Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference
|
|
|
- Agatha Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:1, No:3, 27 waset.org/publication/1741 Abstract In the last couple of years Bluetooth has gained a large share in the market of home and personal appliances. It is now a well established technology a short range supplement to the wireless world of The two main trends of research that have sprung from these developments are directed towards the coexistence and performance issues of Bluetooth and as well as the coexistence in the very short range of multiple Bluetooth devices. Our work aims at thoroughly investigating different aspects of co-channel interference and effects of transmission power, distance and interference on Bluetooth connections. Keywords Bluetooth, co-channel interference, 82.11, performance analysis O I. INTRODUCTION NE of the dominant technologies in the current short range wireless world is undoubtedly Bluetooth. Over 9 million Bluetooth-enabled devices are expected to be in existence 5 years from now. This poses the case of studying possible interference issues as a major one. Users of Bluetooth can experience interference from different source using the same ISM band mainly Wireless LAN, home appliances and other Bluetooth devices in the vicinity. Channel interference greatly reduces the so precious bandwidth and adversely affects the achievable. Performance analysis is based simulation tools like the Network Simulator ver.2 (NS-2) and its Bluehoc and Blueware extensions[8, 9, 11]. However these studies focus mainly on the scatternet formation and less on the mutual independent existence of separate piconets in very close vicinity. There are very few analytical and simulation results concentrating on the co-channel interference, observed between independent neighboring piconets hopping on the same frequence. Users of Bluetooth enabled communication devices can experience interference from two major groups of devices on the one hand we have devices that work in the same ISM band but use different transmission technique like for example microwave ovens, baby monitors, cordless phones etc. The effects of these are to a great extend reduced by the FHSS used in the Bluetooth transmission. Another big interferer is the wireless LAN and transmissions following the standard. As they use a very wide band of 22 MHz (compared to the 1Mhz band used in Bluetooth FHSS), it is expected that they should show quite a negative effect on the performance of the Bluetooth devices. Another very important but so far little investigated is the so-called co-channel interference which arises when two independent piconets hop on the same frequency of the desired signal. This results in an adverse effect on the achievable and consequently the data rate for each user. Because of the specifics of the software used in most research so far this subject has been neglected to a certain extend while more stress has been put on creating and organizing transmissions among connected piconets forming the so called scatternets. Obviously the situation is different in a scatternet when there is synchronization between the participating piconets. Actually in near future with the exploding increase in the number of Bluetooth enabled devices the interference, experienced in independent adjacent piconets, might easily turn into a serious problem. There are very few studies in this respect known to the authors [2,4,5]. In the analytical model presented in [5] the distribution of the devices is taken as uniform, without a possibility of directly observing the effects of the distance between pairs of devices and the strength of the transmitted signals. The included simulation based on NS-2 provides insight based on the topology for the success rate in the case of data packets but does not cover the subject of SCO links. In [8, 9] a comparison is presented based on NS-2 simulation model between the performance of Bluetooth and WaveLAN. A valuable work that gives more inside on how Matlab tools can be incorporated in physical modeling of Bluetooth radio links is presented in [1]. Our study concentrates on the co-channel interference analysis on the physical layer in the presence of more than one adjacent Bluetooth piconets. We examine several metrics as the and the in the presence of a noisy channel, a IEEE interfering transmission, taking into consideration the different packet types as specified for the SCO links in the standard. From here on the paper is organized as follows: in the second part we review the main specifics of the Bluetooth physical layer; in the third we explain the simulation environment we are using and describe the models that we have studied. In the last part we give the results and some concluding remarks. International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 1(3) scholar.waset.org/ /1741
2 Vol:1, No:3, 27 International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:1, No:3, 27 waset.org/publication/1741 II. THE BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY A. The Bluetooth Protocol Architecture The Bluetooth standard [1] gives details on the architecture of the communication protocols. It specifies voice and data transfer over a radio channel with a maximum capacity of up to 1 Mbps. According to the standard Bluetooth works in two modes of short range the low power (1mW) 1m and the higher power (1mW) for up to 1 m distance. It was aimed at replacing cable connections between devices which in most cases form a personal area network (PAN) like mobile phones and earphones, labtops and PDAs. Nowadays though, due to its flexibility and very little power consumption, Bluetooth enabled devices find applications in different control systems in Home Networking as well as in small mobile ad-hoc sensor networks used in medical and industrial settings. Such type of integrated Bluetooth applications are envisaged as the greater share of the future Bluetooth market. [6] Bluetooth provides a point-to-point (only two Bluetooth devices sharing a channel) or point-to-multipoint connections where more than two devices share the channel. It uses a master-slave communication model with frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) transmission technique in the ISM band. The bandwidth of 81 MHz is allocated from 2.42GHz to GHz (in USA and most European countries) and is divided into 79 radio frequency channels of 1-MHz each, providing a raw data rate of 1 Mbps. The modulation scheme is Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK). In a piconet the transmissions of separate devices (in a point-to-point connection) or receiving by separate devices (in a point-tomultipoint connection) do not collide because the hopping frequency is governed by the master. The channel is represented by a pseudo-random hopping sequence hopping through the 79 channels. The hopping sequence is unique for the piconet and is determined by the Bluetooth device address of the master; the phase in the hopping sequence is determined by the Bluetooth clock of the master device. The nominal hop rate is 16 hops/s. Transmission is organized in a time division duplex (TDD) manner where in a slot of 625 µs a master polls a device and the device has to answer in the next following slot. B. Specifics of the Physical Link The Bluetooth standard defines two types of links for the support of voice and data transmissions. The synchronous connection-oriented (SCO) link is devised to meet the special requirements of time bounded transmissions with higher error tolerance then data transmissions. The SCO link is a symmetric, point-to-point link between the master and a specific device from the piconet. It reserves slots and can be considered as a circuit switched connection between the master and the slave. Due to the time constrain the SCO link does not allow retransmission. A master can support up to three simultaneous SCO links. The asynchronous connectionless (ACL) link is devised for data transmissions. The master exchanges packets with a slave on a per-slot basis. The ACL link provides a packet-switched connection between the master and all the slaves in the piconet. Only one ACL link is allowed between a master and a slave. To assure data integrity and lower bit error rate () packet retransmission is applied. A slave has to answer the master in the next following slot but only if it has been addressed by the master in the previous master-to-slave slot. C. Definition of the Packet Formats in the Baseband Specification The packet types used on the piconet are related to the physical link they are used in. Altogether there are 12 packet types defined, 5 of which are common for both the SCO and ACL link the ID, the NULL,, the POLL and the FHS packet which serve mostly OAM functions and the DM1 packet type which can carry both control information and data. The SCO packets used mainly for 64 kb/s voice do not include a CRC and are never retransmitted. There are three pure types of SCO packets HV1, HV2 and HV3 (Fig.1). The HV1 carries 1 bytes of information, protected by 1/3 FEC (Forward Error Correction) thus the payload length is fixed at 24 bits An HV1 packet carries 1,25 ms of speech at 64 kb/s rate, which means that an HV1 packet occupies one slot and has to be sent every two time slots. A new hop frequency is used at every new slot for the voice transmission. The HV2 has the same fixed payload length of 24 bits, but it is protected by 2/3 FEC and thus can carry 2 bytes of information. An HV2 reserves two tie slots in each direction and has to be sent every 4 time slots, providing 2.5ms of speech at 64 kb/s rate. The HV3 carries 3 bytes of information with no FEC or CRC present, resulting in an equivalent 24 bits payload length. It can carry 3.75 ms of voice, one HV3 packet being sent every 6 slots. Another type of packet specified for the SCO links is the hybrid DV packet which carries both voice and data in respectively 8 and 15 bits fields. The voice and data field are treated completely separately and the voice part is never retransmitted. (each new DV packet contains a new voice field). The voice field is not protected by FEC, but the data field contains a 16-bit CRC and is additionally encoded with a 2/3 rate FEC. Voice Packets (HV1, HV2, HV3) 72 bits 54 bits 24 bits Access code Header 3 bytes Payload HV1 HV2 HV3 2.5ms 1.25ms (HV1) 1 bytes 3.75ms (HV2) 2 bytes 3 bytes (HV3) + 1/3 FEC + 2/3 FEC Fig. 1 Structure of the voice packets = 366 bits International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 1(3) scholar.waset.org/ /1741
3 Vol:1, No:3, 27 International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:1, No:3, 27 waset.org/publication/1741 The ACL packets on the other hand require heavy retransmission, FEC and CRC protection (Fig.2). There are 6 pure ACL packets defined. The DM1 (data medium rate) carries up to 18 bytes of information plus CRC encoded with 2/3 FEC. It occupies a single slot. There is also a DH1 (Data High ) packet specified for one slot transmission, where the information is not protected by FEC but includes only 16 bit CRC thus providing a possibility of carrying up to 28 bytes of information. The DM3 packet is a DM1 packet with an extended payload, carrying up to 123 bytes of information. It covers three slots and the hopping frequency is kept the same for transmission of whole packet. The corresponding DH3 is similar to the DM3 packet except that it does not have FEC. The DM5 is a DM1 packet with an extended payload, up to 226 bytes, that spans 5 slots. The hopping frequency remains the same as in the first slot where the access code is transmitted. The highest possible asymmetrical transmission rate is achieved by the use of a DH5 packet. It is similar to the DM5 packet but does not include FEC and can carry up to 341 bits of information plus the 16 bit CRC code. In an asymmetric ACL link it can provide throughput up to 721. kbps in one direction and 57.6 in the other direction. 2/3 FEC No FEC DM1 DM3 DM5 DH1 DH3 DH5 Data Packet Types Symmetric Symmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric Fig.2 Structure of the Data Packets III. THE MATLAB SIMULATION ENVIRONMENT Even though there has been quite a few successful attempts to model and simulate the Bluetooth operation most of them utilize the NS-.2 and its extensions for specific Linux environments (Blueware and Bluehoc) [5,7,8,9]. All these tools provide very high level description possibilities and do not allow detailed capture of the physical specifics of the Bluetooth Baseband transmission. Recently the authors have found a nice example [1] of utilizing the possibilities of the very powerful Matlab Simulink environment. In our work we have concentrated on testing the possibilities of a Matlab model and compare the performance results for different cases of co-channel interference. The communication system described in part II, including the details of the packet types and their specific transmission characteristics can be very precisely constructed using blocks in the Simulink like the DSP Blockset and the Communications Blockset libraries. The communication link between the master transmitter and the slave receiver for voice transmissions is composed of speech processing, framing, coding, modulation, frequency hopping, radio interference and a radio channel model. These can be implemented one by one according to Bluetooth specification [1] and then can be put together in the Simulink tool. In our simulations, Bluetooth Simulink block libraries are used [1] and three separate Matlab/Simulink programs are constructed for performing the tests. IV. THE SIMULATION MODEL In our studies the simulation model comprises a master transmitter and a slave receiver, a radio channel, 82.11b interfering module, another Bluetooth pair operating in a separate piconet thus causing interference for our set, error meters and instrumentation. The model allows us to control and record precisely all the physical parameters and changes that affect the Bluetooth transmission thus influencing the performance that we a trying to evaluate. In the Matlab environment the noisy channel is simulated by an AWGN channel whose SNR can be controlled. The is generated by a separate independent block which allows us to control precisely the rate of transmission. In the first set of simulations we have studied the combined influence of the noisy environment worsened by a neighboring transmitting wireless device. We have also made a point to examine if there is any difference in the performance and the way the is affected in different types of packets. The simulation parameters for these cases are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. Opposing to other known studies and analytical models mentioned before our simulation model allows us to carry a set of experiments directly investigating the effects of the distance between the transmitting devices on the. The simulation parameters for the different packet types are presented in Table 3. V. DISCUSSION OF SIMULATION RESULTS In order to study the behavior of a Bluetooth connection we have devised the following simulation cases. CASE 1: Examine the versus hop frequency. In this case we have included the situation when in the close vicinity of the Bluetooth devices we have a noisy channel as well as interference. The effect is cumulative but definitely the has a decisive part. Our simulation shows that despite the fact that different types of voice packets (HV1, HV2 and HV3) have different FEC schemes the longer presence of interference leads to substantial, unacceptable levels of. It is also interesting to notice that the HV2 are most sensitive to this type of interference. The results are presented in Table 1. and Figs Table 1. versus hop frequency for HV1, HV2 and HV3 packets AWG N Time [ s] db 999 2/16-4 db -4 db International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 1(3) scholar.waset.org/ /1741
4 Vol:1, No:3, rate: rate: International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:1, No:3, 27 waset.org/publication/ Fig. 3 Performance of HV1 packets Fig.4 Performance of HV2 packets Fig. 5 Performance of HV3 packets The decisive effect of the interference and its strength is clearly noticeable from the comparison presented in Fig.6. We have observed a nearly 1 fold increase between the min IEEE packet rate of 2 and the max of Fig. 6 Comparison of for light and heavy interference for HV3 packets CASE 2: Another interesting case is how the performance of Bluetooth connections is influenced by the distance between the master and the slave. According to the Bluetooth standards the effective range of.1 W devices is up to 1 meters. But in the presence of a noisy channel and a interfering transmission this distance is much reduced. The behavior as can be seen from Fig. 7 is non-linear. There is a very short optimal range up to 4 meters. It is also possible to study the different behavior of HV1, HV2 and HV3 packets. At 2m the HV2 packets experience a.5 compared to.25 for the HV1 type and.4 for the HV3 type. HV2 type does not only show better performance but it is also least sensitive to the increase in the distance. It is interesting to note that similar results have been reported by the analytical and simulation findings in [5] for specific ACL packets. Table 2. versus distance for HV1, HV2 and HV3 packets AWG N Time[ s] db 2 2/16 up to 2m -4 db HV1 HV2 HV Distance [m] Fig. 5. versus distance between the master and the slave International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 1(3) scholar.waset.org/ /1741
5 Vol:1, No:3, 27 International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:1, No:3, 27 waset.org/publication/1741 CASE 3: As we have observed out of all types of interference the strongest is the interference experienced by neighboring independent piconets hoping simultaneously (Table 3. and Fig.6). To study their performance we have devised a simulation that examines the for a master-slave piconet pair and introduced the active transmission of another master slave pair in the vicinity. In this case the interference is turned off. The simulations have been repeated for the different types of packets. The is varied in the range of -1 to 1 db. The 3D results presentation allows us to determine a transmission effective zone depending on the ratio. Table 3. versus distance and for HV3 AWGN Time [ s] dB 2 2/16-4 db up to 1m Distance [m] Fig.6 3D mesh of simultaneously transmitting Bluetooth pairs VI. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK In this paper we have presented some initial results on using the powerful Matlab tool for simulating and investigating the performance of Bluetooth connections. We have shown that for the physical layer simulation Matlab Simulink allows us to keep close to the details of the Bluetooth communication link and examine in detail the influence of separate parameters. We have done this for the SCO links so far but we intend to extend the model to cover the ACL links as well. The result will be a powerful alternative simulation environment for studying the details Bluetooth devices and Bluetooth enabled devices in different configurations. [3] J. Haarsten, Bluetooth the universal radio interface for ad hoc, wireless connectivity, Erricsson Review, no.3, pp , [4] S.Zurbes, Considerations on Link and System Throughput of Bluetooth Networks, PIMRC 2, pp [5] C.M.Cordeiro, D.P.Agrawal, D.H.Sadok, Interference Modelling and Performance of Bluetooth MAC protocol, IEEE Trans. Comm. Vol 2, No.6, Nov. 23. pp [6] J.P.Lynch, Co-channel Interference in Bluetooth Piconets, Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Master of Science Thesis, Ch.3, 22 [7] C.Hsu, Y.J.Joung, An NS Based Bluetooth Topology Construction Environment, Proceedings of the 36 th annual Symposium, ANSS 23 [8] G.Tan, Blueware: Bluetooth Simulator for NS-2, [Online], Available from: godfreyt@lcs.mit.edu [9] Bluetooth Extension for NS, [Online}, Available: [1] Matlab Simulink, [Online], Available: [11] Network Simulator (NS-2), [Online], Available: Radosveta Sokullu received an M.Sc. degree in 1985 and a PhD in 1991 from the Sofia Technical University, Sofia, Bulgaria. She specialized in Advanced mathematics and programming as a postgraduate student at the Center of Applied Mathematics. In 2 she became an Assistant Professor at the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at Ege University, Izmir, Turkey and in 22 she was appointed Chair of the Telecommunications Branch. Her research interests are in the field of teletraffic modeling and simulation and more recently mobile and wireless systems especially ad-hoc networks. Engin Karatepe received the B.Sc. degree from Gaziantep University, Gaziantep, Turkey, in 1995, the M.Sc. degree from Ege University, Izmir, Turkey, in 2. He is presently working towards the Ph.D. degree in energy technologies at the Ege University. Since 1996, he has been with the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Ege University, where he is currently a Research Assistant. His research interests are in measurement and control of photovoltaic systems, renewable energy system modeling, fuzzy logic control, neural network, and Bluetooth networks modeling. References [1] Bluetooth Specivication SIG,[Online], Available: [2] N. Abramson, The throughput of packet broadcasting channels, IEEE Trans.Comm., vol. COM-25, pp , Jan.1997 International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 1(3) scholar.waset.org/ /1741
ADAPTIVE PACKET SELECTION ALGORITHM FOR BLUETOOTH DATA PACKETS
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Computer Science, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 2007 160 ADAPTIVE PACKET SELECTION ALGORITHM FOR BLUETOOTH DATA PACKETS RADOSVETA SOKULLU
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Computer Science, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 2007 160 ADAPTIVE PACKET SELECTION ALGORITHM FOR BLUETOOTH DATA PACKETS RADOSVETA SOKULLU
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
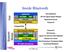 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING
 Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela
 By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
An Efficient Tool for the Evaluation of the Impact of WiFi Interference on Bluetooth Performance
 1 An Efficient Tool for the Evaluation of the Impact of WiFi Interference on Bluetooth Performance Madani Zeghdoud 1, Pascal Cordier 1, and Michel Terré 2 1 France Telecom R&D, Issy les Moulineaux, France.
1 An Efficient Tool for the Evaluation of the Impact of WiFi Interference on Bluetooth Performance Madani Zeghdoud 1, Pascal Cordier 1, and Michel Terré 2 1 France Telecom R&D, Issy les Moulineaux, France.
Improving Bluetooth EDR Data Throughput Using FEC and Interleaving
 Improving Bluetooth EDR Data Throughput Using FEC and Interleaving Ling-Jyh Chen 1, Tony Sun 2, and Yung-Chih Chen 1 1 Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica, Taipei 11529, Taiwan {cclljj, ycchen}@iis.sinica.edu.tw
Improving Bluetooth EDR Data Throughput Using FEC and Interleaving Ling-Jyh Chen 1, Tony Sun 2, and Yung-Chih Chen 1 1 Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica, Taipei 11529, Taiwan {cclljj, ycchen}@iis.sinica.edu.tw
Correct Bluetooth EDR FEC Performance with SEC-DAEC Decoding
 Correct Bluetooth EDR FEC Performance with SEC-DAEC Decoding R. Razavi, M. Fleury and M. Ghanbari By selecting from Bluetooth s Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) packet types according to channel conditions, optimal
Correct Bluetooth EDR FEC Performance with SEC-DAEC Decoding R. Razavi, M. Fleury and M. Ghanbari By selecting from Bluetooth s Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) packet types according to channel conditions, optimal
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM
 IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM SCORT - An Alternative to the Bluetooth SCO Link for Voice Operation in an Interference Environment Slide 1 Bluetooth SCO Link The Bluetooth
IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM SCORT - An Alternative to the Bluetooth SCO Link for Voice Operation in an Interference Environment Slide 1 Bluetooth SCO Link The Bluetooth
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
A Dynamic Interference-Avoidance Algorithm for Frequency Hopping Systems
 7 JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS SOFTWARE AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 5, NO. 2, JUNE 2009 A Dynamic Interference-Avoidance Algorithm for Frequency Hopping Systems Ivo Stojan Original scientific paper Abstract: In this
7 JOURNAL OF COMMUNICATIONS SOFTWARE AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 5, NO. 2, JUNE 2009 A Dynamic Interference-Avoidance Algorithm for Frequency Hopping Systems Ivo Stojan Original scientific paper Abstract: In this
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems
 Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems Abstract In the Bluetooth system, isochronous applications, such as voice and audio, are carried by Synchronous Connection Oriented
Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems Abstract In the Bluetooth system, isochronous applications, such as voice and audio, are carried by Synchronous Connection Oriented
PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin
 Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Tools for Evaluating Bluetooth Coexistence with Other 2.4GHz ISM Devices
 Tools for Evaluating Bluetooth Coexistence with Other 2.4GHz ISM Devices Ivan Howitt, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee Jose Gutierrez, Eaton Corporation Innovation Center Vinay Mitter, University of Wisconsin
Tools for Evaluating Bluetooth Coexistence with Other 2.4GHz ISM Devices Ivan Howitt, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee Jose Gutierrez, Eaton Corporation Innovation Center Vinay Mitter, University of Wisconsin
A Guide. Wireless Network Library Bluetooth
 A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF IEEE WIRELESS-LAN AND BLUETOOTH PICONET RANGE INTERFERENCE
 MODELING AND SIMULATION OF IEEE 802.11 WIRELESS-LAN AND BLUETOOTH PICONET RANGE INTERFERENCE Patrick O. Bobbie and Abdul-Lateef Yussiff School of Computing and Software Engineering Southern Polytechnic
MODELING AND SIMULATION OF IEEE 802.11 WIRELESS-LAN AND BLUETOOTH PICONET RANGE INTERFERENCE Patrick O. Bobbie and Abdul-Lateef Yussiff School of Computing and Software Engineering Southern Polytechnic
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
Evaluation of DSSS WLAN Beacon Caused by Interference with BLE Advertising Packet Considering the Difference in Frequency
 Journal of Signal Processing, Vol.21, No.6, pp.249-256, November 2017 PAPER Evaluation of DSSS WLAN Beacon Caused by Interference with BLE Advertising Packet Considering the Difference in Frequency Junya
Journal of Signal Processing, Vol.21, No.6, pp.249-256, November 2017 PAPER Evaluation of DSSS WLAN Beacon Caused by Interference with BLE Advertising Packet Considering the Difference in Frequency Junya
Co-Channel Interference in Bluetooth Piconets
 Co-Channel Interference in Bluetooth Piconets By Jamel Pleasant Lynch Jr. Committee Chairman: Dr. Brian Woerner ABSTRACT Bluetooth is an emerging short-range RF wireless voice and data communication technology
Co-Channel Interference in Bluetooth Piconets By Jamel Pleasant Lynch Jr. Committee Chairman: Dr. Brian Woerner ABSTRACT Bluetooth is an emerging short-range RF wireless voice and data communication technology
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Image acquisition and Communication
 Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
AC : A STUDY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF BLUETOOTH AND IEEE B COEXISTENCE
 AC 2007-1360: A STUDY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.11B COEXISTENCE Warith Al-Sulaimani, Modern College of Business and Science-Sultanate of Oman Warith Al-Sulaimani is a Lecturer and Consultant
AC 2007-1360: A STUDY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.11B COEXISTENCE Warith Al-Sulaimani, Modern College of Business and Science-Sultanate of Oman Warith Al-Sulaimani is a Lecturer and Consultant
Influence of the Interfernce Due to Co-Existence of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Transmissions
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 3 August 2014 ISSN : 2349-6010 Influence of the Interfernce Due to Co-Existence of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Transmissions
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 3 August 2014 ISSN : 2349-6010 Influence of the Interfernce Due to Co-Existence of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Transmissions
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Medium Access Control. MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols
 Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via Maximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of ARQ Protocol
 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via aximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol Xiang Li 1,2,*, an-tian Li 1, Zhen-Guo Gao 2, and Li-Ning Sun 1 1 obot esearch Institute, Harbin Institute
Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via aximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol Xiang Li 1,2,*, an-tian Li 1, Zhen-Guo Gao 2, and Li-Ning Sun 1 1 obot esearch Institute, Harbin Institute
Interference Mitigation Technique for Performance Enhancement in Coexisting Bluetooth and WLAN
 2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Interference Mitigation Technique for Performance Enhancement in Coexisting
2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Interference Mitigation Technique for Performance Enhancement in Coexisting
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Bhopal, , India 3 M.Tech Scholor,Department Of Computer Science, BIST Bhopal. Bhopal, , India
 Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Ethernet. Lecture 6. Outline. Ethernet - Physical Properties. Ethernet - Physical Properties. Ethernet
 Lecture 6 Ethernet Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on 9/20/12. Thick-net Thin-net Twisted Pair Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks
Lecture 6 Ethernet Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on 9/20/12. Thick-net Thin-net Twisted Pair Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Experimental Study on Co-existence of b with Alien Devices
 Experimental Study on Co-existence of 8.b with Alien Devices Javier del Prado and Sunghyun Choi Philips Research Briarcliff USA, Briarcliff Manor, New York Email: {javier.delprado,sunghyun.choi}@philips.com
Experimental Study on Co-existence of 8.b with Alien Devices Javier del Prado and Sunghyun Choi Philips Research Briarcliff USA, Briarcliff Manor, New York Email: {javier.delprado,sunghyun.choi}@philips.com
Proper Relay Reduction And Route Breakage Prediction In Blueooth Scatternet Scheduling
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 3 Issue 12 December 2014, Page No. 9712-9716 Proper Relay Reduction And Route Breakage Prediction In Blueooth
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 3 Issue 12 December 2014, Page No. 9712-9716 Proper Relay Reduction And Route Breakage Prediction In Blueooth
Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation
 Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation Ling-Jyh Chen, Rohit Kapoor, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 995, USA {cclljj, rohitk,
Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation Ling-Jyh Chen, Rohit Kapoor, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 995, USA {cclljj, rohitk,
Chapter 5. Wireless PANs
 Chapter 5 Wireless PANs 5.1 Introduction Introduction of Wireless PANs (WPANs) has caused the latest revolution in the area of wireless technologies. WPANs are short to very short-range (from a couple
Chapter 5 Wireless PANs 5.1 Introduction Introduction of Wireless PANs (WPANs) has caused the latest revolution in the area of wireless technologies. WPANs are short to very short-range (from a couple
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Lecture 6. Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1
 Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Experimental Assessment of Media Synchronization Quality in IEEE b under Bluetooth Interference
 Experimental Assessment of Media Synchronization Quality in IEEE 802.11b under Bluetooth Interference Masami KATO, Hirotsugu OKURA, Kiyoshige ITO and Shuji TASAKA Digital Systems Development Center BU,
Experimental Assessment of Media Synchronization Quality in IEEE 802.11b under Bluetooth Interference Masami KATO, Hirotsugu OKURA, Kiyoshige ITO and Shuji TASAKA Digital Systems Development Center BU,
Wireless multipoint communication for optical sensors in the industrial environment using the new Bluetooth standard
 Wireless multipoint communication for optical sensors in the industrial environment using the new Bluetooth standard Stephan Hussmann*a, Wing Yan Laua, Terry ChUa, Markus Grothofb aschool of Engineering,
Wireless multipoint communication for optical sensors in the industrial environment using the new Bluetooth standard Stephan Hussmann*a, Wing Yan Laua, Terry ChUa, Markus Grothofb aschool of Engineering,
November 1998 doc.: IEEE /378 IEEE P Wireless LANs Extension of Bluetooth and Direct Sequence Interference Model.
 IEEE P802.11 Wireless LANs Extension of Bluetooth and 802.11 Direct Sequence Interference Model Date: November 11, 1998 Author: Jim Zyren Harris Semiconductor Melbourne, FL, USA Phone: (407)729-4177 Fax:
IEEE P802.11 Wireless LANs Extension of Bluetooth and 802.11 Direct Sequence Interference Model Date: November 11, 1998 Author: Jim Zyren Harris Semiconductor Melbourne, FL, USA Phone: (407)729-4177 Fax:
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth
 Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Performance Analysis of b Networks in the Presence of Interference-Aware Bluetooth Devices
 Performance Analysis of.b Networks in the Presence of Interference-Aware Bluetooth Devices Deepthi Gopalpet Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Old Dominion University Norfolk, VA 9 USA dgopa@odu.edu
Performance Analysis of.b Networks in the Presence of Interference-Aware Bluetooth Devices Deepthi Gopalpet Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Old Dominion University Norfolk, VA 9 USA dgopa@odu.edu
A cluster based interference mitigation scheme for performance enhancement in IEEE
 756 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research J SCI IND RES VOL 7 SEPTEMBER 2 Vol. 7, September 2, pp. 756-76 A cluster based interference mitigation scheme for performance enhancement in IEEE 82.5.4
756 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research J SCI IND RES VOL 7 SEPTEMBER 2 Vol. 7, September 2, pp. 756-76 A cluster based interference mitigation scheme for performance enhancement in IEEE 82.5.4
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING
 A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF LOW RATE WPANS FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF LOW RATE WPANS FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS Nada Golmie, David Cypher, and Olivier Rebala National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, Maryland ABSTRACT In this article
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF LOW RATE WPANS FOR MEDICAL APPLICATIONS Nada Golmie, David Cypher, and Olivier Rebala National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, Maryland ABSTRACT In this article
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee. Dmitri A. Moltchanov kurssit/elt-53306/
 WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Comparative Analysis of ZigBee, WLAN and Bluetooth System and its Throughput Enhancement
 Comparative Analysis of ZigBee, WLAN and Bluetooth System and its Throughput Enhancement Ms. Hina Dhiman Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunication Sinhgad College of Engineering Pune, India Prof. Mrs.
Comparative Analysis of ZigBee, WLAN and Bluetooth System and its Throughput Enhancement Ms. Hina Dhiman Dept. of Electronics and Telecommunication Sinhgad College of Engineering Pune, India Prof. Mrs.
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth
 Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Optimizing Packet Size via Maximizing Throughput Efficiency of ARQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication Link
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED INFOATICS and COUNICATIONS, alta, September -7, 25 (pp24-28 Optimizing Pacet Size via aximizing Throughput Efficiency of AQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED INFOATICS and COUNICATIONS, alta, September -7, 25 (pp24-28 Optimizing Pacet Size via aximizing Throughput Efficiency of AQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Interference of Bluetooth and IEEE : Simulation Modeling and Performance Evaluation
 1 Interference of Bluetooth and IEEE 82.11: Simulation Modeling and Performance Evaluation N. Golmie, R. E. Van Dyck, and A. Soltanian National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, Maryland
1 Interference of Bluetooth and IEEE 82.11: Simulation Modeling and Performance Evaluation N. Golmie, R. E. Van Dyck, and A. Soltanian National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, Maryland
EC Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank
 EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
101seminartopics.com. Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks
 Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Bluetooth. Acknowledgements. Based on Jochen Schiller slides. Supporting text
 BT 1 Bluetooth FEUP PR BT 2 Acknowledgements Based on Jochen chiller slides upporting text» Jochen chiller, obile Comunications, Addison-Wesley» ection 7.5 Bluetooth BT 3 Bluetooth» Universal radio interface
BT 1 Bluetooth FEUP PR BT 2 Acknowledgements Based on Jochen chiller slides upporting text» Jochen chiller, obile Comunications, Addison-Wesley» ection 7.5 Bluetooth BT 3 Bluetooth» Universal radio interface
Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be
 IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
Performance Analysis of Bluetooth Network in the Presence of WI-FI System
 Performance Analysis of Bluetooth Network in the Presence of WI-FI System Shehu Hassan Ayagi IAA Associates limited,no. 1 Myohangu Road, Nassarawa, Kano, NigeriaP. O. BOX 4539 Email ashass20@yahoo.com
Performance Analysis of Bluetooth Network in the Presence of WI-FI System Shehu Hassan Ayagi IAA Associates limited,no. 1 Myohangu Road, Nassarawa, Kano, NigeriaP. O. BOX 4539 Email ashass20@yahoo.com
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
