SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
|
|
|
- Briana Brooks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida Abstract Many of the electronic devices currently in use, such as desktop computers, printers, and scanners, are connected by using cables. As the number of devices in a local environment increases, and the desire to remain connected in mobile communication environment becomes popular, wireless connectivity will be a natural choice. In such situations, Bluetooth technology is rapidly becoming a popular choice of connecting devices together. Bluetooth technology is essentially a cable replacement technology for communication within a small geographic area. The research presented in this paper deals with the performance analysis of Bluetooth networks using simulation. The primary focus of this simulation study is to observe the effects of network traffic and the network size on the packet transmission delay. The simulation results are presented in terms of packet delay versus network traffic. Keywords: Bluetooth technology, performance analysis, simulation. 1 INTRODUCTION The worldwide growth of wireless cellular phone subscription has demonstrated that wireless communication is a viable, robust multimedia communication mechanism. In addition, emerging technologies have made it possible to develop smaller, inexpensive yet powerful portable computers that allow people to conduct their business and personal activities while on the move. These mobile devices can interact with other devices. Participants with these mobile devices can share documents or presentations, business cards can automatically find their way into the address book on a laptop; as commuters exit a train, their laptops could remain online; likewise, incoming could now be diverted to their PDAs; finally, as they enter the office, all communication could automatically be routed through the wireless corporate campus network. Next generation cellular networks are being designed to facilitate high-speed data communication traffic in addition to voice traffic. New technologies and standards are being implemented to replace fiber optic or copper lines between fixed points several kilometers apart. Wireless networks have been used increasingly in homes, buildings and small office settings through deployment of wireless local area networks (WLANs). The evolving Bluetooth technology promises to replace troublesome appliance communication cords with invisible connections within an individual s personal workplace. The Bluetooth and WLAN are used within buildings and the both systems use low power and do not require a license for spectrum use. Most electronic devices these days, such as computers, printers and scanners etc., are literally connected through cables. One could get confused when there is a need to change or rewire the cables for some or the other reasons when there are lot of wires connecting computers, printers, scanners and PDAs etc. In these situations Bluetooth technology [1,2,3,4] comes to rescue. Bluetooth is a cable replacement technology, which will help the electronic devices to communicate without the help of cables. Developed initially by Ericsson, before being adopted by many other companies, Bluetooth is a standard for a small, low power, in-expensive chip to be plugged into computers, printers, mobile phones, etc. A transmitter in a Bluetooth chip is designed to transmit information to a receiver in another Bluetooth chip using a special radio frequency, which is otherwise normally transmitted by cables. Bluetooth is basically a short-range radio link intended to replace cables connecting portable and/or fixed electronic devices. The main features are robustness, low complexity and low cost. Bluetooth operates in the unlicensed ISM (Industrial Scientific Medicine) band of 2.4 GHz. In majority of countries around the world the range of this frequency band is MHz. To combat interference and fading, a frequency hopping mechanism is applied. The frequency hopping mechanism hops 1600 times in a minute. One hop in this hopping mechanism consumes 625 µs and consists of one ISBN: SPECTS '03
2 frequency slot. Time division duplex scheme is used for duplex communication. A packet normally covers a single slot but can be extended to cover up to 3 or 5 slots. A piconet is formed when one master device and one or more slave devices (up to 7) agree to communicate between them. A master device starts sending its packets in the even numbered slot and the slave device starts its packets in the odd numbered slot. The master device is responsible for coordinating with other devices to form and allocate the channel slots between the piconet units. A scatternet is formed when more than one piconets are involved in communicating between each other. This objective of this paper is to analyze the performance characteristics of Bluetooth Piconet and Scatternet systems under different link configurations based on the number of links, packet types and traffic patterns. To achieve the objective of analyzing the performance issues of Bluetooth systems in general using a simulation model, the Bluetooth system with its basic protocols need to be modeled. Bluehoc, a simulation tool developed by IBM specifically to study Bluetooth related networking issues, modeled the very basic layers, which are needed to simulate the virtual Bluetooth system units. Bluehoc simulates the Baseband, LMP and L2CAP protocols. NS (network simulator) based tools such as Telnet and Exponential Traffic were used for the purpose of traffic generation. In this research work the Bluehoc layered on top of Network Simulator is used to build the basic Bluetooth systems and modifications are made to suit the requirements. For different variation of traffic patterns and with varying number of devices the Delay characteristics of data sent, number of packets sent and Piconet generation time delay are analyzed. The next section describes a general overview of the communications systems with reference to Bluetooth system. Section 3 explains the simulation tool used and the also explains about a simulation script used with information regarding the simulation parameters etc. Simulation results are presented in section 4 and finally conclusions are presented in section 5. 2 BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Bluetooth is an open specification for short-range communication through radio frequencies. A Bluetooth transceiver operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial Scientific Medicine) band with a data rate of 1 MBPS. In most countries the range of the frequency bandwidth is GHz. Some countries have a limitation in this range. To comply with this situation, special frequency hopping algorithms have been developed. To comply with outof band regulations, a guard band is used at the lower and upper end of the range. For example, in USA, Europe and most other countries the lower guard band is 2 MHz and the upper guard band is 3.5 MHz. So the actual communication channel width for the Bluetooth systems is MHz. With 1 MHz channel spacing this results in 79 unique frequencies for actual use by Bluetooth units. A combination of circuit switching and packet switching is employed in Bluetooth communications. Bluetooth can support an asynchronous data channel, up to three simultaneous synchronous voice channels. It can also simultaneously support an asynchronous data and synchronous voice channel. Each voice channel supports 64 Kb/s synchronous (voice) channel in each direction. The asynchronous data channel can support maximum of Kb/s asymmetric (and still up to 57.6 Kb/s in the return direction), or Kb/s symmetric. A Bluetooth system consists of a radio unit, link control unit and a support unit for link management and host terminal interface. The Bluetooth link controller unit carries out the Baseband protocol functionality and other low-level link routines. Point-to-point connection is established between two Bluetooth radios or a point-to-multipoint connection is established when a there are more than two Bluetooth systems involved wherein channel is shared among the several units. These multiple units form a Piconet, where one unit acts as a master and the other units (maximum up to 7) acts as slaves. A piconet as shown in Figure 1 can have up to seven slaves active any time, and other radios, if they exist, can stay in parked mode and become active when the active mode devices leaves the piconet or goes on to any state other than active state. The master device supervises channel allocation for both active mode and the parked mode are synchronized to the master any time. A Scatternet is formed to assist in communication between more than one piconets. Each piconet master has its own unique frequency sequence based on the BD_ADDR of the master device. Data is transmitted to other piconet through a particular slave/master which acts as a bridge device between two piconets on a Time Division Multiplexing basis. A master in one piconet can also act as a slave in another piconet. Each piconet has only one master. There is a unique frequency sequence for each piconet, which is controlled by the Bluetooth device address of the master device. The channel is represented by pseudo-random hopping sequence hopping through 79 or 23 unique frequencies. The channel is divided into time slots where each slot corresponds ISBN: SPECTS '03
3 to a single radio frequency. Nominal slot length of 625 µs leads to 1600 slots per second. Two types of links have been defined between the master and slave. SCO- Synchronous Connection Oriented and ACL- Synchronous Connectionless link. SCO connection is between the master and a single slave and is point-to-point. Slots are reserved for an SCO connection by the master device. An ACL link is a pointto-multipoint link between the master and all the active slaves. On the slots not reserved for SCO connections the master can establish ACL links, even with the slaves already connected with an SCO link. Slave Master Figure: 2 Single Slot Packet [2] Figure: 1 Piconet with Single slave (a), with multi slave (b) and a Scatternet Arrangement (c) [2] The time slots are numbered according to the Bluetooth clock of the piconet master and the number ranges from 0 to and is cyclic with a cycle length of A TDD scheme is used where the master and the slave devices transmits alternatively. Figure 2 represents the schematic of a single slot packet and Figure 3 represents the schematic of multi-slot packets. The master device shall start its transmission in the even numbered slots only. And the slave device shall start its transmission in the odd numbered slot. Packets transmitted by the master or slave may extend up to 5 slots depending upon the packet data size. The RF frequency shall remain fixed for the entire duration of the packet transmission. For a single slot packet, the RF hop frequency to be used is derived from the Bluetooth clock of the master device. And for a multislot packet the RF hop frequency to be used for the remaining slots is same as the one for the first slot. The RF frequency for the first slot after a multi-slot packet is based upon the current value of the Bluetooth clock of the piconet master. Figure: 3 Multi Slot Packet [2] The SCO link is like a circuit-switched connection between master and the slave, since slots are reserved for the purpose of SCO links. SCO can support time-bounded information like voice. Master supports up to three SCO links to the same slave or different slaves. Slave can support up to three SCO links if the links are from the same master or two SCO links if the links are from different masters. An SCO link is established by the master through an SCO setup message in the Link Manager Protocol. The link setup message will contain parameters like T SCO (SCO interval) and the D SCO (Offset) to identify the reserved slots. The SCO packets are sent at a regular interval, T SCO (slots) in the reserved SCO slots. SCO slots are never re-transmitted. SCO slave can always respond an SCO reception in the following slave-to-master slot even if the slave fails to receive the master-to-slave packet unless a ISBN: SPECTS '03
4 different slave was addressed in the previous master-toslave slot. An ACL connection can exist between master and a slave in the slots not reserved for SCO connection. An ACL link provides a connection similar to that of a packet switched connection. Only a single ACL connection can exist between a master and a slave. ACL packets are retransmitted to recover dropped/failed packets. An ACL slave can respond in the slot following the master-to-slave slot provided it has been addressed in the master-to-slave slot. If the slave fails to receive the packet or fails to decode the slave address in the packet, then it shall wait for the next turn. If a specific slave address is not mentioned in the ACL packet then it is considered as a broadcast message and is read by every device in the piconet. If there is no data to be sent and no polling required then no transmission shall take place. A packet has three entities such as Access Code, header and Payload. As shown in the Figure 4, Access Code and Header have fixed sizes whereas payload ranges from bits. Different packet types have been defined. A Packet may consist of the Access code only or of the access code - header or access code - header - payload based on the type of packet being sent. In the receiving side Access Code is compared against a sliding correlator, which triggers if a threshold is reached. If there is a match the packet is received. 3 SIMULATION Figure: 4 General Packet Format [2] Bluetooth technology is a low cost, low power and low complexity cable replacement technology capable of connecting wide variety of devices like Personal Digital Assistants (PDA), mobile phones, cordless phones, headsets, laptops, home appliances, digital cameras etc. Since this is basically a cable replacement technology that s it connects all the above-mentioned devices through 2.4 GHz ISM band of Radio Frequency waves. A Bluetooth enabled device is able to connect to another Bluetooth enabled device virtually without any knowledge about each other. As explained earlier the Bluetooth technology enables the devices to form a smallconnected network what is known as Piconet with one unit being a master and up to seven units acting as slaves. A Scatternet scheme is proposed to connect devices in different piconets to communicate each other by this the extent of the communication range may be increased. In this present study the performance of the Bluetooth piconet communication and Scatternet communication is analyzed with reference to number of Bluetooth devices in the piconet and number of piconets in the scatternet arrangement with Exponential Traffic Pattern and FTP traffic pattern. For the purpose of this research, at least, the following layers need to be implemented. Radio Layer Baseband Layer Link Manager Protocol Layer Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol layer. Bluehoc simulator developed by IBM simulates the four basic layers. Bluehoc is an extension to the Network Simulator (NS) [5]. NS is object-oriented, discrete event driven network simulator developed at University of Berkeley written in C++ targeted at networking research. NS is primarily used for Local and Wide area networks. It implements network protocols such as TCP and UDP, traffic source behavior such as FTP, Telnet, Web, CBR and VBR, router queue management mechanism such as Drop Tail, RED and CBQ, routing algorithms such as Dijkstra, and more. NS also implements multicasting and some of the MAC layer protocols for LAN simulations. Bluehoc deals with frequency generation, frequency hopping, system clock management, frequency synchronization, piconet management, link configuration, QOS setup and scatternet management. Since it is paramount to have at least the above said layers simulated to study the performance of Bluetooth piconets and scatternets Bluehoc was chosen to be the right tool. To achieve the objective of analyzing the performance issues of Bluetooth systems, the above said functionalities that form the part of the Bluetooth core protocols such as Baseband protocol, Link Manager Protocol (LMP), Logical Link Control and Adaptation protocol (L2CAP) are implemented in the Bluehoc tool. A detailed set of parameters used for simulation for different studies have been defined. Various sets of data are applied in different circumstances to study the effects of congestion, mobility, data delivery rate, effect of queue size, data packet size, node range and slot size. A brief description of the parameters used in the simulation is as follows: Slot size - the size of slots can vary from 256 to 4096 bytes. In CDMA mode, the packets generated must be accommodated in a slot before transfer. This means that slot size must be consistent with the total size of data in all the packets to be packed in the slot. ISBN: SPECTS '03
5 Packet Generation Rate (PGR) - the program running at a node generates packets at the rate of 4 packets per second. Regardless of the size of the packet, these packets generate with a constant factor and are en-queued in the packet sending priority queue. If the queue is filled, the newly generated packets are dropped. If a packet stays in the queue for more than 30 seconds it is also expired and dropped. Throughput - each node is fixed to have a 16kbps data transfer rate i.e. each node can transfer up to 16,384 bytes of data per second. A combination of varying packet sizes may be used to accommodate this transfer space. If the packet size is set to be 512 bytes then (16384/512) = 32 packets can be transferred at maximum. If packet size is 4096 bytes then only 4 packets can be sent per second. Mobility-three levels of mobility are used; low, moderate, and high. In low mobility, only 20% of the nodes are allowed to move, in moderate mobility, 50% of the nodes are allowed, and in high mobility, 80% of the nodes are allowed to move. Unit Range - can be 250 meters or 500 meters. Area of the field is set to be by Queue Size - it is always set to be 50. The simulation has a total of 30 nodes scattered around in the field by randomly determining individual s x and y coordinates. Each node is given an address. Before initialization each node calls the find neighbor module to locate adjacent nodes if applicable. Once the adjacent nodes are located and their information is entered in the local node s routing table, the simulation can be started. To determine the behavior, the simulation can be paused at intervals of pre-selected time. 4 SIMULATION RESULTS This section presents analysis of a limited number of simulation results. The results mainly show the delay of piconet and scatternet formation under different traffic conditions. The Figure 5 represents the graph of Time duration for piconet establishment and the number of devices involved in a piconet. As can be seen from the figure, maximum time duration for piconet establishment for a piconet with any number of devices (maximum up to 7) is around 10 seconds and this complies with the Bluetooth specification. This can be taken as a basis for further consideration of this simulation tool as a right tool for achieving the objectives specified in the introduction. A paper Performance of a New Bluetooth Scatternet Formation Protocol, [5] by students at MIT has also used Bluehoc as a simulation tool and obtained reasonable results. Time Delay for Piconet Establishment Time in s Number of Devices:7 Simulation Time : 20 s Number of Devices Figure: 5 Number of Devices versus Time Delay for Piconet Establishment Figure 6 shows the graphical representation of relation between piconet data transfer delay and number of links in the piconet when the data packets created are using Exponential traffic. The relation is obtained for two different values of simulation timings, 20 sec and 40 sec. The time delay increases as the number of links in the piconet increase, though not very steep it has a linear relationship. The result is same even with duration of different simulation timings. This is due to the fact that as the number of links increases the master device distributes the available slots evenly to all the slaves participating in the piconet, hence resulting in less number of slots for a piconet that has more number of slave units. Figure 7 shows the graph of number of piconets and the data transfer time delay for FTP traffic pattern and Exponential traffic pattern. The FTP traffic pattern is encoded with the FEC while Exponential traffic pattern is not encoded with FEC. 5 CONCLUSIONS The paper has presented a simulation study to observe the effects of network traffic and the network size on the packet transmission delay. The simulation results are presented in ISBN: SPECTS '03
6 terms of packet delay versus network traffic. The delay in packet transmission increases proportionally to number of devices in a piconet when the traffic pattern used is Exponential pattern. The delay in packet transmission increases proportionally when the traffic pattern used is of FTP pattern. It has been observed that that the packets with FEC (Forward Error Correction) offers more delay in transmission than the one without FEC. Suggesting use of packets without FEC where an error free Bluetooth environment exists. The data transmission delay in a Scatternet environment is proportional to the number of Piconets involved in the transmission, the result holds true for both FTP and Exponential pattern traffic. Suggesting that the data transmission delay can cause hindrance to quality of the information sent, the Bluetooth system user might feel awkward. To avoid deteriorating performance a Scatternet should always have lowest possible number of Piconets. While comparing a packet transmission delay for an FEC packet and a non-fec packet, the delay is more for a packet with FEC than the one without FEC as is for a Piconet environment. Here also suggesting use of packet without FEC data in an error free environment, as is the case for a Piconet environment. REFERENCES 1. T. Salonidis, P. Bhagwat, L. Tassiulas, and R. LaMaire, Distributed Topology Construction of Bluetooth Personal Area Networks, IEEE INFOCOM, J. Haarsen, Bluetooth The Universal Radio Interface for Ad Hoc Wireless Connectivity, Ericsson Review, M. Frodigh, Wireless Ad Hoc Networking The Art of Networking Without a Network, Ericsson Review, C. Law, A. Mehta, and K. Yeung, Performance of a New Bluetooth Scatternet Formation Protocol, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA. Piconet Data transfer Delay with FTP traffic Delay in s Number of Devices: 7 Packet Type: DH5 Packet Capacity: 341 Bytes Number of Links Simulation Time: 20 s Simulation Time: 40 s Simulation Time: 60 s Simulation Time: 80 s Figure: 6 Number of Links Vs Piconet Data Transfer Delay with FTP traffic ISBN: SPECTS '03
7 Scatternet FTP Data Transfer Delay Delay in s Number of Devices/Piconet: 7 Packet Type: DH5 Capacity: 341 Bytes Simulation Time: 20 s Number of Piconets Figure: 7 Number of Piconets Vs Data Transfer Delay in Seconds ISBN: SPECTS '03
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
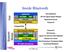 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth
 Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Analysis of UDP Performance over Bluetooth Martin Connolly, Cormac J. Sreenan University College Cork Department of Computer Science Email: cjs@cs.ucc.ie Abstract The Bluetooth protocol is one of the better-known
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth
 Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference
 Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING
 Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Delivering Voice over IEEE WLAN Networks
 Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology
 Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
Research on Modern Bluetooth Technology D.Annal 1, T.Indira 2, K.Poojitha 3, R.Rajashree 4 Student, Dept. of CSE, Magna College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India 1,2,3,4 ABSTRACT: The seemingly
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin
 Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology
 SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
SE 4C03 Winter 2005 Bluetooth Wireless Network Technology Researcher: Daren Tan Shen Hau Last Revised: April 4, 2005 Bluetooth As everyone will ask, what is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is a new technology that
Bhopal, , India 3 M.Tech Scholor,Department Of Computer Science, BIST Bhopal. Bhopal, , India
 Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Link Repairing for Inter-Piconet Communication Technique in Bluetooth Scatternet
 Link Repairing for Inter-Piconet Communication Technique in Bluetooth Scatternet Sabeen Tahir, Abas Md Said, and Sheikh Tahir Bakhsh Abstract A mobile ad-hoc network (MANET) is a collection of wireless
Link Repairing for Inter-Piconet Communication Technique in Bluetooth Scatternet Sabeen Tahir, Abas Md Said, and Sheikh Tahir Bakhsh Abstract A mobile ad-hoc network (MANET) is a collection of wireless
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
A Guide. Wireless Network Library Bluetooth
 A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
Lecture 6. Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1
 Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Lecture 6 Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0002906A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0002906A1 Rune (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2001 (54) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT INA COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2001.0002906A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0002906A1 Rune (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2001 (54) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT INA COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75) Inventor:
Extending or Interconnecting LANS. Physical LAN segment. Virtual LAN. Forwarding Algorithm 11/9/15. segments. VLAN2, Port3. VLAN1, Port1.
 Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems
 Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems Abstract In the Bluetooth system, isochronous applications, such as voice and audio, are carried by Synchronous Connection Oriented
Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems Abstract In the Bluetooth system, isochronous applications, such as voice and audio, are carried by Synchronous Connection Oriented
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
Ethernet. Lecture 6. Outline. Ethernet - Physical Properties. Ethernet - Physical Properties. Ethernet
 Lecture 6 Ethernet Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on 9/20/12. Thick-net Thin-net Twisted Pair Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks
Lecture 6 Ethernet Reminder: Homework 2, Programming Project 2 due on 9/20/12. Thick-net Thin-net Twisted Pair Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 6 1 Thursday, September 13 CS 475 Networks
Introducing Bluetooth
 Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Wireless LAN. Access Point. Provides network connectivity over wireless media
 LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
A Study of Wireless Compressed Digitalaudio
 A Study of Wireless Compressed Digital Transmission Andreas Floros 1, Marios Koutroubas 2, Nicolas-Alexander Tatlas 2 and John Mourjopoulos 2 1 ATMEL Hellas S.A., Patras Science Park, Platani, 26 500 Patras,
A Study of Wireless Compressed Digital Transmission Andreas Floros 1, Marios Koutroubas 2, Nicolas-Alexander Tatlas 2 and John Mourjopoulos 2 1 ATMEL Hellas S.A., Patras Science Park, Platani, 26 500 Patras,
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
WiFi Networks: IEEE b Wireless LANs. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018
 WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
Wireless networks: from cellular to ad hoc
 Wireless networks: from cellular to ad hoc The three wireless waves Wave #1: cellular telephony Still, biggest profit maker Wave #2 : wireless Internet access Most Internet access on US campuses is wireless
Wireless networks: from cellular to ad hoc The three wireless waves Wave #1: cellular telephony Still, biggest profit maker Wave #2 : wireless Internet access Most Internet access on US campuses is wireless
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING
 A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
A COLLOCATED APPROACH FOR COEXISTENCE RESOLUTION IN WIRELESS HOME NETWORKING Md Enamul Islam, Sanjay Jha, Dr. Paul W.H. Kwan, Monzurur Rahman School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
A Dynamic Slot Assignment Scheme for Slave-to-Slave and Multicast-like Communication in Bluetooth Personal Area Networks
 A Dynamic Slot Assignment Scheme for Slave-to-Slave and Multicast-like Communication in Bluetooth Personal Area Networks Carlos Cordeiro, Sachin Abhyankar, and Dharma P. Agrawal OBR Center for Distributed
A Dynamic Slot Assignment Scheme for Slave-to-Slave and Multicast-like Communication in Bluetooth Personal Area Networks Carlos Cordeiro, Sachin Abhyankar, and Dharma P. Agrawal OBR Center for Distributed
Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation
 Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation Ling-Jyh Chen, Rohit Kapoor, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 995, USA {cclljj, rohitk,
Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation Ling-Jyh Chen, Rohit Kapoor, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 995, USA {cclljj, rohitk,
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth
 Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Communication Networks
 Communication Networks Chapter 3 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency
Communication Networks Chapter 3 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
BASEBAND SPECIFICATION
 Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Lecture Computer Networks
 Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM
 IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM SCORT - An Alternative to the Bluetooth SCO Link for Voice Operation in an Interference Environment Slide 1 Bluetooth SCO Link The Bluetooth
IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM SCORT - An Alternative to the Bluetooth SCO Link for Voice Operation in an Interference Environment Slide 1 Bluetooth SCO Link The Bluetooth
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela
 By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
A Scatternet Formation Protocol for Ad hoc Networks of Bluetooth Devices
 A Scatternet Formation Protocol for Ad hoc Networks of Bluetooth Devices Stefano Basagni Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University E-mail: basagni@ece.neu.edu Chiara Petrioli
A Scatternet Formation Protocol for Ad hoc Networks of Bluetooth Devices Stefano Basagni Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University E-mail: basagni@ece.neu.edu Chiara Petrioli
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology
 Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Bikash Sadhukhan. M.Tech(CSE) Lecturer. Dept of CSE/IT Techno India College of Technology Mobile Communication Entails transmission of data to and from handheld devices Two or more communicating devices
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
CS610- Computer Network Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers
 Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers May 08,2012 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 CS610- Computer Network Midterm Examination - Fall 2011 1. Where are destination and source
Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers May 08,2012 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 CS610- Computer Network Midterm Examination - Fall 2011 1. Where are destination and source
Bluetooth. 3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network. What is BLUETOOTH: Bluetooth 2/17/2016
 3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network Bluetooth Bluetooth Bluetooth is a high-speed, low-power microwave wireless link technology, designed to connect phones, laptops, PDAs and other portable equipment
3.3 Latest Technology in Wireless Network Bluetooth Bluetooth Bluetooth is a high-speed, low-power microwave wireless link technology, designed to connect phones, laptops, PDAs and other portable equipment
Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks 9.1 Uses of a network Networks are used in many situations. We can see networks in places like offices, airports and factories. In fact we use networks in many situations
Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks 9.1 Uses of a network Networks are used in many situations. We can see networks in places like offices, airports and factories. In fact we use networks in many situations
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Lecture 16: QoS and "
 Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Optimizing Packet Size via Maximizing Throughput Efficiency of ARQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication Link
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED INFOATICS and COUNICATIONS, alta, September -7, 25 (pp24-28 Optimizing Pacet Size via aximizing Throughput Efficiency of AQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED INFOATICS and COUNICATIONS, alta, September -7, 25 (pp24-28 Optimizing Pacet Size via aximizing Throughput Efficiency of AQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication
101seminartopics.com. Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks
 Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Initial PHY Layer System Proposal for Sub 11 GHz BWA
 Initial PHY Layer System Proposal for Sub 11 GHz BWA Document Number: 802.16.3p-00/40 Date Submitted: 2000-11-08 Source: Anader Benyamin-Seeyar Voice: (514) 822-2014 Harris Corporation Inc. Fax: (514)
Initial PHY Layer System Proposal for Sub 11 GHz BWA Document Number: 802.16.3p-00/40 Date Submitted: 2000-11-08 Source: Anader Benyamin-Seeyar Voice: (514) 822-2014 Harris Corporation Inc. Fax: (514)
Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via Maximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of ARQ Protocol
 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via aximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol Xiang Li 1,2,*, an-tian Li 1, Zhen-Guo Gao 2, and Li-Ning Sun 1 1 obot esearch Institute, Harbin Institute
Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via aximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol Xiang Li 1,2,*, an-tian Li 1, Zhen-Guo Gao 2, and Li-Ning Sun 1 1 obot esearch Institute, Harbin Institute
Chapter 5. Wireless PANs
 Chapter 5 Wireless PANs 5.1 Introduction Introduction of Wireless PANs (WPANs) has caused the latest revolution in the area of wireless technologies. WPANs are short to very short-range (from a couple
Chapter 5 Wireless PANs 5.1 Introduction Introduction of Wireless PANs (WPANs) has caused the latest revolution in the area of wireless technologies. WPANs are short to very short-range (from a couple
Bluetooth Vs : state-of-the-art and research challenges
 Bluetooth Vs. 802.11: state-of-the-art and research challenges Pravin Bhagwat ReefEdge, Inc. pravin@reefedge.com or pravin@acm.org http://www.cs.umd.edu/~pravin WINLAB, Rutgers Oct 28, 2001 10/29/2001
Bluetooth Vs. 802.11: state-of-the-art and research challenges Pravin Bhagwat ReefEdge, Inc. pravin@reefedge.com or pravin@acm.org http://www.cs.umd.edu/~pravin WINLAB, Rutgers Oct 28, 2001 10/29/2001
