Wireless Networked Systems
|
|
|
- Arabella Pope
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science
2 Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
3 Overview Bluetooth is a specification for the use of low power wireless communications over short distance. Although Bluetooth standard utilizes the same 2.4 GHz range of Wi-Fi Compared to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth networking is slower, a bit more limited in range, and supports many fewer devices Page 3 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
4 History In 1994 need for low power consumption wireless devices to substitute for cable Ericsson driving force behind Bluetooth Pre-Cell phone 1998, Ericsson, Nokia, IBM, Toshiba, Intel formed the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) 1999 Release of Bluetooth protocol 2002 IEEE adopted Bluetooth standard, working group Connections will be done seamlessly without need for installations and software drivers Devices can discover other Bluetooth-enabled devices Determine its capabilities and applications, and establish connections for data exchange Page 4 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
5 Bluetooth Usages Landline Cable Replacement Data/Voice Access Points Personal Ad-hoc Networks Page 5 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
6 Piconets / Scatternet Whenever there is a connection between two Bluetooth devices, a piconet is formed Always 1 master and up to 7 active slaves Any Bluetooth device can be either a master or a slave Can be a master of one piconet and a slave of another piconet at the same time (scatternet) Piconet uses centralized Time Division Multiplexing. All devices have the same timing and frequency hopping sequence Every Bluetooth device has its own clock and can be uniquely identified by its Bluetooth device address Slaves in a piconet use master's Bluetooth device address and clock to determine the frequency hopping sequence No time or frequency synchronization between piconets Page 6 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
7 Bluetooth Communication Bluetooth operates in unlicensed Industrial Scientific Medical (ISM) band at 2.4 GHz Band is divided into 79 channels with 1 MHz each Bluetooth devices use a Time-Division Duplex (TDD) scheme Channel is divided into consecutive slots (each 625 µs) One packet can be transmitted per slot Subsequent slots are alternatively used for transmitting and receiving Master can send only in EVEN slots while Slave can send only in ODD slots Page 7 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
8 Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) Reduce interference, Bluetooth uses Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) technology During a connection, radio transceivers hop from one channel to another 1600 hops per second through 79 1MHz channels One packet is sent on a channel, two devices then retune their frequencies (hop) to send the next packet on a different channel. So, if one frequency channel is blocked, limited disturbance to the Bluetooth communication Allows several Bluetooth networks to run concurrently without interrupting one other Link rate: 1 Mbps, but with overhead, this reduces to 721 kbps Typical range for Bluetooth is 10m, can reach up to 100m depending on the power class of the device Page 8 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
9 Bluetooth Protocol Stack The Baseband layer is responsible for channel coding and decoding Digitizes signals received by the radio for passing up the stack and it formats the data it receives from the Link Controller for transmission over the channel Host Controller Interface (HCI) defines uniform methods for accessing and controlling lower layers of the protocol stack, namely baseband and the link manager Link Manager Protocol (LMP) handles piconet management and link configuration. It also includes link security The Radio is the interface between the on-air channel medium and the Baseband The Link Controller is responsible for establishing and maintaining links between Bluetooth units Page 9 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
10 Bluetooth Protocol Stack Object Exchange Protocol (OBEX) is for object data exchange over infrared (IR) links Telephony Control Protocol Specification (TCS) defines call control signaling for establishing speech and data calls between Bluetooth devices, provides them with telephony services RFCOMM protocol defines a transport protocol for emulating RS-232 serial ports. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) includes interoperability requirements for Bluetooth Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) defines procedures for discovering services of other devices as well as determining the characteristics of those services. Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) provides connection-oriented and connectionless data services to the other higher level protocol layers Page 10 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
11 Bluetooth Transport Protocol Group " Radio Frequency (RF) " Baseband " Sending and receiving modulated bit streams " Defines the timing, framing " Flow control on the link. " Link Manager " Managing the connection states. " Enforcing Fairness among slaves. " Power Management " Logical Link Control & Adaptation Protocol " Handles multiplexing of higher level protocols " Segmentation & reassembly of large packets " Device discovery & QoS Page 11 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
12 Bluetooth Middleware Protocol Group " Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) " TCP/IP " Means for applications to discover device info, services and its characteristics. " Network Protocols for packet data communication, routing " RFCOMM " Cable replacement protocol, emulation of serial ports over wireless network Page 12 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
13 Physical Link Types " Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) " Point to Point Full Duplex between Master & Slave " Established once by master & kept alive till released by Master " Typically used for Voice connection ( to guarantee continuity ) " Master reserves slots used for SCO link on the channel to preserve time sensitive information " Asynchronous Connection Link (ACL) " It is a momentary link between master and slave. " No slots are reserved. " It is a Point to Multipoint connection. " Symmetric & Asymmetric links possible Page 13 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
14 Bluetooth State Machine Page 14 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
15 Bluetooth State Machine " Inquiry Scan " Inquiry " A device that wants to be discovered will periodically enter this mode and listen for inquiry packets. " Device sends an Inquiry packet addressed to GIAC or DIAC " Transmission is repeated on the inquiry hop sequence of frequencies. " Inquiry Response " When an inquiry message is received in the inquiry scan state, a response packet (FHS) containing the responding device address must be sent after a random number of slots. Page 15 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
16 Bluetooth State Machine " Page " The master uses the clock information, about the slave to be paged, to determine where in the hop sequence, the slave might be listening in the page scan mode. " The master sends a page message " Page Scan " The page scan substate can be entered by the slave from the standby state or the connection state. It listens to packets addressed to its DAC. " Page Response " On receiving the page message, the slave enters the slave page response substate. It sends back a page response consisting of its ID packet which contains its DAC, at the frequency for the next slot from the one in which page message was received. Page 16 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
17 Power Control Modes " Sniff Mode " This is a low power mode in which the listening activity of the slave is reduced. " In the sniff mode, the slave listens for transmissions only at fixed intervals T sniff, at the offset slot D sniff for N sniff times. These parameters are given by the master when it issues the SNIFF command to the slave. " Hold Mode " Slave temporarily (for T hold sec) does not support ACL packets on the channel (possible SCO links will still be supported). " By this capacity can be made free to do other things like scanning, paging, inquiring, or attending another piconet. " The slave unit keeps its active member address (AM_ADDR). Page 17 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
18 Power Control Modes " Park Mode " This is a very low power mode with very little activity. " The slave however, stays synchronized to the channel. " The parked slaves regularly listen for beacon signals at intervals decided by the beacon structure communicated to the slave during the start of parking. " The parked slave has to be informed about a transmission in a beacon channel which is supported by the master to keep parked slaves in synchronization and send them any other information. " Any message to be sent to a parked member are sent over the broadcast channel. " It also helps the master to have more than seven slaves. Page 18 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
19 Functional Overview Standby Waiting to join a piconet Unconnected Standby Standby Inquire Ask about radios to connect to Page Connect to a specific radio Connected Connecting States Active States Detach Transmit data AMA Inquiry T typical=2s Connected AMA Page T typical=0.6s Actively on a piconet (master or slave) T typical=2 ms T typical=2 ms Park/Hold Low Power connected states Low Power States Releases AMA Address PARK PMA HOLD AMA Page 19 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
20 Functional Overview Devices not connected to a piconet are in STANDBY mode, using low power. A connection is made by either a PAGE command if the address is known or by the INQUIRY command followed by a PAGE When a radio sends an INQUIRE command, all the listening radios respond with their FHS packets, which tells the inquiring radio of all the radios in the area. All listening radios perform a page scan and/or an inquiry scan every 1.25 seconds. The master radio sends an FHS to the paged radio. Page 20 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
21 Functional Overview When a radio joins a piconet it is assigned a 3 bit Active Member Address(AMA). Once the piconet has eight radios, the master assigns puts a radio into the PARK mode. This is one of the low power states, in which the radio releases its AMA for a 8 bit PMA (Passive Member Address). The freed AMA can be assigned to another radio wishing to join the piconet. Though upto 256 radios can actively reside on a piconet, only 8 of them with AMA s can transfer data. Page 21 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
22 Ex: Bluetooth Connection with a Device with Dial-up Service First, Bluetooth device looks for devices that it might connect to Step 1 - the Inquiry Process. Inquiring device, A, sends out an inquiry packet or repeated inquiry packets and waits to receive responses back Discoverable devices in range respond to an inquiry by sending a Frequency Hop Synchronization (FHS) packet, which contains all the information device A needs to connect to the responding device, including the Bluetooth device's address, page scan modes, and clock offset All devices that respond to the inquiry are reported to the host controller of device A. List of all devices discovered is presented to the user - is applicationdependent Page 22 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
23 Ex: Bluetooth Connection with a Device with Dial-up Service At this point, A knows which devices are in range, but it doesn t know which devices support dial-up Step 2 - Using information retrieved from inquiry, A now attempts to connect to different devices that responded to its inquiry in order to find out what services they support Depending on the application, device A may either 1) Establish links to all devices that responded to its inquiry and get information about their services and later on reconnect with one that supports dial-up networking; or 2) Upon seeing that a device supports dial-up networking, directly proceed to setting up a connection with that device without finding out the services from the rest of the devices in the list. In following slide, second option is adopted. Page 23 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
24 Ex: Bluetooth Connection with a Device with Dial-up Service Step 2 continued Device A wants to find out services of a device, so, device A sends out paging packets Connectable device will respond and a baseband link can be established between the two devices Following that, a L2CAP connection will be established before they can exchange service information. Information exchange is handled by Service Discovery Protocol Device B responds, I have dial-up networking service RFCOMM connection can then be established across the already existing L2CAP link After this, a dial-up networking connection can then be established on top of the RFCOMM connection Laptop can then start using the cell phone to access the phone network without any cables being needed for connections Page 24 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
25 Ex: Bluetooth Connection with a Device with Dial-up Service Step 1 Step 2 Page 25 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
26 Bluetooth Inquiry Process Uses 32 inquire channels to send out inquiry messages Send out inquiry on 32 channels, broken up into 2 inquiry hop trains (16 different channels to transmit packets) A device periodically listens for inquiry packets at a single frequency chosen out of 16 frequencies Stays in the state long enough for a inquiring device to cover 16 frequencies Receiver does an inquire scan frequent enough so that it is guaranteed to wake up during a 16 channel train Devices that allow themselves to be discoverable issue an inquiry response Will re-enter inquiry scan state even after responding to an inquire O D J F E I H A K G C B Note that a device can be Undiscoverable M L P N Q Page 26 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
27 Bluetooth Inquiry Process Each full scan of a 16 channel train takes about 1.28 seconds 16 channels * 625us * 128 trains = 1.28 seconds One full 16 channel train takes 10ms. Receiver enters inquiry scan state at least once every 1.28 seconds, and stays in that state for 10ms. The 128 train scan is repeated up to 4 times for each train (10.24 seconds), after which the inquiring device should know everyone nearby Page 27 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
28 Bluetooth Paging Process Step 1: Device broadcasts a page message out to the device that it wants to set up a connection with Does this in a similar manner as inquire messages (on 2 frequency trains of 16 frequencies each) Once the device receives a page response, it will stop paging Step 2: In the page response, an acknowledgement is sent back to the master containing the slave ID Step 3: In the master response, the frequency hopping generator is stopped and the master issues an FHS packet to the slave Step 4: The slave issues a final slave response transmission that is aligned to the slave s native clock Using the data from the FHS packet, the slave calculates adopts the master s frequency hopping pattern and synchronizes to its clock Page 28 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
29 Bluetooth Paging Process Step 5: When the master receives the packet, it jumps back to its frequency hopping pattern and assigns the slave an Active Member Address (AMA) for the piconet Master sends out a poll packet to ensure that the slave is on its frequency hopping pattern Step 6: Once the slave receives the poll packet, the slave replies with any kind of packet to ensure that it is on the right channel The acknowledgement must be received by the Master within the timeout period At the conclusion of step 6, a new synchronized connection is established between the master and the slave Page 29 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
30 Bluetooth Profiles Bluetooth is different from most network protocols. Most network protocols focus defining how the channels are to be used and leave application designers to define what they will be used for. Bluetooth V 1.1 defines 13 specific profiles (applications) that will be supported along with the different protocol stacks for each of them. Generic access profile provides secure channels between the master and slave. Service discovery profile allows devices to discover what services are available from other devices. Serial port profile for applications that need a serial port communication 30 Page 30 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
31 Bluetooth Profiles Generic object exchange profile provide support for the client/server model. note that a slave can be a client or a server. LAN access profile is a direct competitor of allows a Bluetooth device to connect to a fixed network. Dialup access profile Ericsson s original motivation allows a notebook computer to communicate to a mobile phone without wires Fax profile allows fax machines to connect to mobile phones wirelessly to send and receive faxes 31 Page 31 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
32 Bluetooth Profiles Cordless Telephony Profile connect a cordless telephone handset to a base station without wires. Intercom profile allows two telephones to connect like walkie-talkies Headset Profile good for hands free telephony I.E. while driving a car The last three profiles are for wireless devices to exchange a wide variety of data Object Push profile for simple objects File transfer profile - general file transfer Synchronization profile - was designed to facilitate the exchange of data in both directions between a P.C. and a P.D.A. 32 Page 32 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
33 Interoperability & Profiles Represents default solution for a usage model Vertical slice through the protocol stack Basis for interoperability and logo requirements Each Bluetooth device supports one or more profiles Protocols Applications Profiles Page 33 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
34 Packet Structure 72 bits 54 bits bits Access Code Header Payload Voice header Data CRC No CRC No retries FEC (optional) ARQ FEC (optional) Page 34 Spring 2013 Bluetooth CS 795/ Wireless Networked Systems
35 Zigbee Page 35 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
36 The ZigBee Alliance Solution Targeted at home and building automation and controls, consumer electronics, PC peripherals, medical monitoring, and toys Industry standard through application profiles running over IEEE radios Primary drivers are simplicity, long battery life, networking capabilities, reliability, and cost Alliance provides interoperability and certification testing Page 36 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
37 The Wireless Market SHORT < RANGE > LONG TEXT GRAPHICS INTERNET ZigBee HI-FI AUDIO Bluetooth 2 Bluetooth1 STREAMING VIDEO b DIGITAL VIDEO MULTI-CHANNEL VIDEO a/HL2 & g LAN PAN LOW < DATA RATE > HIGH Page 37 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
38 Applications security HVAC AMR lighting control access control BUILDING AUTOMATION CONSUMER ELECTRONICS TV VCR DVD/CD remote patient monitoring fitness monitoring PERSONAL HEALTH CARE ZigBee Wireless Control that Simply Works PC & PERIPHERALS mouse keyboard joystick asset mgt process control environmental energy mgt INDUSTRIAL CONTROL RESIDENTIAL/ LIGHT COMMERCIAL CONTROL security HVAC lighting control access control lawn & garden irrigation Page 38 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
39 IEEE & ZigBee In Context Application Customer API Security 32- / 64- / 128-bit encryption Network Star / Mesh / Cluster-Tree MAC PHY 868MHz / 915MHz / 2.4GHz Silicon Stack App ZigBee Alliance IEEE the software Network, Security & Application layers Brand management IEEE the hardware Physical & Media Access Control layers Page 39 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
40 Development of the Standard APPLICATIONS APPLICATION INTERFACE SECURITY NETWORK LAYER Star/Cluster/Mesh MAC LAYER MAC LAYER PHY LAYER 2.4 GHz 915MHz 868 MHz Application ZigBee Stack Customer IEEE ZigBee Alliance Silicon ZigBee Alliance 50+ companies: semiconductor mfrs, IP providers, OEMs, etc. Defining upper layers of protocol stack: from network to application, including application profiles First profiles published mid 2003 IEEE Working Group Defining lower layers of protocol stack: MAC and PHY scheduled for release in April Page 40 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
41 Stack Reference Model End developer applications, designed using application profiles ZA1 ZA2 ZAn IA1 IAn Application interface designed using general profile API UDP Topology management, MAC management, routing, discovery protocol, security management Channel access, PAN maintenance, reliable data transport Transmission & reception on the physical radio channel ZigBee NWK IEEE MAC (CPS) IEEE PHY IP LLC MAC (SSCS) Page 41 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
42 IEEE Basics is a simple packet data protocol for lightweight wireless networks Channel Access is via Carrier Sense Multiple Access with collision avoidance and optional time slotting Message acknowledgement and an optional beacon structure Multi-level security Three bands, 27 channels specified 2.4 GHz: 16 channels, 250 kbps MHz : 1 channel, 20 kbps MHz: 10 channels, 40 kbps Works well for Long battery life, selectable latency for controllers, sensors, remote monitoring and portable electronics Features of the MAC: Association/dissociation, ACK, frame delivery, channel access mechanism, frame validation, guaranteed time slot management, beacon management, channel scan Page 42 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
43 IEEE MAC Overview Employs 64-bit IEEE & 16-bit short addresses Ultimate network size can reach 2 64 nodes (more than we ll probably need ) Using local addressing, simple networks of more than 65,000 (2^16) nodes can be configured, with reduced address overhead Three devices specified Network Coordinator Full Function Device (FFD) Reduced Function Device (RFD) Simple frame structure Reliable delivery of data Association/disassociation AES-128 security CSMA-CA channel access Optional superframe structure with beacons Page 43 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
44 ZigBee Network Topologies Supports multiple network topologies including Star, Cluster Tree and Mesh Mesh Star Cluster Tree PAN coordinator Full Function Device Reduced Function Device Page 44 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
45 IEEE Device Types Three device types Network Coordinator Maintains overall network knowledge; most sophisticated of the three types; most memory and computing power Full Function Device Carries full functionality and all features specified by the standard Additional memory, computing power make it ideal for a network router function Could also be used in network edge devices (where the network touches the real world) Reduced Function Device Carriers limited (as specified by the standard) functionality to control cost and complexity General usage will be in network edge devices All of these devices can be no more complicated than the transceiver, a simple 8-bit MCU and a pair of AAA batteries! Page 45 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
46 IEEE MAC Layer Traffic Type Periodic data (e.g. sensors) Intermittent data (e.g. light switch) Repetitive low latency data (e.g. mouse) Frame Types Data Frame used for all transfers of data Beacon Frame used by a coordinator to transmit beacons Acknowledgment Frame used for confirming successful frame reception MAC Command Frame used for handling all MAC peer entity control transfers Page 46 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
47 MAC Options Two channel access mechanisms Non-beacon network Standard ALOHA CSMA-CA communications Positive acknowledgement for successfully received packets Beacon-enabled network Superframe structure For dedicated bandwidth and low latency Set up by network coordinator to transmit beacons at predetermined intervals 15ms to 252sec (15.38ms*2n where 0 n 14) 16 equal-width time slots between beacons Channel access in each time slot is contention free Three security levels specified None Access control lists Symmetric key employing AES-128 Page 47 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
48 PHY frame structure PHY packet fields Preamble (32 bits) synchronization Start of packet delimiter (8 bits) shall be formatted as PHY header (8 bits) PSDU length PSDU (0 to 127 bytes) data field Sync Header Start of Preamble Packet Delimiter 4 Octets PHY Header Frame Length (7 bit) 1 Octets 1 Octets Reserve (1 bit) PHY Payload PHY Service Data Unit (PSDU) Bytes Page 48 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
49 ZigBee and Bluetooth Optimized for different applications ZigBee Smaller packets over large network Mostly Static networks with many, infrequently used devices Home automation, toys, remote controls, etc. Bluetooth Larger packets over small network Ad-hoc networks File transfer Screen graphics, pictures, handsfree audio, Mobile phones, headsets, PDAs, etc. Page 49 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
50 Page 50 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems Copyright 2002 The ZigBee and Bluetooth Air interface ZigBee DSSS- 11 chips/ symbol 62.5 K symbols/s 4 Bits/ symbol Peak Information Rate ~128 Kbit/second Bluetooth FHSS 1 M Symbol / second Peak Information Rate ~720 Kbit / second
51 ZigBee and Bluetooth Protocol Stack Comparison Silicon Application Application Interface Network Layer Data Link Layer MAC Layer MAC Layer PHY Layer ZigBee Stack Zigbee Application Voice Intercom Headset Cordless Group Call Telephony Control Protocol Silicon vcard User Interface vcal vnote OBEX vmessage Dial-up Networking RFCOMM (Serial Port) L2CAP Host Control Interface Link Manager Link Controller Baseband RF Bluetooth Stack Bluetooth Fax Service Discovery Protocol Applications Page 51 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
52 ZigBee and Bluetooth Timing Considerations ZigBee: Network join time = 30ms typically Sleeping slave changing to active = 15ms typically Active slave channel access time = 15ms typically Bluetooth: Network join time = >3s Sleeping slave changing to active = 3s typically Active slave channel access time = 2ms typically ZigBee protocol is optimized for timing critical applications Page 52 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
53 ZigBee and Bluetooth Comparison Overview Bluetooth ZigBee AIR INTERFACE FHSS DSSS PROTOCOL STACK 250 kb 28 kb BATTERY rechargeable non-rechargeable DEVICES/NETWORK LINK RATE 1 Mbps 250 kbps RANGE ~10 meters (w/o pa) ~30 meters Page 53 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
54 Wireless Networking Standards Market Name Standard Application Focus System Resources Battery Life (days) Network Size Bandwidth (KB/s) Transmissio n Range (meters) Success Metrics GPRS/GSM 1xRTT/ CDMA Wide Area Voice & Data Wi-Fi b Web, , Video Bluetooth Cable Replaceme nt 16MB+ 1MB+ 250KB ZigBee Monitoring & Control 4KB - 32KB 100-1, / 65,000 11, , Reach, Quality Speed, Flexibility Cost, Convenien ce Reliability, Power, Cost Page 54 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
55 Questions Page 55 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked Systems
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
ZigBee & Wireless Sensor Networks Case Study: ZigBee & IEEE S.rou.2. ZigBee Solution. What is ZigBee?
 S.rou.2-2 Wireless Sensor Networks Case Study: ZigBee & IEEE802.15.4 S.rou.2 ZigBee & 802.15.4 ZigBee overview IEEE 802.15.4 overview ZigBee & bluetooth End Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai,
S.rou.2-2 Wireless Sensor Networks Case Study: ZigBee & IEEE802.15.4 S.rou.2 ZigBee & 802.15.4 ZigBee overview IEEE 802.15.4 overview ZigBee & bluetooth End Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai,
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
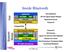 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Electromagnetic Spectrum (3kHz 300GHz)
 Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
ZigBee/ David Sanchez Sanchez.
 ZigBee/802.15.4 David Sanchez Sanchez david.sanchezs@upf.edu Lecture Overview 1. Introduction and motivation to ZigBee 2. ZigBee/802.15.4 specification 1. Definitions 2. MAC communication modes 3. Network
ZigBee/802.15.4 David Sanchez Sanchez david.sanchezs@upf.edu Lecture Overview 1. Introduction and motivation to ZigBee 2. ZigBee/802.15.4 specification 1. Definitions 2. MAC communication modes 3. Network
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Message acknowledgement and an optional beacon. Channel Access is via Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
 ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU
 Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Wireless control that simply works CES January 9, Bob Heile Chairman, Zigbee Alliance
 Wireless control that simply works CES 2004 January 9, 2004 Bob Heile Chairman, Zigbee Alliance 2 What is the ZigBee Alliance? A rapidly growing, worldwide, non-profit industry consortium consisting of
Wireless control that simply works CES 2004 January 9, 2004 Bob Heile Chairman, Zigbee Alliance 2 What is the ZigBee Alliance? A rapidly growing, worldwide, non-profit industry consortium consisting of
Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) Wireless PAN
 Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) IEEE P802.15 Working Group Wireless PAN Applications Home Networking Automotive Networks Industrial Networks Interactive Toys Remote Metering Overview Data rates
Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) IEEE P802.15 Working Group Wireless PAN Applications Home Networking Automotive Networks Industrial Networks Interactive Toys Remote Metering Overview Data rates
ZIGBEE. Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS
 ZIGBEE Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS OUTLINE ZIGBEE AND APPLICATIONS IEEE 802.15.4 PROTOCOL ZIGBEE PROTOCOL ZIGBEE ALLIANCE ZIGBEE APPLICATIONS PHYSICAL LAYER MAC LAYER ZIGBEE
ZIGBEE Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS OUTLINE ZIGBEE AND APPLICATIONS IEEE 802.15.4 PROTOCOL ZIGBEE PROTOCOL ZIGBEE ALLIANCE ZIGBEE APPLICATIONS PHYSICAL LAYER MAC LAYER ZIGBEE
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Outline. TWR Module. Different Wireless Protocols. Section 7. Wireless Communication. Wireless Communication with
 Section 7. Wireless Communication Outline Wireless Communication with 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol Introduction to Freescale MC12311 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol TWR-12311 Module TWR-MC12311 Smart Radio Features
Section 7. Wireless Communication Outline Wireless Communication with 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol Introduction to Freescale MC12311 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol TWR-12311 Module TWR-MC12311 Smart Radio Features
Wireless communication standards: What makes them unattractive for WSN:
 Wireless communication standards: IEEE 802.11 a/b/g Bluetooth GSM What makes them unattractive for WSN: Power hungry (need big batteries) Complexity (need lots of clock cycles and memory) New protocol
Wireless communication standards: IEEE 802.11 a/b/g Bluetooth GSM What makes them unattractive for WSN: Power hungry (need big batteries) Complexity (need lots of clock cycles and memory) New protocol
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee. Dmitri A. Moltchanov kurssit/elt-53306/
 WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Chapter 7. ZigBee (IEEE ) Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel
 Chapter 7 ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4) Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Chapter 7 ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4) Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be
 IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
ZigBee Technology: Wireless Control that Simply Works
 ZigBee Technology: Wireless Control that Simply Works Patrick Kinney Kinney Consulting LLC Chair of IEEE 802.15.4 Task Group Secretary of ZigBee BoD Chair of ZigBee Building Automation Profile WG - 1 -
ZigBee Technology: Wireless Control that Simply Works Patrick Kinney Kinney Consulting LLC Chair of IEEE 802.15.4 Task Group Secretary of ZigBee BoD Chair of ZigBee Building Automation Profile WG - 1 -
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
What is a personal area network?
 Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)
Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)
A Comprehensive Study of ZigBee. Presented by Dr. K F Tsang Citycom Technology Ltd. Tel:
 A Comprehensive Study of ZigBee Presented by Dr. K F Tsang Citycom Technology Ltd. Tel: 2788-7806 Email: ee330015@cityu.edu.hk 1 1 Outline Introduction of ZigBee Market analysis Characteristics of ZigBee
A Comprehensive Study of ZigBee Presented by Dr. K F Tsang Citycom Technology Ltd. Tel: 2788-7806 Email: ee330015@cityu.edu.hk 1 1 Outline Introduction of ZigBee Market analysis Characteristics of ZigBee
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Chapter 7. IEEE ZigBee. Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel
 Chapter 7 IEEE 802.15.4 ZigBee Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Chapter 7 IEEE 802.15.4 ZigBee Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN, Meshes...
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN, Meshes... Introduction Bluetooth Zigbee Ad-Hoc: Routing and Topology Mgmnt Meshes: Applications and Specific Problems Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/didattica/nc/ Ad-Hoc Networks
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN, Meshes... Introduction Bluetooth Zigbee Ad-Hoc: Routing and Topology Mgmnt Meshes: Applications and Specific Problems Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/didattica/nc/ Ad-Hoc Networks
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea
 Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea http://usn.konkuk.ac.kr/~jskim 1 IEEE 802.x Standards 802.11 for Wireless Local Area Network 802.11 legacy clarified 802.11 legacy
Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea http://usn.konkuk.ac.kr/~jskim 1 IEEE 802.x Standards 802.11 for Wireless Local Area Network 802.11 legacy clarified 802.11 legacy
Topics. Introduction Architecture Node Types Network Topologies Traffic Modes Frame Format Applications Conclusion
 ZigBee Topics Introduction Architecture Node Types Network Topologies Traffic Modes Frame Format Applications Conclusion Introduction The Wireless technologies (WiFi,GSM,and Bluetooth) All have one thing
ZigBee Topics Introduction Architecture Node Types Network Topologies Traffic Modes Frame Format Applications Conclusion Introduction The Wireless technologies (WiFi,GSM,and Bluetooth) All have one thing
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY
 Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Networking Sensors, I
 Networking Sensors, I Sensing Networking Leonidas Guibas Stanford University Computation CS428 Networking Sensors Networking is a crucial capability for sensor networks -- networking allows: Placement
Networking Sensors, I Sensing Networking Leonidas Guibas Stanford University Computation CS428 Networking Sensors Networking is a crucial capability for sensor networks -- networking allows: Placement
Davide Quaglia Assistant CS depart University of Verona, Italy
 Emad Ebeid Ph.D. student @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy EmadSamuelMalki.Ebeid@univr.it Davide Quaglia Assistant Professor @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy Davide.Quaglia@univr.it 2 1 ZigBee
Emad Ebeid Ph.D. student @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy EmadSamuelMalki.Ebeid@univr.it Davide Quaglia Assistant Professor @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy Davide.Quaglia@univr.it 2 1 ZigBee
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Image acquisition and Communication
 Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology
 SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
Zigbee protocol stack overview
 Zigbee protocol stack overview 2018 ASSUMPTIONS FOR USING THIS TEACHING MATERIAL DSR and OTSL takes no responsibility about the problem which occurs as a result of applying the technical information written
Zigbee protocol stack overview 2018 ASSUMPTIONS FOR USING THIS TEACHING MATERIAL DSR and OTSL takes no responsibility about the problem which occurs as a result of applying the technical information written
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
BASEBAND SPECIFICATION
 Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies
 Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
A Guide. Wireless Network Library Bluetooth
 A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Victor Kwong Marketing Manager
 Nov, 2008 Introduction to Freescale's Synkro Platform: Wireless Control and Automation for Next-Generation Home Entertainment Products PC106 Victor Kwong Marketing Manager of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Nov, 2008 Introduction to Freescale's Synkro Platform: Wireless Control and Automation for Next-Generation Home Entertainment Products PC106 Victor Kwong Marketing Manager of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Seminar: Mobile Systems. Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht
 Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
