(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
|
|
|
- Marion Whitehead
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
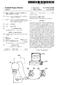
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 Acosta et al. US A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) TRANSFERENCE OF DATA ASSOCATED WITH A PRODUCT AND/OR PRODUCT PACKAGE Applicant: Disney Enterprises, Inc., Burbank, CA (US) Inventors: Evan Acosta, La Crescenta, CA (US); Edward Drake, Stevenson Ranch, CA (US); Mark Arana, West Hills, CA (US) Appl. No.: 13/911,067 Filed: Jun. 5, 2013 Related U.S. Application Data Provisional application No. 61/766,065, filed on Feb. 18, Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. G06Q 30/02 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06O 30/0261 ( ); G06Q30/0267 ( ) USPC /14.58; 705/14.64 (57) ABSTRACT A proximity-based device within a product a product package sends data associated with the product the product package to a mobile device based upon the mobile device being within a proximity to the proximity-based device. Another proximity-based receiver within a mobile device receives data associated with a product a prod uct package from a proximity-based transmitter within the product the product package based upon the proxim ity-based receiver being within a proximity to the proximity based transmitter Mobile Device 108 l?. Data ASSociated with 104. Sensor andfor Transceiver Data Associated with Reader
2 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 1 of 10 US 2014/ A ASSOCiated with Sensor Transceiver Data ASSociated with Reader Figure 1
3 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 2 of 10 US 2014/ A Request Second Portion of Data Associated with Second Portion of Data Associated With Mobile Device ? y Data ASSociated with Sensor TranSceiver First Portion. Of Data Associated with Web Address 110 Reader Figure 2
4 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 3 of 10 US 2014/ A Request Data Associated with and/ or Request Data ASSOCiated With Mobile Device y ASSociated with Sensor Transceiver Web Address Read eacer Figure 3
5 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 4 of 10 US 2014/ A send, from a proximity-based device within a product a product package, data associated with the product the product package to a mobile device based upon the mobile device being within a proximity to the proximity-based device Figure 4
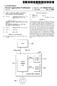
6 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 5 of 10 US 2014/ A Mobile Device 110 Reader 504 Data Storage Device Processor Memory 508 Transmitter 510 Receiver Figure 5
7 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 6 of 10 US 2014/ A1 600 identifier Database Playback 204 Indication User Preferences Content Playback Device O6 dentifier and User Preferences Mobile Device ASSOCiated with SensOr Transceiver identifier Reader Figure 6
8 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 7 of 10 US 2014/ A1. receive, at a server, a user preference from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier 702 store the user preference and the product identifier in a database 704 receive, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated send the user preference to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference 708 Figure 7
9 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 8 of 10 US 2014/ A O2? 802 O Server User identifier identifier Database Database Playback 204 indication User Preferences identifier and User if dentifier S-1 - Mobile Device 108 Content -r 1. Playback Device 102 ASSOCiated With 1. PrOduct 04. Sensor Transceiver identifier Reader Figure 8
10 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 9 of 10 US 2014/ A receive, at a server, a user identifier from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier 904 store the user identifier and the product identifier in a database 906 receive, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated 908 search a profile database to determine a user preference based upon the user identifier 910 send the user preference to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference Figure 9
11 Patent Application Publication Aug. 21, 2014 Sheet 10 of 10 US 2014/ A1 O6 Advertisements O 6 N Coupons Trailer Related Movies Actors/Actresses Info or interviews Related Video Games 1012 Director info s or interviews User Preferences Figure 10
12 US 2014/ A1 Aug. 21, 2014 TRANSFERENCE OF DATA ASSOCATED WITH A PRODUCT AND/OR PRODUCT PACKAGE RELATED APPLICATIONS This application claims priority to U.S. Provisional Patent Application Serial No. 61/766,065, filed on Feb. 18, 2013, entitled TRANSFERENCE OF DATA TO PROVIDE CONTENT, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. BACKGROUND Field This disclosure generally relates to the field of data transference General Background 0005 Media products are typically placed in packaging on store shelves that allow consumers to read information about the content of the media products. Examples of Such media products are Blu-ray discs or DVDs with movies, television shows, video games, or the like. Consumers typically peruse different packages to find out more information about the products of potential interest. Although technology has vastly progressed, the packaging configurations for media products have mainly remained stagnant. Users often have a limited experience for reading and learning about the content of the media product prior to purchase Stores often have to compete with newer online websites that sell the same media products. Such online web sites sell those media products and often provide various information to the user that is perusing the online website. As a result of Such competition, Stores selling media products have faced newer challenges in maintaining the same base of customers that previously purchased media products from those stores. SUMMARY A proximity-based device within a product a product package sends data associated with the product and/ or the product package to a mobile device when the mobile device is within a proximity to the proximity-based device. A proximity-based receiver within a mobile device receives data associated with a product a product package from a proximity-based transmitter within the product the product package based upon the proximity-based receiver being within a proximity to the proximity-based transmitter Yet another process and apparatus receive, at a server, a user preference from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier, store the user preference and the product identifier in a database, receive, from a content play back device, an indication that playback for content corre sponding to the product identifier has been initiated, and send the user preference to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference. Another process and apparatus receive a user identifier from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier, store the user identifier and the product identifier in a database, receive, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated, search a profile database to determine a user preference based upon the user identifier, and send the user preference to the content play back device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above-mentioned features of the present disclo sure will become more apparent with reference to the follow ing description and accompanying drawings, wherein like reference numerals denote like elements and in which: 0010 FIG. 1 illustrates a data transference configuration that allows for proximity-based detection and transfer of data FIG. 2 illustrates a data transference configuration in which a network connection is utilized to obtain at least a portion of the data associated with the product product package FIG. 3 illustrates an alternative configuration in which a data transference configuration is utilized without any content being received by the mobile device directly from the proximity-based sensor transceiver FIG. 4 illustrates a process that is utilized to send data associated with the product product package illus trated in FIGS FIG. 5 illustrates an expanded view of the internal components of the mobile device FIG. 6 illustrates a data transference configuration that customizes playback of the product by a content play back device FIG. 7 illustrates a process that is utilized to cus tomize playback of the product FIG. 8 illustrates an alternative content playback customization configuration FIG. 9 illustrates an alternative process that is uti lized to customize playback of the product FIG. 10 illustrates a user interface for the mobile device illustrated in FIG. 1. DETAILED DESCRIPTION A data transference configuration presents media associated with a product a product package to a mobile device of a user prior to the purchase of the product by the user after the purchase. The product may be a media product, e.g., a Blu-ray disc, DVD, video game, or the like. Alternatively, the product may be an entertainment prod uct that is not a media product, e.g., an action figure, a doll, or the like The media provided to the user may include infor mation about the contents of the package or the product, e.g., a menu of the discs inside the package, a list of items inside the package, previews, bonus games, quantity of discs, pro motions, coupons, special offers, a video (Such as a video involving an action figure a movie), music (Such as music corresponding to an action figure a movie), an offer to purchase a digital copy of a movie (such as with a movie character corresponding to an action figure), additional information, or the like. The mobile device of the user obtains the media when the user places the mobile device within proximity of the product product package FIG. 1 illustrates a data transference configuration 100 that allows for proximity-based detection and transfer of data. A product product package 102 may be placed on store shelves, in an amusement park, in various enter tainment environments. The product package 102 may have various information, e.g., pictures, text, or the like, on differ
13 US 2014/ A1 Aug. 21, 2014 ent portions of the product package 102 so that the user may learn about the product 102 prior to purchase In one aspect, the product product package 102 has a proximity-based sensor transceiver 104, e.g., RFID chip, RFID tag, Near Field Communication ( NFC) chip, NFC tag, Bluetooth, or the like. The proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 may establish radio or other communication with another device 106 based upon a set of standards, e.g., NFC Standards The data transference configuration 100 also has a mobile device 106. The mobile device 106 is a device such as a smartphone, tablet, laptop, or the like. The mobile device 106 has a display 108 that displays data such as text, video, or the like on the mobile device 106. The display 108 may be a display that is integrated within the mobile device 106, e.g., a smartphone display. Alternatively, the display 108 may be a display that is operably connected to the mobile device, e.g., an LED monitor, an LCD monitor, or the like. Further, the mobile device 106 has a proximity-based reader 110. The proximity-based reader 110 is a receiver that detects the pres ence of the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 and receives the data associated with the product prod uct package 102 when in proximity with the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 of the product the prod uct package Upon detection of the proximity based sensor transceiver 104, the proximity-based reader 110 receives proximity data from the proximity based sensor trans ceiver 104. The proximity data may be an application, an instruction to launch an application, a link to a website, a menu preview, an offer, a bonus feature, a bonus game, a trailer, a link to a trailer, or the like. In other words, the proximity data can be any data or content associated with the product product package 102. For example, a user may tap or place the mobile device 106 with an NFC reader in proximity to a Blu-ray disc package that has an NFC chip. As a result, the mobile device 106 may receive a trailer of a movie that is on a Blu-ray disc within the Blu-ray disc package. The display 108 may then display the data associated with the product product package 102, e.g., a movie trailer Alternatively, the NFC chip may be positioned or within the Blu-ray disc rather than the Blu-ray disc package. The tap of the mobile device 106 on the Blu-ray disc package positions the mobile device 106 within enough proximity to the NFC chip on or within the Blu-ray disc so that the mobile device 106 may receive the movie trailer from the NFC chip within the Blu-ray disc When the user brings the mobile device 106 in prox imity to a proximity-based device (e.g., sensor trans ceiver 104, e.g., NFC chip in a disc package), the proximity based reader 110, e.g., NFC reader, in the mobile device 106 reads content from the NFC chip. The reading may be per formed with or without connecting to a network Such as the Internet to access more content. The content from the prox imity-based sensor transceiver 104 may trigger the mobile device 106 to display an X-ray view of the physical and virtual contents inside the package, e.g., images, videos, quantity of discs, a menu of content and functions stored by the discs, chapter menu, short preview clips of scenes, deleted scenes, director commentary, actor/actress interview(s). bonus content games, contest, special offers, advertisements, marketing, coupons for other products, movie reward point redemptions, previews, or the like In one aspect, an interactive menu is provided. In another aspect, a display is generated to provide the user with a virtual magazine of the contents of the media product. Rather than having to turn a package/box in different direc tions to view the data associated with the media product, the user may swipe through all of that data in a digital magazine format. Further, information from other associated media products, e.g., prequels, sequels, similar genres, similar actors/actresses, or the like may be presented together. In one aspect, placeholders may be illustrated for missing data. For example, a placeholder may be illustrated on the mobile device 106 for a sequel for which the user has not placed the mobile device 106 in proximity to the corresponding media product packaging In one aspect, the data transference configuration 100 provides an enhanced presentation of data associated with the media stored within the product product pack age 102. The user is provided with a more immersive expe rience before the product product package 102 is pur chased. The user may also be provided with coupons, offers, or the like as an incentive to purchase the product product package 102 in the store. As a result, consumers have more incentives to peruse products in the store environment The store environment is provided herein only as an example. The data transference configuration 100 and other configurations provided herein may be utilized in various promotional environments such as sell sheets, amusement parks, theatrical posters at bus stops, theaters, and other loca tions, or the like Further, computing devices other than the mobile device 106, e.g., desktop computer, kiosk, wearable comput ing devices such as watches, glasses, etc., or the like may be utilized for the data transference configuration 100 and other configurations provided herein In contrast with previous configurations that allow for a user to utilize a camera in a Smartphone that takes a picture of a bar code on a media product package, the data transference configuration 100 does not require a Smartphone to have a camera or an Internet connection. Further, the user does not have to download an application on the Smartphone in order to read a code. As an example, a user can activate an NFC chip reader in a smartphone so that the smartphone is constantly scanning for data. In addition, the bar code in previous configurations only redirects the user to a website and does not allow for media to be transferred from a product package to a phone Although a proximity-based reader 110 is illus trated in FIG. 1, a variety of devices may be utilized in place of or in addition to the proximity-based reader 110. For example, a proximity-based sensor transceiver may be utilized Although a proximity-based sensor trans ceiver 104 is illustrated in FIG. 1, a variety of devices may be utilized in place of or in addition to the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104. For example, a proximity based reader may be utilized In one aspect, the proximity is predefined. In other words, a predefined distance may be established for which the mobile device 106 has to be with respect to the product product package 102. For example, the predefined distance may be established such that a tap of the product product package 102 has to be performed so that the mobile device 106 receives the data associated with the product and/
14 US 2014/ A1 Aug. 21, 2014 or product package 102. Alternatively, the predefined dis tance may be a distance that does not have a tap The data transference configuration 100 illustrated in FIG. 1 may be utilized without a connection to a network such as the Internet. In other words, the mobile device 106 obtains data associated with the product product pack age 102, e.g., a preview video trailer, directly from the prox imity-based sensor transceiver 104, e.g., an NFC chip. The NFC chip stores the entirety of the preview video trailer In an alternative aspect, the data associated with the product product package 102 is an activator, e.g., a code, that activates a Software application stored in the mobile device 106. For example, a user may download a software application to the mobile device 106 Such as a game associ ated with a movie on a Blu-ray disc or DVD. The mobile device 106 may be restricted from playing the game until the mobile device 106 is within proximity of the Blu-ray disc or DVD. The content on the disc NFC chip may trigger or unlock certain functions of the application retrieve other con tent from the Internet Such as certain games, trailers, wallpa per, personalized screensavers, or the like. Such data may be associated with the product product package FIG. 2 illustrates a data transference configuration 200 in which a network connection is utilized to obtain at least a portion of the data associated with the product prod uct package 102. Upon the mobile device 102 being in prox imity to the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 stored in the product product package 102, the prox imity-based sensor transceiver 104 sends a first portion of the data associated with the product product pack age 102. The proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 may also send a web address to the mobile device 106. For example, the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 may send twenty percent of a video trailer to the mobile device 106. The mobile device 106 may then obtain the remaining eighty percent of the video trailer from a website at the web address. Accordingly, the mobile device 106 sends a request to a server 202 through a network 204. The server 202 then sends the second portion of the data associated with the product product package 102 to the mobile device 106. The mobile device 102 then aggregates the first portion of the data associated with the product product package 102 and the second portion of the data associated with the product product package 102 to form the entirety of the data associated with the product product package 102 for display on the display 108 of the mobile device In one aspect, the data is preloaded into a chipset of the product product package 102. That data is then available for transmission. In another aspect, only a Subset of the data is preloaded into a chipset of the product product package 102. The mobile device 106 may then request a remainder of the data from the server 202 through the network FIG. 3 illustrates an alternative configuration in which a data transference configuration 300 is utilized with out any content being received by the mobile device 106 directly from the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104. The proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 pro vides a web address to the mobile device 106. The mobile device 106 then obtains the entirety of the data associated with the product product package 102 from the server 202 through the network FIG. 4 illustrates a process 400 that is utilized to send data associated with the product product package 102 illustrated in FIGS At a process block 402, the process 400 sends, from a proximity-based device within a product a product package, data associated with the product the product package to a mobile device 106 based upon the mobile device 106 being within a proximity to the proximity-based device FIG. 5 illustrates an expanded view of the internal components of the mobile device 106. The mobile device 106 has a processor 502 that provides instructions to the proxim ity-based reader 110, a data storage device 504, a memory 506, a transmitter 508, and a receiver 510. In one aspect, the data storage device 504 stores user preferences. The user preferences may include preferences particular to that user, e.g., favorite movies, favorite scenes of movies, favorite actors actresses, spoken languages, favorite music, or the like The internal components illustrated in FIG. 5 are provided as examples of internal components. As a variety of mobile devices 106 may be utilized with any of the configu rations provided for herein, different internal components may be utilized. For example, the internal components of a mobile device 106 may have different internal components if the mobile device 106 is a wearable computing device. Fur ther, the internal components of the mobile device 106 may be different than those illustrated in FIG. 5 based upon the type of proximity-based technology utilized, e.g., NFC, RFID, etc In one aspect, the processor 502 of the mobile device 106 customizes the data associated with the product product package 102 illustrated in FIGS. 1-3 accord ing to the user preferences. In yet another aspect, a custom ized preview is provided for a particular user. The mobile device 106 may utilize personal preferences of the user, e.g., a type of scene, actor, or the like Stored on the phone to select content from the media product package NFC chip to display. Further, the mobile device 106 may retrieve additional con tent from the network 204, e.g., the Internet, based upon the userpreferences. As an example, the mobile device 106 reads a generic menu off of the NFC chip in a media product package and combines that generic menu via Software with data particular to the user stored on the mobile device 106 for display The user preferences stored by the data storage device 504 may be utilized in the alternative or in addition to customization of the data associated with the product product package 102. For example, the user preferences may be utilized to customize the playback of the product, e.g., a Blu-ray disc. FIG. 6 illustrates a data transference configura tion 600 that customizes playback of the product 102 by a content playback device 602. The proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 of the product product package 102 sends a product identifier to the proximity-based reader 110 of the mobile device 106. An example of the product identifier is a unique movie identifier such as a Pre-recorded Media Serial Number ( PMSN). The PMSN of the product 102, e.g., a DVD, may be the same as the PMSN of the proximity-based sensor transceiver 104 in the product package The mobile device 106 then sends the product iden tifier and user preferences stored in the data storage device 504 illustrated in FIG.5 to the server 202 through the network 204 in FIG. 6. In one aspect, the server 202 is in operable communication, e.g., through wireline or wireless communi cation, with a product identifier database, e.g., a PMSN data base. The product identifier database 604 stores the product
15 US 2014/ A1 Aug. 21, 2014 identifier and the user preferences. The content playback device 602, e.g., Blu-ray disc player, may then send a play back indication to the server 202 through the network 204 to indicate that playback of the product 102 has been initiated. The server 202 may then send the user preferences to the playback device 602. Accordingly, the playback device 602 may customize playback of the product 102 according to the user preferences For instance, a user may place the mobile device 106 illustrated in FIG. 1 in proximity to a Blu-ray disc package. The user may then obtain a customized trailer of the movie corresponding to the Blu-ray disc on the display 108. The user may then decide to purchase the Blu-ray disc. Prior to the user playing the Blu-ray disc in a Blu-ray player, the user prefer ences of the user may be sent to the product identifier database 604. Upon the user placing the Blu-ray disc into the Blu-ray disc player, the Blu-ray disc player obtains the user prefer ences from the product identifier database 604. As a result, the Blu-ray disc player customizes the playback of the Blu-ray disc according to the user preferences As an example, a Blu-ray disc player may be preset to perform playback in a certain language, e.g., audio subtitles. The user interface of the mobile device 106 is con figured to that particular language. The disc may then be configured to Subsequently utilize that language FIG. 7 illustrates a process 700 that is utilized to customize playback of the product 102. At a process block 702, the process 700 receives, at a server, a user preference from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier. Further, at a process block 704, the process 700 stores the user preference and the product identifier in a database. In addi tion, at a process block 706, the process 700 receives, from a second playback device, an indication that playback for con tent corresponding to the identifier has been initiated. At a process block 708, the process 700 sends the user preference to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user prefer CCC In an alternative aspect, the user preferences are not obtained directly from the product identifier database 604. FIG. 8 illustrates an alternative content playback customiza tion configuration 800. The mobile device 106 sends a prod uct identifier and a user identifier to the server 202 through the network 204. The server 202 stores the product identifier and the user identifier in the product identifier database 604. Upon receiving a playback indication from the content playback device 602, the server 202 determines the user preference from a user identifier database 802. The user identifier data base 802 stores a profile for each user identifier. The profile includes the userpreferences. Accordingly, the mobile device 106 only has to send a user identifier rather than the user preferences to the server 202 through the network FIG. 9 illustrates an alternative process 900 that is utilized to customize playback of the product 102. At a pro cess block 902, the process 900 receives, at a server, a user identifier from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier. Further, at a process block 904, the process 900 stores the user identifier and the product identifier in a data base. In addition, at a process block 906, the process receives, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated. At a process block 908, the process 900 searches a profile database to determine a user preference based upon the user identifier. Further, at a process block 910, the process 900 sends the user preference to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference In yet another aspect, the placement of a plurality of product packages together causes the NFC chips to send additional content to the NFC reader in the mobile device 106. For example, placement of DVD packages for a movie series together may provide a trailer based upon all of the movies in the series that would not be accessible if the mobile device 106 was in proximity to each DVD individually. Further, additional content may be available or unlocked after pur chase In another aspect, bonus content, e.g., deleted scenes may be unlocked after purchase of the product 102. In one configuration, the checkout counter sends a code to the NFC chip in the package 102. In another configuration, a server sends a code or key to the mobile device 106. The mobile device 106 then sends the code or key to the NFC chip in the media product package In yet another aspect, the product 102 is a Secure Digital ( SD) card. The mobile device 106 sends an indica tion to an NFC chip in the media product package 102. The indication is an activator that activates a process to update the SD card to personalize the content, e.g., the user's name on a C FIG. 10 illustrates a user interface 1002 for the mobile device 106 illustrated in FIG. 1. The user interface 1002 has the following features: disc one menu 1004, disc two menu 1006, trailer 1008, actors/actresses info or interviews 1010, director info or interviews 1012, advertisements 1014, coupons 1016, related movies 1018, related video games 1020, and user preferences The processes described herein may be imple mented in a general, multi-purpose or single purpose proces sor. Such a processor will execute instructions, either at the assembly, compiled or machine-level, to perform the pro cesses. Those instructions can be written by one of ordinary skill in the art following the description of the figures corre sponding to the processes and stored or transmitted on a computer readable medium. The instructions may also be created using source code or any other known computer aided design tool. A computer readable medium may be any medium capable of carrying those instructions and include a CD-ROM, DVD, magnetic or other optical disc, tape, silicon memory (e.g., removable, non-removable, Volatile or non Volatile), packetized or non-packetized data through wireline or wireless transmissions locally or remotely through a net work It is understood that the apparatuses, systems, com puter program products, and processes described herein may also be applied in other types of apparatuses, systems, com puter program products, and processes. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the various adaptations and modifica tions of the aspects of the apparatuses, systems, computer program products, and processes described herein may be configured without departing from the Scope and spirit of the present apparatuses, systems, computer program products, and processes. Therefore, it is to be understood that, within the scope of the appended claims, the present apparatuses, systems, computer program products, and processes may be practiced other than as specifically described herein.
16 US 2014/ A1 Aug. 21, 2014 We claim: 1. A method comprising: sending, from a proximity-based device within a product a product package, data associated with the prod uct the product package to a mobile device based upon the mobile device being within a proximity to the proximity-based device. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein the data associated with the product the product package is a preview of content stored by the product the product package. 3. The method of claim 1, wherein the data associated with the product the product package is selected from the group consisting of a plurality of images, a plurality of videos, a quantity of discs, a menu of content, a menu of functionality, a chapter menu, a list of deleted Scenes, director commentary, interviews, bonus content, games, contents, special offers, advertisements, promotions, coupons, and movie reward redemptions. 4. The method of claim 1, wherein the data associated with the product the product package is obtained by the mobile device without the mobile device connecting to the Internet. 5. The method of claim 1, further comprising sending a web address link to the mobile device, the web address link indicating a web address of a server to which the mobile device connects via the Internet to obtain a remainder of data associated with the product the product package. 6. The method of claim 1, further comprising activating, from the proximity-based device, functionality of a software application stored on the mobile device. 7. The method of claim 1, wherein the proximity-based device is a Near Field Communication transmitter. 8. The method of claim 1, wherein the mobile device com prises a proximity-based receiver. 9. The method of claim 8, wherein the proximity-based receiver is a Near Field Communication receiver. 10. The method of claim 1, wherein the proximity is pre defined. 11. An apparatus comprising: a proximity-based transmitter stored within a product and/ or a product package that sends data associated with the product the product package to a mobile device based upon the mobile device being within a proximity to the proximity-based device. 12. A method comprising: receiving, at a proximity-based receiver within a mobile device, data associated with a product a product package from a proximity-based transmitter within the product the product package based upon the proximity-based receiver being within a proximity to the proximity-based transmitter. 13. The method of claim 12, wherein the data associated with the product the product package is a preview of content stored by a product stored within the product the product package. 14. The method of claim 12, wherein the mobile device selects a subset of the data associated with the product the product package according to user preferences stored by the mobile device and displays the subset of the data associ ated with the product the product package. 15. The method of claim 12, wherein the mobile device obtains additional data from a server through a network, the additional data being associated with the product the product package, the additional data being obtained based upon user preferences stored by the mobile device. 16. The method of claim 15, wherein the mobile device displays the data associated with the product the prod uct package in conjunction with the additional data. 17. The method of claim 12, wherein the data associated with the product the product package is a Pre-recorded Media Serial Number of the product. 18. The method of claim 12, further comprising determin ing a user preference from data stored in the mobile device and sending the user preference to a Pre-recorded Media Serial Number database. 19. The method of claim 12, further comprising determin ing a user identifier from data stored in the mobile device and sending the user identifier to a Pre-recorded Media Serial Number database. 20. The method of claim 12, wherein the data is preloaded into a chipset of the product product package. 21. The method of claim 12, wherein a subset of the data is preloaded into a chipset of the product product pack age. 22. The method of claim 21, wherein the mobile device requests a remainder of the data from a server through a network. 23. An apparatus comprising: a proximity-based receiver that receives data associated with a product a product package from a proxim ity-based transmitter within the product the prod uct package based upon the proximity-based receiver being within a proximity to the proximity-based trans mitter. 24. A method comprising: receiving, at a server, a user preference from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier; storing the user preference and the product identifier in a database; receiving, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated; sending the user preference to the content playback device So that the content playback device plays back the con tent according to the user preference. 25. The method of claim 24, wherein the database is a Pre-recorded Media Serial Number database. 26. The method of claim 24, wherein the user preference is a language. 27. An apparatus comprising: a server that receives a user preference from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier, stores the user preference and the product identifier in a database, receives, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated, and sends the user prefer ence to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference. 28. An apparatus comprising: a content playback device that receives a product having content stored thereon for playback and having a prod uct identifier stored thereon, sends an indication to a server that that the product has been received for play back, receives a user preference from the server based upon the product identifier, and configures the playback of the content according to the user preference.
17 US 2014/ A1 Aug. 21, A method comprising: receiving, at a server, a user identifier from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier; storing the user identifier and the product identifier in a database; receiving, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated; searching a profile database to determine a user preference based upon the user identifier; sending the user preference to the content playback device so that the content playback device plays back the con tent according to the user preference. 30. The method of claim 29, wherein the database is a Pre-recorded Media Serial Number database. 31. The method of claim 29, wherein the user preference is a language. 32. An apparatus comprising: a server that receives a user identifier from data stored in a mobile device and a product identifier, stores the user identifier and the product identifier in a database, receives, from a content playback device, an indication that playback for content corresponding to the product identifier has been initiated, searches a profile database to determine a user preference based upon the user iden tifier, and sends the user preference to the content play back device so that the content playback device plays back the content according to the user preference. 33. An apparatus comprising: a content playback device that receives a product having content stored thereon for playback and having a prod uct identifier stored thereon, sends an indication to a server that that the product has been received for play back, receives a user identifier from the server based upon the product identifier, searches a user profile data base according to the user identifier to determine a user preference, and configures the playback of the content according to the user preference. 34. A method comprising: receiving, at a proximity-based receiver within a mobile device, data associated with a plurality of products and/ or product packages from a plurality of proximity-based transmitters stored within the plurality of products and/ or product packages based upon the proximity-based receiver being within a first proximity to the plurality of proximity-based transmitters and the plurality of prox imity-based transmitters being within second proximity of each other. 35. The method of claim 34, wherein the data associated with the plurality of products product packages is data other than that received and aggregated by the proximity based receiver being with the first proximity of each of the plurality of products product packages.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0352797 A1 Marusich et al. US 20160352797A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) COORONATING METADATA Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0352797 A1 Marusich et al. US 20160352797A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) COORONATING METADATA Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, (54) E-CARD Publication Classification
 (19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0201065 A1 COX et al. US 201402O1065A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 17, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) SYSTEM FOR AND METHOD
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0201065 A1 COX et al. US 201402O1065A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 17, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) SYSTEM FOR AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013
 (19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,694,666 B2
 US8694666B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,694,666 B2 Dixon (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2014 (54) PERSNALIZED STREAMING DIGITAL 2002/0152278 A1* 10, 2002 PontenZone et al.... 709/217
US8694666B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,694,666 B2 Dixon (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2014 (54) PERSNALIZED STREAMING DIGITAL 2002/0152278 A1* 10, 2002 PontenZone et al.... 709/217
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 US 20150067353A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0067353 A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2015 (54) STORAGE MANAGEMENT DEVICE AND (52) US. Cl. STORAGE MANAGEMENT
US 20150067353A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0067353 A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2015 (54) STORAGE MANAGEMENT DEVICE AND (52) US. Cl. STORAGE MANAGEMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE
 Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE PRIORITY This application is a Continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 14/540,447, which was filed in the U.S.
Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE PRIORITY This application is a Continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 14/540,447, which was filed in the U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150302381A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0302381 A1 Baig (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATICALLY EMAILING RECEIPTAT (52) U.S. Cl. POS CPC... G06O20/209
(19) United States US 20150302381A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0302381 A1 Baig (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATICALLY EMAILING RECEIPTAT (52) U.S. Cl. POS CPC... G06O20/209
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. Hobbs et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2015
 US 2015O163765A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0163765 A1 Hobbs et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMINDERS BASED ON DEVICE Publication Classification PROXMITY
US 2015O163765A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0163765 A1 Hobbs et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMINDERS BASED ON DEVICE Publication Classification PROXMITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0213301 A1 Evans et al. US 20140213301A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 31, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0213301 A1 Evans et al. US 20140213301A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 31, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(12) United States Patent
 US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O132798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0132798 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2008 (54) WIRELESS HEADSETS AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 2008O132798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0132798 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2008 (54) WIRELESS HEADSETS AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction
 ( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
SYSTEM AND PROCESS FOR ALTERING MUSICAL OUTPUT FOR AUDIO ENTERTAINMENT BASED ON LOCATION
 SYSTEM AND PROCESS FOR ALTERING MUSICAL OUTPUT FOR AUDIO ENTERTAINMENT BASED ON LOCATION BACKGROUND [001] Embodiments of the invention described in this specification relate generally to audio entertainment
SYSTEM AND PROCESS FOR ALTERING MUSICAL OUTPUT FOR AUDIO ENTERTAINMENT BASED ON LOCATION BACKGROUND [001] Embodiments of the invention described in this specification relate generally to audio entertainment
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0095237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0095237 A1 Turakhia (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010.0095237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0095237 A1 Turakhia (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1297.55A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0129755A1 Jadhav et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) EXTERNAL BOOST OF PROCESSING (52) U.S. Cl. THROUGH
(19) United States US 2014O1297.55A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0129755A1 Jadhav et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) EXTERNAL BOOST OF PROCESSING (52) U.S. Cl. THROUGH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201603 00023A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0300023 A1 Leonard (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2016 (54) PROVIDER RATING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 19/327
US 201603 00023A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0300023 A1 Leonard (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2016 (54) PROVIDER RATING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 19/327
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/ A1* 11/2004 Koda et al , 183
 (12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170033839A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0033839 A1 ABBONDANZO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CAPTURING PHYSICAL INVENTORY IN A H04W 76/02 (2006.01) DATA
(19) United States US 20170033839A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0033839 A1 ABBONDANZO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CAPTURING PHYSICAL INVENTORY IN A H04W 76/02 (2006.01) DATA
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0165014 A1 Nainar et al. US 2016O165O14A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) INTER-DOMAIN SERVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0165014 A1 Nainar et al. US 2016O165O14A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) INTER-DOMAIN SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 2014.0004952A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0004952 A1 Kern (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXCHANGINGVIRTUAL REWARDS FOR (52) U.S. Cl. COMPUTING RESOURCES USPC...
US 2014.0004952A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0004952 A1 Kern (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXCHANGINGVIRTUAL REWARDS FOR (52) U.S. Cl. COMPUTING RESOURCES USPC...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/ A1 Brenner (43) Pub. Date: NOV.
 US 20050246470A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: Brenner (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 3, 2005 (54) WIRELESS DOCKING STATION (57) ABSTRACT (76) Inventor: David G- Brenner>
US 20050246470A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: Brenner (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 3, 2005 (54) WIRELESS DOCKING STATION (57) ABSTRACT (76) Inventor: David G- Brenner>
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0046424 A1 Horton US 20080046424A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF SELECTING IMAGES ACCORDING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0046424 A1 Horton US 20080046424A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF SELECTING IMAGES ACCORDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150254902A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254902 A1 MACIA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) BRINGING MAIL TO LIFE VIA MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20150254902A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254902 A1 MACIA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) BRINGING MAIL TO LIFE VIA MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140376386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0376386 A1 Koshy (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM FOR INTERCONNECTING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICES FOR CREATING AUTOMATION
(19) United States US 20140376386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0376386 A1 Koshy (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM FOR INTERCONNECTING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICES FOR CREATING AUTOMATION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
Storing metadata about each media item 10
 US 2007 O1987.46A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/019874.6 A1 Myllyla et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, COMPUTER Related U.S. Application Data PROGRAMS
US 2007 O1987.46A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/019874.6 A1 Myllyla et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, COMPUTER Related U.S. Application Data PROGRAMS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. streaming media server
 (19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. ? 200
 (19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/013524.0 A1 Miller US 2013 O135240A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) APPARATUS FOR REMOTELY CONTROLLING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/013524.0 A1 Miller US 2013 O135240A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) APPARATUS FOR REMOTELY CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
Wireless devices supports in a simple environment
 USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 20020002707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0002707 A1 Ekel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD TO DISPLAY Publication Classification
US 20020002707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0002707 A1 Ekel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD TO DISPLAY Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO853.8494B2 (12) United States Patent Hsu (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,538,494 B2 Sep. 17, 2013 (54) MOBILE PHONE AND METHOD FOR TRANSFERRING BATTERY POWER OF THE MOBILE PHONE (75) Inventor:
USOO853.8494B2 (12) United States Patent Hsu (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,538,494 B2 Sep. 17, 2013 (54) MOBILE PHONE AND METHOD FOR TRANSFERRING BATTERY POWER OF THE MOBILE PHONE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160302386A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0302386 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) GESTURE CONTROL AND DIRECTIONAL AOIK 27/00 (2006.01) FORCE ON
US 20160302386A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0302386 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) GESTURE CONTROL AND DIRECTIONAL AOIK 27/00 (2006.01) FORCE ON
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O183076A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0183076 A1 Colangelo et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BROWSER-INDEPENDENT POP-UP WINDOWS (76) Inventors: Agatha
(19) United States US 2005O183076A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0183076 A1 Colangelo et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BROWSER-INDEPENDENT POP-UP WINDOWS (76) Inventors: Agatha
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
