Research Article International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology ISSN: (Volume-3, Issue-4)
|
|
|
- Teresa Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A survey on short Ad Hoc network Vaibhav V. Bhujade 1,Jagdish R. Yadav 2,Priti v. Bhagat 3,Anand V. Saurkar 4 Faculty of Department of CSE DMIETR, Sawangi India Abstract Mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) represent complex distributed systems that comprise wireless mobile nodes that can freely and dynamically self-organize into arbitrary and temporary, ad-hoc network topologies, allowing people and devices to seamlessly internetwork in areas with no pre-existing communication infrastructure, e.g., disaster recovery environments. Ad hoc networking concept is not a new one, having been around in various forms for over 20years. Traditionally, tactical networks have been the only communication networking application that followed the Ad hoc paradigm. Recently, the introduction of new technologies such as the Bluetooth, IEEE and Hyper LAN are helping enable eventual commercial MANET deployments outside the military domain. These recent evolutions have been generating a renewed and growing interest in the research and development of MANET. This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive overview of this dynamic field. It first explains the important role that mobile ad hoc networks play in the evolution of future wireless technologies. Key Words :- Bluetooth, WPAN, WLAN I. INTRODUCTION An ad hoc network is a network with temporary plug-in connections, in which the network devices are part of the network only for the duration of a communications session or, in the case of mobile or portable devices, while in some close proximity to the rest of the network. Ad hoc network is often local area network or other small area network formed by wireless devices. In Latin, ad hoc literally means "for this," further meaning "for this purpose only," and thus usually temporary. The term has been applied to future office, home and personal area networks in which new network nodes can be quickly added and removed. The area of ad hoc networking has gathered much research interests in the past years. Many studies have concentrated on the routing issues of ad hoc networking [1]. Bluetooth is one of the technologies that can be used for ad hoc networking. Bluetooth specification is a computing and telecommunications industry specification that describes how e.g. mobile phones, computers, and personal digital assistants (PDAs) can easily interconnect and communicate with each other by using wireless transmission in a short-range. The goal of the specification is to eliminate the need for any cable connectivity and promote ad hoc networking. By using this technology, users of cellular phones, laptops, PDAs, etc. portable devices can quickly share information with each other, for example, in a conference room using ad hoc networking. [1] II. BLUETOOTH AND WIRELESS PANS In the past quarter century we have seen the rollout of three generations of wireless cellular systems attracting end-users by providing efficient mobile communications. On another front, wireless technology became an important component in providing networking infrastructure for localized data delivery. This later revolution was made possible by the induction of new networking technologies and paradigms, such as wireless local area networks (WLAN) and wireless personal area networks (WPAN). Wireless personal area networks (WPANs) are short to very short-range (from a couple centimeters to a couple of meters) wireless networks that can be used to exchange information between devices in the reach of a person. WPANs can be used to replace cables between computers and their peripherals, to establish communities helping people do their every day chores making them more productive, or to establish location aware services. Wireless local area networks (WLANs) on the other hand provide with a larger transmission range. Although WLAN equipment usually carries the capability to be set up for ad hoc networking, the premier choice of deployment is yet a cellular like infrastructure mode to interface wireless users with the Internet. The best example representing WPANs is the recent industry standard: Bluetooth, other examples include Spike [Spike], and in the broad sense Home RF[Negus 2000]. For WLANs, the most well known representatives are based on the standards IEEE [Crow 1997] and Hiper LAN [Hiper LAN 1995] with all their variations. The IEEE 802 committee has also realized the importance of short-range wireless networking and initiated the establishment of the IEEE WG for WPANs [WPAN] to standardize protocols and interfaces for wireless personal area networking. Altogether, the working group is formed by four Task Groups (TG): 1) IEEE WPAN/Bluetooth TG 1 The TG 1 was established to support applications which require medium-rate WPANs (such as Bluetooth). These WPANs will handle a variety of tasks ranging from cell phones to PDA communications and have a QoS suitable for voice applications. Vaibhav et al. Page 182
2 2) IEEE Coexistence TG 2 Several wireless standards, such as Bluetooth and IEEE b, and appliances, such as microwaves operate, in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial-Scientific-Medical) frequency band. The TG 2 is developing specifications on the ISM band due to the unlicensed nature and available bandwidth. Thus, the IEEE Coexistence TG 2 ( ) for Wireless Personal Area Networks is developing Recommended Practices to facilitate coexistence of Wireless Personal Area Networks (802.15) and Wireless Local Area Networks (802.11). 3) IEEE WPAN/High Rate TG 3 The TG3 for WPANs is chartered to draft and publish a new standard for high-rate (20Mbit/s or greater) WPANs. Besides a high data rate, the new standard will provide for low power, low cost solutions addressing the needs of portable consumer digital imaging and multimedia applications. 4) IEEE WPAN/Low Rate TG 4 The goal of the TG 4 is to provide a standard having ultra-low complexity, cost, and power for a low-data-rate (200Kb/s or less) wireless connectivity among inexpensive fixed, portable, and moving devices. Location awareness is being considered as a unique capability of the standard. The scope of the TG 4 is to define the physical and media access control (MAC) layer specifications. Potential applications are sensors, interactive toys, smart badges, remote controls, and home automation. One key issue in the feasibility of WPANs is the inter-working of wireless technologies to create heterogeneous wireless networks. For instance, WPANs and WLANs will enable an extension of the third generation (3G) cellular networks (i.e., UMTS and cdma2000) into devices without direct cellular access. Moreover, devices interconnected in a WPAN may be able to utilize a combination of 3G access and WLAN access by selecting the access that is best for the moment. In such networks 3G, WLAN and WPAN technologies do not compete against each other but enable the user to select the best connectivity for his/her purposes Figure clearly shows the operating space of the various 802 wireless standards and activities still in progress. Given the importance within the WPAN operating space, intensive research activities, and availability of devices, we will now devote a little time in, first, giving a brief introduction on Bluetooth and then provide an overview of the Bluetooth standard as defined by the Bluetooth SIG (Special Interest Group) [Bluetooth] Fig1. The scope of the various WLAN and WPAN standards III. BRIEF HISTORY AND APPLICATIONS OF BLUETOOTH In the context of ad hoc wireless networks, the Bluetooth technology came to light in May 1998, and since then the Bluetooth SIG has steered the development of the technology through the development of an open industry specification, including both protocols and applications scenarios. It is predicted that in 2006 Bluetooth will be present in 73 percent of phones and 44 percent of PDAs. It will provide device-to-device communication, enabling seamless communication between phones, printers, PDAs and scanners in the office and between phones, smart home control units, TVs and VCRs in the home. The Bluetooth specification comprises of an end-to-end description for both protocols and application profiles that guarantee value-added to its users right out-of-the-box. As per the current specification (version 1.1), it consists of the following two parts: 1) The core specification defining the radio characteristics and the communication protocols for exchanging data between devices and Bluetooth radio links. 2) The profile specification that defines how the Bluetooth protocols are to be used to realize a number of selected applications. Bluetooth has a tremendous potential in moving and synchronizing information in a localized setting. Potential for Bluetooth applications is huge, because we do business transactions and communicate more frequently with the people who are close by as compared to those who are far away - a natural phenomenon of human interaction. 3.1 Ad hoc connectivity Most wireless communication systems like the public cellular phone networks- GSM, DAMPS, IS-95or other private networks like Hiper LAN-II, DECT or Personal Handy phony system, use a network architecture in which the radio units: base stations and mobile terminals are strictly distinct. This is advantage in design as channel access, channel allocation, traffic control, interference minimization etc. can be taken care by the base stations, making the design of Vaibhav et al. Page 183
3 mobile terminals simpler. In ad hoc networks, there is no difference between radio units. Communication is peer to peer with no central controller. Conventionally in ad hoc wireless networks, all devices sharing a common space will share the same channel, and will mutually coordinate in its sharing. In Bluetooth usage models however, even this is not sufficient as the number of Bluetooth devices in a given region of space may be very large and only a few of them may need to communicate among themselves, making mutual coordination among them very difficult and unlikely. This has led to the concept of scatter nets: a group of networks in the same space but communicating over different channels, with some overlapping devices. There need not be any coordination among devices belonging to different networks within the scatter net. Fig2. A cellular network with squares representing stationary base stations Fig3. a conventional ad hoc system Fig4. scatter ad hoc network 3.2 Bluetooth in the nets One of the biggest advantages, and where we can see the versatility of the design of the Bluetooth technology, is in the easy confection and arrangement of nets between different devices of Bluetooth technology. Bluetooth has been designed to operate in a multi-user environment. Presents two types of possible configurations, which can expand to a considerable number of elements to expand this way the networks and subnet works. The structure that handles this technology is composed, in the more basic form, by what it is named a Piconet and in an a bit more complex structure which it is named a Scatter net. Up to eight users or devices can form a "piconet" and even ten "piconets" can coexist in the same area of coverage. If we realize that every link is codified and protected against interference and loss of link, Bluetooth can be considered to be a wireless very sure short scope network. The Piconet is several devices that are in the same radio of coverage where they share the same channel and that is constituted between two and eight of these units. Every device has the unique direction of 48 bits, based on the standard IEEE for WLAN, whereas the Scatter net formed by the connection of a Piconet to other one, with a maximum of interconnections of ten Piconets. In the following figure it is possible to observe and understand with major facility these two configurations. Fig 4. Piconets with single slave operation (a), multi-slave operation (b) and scatternet operation (c). Vaibhav et al. Page 184
4 In the figure "a" we can observe the simplest Piconet which is constituted by two devices. In the "b" figure we have a Piconet constituted by four of these devices. The "c" figure is an example of a Scatter net that possesses three Piconet, one constituted for four units, the other one for two and the last one for 3 units respectively. The equipments that share the same channel will divide the resources and the capacity of this one. Though the channels have a bandwidth of one 1 Mhz, as more users join to the Piconet, minor resources they will have for each user. That is the reason why the Scatter net was introduced to solve the problem of the low bandwidth that every user of a Piconet has if they find great quantity of connected units. The performance, as a whole and individually of the users of a Scatter net is major that the one that has every user when takes part in the same channel of 1 MHz 3.3 Personal Area Networks (PAN) The final communication profile that Bluetooth focuses on is Personal Area Networks (PAN). This is similar to the peripheral interconnects profile except that it focuses on Ad hoc configurations. These are applications where devices enter and leave the network area. For example, a businessman might meet a co-worker in the airport, and using their Bluetooth enabled PDAs, they would be able to transfer a document to each other as well as synchronize their calendars and contact lists before they part ways. Numerous devices possessing PAN functionality have appeared on the market since Bluetooth s introduction, and like peripherals, they appear ready to quickly grow in number due to consumer demand. 3.4 Core Specification The core specification defines the internal design of Bluetooth technology. The basic interface stack can be found in Figure 1. It is important to note that the bottom three layers in the figure are generally known as the Bluetooth core. The other layers in the figure are present merely to give some reference to where the Bluetooth core sits in a system. The lowest level of Bluetooth is the Radio Frequency (RF) layer, which performs the actual sending and receiving of radio frequency data to/from the device. The typical range of a Bluetooth device is 1-10m, but with an amplified antenna, the range can reach up to 100m. Fir5. Bluetooth core stack Formation of the frames that are transmitted by the RF layer. The baseband layer is also responsible for creating the connection between two Bluetooth devices. This connection is known as a piconet. Many devices can connect to form a piconet, with one device being specified as the master and the other devices acting as slaves. The master is then in control of the frequency hopping behaviors of the piconet. It is also possible for multiple piconets to connect to form a scatter net. Next is the Link Manager which is responsible for the creation, modification, and release of logical links and the update and communication of altered device parameters to the physical links. The Link Manager is also responsible for handling the power management responsibilities of the Bluetooth core. Above this are the higher level protocol layers such as TCP/IP which are located close to the application layer. These are not typically considered part of the Bluetooth architecture since they are common to many different protocols. Each device also possesses a Bluetooth PIN (sometimes called a passkey) that is used in the communication setup of two devices that have no previous connection history. This PIN or passkey can be either entered into the device at the user interface (UI) level or be hard-coded into the device at manufacture. The latter option is often used in devices with small internal memory capabilities (peripherals, etc.). IV. AD HOC SECURITY CONCERNS Bluetooth devices communicating in the wild form various sizes of ad hoc networks. Since it is possible for varying numbers of devices to be entering and leaving the piconets and scatter nets created by the devices, Bluetooth poses some difficult safety requirements to maintain good security in these ad hoc networks. The first aspect of the ad hoc network that is important to Bluetooth uses is availability. Users should have access to other users even if some devices are experiencing difficulties on the network. Unfortunately, this is difficult to guarantee in Bluetooth because devices are dependent on other devices for the transmission of data. This means that an attacker who is capable of interrupting a few devices in a piconet can severely degrade the performance of all devices. It is also difficult to maintain Vaibhav et al. Page 185
5 perfect availability because of the nature of wireless communications. There is always interference to deal with in any wireless system, and an attacker who can jam the frequencies of Bluetooth transmission scan again cause problems for users. Another aspect of the ad hoc network that is difficult to guarantee is authorization. Inherent to the nature of ad hoc networks is the lack of any structure or identifying characteristics of the devices. This creates problems with authentication. Bluetooth attempts to combat these problems by implementing a mildly complex authentication scheme. Finally, confidentiality must be maintained in order for an ad hoc network to successfully offer security. Unfortunately, wireless communication makes this difficult since any one can sniff the airwaves for data. Bluetooth does offer encryption for transmitting data, but only certain situations present full encryption of all transmissions. Since Bluetooth is an ad hoc network protocol, creating a perfectly secure system is very difficult, and unfortunately, creating antagonists have been able to penetrate the Bluetooth specification. [4] V. CONCLUSION Bluetooth is a standard used in links of radio of short scope, destined to replace wired connections between electronic devices like cellular telephones, Personal Digital Assistants (PDA), computers, and many other devices. Every year we have to add new peripherals to our computers and the need to replace the wired connections is more important every year. That is why the Bluetooth technology is going continue expanding with the support of the industry of Computer science and of Telecommunications, which in some way guarantees the success. One of the biggest attractions of the implementation of this technology is the creation of networks; with the Bluetooth technology is possible to form different networks in the same geographical point, with relatively high speed of transmission. Anyway the Bluetooth technology has a limited scope, this characteristic of limited scope presents a great disadvantage if we try to implement a net in one extensive geographical area. Another positive aspect that presents this technology is the easy manipulation and configuration of networks and sub-networks inside the same space with the implementation of diverse Piconets interlaced across Scatter nets with different configurations. REFERENCES [1] BLUETOOTH AND AD HOC NETWORKING Jari Välimäki Networking Laboratory Helsinki University of Technology jari.valimaki@hut.fi [2] Bluetooth Security James Lewis ECE March 2005 [3] Bluetooth Primer Author: Aman Kansal [4] Bluetooth Author: Inigo Puy Mtknr: Course: E-Business Professor: Eduard Heindl Date: 05/05/08 [5] [6] [Haarsten 1998] J. Haarsten, "Bluetooth The Universal Radio Interface for Ad Hoc Wireless Connectivity," Ericsson Review (3), 1998 [7] [Bluetooth] Bluetooth SIG, Vaibhav et al. Page 186
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology
 Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Bluetooth. 3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network. What is BLUETOOTH: Bluetooth 2/17/2016
 3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network Bluetooth Bluetooth Bluetooth is a high-speed, low-power microwave wireless link technology, designed to connect phones, laptops, PDAs and other portable equipment
3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network Bluetooth Bluetooth Bluetooth is a high-speed, low-power microwave wireless link technology, designed to connect phones, laptops, PDAs and other portable equipment
Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Basic Concepts and Research Issues
 Mobile Ad Hoc s: Basic Concepts and Research Issues Ing. Alessandro Leonardi aleonardi@dieei.unict.it Wireless s Generations (1/3) Generation 1G 2G 2.5G 3G 4/5G Time 1980s 1990s Late1990s 2000s (2010 full
Mobile Ad Hoc s: Basic Concepts and Research Issues Ing. Alessandro Leonardi aleonardi@dieei.unict.it Wireless s Generations (1/3) Generation 1G 2G 2.5G 3G 4/5G Time 1980s 1990s Late1990s 2000s (2010 full
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING
 A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Seminar: Mobile Systems. Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht
 Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs. Agenda (1) Agenda (2) Wireless Spectrum (1)
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Chapter 7. Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration. Part I
 Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
101seminartopics.com. Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks
 Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
WIMAX. WIMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access ): Field of application:
 WIMAX WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a technology that focuses on providing data over long distances in a wireless mode, very similar to the cellular mobile concept. WiMAX is
WIMAX WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a technology that focuses on providing data over long distances in a wireless mode, very similar to the cellular mobile concept. WiMAX is
Learning Objectives. Introduction. Advantages of WLAN. Information Technology. Mobile Computing. Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.
 Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
COMPUTER SKILLS COMP101
 COMPUTER SKILLS COMP101 Chapter 4 Introduction to Computer Networks Definitions and Terminologies Computer Network A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources
COMPUTER SKILLS COMP101 Chapter 4 Introduction to Computer Networks Definitions and Terminologies Computer Network A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
The Open System Interconnect model
 The Open System Interconnect model Telecomunicazioni Undergraduate course in Electrical Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2007-2008 1 Layered network design Data networks are usually
The Open System Interconnect model Telecomunicazioni Undergraduate course in Electrical Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2007-2008 1 Layered network design Data networks are usually
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Case study of Wireless Technologies in Industrial Applications
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2017 257 Case study of Wireless Technologies in Industrial Applications Rahul Hanumanth Rao Computer Information
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2017 257 Case study of Wireless Technologies in Industrial Applications Rahul Hanumanth Rao Computer Information
Wireless networks: from cellular to ad hoc
 Wireless networks: from cellular to ad hoc The three wireless waves Wave #1: cellular telephony Still, biggest profit maker Wave #2 : wireless Internet access Most Internet access on US campuses is wireless
Wireless networks: from cellular to ad hoc The three wireless waves Wave #1: cellular telephony Still, biggest profit maker Wave #2 : wireless Internet access Most Internet access on US campuses is wireless
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology
 Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK
 Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs
 Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
802 Wireless Access Techniques Overview
 802 Wireless Access Techniques Overview Markku Renfors Institute of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology TLT-6556 15.2.2007/MR 1 Wireless Access Techniques WLAN,, Wireless Local
802 Wireless Access Techniques Overview Markku Renfors Institute of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology TLT-6556 15.2.2007/MR 1 Wireless Access Techniques WLAN,, Wireless Local
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
UC Santa Cruz Wireless Access Policy
 UC Santa Cruz Wireless Access Policy VERSION: 1.4 STATUS: DRAFT DATE: 26 APRIL 2004 STEWARD: Director, Network & Telecommunications Services Tad Reynales AUTHORITY: Vice-Provost, Information Technology
UC Santa Cruz Wireless Access Policy VERSION: 1.4 STATUS: DRAFT DATE: 26 APRIL 2004 STEWARD: Director, Network & Telecommunications Services Tad Reynales AUTHORITY: Vice-Provost, Information Technology
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a. worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the
 Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Bluetooth technology, developed by Ericsson Mobile Communications, a worldwide telecommunications company based in Sweden, is fast becoming the worldwide standard for short-range wireless communication.
Wireless Networks (CSC-7602) Lecture 1 (27 Aug 2007)
 Wireless Networks (CSC-7602) Lecture 1 (27 Aug 2007) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 Handouts Class information Schedule (check online frequently) 2 1 Goals Principles on Wireless
Wireless Networks (CSC-7602) Lecture 1 (27 Aug 2007) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 Handouts Class information Schedule (check online frequently) 2 1 Goals Principles on Wireless
Wireless Network Introduction
 Wireless Network Introduction Module W.bas.1 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA 1 Wireless network introduction W.bas.1-2
Wireless Network Introduction Module W.bas.1 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA 1 Wireless network introduction W.bas.1-2
G o i n g W i r e l e s s
 WLANs Going Wireless Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs), are not far more differentiated from the traditional LANs that are commonly used to connect computers and other communicating devices within a
WLANs Going Wireless Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs), are not far more differentiated from the traditional LANs that are commonly used to connect computers and other communicating devices within a
1 Wireless Network Architecture
 CHAPTER 1 Wireless Network Architecture INTRODUCTION Wireless networks come in all shapes and sizes. While many aspects of these diverse networks have common foundations, there are several other aspects
CHAPTER 1 Wireless Network Architecture INTRODUCTION Wireless networks come in all shapes and sizes. While many aspects of these diverse networks have common foundations, there are several other aspects
Ethernet. Lecture 6. Outline. Ethernet - Physical Properties. Ethernet - Physical Properties. Ethernet
 Lecture 6 Ethernet Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on 9/20/12. Thick-net Thin-net Twisted Pair Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks
Lecture 6 Ethernet Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on 9/20/12. Thick-net Thin-net Twisted Pair Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks
IEEE 802 Standard Network s Comparison under Grid and Random Node Arrangement in 2.4 GHz ISM Band for Single and Multiple CBR Traffic
 3118 IEEE 802 Standard Network s Comparison under Grid and Random Node Arrangement in 2.4 GHz ISM Band for Single and Multiple CBR Traffic J.Jaslin deva gifty Department of ECE, Dr. Mahalingam College
3118 IEEE 802 Standard Network s Comparison under Grid and Random Node Arrangement in 2.4 GHz ISM Band for Single and Multiple CBR Traffic J.Jaslin deva gifty Department of ECE, Dr. Mahalingam College
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Introduction. Computer Networks Term B10
 Introduction Computer Networks Term B10 Introduction Outline Preliminary Definitions Internet Components Network Application Paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology by size/scale by topology
Introduction Computer Networks Term B10 Introduction Outline Preliminary Definitions Internet Components Network Application Paradigms Classifying networks by transmission technology by size/scale by topology
IPv6-based Beyond-3G Networking
 IPv6-based Beyond-3G Networking Motorola Labs Abstract This paper highlights the technical issues in IPv6-based Beyond-3G networking as a means to enable a seamless mobile Internet beyond simply wireless
IPv6-based Beyond-3G Networking Motorola Labs Abstract This paper highlights the technical issues in IPv6-based Beyond-3G networking as a means to enable a seamless mobile Internet beyond simply wireless
Lecture 6. Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1
 Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
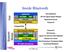 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Securing A Bluetooth Device
 Securing A Bluetooth Device Mrs. Dhanashri D. Dhokate 1, Mr. Milind C. Butale 2, Mr. Babasaheb S. Patil 3 Assistant Professor, Information Technology, PVPIT, Budhgaon, India 1. Associate Professor, Electronics
Securing A Bluetooth Device Mrs. Dhanashri D. Dhokate 1, Mr. Milind C. Butale 2, Mr. Babasaheb S. Patil 3 Assistant Professor, Information Technology, PVPIT, Budhgaon, India 1. Associate Professor, Electronics
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK MOBILE COMMUNICATION AMOL RATAN VAIDKAR 1, PROF. G. D. GULHANE 2, DR. H. R. DESHMUKH
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK MOBILE COMMUNICATION AMOL RATAN VAIDKAR 1, PROF. G. D. GULHANE 2, DR. H. R. DESHMUKH
Autonomous Infrastructure Wireless Networks: A Perspective on 4G
 Autonomous Infrastructure Wireless Networks: A Perspective on 4G Elvino S. Sousa Jeffrey Skoll Chair in Computer Networks and Innovation Wireless Lab University of Toronto Canada 1 Wireless System Evolution
Autonomous Infrastructure Wireless Networks: A Perspective on 4G Elvino S. Sousa Jeffrey Skoll Chair in Computer Networks and Innovation Wireless Lab University of Toronto Canada 1 Wireless System Evolution
2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork. 3. Each machine is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection.
 نموذج أسئلة اختبار النهائي عام 2017 الفصل الدراسي الثاني لمقرر شبكات الحاسب CHOSE 1. channel spectrum divided into frequency bands "FDMA" 2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork
نموذج أسئلة اختبار النهائي عام 2017 الفصل الدراسي الثاني لمقرر شبكات الحاسب CHOSE 1. channel spectrum divided into frequency bands "FDMA" 2. A collection of interconnected networks is called an internetwork
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 1 Introduction to Wireless Communications Jorge Olenewa jolenewa@georgebrown.ca Office: E425 ext. 6809 Objectives Explain how the major wireless technologies
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 1 Introduction to Wireless Communications Jorge Olenewa jolenewa@georgebrown.ca Office: E425 ext. 6809 Objectives Explain how the major wireless technologies
This tutorial has been designed to help beginners understand the basic concepts of WiMAX.
 About the Tutorial WiMAX is one of the hottest broadband wireless technologies around today. It is based on IEEE 802.16 specification and it is expected to deliver high quality broadband services. This
About the Tutorial WiMAX is one of the hottest broadband wireless technologies around today. It is based on IEEE 802.16 specification and it is expected to deliver high quality broadband services. This
Wireless LAN. Access Point. Provides network connectivity over wireless media
 LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
Introduction. Chapter 1: Mobile Communications SS A case for mobility History of mobile communication Market Areas of research
 Mobile Communications SS 2002 Chapter 1: Introduction A case for mobility History of mobile communication Market Areas of research Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02
Mobile Communications SS 2002 Chapter 1: Introduction A case for mobility History of mobile communication Market Areas of research Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02
Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks
 Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks John M. Shea April 22, 2008 Overview Wireless networks fundamentals vulnerabilities WING testbed Demonstration of Denial-of-Service Attack and Defense Classification:
Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks John M. Shea April 22, 2008 Overview Wireless networks fundamentals vulnerabilities WING testbed Demonstration of Denial-of-Service Attack and Defense Classification:
EC Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank
 EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
Chapter 5 Ad Hoc Wireless Network. Jang Ping Sheu
 Chapter 5 Ad Hoc Wireless Network Jang Ping Sheu Introduction Ad Hoc Network is a multi-hop relaying network ALOHAnet developed in 1970 Ethernet developed in 1980 In 1994, Bluetooth proposed by Ericsson
Chapter 5 Ad Hoc Wireless Network Jang Ping Sheu Introduction Ad Hoc Network is a multi-hop relaying network ALOHAnet developed in 1970 Ethernet developed in 1980 In 1994, Bluetooth proposed by Ericsson
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Celestix Networks, Inc. 702 Brown Road. Fremont, California Ph Fx Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network
 Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network white paper Introduction A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a flexible data communications system that can use either infrared or radio frequency (RF) technology
Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network white paper Introduction A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a flexible data communications system that can use either infrared or radio frequency (RF) technology
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Network Systems. Wireless Network. Claude Duvallet - 1/27
 Network System Wireless Network Claude Duvallet University of Le Havre Faculty of Sciences and Technology 25 rue Philippe Lebon - BP 540 76058 LE HAVRE CEDEX, FRANCE Claude.Duvallet@gmail.com http://litis.univ-lehavre.fr/
Network System Wireless Network Claude Duvallet University of Le Havre Faculty of Sciences and Technology 25 rue Philippe Lebon - BP 540 76058 LE HAVRE CEDEX, FRANCE Claude.Duvallet@gmail.com http://litis.univ-lehavre.fr/
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Wi-Fi Scanner. Glossary. LizardSystems
 Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems 2 Table of Contents 802 6 802.11 6 802.11a 6 802.11b 6 802.11d 6 802.11e 6 802.11g 6 802.11h 6 802.11i 6 802.11j 6 802.11n 7 802.1X 7 802.3 7 A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES
Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems 2 Table of Contents 802 6 802.11 6 802.11a 6 802.11b 6 802.11d 6 802.11e 6 802.11g 6 802.11h 6 802.11i 6 802.11j 6 802.11n 7 802.1X 7 802.3 7 A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless networks. Wireless Network Taxonomy
 Wireless networks two components to be considered in deploying applications and protocols wireless links ; mobile computing they are NOT the same thing! wireless vs. wired links lower bandwidth; higher
Wireless networks two components to be considered in deploying applications and protocols wireless links ; mobile computing they are NOT the same thing! wireless vs. wired links lower bandwidth; higher
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
15-441: Computer Networking. Wireless Networking
 15-441: Computer Networking Wireless Networking Outline Wireless Challenges 802.11 Overview Link Layer Ad-hoc Networks 2 Assumptions made in Internet Host are (mostly) stationary Address assignment, routing
15-441: Computer Networking Wireless Networking Outline Wireless Challenges 802.11 Overview Link Layer Ad-hoc Networks 2 Assumptions made in Internet Host are (mostly) stationary Address assignment, routing
OPNET BASED SIMULATION AND INVESTIGATION OF WIMAX NETWORK USING DIFFERENT QoS
 OPNET BASED SIMULATION AND INVESTIGATION OF WIMAX NETWORK USING DIFFERENT QoS Kamini Jaswal 1, Jyoti 2, Kuldeep Vats 3 1 M.tech, Department of electronics and communication, South point institute of engineering
OPNET BASED SIMULATION AND INVESTIGATION OF WIMAX NETWORK USING DIFFERENT QoS Kamini Jaswal 1, Jyoti 2, Kuldeep Vats 3 1 M.tech, Department of electronics and communication, South point institute of engineering
AC : A STUDY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF BLUETOOTH AND IEEE B COEXISTENCE
 AC 2007-1360: A STUDY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.11B COEXISTENCE Warith Al-Sulaimani, Modern College of Business and Science-Sultanate of Oman Warith Al-Sulaimani is a Lecturer and Consultant
AC 2007-1360: A STUDY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.11B COEXISTENCE Warith Al-Sulaimani, Modern College of Business and Science-Sultanate of Oman Warith Al-Sulaimani is a Lecturer and Consultant
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
IT 4504 Section 4.0. Network Architectures. 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1
 IT 4504 Section 4.0 Network Architectures 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 Section 4.1 Introduction to Computer Networks 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 2 Introduction
IT 4504 Section 4.0 Network Architectures 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 Section 4.1 Introduction to Computer Networks 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 2 Introduction
Architecture. Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change
 802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
Security. Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011
 Security Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011 What is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is an open standard for short-range radio frequency (RF) communication. Bluetooth technology is used primarily to establish
Security Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011 What is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is an open standard for short-range radio frequency (RF) communication. Bluetooth technology is used primarily to establish
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM COMPONENTS 1/28/2015. Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com
 INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide
 Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea
 Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea http://usn.konkuk.ac.kr/~jskim 1 IEEE 802.x Standards 802.11 for Wireless Local Area Network 802.11 legacy clarified 802.11 legacy
Junseok Kim Wireless Networking Lab (WINLAB) Konkuk University, South Korea http://usn.konkuk.ac.kr/~jskim 1 IEEE 802.x Standards 802.11 for Wireless Local Area Network 802.11 legacy clarified 802.11 legacy
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks
 Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Dr. Hwee-Pink Tan http://www.cs.tcd.ie/hweepink.tan Outline Part 1 Motivation Wireless Ad hoc networks Comparison with infrastructured networks Benefits Evolution Topologies Types
Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Dr. Hwee-Pink Tan http://www.cs.tcd.ie/hweepink.tan Outline Part 1 Motivation Wireless Ad hoc networks Comparison with infrastructured networks Benefits Evolution Topologies Types
CTIS 487: Lecture Notes 1
 CTIS 487: Lecture Notes 1 Mobile phones got their name due to the fact that they allow users to make phone calls while being mobile. The communication architecture was dominated by base stations communicating
CTIS 487: Lecture Notes 1 Mobile phones got their name due to the fact that they allow users to make phone calls while being mobile. The communication architecture was dominated by base stations communicating
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Employing Wireless Bluetooth for C 3 in Industrial Automation C. Norz C. Miller
 1 Employing Wireless Bluetooth for C 3 in Industrial Automation C. Norz C. Miller Abstract: This paper discusses the use of wireless Bluetooth for controllerto-controller coordination (C 3 ) within industrial
1 Employing Wireless Bluetooth for C 3 in Industrial Automation C. Norz C. Miller Abstract: This paper discusses the use of wireless Bluetooth for controllerto-controller coordination (C 3 ) within industrial
ZIGBEE. Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS
 ZIGBEE Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS OUTLINE ZIGBEE AND APPLICATIONS IEEE 802.15.4 PROTOCOL ZIGBEE PROTOCOL ZIGBEE ALLIANCE ZIGBEE APPLICATIONS PHYSICAL LAYER MAC LAYER ZIGBEE
ZIGBEE Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS OUTLINE ZIGBEE AND APPLICATIONS IEEE 802.15.4 PROTOCOL ZIGBEE PROTOCOL ZIGBEE ALLIANCE ZIGBEE APPLICATIONS PHYSICAL LAYER MAC LAYER ZIGBEE
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work on the part
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work on the part
Jeffrey Price Dr. Konak IST 220 Bluetooth Technology
 Jeffrey Price Dr. Konak IST 220 Bluetooth Technology 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. COMPONENTS 3. BLUETOOTH ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES 4. USES OF BLUETOOTH 5. THE FUTURE 7. DOCUMENTATION 2 1. INTRODUCTION
Jeffrey Price Dr. Konak IST 220 Bluetooth Technology 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. COMPONENTS 3. BLUETOOTH ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES 4. USES OF BLUETOOTH 5. THE FUTURE 7. DOCUMENTATION 2 1. INTRODUCTION
ECE 586 Advanced Topics: Wireless Networking
 ECE 586 Advanced Topics: Wireless Networking http://www.ece.rochester.edu/courses/ece586 Spring 2005 TR 2-3:15, CSB 523 Wendi Heinzelman OH: T 3:30-4:30 Hopeman 307 wheinzel@ece.rochester.edu Class information
ECE 586 Advanced Topics: Wireless Networking http://www.ece.rochester.edu/courses/ece586 Spring 2005 TR 2-3:15, CSB 523 Wendi Heinzelman OH: T 3:30-4:30 Hopeman 307 wheinzel@ece.rochester.edu Class information
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology
 LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
