Amplifying. Examples
|
|
|
- Rodger Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Amplifying Allows temporary increase of privileges Needed for modular programming Module pushes, pops data onto stack module stack endmodule. Variable x declared of type stack var x: module; Only stack module can alter, read x So process doesn t get capability, but needs it when x is referenced??? May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #1 Examples HYDRA: templates Associated with each procedure, function in module Adds rights to process capability while the procedure or function is being executed Rights deleted on exit Intel iapx 432: access descriptors for objects These are really capabilities 1 bit in this controls amplification When ADT constructed, permission bits of type control object set to what procedure needs On call, if amplification bit in this permission is set, the above bits or ed with rights in access descriptor of object being passed May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #2 1
2 Revocation Scan all C-lists, remove relevant capabilities Far too expensive! Use indirection Each object has entry in a global object table Names in capabilities name the entry, not the object To revoke, zap the entry in the table Can have multiple entries for a single object to allow control of different sets of rights and/or groups of users for each object Example: Amoeba: owner requests server change random number in server table All capabilities for that object now invalid May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #3 Limits Problems if you don t control copying of capabilities Heidi (High) C-List r*lough Lough (Low) rw*lough Lou (Low) C-List rw*lough Heidi (High) C-List r*lough Lough (Low) rw*lough rw*lough Lou (Low) C-List rw*lough The capability to write file lough is Low, and Heidi is High so she reads (copies) the capability; now she can write to a Low file, violating the *-property! May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #4 2
3 Remedies Label capability itself Rights in capability depends on relation between its compartment and that of object to which it refers In example, as as capability copied to High, and High dominates object compartment (Low), write right removed Check to see if passing capability violates security properties In example, it does, so copying refused Distinguish between read and copy capability Take-Grant Protection Model does this ( read, take ) May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #5 ACLs vs. Capabilities Both theoretically equivalent; consider 2 questions 1. Given a subject, what objects can it access, and how? 2. Given an object, what subjects can access it, and how? ACLs answer second easily; C-Lists, first Suggested that the second question, which in the past has been of most interest, is the reason ACLbased systems more common than capabilitybased systems As first question becomes more important (in incident response, for example), this may change May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #6 3
4 Locks and Keys Associate information (lock) with object, information (key) with subject Latter controls what the subject can access and how Subject presents key; if it corresponds to any of the locks on the object, access granted This can be dynamic ACLs, C-Lists static and must be manually changed Locks and keys can change based on system constraints, other factors (not necessarily manual) May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #7 Cryptographic Implementation Enciphering key is lock; deciphering key is key Encipher object o; store E k (o) Use subject s key to compute D k (E k (o)) Any of n can access o: store ó = (E 1 (o),, E n (o)) Requires consent of all n to access o: store ó = (E 1 (E 2 ( (E n (o)) )) May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #8 4
5 Example: IBM IBM 370: process gets access key; pages get storage key and fetch bit Fetch bit clear: read access only Fetch bit set, access key 0: process can write to (any) page Fetch bit set, access key matches storage key: process can write to page Fetch bit set, access key non-zero and does not match storage key: no access allowed May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #9 Example: Cisco Router Dynamic access control lists access-list 100 permit tcp any host eq telnet access-list 100 dynamic test timeout 180 permit ip any host \ time-range my-time time-range my-time periodic weekdays 9:00 to 17:00 line vty 0 2 login local autocommand access-enable host timeout 10 Limits external access to to 9AM 5PM Adds temporary entry for connecting host once user supplies name, password to router Connections good for 180 minutes Drops access control entry after that May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #10 5
6 Type Checking Lock is type, key is operation Example: UNIX system call write can t work on directory object but does work on file Example: split I&D space of PDP-11 Example: countering buffer overflow attacks on the stack by putting stack on nonexecutable pages/segments Then code uploaded to buffer won t execute Does not stop other forms of this attack, though May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #11 More Examples LOCK system: Compiler produces data Trusted process must change this type to executable becore program can be executed Sidewinder firewall Subjects assigned domain, objects assigned type Example: ingress packets get one type, egress packets another All actions controlled by type, so ingress packets cannot masquerade as egress packets (and vice versa) May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #12 6
7 Ring-Based Access Control Privileges increase 0 1 n Process (segment) accesses another segment Read Execute Gate is an entry point for calling segment Rights: r read w write a append e execute May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #13 Reading/Writing/Appending Procedure executing in ring r Data segment with access bracket (a 1, a 2 ) Mandatory access rule r a 1 allow access a 1 < r a 2 allow r access; not w, a access a 2 < r deny all access May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #14 7
8 Executing Procedure executing in ring r Call procedure in segment with access bracket (a 1, a 2 ) and call bracket (a 2, a 3 ) Mandatory access rule r < a 1 allow access; ring-crossing fault a 1 r a 2 allow access; no ring-crossing fault a 2 < r a 3 allow access if through valid gate a 3 < r deny all access May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #15 Versions Multics 8 rings (from 0 to 7) Digital Equipment s VAX 4 levels of privilege: user, monitor, executive, kernel Older systems 2 levels of privilege: user, supervisor May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #16 8
9 PACLs Propagated Access Control List Implements ORGON Creator kept with PACL, copies Only owner can change PACL Subject reads object: object s PACL associated with subject Subject writes object: subject s PACL associated with object Notation: PACL s means s created object; PACL(e) is PACL associated with entity e May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #17 Multiple Creators Betty reads Ann s file dates PACL(Betty) = PACL Betty PACL(dates) = PACL Betty PACL Ann Betty creates file dc PACL(dc) = PACL Betty PACL Ann PACL Betty allows Char to access objects, but PACL Ann does not; both allow June to access objects June can read dc Char cannot read dc May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #18 9
10 Key Points Access control mechanisms provide controls for users accessing files Many different forms ACLs, capabilities, locks and keys Type checking too Ring-based mechanisms (Mandatory) PACLs (ORCON) May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #19 Overview Trust Problems from lack of assurance Types of assurance Life cycle and assurance Waterfall life cycle model Other life cycle models May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #20 10
11 Trust Trustworthy entity has sufficient credible evidence leading one to believe that the system will meet a set of requirements Trust is a measure of trustworthiness relying on the evidence Assurance is confidence that an entity meets its security requirements based on evidence provided by applying assurance techniques May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #21 Relationships Policy Assurance Mechanisms Statement of requirements that explicitly defines the security expectations of the mechanism(s) Provides justification that the mechanism meets policy through assurance evidence and approvals based on evidence Executable entities that are designed and implemented to meet the requirements of the policy May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #22 11
12 Problem Sources 1. Requirements definitions, omissions, and mistakes 2. System design flaws 3. Hardware implementation flaws, such as wiring and chip flaws 4. Software implementation errors, program bugs, and compiler bugs 5. System use and operation errors and inadvertent mistakes 6. Willful system misuse 7. Hardware, communication, or other equipment malfunction 8. Environmental problems, natural causes, and acts of God 9. Evolution, maintenance, faulty upgrades, and decommissions May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #23 Examples Challenger explosion Sensors removed from booster rockets to meet accelerated launch schedule Deaths from faulty radiation therapy system Hardware safety interlock removed Flaws in software design Bell V22 Osprey crashes Failure to correct for malfunctioning components; two faulty ones could outvote a third Intel 486 chip May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #24 12
13 Role of Requirements Requirements are statements of goals that must be met Vary from high-level, generic issues to lowlevel, concrete issues Security objectives are high-level security issues Security requirements are specific, concrete issues May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #25 Types of Assurance Policy assurance is evidence establishing security requirements in policy is complete, consistent, technically sound Design assurance is evidence establishing design sufficient to meet requirements of security policy Implementation assurance is evidence establishing implementation consistent with security requirements of security policy May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #26 13
14 Types of Assurance Operational assurance is evidence establishing system sustains the security policy requirements during installation, configuration, and day-to-day operation Also called administrative assurance May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #27 Life Cycle Assurance justification Security requirements 2 4 Design 1 3 Implementation Design and implementation refinement May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #28 14
15 Life Cycle Conception Manufacture Deployment Fielded Product Life May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #29 Conception Idea Decisions to pursue it Proof of concept See if idea has merit High-level requirements analysis What does secure mean for this concept? Is it possible for this concept to meet this meaning of security? Is the organization willing to support the additional resources required to make this concept meet this meaning of security? May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #30 15
16 Manufacture Develop detailed plans for each group involved May depend on use; internal product requires no sales Implement the plans to create entity Includes decisions whether to proceed, for example due to market needs May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #31 Deployment Delivery Assure that correct masters are delivered to production and protected Distribute to customers, sales organizations Installation and configuration May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #32 16
17 Fielded Product Life Routine maintenance, patching Responsibility of engineering in small organizations Responsibility may be in different group than one that manufactures product Customer service, support organizations Retirement or decommission of product May 25, 2004 ECS 235 Slide #33 17
Amplifying. Only stack module can alter, read x So process doesn t get capability, but needs it when x is referenced a problem!
 Amplifying Allows temporary increase of privileges Needed for modular programming Module pushes, pops data onto stack module stack endmodule. Variable x declared of type stack var x: module; Only stack
Amplifying Allows temporary increase of privileges Needed for modular programming Module pushes, pops data onto stack module stack endmodule. Variable x declared of type stack var x: module; Only stack
Access Control Mechanisms
 Access Control Mechanisms Chapter 16 Version 1.0 Computer Security: Art and Science, 2 nd Edition Slide 16-1 Overview Access control lists Capability lists Locks and keys Secret sharing Rings-based access
Access Control Mechanisms Chapter 16 Version 1.0 Computer Security: Art and Science, 2 nd Edition Slide 16-1 Overview Access control lists Capability lists Locks and keys Secret sharing Rings-based access
Introduction to Assurance
 Introduction to Assurance Overview Why assurance? Trust and assurance Life cycle and assurance April 1, 2015 Slide #1 Overview Trust Problems from lack of assurance Types of assurance Life cycle and assurance
Introduction to Assurance Overview Why assurance? Trust and assurance Life cycle and assurance April 1, 2015 Slide #1 Overview Trust Problems from lack of assurance Types of assurance Life cycle and assurance
L17: Assurance. Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806
 L17: Assurance Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806 11/06/2015 CSCI 451 - Fall 2015 1 Acknowledgement Many slides are from or are revised
L17: Assurance Hui Chen, Ph.D. Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science Virginia State University Petersburg, VA 23806 11/06/2015 CSCI 451 - Fall 2015 1 Acknowledgement Many slides are from or are revised
Application Layer. Presentation Layer. Session Layer. Transport Layer. Network Layer. Data Link Layer. Physical Layer
 ISO/OSI Model SSL: Security at Transport Layer Application Layer Peer-to-peer Application Layer Network Security Assurance Presentation Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer
ISO/OSI Model SSL: Security at Transport Layer Application Layer Peer-to-peer Application Layer Network Security Assurance Presentation Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer
Chapter 14: Protection. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 14: Protection Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 14: Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection Domain of Protection Access Matrix Implementation of Access Matrix Access
Chapter 14: Protection Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 14: Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection Domain of Protection Access Matrix Implementation of Access Matrix Access
Chapter 13: Protection. Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition
 Chapter 13: Protection Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 13: Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection Domain of Protection Access
Chapter 13: Protection Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 13: Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection Domain of Protection Access
Last time. Security Policies and Models. Trusted Operating System Design. Bell La-Padula and Biba Security Models Information Flow Control
 Last time Security Policies and Models Bell La-Padula and Biba Security Models Information Flow Control Trusted Operating System Design Design Elements Security Features 10-1 This time Trusted Operating
Last time Security Policies and Models Bell La-Padula and Biba Security Models Information Flow Control Trusted Operating System Design Design Elements Security Features 10-1 This time Trusted Operating
Advanced Systems Security: Multics
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
May 1: Integrity Models
 May 1: Integrity Models Biba Clark-Wilson Comparison Trust models May 1, 2017 ECS 235B Spring Quarter 2017 Slide #1 Integrity Overview Requirements Very different than confidentiality policies Biba s models
May 1: Integrity Models Biba Clark-Wilson Comparison Trust models May 1, 2017 ECS 235B Spring Quarter 2017 Slide #1 Integrity Overview Requirements Very different than confidentiality policies Biba s models
Cisco CCNA ACL Part II
 Cisco CCNA ACL Part II Cisco CCNA Access List Applications This slide illustrates common uses for IP access lists. While this chapter focuses on IP access lists, the concept of access lists as mechanisms
Cisco CCNA ACL Part II Cisco CCNA Access List Applications This slide illustrates common uses for IP access lists. While this chapter focuses on IP access lists, the concept of access lists as mechanisms
CS 392/681 - Computer Security. Module 5 Access Control: Concepts and Mechanisms
 CS 392/681 - Computer Security Module 5 Access Control: Concepts and Mechanisms Course Policies and Logistics Midterm next Thursday!!! Read Chapter 2 and 15 of text 10/15/2002 Module 5 - Access Control
CS 392/681 - Computer Security Module 5 Access Control: Concepts and Mechanisms Course Policies and Logistics Midterm next Thursday!!! Read Chapter 2 and 15 of text 10/15/2002 Module 5 - Access Control
Access Control Lists (Beyond Standard and Extended)
 Access Control Lists (Beyond Standard and Extended) www.ine.com Course Prerequisites and Assumptions» Prerequisite = CCNA ACL Videos» ACLs are used as a classification tool by many different features this
Access Control Lists (Beyond Standard and Extended) www.ine.com Course Prerequisites and Assumptions» Prerequisite = CCNA ACL Videos» ACLs are used as a classification tool by many different features this
Process Description and Control. Chapter 3
 Process Description and Control Chapter 3 Contents Process states Process description Process control Unix process management Process From processor s point of view execute instruction dictated by program
Process Description and Control Chapter 3 Contents Process states Process description Process control Unix process management Process From processor s point of view execute instruction dictated by program
Operating Systems Security Access Control
 Authorization and access control Operating Systems Security Access Control Ozalp Babaoglu From authentication to authorization Once subjects have been authenticated, the next problem to confront is authorization
Authorization and access control Operating Systems Security Access Control Ozalp Babaoglu From authentication to authorization Once subjects have been authenticated, the next problem to confront is authorization
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security. Module: Operating System Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Operating System Security Professor Trent Jaeger 1 OS Security An secure OS should provide (at least) the following mechanisms Memory protection
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Operating System Security Professor Trent Jaeger 1 OS Security An secure OS should provide (at least) the following mechanisms Memory protection
CS 392/681 - Computer Security. Module 6 Access Control: Concepts and Mechanisms
 CS 392/681 - Computer Security Module 6 Access Control: Concepts and Mechanisms Course Policies and Logistics Midterm grades Thursday. Read Chapter 2 and 15 th of text Lab 4 postponed - due next week.
CS 392/681 - Computer Security Module 6 Access Control: Concepts and Mechanisms Course Policies and Logistics Midterm grades Thursday. Read Chapter 2 and 15 th of text Lab 4 postponed - due next week.
Architectural Support for A More Secure Operating System
 Architectural Support for A More Secure Operating System Edward L. Bosworth, Ph.D. TSYS Department of Computer Science Columbus State University Columbus, GA A Few Comments The term Secure Operating System
Architectural Support for A More Secure Operating System Edward L. Bosworth, Ph.D. TSYS Department of Computer Science Columbus State University Columbus, GA A Few Comments The term Secure Operating System
Operating systems and security - Overview
 Operating systems and security - Overview Protection in Operating systems Protected objects Protecting memory, files User authentication, especially passwords Trusted operating systems, security kernels,
Operating systems and security - Overview Protection in Operating systems Protected objects Protecting memory, files User authentication, especially passwords Trusted operating systems, security kernels,
Operating systems and security - Overview
 Operating systems and security - Overview Protection in Operating systems Protected objects Protecting memory, files User authentication, especially passwords Trusted operating systems, security kernels,
Operating systems and security - Overview Protection in Operating systems Protected objects Protecting memory, files User authentication, especially passwords Trusted operating systems, security kernels,
INFLUENTIAL OPERATING SYSTEM RESEARCH: SECURITY MECHANISMS AND HOW TO USE THEM CARSTEN WEINHOLD
 Faculty of Computer Science Institute of Systems Architecture, Operating Systems Group INFLUENTIAL OPERATING SYSTEM RESEARCH: SECURITY MECHANISMS AND HOW TO USE THEM CARSTEN WEINHOLD OVERVIEW Fundamental
Faculty of Computer Science Institute of Systems Architecture, Operating Systems Group INFLUENTIAL OPERATING SYSTEM RESEARCH: SECURITY MECHANISMS AND HOW TO USE THEM CARSTEN WEINHOLD OVERVIEW Fundamental
Process Description and Control. Major Requirements of an Operating System
 Process Description and Control Chapter 3 1 Major Requirements of an Operating System Interleave the execution of several processes to maximize processor utilization while providing reasonable response
Process Description and Control Chapter 3 1 Major Requirements of an Operating System Interleave the execution of several processes to maximize processor utilization while providing reasonable response
Major Requirements of an Operating System Process Description and Control
 Major Requirements of an Operating System Process Description and Control Chapter 3 Interleave the execution of several processes to maximize processor utilization while providing reasonable response time
Major Requirements of an Operating System Process Description and Control Chapter 3 Interleave the execution of several processes to maximize processor utilization while providing reasonable response time
Access Control. Discretionary Access Control
 Access Control Discretionary Access Control 1 Outlines Access Control Discretionary Access Control (DAC) Mandatory Access Control (MAC) Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) 2 Access Control Access control
Access Control Discretionary Access Control 1 Outlines Access Control Discretionary Access Control (DAC) Mandatory Access Control (MAC) Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) 2 Access Control Access control
Complex Access Control. Steven M. Bellovin September 10,
 Complex Access Control Steven M. Bellovin September 10, 2013 1 Access Control Matrix List all proceses and files in a matrix Each row is a process ( subject ) Each column is a file ( object ) Each matrix
Complex Access Control Steven M. Bellovin September 10, 2013 1 Access Control Matrix List all proceses and files in a matrix Each row is a process ( subject ) Each column is a file ( object ) Each matrix
Operating Systems Design Exam 3 Review: Spring 2011
 Operating Systems Design Exam 3 Review: Spring 2011 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 1. Why does an IP driver need to use ARP, the address resolution protocol? IP is a logical network. An IP address
Operating Systems Design Exam 3 Review: Spring 2011 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 1. Why does an IP driver need to use ARP, the address resolution protocol? IP is a logical network. An IP address
Operating Systems Design Exam 3 Review: Spring Paul Krzyzanowski
 Operating Systems Design Exam 3 Review: Spring 2012 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Question 1 An Ethernet device driver implements the: (a) Data Link layer. (b) Network layer. (c) Transport layer.
Operating Systems Design Exam 3 Review: Spring 2012 Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Question 1 An Ethernet device driver implements the: (a) Data Link layer. (b) Network layer. (c) Transport layer.
Operating System Control Structures
 Operating System Control Structures Information about the current status of each process and resource Tables are constructed for each entity the operating system manages 26 Memory Tables Allocation of
Operating System Control Structures Information about the current status of each process and resource Tables are constructed for each entity the operating system manages 26 Memory Tables Allocation of
Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security
 Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security CS 161: Computer Security Prof. Raluca Ada Popa January 17, 2016 Some slides credit to David Wagner and Nick Weaver Announcements Discussion sections and office
Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security CS 161: Computer Security Prof. Raluca Ada Popa January 17, 2016 Some slides credit to David Wagner and Nick Weaver Announcements Discussion sections and office
Firewall Configuration and Management Policy
 Firewall Configuration and Management Policy Version Date Change/s Author/s Approver/s 1.0 01/01/2013 Initial written policy. Kyle Johnson Dean of Information Services Executive Director for Compliance
Firewall Configuration and Management Policy Version Date Change/s Author/s Approver/s 1.0 01/01/2013 Initial written policy. Kyle Johnson Dean of Information Services Executive Director for Compliance
Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists)
 Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists) Feature History Release Modification Cisco IOS For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This chapter
Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists) Feature History Release Modification Cisco IOS For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This chapter
CSC 553 Operating Systems
 CSC 553 Operating Systems Lecture 12 - File Management Files Data collections created by users The File System is one of the most important parts of the OS to a user Desirable properties of files: Long-term
CSC 553 Operating Systems Lecture 12 - File Management Files Data collections created by users The File System is one of the most important parts of the OS to a user Desirable properties of files: Long-term
Process Description and Control
 Process Description and Control Chapter 3 Muhammad Adri, MT 1 Major Requirements of an Operating System Interleave the execution of several processes to maximize processor utilization while providing reasonable
Process Description and Control Chapter 3 Muhammad Adri, MT 1 Major Requirements of an Operating System Interleave the execution of several processes to maximize processor utilization while providing reasonable
IP Named Access Control Lists
 Access control lists (ACLs) perform packet filtering to control the movement of packets through a network. Packet filtering provides security by limiting the access of traffic into a network, restricting
Access control lists (ACLs) perform packet filtering to control the movement of packets through a network. Packet filtering provides security by limiting the access of traffic into a network, restricting
Test Conditions. Closed book, closed notes, no calculator, no laptop just brains 75 minutes. Steven M. Bellovin October 19,
 Test Conditions Closed book, closed notes, no calculator, no laptop just brains 75 minutes Steven M. Bellovin October 19, 2005 1 Form 8 questions I m not asking you to write programs or even pseudo-code
Test Conditions Closed book, closed notes, no calculator, no laptop just brains 75 minutes Steven M. Bellovin October 19, 2005 1 Form 8 questions I m not asking you to write programs or even pseudo-code
T Salausjärjestelmät (Cryptosystems) Introduction to the second part of the course. Outline. What we'll cover. Requirements and design issues
 T-110.470 Salausjärjestelmät (Cryptosystems) Requirements and design issues Introduction to the second part of the course 25.10.2004 1 3 Outline What we'll cover Introduction to the second part of the
T-110.470 Salausjärjestelmät (Cryptosystems) Requirements and design issues Introduction to the second part of the course 25.10.2004 1 3 Outline What we'll cover Introduction to the second part of the
Operating Systems. Week 13 Recitation: Exam 3 Preview Review of Exam 3, Spring Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University.
 Operating Systems Week 13 Recitation: Exam 3 Preview Review of Exam 3, Spring 2014 Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2015 April 22, 2015 2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Question 1 A weakness of using
Operating Systems Week 13 Recitation: Exam 3 Preview Review of Exam 3, Spring 2014 Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2015 April 22, 2015 2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Question 1 A weakness of using
CS 416: Operating Systems Design April 22, 2015
 Question 1 A weakness of using NAND flash memory for use as a file system is: (a) Stored data wears out over time, requiring periodic refreshing. Operating Systems Week 13 Recitation: Exam 3 Preview Review
Question 1 A weakness of using NAND flash memory for use as a file system is: (a) Stored data wears out over time, requiring periodic refreshing. Operating Systems Week 13 Recitation: Exam 3 Preview Review
IPv6 Access Control Lists
 Access lists determine what traffic is blocked and what traffic is forwarded at device interfaces and allow filtering of traffic based on source and destination addresses, and inbound and outbound traffic
Access lists determine what traffic is blocked and what traffic is forwarded at device interfaces and allow filtering of traffic based on source and destination addresses, and inbound and outbound traffic
Silberschatz and Galvin Chapter 19
 Silberschatz and Galvin Chapter 19 Protection CPSC 410--Richard Furuta 4/26/99 1 Protection Goals of protection schemes Domain of protection Mechanisms Ð access matrix implementation of access matrix revocation
Silberschatz and Galvin Chapter 19 Protection CPSC 410--Richard Furuta 4/26/99 1 Protection Goals of protection schemes Domain of protection Mechanisms Ð access matrix implementation of access matrix revocation
Access Control. Steven M. Bellovin September 13,
 Access Control Steven M. Bellovin September 13, 2016 1 Security Begins on the Host Even without a network, hosts must enforce the CIA trilogy Something on the host the operating system aided by the hardware
Access Control Steven M. Bellovin September 13, 2016 1 Security Begins on the Host Even without a network, hosts must enforce the CIA trilogy Something on the host the operating system aided by the hardware
Configuring IP Services
 This module describes how to configure optional IP services. For a complete description of the IP services commands in this chapter, refer to the Cisco IOS IP Application Services Command Reference. To
This module describes how to configure optional IP services. For a complete description of the IP services commands in this chapter, refer to the Cisco IOS IP Application Services Command Reference. To
Labels and Information Flow
 Labels and Information Flow Robert Soulé March 21, 2007 Problem Motivation and History The military cares about information flow Everyone can read Unclassified Few can read Top Secret Problem Motivation
Labels and Information Flow Robert Soulé March 21, 2007 Problem Motivation and History The military cares about information flow Everyone can read Unclassified Few can read Top Secret Problem Motivation
Influential OS Research Security. Michael Raitza
 Influential OS Research Security Michael Raitza raitza@os.inf.tu-dresden.de 1 Security recap Various layers of security Application System Communication Aspects of security Access control / authorization
Influential OS Research Security Michael Raitza raitza@os.inf.tu-dresden.de 1 Security recap Various layers of security Application System Communication Aspects of security Access control / authorization
CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Protection
 Objectives CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Protection last revised 9/5/12 1. To explain the use of two CPU modes as the basis for protecting privileged instructions and memory 2. To introduce basic protection
Objectives CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Protection last revised 9/5/12 1. To explain the use of two CPU modes as the basis for protecting privileged instructions and memory 2. To introduce basic protection
Chapter 9: Key Management
 Chapter 9: Key Management Session and Interchange Keys Key Exchange Cryptographic Key Infrastructure Storing and Revoking Keys Digital Signatures Slide #9-1 Overview Key exchange Session vs. interchange
Chapter 9: Key Management Session and Interchange Keys Key Exchange Cryptographic Key Infrastructure Storing and Revoking Keys Digital Signatures Slide #9-1 Overview Key exchange Session vs. interchange
Advanced Systems Security: Ordinary Operating Systems
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Implementing Firewall Technologies
 Implementing Firewall Technologies Network firewalls separate protected from non-protected areas preventing unauthorized users from accessing protected network resources. Technologies used: ACLs Standard,
Implementing Firewall Technologies Network firewalls separate protected from non-protected areas preventing unauthorized users from accessing protected network resources. Technologies used: ACLs Standard,
Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection principle of least privilege Domain Structure need to know principle
 Protection Discuss the goals and principles of protection in a modern computer system Explain how protection domains combined with an access matrix are used to specify the resources a process may access
Protection Discuss the goals and principles of protection in a modern computer system Explain how protection domains combined with an access matrix are used to specify the resources a process may access
Improving the Granularity of Access Control for Windows 2000
 Improving the Granularity of Access Control for Windows 2000 MICHAEL M. SWIFT and ANNE HOPKINS University of Washington and PETER BRUNDRETT, CLIFF VAN DYKE, PRAERIT GARG, SHANNON CHAN, MARIO GOERTZEL,
Improving the Granularity of Access Control for Windows 2000 MICHAEL M. SWIFT and ANNE HOPKINS University of Washington and PETER BRUNDRETT, CLIFF VAN DYKE, PRAERIT GARG, SHANNON CHAN, MARIO GOERTZEL,
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture. Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function CPU Structure CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Registers
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 11 CPU Structure and Function CPU Structure CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Registers
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions
 CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
Software Quality. What is Good Software?
 Software Quality CS A470 What is Good Software? Depends on your point of view Five perspectives Transcendental view. Quality can be recognized but hard to define User view. Fitness for purpose Often adopted
Software Quality CS A470 What is Good Software? Depends on your point of view Five perspectives Transcendental view. Quality can be recognized but hard to define User view. Fitness for purpose Often adopted
Condor Local File System Sandbox Requirements Document
 Condor Local File System Sandbox Requirements Document Requirements Document 1 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents 2 2 Introduction 3 3 Describing the problem space 3 4 Defining the project's scope
Condor Local File System Sandbox Requirements Document Requirements Document 1 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents 2 2 Introduction 3 3 Describing the problem space 3 4 Defining the project's scope
19.1. Security must consider external environment of the system, and protect it from:
 Module 19: Security The Security Problem Authentication Program Threats System Threats Securing Systems Intrusion Detection Encryption Windows NT 19.1 The Security Problem Security must consider external
Module 19: Security The Security Problem Authentication Program Threats System Threats Securing Systems Intrusion Detection Encryption Windows NT 19.1 The Security Problem Security must consider external
CompTIA SY CompTIA Security+
 CompTIA SY0-501 CompTIA Security+ https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/sy0-501 QUESTION: 338 The help desk is receiving numerous password change alerts from users in the accounting department. These
CompTIA SY0-501 CompTIA Security+ https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/sy0-501 QUESTION: 338 The help desk is receiving numerous password change alerts from users in the accounting department. These
Access Control List Enhancements on the Cisco Series Router
 Access Control List Enhancements on the Cisco 12000 Series Router Part Number, May 30, 2008 The Cisco 12000 series router filters IP packets using access control lists (ACLs) as a fundamental security
Access Control List Enhancements on the Cisco 12000 Series Router Part Number, May 30, 2008 The Cisco 12000 series router filters IP packets using access control lists (ACLs) as a fundamental security
Our Narrow Focus Computer Networking Security Vulnerabilities. Outline Part II
 Our Narrow Focus 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 22 Security: DOS Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 Yes: Creating a secure channel for communication (Part I) Protecting
Our Narrow Focus 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 22 Security: DOS Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 Yes: Creating a secure channel for communication (Part I) Protecting
Discretionary Vs. Mandatory
 Discretionary Vs. Mandatory Discretionary access controls (DAC) Privilege propagated from one subject to another Possession of an access right is sufficient to access the object Mandatory access controls
Discretionary Vs. Mandatory Discretionary access controls (DAC) Privilege propagated from one subject to another Possession of an access right is sufficient to access the object Mandatory access controls
IP Services Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 1 of 3: Addressing and Services IP1R-157
 Use the commands in this chapter to configure various IP services. For configuration information and examples on IP services, refer to the Configuring IP Services chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Configuration
Use the commands in this chapter to configure various IP services. For configuration information and examples on IP services, refer to the Configuring IP Services chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Configuration
CCM Lecture 12. Security Model 1: Bell-LaPadula Model
 CCM 4350 Lecture 12 Security Model 1: Bell-LaPadula Model Why Security Models? When we have implemented a security policy, do we know that it will (and can) be enforced? E.g., if policies get too intricate,
CCM 4350 Lecture 12 Security Model 1: Bell-LaPadula Model Why Security Models? When we have implemented a security policy, do we know that it will (and can) be enforced? E.g., if policies get too intricate,
Access Control Mechanisms
 Access Control Mechanisms Week 11 P&P: Ch 4.5, 5.2, 5.3 CNT-4403: 26.March.2015 1 In this lecture Access matrix model Access control lists versus Capabilities Role Based Access Control File Protection
Access Control Mechanisms Week 11 P&P: Ch 4.5, 5.2, 5.3 CNT-4403: 26.March.2015 1 In this lecture Access matrix model Access control lists versus Capabilities Role Based Access Control File Protection
CS603: Distributed Systems
 CS603: Distributed Systems Lecture 1: Basic Communication Services Cristina Nita-Rotaru Lecture 1/ Spring 2006 1 Reference Material Textbooks Ken Birman: Reliable Distributed Systems Recommended reading
CS603: Distributed Systems Lecture 1: Basic Communication Services Cristina Nita-Rotaru Lecture 1/ Spring 2006 1 Reference Material Textbooks Ken Birman: Reliable Distributed Systems Recommended reading
Access Control. Steven M. Bellovin September 2,
 Access Control Steven M. Bellovin September 2, 2014 1 Security Begins on the Host Even without a network, hosts must enforce the CIA trilogy Something on the host the operating system aided by the hardware
Access Control Steven M. Bellovin September 2, 2014 1 Security Begins on the Host Even without a network, hosts must enforce the CIA trilogy Something on the host the operating system aided by the hardware
Cisco Router Security: Principles and Practise. The foundation of network security is router security.
 The foundation of network security is router security. 1) Router security within a general IT security plan, IOS software and standard access. 2) Password security and authentication. 3) Services, applications
The foundation of network security is router security. 1) Router security within a general IT security plan, IOS software and standard access. 2) Password security and authentication. 3) Services, applications
Operating System Security
 Operating System Security Operating Systems Defined Hardware: I/o...Memory.CPU Operating Systems: Windows or Android, etc Applications run on operating system Operating Systems Makes it easier to use resources.
Operating System Security Operating Systems Defined Hardware: I/o...Memory.CPU Operating Systems: Windows or Android, etc Applications run on operating system Operating Systems Makes it easier to use resources.
Last time. User Authentication. Security Policies and Models. Beyond passwords Biometrics
 Last time User Authentication Beyond passwords Biometrics Security Policies and Models Trusted Operating Systems and Software Military and Commercial Security Policies 9-1 This time Security Policies and
Last time User Authentication Beyond passwords Biometrics Security Policies and Models Trusted Operating Systems and Software Military and Commercial Security Policies 9-1 This time Security Policies and
Sample Security Risk Analysis ASP Meaningful Use Core Set Measure 15
 Sample Security Risk Analysis ASP Meaningful Use Core Set Measure 15 Risk Analysis with EHR Questions Example Answers/Help: Status What new electronic health information has been introduced into my practice
Sample Security Risk Analysis ASP Meaningful Use Core Set Measure 15 Risk Analysis with EHR Questions Example Answers/Help: Status What new electronic health information has been introduced into my practice
CSE 127: Computer Security. Security Concepts. Kirill Levchenko
 CSE 127: Computer Security Security Concepts Kirill Levchenko October 3, 2014 Computer Security Protection of systems against an adversary Secrecy: Can t view protected information Integrity: Can t modify
CSE 127: Computer Security Security Concepts Kirill Levchenko October 3, 2014 Computer Security Protection of systems against an adversary Secrecy: Can t view protected information Integrity: Can t modify
Access Control. Discretionary Access Control
 Access Control Discretionary Access Control 1 Access Control Access control is where security engineering meets computer science. Its function is to control which (active) subject have access to a which
Access Control Discretionary Access Control 1 Access Control Access control is where security engineering meets computer science. Its function is to control which (active) subject have access to a which
Announcement. Exercise #2 will be out today. Due date is next Monday
 Announcement Exercise #2 will be out today Due date is next Monday Major OS Developments 2 Evolution of Operating Systems Generations include: Serial Processing Simple Batch Systems Multiprogrammed Batch
Announcement Exercise #2 will be out today Due date is next Monday Major OS Developments 2 Evolution of Operating Systems Generations include: Serial Processing Simple Batch Systems Multiprogrammed Batch
Control Device Administration Using TACACS+
 Device Administration, page 1 Device Administration Work Center, page 3 Data Migration from Cisco Secure ACS to Cisco ISE, page 3 Device Admin Policy Sets, page 3 TACACS+ Authentication Settings, page
Device Administration, page 1 Device Administration Work Center, page 3 Data Migration from Cisco Secure ACS to Cisco ISE, page 3 Device Admin Policy Sets, page 3 TACACS+ Authentication Settings, page
Control Device Administration Using TACACS+
 Device Administration, page 1 Device Administration Work Center, page 3 Data Migration from Cisco Secure ACS to Cisco ISE, page 3 Device Administration Deployment Settings, page 3 Device Admin Policy Sets,
Device Administration, page 1 Device Administration Work Center, page 3 Data Migration from Cisco Secure ACS to Cisco ISE, page 3 Device Administration Deployment Settings, page 3 Device Admin Policy Sets,
VRF-Aware Cloud Web Security
 The feature adds virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) support to the Cisco Cloud Web Security configuration. VRF instances in IP-based networks enable a device to have multiple instances of the routing
The feature adds virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) support to the Cisco Cloud Web Security configuration. VRF instances in IP-based networks enable a device to have multiple instances of the routing
Advanced Systems Security: Ordinary Operating Systems
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Threat Modeling. Bart De Win Secure Application Development Course, Credits to
 Threat Modeling Bart De Win bart.dewin@ascure.com Secure Application Development Course, 2009 Credits to Frank Piessens (KUL) for the slides 2 1 Overview Introduction Key Concepts Threats, Vulnerabilities,
Threat Modeling Bart De Win bart.dewin@ascure.com Secure Application Development Course, 2009 Credits to Frank Piessens (KUL) for the slides 2 1 Overview Introduction Key Concepts Threats, Vulnerabilities,
The Operating System. Chapter 6
 The Operating System Machine Level Chapter 6 1 Contemporary Multilevel Machines A six-level l computer. The support method for each level is indicated below it.2 Operating System Machine a) Operating System
The Operating System Machine Level Chapter 6 1 Contemporary Multilevel Machines A six-level l computer. The support method for each level is indicated below it.2 Operating System Machine a) Operating System
OS security mechanisms:
 OS security mechanisms: Memory Protection: One of the important aspects of Operating system security is Memory Protection. Memory provides powerful indirect way for an attacker to circumvent security mechanism,
OS security mechanisms: Memory Protection: One of the important aspects of Operating system security is Memory Protection. Memory provides powerful indirect way for an attacker to circumvent security mechanism,
Chapter 15: Information Flow
 Chapter 15: Information Flow Definitions Compiler-based mechanisms Execution-based mechanisms Examples Slide #15-1 Overview Basics and background Compiler-based mechanisms Execution-based mechanisms Examples
Chapter 15: Information Flow Definitions Compiler-based mechanisms Execution-based mechanisms Examples Slide #15-1 Overview Basics and background Compiler-based mechanisms Execution-based mechanisms Examples
Control Plane Policing
 The feature allows you to configure a quality of service (QoS) filter that manages the traffic flow of control plane packets to protect the control plane of Cisco IOS XE routers and switches against reconnaissance
The feature allows you to configure a quality of service (QoS) filter that manages the traffic flow of control plane packets to protect the control plane of Cisco IOS XE routers and switches against reconnaissance
Cisco Nexus 7000 Series Switches Configuration Guide: The Catena Solution
 Cisco Nexus 7000 Series Switches Configuration Guide: The Catena Solution First Published: 2016-12-21 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com
Cisco Nexus 7000 Series Switches Configuration Guide: The Catena Solution First Published: 2016-12-21 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com
Protection and Security
 Protection and Security CS 502 Spring 99 WPI MetroWest/Southboro Campus Three Circles of Computer Security Inner Circle Memory, CPU, and File protection. Middle Circle Security Perimeter. Authentication
Protection and Security CS 502 Spring 99 WPI MetroWest/Southboro Campus Three Circles of Computer Security Inner Circle Memory, CPU, and File protection. Middle Circle Security Perimeter. Authentication
SE420 Software Quality Assurance
 SE420 Software Quality Assurance Encryption Backgrounder September 5, 2014 Sam Siewert Encryption - Substitution Re-map Alphabet, 1-to-1 and On-to (function) A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V
SE420 Software Quality Assurance Encryption Backgrounder September 5, 2014 Sam Siewert Encryption - Substitution Re-map Alphabet, 1-to-1 and On-to (function) A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V
Examples of Cisco APE Scenarios
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes three example scenarios with which to use Cisco APE: Access to Asynchronous Lines, page 5-1 Cisco IOS Shell, page 5-3 Command Authorization, page 5-5 Note For intructions
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes three example scenarios with which to use Cisco APE: Access to Asynchronous Lines, page 5-1 Cisco IOS Shell, page 5-3 Command Authorization, page 5-5 Note For intructions
Key Management. Digital signatures: classical and public key Classic and Public Key exchange. Handwritten Signature
 Key Management Digital signatures: classical and public key Classic and Public Key exchange 1 Handwritten Signature Used everyday in a letter, on a check, sign a contract A signature on a signed paper
Key Management Digital signatures: classical and public key Classic and Public Key exchange 1 Handwritten Signature Used everyday in a letter, on a check, sign a contract A signature on a signed paper
PROTECTION CHAPTER 4 PROTECTION
 Protection 4 CHAPTER 4 PROTECTION In protected mode, the Intel Architecture provides a protection mechanism that operates at both the segment level and the page level. This protection mechanism provides
Protection 4 CHAPTER 4 PROTECTION In protected mode, the Intel Architecture provides a protection mechanism that operates at both the segment level and the page level. This protection mechanism provides
Secure Configuration Guide for Oracle9iR2
 Secure Configuration Guide for Oracle9iR2 An Oracle white paper Information security, privacy and protection of corporate assets and data are of pivotal importance in any business. Oracle9iR2 comprehensively
Secure Configuration Guide for Oracle9iR2 An Oracle white paper Information security, privacy and protection of corporate assets and data are of pivotal importance in any business. Oracle9iR2 comprehensively
Configuring Network Security with ACLs
 26 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to use access control lists (ACLs) to configure network security on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the switch
26 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to use access control lists (ACLs) to configure network security on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the switch
Developing a Network:
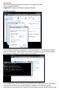 Developing a Network: This is setting up IP addresses in properties in Local Area Connection in the Network and Sharing Centre in Control Panel. I deselected all of the networks checkboxes accept the TCP/IP4
Developing a Network: This is setting up IP addresses in properties in Local Area Connection in the Network and Sharing Centre in Control Panel. I deselected all of the networks checkboxes accept the TCP/IP4
Team Project Management
 TEAM PROJECT MANAGEMENT 149 Team Project Management Tasks of the Project Administrator When working in teams, one person should be the designated administrator. Sets up the Project The project administrator
TEAM PROJECT MANAGEMENT 149 Team Project Management Tasks of the Project Administrator When working in teams, one person should be the designated administrator. Sets up the Project The project administrator
Firewalls Network Security: Firewalls and Virtual Private Networks CS 239 Computer Software March 3, 2003
 Firewalls Network Security: Firewalls and Virtual Private Networks CS 239 Computer Software March 3, 2003 A system or combination of systems that enforces a boundary between two or more networks - NCSA
Firewalls Network Security: Firewalls and Virtual Private Networks CS 239 Computer Software March 3, 2003 A system or combination of systems that enforces a boundary between two or more networks - NCSA
Chapter 17: System Protection
 Chapter 17: System Protection Chapter 17: System Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection Domain of Protection Access Matrix Implementation of Access Matrix Access Control Revocation of
Chapter 17: System Protection Chapter 17: System Protection Goals of Protection Principles of Protection Domain of Protection Access Matrix Implementation of Access Matrix Access Control Revocation of
(Refer Slide Time: 1:26)
 Information Security-3 Prof. V Kamakoti Department of Computer science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Basics of Unix and Network Administration Operating Systems Introduction Mod01,
Information Security-3 Prof. V Kamakoti Department of Computer science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Basics of Unix and Network Administration Operating Systems Introduction Mod01,
Waterfall Life Cycle Model
 Waterfall Life Cycle Model Requirements definition and analysis Functional and non-functional General (for customer), specifications System and software design Implementation and unit testing Integration
Waterfall Life Cycle Model Requirements definition and analysis Functional and non-functional General (for customer), specifications System and software design Implementation and unit testing Integration
Chapter 6: Integrity Policies
 Chapter 6: Integrity Policies Overview Requirements Biba s models Clark-Wilson model Slide #6-1 Overview Requirements Very different than confidentiality policies Biba s model Clark-Wilson model Slide
Chapter 6: Integrity Policies Overview Requirements Biba s models Clark-Wilson model Slide #6-1 Overview Requirements Very different than confidentiality policies Biba s model Clark-Wilson model Slide
Unix, History
 Operating systems Examples from Unix, VMS, Windows NT on user authentication, memory protection and file and object protection. Trusted Operating Systems, example from PitBull Unix, History Unix, History
Operating systems Examples from Unix, VMS, Windows NT on user authentication, memory protection and file and object protection. Trusted Operating Systems, example from PitBull Unix, History Unix, History
ms-help://ms.technet.2004apr.1033/ad/tnoffline/prodtechnol/ad/windows2000/howto/mapcerts.htm
 Page 1 of 8 Active Directory Step-by-Step Guide to Mapping Certificates to User Accounts Introduction The Windows 2000 operating system provides a rich administrative model for managing user accounts.
Page 1 of 8 Active Directory Step-by-Step Guide to Mapping Certificates to User Accounts Introduction The Windows 2000 operating system provides a rich administrative model for managing user accounts.
CSCI 420: Mobile Application Security. Lecture 7. Prof. Adwait Nadkarni. Derived from slides by William Enck, Patrick McDaniel and Trent Jaeger
 CSCI 420: Mobile Application Security Lecture 7 Prof. Adwait Nadkarni Derived from slides by William Enck, Patrick McDaniel and Trent Jaeger 1 cryptography < security Cryptography isn't the solution to
CSCI 420: Mobile Application Security Lecture 7 Prof. Adwait Nadkarni Derived from slides by William Enck, Patrick McDaniel and Trent Jaeger 1 cryptography < security Cryptography isn't the solution to
24-vm.txt Mon Nov 21 22:13: Notes on Virtual Machines , Fall 2011 Carnegie Mellon University Randal E. Bryant.
 24-vm.txt Mon Nov 21 22:13:36 2011 1 Notes on Virtual Machines 15-440, Fall 2011 Carnegie Mellon University Randal E. Bryant References: Tannenbaum, 3.2 Barham, et al., "Xen and the art of virtualization,"
24-vm.txt Mon Nov 21 22:13:36 2011 1 Notes on Virtual Machines 15-440, Fall 2011 Carnegie Mellon University Randal E. Bryant References: Tannenbaum, 3.2 Barham, et al., "Xen and the art of virtualization,"
IT Service Delivery And Support Week Four - OS. IT Auditing and Cyber Security Fall 2016 Instructor: Liang Yao
 IT Service Delivery And Support Week Four - OS IT Auditing and Cyber Security Fall 2016 Instructor: Liang Yao 1 What is an Operating System (OS)? OS is a software that designed to run on specific hardware
IT Service Delivery And Support Week Four - OS IT Auditing and Cyber Security Fall 2016 Instructor: Liang Yao 1 What is an Operating System (OS)? OS is a software that designed to run on specific hardware
