Networking Solution for OpenStack Product Overview Extend enterprise-class networking features to OpenStack cloud environments. A reliable virtual network infrastructure that provides
Data Sheet Cisco Virtual Networking Solution for OpenStack Product Overview Extend enterprise-class networking features to OpenStack cloud environments. A reliable virtual network infrastructure that provides
Adaptive Spatiotemporal Node Selection in Dynamic Networks
 Adaptive Spatiotemporal Node Selection in Dynamic Networks Pradip Hari, John B. P. McCabe, Jonathan Banafato, Marcus Henry, Ulrich Kremer, Dept. of Computer Science, Rutgers University Kevin Ko, Emmanouil
Adaptive Spatiotemporal Node Selection in Dynamic Networks Pradip Hari, John B. P. McCabe, Jonathan Banafato, Marcus Henry, Ulrich Kremer, Dept. of Computer Science, Rutgers University Kevin Ko, Emmanouil
Outline. CS5984 Mobile Computing. Host Mobility Problem 1/2. Host Mobility Problem 2/2. Host Mobility Problem Solutions. Network Layer Solutions Model
 CS5984 Mobile Computing Outline Host Mobility problem and solutions IETF Mobile IPv4 Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia Tech Mobile IPv4 1 2 Host Mobility Problem 1/2 Host Mobility
CS5984 Mobile Computing Outline Host Mobility problem and solutions IETF Mobile IPv4 Dr. Ayman Abdel-Hamid Computer Science Department Virginia Tech Mobile IPv4 1 2 Host Mobility Problem 1/2 Host Mobility
Mesh Network. Kiran Mathews Seminar: Verteilte und vernetzte Systeme
 Mesh Network Kiran Mathews (kmathews@rhrk.uni-kl.de) Seminar: Verteilte und vernetzte Systeme February 8, 2016 Outline 1 Why Mesh Networks? Existing System imesh 2 Architectural Overview Frame Structure
Mesh Network Kiran Mathews (kmathews@rhrk.uni-kl.de) Seminar: Verteilte und vernetzte Systeme February 8, 2016 Outline 1 Why Mesh Networks? Existing System imesh 2 Architectural Overview Frame Structure
