COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Exercises
|
|
|
- Jonah Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Exercises Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 For the 1st Date: February , 1.00pm-2.30pm Topics: discussed on the next pages You can have 3 sheets of handwritten notes you can write on both sides of each sheet any pages containing non-handwritten items will be removed during the quiz and student will get 0% for that quiz you have to write it yourself, not copy/xerox it from somebody else. Pages that have been xeroxed from somebody else will be treated as non-handwritten. 1
2 Reading list Appendex A: A.1 A.7 Appendix B: B.1 - B.4 Appendix C: C.1 - C.2 Chapter 1: , Chapter 2: , 2.6 (Intel Core i7 only) Exercise 1 1. Caches a. The average memory access time (AMAT) can be modeled using the following formula: AMAT = Hit time + Miss rate * Miss penalty Name and explain (briefly) one technique for each of the three components of the formula in order to decrease the average memory access time. 2
3 Exercise 1 b. Consider two identical machines differing only in the cache organization. The first machine has a 2-way set-associative cache, the second machine has a 4-way set-associative cache. The 1 st machine has a clock cycle time of 1.25ns and a miss rate of 1.0%, while the 2 nd machine has a clock cycle time of 1.4ns. Assuming a CPI of 2.0 for perfect cache behavior, 1.5 memory references per instruction, a cache miss penalty of 75ns, and a cache hit time of 1 clock cycle, determine the miss rate of the second machine in order for the four-way set associative cache to have a lower average memory access time than the first machine. Exercise 1 c. In the following, we would like to determine the set associativity leading to the minimal average memory access time. The miss penalty is still 75ns. A cache hit takes one clock cycle. However, the clock cycle time is depending on the set associativity n, with n=1 being a direct mapped cache, n=2 being a 2-way set associative cache etc. The formula describing the dependence between the clock cycle time and the set associativity is: Clock cycle time(n) = *n 2 Similarly, the Miss rate depends on n and can be described by the formula Miss rate = *n Give the formula for the overall Average Memory Access Time (AMAT) depending on n. 3
4 Exercise 1 d. Determine the value of n leading the minimal AMAT. Please note that you will have to round n to closest integer value. Exercise 2 2. Given the following code sequence to implement a matrix-vector multiply operation: for (i=0; i<96; i++ ) { for (j=0; j<96; j++ ) { c[i] = c[i]+ A[i][j] * b[j]; } } a. Determine the number of cache misses and the cache miss rate for the code sequence above, assuming that: 4
5 Exercise 2 all data items are 8-byte double precision floating point numbers, C-style row major ordering for multi-dimensional matrices no limitation on the cache size, each cache line is 64 bytes, no data item of A, b and c are in the cache upon start of the execution of the code sequence above the array c has been initialized to zero much earlier in the code and has subsequently been discarded from the cache we only worry about compulsory misses, not about capacity or conflict misses. Note: please give some details for your calculations in order to get partial points in case of a mistake. b. In the following, we would like to determine the impact of capacity and conflict misses. For the sake of simplicity, we focus on the variable A in the code sequence above. You can assume that A has a direct mapped cache of 4 KB ( = 4,096 bytes) on its own, i.e. the variables b and c use a different cache. Assuming that A[0][0] maps to the first cache block, cache block size of 64 bytes, what is the value for i,j for which A[i][j] replaces A[0][0] in the first cache block? 5
6 Exercise 3 3. Magnetic hard drives are accounting for the largest number of failures in today s computer systems. In order to increase the reliability of hard drives, servers typically use hard drives in a RAID 5 configuration, where four hard drives are used to store the data, and a fifth hard drive is used to store parity bits. These parity bits can be used to reconstruct the data of a failed hard drive. (Note, that a RAID 5 configuration cannot tolerate the failure of two hard drives simultaneously). For the following calculations, please assume the MTTF of each individual hard drive is 250,000 hours a. For the first step of the reliability calculation, let s assume that it takes on average 50 hours to get the replacement hard drive from the manufacturer of the server. Assuming that MTTR is 50h, how large is the MTFF of a RAID 5 configuration consisting of five hard drives in which the disk containing the parity bits is considered to be a backup to any of the other four hard drives? Exercise 3 b. In case a hard drive fails, data of the failed hard drive has to be reconstructed using the parity information bit-by-bit. Therefore, the MTTR depends not only on the time it takes to deliver the replacement hard drive, but also on the data reconstruction time. Thus, an improved formula for MTTR involves both components and depends on the size of the hard drives s which is given in GB, and can be described by the formula MTTR(s) = 50 hours hour * s (i.e. it takes 0.1 hours to reconstruct 1 GB of data.). Using the new, improved formula for MTTR, determine the according MTTF as a function of the size of the hard drive s. 6
7 Exercise 3 c. What is the formula for the MTTF(s) of a computer system having two such RAID 5 configurations using five hard drives each as a function of the disk capacity s? Note that the two RAID 5 systems are assumed to be completely independent sets of disks, and are not backing up each other. d. What is the formula for the MTTF(s,k) of a computer system having k independent RAID 5 disk systems with five disks each? Exercise 3 e. In order to provide a customer a 10 Terabyte storage solution, a company has the option to use either 250 GB disks, which would require 10 RAID 5 systems utilizing five disks each. Alternatively, one could use 500GB disks and have 5 RAID 5 configurations with five disks each. Which one of the two systems (system 1: k=10, s=250gb; system 2: k=5, s=500gb) promises a higher MTTF according to the formula developed in part d? 7
Name: 1. Caches a) The average memory access time (AMAT) can be modeled using the following formula: AMAT = Hit time + Miss rate * Miss penalty
 1. Caches a) The average memory access time (AMAT) can be modeled using the following formula: ( 3 Pts) AMAT Hit time + Miss rate * Miss penalty Name and explain (briefly) one technique for each of the
1. Caches a) The average memory access time (AMAT) can be modeled using the following formula: ( 3 Pts) AMAT Hit time + Miss rate * Miss penalty Name and explain (briefly) one technique for each of the
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz 1 (30 minutes) January 21, 2015
 University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. [ 20 marks] To capture the fact
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. [ 20 marks] To capture the fact
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring Caches and the Memory Hierarchy
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2019 Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned February 13 Problem Set #2 Due Wed, February 27 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp19
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2019 Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned February 13 Problem Set #2 Due Wed, February 27 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp19
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz 1 (30 minutes) January 21, 2015
 University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. In the following list of performance
University of Western Ontario, Computer Science Department CS3350B, Computer Architecture Quiz (30 minutes) January 2, 205 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Exercise. In the following list of performance
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned 9/17/2016 Problem Set #2 Due Tue, Oct 4 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/fa16 The problem sets are intended to help
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned 9/17/2016 Problem Set #2 Due Tue, Oct 4 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/fa16 The problem sets are intended to help
CS 433 Homework 4. Assigned on 10/17/2017 Due in class on 11/7/ Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page.
 CS 433 Homework 4 Assigned on 10/17/2017 Due in class on 11/7/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS 433 Homework 4 Assigned on 10/17/2017 Due in class on 11/7/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS422 Computer Architecture
 CS422 Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Lecture 19, 04 Mar 2004 Bhaskaran Raman Department of CSE IIT Kanpur http://web.cse.iitk.ac.in/~cs422/index.html Topics for Today Cache Performance Cache Misses:
CS422 Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Lecture 19, 04 Mar 2004 Bhaskaran Raman Department of CSE IIT Kanpur http://web.cse.iitk.ac.in/~cs422/index.html Topics for Today Cache Performance Cache Misses:
COSC 3406: COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 COSC 3406: COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Home-Work 5 Due Date: Friday, December 8 by 2.00 pm Instructions for submitting: Type your answers and send it by email or take a printout or handwritten (legible) on paper,
COSC 3406: COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Home-Work 5 Due Date: Friday, December 8 by 2.00 pm Instructions for submitting: Type your answers and send it by email or take a printout or handwritten (legible) on paper,
Agenda. Cache-Memory Consistency? (1/2) 7/14/2011. New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!)
 7/4/ CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches II Instructor: Michael Greenbaum New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!) Parallel Requests Assigned to
7/4/ CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches II Instructor: Michael Greenbaum New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!) Parallel Requests Assigned to
Adapted from David Patterson s slides on graduate computer architecture
 Mei Yang Adapted from David Patterson s slides on graduate computer architecture Introduction Ten Advanced Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory Technology and Optimizations Virtual Memory and Virtual
Mei Yang Adapted from David Patterson s slides on graduate computer architecture Introduction Ten Advanced Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory Technology and Optimizations Virtual Memory and Virtual
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures. Performance of Multilevel Cache
 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Memory Hierarchy (5) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Performance of Multilevel Cache Main Memory CPU L1 cache L2 cache Given CPU base
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Memory Hierarchy (5) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Performance of Multilevel Cache Main Memory CPU L1 cache L2 cache Given CPU base
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19. Cache
 COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19 Cache Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Cache Topics 3 Cache Hardware Cost How many total bits are required
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19 Cache Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Cache Topics 3 Cache Hardware Cost How many total bits are required
Lecture 12. Memory Design & Caches, part 2. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016
 211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - Call-chain - Factorial - Storage: - RAM - Caching - Direct - Mapping Rutgers University
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - Call-chain - Factorial - Storage: - RAM - Caching - Direct - Mapping Rutgers University
Solutions for Chapter 7 Exercises
 olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 1 olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 7.1 There are several reasons why you may not want to build large memories out of RAM. RAMs require more transistors to build than DRAMs
olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 1 olutions for Chapter 7 Exercises 7.1 There are several reasons why you may not want to build large memories out of RAM. RAMs require more transistors to build than DRAMs
Alexandria University
 Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 3 1. A cache has the following parameters: b, block size given in numbers of words;
Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 3 1. A cache has the following parameters: b, block size given in numbers of words;
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350):
 The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
Review: Performance Latency vs. Throughput. Time (seconds/program) is performance measure Instructions Clock cycles Seconds.
 Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
CSE 141 Spring 2016 Homework 5 PID: Name: 1. Consider the following matrix transpose code int i, j,k; double *A, *B, *C; A = (double
 CSE 141 Spring 2016 Homework 5 PID: Name: 1. Consider the following matrix transpose code int i, j,k; double *A, *B, *C; A = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n); B = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n);
CSE 141 Spring 2016 Homework 5 PID: Name: 1. Consider the following matrix transpose code int i, j,k; double *A, *B, *C; A = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n); B = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*n*n);
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (III)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (III) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 Memory Technology Performance metrics Latency problems handled through caches Bandwidth main concern for main memory
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (III) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 Memory Technology Performance metrics Latency problems handled through caches Bandwidth main concern for main memory
Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3
 Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
Memory Hierarchies 2009 DAT105
 Memory Hierarchies Cache performance issues (5.1) Virtual memory (C.4) Cache performance improvement techniques (5.2) Hit-time improvement techniques Miss-rate improvement techniques Miss-penalty improvement
Memory Hierarchies Cache performance issues (5.1) Virtual memory (C.4) Cache performance improvement techniques (5.2) Hit-time improvement techniques Miss-rate improvement techniques Miss-penalty improvement
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
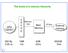 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Some slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Some slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05
CS 351 Exam 3 Mon. 5/11/2015
 CS 351 Exam 3 Mon. 5/11/2015 Name: Rules and Hints You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only additional resource you may consult during this exam. No calculators.
CS 351 Exam 3 Mon. 5/11/2015 Name: Rules and Hints You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only additional resource you may consult during this exam. No calculators.
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Module Outline. CPU Memory interaction Organization of memory modules Cache memory Mapping and replacement policies.
 M6 Memory Hierarchy Module Outline CPU Memory interaction Organization of memory modules Cache memory Mapping and replacement policies. Events on a Cache Miss Events on a Cache Miss Stall the pipeline.
M6 Memory Hierarchy Module Outline CPU Memory interaction Organization of memory modules Cache memory Mapping and replacement policies. Events on a Cache Miss Events on a Cache Miss Stall the pipeline.
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2018 SOLUTIONS Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned February 8 Problem Set #2 Due Wed, February 21 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp18
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS252 Graduate Computer Architecture Spring 2018 SOLUTIONS Caches and the Memory Hierarchy Assigned February 8 Problem Set #2 Due Wed, February 21 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp18
LECTURE 11. Memory Hierarchy
 LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. - Memory Hierarchies (II)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Fall 2008 Cache Performance Avg. memory access time = Hit time + Miss rate x Miss penalty with Hit time: time to access a data item which is available
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Fall 2008 Cache Performance Avg. memory access time = Hit time + Miss rate x Miss penalty with Hit time: time to access a data item which is available
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng
 Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/24/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #16 1 Software
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/24/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #16 1 Software
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Storage Systems
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Storage Systems Edgar Gabriel Spring 2016 I/O problem Current processor performance: e.g. Pentium 4 3 GHz ~ 6GFLOPS Memory Bandwidth: 133 MHz * 4 * 64Bit ~ 4.26 GB/s Current
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Storage Systems Edgar Gabriel Spring 2016 I/O problem Current processor performance: e.g. Pentium 4 3 GHz ~ 6GFLOPS Memory Bandwidth: 133 MHz * 4 * 64Bit ~ 4.26 GB/s Current
General Instructions. You can use QtSpim simulator to work on these assignments.
 General Instructions You can use QtSpim simulator to work on these assignments. Only one member of each group has to submit the assignment. Please Make sure that there is no duplicate submission from your
General Instructions You can use QtSpim simulator to work on these assignments. Only one member of each group has to submit the assignment. Please Make sure that there is no duplicate submission from your
Caches Concepts Review
 Caches Concepts Review What is a block address? Why not bring just what is needed by the processor? What is a set associative cache? Write-through? Write-back? Then we ll see: Block allocation policy on
Caches Concepts Review What is a block address? Why not bring just what is needed by the processor? What is a set associative cache? Write-through? Write-back? Then we ll see: Block allocation policy on
Q1: Finite State Machine (8 points)
 Q1: Finite State Machine (8 points) Answer the questions below for the finite state machine in this diagram: 1. Complete the truth table shown below. (2 points) Input Output State In State Out S 0 = 00
Q1: Finite State Machine (8 points) Answer the questions below for the finite state machine in this diagram: 1. Complete the truth table shown below. (2 points) Input Output State In State Out S 0 = 00
CS 341l Fall 2008 Test #4 NAME: Key
 CS 341l all 2008 est #4 NAME: Key CS3411 est #4, 21 November 2008. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible
CS 341l all 2008 est #4 NAME: Key CS3411 est #4, 21 November 2008. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible
Memory Technology. Chapter 5. Principle of Locality. Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 1
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 5 th Edition Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 5 th Edition Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic
Lab #10 Multi-dimensional Arrays
 Multi-dimensional Arrays Sheet s Owner Student ID Name Signature Group partner 1. Two-Dimensional Arrays Arrays that we have seen and used so far are one dimensional arrays, where each element is indexed
Multi-dimensional Arrays Sheet s Owner Student ID Name Signature Group partner 1. Two-Dimensional Arrays Arrays that we have seen and used so far are one dimensional arrays, where each element is indexed
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and login ID on the front.
 ETH login ID: (Please print in capital letters) Full name: 63-300: How to Write Fast Numerical Code ETH Computer Science, Spring 015 Midterm Exam Wednesday, April 15, 015 Instructions Make sure that your
ETH login ID: (Please print in capital letters) Full name: 63-300: How to Write Fast Numerical Code ETH Computer Science, Spring 015 Midterm Exam Wednesday, April 15, 015 Instructions Make sure that your
Main Memory Supporting Caches
 Main Memory Supporting Caches Use DRAMs for main memory Fixed width (e.g., 1 word) Connected by fixed-width clocked bus Bus clock is typically slower than CPU clock Cache Issues 1 Example cache block read
Main Memory Supporting Caches Use DRAMs for main memory Fixed width (e.g., 1 word) Connected by fixed-width clocked bus Bus clock is typically slower than CPU clock Cache Issues 1 Example cache block read
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Parallelizing The Matrix Multiplication. 6/10/2013 LONI Parallel Programming Workshop
 Parallelizing The Matrix Multiplication 6/10/2013 LONI Parallel Programming Workshop 2013 1 Serial version 6/10/2013 LONI Parallel Programming Workshop 2013 2 X = A md x B dn = C mn d c i,j = a i,k b k,j
Parallelizing The Matrix Multiplication 6/10/2013 LONI Parallel Programming Workshop 2013 1 Serial version 6/10/2013 LONI Parallel Programming Workshop 2013 2 X = A md x B dn = C mn d c i,j = a i,k b k,j
Case Study 1: Optimizing Cache Performance via Advanced Techniques
 6 Solutions to Case Studies and Exercises Chapter 2 Solutions Case Study 1: Optimizing Cache Performance via Advanced Techniques 2.1 a. Each element is 8B. Since a 64B cacheline has 8 elements, and each
6 Solutions to Case Studies and Exercises Chapter 2 Solutions Case Study 1: Optimizing Cache Performance via Advanced Techniques 2.1 a. Each element is 8B. Since a 64B cacheline has 8 elements, and each
CS 33. Caches. CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVIII 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 33 Caches CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVIII 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Cache Performance Metrics Miss rate fraction of memory references not found in cache (misses
CS 33 Caches CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVIII 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Cache Performance Metrics Miss rate fraction of memory references not found in cache (misses
Cache Memory and Performance
 Cache Memory and Performance Cache Performance 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
Cache Memory and Performance Cache Performance 1 Many of the following slides are taken with permission from Complete Powerpoint Lecture Notes for Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (CS:APP)
I, J A[I][J] / /4 8000/ I, J A(J, I) Chapter 5 Solutions S-3.
![I, J A[I][J] / /4 8000/ I, J A(J, I) Chapter 5 Solutions S-3. I, J A[I][J] / /4 8000/ I, J A(J, I) Chapter 5 Solutions S-3.](/thumbs/81/83055456.jpg) 5 Solutions Chapter 5 Solutions S-3 5.1 5.1.1 4 5.1.2 I, J 5.1.3 A[I][J] 5.1.4 3596 8 800/4 2 8 8/4 8000/4 5.1.5 I, J 5.1.6 A(J, I) 5.2 5.2.1 Word Address Binary Address Tag Index Hit/Miss 5.2.2 3 0000
5 Solutions Chapter 5 Solutions S-3 5.1 5.1.1 4 5.1.2 I, J 5.1.3 A[I][J] 5.1.4 3596 8 800/4 2 8 8/4 8000/4 5.1.5 I, J 5.1.6 A(J, I) 5.2 5.2.1 Word Address Binary Address Tag Index Hit/Miss 5.2.2 3 0000
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Introduction to Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Caches hold a subset of data from the main
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Introduction to Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Caches hold a subset of data from the main
Computer Architecture and Engineering. CS152 Quiz #2. March 3rd, Professor Krste Asanovic. Name:
 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #2 March 3rd, 2009 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: Notes: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 10 Pages Not all questions are of equal difficulty,
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #2 March 3rd, 2009 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: Notes: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 10 Pages Not all questions are of equal difficulty,
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design, part 1 - Introducation. Advanced Computer Architecture Mehran Rezaei
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design, part 1 - Introducation Advanced Computer Architecture Mehran Rezaei Temporal Locality The principle of temporal locality in program references says that if you access
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design, part 1 - Introducation Advanced Computer Architecture Mehran Rezaei Temporal Locality The principle of temporal locality in program references says that if you access
LRU. Pseudo LRU A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G H H H C. Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 LRU A list to keep track of the order of access to every block in the set. The least recently used block is replaced (if needed). How many bits we need for that? 27 Pseudo LRU A B C D E F G H A B C D E
LRU A list to keep track of the order of access to every block in the set. The least recently used block is replaced (if needed). How many bits we need for that? 27 Pseudo LRU A B C D E F G H A B C D E
1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory
 Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
b A bit is the basic unit for storing electronic data, for example an MP3 file. The term bit is a
 Digital download and file storage Syllabus: FSCo2 Focus Study: Mathematics and Communication Digital Storage b A bit is the basic unit for storing electronic data, for example an MP3 file. The term bit
Digital download and file storage Syllabus: FSCo2 Focus Study: Mathematics and Communication Digital Storage b A bit is the basic unit for storing electronic data, for example an MP3 file. The term bit
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2011/12 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2011/12 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2011/12 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2011/12 1 2
Submission instructions (read carefully): SS17 / Assignment 4 Instructor: Markus Püschel. ETH Zurich
 263-2300-00: How To Write Fast Numerical Code Assignment 4: 120 points Due Date: Th, April 13th, 17:00 http://www.inf.ethz.ch/personal/markusp/teaching/263-2300-eth-spring17/course.html Questions: fastcode@lists.inf.ethz.ch
263-2300-00: How To Write Fast Numerical Code Assignment 4: 120 points Due Date: Th, April 13th, 17:00 http://www.inf.ethz.ch/personal/markusp/teaching/263-2300-eth-spring17/course.html Questions: fastcode@lists.inf.ethz.ch
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
Final Exam Fall 2008
 COE 308 Computer Architecture Final Exam Fall 2008 page 1 of 8 Saturday, February 7, 2009 7:30 10:00 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of
COE 308 Computer Architecture Final Exam Fall 2008 page 1 of 8 Saturday, February 7, 2009 7:30 10:00 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of
Lecture 23: Storage Systems. Topics: disk access, bus design, evaluation metrics, RAID (Sections )
 Lecture 23: Storage Systems Topics: disk access, bus design, evaluation metrics, RAID (Sections 7.1-7.9) 1 Role of I/O Activities external to the CPU are typically orders of magnitude slower Example: while
Lecture 23: Storage Systems Topics: disk access, bus design, evaluation metrics, RAID (Sections 7.1-7.9) 1 Role of I/O Activities external to the CPU are typically orders of magnitude slower Example: while
Lecture 33 Caches III What to do on a write hit? Block Size Tradeoff (1/3) Benefits of Larger Block Size
 CS61C L33 Caches III (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 27-4-11 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks
CS61C L33 Caches III (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 27-4-11 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks
The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory System Performance. March 22, 2001
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory System Performance March 22, 2001 Topics Impact of cache parameters Impact of memory reference patterns memory mountain range matrix multiply Basic Cache
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory System Performance March 22, 2001 Topics Impact of cache parameters Impact of memory reference patterns memory mountain range matrix multiply Basic Cache
Solutions to exercises on Memory Hierarchy
 Solutions to exercises on Memory Hierarchy J. Daniel García Sánchez (coordinator) David Expósito Singh Javier García Blas Computer Architecture ARCOS Group Computer Science and Engineering Department University
Solutions to exercises on Memory Hierarchy J. Daniel García Sánchez (coordinator) David Expósito Singh Javier García Blas Computer Architecture ARCOS Group Computer Science and Engineering Department University
CISC 360. Cache Memories Nov 25, 2008
 CISC 36 Topics Cache Memories Nov 25, 28 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based
CISC 36 Topics Cache Memories Nov 25, 28 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based
Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles. Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!)
 Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!) Cache memory idea Use a small faster memory, a cache memory, to store recently
Basic Memory Hierarchy Principles Appendix C (Not all will be covered by the lecture; studying the textbook is recommended!) Cache memory idea Use a small faster memory, a cache memory, to store recently
Chapter 02. Authors: John Hennessy & David Patterson. Copyright 2011, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved. 1
 Chapter 02 Authors: John Hennessy & David Patterson Copyright 2011, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved. 1 Figure 2.1 The levels in a typical memory hierarchy in a server computer shown on top (a) and in
Chapter 02 Authors: John Hennessy & David Patterson Copyright 2011, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved. 1 Figure 2.1 The levels in a typical memory hierarchy in a server computer shown on top (a) and in
Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches
 Cache Memories 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal locality
Cache Memories 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal locality
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Computer Architecture ECE 568
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Computer Architecture ECE 568 Final Exam - Review Israel Koren ECE568 Final_Exam.1 1. A computer system contains an IOP which may
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Computer Architecture ECE 568 Final Exam - Review Israel Koren ECE568 Final_Exam.1 1. A computer system contains an IOP which may
And in Review! ! Locality of reference is a Big Idea! 3. Load Word from 0x !
 CS61C L23 Caches II (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 23 Caches II 2010-07-29!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! TOOLS THAT AUTOMATICALLY FIND SOFTWARE BUGS! Black Hat (a security
CS61C L23 Caches II (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 23 Caches II 2010-07-29!!!Instructor Paul Pearce! TOOLS THAT AUTOMATICALLY FIND SOFTWARE BUGS! Black Hat (a security
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Direct Mapped Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
Cache Memories. EL2010 Organisasi dan Arsitektur Sistem Komputer Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB 2010
 Cache Memories EL21 Organisasi dan Arsitektur Sistem Komputer Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB 21 Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of
Cache Memories EL21 Organisasi dan Arsitektur Sistem Komputer Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB 21 Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of
Chapter-5 Memory Hierarchy Design
 Chapter-5 Memory Hierarchy Design Unlimited amount of fast memory - Economical solution is memory hierarchy - Locality - Cost performance Principle of locality - most programs do not access all code or
Chapter-5 Memory Hierarchy Design Unlimited amount of fast memory - Economical solution is memory hierarchy - Locality - Cost performance Principle of locality - most programs do not access all code or
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Review : Pipelining. Memory Hierarchy
 CS61C L11 Caches (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Review : Pipelining The Big Picture Lecture #11 Caches 2009-07-29 Jeremy Huddleston!! Pipeline challenge is hazards "! Forwarding helps w/many data hazards
CS61C L11 Caches (1) CS61CL : Machine Structures Review : Pipelining The Big Picture Lecture #11 Caches 2009-07-29 Jeremy Huddleston!! Pipeline challenge is hazards "! Forwarding helps w/many data hazards
Memory hier ar hier ch ar y ch rev re i v e i w e ECE 154B Dmitri Struko Struk v o
 Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Opteron example Cache performance Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Processor DRAM gap (latency) Four issue superscalar
Memory hierarchy review ECE 154B Dmitri Strukov Outline Cache motivation Cache basics Opteron example Cache performance Six basic optimizations Virtual memory Processor DRAM gap (latency) Four issue superscalar
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Direct Mapped Cache Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Intel 8-core i7-5960x 3 GHz, 8-core, 20 MB of cache, 140
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Direct Mapped Cache Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Intel 8-core i7-5960x 3 GHz, 8-core, 20 MB of cache, 140
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 25: Multilevel Caches & Data Access Strategies Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 25: Multilevel Caches & Data Access Strategies Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative
Lecture 2. Memory locality optimizations Address space organization
 Lecture 2 Memory locality optimizations Address space organization Announcements Office hours in EBU3B Room 3244 Mondays 3.00 to 4.00pm; Thurs 2:00pm-3:30pm Partners XSED Portal accounts Log in to Lilliput
Lecture 2 Memory locality optimizations Address space organization Announcements Office hours in EBU3B Room 3244 Mondays 3.00 to 4.00pm; Thurs 2:00pm-3:30pm Partners XSED Portal accounts Log in to Lilliput
and data combined) is equal to 7% of the number of instructions. Miss Rate with Second- Level Cache, Direct- Mapped Speed
 5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
Lecture 16: Memory Hierarchy Misses, 3 Cs and 7 Ways to Reduce Misses Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996
 Lecture 16: Memory Hierarchy Misses, 3 Cs and 7 Ways to Reduce Misses Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996 RHK.S96 1 Review: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor Only Thus
Lecture 16: Memory Hierarchy Misses, 3 Cs and 7 Ways to Reduce Misses Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996 RHK.S96 1 Review: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor Only Thus
CSE 141 Computer Architecture Spring Lectures 17 Virtual Memory. Announcements Office Hour
 CSE 4 Computer Architecture Spring 25 Lectures 7 Virtual Memory Pramod V. Argade May 25, 25 Announcements Office Hour Monday, June 6th: 6:3-8 PM, AP&M 528 Instead of regular Monday office hour 5-6 PM Reading
CSE 4 Computer Architecture Spring 25 Lectures 7 Virtual Memory Pramod V. Argade May 25, 25 Announcements Office Hour Monday, June 6th: 6:3-8 PM, AP&M 528 Instead of regular Monday office hour 5-6 PM Reading
CS433 Homework 2 (Chapter 3)
 CS Homework 2 (Chapter ) Assigned on 9/19/2017 Due in class on 10/5/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration..
CS Homework 2 (Chapter ) Assigned on 9/19/2017 Due in class on 10/5/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration..
Giving credit where credit is due
 CSCE 23J Computer Organization Cache Memories Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu http://cse.unl.edu/~goddard/courses/csce23j Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based
CSCE 23J Computer Organization Cache Memories Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu http://cse.unl.edu/~goddard/courses/csce23j Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based
How to declare an array in C?
 Introduction An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type. Representation of a large number of homogeneous values.
Introduction An array is a collection of data that holds fixed number of values of same type. It is also known as a set. An array is a data type. Representation of a large number of homogeneous values.
CSCI-UA.0201 Computer Systems Organization Memory Hierarchy
 CSCI-UA.0201 Computer Systems Organization Memory Hierarchy Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) mzahran@cs.nyu.edu http://www.mzahran.com Programmer s Wish List Memory Private Infinitely large Infinitely fast Non-volatile
CSCI-UA.0201 Computer Systems Organization Memory Hierarchy Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) mzahran@cs.nyu.edu http://www.mzahran.com Programmer s Wish List Memory Private Infinitely large Infinitely fast Non-volatile
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
10/19/17. You Are Here! Review: Direct-Mapped Cache. Typical Memory Hierarchy
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
Memory Hierarchy. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Memory Hierarchy Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Time (ns) The CPU-Memory Gap The gap widens between DRAM, disk, and CPU speeds
Memory Hierarchy Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Time (ns) The CPU-Memory Gap The gap widens between DRAM, disk, and CPU speeds
CS/CoE 1541 Exam 2 (Spring 2019).
 CS/CoE 1541 Exam 2 (Spring 2019) Name: Question 1 (5+5+5=15 points): Show the content of each of the caches shown below after the two memory references 35, 44 Use the notation [tag, M(address),] to describe
CS/CoE 1541 Exam 2 (Spring 2019) Name: Question 1 (5+5+5=15 points): Show the content of each of the caches shown below after the two memory references 35, 44 Use the notation [tag, M(address),] to describe
Sarah L. Harris and David Money Harris. Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition Chapter 8 <1>
 Chapter 8 Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition Sarah L. Harris and David Money Harris Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition 215 Chapter 8 Chapter 8 :: Topics Introduction
Chapter 8 Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition Sarah L. Harris and David Money Harris Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition 215 Chapter 8 Chapter 8 :: Topics Introduction
Cache Memories October 8, 2007
 15-213 Topics Cache Memories October 8, 27 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance The memory mountain class12.ppt Cache Memories Cache
15-213 Topics Cache Memories October 8, 27 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance The memory mountain class12.ppt Cache Memories Cache
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter 2015 Lecture 3.1: Memory Hierarchy: What and Why? Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs3350b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson
CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter 2015 Lecture 3.1: Memory Hierarchy: What and Why? Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs3350b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson
