웹기술및응용. XML Basics 2018 년 2 학기. Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering
|
|
|
- Ashley Amelia Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 웹기술및응용 XML Basics 2018 년 2 학기 Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering
2 목차 q Introduction to XML q XML Document Structure and Basic Syntax 2
3 Introduction to XML
4 XML (extensible Markup Language) 개요 (1) q What extensible means in XML Ø Capable of being extended Ø Means that you can define your own markups q Markups (Tags) Ø Information added to content of a text that enhances its meaning o Demarcates or labels parts of a text Ø Types of markups in HTML o Semantic Markup: describes the meaning of content E.g.) <TITLE>, <BODY> o Stylistic Markup: describes how to present the content E.g.) <FONT>, <B> o Structural Markup: describes the structure of content E.g.) <P> 4
5 XML (extensible Markup Language) 개요 (2) q Markup language Ø A set of markups that can be placed in a text for a specific purpose Ø E.g., HTML, WML, VRML, SensorML, MathML, VoiceXML, q XML Ø Extensible markup language = meta-markup language Ø A set of rules to build a markup language and to handle the documents o I.e., family of technologies to describe how to define tags, transform documents, retrieve data, present data, and so on q XML document Ø A document having its content demarcated by XML tags Ø Set of new tag definitions with XML tags 5
6 XML 의역사 1970 GML (IBM) SGML HTML WWW q 1986: SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) à International Standard (ISO) q 1998: XML 1.0 à De Facto Standard (W3C) 1998 XML q 2004: XML 1.1 q 2006: XML 1.1 (2nd Edition) q 2008: XML 1.0 (5th Edition) 6
7 Example of XML Document (1) q All XML documents are made up of markups and contents Ø Semi-structured documents Ø Markups and contents complement each other Ø Markups create an information entity with partitions Ø Markups create an labeled data in a handy package <?xml version= 1,0?> <letter priority= important > <to>john</to> <subject>cs760</subject> <message> Don t forget to attend the class <emphasis>on Friday </emphasis> Good luck to you. </message> <from>tomas</from> </letter> 7
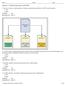
8 Example of XML Document (2) 3 BMW 차에대한 XML 문서 2 XML 저작도구 : BMW 차에대한 XML 문서작성 1 실세계의 BMW 차 BMW 8
9 XML vs. HTML (1) q HTML 은미리정의된 tag 만을사용, XML 은 tag 를확장가능 q HTML tag 들은주로 content 를화면에보여주기위한방법제공, XML tag 들은문서의구조화혹은 content 에대한 labeling 방법제공 q XML 은 tag 명칭의대 / 소문자를구분 화양동 화양동 우편번호라는사실을알기어려움 9
10 XML vs. HTML (2) q XML 문서 Ø XML tag 를이용해서 labeling 함으로써 content 의의미를표현가능 <zip> </zip> 화양동 10
11 XML vs. Other Electronic Documents q HWP 및 MS Word 문서 Ø 비표준화된전용의이진파일형태로저장 Ø 문서구조정보가없고문서내용과스타일이혼합 Ø 외부프로그램에서문서사용및처리의자동화가어려움 q XML 문서 Ø 일반 text 파일형태로저장하여모든컴퓨팅플랫폼에서판독가능 Ø 문서를구조, 내용및스타일로각각분리하여관리 o 문서구조 : DTD나 XML Schema를기반으로정의 (document model) o 문서내용 : document model에맞추어 content 작성 (valid XML document) o 문서스타일 : 문서내용을표현하기위한스타일정의 (XSL, CSS) Ø 외부프로그램에서문서사용및자동화된처리가용이함 11
12 Benefits of XML Documents q 다른전자문서와비교한 XML 문서의장점 Ø 데이터의독립성 o 문서의구조 (DTD, XML Schema) 와내용 (document) 을분리 Ø 다양한표현 o 동일한문서내용을다양하게표현이가능 (CSS, XSL) Ø 데이터교환이용이 o Text 및개방형웹표준기반 Ø 데이터검색기능강화 o Semi-structured 문서로서데이터검색이용이 (XPath, XQuery) Ø 문서구조의변형 (transform) 이용이 o E.g., XML 문서 à HTML 문서 (XSLT) o E.g., XML 문서 à MS Word, HWP, PDF 등 binary 문서 (XSLT-FO) 12
13 XML Technology Family 문서구조 DTD XML Schema SOX 문서스타일 XSLT XSLT-FO XSL, CSS 문서 API SAX DOM JDOM 문서링크 XPath XPointer Xlink XML SOAP WSDL UDDI 서비스 파생언어 WML XHTML MathML 보안 Encryption Signature 저장및검색 XML-DBMS NXD XQuery 13
14 XML Document Structure and Basic Syntax
15 XML 기본용어 (1) q Element Ø Labeled container of content Ø Basic building block of XML documents 시작태그 (Start tag) Element to <to type = name > Hong Gildong </to> 내용 (Content) 속성 (Attribute) 마침태그 (End tag) 15
16 XML 기본용어 (2) q 적절한문서 (Well-formed document) Ø 브라우저나다른프로그램에의해처리될수있도록해주는최소한의규약인 XML 기본문법을준수한문서 1) It contains only properly-encoded legal Unicode characters 2) None of the special syntax characters such as "<" and "&" appear except when performing their markup-delineation roles 3) The begin, end, and empty-element tags which delimit the elements are correctly nested, without missing and overlapping 4) The element tags are case-sensitive; the start and end tags must match exactly 5) There is a single root element which contains all the other elements q 유효한문서 (Valid document) Ø 해당문서의문서모델에맞는문서 o o DTD (Document Type Definition) XML Schema 16
17 적절한 (Well-Formed) 문서의예 q 정확히하나의최상위 (root) 엘리먼트를가져야함 Ø 적절한문서 : <jumin> </jumin> q 태그가올바르게둘러싸여져야함 (correctly nested) Ø 적절한문서 : <jumin><name>kim</name></jumin> Ø 적절하지못한문서 : <jumin><name>kim</jumin></name> q 각엘리먼트가시작태그와마침태그를모두가져야함 Ø 적절하지못한문서 : <name>kim 또는 kim</name> q 시작태그명과마침태그명이같아야함 ( 대 / 소문자구분포함 ) Ø 적절한문서 : <name>kim</name> Ø 적절하지못한문서 : <name>kim</age>, <name>kim</name> 17
18 Well-formed 및 Valid Document 검사 18
19 XML 문서구조 <?xml version= 1.0 encoding= euc-kr?> <!DOCUMENT memo [ <!ELEMENT memo (to, )> ]> XML Declaration Document Type Declaration ( 생략가능 ) Prolog ( 생략가능 ) <memo> <to what= name > 홍길동 </to> <date>2002/04/05</date> <contents> 전화요망 </contents> <from> 허준 </from> </memo> Elements (Contents) 19
20 간단한 XML 문서구조의예 XML 선언 XML 문서내용 (Elements) 20
21 Example of XML Document XML 선언 XML 문서내용 (Elements) 21
22 Tree View of the Example Document Structure Root Element Element Attribute Content 22
23 Structure of XML Documents q XML Document := Prolog? Element q Prolog Ø Tips off the world that the document is marked up in XML q Element Ø Root element (Document element) Ø Other elements 23
24 Prolog q Prolog := XMLDecl DocTypeDecl? q Top of XML document is graced with special information Ø XML Declaration o The document is marked up in XML o Example <?xml version= 1.0?> Ø Document Type Declaration o Defines name of the root element o Defines DTD (Document Type Definition) reference à document model 24
25 XML Declaration q XMLDecl := <?xml versioninfo encodinginfo? standaloneinfo??> Ø version o E.g., version= 1.0 Ø encoding o euc-kr : Korean encoding o UTF-8 : 8-bit Unicode (default) Ø standalone o yes : No external file to load o no : Some files to load (default) When there is an External Entity When DTD is in an external file * Note <??> tag comes from SGML q Examples <?xml version= 1.0?> <?xml version= 1.0 encoding= euc-kr?> 25
26 Document Type Declaration q DocTypeDecl := <!DOCTYPE root-element extid-of-dtd? > ( [ internal-subset ] )? * Note <!!> and [ ] tags come from SGML q Document Type Declaration Ø Defines name of the root element Ø Defines DTD (internal subset) o For document validity checking o Defines ELEMENT and ENTITY declarations q External subset reference Ø extid-of-dtd refers to an external subset for document type declaration 26
27 Document Type Declaration Example (1) Root Element DTD 27
28 Document Type Declaration Example (2) External ID of DTD 28
29 Element: Building Block of XML Documents q Element := <name (att1= value1 att2= value2 )? > content </name> q Empty Element := <name (att1= value1 att2= value2 )? /> q Example <Caution class= info > Start, End tag should be pair! Name is case-sensitive! Whitespace in content is preserved! Following element is empty element. <EmptyElement/> </Caution> 29
30 Element: Building Block of XML (cont d) q Naming rules Ø Starts with a letter or underscore (_) Ø Should not start with xml, Xml, xml, xml,, or XML Ø Contains letters, numbers, hyphen (-), period (.) and underscore (_) q Positioning rules for well-formed documents Ø End tag must come after the start tag Ø Elements should be correctly nested o There should be no overlapping elements o An element s start and end tags must both reside in the same parent 30
31 Element: Building Block of XML (cont d) q Element definition examples Ø <Err>Case-sensitive</err> à </Err>just do it</err> Ø <1st>Don t Start with Number</1st> à <first> </first> Ø <Xml_tag>Don t Start with xml <Xml_tag> Ø < err></err> à <err></err> Ø <e rr></err> à <err></err> Ø <emptyelement/> o Is equal to <emptyelement></emptyelement> o Is not equal to <emptyelement> </emptyelement> because whitespaces are preserved in XML content 31
32 Attribute: More Muscle for Elements q Attribute := name = value value Ø Gives elements unique properties Ø There can be many attributes in an element (unordered) Ø Attributes are separated by whitespaces (not comma) Ø Attribute names should be unique within an element Ø If the attribute value itself contains double (or single) quotes we can use single (or double) quotes around them q Examples Ø <letter priority= high type= 1 /> == <letter type= 1 priority= high /> Ø <choice test= msg= hi > or <choice test= msg= hi > Ø <team person= sue person= joe > à <team person1= sue person2= joe > 32
33 Attribute: More Muscle for Elements (cont d) q Attribute Value Types (in DTD) Ø ID o Validating XML parser warns you if the ID doesn t have a unique value through out the document (attribute no in the example below) Ø IDREF(S) o Validating XML parser warns you if the IDREF points to a nonexistent element (attribute with in the example below) Ø Other types: ENUMERATED, CDATA, ENTITY(S), NMTOKEN(S) q Example <part no= bolt-100 /> <part no= bolt-100 /> <part no= bolt-123 /> <part no= nut-123 > <compatible with= bolt-123 /> <compatible with= bolt-456 /> </part> 33
34 Entity: Placeholder for Content q Entity Ø Contains a part of XML document Ø Something like macro in C (#define): Declare once, use many times Ø Doesn t add anything semantically to the markup Ø Always eliminate an inconvenience o From standing in impossible-to-type characters o To marking the place where a file should be imported (external entity) q Example in the internal-subset <!DOCTYPE letter... [ ]> <!ENTITY w3url > <letter> <message>hi. John. W3 URL is &w3url;</message> </letter> <message> Hi. John. W3 URL is </message> 34
35 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) Used in DTD 35
36 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) q Character Entity Ø Predefined o Ampersand(&): amp o Apostrophe( ): apos o Greater than(>): gt o Less than(<): lt o Quotation( ): quot Ø Numbered (Unicode from #0 to #65536) o E.g., cedilla(ç): #231 o Alphabetic, syllabic, ideographic scripts Latin Greek 20,000 Han ideographs 11,000 Hangul ideographs,... Ø Named (user defined) o E.g., <!ENTITY cedilla ç > <!ENTITY name Kim > 36
37 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) q Mixed-Content Entity Ø Contains content of unlimited length Ø Can include markup as well as text o Internal entity E.g., <!ENTITY phone <number> </number> > o External entity E.g., <!ENTITY signature SYSTEM./signature.xml > 37
38 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) q Example à External entity 38
39 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) External entity imported from./signature.xml 39
40 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) q External Entity Example <!ENTITY part1 SYSTEM./p1.xml > <!ENTITY part2 SYSTEM > <!ENTITY part3 SYSTEM > à Local file à à 40
41 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) q Unparsed Entity Ø Should not be parsed by XML parser o Tells parser not to load the entity s content o Normally used for applications Ø May contain something other than text o E.g.) Binary image files <!ENTITY mypic SYSTEM./erik.gif NDATA GIF> à GIF is name of notation data (NDATA) declared as <!NOTATION GIF SYSTEM image/gif > 41
42 Entity: Placeholder for Content (cont d) q Parameter Entity Ø Only occur in the document type declaration section o Preceded by % (not by & ) Ø Parameter entity references are immediately expanded in the document type declaration o E.g., without parameter entity <!ELEMENT burns (#PCDATA quote)*> <!ELEMENT allen (#PCDATA quote)*> o E.g., with parameter entity <!ENTITY % pcont "#PCDATA quote"> <!ELEMENT burns (%pcont;)*> <!ELEMENT allen (%pcont;)*> 42
43 Miscellaneous Markups q Comment := <!-- any_text_and_markup --> Ø Tells parser to ignore those regions Ø Within comments, -- should not occur Ø E.g., <!-- <address>59 Sunspot Avene</address> --> q Processing Instruction := <? keyword data??> Ø Container for data targeted toward specific applications or parsers Ø E.g., <?linebreak?> <?xml version= 1.0?> 43
44 Miscellaneous Markups (cont d) q CDATA Section := <![CDATA[ any_text_and_markup ]]> Ø Tells parser the section contains no markup o Should be treated as a regular text Ø Within a CDATA section, ]]> should not occur o You can use ]]> instead of ]]> Ø E.g.) Using < and > in CDATA section ]]> with CDATA Section 44
45 References q XML 1.0 (Fifth Edition) Ø W3C Recommendation 26 Nov Ø 45
XML: Introduction. !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... Directive... 9:11
 !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
!important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda
 NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
Chapter 1: Getting Started. You will learn:
 Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Introduction to XML. An Example XML Document. The following is a very simple XML document.
 Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Introduction to XML. XML: basic elements
 Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
SDPL : XML Basics 2. SDPL : XML Basics 1. SDPL : XML Basics 4. SDPL : XML Basics 3. SDPL : XML Basics 5
 2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or remote-live attendance.
 XML Programming Duration: 5 Days Price: $2795 *California residents and government employees call for pricing. Discounts: We offer multiple discount options. Click here for more info. Delivery Options:
XML Programming Duration: 5 Days Price: $2795 *California residents and government employees call for pricing. Discounts: We offer multiple discount options. Click here for more info. Delivery Options:
2009 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XML Syntax
 Data-centric XML XML Syntax 2 What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language Derived from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) Two goals: large-scale electronic publishing exchange of wide variety of data
Data-centric XML XML Syntax 2 What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language Derived from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) Two goals: large-scale electronic publishing exchange of wide variety of data
Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or via remote-live attendance.
 XML Programming Duration: 5 Days US Price: $2795 UK Price: 1,995 *Prices are subject to VAT CA Price: CDN$3,275 *Prices are subject to GST/HST Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or
XML Programming Duration: 5 Days US Price: $2795 UK Price: 1,995 *Prices are subject to VAT CA Price: CDN$3,275 *Prices are subject to GST/HST Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or
Data Presentation and Markup Languages
 Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
M359 Block5 - Lecture12 Eng/ Waleed Omar
 Documents and markup languages The term XML stands for extensible Markup Language. Used to label the different parts of documents. Labeling helps in: Displaying the documents in a formatted way Querying
Documents and markup languages The term XML stands for extensible Markup Language. Used to label the different parts of documents. Labeling helps in: Displaying the documents in a formatted way Querying
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets
 CSS, Cascading Style Sheets HTML was intended to define the content of a document This is a heading This is a paragraph This is a table element Not how they look (aka style)
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets HTML was intended to define the content of a document This is a heading This is a paragraph This is a table element Not how they look (aka style)
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
Markup Languages SGML, HTML, XML, XHTML. CS 431 February 13, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 Markup Languages SGML, HTML, XML, XHTML CS 431 February 13, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University Problem Richness of text Elements: letters, numbers, symbols, case Structure: words, sentences, paragraphs,
Markup Languages SGML, HTML, XML, XHTML CS 431 February 13, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University Problem Richness of text Elements: letters, numbers, symbols, case Structure: words, sentences, paragraphs,
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa
 NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
XML: Managing with the Java Platform
 In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
The concept of DTD. DTD(Document Type Definition) Why we need DTD
 Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
What is XML? XML is designed to transport and store data.
 What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
Overview. Introduction. Introduction XML XML. Lecture 16 Introduction to XML. Boriana Koleva Room: C54
 Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
Structured documents
 Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
Introduction to XML. Chapter 133
 Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML)
 11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
Well-formed XML Documents
 Well-formed XML Documents Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Agenda Types of XML documents Why Well-formed XML Documents
Well-formed XML Documents Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Agenda Types of XML documents Why Well-formed XML Documents
 XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
The XML Metalanguage
 The XML Metalanguage Mika Raento mika.raento@cs.helsinki.fi University of Helsinki Department of Computer Science Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage p.1/442 2003-09-15 Preliminaries Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage
The XML Metalanguage Mika Raento mika.raento@cs.helsinki.fi University of Helsinki Department of Computer Science Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage p.1/442 2003-09-15 Preliminaries Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage
Outline. XML vs. HTML and Well Formed vs. Valid. XML Overview. CSC309 Tutorial --XML 4. Edward Xia
 CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
XML & Related Languages
 Unit 1 1 Introduction: XML XML = extensible Markup Language the universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. www.w3c.org/xml simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879).
Unit 1 1 Introduction: XML XML = extensible Markup Language the universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. www.w3c.org/xml simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879).
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
extensible Markup Language (XML) Basic Concepts
 (XML) Basic Concepts Giuseppe Della Penna Università degli Studi di L Aquila dellapenna@univaq.it http://www.di.univaq.it/gdellape This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
(XML) Basic Concepts Giuseppe Della Penna Università degli Studi di L Aquila dellapenna@univaq.it http://www.di.univaq.it/gdellape This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Fundamentals of Web Programming a
 Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
XML Information Set. Working Draft of May 17, 1999
 XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xml-infoset-19990517 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xml-infoset Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright
XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xml-infoset-19990517 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xml-infoset Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright
2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. Document Types
 Data-centric XML Document Types Purpose 2006 Martin v. Löwis Document Type Definitions define a vocabulary set of allowed element names set of attributes per element name data type given for each attribute
Data-centric XML Document Types Purpose 2006 Martin v. Löwis Document Type Definitions define a vocabulary set of allowed element names set of attributes per element name data type given for each attribute
Fundamentals of Web Programming a
 Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Web Services Part I. XML Web Services. Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009
 Web Services Part I Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 CS 437/637 Database-Backed Web Sites and Web Services 1 XML Web Services XML Web Services = Web Services A Web service is a different kind of Web
Web Services Part I Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 CS 437/637 Database-Backed Web Sites and Web Services 1 XML Web Services XML Web Services = Web Services A Web service is a different kind of Web
XML. extensible Markup Language. Overview. Overview. Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema
 XML extensible Markup Language An introduction in XML and parsing XML Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema 3011 Compiler Construction 2 Overview Overview
XML extensible Markup Language An introduction in XML and parsing XML Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema 3011 Compiler Construction 2 Overview Overview
Introduction to XML. National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore. Shafiq Ur Rahman. Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing
 Introduction to XML Shafiq Ur Rahman Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore XMLXML DTDDTD Related Related Standards Overview What
Introduction to XML Shafiq Ur Rahman Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore XMLXML DTDDTD Related Related Standards Overview What
XML. extensible Markup Language. ... and its usefulness for linguists
 XML extensible Markup Language... and its usefulness for linguists Thomas Mayer thomas.mayer@uni-konstanz.de Fachbereich Sprachwissenschaft, Universität Konstanz Seminar Computerlinguistik II (Miriam Butt)
XML extensible Markup Language... and its usefulness for linguists Thomas Mayer thomas.mayer@uni-konstanz.de Fachbereich Sprachwissenschaft, Universität Konstanz Seminar Computerlinguistik II (Miriam Butt)
XML. Jonathan Geisler. April 18, 2008
 April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
Solutions. a. Yes b. No c. Cannot be determined without the DTD. d. Schema. 9. Explain the term extensible. 10. What is an attribute?
 Chapter 7: Information Representation Method XML Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. XML was developed to overcome the limitations of the markup language. a. EDI b. SGML
Chapter 7: Information Representation Method XML Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. XML was developed to overcome the limitations of the markup language. a. EDI b. SGML
Semistructured data, XML, DTDs
 Semistructured data, XML, DTDs Introduction to Databases Manos Papagelis Thanks to Ryan Johnson, John Mylopoulos, Arnold Rosenbloom and Renee Miller for material in these slides Structured vs. unstructured
Semistructured data, XML, DTDs Introduction to Databases Manos Papagelis Thanks to Ryan Johnson, John Mylopoulos, Arnold Rosenbloom and Renee Miller for material in these slides Structured vs. unstructured
XML. XML Syntax. An example of XML:
 XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. Defined in the XML 1.0 Specification
XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. Defined in the XML 1.0 Specification
Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards
 Disclaimer: All words, pictures are adopted from Learning Web Design (3 rd eds.) by Jennifer Niederst Robbins, published by O Reilly 2007. Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards CSc2320 In this chapter
Disclaimer: All words, pictures are adopted from Learning Web Design (3 rd eds.) by Jennifer Niederst Robbins, published by O Reilly 2007. Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards CSc2320 In this chapter
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 4. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2
 Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013
 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
markup language carry data define your own tags self-descriptive W3C Recommendation
 XML intro What is XML? XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined. You must define
XML intro What is XML? XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined. You must define
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Overview. How the Web is Today. Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington
 Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
XML Structures. Web Programming. Uta Priss ZELL, Ostfalia University. XML Introduction Syntax: well-formed Semantics: validity Issues
 XML Structures Web Programming Uta Priss ZELL, Ostfalia University 2013 Web Programming XML1 Slide 1/32 Outline XML Introduction Syntax: well-formed Semantics: validity Issues Web Programming XML1 Slide
XML Structures Web Programming Uta Priss ZELL, Ostfalia University 2013 Web Programming XML1 Slide 1/32 Outline XML Introduction Syntax: well-formed Semantics: validity Issues Web Programming XML1 Slide
10/24/12. What We Have Learned So Far. XML Outline. Where We are Going Next. XML vs Relational. What is XML? Introduction to Data Management CSE 344
 What We Have Learned So Far Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 12: XML and XPath A LOT about the relational model Hand s on experience using a relational DBMS From basic to pretty advanced
What We Have Learned So Far Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 12: XML and XPath A LOT about the relational model Hand s on experience using a relational DBMS From basic to pretty advanced
Introduction to Data Management CSE 344
 Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 11: XML and XPath 1 XML Outline What is XML? Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XPath 2 What is XML? Stands for extensible Markup Language 1. Advanced, self-describing
Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 11: XML and XPath 1 XML Outline What is XML? Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XPath 2 What is XML? Stands for extensible Markup Language 1. Advanced, self-describing
XML module 2. Creating XML. Hans C. Arents. senior IT market analyst. I.T. Works. Guiding the IT Professional
 XML module 2 Creating XML Hans C. Arents senior IT market analyst I.T. Works Guiding the IT Professional Innovation Center, Technologiepark 3, B-9052 Gent (Belgium), Tel: +32 (0)9 241 56 21 - Fax: +32
XML module 2 Creating XML Hans C. Arents senior IT market analyst I.T. Works Guiding the IT Professional Innovation Center, Technologiepark 3, B-9052 Gent (Belgium), Tel: +32 (0)9 241 56 21 - Fax: +32
Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML
 Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML Abstract John W. Shipman 2013-08-24 12:16 Describes the Document Type Definition notation for describing the schema of an SGML or XML document type.
Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML Abstract John W. Shipman 2013-08-24 12:16 Describes the Document Type Definition notation for describing the schema of an SGML or XML document type.
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is a text-based markup language derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML).
 About the Tutorial XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is a text-based markup language derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). This tutorial will teach you the basics of XML.
About the Tutorial XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is a text-based markup language derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). This tutorial will teach you the basics of XML.
UNIT I. A protocol is a precise set of rules defining how components communicate, the format of addresses, how data is split into packets
 UNIT I Web Essentials: Clients, Servers, and Communication. The Internet- Basic Internet Protocols -The World Wide Web-HTTP request message-response message- Web Clients Web Servers-Case Study. Markup
UNIT I Web Essentials: Clients, Servers, and Communication. The Internet- Basic Internet Protocols -The World Wide Web-HTTP request message-response message- Web Clients Web Servers-Case Study. Markup
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES. XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
Chapter 1: XML Syntax
 1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
Semistructured Data and XML
 Semistructured Data and XML Computer Science E-66 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Structured Data The logical models we've covered thus far all use some type of schema to define the structure
Semistructured Data and XML Computer Science E-66 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Structured Data The logical models we've covered thus far all use some type of schema to define the structure
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language
 Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
Introduction to XML (Extensible Markup Language)
 Introduction to XML (Extensible Markup Language) 1 History and References XML is a meta-language, a simplified form of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) XML was initiated in large parts by Jon
Introduction to XML (Extensible Markup Language) 1 History and References XML is a meta-language, a simplified form of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) XML was initiated in large parts by Jon
[MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document
![[MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document [MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document](/thumbs/76/73543375.jpg) [MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
[MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
Contents. Markup Language and the need of XML. Using environment XML and growth direction. To understand dxml standard.
 Contents Markup Language and the need of XML. Using environment XML and growth direction. To understand dxml standard. d An application of XML documents. Markup Language and the need of XML Markup definition
Contents Markup Language and the need of XML. Using environment XML and growth direction. To understand dxml standard. d An application of XML documents. Markup Language and the need of XML Markup definition
W3C XML XML Overview
 Overview Jaroslav Porubän 2008 References Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com Specifications, World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org David Hunter, et al.: Beginning, 4th Edition, Wrox, 2007, 1080
Overview Jaroslav Porubän 2008 References Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com Specifications, World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org David Hunter, et al.: Beginning, 4th Edition, Wrox, 2007, 1080
TagSoup: A SAX parser in Java for nasty, ugly HTML. John Cowan
 TagSoup: A SAX parser in Java for nasty, ugly HTML John Cowan (cowan@ccil.org) Copyright This presentation is: Copyright 2002 John Cowan Licensed under the GNU General Public License ABSOLUTELY WITHOUT
TagSoup: A SAX parser in Java for nasty, ugly HTML John Cowan (cowan@ccil.org) Copyright This presentation is: Copyright 2002 John Cowan Licensed under the GNU General Public License ABSOLUTELY WITHOUT
Chapter 1. Creating XML Documents
 4033ch01.qxd 9/11/01 9:18 AM Page 3 Chapter 1 Creating XML Documents The extensible Markup Language (XML) is a text- and data-formatting language that, like HTML, has a tagbased syntax. At first glance,
4033ch01.qxd 9/11/01 9:18 AM Page 3 Chapter 1 Creating XML Documents The extensible Markup Language (XML) is a text- and data-formatting language that, like HTML, has a tagbased syntax. At first glance,
Tutorial 2: Validating Documents with DTDs
 1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
Data Exchange. Hyper-Text Markup Language. Contents: HTML Sample. HTML Motivation. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Problems w/html
 Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY- VIRUDHUNAGAR
 UNIT IV Part A 1. WHAT IS THE USE OF XML NAMESPACE? XML allows document authors to create custom elements. This extensibility can result in naming collisions (i.e. different elements that have the same
UNIT IV Part A 1. WHAT IS THE USE OF XML NAMESPACE? XML allows document authors to create custom elements. This extensibility can result in naming collisions (i.e. different elements that have the same
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 14-15: XML CSE 414 - Spring 2013 1 Announcements Homework 4 solution will be posted tomorrow Midterm: Monday in class Open books, no notes beyond one hand-written
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 14-15: XML CSE 414 - Spring 2013 1 Announcements Homework 4 solution will be posted tomorrow Midterm: Monday in class Open books, no notes beyond one hand-written
- XML. - DTDs - XML Schema - XSLT. Web Services. - Well-formedness is a REQUIRED check on XML documents
 Purpose of this day Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Introduce the principal aspects of electronic management
Purpose of this day Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Introduce the principal aspects of electronic management
IT2353 WEB TECHNOLOGY Question Bank UNIT I 1. What is the difference between node and host? 2. What is the purpose of routers? 3. Define protocol. 4.
 IT2353 WEB TECHNOLOGY Question Bank UNIT I 1. What is the difference between node and host? 2. What is the purpose of routers? 3. Define protocol. 4. Why are the protocols layered? 5. Define encapsulation.
IT2353 WEB TECHNOLOGY Question Bank UNIT I 1. What is the difference between node and host? 2. What is the purpose of routers? 3. Define protocol. 4. Why are the protocols layered? 5. Define encapsulation.
Chapter 1: XML Syntax
 1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD
![Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD](/thumbs/72/67474201.jpg) Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 4. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
XML: and related technologies
 XML" XML: and related technologies extensible Markup Language (XML) Is a meta-language that describes the content of the document (self-describing data) XML does not specify the tag set or grammar of the
XML" XML: and related technologies extensible Markup Language (XML) Is a meta-language that describes the content of the document (self-describing data) XML does not specify the tag set or grammar of the
Additional Readings on XPath/XQuery Main source on XML, but hard to read:
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 444 Lecture 10 XML XML (4.6, 4.7) Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XML Outline April 21, 2008 1 2 Further Readings on XML Additional Readings on XPath/XQuery Main source
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 444 Lecture 10 XML XML (4.6, 4.7) Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XML Outline April 21, 2008 1 2 Further Readings on XML Additional Readings on XPath/XQuery Main source
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar..
 .. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar.. XML in a Nutshell XML, extended Markup Language is a collection of rules for universal markup of data. Brief History
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar.. XML in a Nutshell XML, extended Markup Language is a collection of rules for universal markup of data. Brief History
Appendix H XML Quick Reference
 HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors
 Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors Topologi Technical Note. August 13, 2002 Rick Jelliffe SGML and XML Editing Concrete Syntax (ECS) This draft paper formalizes the lexical
Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors Topologi Technical Note. August 13, 2002 Rick Jelliffe SGML and XML Editing Concrete Syntax (ECS) This draft paper formalizes the lexical
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 000-141 Title : XML and related technologies Vendors : IBM Version : DEMO
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 000-141 Title : XML and related technologies Vendors : IBM Version : DEMO
Copyright 2007 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe. Slide 27-1
 Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Semantic Web. XML and XML Schema. Morteza Amini. Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95
 ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Contents
 Contents Overview... 106 What is XML?... 106 How the Web is Today... 108 New Universal Data Exchange Format: XML... 108 What is the W3C?... 108 Semistructured Data... 110 What is Self-describing Data?...
Contents Overview... 106 What is XML?... 106 How the Web is Today... 108 New Universal Data Exchange Format: XML... 108 What is the W3C?... 108 Semistructured Data... 110 What is Self-describing Data?...
XML Extensible Markup Language
 XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured representation of data. DD1335 (Lecture 9) Basic Internet Programming Spring 2010 1 / 34 XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured
XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured representation of data. DD1335 (Lecture 9) Basic Internet Programming Spring 2010 1 / 34 XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured
A tutorial report for SENG Agent Based Software Engineering. Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far. XML Tutorial.
 A tutorial report for SENG 609.22 Agent Based Software Engineering Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far XML Tutorial Yanan Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Calgary
A tutorial report for SENG 609.22 Agent Based Software Engineering Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far XML Tutorial Yanan Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Calgary
XML (Extensible Markup Language
 XML (Extensible Markup Language XML is a markup language. XML stands for extensible Markup Language. The XML standard was created by W3C to provide an easy to use and standardized way to store self describing
XML (Extensible Markup Language XML is a markup language. XML stands for extensible Markup Language. The XML standard was created by W3C to provide an easy to use and standardized way to store self describing
Informatique de Gestion 3 èmes Bachelier Groupes 230x
 Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique de Gestion 3 èmes Bachelier Groupes 230x Année Académique 2014 2015 21/10/14 07:53 Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique
Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique de Gestion 3 èmes Bachelier Groupes 230x Année Académique 2014 2015 21/10/14 07:53 Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique
XML and DTD. Mario Alviano A.Y. 2017/2018. University of Calabria, Italy 1 / 28
 1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 13: XML and XPath 1 Announcements Current assignments: Web quiz 4 due tonight, 11 pm Homework 4 due Wednesday night, 11 pm Midterm: next Monday, May 4,
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 13: XML and XPath 1 Announcements Current assignments: Web quiz 4 due tonight, 11 pm Homework 4 due Wednesday night, 11 pm Midterm: next Monday, May 4,
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 444
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 444 Lecture 25: XML 1 XML Outline XML Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XPath Coverage of XML is much better in new edition Readings Sections 11.1 11.3 and 12.1 [Subset
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 444 Lecture 25: XML 1 XML Outline XML Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XPath Coverage of XML is much better in new edition Readings Sections 11.1 11.3 and 12.1 [Subset
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps
 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps Erik Wilde 16.7.2001 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps 1 Outline what is XML? a syntax (not a data model!) what is the data model behind XML? XML Information Set
XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps Erik Wilde 16.7.2001 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps 1 Outline what is XML? a syntax (not a data model!) what is the data model behind XML? XML Information Set
