(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
|
|
|
- Morgan Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
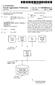
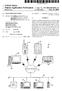
1 US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1 Mahadevan et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATED WEB PAGE CLASSIFICATION (52) U.S. Cl /737, 707/E (75) Inventors: Indra Devi Mahadevan, Madurai (IN); Selvakuberan Karuppasamy, Chennai (IN) (57) ABSTRACT Described herein are methods and systems implementing a (73) Assignee: Tata Consultancy Services web page classification system for automatically generating Limited, Mumbai (IN) at least one context feature for a web page and classifying the web page based on the at least one context feature. In one (21) Appl. No.: 12/974,355 implementation, a context feature generating module of the web page classification system is configured to automatically (22) Filed: Dec. 21, 2010 generate at least one context feature based on at least two of O O uniform resource locator (URL) features, title features, and Publication Classification meta tags features of a web page and a classifying module is (51) Int. Cl. configured to classify the web page based on the at least one G06F 7/30 ( ) context feature. 3OO Y RECEIVING AT LEAST TWO OF A URL, A TITLE, OR ONE OR MORE META TAGS ASSOCATED WITH A WEB PAGE 304 GENERATING TOKENS BASED ON THE RECEIVEDAT LEAST TWO OF THE URL, THE TITLE, AND ONE OR MORE META TAGS 306 GENERATING AT LEAST ONE CONTEXT FEATURE ON BASIS OF THE GENERATED TOKENS 308 CLASSIFYING THE WEBPAGE BASED ON THE AT LEAST ONE CONTEXT FEATURE
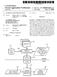
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 3 US 2012/ A CONTEXT FEATURE GENERATING MODULE 108 NETWORK 104 Fig. 1
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 3 US 2012/ A1 WEB PAGE CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM 102 PROCESSOR(S) I/O INTERFACES MODULES 208 CONTEXT FEATURE CLASSIFYING MODULE GENERATING MODULE OTHER MoDULE(S) 214 METADATA DATA 210 WEB PAGES DATA OTHER DATA 220
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 3 US 2012/ A1 3OO Y RECEIVING AT LEAST TWO OF A URL, A TITLE, OR ONE OR MORE META TAGS ASSOCATED WITH A WEB PAGE GENERATING TOKENS BASED ON THE RECEIVEDAT LEAST TWO OF THE URL, THE TITLE, AND ONE OR MORE META TAGS GENERATING AT LEAST ONE CONTEXT FEATURE ON BASIS OF THE GENERATED TOKENS CLASSIFYING THE WEB PAGE BASED ON THE AT LEAST ONE CONTEXT FEATURE Fig. 3
5 AUTOMATED WEB PAGE CLASSIFICATION TECHNICAL FIELD The present subject matter relates, in general, to web page classification and in particular, to automatically gener ating context features for web page classification. BACKGROUND 0002 The internet has become indispensable in many aspects of our lives. The importance of the Internet lies in providing users access to an enormous amount of data related to almost any conceivable Subject. The amount of data avail able on the Internet is enormous and the enormity of data has its own disadvantages. A major disadvantage being difficulty in finding relevant information from the enormous amount of the data. Generally, tools like search engines assist users in locating information on the Internet. However, the search engines generally provide the users with a large number of web pages in response to keywords provided by the user. 0003) To find web pages that may be relevant to a given keyword, various techniques have been developed. One Such technique is web page classification. Web page classification attempts to classify web pages available on World Wide Web (the web) under appropriate categories. Conventionally, web page classification may be performed manually or automati cally, Such as performed by search engines. Once Such clas sification is done, the web pages may be identifiable through Such classification. On the other hand, manual web page classification may be difficult and time consuming technique in cases where volume of data available on the web is enor OUS Further, the web pages are heterogeneous in nature thus making the classification complex. For example, the web pages may be unstructured documents like text document, semi structured documents like HyperTextMarkup Language (HTML) files, or fully structured documents like Extensible Markup Language (XML) file. The web pages may also con tain files of various formats, such as image files, audio files, and video files. Thus the distinct varieties of the web pages may pose a challenge in web page classification. SUMMARY The subject matter described herein relates to a sys tem and method for automatically classifying web pages, which are further described below in the detailed description. This summary is not intended to identify essential features of the claimed subject matter nor is it intended for use in deter mining or limiting the scope of the claimed subject matter In accordance with one embodiment of the subject matter, a web page classification system for automatically generating context features for web pages and classifying the web pages based on the automatically generated context fea tures is implemented. The web page classification system includes a context feature generating module configured to generate at least one context feature for the web page, wherein the at least one context feature includes at least two of uni form resource locator (URL) features, title features, and meta features; and a classifying module for classifying the web page based on the generated at least one context feature. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS The above and other features, aspects, and advan tages of the subject matter will be better understood with regard to the following description, appended claims, and accompanying figures. In the figures, the left-most digit(s) of a reference number identifies the figure in which the reference number first appears. The use of the same reference number in different figures indicates similar or identical items FIG. 1 illustrates a network environment for imple menting a web page classification system, in accordance with an embodiment of the present Subject matter FIG. 2 illustrates the web page classification system, in accordance with an embodiment of the present Subject matter FIG. 3 illustrates a method for classifying web pages, according to an embodiment of the present Subject matter. DETAILED DESCRIPTION The present subject matter relates to systems and methods for web page classification Web page classification is a technique used to clas sify documents, such as the web pages available on World WideWeb (the web) under appropriate categories. Web page classification is used by searching tools, such as search engines to search and provide data relevant to a keyword search made by a user looking for some particular informa tion on Internet Most of the web pages today are created using markup languages including but not limited to HyperText Markup Language (HTML) and extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML). For improving web page rep resentation, HTML structure of a web page is exploited. This helps in identifying more representative terms of the web page. A web page can be represented using several elements of the web page including the body part of a web page (BODY), the title of a web page (TITLE), section headings (H1-H6), emphasized content (EM), uniform resource loca tor (URL), and/or meta description of a web page (meta tags). URLs are hyperlinks that may contain descriptors for the linked web pages. If keywords can be extracted from a URL, these keywords are relatively important. Meta tags describe meta description of a web page and are generally invisible to users, but it may provide description, keywords, and date for a web page. A term enclosed within the tags: <title> and </title> in a source code of a web page represents the title of the web page and is generally more representative of the topic of the web page than a term enclosed within the tags: <body) and </body that represents the content of the web page In the web page classification technique, the search engines generally classify a web page based on metadata associated with the web page. Metadata may be defined as structured data that Supports functions associated with a des ignated object, for example, tables and structures used in a web page. Metadata may include terms; meta tags etc. occur ring in the web pages. Generally, the metadata for the web pages is stored in the form of HTML meta tags that may be used by search engines for classifying the web pages. How ever, the meta tags usually lack consistency and may also be misused by a web page author to increase the chances of Surfacing the web page in web searches. Moreover, web pages typically do not contain meta tags As most of the current web pages do not contain any meta tags provided by the web page authors, thus web page classification using the meta tags is typically not performed by the search engines. Although, human experts can easily identify the metadata in a web page but the number of web
6 pages and the expertise needed to classify all type of web pages make it difficult to generate metadata manually. Thus, web page classification is usually performed using at least the content features Another approach described in conventional sys tems for automated web page classification is using uniform resource locator (URL) of the web pages. Web page classifi cation using only the URL provides a faster method as com pared to typical web page classification using the content features, as the web pages do not have to be fetched and analyzed. However the classification accuracy is not very high since URL alone is used to classify the web pages The present subject matter discloses systems and methods for automatically generating context features for the web pages and using the context features to classify the web pages. A web page classification system, according to the present Subject matter, generates the context features for the web page by evaluating a Substantially small portion of the web page and stores the contextual features as metadata to be used by search engines. The web page classification system, hereinafter referred to as the system, according to the present Subject matter improves web page classification accuracy significantly According to one embodiment of the present subject matter, the context features considered for web page classifi cation includes URL, title or meta tags associated with the web pages. These features can be retrieved quickly as there is no need to process the body of the XHTML/HTML docu ments to retrieve these features. This approach reduces the memory/computational resources requirements. The context features for a web page are generated by evaluating a Sub stantially small portion of the web page that may include the URL, title or meta tags associated with the web page. Accord ingly, the context features generation for the web page requires reduced amount of time The context features generated for a web page are specific for the given web page, therefore, the context features can be used to find a category to which the web page may belong. Further, the context features can be used to find another category to which the web page may associated with In one embodiment of the present subject matter, the web page classification system retrieves the URL of the web page to be classified. The web page classification system generates tokens from the retrieved URL. The tokens are generated by checking delimiters, such as punctuation sym bols in the URL. Any string between the delimiters is consid ered as a token. All the URLs contain words like http, which are not useful for classification and there fore the generating module disregards such common words from the token list. The generated tokens resulted from the retrieved URL are stemmed using any conventional stem ming algorithm, for example, Poter's Stemming algorithm. The Stemming of the tokens generates root words of the tokens which are called as URL features. Similarly, title fea tures are generated by extracting the tokens from the title and applying stemming to find the tokens Further, the web page is checked to determine whether it contains meta tags. If so, the generating module generates meta features by using information stored using the meta tags and applying stemming to the meta tags. The gen erating module combines the URL features, the title features and the meta features. The generating module further checks for redundancy and removes redundant features. Also, the generating module stores the context features as the metadata of the web page. The classifying module retrieves the meta data and classifies the web page on the basis of the metadata. The classifying module performs web page classification using machine learning techniques, for example, Bayesian classification According to one embodiment of the present subject matter, other tags like anchor, table, and frame which also contain descriptive information about the category of the web page may be processed. In said embodiment, web structure mining techniques may be applied to find additional informa tive features of the web page The following disclosure describes systems and methods for web page classification using a web page classi fication system. While aspects of the described systems and methods can be implemented in any number of different computing systems, environments, and/or configurations, embodiments for the web page classification system are described in the context of the following exemplary system(s) and method(s) It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the words during, while, and when as used herein are not exact terms that mean an action takes place instantly upon an initiating action but that there may be some Small but reason able delay, such as a propagation delay, between the initial action and the reaction that is initiated by the initial action. Additionally, the word connected' is used throughout for clarity of the description and can include either a direct con nection or an indirect connection FIG. 1 illustrates network environment 100 imple menting a web page classification system 102 for automati cally generating metadata for web page classification, according to an embodiment of the present Subject matter. The network environment 100 includes data 106, for example, that may be stored on the World Wide Web, in communication with the web page classification system 102 through a network 104. Communication links between the data 106 and the web page classification system 102 are enabled through a desired form of communication, for example, via dial-up modem connections, cable links, digital subscriberlines (DSL), wireless or satellite links, or any other Suitable form of communication The network 104 may be a wireless network, a wired network, or a combination thereof. The network 104 can also be an individual network or a collection of many such indi vidual networks, interconnected with each other and func tioning as a single large network, e.g., the Internet or an intranet. The network 104 can be implemented as one of the different types of networks, such as intranet, local area net work (LAN), wide area network (WAN), the internet, and such. The network 104 may either be a dedicated network or a shared network, which represents an association of the different types of networks that use a variety of protocols, for example, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), Wireless Appli cation Protocol (WAP), etc., to communicate with each other. Further, the network 104 may include network devices, such as network Switches, hubs, routers, HBAS, for providing a link between the web page classification system 102 and the data 106. The network devices within the network 104 may interact with the web page classification system 102 and the data 106 through communication links The web page classification system 102 may be any computing device connected to the network 104. For instance, the web page classification system 102 may be
7 implemented as mainframe computers, workstations, per Sonal computers, desktop computers, hand-held devices, multiprocessor Systems, personal digital assistants (PDAs), laptops, network computers, minicomputers, servers and the like. In addition, the web page classification system 102 may include multiple servers to perform mirrored tasks for users, thereby relieving congestion or minimizing traffic. The data 106 and the web page classification system 102 both include computer readable data storage media, Such as hard disk drives and RAM memory, which store program instructions and data The web page classification system 102 accesses data 106 through the network 104. The data 106 is usually stored on the World WideWeb but may also be stored else where Such as on a server internal to an organization or may be available from in one more data repository from different Sources. The data 106 is accessed and stored as web pages data for generating the context features. The web page clas sification system 102 uses three types of data, namely URL, title, and meta tags for the classification. URL of a web page is unique for the web page and sometimes provides clue about the category of the web page. Title and meta tags in the XHTML/HTML tags also provide information about the cat egory of the web page In one embodiment of the present subject matter, the web page classification system 102 uses XHTML/HTML tags including but not limited to anchor, link, form, and frame to get features that are in the body portion of a XHTML/ HTML document The web page classification system 102 in accor dance with the present Subject matter, employs a context feature generating module 108that may use machine learning methods to generate context features for a given set of web pages. Web content mining may require more resources there fore the web page classification system 102 employs web structure mining techniques. After the generation of the con text features, the web pages are classified based on the context features. The web page classification system 102 uses machine learning techniques to build document classifiers. Rather than actually using the document classifiers to catego rize individual documents, the web page classification system 102 extracts classification rules from the document classifi ers. The classification rules are then transformed into a set of queries that can be sent to a search interface of a text database for example, the data 106. The search interface then may search the text database and provide the number of web pages having context features corresponding to the queries provided by the web page classification system 102. The web page classification system 102 uses the number of matches reported for each query to make classification decisions, without having to retrieve and analyze any of the actual docu ments stored in the data FIG. 2 illustrates the web page classification system 102 in accordance with one embodiment of the present sub ject matter. The web page classification system 102 includes processor(s) 202, I/O interfaces 204, and a memory The processor(s) 202 can be a single processing unit or a combination of multiple processing units. The processor (s) 202 can be implemented as one or more microprocessors, microcomputers, microcontrollers, digital signal processors, central processing units, state machines, logic circuitries, or any devices that manipulate signals based on operational instructions. Among other capabilities, the processor(s) 202 are configured to fetch and execute computer-readable instructions and data stored in the memory The I/O interfaces 204 may include a variety of software and hardware interfaces, for example, interface for peripheral device(s) Such as a keyboard, a mouse, an external memory, a printer, etc. Further, the I/O interfaces 204 may enable the web page classification system 102 to communi cate with other computing devices. Such as web servers and external databases. The I/O interfaces 204 may facilitate mul tiple communications within a wide variety of protocols and networks, such as the network 104, including wired networks, e.g., LAN, cable, etc., and wireless networks, e.g., WLAN, cellular, satellite, etc. The I/O interfaces 204 may include one or more ports for connecting the web page classification system 102 to the data The memory 206 can include any computer-read able medium known in the art including, for example, Volatile memory such as static random access memory (SRAM) and dynamic random access memory (DRAM), and/or non-vola tile memory, such as read only memory (ROM), erasable programmable ROM, flash memories, hard disks, optical disks, and magnetic tapes. The memory 206 includes mod ules 208 and data The modules 208 include the aforementioned con text feature generating module 108 (hereinafter referred to as generating module 108), a classifying module 212, and other module(s) 214. The other module(s) 214, in general, include routines, programs, objects, components, data structures, etc., that perform particular task or implement particular abstract data types and may include programs that Supple ment applications implemented by the web page classifica tion system The generating module 108 automatically generates context features for a web page and stores the context features as metadata 216 of the web page. The classifying module 212 retrieves the metadata 216 and classifies the web page on the basis of the metadata 216. In one embodiment, the classifying module 212 is configured to categorize the web page in more than one category The data 210 includes the metadata 216 and web pages data 218 and other data 220 in addition to the metadata 216. As described above, the metadata 216 may be defined as structured data that Supports functions associated with a des ignated object. The metadata 216 enables the system 102 to retrieve information in a short duration of time. The context features generated by the generating module 108 are saved in the metadata 216. The web pages data 218 includes data, associated with the web pages to be classified, that might be used by the web page classification system 102 for classifying the web pages. The other data 220 may include any of the instructions, inference rules which might be required for the functioning of the web page classification system 102. For example, the other data 220 might include feature extraction and classification algorithms In one embodiment of the present subject matter, the generating module 108 may access a web page stored in the web pages data 218. The generating module 108 then retrieves the URL of the web page and generates tokens from the retrieved URL. In one implementation, the tokens are generated by checking delimiters, such as punctuation sym bols in the URL. Any string between the delimiters is consid ered as a token. Terms like http, WWW,.htm or.html, com monly include in all the URLs, are not useful for classification and therefore may be discarded from the token list by the
8 generating module 108. The generating module 108 further removes words that appear more than once in the token list. The generated tokens are Stemmed using any conventional Stemming algorithm, for example, Poter's stemming algo rithm. The stemming of the tokens generates root words of the tokens called as URL features. For example, consider a URL Here delimiters are :, /, and... The words http, com, careers, pages, default and aspx are tokens. The words http, aspx are common words that occur in many URLS and are not useful for the classification of the web page. Accordingly, the common words are removed from the token list. Further, the words careers and pages may be stemmed to career and page respectively. Therefore the web page classification system 102 may take tcs, career, and page as URL features Similarly title features are generated by extracting the tokens from the title of the web pages. Stemming may be performed upon the terms occurring in the title to find the tokens. Further, the web page is evaluated to check whether it contains meta tags. If so, the generating module 108 gener ates meta features by using information stored using these tags and applying Stemming to the meta tags. The generating module 108 combines the URL features, the title features, and the meta features. The generating module 108 further checks for redundancy and removes redundant features. The gener ating module 108 stores the combined features, called context features, in the metadata The classifying module 212 retrieves the metadata 216 and classifies the web page on the basis of the metadata 216. The classifying module performs web page classifica tion using machine learning techniques, for example, Baye sian classification. Bayesian methods provide the basis for probabilistic learning methods that accommodate and require knowledge about the prior possibilities of alternative hypoth eses and about the probability of observing various data given the hypothesis. Bayesian methods allow assigning a posterior probability to each candidate hypothesis, based on these assumed priors and the observed data. The classifying mod ule 212 may further categorize the web page according to a hierarchical structure FIG. 3 illustrates a method for classifying web pages, in accordance with one embodiment of the present subject matter. The exemplary method may be described in the general context of computer executable instructions. Gen erally, computer executable instructions can include routines, programs, objects, components, data structures, procedures, modules, functions, etc., that perform particular functions or implement particular abstract data types. The method may also be practiced in a distributed computing environment where functions are performed by remote processing devices that are linked through a communications network. In a dis tributed computing environment, computer executable instructions may be located in both local and remote com puter storage media, including memory storage devices The order in which the method is described is not intended to be construed as a limitation, and any number of the described method blocks can be combined in any order to implement the method, or an alternative method. Addition ally, individual blocks may be deleted from the method with out departing from the spirit and scope of the Subject matter described herein. Furthermore, the method can be imple mented in any suitable hardware, software, firmware, or com bination thereof. The method is presently provided for a recovery of mail-items pertaining to a single user. It would be appreciated that the same method can also be implemented for a plurality of users without deviating from the scope of the present Subject matter At block 302, at least two of a URL, a title or meta tags are associated with a web page. In one embodiment, the generating module 108 of the web page classification system 102 may receive at least two of the URL, title or meta tags associated with a web page. For example, the URL, title or meta tags may be received from the web pages data 218. In one example, the URL, the title or the meta tags may be received in any predefined order, for example, the URL may be received prior to the title and the meta tags At block 304, tokens are generated on the basis of at least one of the URL, the title or the meta tags. The generation of tokens includes extraction of the terms useful for the clas sification. For example, when the URL is received by the generating module 108, several operations are performed on the received URL. For example, the generating module 108 identifies delimiters, like punctuation symbols in the URL. In one embodiment, the identification may be performed by any other Suitably configured module which may work in coop eration with the generating module 108. The generating mod ule 108 considers any string between the delimiters as a token and stores it in a token list. A set of predefined words such as, http, Words which consistently appear in the URLs are not are not taken into consideration for classi fication purposes and are removed from the token list. The tokens in the token list are stemmed to generate the roots of the terms. For example, a token manifestation may be Stemmed to a root manifest. In one embodiment, the stem ming may be performed using Poter's stemming method. In other embodiments, various other Stemming techniques may be exploited for the purpose. The roots so generated from the URL features. Similarly, title features and meta features are generated from the title and meta tags respectively At block 306, the URL features, the title features and meta features generated at the block 304 are used for generating the context features. In one embodiment, the URL features, the title features, and the metafeatures are combined for generating at least one context feature. For example, if there are three features generated from the URL, two features are generated from the title of the web page corresponding to the URL, and two features are generated from the meta tags found in the Source code of the web page, a total of seven features are generated. The redundant features, if any are removed from the seven features, and the remaining features are the context features. The context features are used to classify the web page. It may be mentioned that at least one context feature is needed to classify the web page. The at least one context feature may be generated from two or more of the URL features, title features, and meta features At block 308, the web page is classified on the basis of the at least one context feature. In one embodiment, the classification is done using Bayesian classifier. Bayesian methods provide the basis for probabilistic learning methods that accommodate and require knowledge about the prior possibilities of alternative hypotheses and about the probabil ity of observing various data given the hypothesis. Bayesian methods allow assigning a posterior probability to each can didate hypothesis, based on these assumed priors and the observed data. The web page classification system 102 thus
9 classifies the web pages in a time efficient and accurate man ner to create a web page classification data for search engines to operate upon The above description has been given in reference to a web page classification system 102 used for classifying web pages but a person skilled in the art would know that the web page classification system 102 can be conveniently used for classifying documents other than web pages Although embodiments for web page classification system 102 for classifying web pages have been described in language specific to structural features and/or methods, it is to be understood that the invention is not necessarily limited to the specific features or methods described. Rather, the spe cific features and methods are disclosed as exemplary embodiments for the web page classification system 102 and methods. I/We claim: 1. A web page classification system for classifying a web page, the System comprising: a processor; a memory coupled to the processor, wherein the memory comprises: a context feature generating module configured to generate at least one context feature for the web page, wherein the at least one context feature includes at least two of uni form resource locator (URL) features, title features, and meta features; and a classifying module for classifying the web page based on the generated at least one context feature. 2. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the context feature generating module processes web pages data forgen erating metadata and wherein the web pages data comprises at least a URL, a title and meta tags. 3. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the web page is an HyperTextMarkup Language (HTML) or an extensible HyperTextMarkup Language (XHTML) document. 4. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the at least one context feature includes one or more of anchor, table, or frame of the web page. 5. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the at least one context feature is metadata for the web page. 6. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the metadata is independent of a category to which the web page previously belonged. 7. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the classify ing module is configured to categorize the web page accord ing to a hierarchical structure. 8. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the classify ing module is configured to categorize the web page in more than one category. 9. The system as claimed in claim 1, wherein the context feature generating module uses web structure mining tech niques for generating the at least one context feature. 10. A method for classification of a web page, the method comprising: receiving at least two of a URL, a title, and one or more meta tags associated with a web page; generating tokens on the basis of the received at least two of the URL, the title, and the one or more meta tags; generating at least one context feature on the basis of the generated tokens; and classifying the web page based on the at least one context feature. 11. The method as claimed in claim 10, wherein the gen erating tokens comprises extracting of the tokens from at least one of the URL, the title, and the one or more meta tags associated with the web page and Stemming of the tokens. 12. The method as claimed in claim 10, wherein the gen erating at least one context feature comprises combining the tokens of at least one of the URL, the title, and the one or more meta tags associated with the web page. 13. The method as claimed in claim 10, wherein the clas Sifying the web page includes categorizing the web page in a hierarchical structure. 14. The method as claimed in claim 10, wherein the clas Sifying the web page includes categorizing the web page in more than one category. 15. The method as claimed in claim 10, wherein the gen erating at least one context feature includes generating the at least one context feature by web structure mining techniques. c c c c c
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013
 (19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090089340A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/008934.0 A1 Ohr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (54) BACKUP CATALOG RECOVERY FROM REPLICATED DATA (76)
(19) United States US 20090089340A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/008934.0 A1 Ohr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (54) BACKUP CATALOG RECOVERY FROM REPLICATED DATA (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Kwan (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2005
 US 2005O177868A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0177868A1 Kwan (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROTECTING Related U.S. Application Data AGAINST
US 2005O177868A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0177868A1 Kwan (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROTECTING Related U.S. Application Data AGAINST
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,103,736 B2. Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006
 United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,418,453 B1
 USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201500 11187A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0011187 A1 WetzOld (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2015 (54) LOCATION BASED S (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H04 W4/02 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 201500 11187A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0011187 A1 WetzOld (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2015 (54) LOCATION BASED S (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H04 W4/02 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O103858A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0103858A1 Bracewell et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TEMPLATE ARCHITECTURE AND RENDERING ENGINE FOR WEB BROWSER
(19) United States US 2002O103858A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0103858A1 Bracewell et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TEMPLATE ARCHITECTURE AND RENDERING ENGINE FOR WEB BROWSER
Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application
 From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012O117328A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0117328A1 McKean et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) MANAGING ASTORAGE CACHE UTILIZING Publication Classification
US 2012O117328A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0117328A1 McKean et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) MANAGING ASTORAGE CACHE UTILIZING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015037.0644A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0370644 A1 Graefe et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOVERING PAGES OF A DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 11/1451
US 2015037.0644A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0370644 A1 Graefe et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOVERING PAGES OF A DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 11/1451
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. ? 200
 (19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0005152A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0005152 A1 Singh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2005 (54) SECURITY VULNERABILITY MONITOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005.0005152A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0005152 A1 Singh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2005 (54) SECURITY VULNERABILITY MONITOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK
 SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/ A1* 11/2004 Koda et al , 183
 (12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Minnaert et al. USOO640521.6B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,405,216 B1 Jun. 11, 2002 (54) INTERNET-BASED APPLICATION PROGRAM INTERFACE (API) DOCUMENTATION INTERFACE
(12) United States Patent Minnaert et al. USOO640521.6B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,405,216 B1 Jun. 11, 2002 (54) INTERNET-BASED APPLICATION PROGRAM INTERFACE (API) DOCUMENTATION INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 0347009 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0347009 A1 Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) API REDIRECTION FOR LIMITED (52) U.S. Cl. CAPABILITY
(19) United States US 2013 0347009 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0347009 A1 Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) API REDIRECTION FOR LIMITED (52) U.S. Cl. CAPABILITY
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0347293A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0347293 A1 SHINet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PREVENTION OF FRAGMENTATION
(19) United States US 2015.0347293A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0347293 A1 SHINet al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PREVENTION OF FRAGMENTATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004OO32936A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0032936A1 Horel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004 (54) TRANSACTION PROCESSING (76) Inventors: Gerald Horel,
(19) United States US 2004OO32936A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0032936A1 Horel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004 (54) TRANSACTION PROCESSING (76) Inventors: Gerald Horel,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction
 ( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090234832A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0234832 A1 Gao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 17, 2009 (54) GRAPH-BASED KEYWORD EXPANSION (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/5:
(19) United States US 20090234832A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0234832 A1 Gao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 17, 2009 (54) GRAPH-BASED KEYWORD EXPANSION (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/5:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O127621A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0127621 A1 KUO (43) Pub. Date: May 7, 2015 (54) USE OF SOLID STATESTORAGE DEVICES (52) U.S. Cl. AND THE LIKE
(19) United States US 2015O127621A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0127621 A1 KUO (43) Pub. Date: May 7, 2015 (54) USE OF SOLID STATESTORAGE DEVICES (52) U.S. Cl. AND THE LIKE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
- 10. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. (19) United States. Dang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2010O231595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231595 A1 Dang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) LARGESCALE DATA VISUALIZATION WITH INTERACTIVE CHART
(19) United States US 2010O231595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231595 A1 Dang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) LARGESCALE DATA VISUALIZATION WITH INTERACTIVE CHART
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
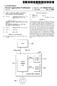 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
