Chapter 0: Introduction. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
|
|
|
- Bernice Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 0: Introduction Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
2 Essentials for the class Homepage Textbook Computer Science An Overview 12 th Ed. By J. Glenn Brookshear and Dennis Brylow from Pearson Education ( 컴퓨터과학총론 12 th Edition, 이광수외공역, 휴먼싸이언스 2015 년 ) Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-2
3 Essentials for the class Evaluation (Relative) Attendance: 15% (5 회초과시 1 회당 3%p 감점 ) Homework: 15% Midterm: 35% Final: 35% If you fail in any one of these four categories, you fail the class. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-3
4 Lecturer Information Homepage Office Lab Engineering Building C-484 MBM(Mobile and Broadcasting Multimedia) Lab 이예지조교 New Engineering Building #1215 Contact Info yoonk_at_konkuk_dot_ac_dot_kr Office Hour: By appointment Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-4
5 Chapter 0: Introduction 0.1 The Role of Algorithms 0.2 The History of Computing 0.3 An Outline of Our Study 0.4 The Overarching Themes of Computer Science Algorithms Abstraction Creativity Data Programming Internet Impact Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-5
6 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms Hardware: Equipment / Machinery Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-6
7 Terminology 알고리즘 : 작업을수행하는방법을정의하는단계들의집합 프로그램 : 알고리즘의한표현 프로그래밍 : 프로그램을개발하는과정 소프트웨어 : 프로그램과알고리즘 하드웨어 : 장비 Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-7
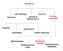
8 Figure 0.1 An algorithm for a magic trick Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-8
9 History of Algorithms The study of algorithms was originally a subject in mathematics. Early examples of algorithms Long division algorithm Euclidean Algorithm Gödel's Incompleteness Theorem: Some problems cannot be solved by algorithms. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-9
10 Figure 0.2 The Euclidean algorithm Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-10
11 History of Computing Early computing devices Abacus: positions of beads represent numbers Gear-based machines (1600s-1800s) Positions of gears represent numbers Blaise Pascal, Wilhelm Leibniz, Charles Babbage Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-11
12 Figure 0.3 Chinese Wooden Abacus Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-12
13 Early Data Storage Punched cards First used in Jacquard Loom (1801) to store patterns for weaving cloth Storage of programs in Babbage s Analytical Engine Popular through the 1970 s Gear positions Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-13
14 Early Computers Based on mechanical relays 1940: Stibitz at Bell Laboratories 1944: Mark I: Howard Aiken and IBM at Harvard Based on vacuum tubes : Atanasoff-Berry at Iowa State 1940s: Colossus: secret German code-breaker 1940s: ENIAC: Mauchly & Eckert at U. of Penn. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-14
15 Figure 0.4 The ENIAC computer Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-15
16 Personal Computer(PC) Altair 8800 Announced: March 1975 Price: US $395 as a kit US $495 assembled CPU: Intel 8080, 2.0 MHz RAM: 256 bytes, 64K max Display: front panel LEDs Controls: front panel switches Expansion: card-cage with 16 card slots Storage: external Cassette or 8" floppy drive OS: CP/M, BASIC Altair 8800 from Micro Instrumentation Telemetry Systems (MITS) of Albuquerque, NM 1975 년 1 월 Popular electronics 잡지에최초소개 최초의대량생산된 Personal Computer 로여겨짐 Bill Gates/Paul Allen 이 Altair BASIC 제작 (a true programming language, and the first commercial Microsoft computer product) Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc From
17 Personal Computer(PC) IBM 5100 Model: 5100 Introduced: September, 1975 Price: US $19,975 w/ 64K RAM Weight: 55 pounds CPU: IBM proprietary, 1.9MHz RAM: 16K, 64K max Display: 5" monochrome monitor 64 X 16 text Storage: Internal 200K tape (DC300) Ports: tape / printer I/O port OS: APL and/or BASIC First Portable Computer (55 lb) Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc From
18 Personal Computer(PC) Apple I Introduced: March 1976 Released: July 1976 Price: US $ w/4k RAM How many? about 200 total CPU: MOS 6502, 1.0 MHz RAM: 4K, 65K max Display: monochrome 280 X 192, 40 X 24 text Keyboard: not included. Ports: composite video output keyboard interface one vertical expansion slot Storage: cassette interface available OS: firmware in ROM (HEX) Apple BASIC on cassette Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Steve Wozniak from HP and Steve Jobs 0-18 From
19 Personal Computer(PC) Apple II Released: April 1977 Price: US $1298 with 4K RAM US $2638 with 48K RAM CPU: MOS 6502, 1.0 MHz RAM: 4K min, 48K max Display: 280 X 192, 40 X 24 text 6 colors maximum Ports: composite video output cassette interface 8 internal expansion slots Storage: generic cassette drive external 143K floppy (1978) OS: Woz Integer BASIC in ROM One of first color display Built-in BASIC language 8 expansion slots memory expansion floppy disk controllers PASCAL and CP/M emulator cards parallel, serial, and SCSI cards processor accelerators video cards Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc From
20 Personal Computer(PC) IBM PC Model: 5150 Released: September 1981 Price: US $1,565 ~ $3,000 CPU: Intel 8088, 4.77MHz RAM: 16K, 640K max Display: 80 X 24 text Storage: dual 160KB 5.25-inch disk drives Ports: cassette & keyboard only 5 internal expansion slots OS: PC-DOS v1.0 Five internal ISA expansion slots on the motherboard additional memory video card optional floppy drive controller RS-232 serial port card modem card for dialing-up remote computer systems Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc From
21 Personal Computer(PC) Compaq Portable Introduced: November 1982 Released: March 1983 Price: US$3590 (two floppy system) How many? 53,000 in 1983, the first year Weight: 28 pounds. CPU: Intel 8088, 4.77MHz RAM: 128K, 640K max Display: 9" monochrome monitor built-in 80 X 25 text Color graphic card Storage: Two 320K 5-1/4" disk drives Ports: 1 parallel (expansion card) OS: MS-DOS The Compaq Portable was the first 100% compatible IBM computer clone. It's transportable, designed so it can easily be taken aboard an airliner as carry-on luggage Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc From
22 Personal Computer(PC) Apple Macintosh Model: M0001 Introduced: January 1984 Price: US$2495 CPU: Motorola 68000, 7.83 Mhz RAM: 128K, later 512K Display: 9-inch monochrome screen 512x342 pixels Ports: Two DB9 serial ports Printer port External floppy port Storage: Internal 400K SSDD floppy optional external floppy ($495) OS: Macintosh GUI (graphical user interface) Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Macintosh is considered to be the first commercially successful computer to use a GUI From
23 Personal Computers First used by hobbyists IBM introduced the PC in Accepted by business Became the standard hardware design for most desktop computers Most PCs use software from Microsoft Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-23
24 Into the Millennium Internet revolutionized communications World Wide Web Search Engines (Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft) Miniaturization of computing machines Embedded (GPS, in automobile engines) Smartphones Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-24
25 Outline of Our Study Chapter 1: Data Storage Chapter 2: Data Manipulation Chapter 3: Operating Systems Chapter 4: Networks and the Internet Chapter 5: Algorithms Chapter 6: Programming Languages Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-25
26 Outline of Our Study (continued) Chapter 7: Software Engineering Chapter 8: Data Abstractions Chapter 9: Database Systems Chapter 10: Computer Graphics Chapter 11: Artificial Intelligence Chapter 12: Theory of Computation Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-26
27 The Overarching Themes of Computer Science Computing technology effects: Governments, economics, scientific research, role of data, communication, Seven Big Ideas that unite computer science: Algorithms, Abstraction, Creativity, Data, Programing, Internet and Impact Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-27
28 Algorithms The science of algorithms Draws from other subjects, including Mathematics Engineering Psychology Business Administration Psychology Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-28
29 Figure 0.5 The central role of algorithms in computer science Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-29
30 Given the Central Role of Algorithms Which problems can be solved by algorithmic processes? How can algorithm discovery be made easier? How can techniques of representing and communicating algorithms be improved? How can characteristics of different algorithms be analyzed and compared? Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-30
31 Given the Central Role of Algorithms (continued) How can algorithms be used to manipulate information? How can algorithms be applied to produce intelligent behavior? How does the application of algorithms affect society? Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-31
32 Abstraction Abstraction: The distinction between the external properties of an entity and the details of the entity s internal composition Abstract tool: A component that can be used without concern for the component s internal properties Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-32
33 추상화 (abstraction) 추상화 : 개체의외적속성과내적구성의세부사항을구별하는것 추상적도구 : 그내적구성을모르고서도사용할수있도록만들어진컴포넌트 2009 Pearson Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved
34 Creativity Computer science is inherently creative Discovering and applying algorithms is a human activity Extends forms of expression in many ways Creating large software systems is like conceiving a grand new sculpture Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-34
35 Data Computers can represent any information That can be discretized and digitized Algorithms process and transform data Massive storage capacities High speed networks Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-35
36 Questions about Data How do computers store data about common digital artifacts? Numbers, text, images, sounds, and video How do computers approximate data about analog artifacts in the real world? How do computers detect and prevent errors in data? What are the ramifications or an ever-growing and interconnected universe of digital data? Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-36
37 Programming Programming is broadly referred to as: Translating human intentions into executable algorithms Computer hardware is capable of only simple algorithmic steps Abstractions in a programming language allow humans to reason and encode solutions to complex problems Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-37
38 Questions about Programming How are programs built? What kind of errors can occur in programs? How are errors in programs found and repaired? What are the effects of errors in modern programs? How are programs documented and evaluated? Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-38
39 Internet Profound impact in the way information is: Stored Retrieved Shared Privacy Security Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-39
40 Impact Social, ethical, legal impacts including: Security concerns Issues of software ownership and liabilities Social impact of database technology Consequences of artificial intelligence Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-40
41 Impact No Correct answers, instead increase awareness of: Various stakeholders Alternatives Short term and long term consequences Character-based ethics Good Behavior is a consequence of Good Character Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 0-41
42 End of Chapter Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
Evolution of the Computer
 Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
You Will Need Floppy Disks for your labs!
 CIS121 Instructor: Lynne Mayer VoiceMail: (847) 697-1000 x 2328 Lmayer@elgin.edu Office Hours: ICT 122 Mon.: 9:15-10:15 AM, 5:15-6:00 PM Wed.: 9:15-10:15 AM Fri.: 2:30-3:30 PM Website: faculty.elgin.edu/lmayer
CIS121 Instructor: Lynne Mayer VoiceMail: (847) 697-1000 x 2328 Lmayer@elgin.edu Office Hours: ICT 122 Mon.: 9:15-10:15 AM, 5:15-6:00 PM Wed.: 9:15-10:15 AM Fri.: 2:30-3:30 PM Website: faculty.elgin.edu/lmayer
COMPUTER HISTORY Compiled by Charles Kim Howard University
 EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY Compiled by Charles Kim Howard University 1 Computers Everywhere Everywhere PC, VCR, DVD,Toys Phones,
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY Compiled by Charles Kim Howard University 1 Computers Everywhere Everywhere PC, VCR, DVD,Toys Phones,
Introduction To Computers. About the Course
 Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Computers in Engineering COMP 208. A Brief History. Mechanical Calculators. A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY. Computers and Microprocessors
 EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY 1 Computers and Microprocessors Everywhere PC, VCR, Toys, etc Hardware and Software Evolution of up First
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY 1 Computers and Microprocessors Everywhere PC, VCR, Toys, etc Hardware and Software Evolution of up First
Unit 4: Emerging Technologies. A History of Personal Computing by Mrs. Ogletree
 Unit 4: Emerging Technologies A History of Personal Computing by Mrs. Ogletree EVOLUTION OF TECHNOLOGY Technology has been constantly changing COMPUTER HISTORY Computers have been around for a very, very,
Unit 4: Emerging Technologies A History of Personal Computing by Mrs. Ogletree EVOLUTION OF TECHNOLOGY Technology has been constantly changing COMPUTER HISTORY Computers have been around for a very, very,
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY
 EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY 1 Computers and Microprocessors Everywhere PC, VCR, DVD,Toys Phones, Cars, etc Hardware and Software Embedded
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY 1 Computers and Microprocessors Everywhere PC, VCR, DVD,Toys Phones, Cars, etc Hardware and Software Embedded
Introduction to Computer Science. What is Computer Science?
 Introduction to Computer Science CS A101 What is Computer Science? First, some misconceptions. Misconception 1: I can put together my own PC, am good with Windows, and can surf the net with ease, so I
Introduction to Computer Science CS A101 What is Computer Science? First, some misconceptions. Misconception 1: I can put together my own PC, am good with Windows, and can surf the net with ease, so I
Algorithm: Program: Programming: Software: Hardware:
 0-1 0-2 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms
0-1 0-2 Terminology Algorithm: A set of steps that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an algorithm Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY
 EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY 1 Computers and Microprocessors Everywhere PC, VCR, Toys, etc Hardware and Software Evolution of up First
EECE416 :Microcomputer Fundamentals and Design ( Microcomputer & Microprocessor ) COMPUTER HISTORY 1 Computers and Microprocessors Everywhere PC, VCR, Toys, etc Hardware and Software Evolution of up First
CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing
 CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information
CS 1 Notes 1 - Early Computing and 2 - Electronic Computing Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information
Computer Basics. Computer Technology
 Computer Basics Computer Technology What is a Computer Information Processor Input Output Processing Storage Are physical parts like monitor, mouse, keyboard essential? Computer History Abacus 3,000 B.C.
Computer Basics Computer Technology What is a Computer Information Processor Input Output Processing Storage Are physical parts like monitor, mouse, keyboard essential? Computer History Abacus 3,000 B.C.
EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS. In the early years, before the computer was invented, there are several inventions of counting machines.
 EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS In the early years, before the computer was invented, there are several inventions of counting machines. 200 BC 500 BC CHINESE ABACUS EGYPTIAN ABACUS 1620 JOHN NAPIER NAPIER'S BONES
EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS In the early years, before the computer was invented, there are several inventions of counting machines. 200 BC 500 BC CHINESE ABACUS EGYPTIAN ABACUS 1620 JOHN NAPIER NAPIER'S BONES
28 October 2004
 28 October 2004 The Apple II, or Apple ][, became one of the most popular computers ever. Although it is a vast improvement over the Apple I, it contains the same processor and runs at the same speed.
28 October 2004 The Apple II, or Apple ][, became one of the most popular computers ever. Although it is a vast improvement over the Apple I, it contains the same processor and runs at the same speed.
Describe the layers of a computer system
 Chapter 1 The Big Picture Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software
Chapter 1 The Big Picture Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe the history of computer hardware and software
Computer System architectures
 CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura 1 Historical Developments 2 Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation-
CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura 1 Historical Developments 2 Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation-
An Incomplete History of Computation
 An Incomplete History of Computation Charles Babbage 1791-1871 Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge University, 1827-1839 First computer designer Ada Lovelace 1815-1852 First computer programmer
An Incomplete History of Computation Charles Babbage 1791-1871 Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge University, 1827-1839 First computer designer Ada Lovelace 1815-1852 First computer programmer
History of Computing. Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech
 History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
THE GENERATIONS OF COMPUTER
 THE GENERATIONS OF COMPUTER FIRST GENERATION (1951-1958) VACUUM TUBE 1. Vacuum tubes as their main logic elements 2. Punch Cards to input and externally stored data 3. Rotating magnetic drums for internal
THE GENERATIONS OF COMPUTER FIRST GENERATION (1951-1958) VACUUM TUBE 1. Vacuum tubes as their main logic elements 2. Punch Cards to input and externally stored data 3. Rotating magnetic drums for internal
Great Inventions written by Bob Barton
 COMPUTER Great Inventions written by Bob Barton Computers Computers help society function in many vital ways, often without our being aware of them. Computers control traffic lights and factory operations.
COMPUTER Great Inventions written by Bob Barton Computers Computers help society function in many vital ways, often without our being aware of them. Computers control traffic lights and factory operations.
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali
 Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
Overview of a computer
 Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Computer Evolution. Computer Generation. The Zero Generation (3) Charles Babbage. First Generation- Time Line
 Computer Generation Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Generation Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems
 Introduction to Computer Systems (1) Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://www.wssk.wroc.pl/~mielecki piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Literature
Introduction to Computer Systems (1) Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://www.wssk.wroc.pl/~mielecki piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Literature
Early Calculating Tools
 Early Calculating Tools Abacus At least 5,000 years old Memory aid for making calculations Cannot perform actual computations Eventually replaced by pencil and paper Early Calculating Tools Pascalene Invented
Early Calculating Tools Abacus At least 5,000 years old Memory aid for making calculations Cannot perform actual computations Eventually replaced by pencil and paper Early Calculating Tools Pascalene Invented
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers
 Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations Characteristic
Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations Characteristic
Welcome to COS151! 1.1
 Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers. In this chapter you will learn about:
 Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Computer Evolution. Budditha Hettige. Department of Computer Science
 Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
The trusted, student-friendly online reference tool. Name: Date:
 World Book Online: The trusted, student-friendly online reference tool. World Book Advanced Database* Name: Date: History of Computers Computers! Virtually no other form of technology has become so powerful
World Book Online: The trusted, student-friendly online reference tool. World Book Advanced Database* Name: Date: History of Computers Computers! Virtually no other form of technology has become so powerful
Computer History CSCE 101
 Computer History CSCE 101 Computer History In 40 years computers went from being giant expensive machines that only corporations could own to the personal computer we see today. Early Calculating Devices
Computer History CSCE 101 Computer History In 40 years computers went from being giant expensive machines that only corporations could own to the personal computer we see today. Early Calculating Devices
CS101 Lecture 29: Brief History of Computing
 CS101 Lecture 29: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 1 August 2013 Some
CS101 Lecture 29: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 1 August 2013 Some
Lyman Briggs Lecture Series. Group Question. Discussion Questions. Definition of Computer. Definition of Modern Computer. Definition of a Computer
 Lyman Briggs Lecture Series Emerging Issues in Abortion: Beyond Prolife and Pro-choice Adrienne Asch TONIGHT! 7:30 PM, C-106 Holmes Hall Group Question Get into a group of three people You have three minutes
Lyman Briggs Lecture Series Emerging Issues in Abortion: Beyond Prolife and Pro-choice Adrienne Asch TONIGHT! 7:30 PM, C-106 Holmes Hall Group Question Get into a group of three people You have three minutes
Computer Systems. Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction
 Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
Introduction to Computer Systems
 Introduction to Computer Systems By Farhan Ahmad farhanahmad@uet.edu.pk Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering & Technology Lahore Introducing Computer Systems Exploring computers
Introduction to Computer Systems By Farhan Ahmad farhanahmad@uet.edu.pk Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Engineering & Technology Lahore Introducing Computer Systems Exploring computers
A Short History of Computers
 A Short History of Computers Geoffrey M. Rockwell x 24072 Togo Salmon 309A grockwel@mcmaster.ca URL: http://www.humanities.mcmaster.ca/~hccrs/ihchome.htm McMaster University Administration u Homework 3
A Short History of Computers Geoffrey M. Rockwell x 24072 Togo Salmon 309A grockwel@mcmaster.ca URL: http://www.humanities.mcmaster.ca/~hccrs/ihchome.htm McMaster University Administration u Homework 3
Learning Objectives. In this chapter you will learn about:
 Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
Ref Page Slide 1/17 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer Data processing Characteristic features of computers Computers evolution to their present form Computer generations
What You Will Learn Today
 CS101 Lecture 2: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 Aaron Stevens 21 January 2011
CS101 Lecture 2: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 Aaron Stevens 21 January 2011
YOUR NEXT HAM RADIO SHACK COMPUTER THE NEXT GENERATION IN PC S. Ken N1RGK
 YOUR NEXT HAM RADIO SHACK COMPUTER THE NEXT GENERATION IN PC S Ken N1RGK What are we going to cover in this presentation? A quick stroll down memory lane Costs of PC s, Old and New A look into the Next
YOUR NEXT HAM RADIO SHACK COMPUTER THE NEXT GENERATION IN PC S Ken N1RGK What are we going to cover in this presentation? A quick stroll down memory lane Costs of PC s, Old and New A look into the Next
CS140 Lecture 09a: Brief History of Computing
 CS140 Lecture 09a: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 17 February 2017
CS140 Lecture 09a: Brief History of Computing "There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home." -- Ken Olson, founder and CEO of Digital Equipment Corp., 1977 John Magee 17 February 2017
1973 MCM-70 Intel 8008 processor 2 kb RAM, 14kB ROM cassette drive 3
 1971 Kenbak-1 First commercially assembled personal computer. Small and large integrated circuits Memory capacity of 256 bytes switches for input/ lights for output 1 limited input/output capabilities
1971 Kenbak-1 First commercially assembled personal computer. Small and large integrated circuits Memory capacity of 256 bytes switches for input/ lights for output 1 limited input/output capabilities
CHAPTER 1: Computers and Systems
 CHAPTER 1: Computers and Systems The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint
CHAPTER 1: Computers and Systems The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint
Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy
 What is Computer? Understand Computers Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy Computer is an electronic devices that under a program s direction and control, perform four basic operations: Input, Processing,
What is Computer? Understand Computers Part 1: Computer and Information Literacy Computer is an electronic devices that under a program s direction and control, perform four basic operations: Input, Processing,
Chapter 1. The Big Picture
 Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for
Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard ) Software The programs that provide the instructions for
Test Bank for Prelude to Programming Chapter 0
 Test Bank for Prelude to Programming Chapter 0 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is not an attribute of a computer? a. can act on intermediate results without human intervention b. has its roots
Test Bank for Prelude to Programming Chapter 0 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is not an attribute of a computer? a. can act on intermediate results without human intervention b. has its roots
ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING
 ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING -2- CSC 2201 Dokuz Eylul University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics 2 History of Computers 2600 (BC) Abacus Simple addition and subtraction 1621 Slide Rule 3 The
ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING -2- CSC 2201 Dokuz Eylul University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics 2 History of Computers 2600 (BC) Abacus Simple addition and subtraction 1621 Slide Rule 3 The
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 1: Introduction!
 COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 1: Introduction! Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Outline for today What are computers? What
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 1: Introduction! Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Outline for today What are computers? What
CS Operating Systems (OS) Introduction. Lecture 2 Sept 12, 2018
 CS 3305 Operating Systems (OS) Introduction Lecture 2 Sept 12, 2018 Operating System (OS) What is an Operating Systems (OS)? The software layer between user applications and hardware Manages / Optimizes
CS 3305 Operating Systems (OS) Introduction Lecture 2 Sept 12, 2018 Operating System (OS) What is an Operating Systems (OS)? The software layer between user applications and hardware Manages / Optimizes
CMPSCI 201: Architecture and Assembly Language
 CMPSCI 201: Architecture and Assembly Language Deepak Ganesan Computer Science Department 1-1 Course Administration Instructor: Deepak Ganesan (dganesan@cs.umass.edu) 250 CS Building Office Hrs: T 10:45-12:15,
CMPSCI 201: Architecture and Assembly Language Deepak Ganesan Computer Science Department 1-1 Course Administration Instructor: Deepak Ganesan (dganesan@cs.umass.edu) 250 CS Building Office Hrs: T 10:45-12:15,
Chapter One. Computers in Context
 Chapter One Computers in Context After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Characterize what a computer is and what it does Describe several ways computers play a critical role in modern life
Chapter One Computers in Context After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Characterize what a computer is and what it does Describe several ways computers play a critical role in modern life
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN
 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN COURSE INTRODUCTION 1 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN ET011G History of Computer Micro-controllers Introduction Course Aims? Course contents? Invisible computing 2 History EARLY
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN COURSE INTRODUCTION 1 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM DESIGN ET011G History of Computer Micro-controllers Introduction Course Aims? Course contents? Invisible computing 2 History EARLY
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about The definition of computer science Algorithms A
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Computer Science Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, 6-th Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about The definition of computer science Algorithms A
The Generations of Computers
 The Generations of Computers The development of computers started with mechanical and electromechanical devices (17 th through 19 th century) and has progressed through four generations of computers. Mechanical
The Generations of Computers The development of computers started with mechanical and electromechanical devices (17 th through 19 th century) and has progressed through four generations of computers. Mechanical
Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS
 Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS History of Computers Outline Generations of Computers Types of Computers 2 History of Computers A computer is a machine that works with data and information
Chapter 2 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS History of Computers Outline Generations of Computers Types of Computers 2 History of Computers A computer is a machine that works with data and information
Babbage Analytical Machine
 Von Neumann Machine Babbage Analytical Machine The basis of modern computers is proposed by a professor of mathematics at Cambridge University named Charles Babbage (1972-1871). He has invented a mechanical
Von Neumann Machine Babbage Analytical Machine The basis of modern computers is proposed by a professor of mathematics at Cambridge University named Charles Babbage (1972-1871). He has invented a mechanical
Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems
 Introduction to Computer Systems (1) Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://mielecki.ristel.pl/ piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Literature 1. Stallings
Introduction to Computer Systems (1) Basic definitions and history of the Computer Systems Piotr Mielecki Ph. D. http://mielecki.ristel.pl/ piotr.mielecki@pwr.edu.pl pmielecki@gmail.com Literature 1. Stallings
time step first instruction second instruction
 COMP1200 2001 Semester 1 61 Parallelism Microprocessors can use a variety of tricks to execute more instructions in a given amount of time. One of the most successful is to execute more than one instruction
COMP1200 2001 Semester 1 61 Parallelism Microprocessors can use a variety of tricks to execute more instructions in a given amount of time. One of the most successful is to execute more than one instruction
ABC Atanasoff-Berry Computer
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers A Brief History of Computers First Generation computers 1939-1959 Use vacuum tubes and wire circuits 1939 ABC computer completed, clock speed of 60 Hz, uses punch cards
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers A Brief History of Computers First Generation computers 1939-1959 Use vacuum tubes and wire circuits 1939 ABC computer completed, clock speed of 60 Hz, uses punch cards
In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science. Algorithms. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition
 Objectives Chapter 1: An Introduction to Com puter S cience Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science Algorithms
Objectives Chapter 1: An Introduction to Com puter S cience Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Third Edition In this chapter, you will learn about: The definition of computer science Algorithms
Objectives. Learn why today almost everyone is a computer operator. Learn about the predecessors of modern computer hardware and software
 Objectives Learn why today almost everyone is a computer operator Learn about the predecessors of modern computer hardware and software Trace the development of computer hardware and software through several
Objectives Learn why today almost everyone is a computer operator Learn about the predecessors of modern computer hardware and software Trace the development of computer hardware and software through several
Computer Architecture Dr. Charles Kim Howard University
 EECE416 Microcomputer Fundamentals Computer Architecture Dr. Charles Kim Howard University 1 Computer Architecture Computer Architecture Art of selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create
EECE416 Microcomputer Fundamentals Computer Architecture Dr. Charles Kim Howard University 1 Computer Architecture Computer Architecture Art of selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create
COMS 1003 Fall Introduction to Computer Programming in C. History & Computer Organization. September 15 th
 COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
Part (01) Introduction to Computer
 Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Fundamentals of Python: First Programs. Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen
 Fundamentals of Python: First Programs Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic features of an algorithm
Fundamentals of Python: First Programs Chapter 1: Introduction Modifications by Mr. Dave Clausen Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the basic features of an algorithm
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing
 INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 1 History of Computing Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 1 History of Computing Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
Week 1 Introduction to Programming
 CME111 Programming Languages I Week 1 Introduction to Programming Assist. Prof. Dr. Caner ÖZCAN Introduction Course Web Site: www.canerozcan.net Office Hours: Tuesday 13:00-15:00 Wednesday 15:30-17:00
CME111 Programming Languages I Week 1 Introduction to Programming Assist. Prof. Dr. Caner ÖZCAN Introduction Course Web Site: www.canerozcan.net Office Hours: Tuesday 13:00-15:00 Wednesday 15:30-17:00
History and Mission of IA
 History and Mission of IA CSH6 Chapter 1 with supplementary information Brief History and Mission of Information System Security Seymour Bosworth & Robert V. Jacobson 1 Copyright 2015 M. E. Kabay. All
History and Mission of IA CSH6 Chapter 1 with supplementary information Brief History and Mission of Information System Security Seymour Bosworth & Robert V. Jacobson 1 Copyright 2015 M. E. Kabay. All
CSC 221: Introduction to Programming. Fall 2018
 CSC 221: Introduction to Programming Fall 2018 History of programming developments in hardware machine language à assembly language high-level languages block-based vs. scripting languages intro to Python
CSC 221: Introduction to Programming Fall 2018 History of programming developments in hardware machine language à assembly language high-level languages block-based vs. scripting languages intro to Python
1: History, Generation & Classification. Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University
 1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW
 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Def: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a variety of operations in accordance with set of instructions called program. DATA Data. Data in
CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Def: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a variety of operations in accordance with set of instructions called program. DATA Data. Data in
THE HISTORY OF COMPUTERS (Introduction)
 Hillingdon U3A Computer Group THE HISTORY OF COMPUTERS (Introduction) U3A Presentation J. Martin 2017 1 Early Calculating Tools 500BC. Counting Boards & Abacus. Tools for simple arithmetic processes. About
Hillingdon U3A Computer Group THE HISTORY OF COMPUTERS (Introduction) U3A Presentation J. Martin 2017 1 Early Calculating Tools 500BC. Counting Boards & Abacus. Tools for simple arithmetic processes. About
Chapter Overview of Computer Systems
 Chapter 1 1.1 Overview of Computer Systems 1.1 The Parts of a Computer System Let us first look at what a Computer and a Computer System is. A computer can be classified as a device that takes in raw data
Chapter 1 1.1 Overview of Computer Systems 1.1 The Parts of a Computer System Let us first look at what a Computer and a Computer System is. A computer can be classified as a device that takes in raw data
Computer Systems. Computer Systems. Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC-Linz) Johannes Kepler University
 Computer Systems Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC-Linz) Johannes Kepler University Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.uni-linz.ac.at http://www.risc.uni-linz.ac.at/people/schreine
Computer Systems Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC-Linz) Johannes Kepler University Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.uni-linz.ac.at http://www.risc.uni-linz.ac.at/people/schreine
EC-333 Microprocessor and Interfacing Techniques
 EC-333 Microprocessor and Interfacing Techniques Lecture 2 Overview of Intel Microprocessors Dr Hashim Ali Spring - 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila Slides taken
EC-333 Microprocessor and Interfacing Techniques Lecture 2 Overview of Intel Microprocessors Dr Hashim Ali Spring - 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila Slides taken
Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was
 1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
PREPARED BY S.RAVINDRAKUMAR, SENIOR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR/ECE,CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Page 1
 TECHNOLOGY Page 1 Intel x86 Microcomputer CPU Characteristics 8086 16 bit Expansion Bus 16 bit External Bus 8 bit Internal Bus 20 bit Memory Address 2 20 = 1,048,576 = 1024 Kb Physical Memory Real Address
TECHNOLOGY Page 1 Intel x86 Microcomputer CPU Characteristics 8086 16 bit Expansion Bus 16 bit External Bus 8 bit Internal Bus 20 bit Memory Address 2 20 = 1,048,576 = 1024 Kb Physical Memory Real Address
History of Computers. What Is A Computer? Egyptian Numbers. Ancient Tools for Computation. Introduction to Computers
 What Is A Computer? History of Computers Introduction to Computers Adapted from slides by Prof. Polly Huang and Prof. KM Chao (National Taiwan University) com put er Pronunciation: kâm-'pyü-ter Function:
What Is A Computer? History of Computers Introduction to Computers Adapted from slides by Prof. Polly Huang and Prof. KM Chao (National Taiwan University) com put er Pronunciation: kâm-'pyü-ter Function:
Downloaded from
 Learning Objectives : After learning the Unit the students will be able to: learn about the various inventions in computers understand the technological changes occurs in computer in terms of hardware
Learning Objectives : After learning the Unit the students will be able to: learn about the various inventions in computers understand the technological changes occurs in computer in terms of hardware
Chapter 1. Computer System Organization
 Chapter 1 Computer System Organization Prepared By: Manish Kumar Prajapati PGT (Comp.Sc.) (First Shift) Kendriya Vidyalaya Bailey Road Patna-14 What is Computer? A computer is an electronic device that
Chapter 1 Computer System Organization Prepared By: Manish Kumar Prajapati PGT (Comp.Sc.) (First Shift) Kendriya Vidyalaya Bailey Road Patna-14 What is Computer? A computer is an electronic device that
CS1101: Lecture 21. Organization: Input/Output. Lecture Outline. Buses. A simple personal computer. Buses
 CS1101: Lecture 21 Computer Systems Organization: Input/Output Dr. Barry O Sullivan b.osullivan@cs.ucc.ie Buses Lecture Outline A simple personal computer Direct Memory Access Interrupts Bus Arbiter &
CS1101: Lecture 21 Computer Systems Organization: Input/Output Dr. Barry O Sullivan b.osullivan@cs.ucc.ie Buses Lecture Outline A simple personal computer Direct Memory Access Interrupts Bus Arbiter &
COURSE OVERVIEW. Introduction to Computer Engineering 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo
 COURSE OVERVIEW Introduction to Computer Engineering 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Course Objectives Introduction to computer engineering For computer engineer-wannabe For students studying other fields
COURSE OVERVIEW Introduction to Computer Engineering 2015 Spring by Euiseong Seo Course Objectives Introduction to computer engineering For computer engineer-wannabe For students studying other fields
Computer Organization CS 206T
 Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization
 Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization Course Outcome (CO) CO1 Explain the basic principles of modern computer systems organization Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization Course Outcome (CO) CO1 Explain the basic principles of modern computer systems organization Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
1.2.1 Electronic computers based on digital switching
 1.2.1 Electronic computers based on digital switching The first true digital electronic computer was created by John V Atanasoff during 1937-1942. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (called ABC figure 2.8) was
1.2.1 Electronic computers based on digital switching The first true digital electronic computer was created by John V Atanasoff during 1937-1942. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (called ABC figure 2.8) was
(History of Computers) Lecture # 03 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Lecturer. URL:
 INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES. (History of Computers) Lecture # 03 By: M.. Lecturer. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1
INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES. (History of Computers) Lecture # 03 By: M.. Lecturer. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1
Chapter 2. The History and Development of Computers
 Chapter 2 The History and Development of Computers Ancient Computing Devices Fingers Tally bones Sticks Stones cal Abacus- 5000 years ago John Napier 1617 Scotland Napier s Bones Square sticks with numbers
Chapter 2 The History and Development of Computers Ancient Computing Devices Fingers Tally bones Sticks Stones cal Abacus- 5000 years ago John Napier 1617 Scotland Napier s Bones Square sticks with numbers
Welcome to COSC Introduction to Computer Science
 Welcome to COSC 1302 Introduction to Computer Science (Syllabus) Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard
Welcome to COSC 1302 Introduction to Computer Science (Syllabus) Chapter 1 The Big Picture 1.1 Computing Systems Hardware The physical elements of a computing system (printer, circuit boards, wires, keyboard
Chapter 1. Introducing the Universal Machine
 Christian Jacob Chapter 1 Introducing the Universal Machine 1.1 The Very Idea of the Universal Machine 1.1.1 Universal versus Special-Purpose Machines 1.1.2 What is a Computer? 1.1.3 Areas of Computer
Christian Jacob Chapter 1 Introducing the Universal Machine 1.1 The Very Idea of the Universal Machine 1.1.1 Universal versus Special-Purpose Machines 1.1.2 What is a Computer? 1.1.3 Areas of Computer
Computer Science 4500 Operating Systems. Welcome! In This Module. Module 1 Introduction, Overview and History
 Computer Science 4500 Operating Systems Module 1 Introduction, Overview and History Updated: January 13, 2015 2008 Stanley A. Wileman, Jr. Operating Systems Slide 1 Welcome! Welcome to Operating Systems.
Computer Science 4500 Operating Systems Module 1 Introduction, Overview and History Updated: January 13, 2015 2008 Stanley A. Wileman, Jr. Operating Systems Slide 1 Welcome! Welcome to Operating Systems.
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science and Engineering MBM Engineering College, Jodhpur November 14, 2013
Computer Organization KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science and Engineering MBM Engineering College, Jodhpur November 14, 2013
Downloaded from various sources on the NET
 Overview Computers. Hardware components of a Computer. Purpose and functions of computer operating systems. Evolution of computer operating systems. Operating systems available today. Downloaded from various
Overview Computers. Hardware components of a Computer. Purpose and functions of computer operating systems. Evolution of computer operating systems. Operating systems available today. Downloaded from various
Characteristics of Computers
 The word computer comes from word compute, which means to calculate. A computer is a programmable machine (or more precisely, a programmable sequential state machine) that operates on data and is used
The word computer comes from word compute, which means to calculate. A computer is a programmable machine (or more precisely, a programmable sequential state machine) that operates on data and is used
Week 1 Introduction to Computer and Algorithm (Part1) UniMAP Sem II 11/12 DKT121: Basic Computer Programming 1
 Week 1 Introduction to Computer and Algorithm (Part1) UniMAP Sem II 11/12 DKT121: Basic Computer Programming 1 General Information Contributes 3 units: 2 hours lectures 2 hours labs and tutorials Main
Week 1 Introduction to Computer and Algorithm (Part1) UniMAP Sem II 11/12 DKT121: Basic Computer Programming 1 General Information Contributes 3 units: 2 hours lectures 2 hours labs and tutorials Main
HISTORY OF COMPUTERS HISTORY OF COMPUTERS. Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English. Punch Card. Digital Data. II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN.
 Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Notes: In the slides, texts enclosed by curly parenthesis, { }, are examples. texts enclosed by square parenthesis,
Mesleki İngilizce - Technical English II Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr Notes: In the slides, texts enclosed by curly parenthesis, { }, are examples. texts enclosed by square parenthesis,
1-1 Computer Structure
 1-1 Computer Structure Computer: A computer is a programmable, multiuse machine that accepts data-raw, fact and figures; processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals,
1-1 Computer Structure Computer: A computer is a programmable, multiuse machine that accepts data-raw, fact and figures; processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals,
Computer Architecture
 IWKS 3300: NAND to Tetris Spring 2018 John K. Bennett Computer Architecture Foundations of Global Networked Computing: Building a Modern Computer From First Principles This course is based upon the work
IWKS 3300: NAND to Tetris Spring 2018 John K. Bennett Computer Architecture Foundations of Global Networked Computing: Building a Modern Computer From First Principles This course is based upon the work
