Intro to XML. An Introduction to extensible Markup Language
|
|
|
- Chastity McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intro to XML An Introduction to extensible Markup Language Welcome to: Introduction to XML XMaLpha Technologies, LLC., Copyright 2007, WolfWare, Inc. All rights reserved. INTRODUCTION TO XML (HANDS-ON) Technical This full-day session provides a comprehensive introduction to the major topic areas in XML technology, and provides an introduction to Advanced XML. Learn what all the fuss is about and how to jump immediately onto the fast-track for XML development. Instructor: Joyce Deeb, Senior Consultant, XMaLpha Technologies, LLC Joyce Deeb is a senior consultant with XMaLpha Technologies ( has considerable experience in software engineering, high-level application design and development, advanced computing techniques, strategic technology planning, curriculum development, and teaching. Her level of technical depth in application programming, Java & XML development, web-based applications, data warehousing, knowledgebased systems, and parallel processing is impressive. Page 1
2 Instructor Info Class Plan Administrivia Class will be a mix of lecture, group exercises and hands-on exercises. XMaLphaTechnologies Consulting & Education Got Meta-Data? XMaLpha Technologies is a premier provider of full-scale, industrial-strength, XML solutions. As experts in analysis, design, and implementation, the talented consultants at XMaLpha understand data integration using XML. Learn how XML can provide a totally extensible, easy-to-learn, and richly featured universal format for structuring data and documents that can be exchanged efficiently over the Web using.net, Java, and other interoperable technologies. Whether your needs call for business-to-business solutions, sophisticated Web Services, Content Management Systems, end-to-end integration with legacy data, structured dynamic content generation, or education and knowledge transfer on the latest XML, Java or.net technologies, XMaLpha can help. Page 2
3 What is XML? extensible Markup Language Uses tags, similar to HTML Used to describe data No pre-defined tags Provide tag definitions via one of: DTD Document Type Definition XSD XML Schema Defintion Not a language like we think of programming languages. It is a markup language, and hence uses tags, but there aren t any predefined tags. It is used to describe, or communicate, data between different endpoints. However, each application of this technology must define tags specific to that application. This is done by defining either a DTD or a schema to accompany the applications XML documents. This DTD or schema describes rules for the XML document. We ll see more on this later. Page 3
4 XML vs HTML vs XHTML All are markup languages HTML is used to display data XML is used to describe data, often to communicate data between various applications XHTML is a stricter version of HTML that conforms to the rules of XML Inevitably, XML always gets compared to other markup languages, especially HTML. There s not much to compare. They are both markup languages in that they use tags embedded in a document. However, HTML is used to display data. The tags tell browsers how to format and display the contained data. XML is used to describe data, typically for communication purposes where you have data being used by multiple applications or even parts of applications. The tags identify what is contained in a given tag. We ll see an example next. HTML does not always need to be well-formed. XHTML is a stricter version of HTML that conforms to the rules of XML. You could say that it is both HTML and XML. More importantly, it is an example of using XML for a specific application. Page 4
5 Brief XML Example <slide> <title> What is XML? </title> <body> <bullet> extensible Markup Language </bullet> <bullet> Uses tags, similar to HTML </bullet> <bullet> Used to describe data </bullet> </body> </slide> This is not a complete XML document, but it gives a general idea of what one might look like. This is one possible XML representation of the previous slide. Your first reaction might be that this is just another version of HTML, mostly because slides are a display of data. While that is true, and probably what you would do with slides, there are other applications that you might want to do with these. For example, what if you want another application that will take the <title> out of each slide and create an outline. There are other things we can do with these, but they most likely require a more elaborate XML document which we ll learn about later. Page 5
6 XML as a Meta-Language XML is used to describe or create other languages Various users agree on XML definition to communicate The resulting DTD or DSD is a language with which they communicate You can think of the M in XML as standing for meta, because XML is a meta-language as well as a markup language. XML is used to define a sort of language to be used by endusers to communicate data. We ll learn about DTDs and DSDs later. Page 6
7 An Overview of XML XML is for structuring data XML looks like HTML XML is text, but is meant to be read by programs XML is verbose by design XML is a family of technologies From See 1. Structuring data Other examples of structured data include spreadsheets and databases. 2. Resembles HTML They look alike, but the similarities end there. Except that you could use XML to define HTML for displaying web pages. In fact, that s what XHTML is. 3. Text Unlike some other structured data which is encoded in proprietary formats, XML is plain text, which can be read by people. However, it is intended to be read by programs that can parse the language and interpret it appropriately. 4. Verbose a typical XML encoding of data is often larger than the data itself. Think of an XML encoded memo, for example. The tradeoff of storage space is worth the advantages of how versatile the data becomes. 5. Family of Technologies XML isn t a language, it is a technology or technique. It is not nearly as useful by itself as it becomes when used with other related technologies such as XSL and XSLT. We ll learn more about these later in class. Page 7
8 An Overview of XML cont. XML is new (not so much anymore) XML is the reason for XHTML XML is modular XML is the basis for RDF and the Semantic Web XML is license-free, platform-independent, and well-supported From Continued: 6. New This all depends on your frame of reference. XML has been around since the mid- 90 s and is based on technologies that have been around since the early 80 s. 7. XHTML a stricter version of HTML which conforms to XML standards. 8. Modular XML definitions can build on each other, and namespaces are used to keep names straight. 9. Basis for RDF RDF is beyond the scope of this course, but briefly, it is a means of describing the resources available on the web, hence the term Semantic Web. 10. Aahhh, the way it should be. Page 8
9 Special first line Root Element Elements are nested Uses tags < > Attribute/Value Pairs Comments XML Syntax The next few slides will discuss each of these individually. Page 9
10 First Line Syntax: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso "?> Not a Tag, not part of a pair Standard line at the top of every XML document Tells the version and encoding scheme Page 10
11 Root Element Each XML file (document) must have a root element The root element typically contains other nested elements This is typically named to correspond to the type of document, such as memo, resume, etc. This is roughly analogous to a class name in object-oriented languages Page 11
12 Elements are Nested Elements other than the root are nested inside the root element Nesting rules are strict Elements must have closing tags Nested elements cannot overlap each other Test Never let lines cross. Page 12
13 Uses Tags XML elements use tags, similar to HTML Tags are enclosed in angle brackets Tags are case-sensitive Again, tags must be in pairs Syntax: <bullet> extensible Markup Language </bullet> Tags are roughly analogous to data members of a class in OOP. Page 13
14 Attribute/Value Pairs Tags can have attributes that describe the tag Each attribute has an associated value Values must be quoted, either single or double Syntax: <bullet icon= diamond > extensible Markup Language </bullet> If you want to continue the OOP analogy, Attribute/Value pairs would be like having contained objects in your class. So the parent class contains objects as compared to primitives. HTML has lots of attribute examples: img tag has src attribute a tag has href attribute table has cellpadding attribute etc Page 14
15 Comments As with programming languages, XML documents should be commented Looks somewhat like a tag, but isn t one Is a singleton (not part of a tag pair) Syntax: <!-- This is a comment --> Page 15
16 Element Content Elements typically have content: Simple Content Text only Element Content Contains other element(s) Complex Content Text and Element Elements can be empty Empty elements can be there as a marker, and often have attributes. Page 16
17 Attribute vs Element You often must choose between using an attribute or a child element There are no clear rules on when to use one or the other Tip If it is data, use an element Tip If it describes the data, use an attribute Data Given a card catalog, things like ISBN, author, title Attribute icon in the bullet example You will see other more elaborate guidelines, but I don t find them very reliable, and can often debate most of them. Page 17
18 Cannot start with: Naming Rules The string xml in any variation of case Most characters that aren t letters or numbers Are unlimited in length Can contain alphanumerics Can contain most other characters, but some of these can cause problems in your software Page 18
19 <catalog> Valid or Not? <item id= 324 >File Cabinet</Item> </item> <color>gray<size>4 drawers</color></size> <item id=698>swivel Chair</item> <color>black</color><size>36 inch<size> </catalogue> Find the errors together in class: (5 minutes max) Errors: /Item or item /color and /size are out of order (lines cross) Second id is not quoted Second size is missing the / catalogue This is not a particularly realistic example, but serves the purpose of this exercise. Although the indentation is not illegal, good form would put color and size on separate lines. For a catalog, id would typically be a child element since it would likely be part of the printed catalog (data). However, audience might be an attribute if they are printing separate catalogs for the public, suppliers, internal use, etc. Page 19
20 Class Exercise Give examples of possible XML Hint think of a document you have Pick one to work with: What are the elements? How are they nested? Can you think of any attributes? For hands on class Go through options together. Pick one, then give students 10 minutes to do bullet 2. Go through example together in class to let them see how they did. Total time: min. For lecture, can do the same, or go through the entire exercise together. In that case, total time is min. Also, homework: Provide a document, and have students turn it into an XML document. Page 20
21 So What? You ve seen how to tag a given XML document What enforces how to do this for the next slide document? Yes, each slide would be in a separate file XML documents need to be validated DTD XSD All of those syntax rules have to be enforced to get well-formed and validated XML. Page 21
22 Well-formed XML Must be validated against either DTD Document Type Definition XSD XML Schema Definition We will look at both methods To have well-formed XML document, it must be validated against either a DTD or a schema that describes the rules for that particular type of document. This is analogous to having an instance of an object correspond to a class definition. DTD is older Schema is becoming more popular Schema allows more enforcement than DTD Page 22
23 DTD Used to define valid XML document One per document type Older than XSD Less restrictive than XSD Can be defined: Inside of XML document (Internal Declaration) In a separate file (External Declaration) Older, and hence more popular, but becoming less-so, as schemata become more popular. Does not allow as detailed of specification as Schema. Internal declaration is legal, but not particularly useful, since it would only apply to that given document. Again, this is analogous to specifying the class definition that determines what instances are legal. Page 23
24 DOCTYPE Definition Both internal and external DTDs require a DOCTYPE definition Internal the DOCTYPE definition contains the DTD External the DOCTYPE definition contains a link to the file that contains the DTD Page 24
25 Contains the DTD Case-sensitive Syntax: Internal DOCTYPE <!DOCTYPE root_element [element_definitions]> Page 25
26 Internal DTD Example <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE memo [ <!ELEMENT memo (date, to, from, subject, body)> <!ELEMENT date (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT to (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT subject (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)> ]> <memo> </memo> Notice where the DOCTYPE ends the ]> Notice that the DOCTYPE is embedded inside the XML document (internal DTD) The XML memo follows the DOCTYPE statement The first!element is the same as the DOCTYPE (the root element) In this case, it says that the memo element contains 5 children elements: date, to, from, subject, body The rest of the!element definitions say that each contains text We ll see more about PCDATA later. Page 26
27 External DOCTYPE Contains a link to the file containing the DTD Case-sensitive Filename is in quotes Syntax: <!DOCTYPE root_element SYSTEM DTD_file"> Page 27
28 External DTD Example <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE memo SYSTEM memo.dtd > <memo> <date>september 4, 2007</date> <to>csci 4131 Students</to> <from>csci 4131 Instructors</from> <subject>tips for Success</subject> <body>pay attention and study hard</body> </memo> Page 28
29 memo.dtd <!ELEMENT memo (date, to, from, subject, body)> <!ELEMENT date (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT to (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT subject (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)> We ll still see more about PCDATA later. Page 29
30 Slide XML <slide> <title> What is XML? </title> <body> <bullet> extensible Markup Language </bullet> <bullet> Uses tags, similar to HTML </bullet> <bullet> Used to describe data </bullet> </body> </slide> Recall slide from beginning of class Page 30
31 Slide DTD <!ELEMENT slide (title, body)> <!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT body (bullet)> <!ELEMENT bullet (#PCDATA)> Is this sufficient? NO It shows that body contains a child element, but only one. How do we specify more than one? Page 31
32 Elements Attributes #PCDATA #CDATA Entities DTD Components We ll look at each of these in the following slides. Page 32
33 Syntax:!ELEMENT <!ELEMENT element_name (element_content)>!element is required The element name is obvious Element content specifies what is allowed inside this specific element There is specific syntax for the element content These rules are on the next slide. Page 33
34 DTD Occurrence Syntax Give credit: Slide is from XMaLpha, Inc. Should give some examples and see if students can read them. Then ask students to create some examples. Page 34
35 Corrected Slide DTD <!ELEMENT slide (title, body)> <!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT body (bullet+)> <!ELEMENT bullet (#PCDATA)> Assuming you are going to require at least one bullet. Page 35
36 Empty Elements Elements can be empty Use the keyword EMPTY DTD Syntax: <!ELEMENT element_name EMPTY> XML Syntax: <marker /> An HTML example is br. Page 36
37 Unspecified Element Content Can specify that elements can have any type of content Use the keyword ANY DTD Syntax: <!ELEMENT element_name ANY> Page 37
38 Specifying Attributes Syntax: <!ATTLIST element_name attribute_name attribute_type default_value> Recall this XML Example: <bullet icon= diamond > extensible Markup Language </bullet> DTD Example: <!ATTLIST bullet icon CDATA dot"> This says that the bullet element can have an icon attribute which is CDATA, and if it s not specified, the value is dot. But we need to look at more than this. Page 38
39 Enumerated List CDATA ID IDREF IDREFS NMTOKEN ENTITY ENTITIES NOTATION xml: Attribute Type We re only concerned with the first 2 in this class. The rest are shown for completeness. Page 39
40 a given value #REQUIRED #IMPLIED #FIXED value Default Value We re only concerned with the first 2 in this class. The rest are shown for completeness. Page 40
41 Bullet Example Possible bullet DTD: <!ATTLIST bullet icon (diamond dot) dot > Another possible bullet DTD: <!ATTLIST bullet icon (diamond dot) #REQUIRED> The first one says that the bullet element can have an icon attribute with a value of either diamond or dot and if not specified, the value is dot. The second one says that the bullet element must have an icon attribute with a value of either diamond or dot. Should give some examples and see if students can read them. Then ask students to create some examples. Page 41
42 PCDATA vs. CDATA #PCDATA is used to describe element content that the author has determined is okay for the parser to parse. (Parsed Character Data) #CDATA is used to describe element content that the author has determined should not be parsed. (Character Data) Talk about parsers and why you would/wouldn t want element content parsed. This leads into the entities topic on the next slide. Page 42
43 Entities Special characters that need special handling < < > > & " &apos & These characters have special meaning in XML, so if you want to use them in PCDATA, you need to handle them specially. Page 43
44 DSD Expected to replace DTD More powerful than DTD Written in XML (DTD is a separate language) Allows complex data types can specify more restrictions on XML better correlates to databases Discuss why data types are important Page 44
45 memo.xsd <?xml version="1.0"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs=" <xs:element name= memo"> <xs:complextype> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name= date" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name= to" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="from" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name= subject" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="body" type="xs:string"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complextype> </xs:element> </xs:schema> This is a simple version, as it does not use namespaces. The first line says this is an XML document. The second line ties this xml file to the w3 xml schema definition. This will ensure that this document follows the rules of XSDs. Memo is a complex type because it contains other elements. It also specifies what namespace this document uses (xs). Notice that the other nodes are prefaced with this namespace. GTC Namespaces are beyond the scope of this course. UMN We ll talk about namespaces later. Page 45
46 More on XSD Further Topics XSL Xtensible Stylesheet Language XSLT - Transformation XSL-FO - Formatting XPath Navigation XML Tools We ve only briefly looked at XSD. There is a lot more to learn there. The next step would be XSL, which is a family of technologies Page 46
47 XML Technologies Credit: source is w3schools.com. Page 47
48 XSL Transformation XSLT Used to transform an XML document into: Another XML document A different type of document Uses XPath to navigate the XML document Done via an xsl file View and go through a sample xsl file. Page 48
49 XSL-FO XSL Formatting Objects Used to format XML documents Called XSL as well as XSL-FO View and go through a sample xsl file. Page 49
50 XPath Used to navigate through an XML document Treats an XML document as a tree structure XPath uses expressions to select nodes in the XML document tree XPath has many built-in functions to facilitate this navigation Go through some Xpath examples. Page 50
51 XML Tools XMLSpy is the most common Can get a 30 day evaluation copy Show XMLSpy. Page 51
52 XMaLpha XML Curriculum Looking for training for yourself or your team?.net Curriculum XMaLpha Course Offerings Denotes Core Course Denotes Related Course Denotes Related Curriculum Introductory Intermediate Advanced From Legacy Systems to XML 1 day XML and Databases 1 day XML SOAP Syntax XML Conceptual Overview for Managers.5 days XML for Managers Overview of e-cms with XML 1 day XML Application Development Microsoft-focus 3 days or XML Schemata or XML APIs DOM vs. SAX 1 day Overview of Web Services 1 day.net Web Services XML Conceptual Overview for Programmers.5 days XML for Programmers XML Application Development Java-focus 3 days or XForms 1 day XSLT Programming XSLT II Advanced Topics 3 days Java Web Services XML Authoring Tools (XML-Spy) XML Authoring Tools (XMetal) Java Curriculum A place for your notes Page 52
53 XMaLpha Web Development Curriculum XML Curriculum XMaLpha Course Offerings Denotes Core Course Denotes Related Course.NET Curriculum Denotes Related Curriculum Web Publishing (Frontpage) HTML for Web Content Publishers or HTML for Web Programmers Introductory Intermediate Advanced Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) 1 day E-Commerce & E-Business For Managers 1 day Web Information Architecture 1 day Web Design That Works or JavaScript for nonprogrammers JavaScript for Web Programmers Dynamic HTML (DHTML) Advanced JavaScript Web Systems Architecture or PHP Active Server Pages (ASP) 3.0 /.NET 3 days E-Business for Developers mysql Advanced ASP & Databases Java Servlets Dreamweaver 4/MX Advanced Dreamweaver MX 1 day Flash MX Advanced Flash MX Java Web Application Development 3 days Java Server Pages (JSP) 3 days Fundamentals of Web Graphics 1 day Fundamentals of Photoshop 1 day Digital Photography for the Web Java Curriculum A place for your notes Page 53
54 XMaLpha.NET Curriculum XMaLpha Course Offerings Denotes Core Course Denotes Related Course Denotes Related Curriculum Java Curriculum Introductory Intermediate Advanced J2EE vs.,net 1 day Installing & Administering.NET Server 2-3 days BizTalk, Commerce & other.net Srvrs 2-3 days Exchange Server &.NET.NET Interop. w/ Unmanaged Code 2-3 days.net Framework for Technical Managers 1-2 day.net Framework for Programmers Integrating.NET with other MS Technologies 2-3 days ADO.NET Programming Active Server Pages (ASP).NET 4-5 days Working with Meta-data in.net 1- Developing Web Services w/ ASP.NET 1- Object-Oriented Thinking (Java) 1 day or C#.NET Programming 5 days or Advanced C#.NET 5 days Common Language Infrastructure 3 days Windows Applications with Vis. Studio.NET.NET Enterprise Services.NET Mobile Services Toolkit 2-3 days VB.NET Programming Advanced VB.NET XML Application Development with.net 2-3 days Web Development Curriculum XML Curriculum A place for your notes Page 54
55 XMaLpha Java Curriculum XMaLpha Course Offerings Denotes Core Course Denotes Related Course Denotes Related Curriculum.NET Curriculum Introductory Intermediate Advanced J2EE vs.,net 1 day JDBC Java Programming with Oracle Java Programming w/ SUN One 4 days Java Messaging Service (JMS) Client-side GUI Development or Object-Oriented Thinking (Java) 1 day Java J2SE Programming 5 days or Swing JFC Java Beans API / Component-level Programming Java Programming w/ IBM Tools 4 days Enterprise Java Beans 4 days J2EE Design Patterns Understanding Enterprise Java for Managers 1 day Java Overview for Managers 1 day Java 2 Intermediate 3 days Java Network Programming 3 days Java Server-side Programming J2EE Essentials 4-5 days Java Security Java Development for Managers Java Servlets Java Web Application Development 2-3 days Java Server Pages (JSP) 3 days XML Application Development Java-focus 3-days Web Application Development Web Development Curriculum XML Curriculum A place for your notes Page 55
56 Consulting Services XMaLpha Consulting Programmers Java, J2EE,.NET Arbortext ACL / AOL SQL XPath XSL Perl JSP PHP Integration Conversion of of legacy data Implementation Quick Start Education XMaLpha Technology Architecture Project Management Current Business Process Document structures DB Design XML composition stylesheets User Interface Design Detailed system design XML schemata or or DTD Composition specs Requirements Collection An independent perspective A proven track record with extensive XML experience in the legislative environment XMaLpha Technologies: Focus on design and analysis using our experience plus proven techniques Build architectural roadmaps and specifications Develop the core services using the selected tools and environments Design, plan, and deliver integration and implementation Page 56
The concept of DTD. DTD(Document Type Definition) Why we need DTD
 Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
XML: Introduction. !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... Directive... 9:11
 !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
!important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
Web Computing. Revision Notes
 Web Computing Revision Notes Exam Format The format of the exam is standard: Answer TWO OUT OF THREE questions Candidates should answer ONLY TWO questions The time allowed is TWO hours Notes: You will
Web Computing Revision Notes Exam Format The format of the exam is standard: Answer TWO OUT OF THREE questions Candidates should answer ONLY TWO questions The time allowed is TWO hours Notes: You will
markup language carry data define your own tags self-descriptive W3C Recommendation
 XML intro What is XML? XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined. You must define
XML intro What is XML? XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined. You must define
Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or remote-live attendance.
 XML Programming Duration: 5 Days Price: $2795 *California residents and government employees call for pricing. Discounts: We offer multiple discount options. Click here for more info. Delivery Options:
XML Programming Duration: 5 Days Price: $2795 *California residents and government employees call for pricing. Discounts: We offer multiple discount options. Click here for more info. Delivery Options:
Chapter 1: Getting Started. You will learn:
 Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or via remote-live attendance.
 XML Programming Duration: 5 Days US Price: $2795 UK Price: 1,995 *Prices are subject to VAT CA Price: CDN$3,275 *Prices are subject to GST/HST Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or
XML Programming Duration: 5 Days US Price: $2795 UK Price: 1,995 *Prices are subject to VAT CA Price: CDN$3,275 *Prices are subject to GST/HST Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or
Introduction Syntax and Usage XML Databases Java Tutorial XML. November 5, 2008 XML
 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
Structured documents
 Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
Data Presentation and Markup Languages
 Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
XML. Jonathan Geisler. April 18, 2008
 April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013
 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
A tutorial report for SENG Agent Based Software Engineering. Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far. XML Tutorial.
 A tutorial report for SENG 609.22 Agent Based Software Engineering Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far XML Tutorial Yanan Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Calgary
A tutorial report for SENG 609.22 Agent Based Software Engineering Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far XML Tutorial Yanan Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Calgary
 XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda
 NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
Introduction to XML. XML: basic elements
 Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
XML (Extensible Markup Language)
 Basics of XML: What is XML? XML (Extensible Markup Language) XML stands for Extensible Markup Language XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined. You must define your
Basics of XML: What is XML? XML (Extensible Markup Language) XML stands for Extensible Markup Language XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined. You must define your
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets
 CSS, Cascading Style Sheets HTML was intended to define the content of a document This is a heading This is a paragraph This is a table element Not how they look (aka style)
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets HTML was intended to define the content of a document This is a heading This is a paragraph This is a table element Not how they look (aka style)
XML. extensible Markup Language. Overview. Overview. Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema
 XML extensible Markup Language An introduction in XML and parsing XML Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema 3011 Compiler Construction 2 Overview Overview
XML extensible Markup Language An introduction in XML and parsing XML Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema 3011 Compiler Construction 2 Overview Overview
Introduction to XML. Chapter 133
 Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
but XML goes far beyond HTML: it describes data
 The XML Meta-Language 1 Introduction to XML The father of markup languages: XML = EXtensible Markup Language is a simplified version of SGML Originally created to overcome the limitations of HTML the HTML
The XML Meta-Language 1 Introduction to XML The father of markup languages: XML = EXtensible Markup Language is a simplified version of SGML Originally created to overcome the limitations of HTML the HTML
Copyright 2007 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe. Slide 27-1
 Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD
![Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD](/thumbs/72/67474201.jpg) Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Overview. How the Web is Today. Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington
 Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa
 NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
XML: some structural principles
 XML: some structural principles Hayo Thielecke University of Birmingham www.cs.bham.ac.uk/~hxt October 18, 2011 1 / 25 XML in SSC1 versus First year info+web Information and the Web is optional in Year
XML: some structural principles Hayo Thielecke University of Birmingham www.cs.bham.ac.uk/~hxt October 18, 2011 1 / 25 XML in SSC1 versus First year info+web Information and the Web is optional in Year
SDPL : XML Basics 2. SDPL : XML Basics 1. SDPL : XML Basics 4. SDPL : XML Basics 3. SDPL : XML Basics 5
 2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
XML. Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior
 XML Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior XML INTRODUCTION 2 THE XML LANGUAGE XML: Extensible Markup Language Standard for the presentation and transmission of information.
XML Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior XML INTRODUCTION 2 THE XML LANGUAGE XML: Extensible Markup Language Standard for the presentation and transmission of information.
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY- VIRUDHUNAGAR
 UNIT IV Part A 1. WHAT IS THE USE OF XML NAMESPACE? XML allows document authors to create custom elements. This extensibility can result in naming collisions (i.e. different elements that have the same
UNIT IV Part A 1. WHAT IS THE USE OF XML NAMESPACE? XML allows document authors to create custom elements. This extensibility can result in naming collisions (i.e. different elements that have the same
Outline. XML vs. HTML and Well Formed vs. Valid. XML Overview. CSC309 Tutorial --XML 4. Edward Xia
 CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
XML: Managing with the Java Platform
 In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
Tutorial 2: Validating Documents with DTDs
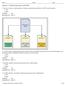 1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 1
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Department of Computer Science & Engineering Academic Year 2011 2012(Odd Semester) QUESTION BANK Subject Code/Name: CS1401-Internet Computing Year/Sem : IV / VII UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Department of Computer Science & Engineering Academic Year 2011 2012(Odd Semester) QUESTION BANK Subject Code/Name: CS1401-Internet Computing Year/Sem : IV / VII UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES. XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
What is XML? XML is designed to transport and store data.
 What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
Overview. Introduction. Introduction XML XML. Lecture 16 Introduction to XML. Boriana Koleva Room: C54
 Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
XML & Related Languages
 Unit 1 1 Introduction: XML XML = extensible Markup Language the universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. www.w3c.org/xml simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879).
Unit 1 1 Introduction: XML XML = extensible Markup Language the universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. www.w3c.org/xml simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879).
Notes. Submit homework on Blackboard The first homework deadline is the end of Sunday, Feb 11 th. Final slides have 'Spring 2018' in chapter title
 Notes Ask course content questions on Slack (is651-spring-2018.slack.com) Contact me by email to add you to Slack Make sure you checked Additional Links at homework page before you ask In-class discussion
Notes Ask course content questions on Slack (is651-spring-2018.slack.com) Contact me by email to add you to Slack Make sure you checked Additional Links at homework page before you ask In-class discussion
The XML Metalanguage
 The XML Metalanguage Mika Raento mika.raento@cs.helsinki.fi University of Helsinki Department of Computer Science Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage p.1/442 2003-09-15 Preliminaries Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage
The XML Metalanguage Mika Raento mika.raento@cs.helsinki.fi University of Helsinki Department of Computer Science Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage p.1/442 2003-09-15 Preliminaries Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage
CS6501 IP Unit IV Page 1
 CS6501 Internet Programming Unit IV Part - A 1. What is PHP? PHP - Hypertext Preprocessor -one of the most popular server-side scripting languages for creating dynamic Web pages. - an open-source technology
CS6501 Internet Programming Unit IV Part - A 1. What is PHP? PHP - Hypertext Preprocessor -one of the most popular server-side scripting languages for creating dynamic Web pages. - an open-source technology
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year/Sem: IV / VII CS1401 INTERNET
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year/Sem: IV / VII CS1401 INTERNET
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML)
 11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 4. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Fundamentals of Web Programming a
 Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language
 Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch : Web Technologies : ACS006 : B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch : Web Technologies : ACS006 : B. Tech
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management Tenth Edition. Chapter 14 Database Connectivity and Web Technologies
 Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management Tenth Edition Chapter 14 Database Connectivity and Web Technologies Database Connectivity Mechanisms by which application programs connect and communicate
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management Tenth Edition Chapter 14 Database Connectivity and Web Technologies Database Connectivity Mechanisms by which application programs connect and communicate
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 4. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Part 2: XML and Data Management Chapter 6: Overview of XML
 Part 2: XML and Data Management Chapter 6: Overview of XML Prof. Dr. Stefan Böttcher 6. Overview of the XML standards: XML, DTD, XML Schema 7. Navigation in XML documents: XML axes, DOM, SAX, XPath, Tree
Part 2: XML and Data Management Chapter 6: Overview of XML Prof. Dr. Stefan Böttcher 6. Overview of the XML standards: XML, DTD, XML Schema 7. Navigation in XML documents: XML axes, DOM, SAX, XPath, Tree
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2
 Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Grid Computing. What is XML. Tags, elements, and attributes. Valid and well formed XML. Grid Computing Fall 2006 Paul A.
 Grid Computing XML Fall 2006 Including material from Amy Apon, James McCartney, Arkansas U. What is XML XML stands for extensible markup language It is a hierarchical data description language It is a
Grid Computing XML Fall 2006 Including material from Amy Apon, James McCartney, Arkansas U. What is XML XML stands for extensible markup language It is a hierarchical data description language It is a
Inf 202 Introduction to Data and Databases (Spring 2010)
 Inf 202 Introduction to Data and Databases (Spring 2010) Jagdish S. Gangolly Informatics CCI SUNY Albany April 22, 2010 Database Processing Applications Standard Database Processing Client/Server Environment
Inf 202 Introduction to Data and Databases (Spring 2010) Jagdish S. Gangolly Informatics CCI SUNY Albany April 22, 2010 Database Processing Applications Standard Database Processing Client/Server Environment
UNIT I. A protocol is a precise set of rules defining how components communicate, the format of addresses, how data is split into packets
 UNIT I Web Essentials: Clients, Servers, and Communication. The Internet- Basic Internet Protocols -The World Wide Web-HTTP request message-response message- Web Clients Web Servers-Case Study. Markup
UNIT I Web Essentials: Clients, Servers, and Communication. The Internet- Basic Internet Protocols -The World Wide Web-HTTP request message-response message- Web Clients Web Servers-Case Study. Markup
HTML. Mohammed Alhessi M.Sc. Geomatics Engineering. Internet GIS Technologies كلية اآلداب - قسم الجغرافيا نظم المعلومات الجغرافية
 HTML Mohammed Alhessi M.Sc. Geomatics Engineering Wednesday, February 18, 2015 Eng. Mohammed Alhessi 1 W3Schools Main Reference: http://www.w3schools.com/ 2 What is HTML? HTML is a markup language for
HTML Mohammed Alhessi M.Sc. Geomatics Engineering Wednesday, February 18, 2015 Eng. Mohammed Alhessi 1 W3Schools Main Reference: http://www.w3schools.com/ 2 What is HTML? HTML is a markup language for
x ide xml Integrated Development Environment Specifications Document 1 Project Description 2 Specifi fications
 x ide xml Integrated Development Environment Specifications Document Colin Hartnett (cphartne) 7 February 2003 1 Project Description There exist many integrated development environments that make large
x ide xml Integrated Development Environment Specifications Document Colin Hartnett (cphartne) 7 February 2003 1 Project Description There exist many integrated development environments that make large
Session 23 XML. XML Reading and Reference. Reading. Reference: Session 23 XML. Robert Kelly, 2018
 Session 23 XML Reading XML Reading and Reference https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/xml Reference: XML in a Nutshell (Ch. 1-3), available in Safari On-line 2 1 Lecture Objectives Understand the goal of application
Session 23 XML Reading XML Reading and Reference https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/xml Reference: XML in a Nutshell (Ch. 1-3), available in Safari On-line 2 1 Lecture Objectives Understand the goal of application
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar..
 .. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar.. XML in a Nutshell XML, extended Markup Language is a collection of rules for universal markup of data. Brief History
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar.. XML in a Nutshell XML, extended Markup Language is a collection of rules for universal markup of data. Brief History
IT6503 WEB PROGRAMMING. Unit-I
 Department of Information Technology Question Bank- Odd Semester 2015-2016 IT6503 WEB PROGRAMMING Unit-I SCRIPTING 1. What is HTML? Write the format of HTML program. 2. Differentiate HTML and XHTML. 3.
Department of Information Technology Question Bank- Odd Semester 2015-2016 IT6503 WEB PROGRAMMING Unit-I SCRIPTING 1. What is HTML? Write the format of HTML program. 2. Differentiate HTML and XHTML. 3.
TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 + INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch : Web Technologies : ACS006
+ INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch : Web Technologies : ACS006
XML Processing & Web Services. Husni Husni.trunojoyo.ac.id
 XML Processing & Web Services Husni Husni.trunojoyo.ac.id Based on Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar Fundamentals of Web Development, Pearson Education, 2015 Objectives 1 XML Overview 2 XML Processing 3
XML Processing & Web Services Husni Husni.trunojoyo.ac.id Based on Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar Fundamentals of Web Development, Pearson Education, 2015 Objectives 1 XML Overview 2 XML Processing 3
- XML. - DTDs - XML Schema - XSLT. Web Services. - Well-formedness is a REQUIRED check on XML documents
 Purpose of this day Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Introduce the principal aspects of electronic management
Purpose of this day Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Introduce the principal aspects of electronic management
HTML and XML. XML stands for extensible Markup Language
 HTML and XML XML stands for extensible Markup Language HTML is used to mark up text so it can be displayed to users HTML describes both structure (e.g. , , ) and appearance (e.g. , ,
HTML and XML XML stands for extensible Markup Language HTML is used to mark up text so it can be displayed to users HTML describes both structure (e.g. , , ) and appearance (e.g. , ,
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institue of Technology
 Branch: - 6th Sem IT Year/Sem : - 3rd /2014 Subject & Subject Code : Faculty Name : - Nitin Padariya Pre Upload Date: 31/12/2013 Submission Date: 9/1/2014 [1] Explain the need of web server and web browser
Branch: - 6th Sem IT Year/Sem : - 3rd /2014 Subject & Subject Code : Faculty Name : - Nitin Padariya Pre Upload Date: 31/12/2013 Submission Date: 9/1/2014 [1] Explain the need of web server and web browser
MANAGING INFORMATION (CSCU9T4) LECTURE 2: XML STRUCTURE
 MANAGING INFORMATION (CSCU9T4) LECTURE 2: XML STRUCTURE Gabriela Ochoa http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~goc/ OUTLINE XML Elements vs. Attributes Well-formed vs. Valid XML documents Document Type Definitions (DTDs)
MANAGING INFORMATION (CSCU9T4) LECTURE 2: XML STRUCTURE Gabriela Ochoa http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~goc/ OUTLINE XML Elements vs. Attributes Well-formed vs. Valid XML documents Document Type Definitions (DTDs)
XML Extensible Markup Language
 XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured representation of data. DD1335 (Lecture 9) Basic Internet Programming Spring 2010 1 / 34 XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured
XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured representation of data. DD1335 (Lecture 9) Basic Internet Programming Spring 2010 1 / 34 XML Extensible Markup Language Generic format for structured
Semistructured data, XML, DTDs
 Semistructured data, XML, DTDs Introduction to Databases Manos Papagelis Thanks to Ryan Johnson, John Mylopoulos, Arnold Rosenbloom and Renee Miller for material in these slides Structured vs. unstructured
Semistructured data, XML, DTDs Introduction to Databases Manos Papagelis Thanks to Ryan Johnson, John Mylopoulos, Arnold Rosenbloom and Renee Miller for material in these slides Structured vs. unstructured
Outline. XML DOCTYPE External - SYSTEM. XML DOCTYPE Internal DTD &6&7XWRULDO ;0/ (GZDUG;LD
 &6&7XWRULDO ;0/ (GZDUG;LD Outline XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI A Complete Example -DQXDU\ 1 CSC309 Tutorial --XML 2 XML DOCTYPE Internal
&6&7XWRULDO ;0/ (GZDUG;LD Outline XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI A Complete Example -DQXDU\ 1 CSC309 Tutorial --XML 2 XML DOCTYPE Internal
Introduction to XML (Extensible Markup Language)
 Introduction to XML (Extensible Markup Language) 1 History and References XML is a meta-language, a simplified form of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) XML was initiated in large parts by Jon
Introduction to XML (Extensible Markup Language) 1 History and References XML is a meta-language, a simplified form of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) XML was initiated in large parts by Jon
XML Primer Plus By Nicholas Chase
 Table of Contents Index XML Primer Plus By Nicholas Chase Publisher : Sams Publishing Pub Date : December 16, 2002 ISBN : 0-672-32422-9 Pages : 1024 This book presents XML programming from a conceptual
Table of Contents Index XML Primer Plus By Nicholas Chase Publisher : Sams Publishing Pub Date : December 16, 2002 ISBN : 0-672-32422-9 Pages : 1024 This book presents XML programming from a conceptual
Part II: Semistructured Data
 Inf1-DA 2011 2012 II: 22 / 119 Part II Semistructured Data XML: II.1 Semistructured data, XPath and XML II.2 Structuring XML II.3 Navigating XML using XPath Corpora: II.4 Introduction to corpora II.5 Querying
Inf1-DA 2011 2012 II: 22 / 119 Part II Semistructured Data XML: II.1 Semistructured data, XPath and XML II.2 Structuring XML II.3 Navigating XML using XPath Corpora: II.4 Introduction to corpora II.5 Querying
Appendix H XML Quick Reference
 HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
W3C XML XML Overview
 Overview Jaroslav Porubän 2008 References Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com Specifications, World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org David Hunter, et al.: Beginning, 4th Edition, Wrox, 2007, 1080
Overview Jaroslav Porubän 2008 References Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com Specifications, World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org David Hunter, et al.: Beginning, 4th Edition, Wrox, 2007, 1080
Web Programming Paper Solution (Chapter wise)
 What is valid XML document? Design an XML document for address book If in XML document All tags are properly closed All tags are properly nested They have a single root element XML document forms XML tree
What is valid XML document? Design an XML document for address book If in XML document All tags are properly closed All tags are properly nested They have a single root element XML document forms XML tree
XML extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
Software Engineering Methods, XML extensible Markup Language. Tutorial Outline. An Example File: Note.xml XML 1
 extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
extensible Markup Language Eshcar Hillel Sources: http://www.w3schools.com http://java.sun.com/webservices/jaxp/ learning/tutorial/index.html Tutorial Outline What is? syntax rules Schema Document Object
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
Introduction to XML. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY PLACEMENT CELL
 PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY PLACEMENT CELL S.K.V. Jayakumar, M.E(CSE)., LMISTE., LCSI., (Ph.D)., Kalapet Placement Co-ordinator Puducherry 605014 Ref. No: PU / PCell / Faculty Sabbatical @ Cognizant / August
PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY PLACEMENT CELL S.K.V. Jayakumar, M.E(CSE)., LMISTE., LCSI., (Ph.D)., Kalapet Placement Co-ordinator Puducherry 605014 Ref. No: PU / PCell / Faculty Sabbatical @ Cognizant / August
CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0
 WEB TECHNOLOGIES A COMPUTER SCIENCE PERSPECTIVE CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0 Modified by Ahmed Sallam Based on original slides by Jeffrey C. Jackson reserved. 0-13-185603-0 HTML HELLO WORLD! Document
WEB TECHNOLOGIES A COMPUTER SCIENCE PERSPECTIVE CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0 Modified by Ahmed Sallam Based on original slides by Jeffrey C. Jackson reserved. 0-13-185603-0 HTML HELLO WORLD! Document
Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5. HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION
 Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5 HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION Objectives Explore the history of the Internet, the Web, and HTML Compare the different versions of HTML Study the syntax
Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5 HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION Objectives Explore the history of the Internet, the Web, and HTML Compare the different versions of HTML Study the syntax
PART. Oracle and the XML Standards
 PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
Semantic Web. XML and XML Schema. Morteza Amini. Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95
 ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
AIM. 10 September
 AIM These two courses are aimed at introducing you to the World of Web Programming. These courses does NOT make you Master all the skills of a Web Programmer. You must learn and work MORE in this area
AIM These two courses are aimed at introducing you to the World of Web Programming. These courses does NOT make you Master all the skills of a Web Programmer. You must learn and work MORE in this area
INTERNET PROGRAMMING XML
 INTERNET PROGRAMMING XML Software Engineering Branch / 4 th Class Computer Engineering Department University of Technology OUTLINES XML Basic XML Advanced 2 HTML & CSS & JAVASCRIPT & XML DOCUMENTS HTML
INTERNET PROGRAMMING XML Software Engineering Branch / 4 th Class Computer Engineering Department University of Technology OUTLINES XML Basic XML Advanced 2 HTML & CSS & JAVASCRIPT & XML DOCUMENTS HTML
Programming the World Wide Web by Robert W. Sebesta
 Programming the World Wide Web by Robert W. Sebesta Tired Of Rpg/400, Jcl And The Like? Heres A Ticket Out Programming the World Wide Web by Robert Sebesta provides students with a comprehensive introduction
Programming the World Wide Web by Robert W. Sebesta Tired Of Rpg/400, Jcl And The Like? Heres A Ticket Out Programming the World Wide Web by Robert Sebesta provides students with a comprehensive introduction
Introduction to XML. National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore. Shafiq Ur Rahman. Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing
 Introduction to XML Shafiq Ur Rahman Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore XMLXML DTDDTD Related Related Standards Overview What
Introduction to XML Shafiq Ur Rahman Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore XMLXML DTDDTD Related Related Standards Overview What
CTI Higher Certificate in Information Systems (Internet Development)
 CTI Higher Certificate in Information Systems (Internet Development) Module Descriptions 2015 1 Higher Certificate in Information Systems (Internet Development) (1 year full-time, 2½ years part-time) Computer
CTI Higher Certificate in Information Systems (Internet Development) Module Descriptions 2015 1 Higher Certificate in Information Systems (Internet Development) (1 year full-time, 2½ years part-time) Computer
Introduction to XML 3/14/12. Introduction to XML
 Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
Introduction to XML. An Example XML Document. The following is a very simple XML document.
 Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Data Exchange. Hyper-Text Markup Language. Contents: HTML Sample. HTML Motivation. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Problems w/html
 Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
