CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROTOTYPING STRATEGIES. Tom Horton. * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford)
|
|
|
- Dwain Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT PROTOTYPING STRATEGIES Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford)
2 WHAT WILL WE BE TALKING ABOUT? Specific Prototyping Strategies! Low-Fidelity Strategies Storyboarding Video Prototypes Paper Prototyping
3 BIG PICTURE! Remember that you should always use stage appropriate tools! Fidelity vs. Time graph! (next slide) The general rule is that you should progress from low to high fidelity slowly as the design process continues.
4 PROTOTYPING OVER TIME
5 STORYBOARDING! Storyboarding is ALL about tasks! NOT focused on specific interface elements and how they look, etc. Thus it is incredibly low-fidelity.
6 STORYBOARDING Storyboarding IS about The tasks users want to complete. The FLOW of the user s interaction. Storyboarding is NOT about Pretty pictures (in fact bad drawing helps focus on task and not on imagery). Showing specific interface elements.
7
8 EXAMPLE STORYBOARD
9 STORYBOARDS SHOULD CONVEY Setting People Involved Environment(s) Task being accomplished Sequence What steps are involved? What leads someone to use the app or system? What task is being illustrated?
10 STORYBOARDS SHOULD CONVEY Satisfaction What motivates people to use the system? What does it enable people to accomplish? What need does system fill?
11 BENEFITS OF STORYBOARDING Holistic Focus: helps emphasize how an interface accomplishes a task. Avoids commitment to a particular user interface (no buttons yet). Helps get ALL stakeholders on the same page in terms of the goal.
12 SOME ADVICE REGARDING STORYBOARDING DO NOT spend too much time on a storyboard. Set a short time limit to enforce this. Focus on tasks and scenarios that are the MOST common for your users.
13 Example from book User Interface Design and Evaluation, p. 119 Shows workflow of mail merging who s involved, responsibilities, etc.
14 This shows high-level of view of users involved in other storyboards From: Usability Case Studies,
15 Storyboard (or is it?) for a website for photographers Sequence of pages based on clicks Explanations / annotations From book: Designing Interactive Systems, 2005
16
17 VIDEO PROTOTYPING What is video prototyping?
18 BENEFITS OF VIDEO PROTOTYPING Cheap and fast Great communication tools Helps achieve common ground Ideally, portable and self-explanatory Can serve as a spec for developers Ties interface designs to tasks Aligns and orients interface choices Makes sure you have a complete interface
19 VIDEO PROTOTYPING Can be any level of fidelity. Can make videos with paper prototype examples. Fancy high fidelity videos are ok too! Usually, dependent on where you are in the design process.
20 WHAT DO YOU PUT IN VIDEO PROTOTYPE? The WHOLE task including motivation and success. Establishing shots and narrative help. Draw on tasks you observe. Illustrate important tasks your system enables. Not in video, probably not necessary for version one of the system. Can help scope a minimum viable product. Changes what design teams argue about (in a good way).
21 STEPS TO VIDEO PROTOTYPING 1) Outline / Storyboard the Video 2) Obtain Equipment. A camera (nothing fancy required). Could be a phone even! People Realistic Location 3) Focus on MESSAGE, not on production value. 4) Film it!!
22 VIDEO PROTOTYPING EXAMPLES! mg (shown in class) k
23 CONSIDERATIONS Audio? Not always necessary. You can verbally describe video in person while showing it to someone. Interface fidelity? Paper, digital, etc. Can even be invisible! Show both success and failure. Several use-cases always a plus. Don t spend too much time editing.
24
25 PAPER PROTOTYPING! Quite literally, using paper to produce a potential interface design. (Cardboard, post-its, tape, index cards, glue-sticks, etc.)
26 BENEFITS OF PAPER PROTOTYPING Very Fast! Very Cheap! Easy to change and adapt Why not code-it, real GUIs, using a builder tool, etc.? (I.e. high-fidelity) Estimated to be 100 times cheaper if NO code is written. (So says Jakob Nielsen, so you know it s true.) Can be used to collect important usability information! Can support interaction: an evaluation session with users Really? But it s just paper, scribbling and post-it notes!
27 USER INTERACTION WITH A PAPER PROTOTYPE Evaluation session What happens: User walks through a task One team member plays computer New screens etc. are moved in and out Team draws on paper, adds things, moves things, etc. Someone ask questions, elicits comments Some records feedback (video, notes) Benefits! Not tempted to focus on fit-and-finish Allows focus on a desired evaluation goals (e.g. flow, conceptual model, visibility (?), etc.) No demo fail. Easy to change on the fly during evaluation session.
28 ADDITIONAL ADVANTAGE: COLLABORATIVE DESIGN Users (and Stakeholders) can get involved and quickly alter / update the interface. Often this leads to a better design because they can show you what they prefer! Scaffold their efforts.
29 DEMONSTRATION VIDEO Hanmail: 0 Coloring App for Kids (good evaluation session example too): A Corel's video on WebPoint product: iphone (color app, presentation by developer): Y
30 PAPER PROTOTYPING TIPS AND TRICKS 1) Keep materials in one place! Small interface widgets tend to get lost or damaged easily. 2) Work quickly and make reusable components. Screen grab UI widgets. Photocopy things. Use scissors (but don t run with them). 3) If something is difficult to simulate (progress indicators, right mouse menus, hyperlinks), have the user ask if it is available and then verbally describe the interaction. E.g. you don t have to construct (or code) everything
31 PAPER PROTOTYPING TIPS AND TRICKS 4) Backgrounds (Poster Board, etc.) can be useful to contain the prototype and provide context for the user. E.g. a ipad or iphone template 5) Don t be afraid to mix and match hardware and software! Maybe a physical block of wood with paper on it! 6) When appropriate, add context by including familiar operating system elements.
32 PAPER PROTOTYPING MATERIALS Widgets!
33 PAPER PROTOTYPING MATERIALS Connectors
34 PAPER PROTOTYPING MATERIALS Drawing
35 ANOTHER EXAMPLE
36 WIREFRAMING
37 WHAT S A WIRE FRAME? A low fidelity representation of a single page or screen Goal: to meet the purpose of that screen, what UI elements are needed, and how are they organized? Should show: All content or features needed Relative sizes and locations of these Should NOT include: Colors Fonts (Other fit and finish characteristics)
38 EXAMPLES
39 ROLE OF WIREFRAMES When in development? After finding user analysis, understand requirements. Perhaps after paper prototypes As a step towards designing the final interface Keep a low-fidelity approach Colors, fonts, etc. people begin to focus on fit and finish, and not on what you want Which is: can this do what we need it to do? Verify against Should reflect what you learned about users, scenarios, etc.
40 WIREFRAMING TOOLS Many! Some are web-based, some are apps Balsamiq Draws things to make things look like paper (lo-fi) Other drawing tools e.g. Microsoft Visio, OmniGraffle Others Pencil Project (free) Sketch Marvel MockFlow FluidUI
41 WIREFRAME VS. PAPER PROTOTYPES Wireframes are More complete More polished (still lo-fi) Often created with computer tools Paper prototypes Done earlier, perhaps Less polished (perhaps) Seem to be used more for evaluating interaction Doing an evaluation with users Perhaps one thing they both don t show well is
42 OVERALL UI FLOW Major UI elements are probably windows or screens (on handhelds) What are they? How are they organized? Do they match users mental models of how they want to achieve tasks? Compare to SW architecture design Major components and their roles How they re related Save detailed design (inside modules) for later
43 GOAL OF MODELING UI FLOW Identify major UI components (windows etc) High-level description of their role Interactions between these Conditions? Two levels possible At conceptual design (more abstract) At physical design (what will be windows/screens/pages)
44 UIDE BOOK S CONTENT DIAGRAMS Content diagram is: lo-fi prototype that shows organization and structure of the UI from the designer s perspective (?) In physical design, can be transformed into GUI or website or May not be a one-to-one match between this level of abstraction and final physical design
45 CREATING A CONTENT DIAGRAM Need to know: Primary tasks, objects, etc. for this UI Probably want to have use-cases, scenarios, etc. Then, Identify containers and task objects Decide which tasks go into each container Define links that show navigation flow
46 CONTENT DIAGRAMS: CONTAINERS Container an abstract representation of some part of a user s work activity includes functions required to do that activity Various levels within the diagram Main container should record Vital tasks and Frequent tasks Lower-level containers
47 CONTENT DIAGRAMS: LINKS Links how the user will navigate in the UI between these functional areas Single link: next container becomes primary focus Double link: second container requires context of first container Example: spell checking window in a wordprocessor Links may have labels to indicate conditions on them
48 REPRESENTING CONTAINERS UIDE book s template Note: Objects are Task Objects
49 EXAMPLE CONTAINER
50 EXAMPLE CONTENT DIAGRAM
51 ANOTHER APPROACH: UI FLOW DIAGRAMS We can do less than this and still benefit Prototype often called a UI Flow Diagram or Navigation Diagram in the Unified Process methodology Post-its or boxes represent major UI elements (e.g. Windows) Each has a title (or short description) and often an ID ID used to refer to a more detailed diagram (perhaps done later) Goals: Get high-level overview Trace through use-cases or scenarios
52 EXAMPLE: UI FLOW DIAGRAM From:
53 WEB DESIGN: SITEMAPS (Note: We don t mean an index-like web page that users look at to understand what s on a website) A design representation for identifying the structure and high-level content of a website What are the pages? How are they linked? For planning and design, we need to know: Goal or purpose of each page What can we learn from this? Tools? Yes. Or, PostIt Notes on whiteboards
CS2501 DESIGN PRINCIPLES AND PAPER PROTOTYPING
 CS2501 DESIGN PRINCIPLES AND PAPER PROTOTYPING * From Norman s Design of Everyday Things and our textbook. DON NORMAN S DESIGN PRINCIPLES 1. Visibility 2. Feedback 3. Affordance 4. Mapping 5. Constraint
CS2501 DESIGN PRINCIPLES AND PAPER PROTOTYPING * From Norman s Design of Everyday Things and our textbook. DON NORMAN S DESIGN PRINCIPLES 1. Visibility 2. Feedback 3. Affordance 4. Mapping 5. Constraint
CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION TO PROTOTYPING. Tom Horton. * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford)
 CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION TO PROTOTYPING Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford) READINGS ID Book. Chapter 11 in published book, Design, Prototyping,
CS3205 HCI IN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INTRODUCTION TO PROTOTYPING Tom Horton * Material from: Floryan (UVa) Klemmer (UCSD, was at Stanford) READINGS ID Book. Chapter 11 in published book, Design, Prototyping,
COSC 341 Human Computer Interaction. Dr. Bowen Hui University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 341 Human Computer Interaction Dr. Bowen Hui University of British Columbia Okanagan 1 Recall: Learning About Your User Common ways to elicit user feedback: Interviews Focus groups Expert reviews
COSC 341 Human Computer Interaction Dr. Bowen Hui University of British Columbia Okanagan 1 Recall: Learning About Your User Common ways to elicit user feedback: Interviews Focus groups Expert reviews
Human-Computer Interaction: An Overview. CS2190 Spring 2010
 Human-Computer Interaction: An Overview CS2190 Spring 2010 There must be a problem because What is HCI? Human-Computer interface Where people meet or come together with machines or computer-based systems
Human-Computer Interaction: An Overview CS2190 Spring 2010 There must be a problem because What is HCI? Human-Computer interface Where people meet or come together with machines or computer-based systems
CS 350 COMPUTER/HUMAN INTERACTION
 CS 350 COMPUTER/HUMAN INTERACTION Lecture 19 Includes selected slides from the companion website for Hartson & Pyla, The UX Book, 2012. MKP, All rights reserved. Used with permission. Notes Reminder: C#
CS 350 COMPUTER/HUMAN INTERACTION Lecture 19 Includes selected slides from the companion website for Hartson & Pyla, The UX Book, 2012. MKP, All rights reserved. Used with permission. Notes Reminder: C#
Lecture 16. Will spend Thursday setting up group projects No exams. 10% added to in-class/homework. 10% added to final group project.
 Lecture 16 Will spend Thursday setting up group projects No exams. 10% added to in-class/homework. 10% added to final group project. 1 Outline Chapter 9 Design iterations Intermediate design Detailed design
Lecture 16 Will spend Thursday setting up group projects No exams. 10% added to in-class/homework. 10% added to final group project. 1 Outline Chapter 9 Design iterations Intermediate design Detailed design
Lecture 6. Design (3) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 6. Design (3) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 28 2009 1 Outline Prototyping techniques: - Paper prototype - Computer prototype - Wizard of Oz Reading: Wickens pp. 50-57 Marc Rettig: Prototyping
Lecture 6. Design (3) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 28 2009 1 Outline Prototyping techniques: - Paper prototype - Computer prototype - Wizard of Oz Reading: Wickens pp. 50-57 Marc Rettig: Prototyping
Agile Software Development Agile UX Work. Kati Kuusinen TUT / Pervasive / IHTE
 Agile Software Development Agile UX Work Kati Kuusinen Researcher @ TUT / Pervasive / IHTE kati.kuusinen@tut.fi Contents 1. Introduction / Motivation 2. Agile software development 3. User experience work
Agile Software Development Agile UX Work Kati Kuusinen Researcher @ TUT / Pervasive / IHTE kati.kuusinen@tut.fi Contents 1. Introduction / Motivation 2. Agile software development 3. User experience work
Prototyping. Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994.
 Prototyping Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994. 1 What is prototyping? producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your
Prototyping Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994. 1 What is prototyping? producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your
Administrative Stuff. Examples of project processbooks and link to a project prototype on the website Next Week: Evaluation methods, cultural probes
 Administrative Stuff Examples of project processbooks and link to a project prototype on the website Next Week: Evaluation methods, cultural probes Prototyping Irene Rae Computer Sciences CS-570 Introduction
Administrative Stuff Examples of project processbooks and link to a project prototype on the website Next Week: Evaluation methods, cultural probes Prototyping Irene Rae Computer Sciences CS-570 Introduction
Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping
 Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping Course announcements Deadlines Individual assignment (extended) deadline: today (June 7) 8:00 am by email User testing summary for paper prototype testing- Thursday June
Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping Course announcements Deadlines Individual assignment (extended) deadline: today (June 7) 8:00 am by email User testing summary for paper prototype testing- Thursday June
The LUCID Design Framework (Logical User Centered Interaction Design)
 The LUCID Design Framework (Logical User Centered Interaction Design) developed by Cognetics Corporation LUCID Logical User Centered Interaction Design began as a way of describing the approach to interface
The LUCID Design Framework (Logical User Centered Interaction Design) developed by Cognetics Corporation LUCID Logical User Centered Interaction Design began as a way of describing the approach to interface
Assignments. Assignment 2 is due TODAY, 11:59pm! Submit one per pair on Blackboard.
 HCI and Design Assignments Assignment 2 is due TODAY, 11:59pm! Submit one per pair on Blackboard. Today Paper prototyping An essential tool in your design toolbox! How do we design things that actually
HCI and Design Assignments Assignment 2 is due TODAY, 11:59pm! Submit one per pair on Blackboard. Today Paper prototyping An essential tool in your design toolbox! How do we design things that actually
CIS4930 / CIS6930: USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN INSTRUCTOR: DR. LISA ANTHONY
 Fall 2015 CIS4930 / CIS6930: USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN INSTRUCTOR: DR. LISA ANTHONY CIS4930/6930 User Experience Design, Fall 2015 -- Dr. Lisa Anthony -- lanthony@cise.ufl.edu 11/05/2015 1 Week 11b HIGH-FIDELITY
Fall 2015 CIS4930 / CIS6930: USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN INSTRUCTOR: DR. LISA ANTHONY CIS4930/6930 User Experience Design, Fall 2015 -- Dr. Lisa Anthony -- lanthony@cise.ufl.edu 11/05/2015 1 Week 11b HIGH-FIDELITY
Low fidelity: omits details High fidelity: more like finished product. Breadth: % of features covered. Depth: degree of functionality
 Fall 2005 6.831 UI Design and Implementation 1 Fall 2005 6.831 UI Design and Implementation 2 Paper prototypes Computer prototypes Wizard of Oz prototypes Get feedback earlier, cheaper Experiment with
Fall 2005 6.831 UI Design and Implementation 1 Fall 2005 6.831 UI Design and Implementation 2 Paper prototypes Computer prototypes Wizard of Oz prototypes Get feedback earlier, cheaper Experiment with
PRO WAYS TO LAUNCH A PRODUCT
 MASTER SVG FILTER EFFECTS Make your websites shine across browsers RAPID PAPER PROTOTYPING Test out interactive BUILD A SLICK RESPONSIVE SITE Get started with the Gumby CSS framework CREATE APPS WITH NODE.JS
MASTER SVG FILTER EFFECTS Make your websites shine across browsers RAPID PAPER PROTOTYPING Test out interactive BUILD A SLICK RESPONSIVE SITE Get started with the Gumby CSS framework CREATE APPS WITH NODE.JS
USERINTERFACE DESIGN & SIMULATION. Fjodor van Slooten
 USERINTERFACE Fjodor van Slooten TODAY USERINTERFACE -Introduction -Interaction design -Prototyping Userinterfaces with Axure -Practice Do Axure tutorial Work on prototype for project vanslooten.com/uidessim
USERINTERFACE Fjodor van Slooten TODAY USERINTERFACE -Introduction -Interaction design -Prototyping Userinterfaces with Axure -Practice Do Axure tutorial Work on prototype for project vanslooten.com/uidessim
dt+ux Design Thinking for User Experience Design, Prototyping & Evaluation Autumn 2016 Prof. James A. Landay Stanford University
 DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Early Stage Prototyping Computer Science Department October 20, 2016 Paper ipad App By 53 2 Hall of Fame or
DESIGN THINKING FOR USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Early Stage Prototyping Computer Science Department October 20, 2016 Paper ipad App By 53 2 Hall of Fame or
Software Quality. Martin Glinz. Thomas Fritz. Lecture 7 UI Design, Usability & Testing. Many thanks to Meghan Allen and Daniel Greenblatt.
 Institut für Informatik Software Quality Lecture 7 UI Design, Usability & Testing Thomas Fritz Martin Glinz Many thanks to Meghan Allen and Daniel Greenblatt. Overview Introduction to UI design User-centered
Institut für Informatik Software Quality Lecture 7 UI Design, Usability & Testing Thomas Fritz Martin Glinz Many thanks to Meghan Allen and Daniel Greenblatt. Overview Introduction to UI design User-centered
Lecture Notes CPSC 491 (Fall 2018) Topics. Peer evals. UI Sketches. Homework. Quiz 4 next Tues. HW5 out. S. Bowers 1 of 11
 Topics Peer evals UI Sketches Homework Quiz 4 next Tues HW5 out S. Bowers 1 of 11 Context Diagrams Context Diagrams describe the system boundaries what is inside ( in scope ) vs outside ( out of scope
Topics Peer evals UI Sketches Homework Quiz 4 next Tues HW5 out S. Bowers 1 of 11 Context Diagrams Context Diagrams describe the system boundaries what is inside ( in scope ) vs outside ( out of scope
User Centered Design Process. Prototyping II. What is a prototype? Prototyping phases Oct 11, 2017
 User Centered Design Process Prototyping II Oct 11, 2017 Produce something tangible Identify challenges Uncover subtleties 2 What is a prototype? A prototype is defined less by form, and more by its function:
User Centered Design Process Prototyping II Oct 11, 2017 Produce something tangible Identify challenges Uncover subtleties 2 What is a prototype? A prototype is defined less by form, and more by its function:
MIT GSL week 4 Wednesday. User Interfaces II
 MIT GSL 2018 week 4 Wednesday User Interfaces II User Centered Design Prototyping! Producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your target interface! Essential in spiral design process, useful in later
MIT GSL 2018 week 4 Wednesday User Interfaces II User Centered Design Prototyping! Producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your target interface! Essential in spiral design process, useful in later
SWEN 444 Human Centered Requirements and Design Project Breakdown
 SWEN 444 Human Centered Requirements and Design Project Breakdown Team Status Reports: (starting in Week 2) Your team will report weekly project status to your instructor, and as you wish, capture other
SWEN 444 Human Centered Requirements and Design Project Breakdown Team Status Reports: (starting in Week 2) Your team will report weekly project status to your instructor, and as you wish, capture other
Ideate. Empathize. Prototype. Define. Test. CS:2520 Human-Computer Interaction. Fall 2016.
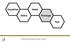 Empathize Ideate Define Prototype Test Designing Prototypes From Preece, Rogers & Sharp s Interaction Design Process Conceptual design What product will do How it will behave Physical design Actual visual
Empathize Ideate Define Prototype Test Designing Prototypes From Preece, Rogers & Sharp s Interaction Design Process Conceptual design What product will do How it will behave Physical design Actual visual
The Experience of Prototyping. Jennifer Kalz, CBAP, CUA, CSM March 28, 2017
 The Experience of Prototyping Jennifer Kalz, CBAP, CUA, CSM March 28, 2017 Agenda Core Concept Model Overview and Benefits of the Technique Fidelity of a Prototype Best Practices with the Technique Usability
The Experience of Prototyping Jennifer Kalz, CBAP, CUA, CSM March 28, 2017 Agenda Core Concept Model Overview and Benefits of the Technique Fidelity of a Prototype Best Practices with the Technique Usability
Prototyping for usability engineering
 analysis of stakeholders, field studies ANALYZE Problem scenarios claims about current practice Prototyping for usability engineering metaphors, information technology, HCI theory, guidelines DESIGN Activity
analysis of stakeholders, field studies ANALYZE Problem scenarios claims about current practice Prototyping for usability engineering metaphors, information technology, HCI theory, guidelines DESIGN Activity
SWEN 444 Human Centered Requirements and Design Project Breakdown
 SWEN 444 Human Centered Requirements and Design Project Breakdown Team Status Reports: (starting in Week 2) Your team will report bi-weekly project status to your instructor, and as you wish, capture other
SWEN 444 Human Centered Requirements and Design Project Breakdown Team Status Reports: (starting in Week 2) Your team will report bi-weekly project status to your instructor, and as you wish, capture other
Human-Computer Interaction IS4300
 Human-Computer Interaction IS4300 1 Ethnography Homework I3 2 1 Team Projects User analysis. Identify stakeholders (primary, secondary, tertiary, facilitating) For Primary Stakeholders Demographics Persona(s)
Human-Computer Interaction IS4300 1 Ethnography Homework I3 2 1 Team Projects User analysis. Identify stakeholders (primary, secondary, tertiary, facilitating) For Primary Stakeholders Demographics Persona(s)
DOWNLOAD PDF ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS GUIDE TO MICROSOFT OFFICE ONENOTE 2003 (ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS GUIDE)
 Chapter 1 : Absolute Beginner's Guide to Microsoft Office OneNoteâ [Book] Absolute Beginner's Guide to Microsoft Office OneNote is a from-scratch reference that helps you get up to speed quickly on this
Chapter 1 : Absolute Beginner's Guide to Microsoft Office OneNoteâ [Book] Absolute Beginner's Guide to Microsoft Office OneNote is a from-scratch reference that helps you get up to speed quickly on this
Human-Computer Interaction Design
 Human-Computer Interaction Design COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI Instructor: Philip Guo Week 2 - Prototyping (2016-10-04) some slides adapted from Scott Klemmer s Intro. HCI course Grading policy: aim for
Human-Computer Interaction Design COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI Instructor: Philip Guo Week 2 - Prototyping (2016-10-04) some slides adapted from Scott Klemmer s Intro. HCI course Grading policy: aim for
Prototyping. Oct 3, 2016
 Prototyping Oct 3, 2016 Announcements A1 marks available A2 due Wednesday Questions? What is a prototype? In interaction design a prototype can be (among other things): a series of screen sketches a storyboard,
Prototyping Oct 3, 2016 Announcements A1 marks available A2 due Wednesday Questions? What is a prototype? In interaction design a prototype can be (among other things): a series of screen sketches a storyboard,
Up and Running Software The Development Process
 Up and Running Software The Development Process Success Determination, Adaptative Processes, and a Baseline Approach About This Document: Thank you for requesting more information about Up and Running
Up and Running Software The Development Process Success Determination, Adaptative Processes, and a Baseline Approach About This Document: Thank you for requesting more information about Up and Running
IPM 15/16 T2.1 Prototyping
 IPM 15/16 T2.1 Prototyping Miguel Tavares Coimbra Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British Columbia University, Vancouver, Canada.
IPM 15/16 T2.1 Prototyping Miguel Tavares Coimbra Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British Columbia University, Vancouver, Canada.
CS 160: Evaluation. Professor John Canny Spring /15/2006 1
 CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 Outline User testing process Severity and Cost ratings Discount usability methods Heuristic evaluation HE vs. user testing 2/15/2006 2 Outline
CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 Outline User testing process Severity and Cost ratings Discount usability methods Heuristic evaluation HE vs. user testing 2/15/2006 2 Outline
CS/ISE 5714 Spring 2013
 CS/ISE 5714 Spring 2013 Chapter 11. Prototyping Chapter 10. UX Goals, Metrics, Targets Introduction A way to evaluate design before it s too late and too expensive Copyright MKP. All rights reserved. 2
CS/ISE 5714 Spring 2013 Chapter 11. Prototyping Chapter 10. UX Goals, Metrics, Targets Introduction A way to evaluate design before it s too late and too expensive Copyright MKP. All rights reserved. 2
Understanding prototype fidelity What is Digital Prototyping? Introduction to various digital prototyping tools
 HCI and Design Today Assignment 1 is graded Assignment 3 is posted Understanding prototype fidelity What is Digital Prototyping? Introduction to various digital prototyping tools Reminder: What is a prototype?
HCI and Design Today Assignment 1 is graded Assignment 3 is posted Understanding prototype fidelity What is Digital Prototyping? Introduction to various digital prototyping tools Reminder: What is a prototype?
CS -213 Human Computer Interaction Spring Prototyping. Imran Ihsan. Assistant Professor (CS) Air University, Islamabad
 CS -213 Human Computer Interaction Spring 2015 07 Prototyping Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor (CS) Air University, Islamabad www.imranihsan.com www.opuseven.com opuseven iimranihsan imranihsan iimranihsan
CS -213 Human Computer Interaction Spring 2015 07 Prototyping Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor (CS) Air University, Islamabad www.imranihsan.com www.opuseven.com opuseven iimranihsan imranihsan iimranihsan
Design Iteration: From Evidence to Design. Slides originally by: Dick Henneman
 Design Iteration: From Evidence to Design Slides originally by: Dick Henneman Foundations: MS-HCI @ Georgia Tech Context of use Context of development Analyze/ Evaluate Design/B uild Evidence-Based Design
Design Iteration: From Evidence to Design Slides originally by: Dick Henneman Foundations: MS-HCI @ Georgia Tech Context of use Context of development Analyze/ Evaluate Design/B uild Evidence-Based Design
Procedure for Developing a Multimedia Presentation
 Procedure for Developing a Multimedia Presentation Procedure for Developing a Multimedia Presentation These first two steps were covered earlier. They are a part of the procedure for creating a multimedia
Procedure for Developing a Multimedia Presentation Procedure for Developing a Multimedia Presentation These first two steps were covered earlier. They are a part of the procedure for creating a multimedia
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique. Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design
 Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Page 1. Ideas to windows. Lecture 7: Prototyping & Evaluation. Levels of prototyping. Progressive refinement
 Ideas to windows Lecture 7: Prototyping & Evaluation How do we go from ideas to windows? Prototyping... rapid initial development, sketching & testing many designs to determine the best (few?) to continue
Ideas to windows Lecture 7: Prototyping & Evaluation How do we go from ideas to windows? Prototyping... rapid initial development, sketching & testing many designs to determine the best (few?) to continue
Interaction Design. Heuristic Evaluation & Cognitive Walkthrough
 Interaction Design Heuristic Evaluation & Cognitive Walkthrough Interaction Design Iterative user centered design and development Requirements gathering Quick design Build prototype Evaluate and refine
Interaction Design Heuristic Evaluation & Cognitive Walkthrough Interaction Design Iterative user centered design and development Requirements gathering Quick design Build prototype Evaluate and refine
Software Compare and Contrast
 Microsoft Software Compare and Contrast Word Easy to navigate. Compatible with all PC computers. Very versatile. There are lots of templates that can be used to create flyers, calendars, resumes, etc.
Microsoft Software Compare and Contrast Word Easy to navigate. Compatible with all PC computers. Very versatile. There are lots of templates that can be used to create flyers, calendars, resumes, etc.
Sketching and Prototyping
 Sketching and Prototyping SWE 632 Spring 2018 Thomas LaToza Administrivia HW 3 due in 1 week In-class midterm exam in two weeks 2 Expectations for midterm exam Multiple choice questions, free response,
Sketching and Prototyping SWE 632 Spring 2018 Thomas LaToza Administrivia HW 3 due in 1 week In-class midterm exam in two weeks 2 Expectations for midterm exam Multiple choice questions, free response,
CS 160: Evaluation. Outline. Outline. Iterative Design. Preparing for a User Test. User Test
 CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 2/15/2006 2 Iterative Design Prototype low-fi paper, DENIM Design task analysis contextual inquiry scenarios sketching 2/15/2006 3 Evaluate
CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 2/15/2006 2 Iterative Design Prototype low-fi paper, DENIM Design task analysis contextual inquiry scenarios sketching 2/15/2006 3 Evaluate
Chapter 2 Web Development Overview
 Chapter 2 Web Development Overview Presented by Thomas Powell Slides adopted from HTML & XHTML: The Complete Reference, 4th Edition 2003 Thomas A. Powell Five Pillars of Sites Web sites have five aspects
Chapter 2 Web Development Overview Presented by Thomas Powell Slides adopted from HTML & XHTML: The Complete Reference, 4th Edition 2003 Thomas A. Powell Five Pillars of Sites Web sites have five aspects
CS 147 Let s Do This! Assignment 6 Report
 CS 147 Let s Do This! Assignment 6 Report 1. Team Name: Value Proposition Let s Do This: Achieve your goals with friends. 2. Team members names and roles Eric - Developer, manager. Video filming, editing,
CS 147 Let s Do This! Assignment 6 Report 1. Team Name: Value Proposition Let s Do This: Achieve your goals with friends. 2. Team members names and roles Eric - Developer, manager. Video filming, editing,
S A M P L E C H A P T E R
 SAMPLE CHAPTER Anyone Can Create an App by Wendy L. Wise Chapter 5 Copyright 2017 Manning Publications brief contents PART 1 YOUR VERY FIRST APP...1 1 Getting started 3 2 Building your first app 14 3 Your
SAMPLE CHAPTER Anyone Can Create an App by Wendy L. Wise Chapter 5 Copyright 2017 Manning Publications brief contents PART 1 YOUR VERY FIRST APP...1 1 Getting started 3 2 Building your first app 14 3 Your
Usable Privacy and Security Introduction to HCI Methods January 19, 2006 Jason Hong Notes By: Kami Vaniea
 Usable Privacy and Security Introduction to HCI Methods January 19, 2006 Jason Hong Notes By: Kami Vaniea Due Today: List of preferred lectures to present Due Next Week: IRB training completion certificate
Usable Privacy and Security Introduction to HCI Methods January 19, 2006 Jason Hong Notes By: Kami Vaniea Due Today: List of preferred lectures to present Due Next Week: IRB training completion certificate
Homework Set 2. A brief discussion
 Homework Set 2 A brief discussion Homework Set 2 A brief discussion (#%" (#$" ("!#'"!#&"!#%"!#$"!"!" )" (!" ()" $!" $)" *!" *)" %!" Problem 4 Hick s Law or Fitt s Law? MT = a + b ID ID = log 2 ( A W +
Homework Set 2 A brief discussion Homework Set 2 A brief discussion (#%" (#$" ("!#'"!#&"!#%"!#$"!"!" )" (!" ()" $!" $)" *!" *)" %!" Problem 4 Hick s Law or Fitt s Law? MT = a + b ID ID = log 2 ( A W +
Module 9: Audience Analysis, Usability, and Information Architecture COM 420
 Module 9: Audience Analysis, Usability, and Information Architecture COM 420 Audience Analysis Needs Capabilities Without addressing these end user factors, time and money can be wasted building a site
Module 9: Audience Analysis, Usability, and Information Architecture COM 420 Audience Analysis Needs Capabilities Without addressing these end user factors, time and money can be wasted building a site
Human-Computer Interaction IS4300
 Human-Computer Interaction IS4300 1 Quiz 3 1 I5 due next class Your mission in this exercise is to implement a very simple Java painting applet. The applet must support the following functions: Draw curves,
Human-Computer Interaction IS4300 1 Quiz 3 1 I5 due next class Your mission in this exercise is to implement a very simple Java painting applet. The applet must support the following functions: Draw curves,
Lecture 8: Rapid Prototyping. CS 338: Graphical User Interfaces. Dario Salvucci, Drexel University.
 Lecture 8: Rapid Prototyping CS 338: Graphical User Interfaces. Dario Salvucci, Drexel University. 1 GUI Prototyping What is prototyping? rapid initial development, sketching & testing many designs to
Lecture 8: Rapid Prototyping CS 338: Graphical User Interfaces. Dario Salvucci, Drexel University. 1 GUI Prototyping What is prototyping? rapid initial development, sketching & testing many designs to
interaction design Thanks to JoEllen Kames
 1 interaction design Thanks to JoEllen Kames Motorola Mobility Consumer experience Design for presenting earlier versions of these slides in our on-campus version of this course before we start a word
1 interaction design Thanks to JoEllen Kames Motorola Mobility Consumer experience Design for presenting earlier versions of these slides in our on-campus version of this course before we start a word
DRAFT. Approach 1: Emphasize evaluation/feedback with target users
 CS8803 6750 Class Project - Part 3 In part 3 of the project, your group will implement a detailed prototype of your interface. You will further develop one design idea from the three five that you generated
CS8803 6750 Class Project - Part 3 In part 3 of the project, your group will implement a detailed prototype of your interface. You will further develop one design idea from the three five that you generated
I m going to be introducing you to ergonomics More specifically ergonomics in terms of designing touch interfaces for mobile devices I m going to be
 I m going to be introducing you to ergonomics More specifically ergonomics in terms of designing touch interfaces for mobile devices I m going to be talking about how we hold and interact our mobile devices
I m going to be introducing you to ergonomics More specifically ergonomics in terms of designing touch interfaces for mobile devices I m going to be talking about how we hold and interact our mobile devices
USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION. Heuristic Evaluation. Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington CSE 440
 USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Heuristic Evaluation Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington CSE 440 February 19, 2013 Hall of Fame or Shame? Pocket By Read It Later Jan. 14-18,
USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Heuristic Evaluation Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington CSE 440 February 19, 2013 Hall of Fame or Shame? Pocket By Read It Later Jan. 14-18,
Designing. Simon Wilson Interaction designer, DWP Digital
 Designing. Simon Wilson Interaction designer, DWP Digital What is design? Design is how it looks. Design is how it looks. Design is how something will work / should work. Designing is working out how something
Designing. Simon Wilson Interaction designer, DWP Digital What is design? Design is how it looks. Design is how it looks. Design is how something will work / should work. Designing is working out how something
Chapter 3! Planning and Design! 2012 Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3! Planning and Design! 2012 Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Road Map The time and effort you put into planning a multimedia project will determine how well (or not) the project hits its mark.!!!
Chapter 3! Planning and Design! 2012 Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Road Map The time and effort you put into planning a multimedia project will determine how well (or not) the project hits its mark.!!!
Making a PowerPoint Accessible
 Making a PowerPoint Accessible Purpose The purpose of this document is to help you to create an accessible PowerPoint, or to take a nonaccessible PowerPoint and make it accessible. You are probably reading
Making a PowerPoint Accessible Purpose The purpose of this document is to help you to create an accessible PowerPoint, or to take a nonaccessible PowerPoint and make it accessible. You are probably reading
Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a
 Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a heuristic evaluation and ending with How to rate severity.
Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a heuristic evaluation and ending with How to rate severity.
NUR - Introduction to HCI. Big picture, design process, UCD, UI issues
 NUR - Introduction to HCI Big picture, design process, UCD, UI issues Contacts Zdeněk Míkovec xmikovec@fel.cvut.cz K321 Jan Balata balatjan@fel.cvut.cz K411 Miroslav Macík macikmir@fel.cvut.cz K411 consultation
NUR - Introduction to HCI Big picture, design process, UCD, UI issues Contacts Zdeněk Míkovec xmikovec@fel.cvut.cz K321 Jan Balata balatjan@fel.cvut.cz K411 Miroslav Macík macikmir@fel.cvut.cz K411 consultation
How to make a prototype? A step-by-step. Step 1. Start with a paper prototype
 How to make a prototype? A step-by-step Step 1. Start with a paper prototype The very first step is to sketch your idea on a sheet of paper. If you consider yourself to be a bad artist - don t let that
How to make a prototype? A step-by-step Step 1. Start with a paper prototype The very first step is to sketch your idea on a sheet of paper. If you consider yourself to be a bad artist - don t let that
Design Heuristics and Evaluation
 Design Heuristics and Evaluation Rapid Evaluation Selected material from The UX Book, Hartson & Pyla Heuristic Evaluation Another method for finding usability problems in a UI design Validation during
Design Heuristics and Evaluation Rapid Evaluation Selected material from The UX Book, Hartson & Pyla Heuristic Evaluation Another method for finding usability problems in a UI design Validation during
Heuristic Evaluation! Hall of Fame or Shame?! Hall of Fame or Shame?! Hall of Fame or Shame?! Hall of Fame!!
 CS 147: HCI+D UI Design, Prototyping, and Evaluation, Autumn 2014 HCI+D: USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Heuristic Evaluation Computer Science Department Autumn
CS 147: HCI+D UI Design, Prototyping, and Evaluation, Autumn 2014 HCI+D: USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Heuristic Evaluation Computer Science Department Autumn
07 Prototyping. Project P3: Prototyping/Mockup Assignment 4: Fitts Law Experiment // 2015S UE Principles of Interaction. A.
 A. Riener 340.301 // 2015S UE Principles of Interaction 07 Prototyping Project P3: Prototyping/Mockup Assignment 4: Fitts Law Experiment May 8, 2015 JKU Linz Priv.-Doz. Dipl.-Ing. Dr. Andreas Riener Institute
A. Riener 340.301 // 2015S UE Principles of Interaction 07 Prototyping Project P3: Prototyping/Mockup Assignment 4: Fitts Law Experiment May 8, 2015 JKU Linz Priv.-Doz. Dipl.-Ing. Dr. Andreas Riener Institute
ekaizen Lessons Table of Contents 1. ebook Basics 1 2. Create a new ebook Make Changes to the ebook Populate the ebook 41
 Table of Contents 1. ebook Basics 1 2. Create a new ebook 20 3. Make Changes to the ebook 31 4. Populate the ebook 41 5. Share the ebook 63 ekaizen 1 2 1 1 3 4 2 2 5 The ebook is a tabbed electronic book
Table of Contents 1. ebook Basics 1 2. Create a new ebook 20 3. Make Changes to the ebook 31 4. Populate the ebook 41 5. Share the ebook 63 ekaizen 1 2 1 1 3 4 2 2 5 The ebook is a tabbed electronic book
User Interfaces for Web Sites and Mobile Devices. System and Networks
 User Interfaces for Web Sites and Mobile Devices System and Networks Computer Systems and Networks: Device-Aware Interfaces Interfaces must take into account physical constraints of computers and networks:
User Interfaces for Web Sites and Mobile Devices System and Networks Computer Systems and Networks: Device-Aware Interfaces Interfaces must take into account physical constraints of computers and networks:
THINK THE FDA DOESN T CARE ABOUT USER EXPERIENCE FOR MOBILE MEDICAL APPLICATIONS? THINK AGAIN.
 THINK THE FDA DOESN T CARE ABOUT USER EXPERIENCE FOR MOBILE MEDICAL APPLICATIONS? THINK AGAIN. When granting regulatory approvals for medical devices, both IEC 62366 and the FDA have emphasized the importance
THINK THE FDA DOESN T CARE ABOUT USER EXPERIENCE FOR MOBILE MEDICAL APPLICATIONS? THINK AGAIN. When granting regulatory approvals for medical devices, both IEC 62366 and the FDA have emphasized the importance
Design, prototyping and construction
 Chapter 11 Design, prototyping and construction 1 Overview Prototyping and construction Conceptual design Physical design Generating prototypes Support for design 2 Prototyping and construction What is
Chapter 11 Design, prototyping and construction 1 Overview Prototyping and construction Conceptual design Physical design Generating prototypes Support for design 2 Prototyping and construction What is
UX Intensive Takeaways In Action. J.J. Kercher December 8, 2011
 UX Intensive Takeaways In Action J.J. Kercher December 8, 2011 The Plan v Brief overview of the event v We have a client! v Break into groups of ~6 v Work fast, don t focus on the details v Most Important:
UX Intensive Takeaways In Action J.J. Kercher December 8, 2011 The Plan v Brief overview of the event v We have a client! v Break into groups of ~6 v Work fast, don t focus on the details v Most Important:
Design, Ideation, and Prototyping
 Design, Ideation, and Prototyping Why User Centered Design is important How Prototyping helps User Centered Design System Centered Design System Centered Design What can be built easily on this platform?
Design, Ideation, and Prototyping Why User Centered Design is important How Prototyping helps User Centered Design System Centered Design System Centered Design What can be built easily on this platform?
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE # 7 TEAM SKILL 2: UNDERSTANDING USER AND STAKEHOLDER NEEDS REQUIREMENT ELICITATION TECHNIQUES-IV
 1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE # 7 TEAM SKILL 2: UNDERSTANDING USER AND STAKEHOLDER NEEDS REQUIREMENT ELICITATION TECHNIQUES-IV 12 th June, 2013 Instructor Information 2 Course Instructor:
1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE # 7 TEAM SKILL 2: UNDERSTANDING USER AND STAKEHOLDER NEEDS REQUIREMENT ELICITATION TECHNIQUES-IV 12 th June, 2013 Instructor Information 2 Course Instructor:
What is a prototype?
 Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Prototyping Unit 4 Learning outcomes Understand the uses of different types of prototypes for different kinds/stages of design and be able to choose appropriately Know the basic techniques for low-fidelity
Interaction Design. Human-Computer. COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI. Instructor: Philip Guo. Week 3 - Heuristic Evaluation ( )
 Human-Computer Interaction Design COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI Instructor: Philip Guo Week 3 - Heuristic Evaluation (2016-10-11) some slides adapted from Scott Klemmer s Intro. HCI course Learning Objective
Human-Computer Interaction Design COGS120/CSE170 - Intro. HCI Instructor: Philip Guo Week 3 - Heuristic Evaluation (2016-10-11) some slides adapted from Scott Klemmer s Intro. HCI course Learning Objective
Cognitive Disability and Technology: Universal Design Considerations
 Cognitive Disability and Technology: Universal Design Considerations Clayton Lewis Coleman Institute for Cognitive Disabilities RERC-ACT clayton.lewis@colorado.edu Prepared for AUCD Training Symposium,
Cognitive Disability and Technology: Universal Design Considerations Clayton Lewis Coleman Institute for Cognitive Disabilities RERC-ACT clayton.lewis@colorado.edu Prepared for AUCD Training Symposium,
User Experience Design
 User Experience Design Hira Javed Usability Specialist Canadian Broadcasting Corporation UX Instructor University of Waterloo Stratford User + Experience What does the word experience mean to you? UX is
User Experience Design Hira Javed Usability Specialist Canadian Broadcasting Corporation UX Instructor University of Waterloo Stratford User + Experience What does the word experience mean to you? UX is
Screenplay. Timing and motion. Martin Constable October 23, RMIT Vietnam
 Screenplay Timing and motion Martin Constable October 23, 2017 RMIT Vietnam The Storyboard A storyboard is made before a movie is shot (i.e. production). A storyboard: Indicate how the story will be told.
Screenplay Timing and motion Martin Constable October 23, 2017 RMIT Vietnam The Storyboard A storyboard is made before a movie is shot (i.e. production). A storyboard: Indicate how the story will be told.
Tracking System for Job Applicants Sprint Schedule and Overview. By Erik Flowers
 Tracking System for Job Applicants Sprint Schedule and Overview By Erik Flowers This overview is to determine and develop the Tracking System for Job Applicants (TSJA), to be used by Recruiters/Managers
Tracking System for Job Applicants Sprint Schedule and Overview By Erik Flowers This overview is to determine and develop the Tracking System for Job Applicants (TSJA), to be used by Recruiters/Managers
UX, UI, Product Design
 UX, UI, Product Design for mobile app development Empathize https://www.nngroup.com/articles/design-thinking/ Research Methods Qualitative: Interviews Observation Quantitative: Survey User Interviews Contextual
UX, UI, Product Design for mobile app development Empathize https://www.nngroup.com/articles/design-thinking/ Research Methods Qualitative: Interviews Observation Quantitative: Survey User Interviews Contextual
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT. BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT. March 2017 PRINCIPLES OF USER INTERFACE DESIGN
 BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT March 2017 PRINCIPLES OF USER INTERFACE DESIGN EXAMINERS REPORT General Comments Candidates should focus
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT March 2017 PRINCIPLES OF USER INTERFACE DESIGN EXAMINERS REPORT General Comments Candidates should focus
User Experience Design
 User + Experience User Experience Design Hira Javed Usability Specialist Canadian Broadcasting Corporation UX Instructor University of Waterloo Stratford What does the word experience mean to you? UX is
User + Experience User Experience Design Hira Javed Usability Specialist Canadian Broadcasting Corporation UX Instructor University of Waterloo Stratford What does the word experience mean to you? UX is
Rapid Prototyping. Sketches, storyboards, mock-ups and scenarios
 Rapid Prototyping Sketches, storyboards, mock-ups and scenarios Agenda Dimensions and terminology Non-computer methods Computer methods 2 Your Project Group 3 An Essential Concept of UCD Requirements for
Rapid Prototyping Sketches, storyboards, mock-ups and scenarios Agenda Dimensions and terminology Non-computer methods Computer methods 2 Your Project Group 3 An Essential Concept of UCD Requirements for
Welcome to CS6452! Blair MacIntyre Monday, August 19, 13
 Welcome to CS6452! Blair MacIntyre blair@cc.gatech.edu 1 Introductions! Me Associate Professor, Interactive Computing Research/Teaching on Augmented Reality (Graphics/HCI/DM) and Games Focus on both experiences
Welcome to CS6452! Blair MacIntyre blair@cc.gatech.edu 1 Introductions! Me Associate Professor, Interactive Computing Research/Teaching on Augmented Reality (Graphics/HCI/DM) and Games Focus on both experiences
Prototyping. Unit 5. Zeno Menestrina, MSc Prof. Antonella De Angeli, PhD
 Prototyping Unit 5 Zeno Menestrina, MSc zeno.menestrina@unitn.it Prof. Antonella De Angeli, PhD antonella.deangeli@unitn.it Assessment Pervasive game to support social life in/from the campus 2 Assessment
Prototyping Unit 5 Zeno Menestrina, MSc zeno.menestrina@unitn.it Prof. Antonella De Angeli, PhD antonella.deangeli@unitn.it Assessment Pervasive game to support social life in/from the campus 2 Assessment
USERINTERFACE DESIGN & SIMULATION. Fjodor van Slooten
 USERINTERFACE DESIGN Fjodor van Slooten TODAY USERINTERFACE DESIGN -Introduction -Interaction design -Prototyping techniques -Practice Collaborative Design Challenge: Paper prototyping Heuristic evaluation
USERINTERFACE DESIGN Fjodor van Slooten TODAY USERINTERFACE DESIGN -Introduction -Interaction design -Prototyping techniques -Practice Collaborative Design Challenge: Paper prototyping Heuristic evaluation
The process of interaction design and Prototyping
 Chapter 6 edited The process of interaction design and Prototyping 1 Overview What is involved in Interaction Design? Importance of involving users Degrees of user involvement What is a user-centered approach?
Chapter 6 edited The process of interaction design and Prototyping 1 Overview What is involved in Interaction Design? Importance of involving users Degrees of user involvement What is a user-centered approach?
Usability. CSE 331 Spring Slides originally from Robert Miller
 Usability CSE 331 Spring 2010 Slides originally from Robert Miller 1 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 2 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 3 Redesigning
Usability CSE 331 Spring 2010 Slides originally from Robert Miller 1 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 2 User Interface Hall of Shame Source: Interface Hall of Shame 3 Redesigning
M150 -B / Unit 12. By Wawi. A good user interface design enables the user to effectively interact with the system and perform his tasks.
 A good user interface design enables the user to effectively interact with the system and perform his tasks. (True) HCI: (Human-Computer Interaction) is the study of how humans interact with computers
A good user interface design enables the user to effectively interact with the system and perform his tasks. (True) HCI: (Human-Computer Interaction) is the study of how humans interact with computers
Hello! ios Development
 SAMPLE CHAPTER Hello! ios Development by Lou Franco Eitan Mendelowitz Chapter 1 Copyright 2013 Manning Publications Brief contents PART 1 HELLO! IPHONE 1 1 Hello! iphone 3 2 Thinking like an iphone developer
SAMPLE CHAPTER Hello! ios Development by Lou Franco Eitan Mendelowitz Chapter 1 Copyright 2013 Manning Publications Brief contents PART 1 HELLO! IPHONE 1 1 Hello! iphone 3 2 Thinking like an iphone developer
YOUR GUIDE TO. Skype for Business
 YOUR GUIDE TO Skype for Business Welcome to Skype for Business This is the Skype for Business app Your profile picture, status & location (you can change these) Your options Your contacts and groups (you
YOUR GUIDE TO Skype for Business Welcome to Skype for Business This is the Skype for Business app Your profile picture, status & location (you can change these) Your options Your contacts and groups (you
Heuristic Evaluation. Hall of Fame or Shame? Hall of Fame or Shame? Hall of Fame! Heuristic Evaluation
 1 USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Heuristic Evaluation Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington Pocket By Read It Later 11/1/2012 2 Hall of Fame or Shame?
1 USER INTERFACE DESIGN + PROTOTYPING + EVALUATION Hall of Fame or Shame? Heuristic Evaluation Prof. James A. Landay University of Washington Pocket By Read It Later 11/1/2012 2 Hall of Fame or Shame?
Prototyping & Building a System
 1 Prototyping & Building a System How Prototyping helps (especially when done with User-Centered Design) Prototyping http://dilbert.com/strip/2009-07-22 2 Designing Your System Decide which users and tasks
1 Prototyping & Building a System How Prototyping helps (especially when done with User-Centered Design) Prototyping http://dilbert.com/strip/2009-07-22 2 Designing Your System Decide which users and tasks
Interaction Design. Task Analysis & Modelling
 Interaction Design Task Analysis & Modelling This Lecture Conducting task analysis Constructing task models Understanding the shortcomings of task analysis Task Analysis for Interaction Design Find out
Interaction Design Task Analysis & Modelling This Lecture Conducting task analysis Constructing task models Understanding the shortcomings of task analysis Task Analysis for Interaction Design Find out
Prototyping. SWE 432, Fall Web Application Development
 Prototyping SWE 432, Fall 2018 Web Application Development Conceptual design Goal: match users mental model Tool: Metaphor - analogies from existing system Offers expectations about what system does &
Prototyping SWE 432, Fall 2018 Web Application Development Conceptual design Goal: match users mental model Tool: Metaphor - analogies from existing system Offers expectations about what system does &
PM Beyond Rendering Making Visualization Easy with the Product Design Collection
 PM124947 Beyond Rendering Making Visualization Easy with the Product Design Collection Rusty Belcher IMAGINiT Technologies Learning Objectives Discuss the simpler approach to rendering with Inventor Studio
PM124947 Beyond Rendering Making Visualization Easy with the Product Design Collection Rusty Belcher IMAGINiT Technologies Learning Objectives Discuss the simpler approach to rendering with Inventor Studio
User Interface. Three Mile Island. January 14, 2011 CSE 403, Winter 2011, Brun
 User Interface Three Mile Island January 14, 2011 CSE 403, Winter 2011, Brun Chernobyl How do we avoid bad UI? Learn from past mistakes Build prototypes Big questions What's the point of prototyping? Should
User Interface Three Mile Island January 14, 2011 CSE 403, Winter 2011, Brun Chernobyl How do we avoid bad UI? Learn from past mistakes Build prototypes Big questions What's the point of prototyping? Should
USER-CENTERED DESIGN KRANACK / DESIGN 4
 USER-CENTERED DESIGN WHAT IS USER-CENTERED DESIGN? User-centered design (UCD) is an approach to design that grounds the process in information about the people who will use the product. UCD processes focus
USER-CENTERED DESIGN WHAT IS USER-CENTERED DESIGN? User-centered design (UCD) is an approach to design that grounds the process in information about the people who will use the product. UCD processes focus
Prezi Quick Guide: Make a Prezi in minutes
 Prezi Quick Guide: Make a Prezi in minutes by Billy Meinke Updated Feb 2016 by Gina Iijima Welcome! This short guide will have you making functional and effective Prezis in no time. Prezi is a dynamic
Prezi Quick Guide: Make a Prezi in minutes by Billy Meinke Updated Feb 2016 by Gina Iijima Welcome! This short guide will have you making functional and effective Prezis in no time. Prezi is a dynamic
evision Review Project - Engagement Simon McLean, Head of Web & IT Support Information & Data Services.
 evision Review Project - Engagement Monitoring Simon McLean, Head of Web & IT Support Information & Data Services. What is Usability? Why Bother? Types of usability testing Usability Testing in evision
evision Review Project - Engagement Monitoring Simon McLean, Head of Web & IT Support Information & Data Services. What is Usability? Why Bother? Types of usability testing Usability Testing in evision
