Lecture 23: Domain-Driven Design (Part 1)
|
|
|
- Samuel Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Lecture 23: Domain-Driven Design (Part 1) Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI Spring Semester, Goals for this lecture Introduce the main concepts of Domain-Driven Design Model-Driven Design Ubiquitous Language Present examples that illustrate these concepts Goals for the Domain-Driven Design Lectures Cover chapters 1-7 and parts of chapter 10 in 4 lectures!
2 3 Domain-Driven Design Eric Evans, the author of Domain-Driven Design, has been programming and designing systems for 25 years He asserts that for most software projects, the primary focus should be on the domain and domain logic Domain-driven design flows from the premise that the heart of software development is knowledge of the subject matter and finding useful ways of understanding that subject matter. The complexity that we should be tackling is the complexity of the domain itself -- not the technical architecture, not the user interface, not even specific features. This means designing everything around our understanding and conception of the most essential concepts of the business and justifying any other development by how it supports that core. From < 4 Model-Driven Design Domain-Driven Design leads to Model-Driven Design since developers capture their knowledge of a domain in models In particular A model-driven design is software structured around a set o domain concepts A model-driven design for a UI framework is one in which UI concepts, such as windows and menus, correspond to software constructs Model-driven design embeds a domain model into the very fabric of a software system. This creates a feedback loop between learning about a domain and implementing a system that addresses a problem in that domain Teams who embrace model-driven design are aware that a change to the code IS a change to the model (and vice versa)
3 5 Model Benefits in DDD The model and its implementation shape each other The link between model and code makes the model relevant and ensures that the work spent on analysis is not wasted Indeed, the results of your analysis are present in the developed system! The model creates a language used by all team members The language spreads domain knowledge throughout a team It allows developers to speak to domain experts (e.g. users) without translation The model is distilled knowledge Analysis is hard; we need to capture the information we get from it The model is the team s agreed-upon way of structuring domain knowledge and and distinguishing the elements of most interest 6 Tackling Complexity The heart of software is its ability to solve domain-related problems for its users Software functionality either solves a domain-related problem or performs a domain-related task All other features support these two goals When a domain is complex, it becomes difficult to accomplish this To be successful, developers must steep themselves in the domain Problem: Most developers are not interested in this! Domain work is messy and demands a lot of knowledge not necessarily related to computer science Developers enjoy quantifiable problems that exercise their technical skills! Evans asserts that domain complexity has to be tackled head-on by developers or they risk irrelevance!
4 7 Crunching Knowledge Domain modeling requires processing (crunching) knowledge In the same way that financial analysts crunch numbers to, e.g., understand the quarterly performance of a corporation While speaking with domain experts, a domain modeler will try one organizing idea (set of concepts) after another create models, try them out, reject some, transform others Success is achieved when the modeler has created a set of abstract concepts that makes sense of all the details provided by the domain experts Domain experts are a critical part of the process Without them, developers tend to create models with concepts that seem naive and shallow to domain experts 8 Ingredients of Effective Modeling Bind the model and the implementation As a model is developed, create rapid prototypes that test the domain These prototypes contain primarily domain concepts no UI, no persistence, no infrastructure Chapter 3 begins with a story of what happens when you don t do this! Cultivate a language based on the model Domain experts teach you their concepts and vocabulary You teach them the basics of class diagrams and sequence diagrams (via the use of lots of examples) Eventually either side can take terms straight out of the model, organize them into sentences consistent with the structure of the model, and be unambiguously understood without translation
5 9 Ingredients of Effective Modeling, continued Develop a knowledge-rich model The objects of your model should have behavior and may follow rules The model should not be just a data schema (think class diagram) but should express behavior, constraints, etc. that help solve domainrelated problems Distill the model It will be easy to add concepts to a model but more important is learning to remove concepts that are no longer useful Be willing to brainstorm and experiement Try out variations of the model with rapid prototypes; think of the model as a laboratory that can enable domain-related experiments Use the results of those experiments to evolve the model 10 Example: PCB Design Chapter 1 contains a brief example of domain-driven design when the author was working with a team of printed-circuit board designers Evans knew nothing about electronic hardware Initial conversations with the designers were difficult Evans was not an electrical engineer and didn t understand the designers concepts or skills The designers were not software developers and could not explain the functionality they needed very well The first breakthrough came with Evans noticing that the concept of a Net kept appearing in the reports that the designers wanted from the software system A net on a PCB is a wire conductor that connects a set of components and can carry an electric signal to each component its connected to
6 11 Example continued This breakthrough led to a sequence of class diagrams and interaction diagrams that eventually led to a greater understanding of the domain PLUS identified a problem within the domain that needed solving See pages 7-11 of domain-driven design The concepts included component type (pin map), component instance, pin, net The problem was detecting the number of hops a signal caused across the components of a PCB One concept, net topology, was dropped when the developer discovered it wasn t needed to solve this problem 12 Knowledge-Rich Design To repeat, models capture more information than just the classes of a domain As Evans says, it goes beyond the find the nouns and verbs heuristic of some object-oriented models In particular, models capture behavior, business activities, and business rules (policies, constraints, etc.) This makes knowledge crunching difficult since there may be inconsistencies between business rules Domain experts (workers) can often detect these inconsistencies and apply common sense or create policies to deal with inconsistencies when they arise Software can t do this! (At least not easily!)
7 13 Example: Modeling Business Rules Consider a simple domain: Booking cargo on ships Voyage * Cargo The associated application might have code that looks like this: public int makebooking(cargo cargo, Voyage voyage) { int confirmation = getordernumber(); voyage.addcargo(cargo, confirmation); return confirmation; } 14 Example, continued A standard practice in the shipping industry is to accept more cargo than a particular ship can carry on voyage This is know as overbooking and is used because there are typically always last-minute cancellations One way of specifying the overbooking policy is via a percentage of the ship s total capacity So, if a requirements documents says Allow 10% overbooking our code might change to look like this public int makebooking(cargo cargo, Voyage voyage) { double maxbooking = voyage.capacity() * 1.1; if ((voyage.bookedcargosize() + cargo.size()) > maxbooking) return -1;... }
8 15 Problem: Hidden Knowledge The problem with this approach is that the overbooking policy is not reflected in our model The policy has been recorded in a requirements document and hidden away inside one method in our application Domain-Driven Design recommends making that knowledge a part of the model: change the model, change the code (and vice versa) Voyage * Cargo {sum(cargo.size) < voyage.capacity * 1.1} Overbooking Policy 16 Example, continued Our code would now look like this public int makebooking(cargo cargo, Voyage voyage) { if (!overbookingpolicy.isallowed(cargo, voyage)) return } and the OverbookingPolicy class would have this method: public boolean isallowed(cargo cargo, Voyage voyage) { return (cargo.size() + voyage.bookedcargosize()) <= (voyage.capacity() * 1.1); }
9 17 Ubiquitous Language A core piece of domain-driven design is the symbiotic nature of the model being created for your software system and the language used by developers to discuss the system under design Evans states Use the model as the backbone of a language. Commit the team to exercising that language relentlessly in all communication within the team and in the code. Use the same language in diagrams, writing, and especially speech Iron out difficulties by experimenting with alternative expressions, which reflect alternative models. Then refactor the code, renaming classes, methods, and modules to conform to the new model This allows developers to use their linguistic abilities to aid software design, resolving ambiguity or confusion over terms in conversation See example on pages 27 to Merging Jargons Ubiquitous Language technical aspects of design technical terms design patterns domain concepts "big picture" view of system subdomains business terms developers don't understand familiar business terms not relevant to the system under design Solution Space Problem Space
10 19 Using Language to Refine a Model When working on a model, speak the relationships out loud until you ve captured requirements in a concise way Three examples (from bad to good) If we give the Routing Service an origin, destination, and arrival time, it can look up the stops the cargo will have to make and, well... stick them in the database. The origin, destination, and so on... it all feeds into the Routing Service, and we get back an Itinerary that has everything we need in it A Routing Service finds an Itinerary that satisfies a Route Specification Once you ve got a statement like the last, you can supplement with additional statements A Routing Service needs an origin, a destination, and an arrival time 20 One Team, One Language Developers will want to hide the model from the domain experts The model is too abstract for them They don t understand objects We have to collect requirements in their terminology Recall that the model is supposed to describe the user s domain! If sophisticated domain experts don t understand the model, something is wrong with the model! Indeed, the domain experts will be your best resource for testing the adequacy of a model They will quickly find problems, notice ambiguity, identify naive assumptions, etc.
11 21 Documents and Diagrams Diagrams are good for anchoring discussions about the model brainstorming changes to the model But diagrams can t capture everything attributes and relationships tell half the story because behavior and constraints are not easily illustrated You can diagram some behaviors but you can t diagram all of them! The vital detail about the design is captured in the code! Documents are needed to capture decisions in large groups but beware entropy! Documents often get left behind! Good documents provide background and record the thinking behind decisions; they should not try to replace code s ability to provide detail See example page What s Next Review the contents of Part II of Domain-Driven Design The Building Blocks of a Model-Driven Design Layered Architecture Entities, Value Objects, Services, Modules Life Cycles of Domain Objects Aggregates Factories Repositories
Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software. Domain-Driven Design 카페서비스개발팀 조영호
 Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software Domain-Driven Design 카페서비스개발팀 조영호 목차 1. Domain & Software 2. What is Domain-Driven Design? 3. Patterns of Domain-Driven Design 4. Conclusion 1. Domain & Software
Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software Domain-Driven Design 카페서비스개발팀 조영호 목차 1. Domain & Software 2. What is Domain-Driven Design? 3. Patterns of Domain-Driven Design 4. Conclusion 1. Domain & Software
Introduction to User Stories. CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014
 Introduction to User Stories CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014 1 Goals Present an introduction to the topic of user stories concepts and terminology benefits and limitations
Introduction to User Stories CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014 1 Goals Present an introduction to the topic of user stories concepts and terminology benefits and limitations
DDD Where s the value and what s in it for me?
 DDD Where s the value and what s in it for me? Dino Esposito JetBrains dino.esposito@jetbrains.com @despos facebook.com/naa4e What does a software architect do? Design software driven by the requirements
DDD Where s the value and what s in it for me? Dino Esposito JetBrains dino.esposito@jetbrains.com @despos facebook.com/naa4e What does a software architect do? Design software driven by the requirements
Architecting and Implementing Domain-driven Design Patterns in.net
 Architecting and Implementing Domain-driven Design Patterns in.net Dino Esposito JetBrains dino.esposito@jetbrains.com @despos facebook.com/naa4e WARNING This is NOT simply a shameless plug but a truly
Architecting and Implementing Domain-driven Design Patterns in.net Dino Esposito JetBrains dino.esposito@jetbrains.com @despos facebook.com/naa4e WARNING This is NOT simply a shameless plug but a truly
cs465 principles of user interface design, implementation and evaluation
 cs465 principles of user interface design, implementation and evaluation Karrie G. Karahalios 24. September 2008 1. Heuristic Evaluation 2. Cognitive Walkthrough 3. Discuss Homework 3 4. Discuss Projects
cs465 principles of user interface design, implementation and evaluation Karrie G. Karahalios 24. September 2008 1. Heuristic Evaluation 2. Cognitive Walkthrough 3. Discuss Homework 3 4. Discuss Projects
CaseComplete Roadmap
 CaseComplete Roadmap Copyright 2004-2014 Serlio Software Development Corporation Contents Get started... 1 Create a project... 1 Set the vision and scope... 1 Brainstorm for primary actors and their goals...
CaseComplete Roadmap Copyright 2004-2014 Serlio Software Development Corporation Contents Get started... 1 Create a project... 1 Set the vision and scope... 1 Brainstorm for primary actors and their goals...
Plan. Design principles: laughing in the face of change. What kind of change? What are we trying to achieve?
 Plan Design principles: laughing in the face of change Perdita Stevens School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are we trying to achieve? Review: Design principles you know from Inf2C-SE Going
Plan Design principles: laughing in the face of change Perdita Stevens School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are we trying to achieve? Review: Design principles you know from Inf2C-SE Going
(2 1) What does evaluate to? What does evaluate to? What does evaluate to?
 Order of Operations (Time 20 minutes) Math is a language, just like English, Spanish, or any other language. We use nouns, like "bread", "tomato", "mustard" and "cheese" to describe physical objects. Math
Order of Operations (Time 20 minutes) Math is a language, just like English, Spanish, or any other language. We use nouns, like "bread", "tomato", "mustard" and "cheese" to describe physical objects. Math
Administrivia. Added 20 more so far. Software Process. Only one TA so far. CS169 Lecture 2. Start thinking about project proposal
 Administrivia Software Process CS169 Lecture 2 Added 20 more so far Will limit enrollment to ~65 students Only one TA so far Start thinking about project proposal Bonus points for proposals that will be
Administrivia Software Process CS169 Lecture 2 Added 20 more so far Will limit enrollment to ~65 students Only one TA so far Start thinking about project proposal Bonus points for proposals that will be
MiPhone Phone Usage Tracking
 MiPhone Phone Usage Tracking Team Scott Strong Designer Shane Miller Designer Sierra Anderson Designer Problem & Solution This project began as an effort to deter people from using their phones in class.
MiPhone Phone Usage Tracking Team Scott Strong Designer Shane Miller Designer Sierra Anderson Designer Problem & Solution This project began as an effort to deter people from using their phones in class.
Heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection technique developed by Jakob Nielsen. The original set of heuristics was derived empirically from an
 Heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection technique developed by Jakob Nielsen. The original set of heuristics was derived empirically from an analysis of 249 usability problems (Nielsen, 1994). -Preece
Heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection technique developed by Jakob Nielsen. The original set of heuristics was derived empirically from an analysis of 249 usability problems (Nielsen, 1994). -Preece
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE # 7 TEAM SKILL 2: UNDERSTANDING USER AND STAKEHOLDER NEEDS REQUIREMENT ELICITATION TECHNIQUES-IV
 1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE # 7 TEAM SKILL 2: UNDERSTANDING USER AND STAKEHOLDER NEEDS REQUIREMENT ELICITATION TECHNIQUES-IV 12 th June, 2013 Instructor Information 2 Course Instructor:
1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS ENGINEERING LECTURE # 7 TEAM SKILL 2: UNDERSTANDING USER AND STAKEHOLDER NEEDS REQUIREMENT ELICITATION TECHNIQUES-IV 12 th June, 2013 Instructor Information 2 Course Instructor:
Designing the M in MVC
 Designing the M in MVC Rob Allen @akrabat ~ May 2017 ~ http://akrabat.com (slides at http://akrabat.com/talks) The business logic is the hard part MVC MVC DDD is an approach to help you manage the model
Designing the M in MVC Rob Allen @akrabat ~ May 2017 ~ http://akrabat.com (slides at http://akrabat.com/talks) The business logic is the hard part MVC MVC DDD is an approach to help you manage the model
Case study on PhoneGap / Apache Cordova
 Chapter 1 Case study on PhoneGap / Apache Cordova 1.1 Introduction to PhoneGap / Apache Cordova PhoneGap is a free and open source framework that allows you to create mobile applications in a cross platform
Chapter 1 Case study on PhoneGap / Apache Cordova 1.1 Introduction to PhoneGap / Apache Cordova PhoneGap is a free and open source framework that allows you to create mobile applications in a cross platform
Understanding. Domain-Driven Design
 Understanding Domain-Driven Design 1 Domain-Driven Design Is about developers and domain experts working together to create software that is both understandable and maintainable. a way to capture and spread
Understanding Domain-Driven Design 1 Domain-Driven Design Is about developers and domain experts working together to create software that is both understandable and maintainable. a way to capture and spread
4 KEY FACTORS FOR DATA QUALITY ON A DATA LAKE (OR: HOW TO AVOID THE DATA SWAMP) JOSH HERRITZ MIOSOFT CORPORATION MIOsoft Corporation.
 4 KEY FACTORS FOR DATA QUALITY ON A DATA LAKE (OR: HOW TO AVOID THE DATA SWAMP) JOSH HERRITZ MIOSOFT CORPORATION The trends in digital business promise that the future holds an unprecedented volume, variety,
4 KEY FACTORS FOR DATA QUALITY ON A DATA LAKE (OR: HOW TO AVOID THE DATA SWAMP) JOSH HERRITZ MIOSOFT CORPORATION The trends in digital business promise that the future holds an unprecedented volume, variety,
Lecture 4: Design Concepts For Responsibility- Driven Design Kenneth M. Anderson January 20, 2005
 Lecture 4: Design Concepts For Responsibility- Driven Design Kenneth M. Anderson 1 of 25 Introduction Chapter 1 of Object Design covers topics that aid understanding of Responsibility-Driven Design Object
Lecture 4: Design Concepts For Responsibility- Driven Design Kenneth M. Anderson 1 of 25 Introduction Chapter 1 of Object Design covers topics that aid understanding of Responsibility-Driven Design Object
Due on: May 12, Team Members: Arpan Bhattacharya. Collin Breslin. Thkeya Smith. INFO (Spring 2013): Human-Computer Interaction
 Week 6 Assignment: Heuristic Evaluation of Due on: May 12 2013 Team Members: Arpan Bhattacharya Collin Breslin Thkeya Smith INFO 608-902 (Spring 2013): Human-Computer Interaction Group 1 HE Process Overview
Week 6 Assignment: Heuristic Evaluation of Due on: May 12 2013 Team Members: Arpan Bhattacharya Collin Breslin Thkeya Smith INFO 608-902 (Spring 2013): Human-Computer Interaction Group 1 HE Process Overview
6.001 Notes: Section 15.1
 6.001 Notes: Section 15.1 Slide 15.1.1 Our goal over the next few lectures is to build an interpreter, which in a very basic sense is the ultimate in programming, since doing so will allow us to define
6.001 Notes: Section 15.1 Slide 15.1.1 Our goal over the next few lectures is to build an interpreter, which in a very basic sense is the ultimate in programming, since doing so will allow us to define
Agile Architecture. The Why, the What and the How
 Agile Architecture The Why, the What and the How Copyright Net Objectives, Inc. All Rights Reserved 2 Product Portfolio Management Product Management Lean for Executives SAFe for Executives Scaled Agile
Agile Architecture The Why, the What and the How Copyright Net Objectives, Inc. All Rights Reserved 2 Product Portfolio Management Product Management Lean for Executives SAFe for Executives Scaled Agile
Design First ITS Instructor Tool
 Design First ITS Instructor Tool The Instructor Tool allows instructors to enter problems into Design First ITS through a process that creates a solution for a textual problem description and allows for
Design First ITS Instructor Tool The Instructor Tool allows instructors to enter problems into Design First ITS through a process that creates a solution for a textual problem description and allows for
Plan. Design principles: laughing in the face of change. What kind of change? What are we trying to achieve?
 Plan Design principles: laughing in the face of change Perdita Stevens School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are we trying to achieve? Review: Design principles you know from Inf2C-SE Going
Plan Design principles: laughing in the face of change Perdita Stevens School of Informatics University of Edinburgh What are we trying to achieve? Review: Design principles you know from Inf2C-SE Going
CS 160: Evaluation. Outline. Outline. Iterative Design. Preparing for a User Test. User Test
 CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 2/15/2006 2 Iterative Design Prototype low-fi paper, DENIM Design task analysis contextual inquiry scenarios sketching 2/15/2006 3 Evaluate
CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 2/15/2006 2 Iterative Design Prototype low-fi paper, DENIM Design task analysis contextual inquiry scenarios sketching 2/15/2006 3 Evaluate
CS 160: Evaluation. Professor John Canny Spring /15/2006 1
 CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 Outline User testing process Severity and Cost ratings Discount usability methods Heuristic evaluation HE vs. user testing 2/15/2006 2 Outline
CS 160: Evaluation Professor John Canny Spring 2006 2/15/2006 1 Outline User testing process Severity and Cost ratings Discount usability methods Heuristic evaluation HE vs. user testing 2/15/2006 2 Outline
DITA for Enterprise Business Documents Sub-committee Proposal Background Why an Enterprise Business Documents Sub committee
 DITA for Enterprise Business Documents Sub-committee Proposal Background Why an Enterprise Business Documents Sub committee Documents initiate and record business change. It is easy to map some business
DITA for Enterprise Business Documents Sub-committee Proposal Background Why an Enterprise Business Documents Sub committee Documents initiate and record business change. It is easy to map some business
Proofwriting Checklist
 CS103 Winter 2019 Proofwriting Checklist Cynthia Lee Keith Schwarz Over the years, we ve found many common proofwriting errors that can easily be spotted once you know how to look for them. In this handout,
CS103 Winter 2019 Proofwriting Checklist Cynthia Lee Keith Schwarz Over the years, we ve found many common proofwriting errors that can easily be spotted once you know how to look for them. In this handout,
Read & Download (PDF Kindle) Data Structures And Other Objects Using Java (4th Edition)
 Read & Download (PDF Kindle) Data Structures And Other Objects Using Java (4th Edition) Data Structures and Other Objects Using Java is a gradual, "just-in-time" introduction to Data Structures for a CS2
Read & Download (PDF Kindle) Data Structures And Other Objects Using Java (4th Edition) Data Structures and Other Objects Using Java is a gradual, "just-in-time" introduction to Data Structures for a CS2
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Why I Am Writing This: Why I am I writing a set of tutorials on compilers and how to build them? Well, the idea goes back several years ago when Rapid-Q, one of the best free BASIC
Chapter 1 Introduction Why I Am Writing This: Why I am I writing a set of tutorials on compilers and how to build them? Well, the idea goes back several years ago when Rapid-Q, one of the best free BASIC
DDD and BDD. Dan North ThoughtWorks
 DDD and BDD Dan North ThoughtWorks BDD and DDD Dan North ThoughtWorks What is Domain Driven Design? It s about focusing on the domain and letting it affect the software very much - Jimmy Nilsson (ADDDP)
DDD and BDD Dan North ThoughtWorks BDD and DDD Dan North ThoughtWorks What is Domain Driven Design? It s about focusing on the domain and letting it affect the software very much - Jimmy Nilsson (ADDDP)
INFORMATION RETRIEVAL AND THE THESAURUS R.M. Needham T. Joyce Cambridge Language Research Unit.
 Introduction INFORMATION RETRIEVAL AND THE THESAURUS R.M. Needham T. Joyce Cambridge Language Research Unit. This paper describes various developments of the retrieval system devised in Cambridge last
Introduction INFORMATION RETRIEVAL AND THE THESAURUS R.M. Needham T. Joyce Cambridge Language Research Unit. This paper describes various developments of the retrieval system devised in Cambridge last
Data Structures And Other Objects Using Java Download Free (EPUB, PDF)
 Data Structures And Other Objects Using Java Download Free (EPUB, PDF) This is the ebook of the printed book and may not include any media, website access codes, or print supplements that may come packaged
Data Structures And Other Objects Using Java Download Free (EPUB, PDF) This is the ebook of the printed book and may not include any media, website access codes, or print supplements that may come packaged
1 Achieving IND-CPA security
 ISA 562: Information Security, Theory and Practice Lecture 2 1 Achieving IND-CPA security 1.1 Pseudorandom numbers, and stateful encryption As we saw last time, the OTP is perfectly secure, but it forces
ISA 562: Information Security, Theory and Practice Lecture 2 1 Achieving IND-CPA security 1.1 Pseudorandom numbers, and stateful encryption As we saw last time, the OTP is perfectly secure, but it forces
Who we are: Kristin Martin, Metadata Librarian, Catalog Department Peter Hepburn, Digitization Librarian, Digital Programs Department
 Introduction Who we are: Kristin Martin, Metadata Librarian, Catalog Department Peter Hepburn, Digitization Librarian, Digital Programs Department Many of the images in this presentation come from the
Introduction Who we are: Kristin Martin, Metadata Librarian, Catalog Department Peter Hepburn, Digitization Librarian, Digital Programs Department Many of the images in this presentation come from the
(Refer Slide Time 6:48)
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 8 Karnaugh Map Minimization using Maxterms We have been taking about
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 8 Karnaugh Map Minimization using Maxterms We have been taking about
Requirements. Requirements. Types of Requirement. What Is a Requirement?
 Beatrice Åkerblom beatrice@dsv.su.se Everything else in software development depends on the requirements. If you cannot get stable requirements you cannot get a predictable plan... What Is a Requirement?!
Beatrice Åkerblom beatrice@dsv.su.se Everything else in software development depends on the requirements. If you cannot get stable requirements you cannot get a predictable plan... What Is a Requirement?!
Domain Driven Design IS. An architectural methodology for evolving a software system that closely aligns to business requirements
 Domain Driven Design IS An architectural methodology for evolving a software system that closely aligns to business requirements Domain Driven Design IS Domain First Focus on the Object Model Focus on
Domain Driven Design IS An architectural methodology for evolving a software system that closely aligns to business requirements Domain Driven Design IS Domain First Focus on the Object Model Focus on
DESIGN AS RISK MINIMIZATION
 THOMAS LATOZA SWE 621 FALL 2018 DESIGN AS RISK MINIMIZATION IN CLASS EXERCISE As you come in and take a seat What were the most important risks you faced in a recent software project? WHAT IS A RISK? WHAT
THOMAS LATOZA SWE 621 FALL 2018 DESIGN AS RISK MINIMIZATION IN CLASS EXERCISE As you come in and take a seat What were the most important risks you faced in a recent software project? WHAT IS A RISK? WHAT
INTRODUCTION. 2. User-centred interface design.
 INTRODUCTION 2. User-centred interface design User-Centred Design ISO 9241-210 : Human-centred design for interactive systems Meets requirements Plan the user centred process 4. Evaluation against requirements
INTRODUCTION 2. User-centred interface design User-Centred Design ISO 9241-210 : Human-centred design for interactive systems Meets requirements Plan the user centred process 4. Evaluation against requirements
1: Introduction to Object (1)
 1: Introduction to Object (1) 김동원 2003.01.20 Overview (1) The progress of abstraction Smalltalk Class & Object Interface The hidden implementation Reusing the implementation Inheritance: Reusing the interface
1: Introduction to Object (1) 김동원 2003.01.20 Overview (1) The progress of abstraction Smalltalk Class & Object Interface The hidden implementation Reusing the implementation Inheritance: Reusing the interface
Credit where Credit is Due. Lecture 29: Test-Driven Development. Test-Driven Development. Goals for this lecture
 Lecture 29: Test-Driven Development Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI 6448 - Spring Semester, 2003 Credit where Credit is Due Some of the material for this lecture is taken from
Lecture 29: Test-Driven Development Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI 6448 - Spring Semester, 2003 Credit where Credit is Due Some of the material for this lecture is taken from
Introduction to Programming
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Programming Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. This method of telling a story is as good today as it was when the King of Hearts prescribed
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Programming Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. This method of telling a story is as good today as it was when the King of Hearts prescribed
Federal Plain Language Guidelines
 Federal Plain Language Guidelines March 2011 Revision 1, May 2011 Table of Contents Introduction... i Revision 1 Changes... ii Table of Contents... iii I. Think about your audience... 1 a. Identify and
Federal Plain Language Guidelines March 2011 Revision 1, May 2011 Table of Contents Introduction... i Revision 1 Changes... ii Table of Contents... iii I. Think about your audience... 1 a. Identify and
Topic C. Communicating the Precision of Measured Numbers
 Topic C. Communicating the Precision of Measured Numbers C. page 1 of 14 Topic C. Communicating the Precision of Measured Numbers This topic includes Section 1. Reporting measurements Section 2. Rounding
Topic C. Communicating the Precision of Measured Numbers C. page 1 of 14 Topic C. Communicating the Precision of Measured Numbers This topic includes Section 1. Reporting measurements Section 2. Rounding
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique. Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design
 Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Scenarios, Storyboards, Wireframes, Critique Jon Kolko Professor, Austin Center for Design Scenarios Creating a written story that explains how a person will use a product, service, or system to achieve
Systems software design
 Systems software design Methods of system analysis and design Who are we? Krzysztof Kąkol Software Developer PGS Software S.A. Jarosław Świniarski Software Developer PGS Software S.A. Presentation based
Systems software design Methods of system analysis and design Who are we? Krzysztof Kąkol Software Developer PGS Software S.A. Jarosław Świniarski Software Developer PGS Software S.A. Presentation based
Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a
 Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a heuristic evaluation and ending with How to rate severity.
Additional reading for this lecture: Heuristic Evaluation by Jakob Nielsen. Read the first four bulleted articles, starting with How to conduct a heuristic evaluation and ending with How to rate severity.
CSCI 403: Databases 13 - Functional Dependencies and Normalization
 CSCI 403: Databases 13 - Functional Dependencies and Normalization Introduction The point of this lecture material is to discuss some objective measures of the goodness of a database schema. The method
CSCI 403: Databases 13 - Functional Dependencies and Normalization Introduction The point of this lecture material is to discuss some objective measures of the goodness of a database schema. The method
Heuristic Evaluation of Team Betamax
 Heuristic Evaluation of Team Betamax Eric Gallimore Connor Riley Becky Scholl Chris Stone November 4, 2006 Overview Evaluation Let s just state for the record that we like this a whole lot better than
Heuristic Evaluation of Team Betamax Eric Gallimore Connor Riley Becky Scholl Chris Stone November 4, 2006 Overview Evaluation Let s just state for the record that we like this a whole lot better than
GUI Design Principles
 GUI Design Principles User Interfaces Are Hard to Design You are not the user Most software engineering is about communicating with other programmers UI is about communicating with users The user is always
GUI Design Principles User Interfaces Are Hard to Design You are not the user Most software engineering is about communicating with other programmers UI is about communicating with users The user is always
Virtualization. Q&A with an industry leader. Virtualization is rapidly becoming a fact of life for agency executives,
 Virtualization Q&A with an industry leader Virtualization is rapidly becoming a fact of life for agency executives, as the basis for data center consolidation and cloud computing and, increasingly, as
Virtualization Q&A with an industry leader Virtualization is rapidly becoming a fact of life for agency executives, as the basis for data center consolidation and cloud computing and, increasingly, as
CS519: Computer Networks. Lecture 2, part 2: Feb 4, 2004 IP (Internet Protocol)
 : Computer Networks Lecture 2, part 2: Feb 4, 2004 IP (Internet Protocol) More ICMP messages These were added over time RFC1191: Path MTU Discovery Added the size of the limiting MTU to the ICMP Packet
: Computer Networks Lecture 2, part 2: Feb 4, 2004 IP (Internet Protocol) More ICMP messages These were added over time RFC1191: Path MTU Discovery Added the size of the limiting MTU to the ICMP Packet
Practical Object-Oriented Design in Ruby
 Practical Object-Oriented Design in Ruby Anyone that has done a decent amount of programming in Ruby is bound hear about the book Practical Object-Oriented Design in Ruby [1] (http://www.poodr.com/) by
Practical Object-Oriented Design in Ruby Anyone that has done a decent amount of programming in Ruby is bound hear about the book Practical Object-Oriented Design in Ruby [1] (http://www.poodr.com/) by
CSCI 1100L: Topics in Computing Lab Lab 11: Programming with Scratch
 CSCI 1100L: Topics in Computing Lab Lab 11: Programming with Scratch Purpose: We will take a look at programming this week using a language called Scratch. Scratch is a programming language that was developed
CSCI 1100L: Topics in Computing Lab Lab 11: Programming with Scratch Purpose: We will take a look at programming this week using a language called Scratch. Scratch is a programming language that was developed
Lecture 10 Notes Linked Lists
 Lecture 10 Notes Linked Lists 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons, André Platzer 1 Introduction In this lecture we discuss the use of linked lists to
Lecture 10 Notes Linked Lists 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons, André Platzer 1 Introduction In this lecture we discuss the use of linked lists to
(Refer Slide Time 3:31)
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 5 Logic Simplification In the last lecture we talked about logic functions
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 5 Logic Simplification In the last lecture we talked about logic functions
Object Persistence Design Guidelines
 Object Persistence Design Guidelines Motivation Design guideline supports architects and developers in design and development issues of binding object-oriented applications to data sources The major task
Object Persistence Design Guidelines Motivation Design guideline supports architects and developers in design and development issues of binding object-oriented applications to data sources The major task
Usability Inspection Report of NCSTRL
 Usability Inspection Report of NCSTRL (Networked Computer Science Technical Report Library) www.ncstrl.org NSDL Evaluation Project - Related to efforts at Virginia Tech Dr. H. Rex Hartson Priya Shivakumar
Usability Inspection Report of NCSTRL (Networked Computer Science Technical Report Library) www.ncstrl.org NSDL Evaluation Project - Related to efforts at Virginia Tech Dr. H. Rex Hartson Priya Shivakumar
Design Heuristics and Evaluation
 Design Heuristics and Evaluation Rapid Evaluation Selected material from The UX Book, Hartson & Pyla Heuristic Evaluation Another method for finding usability problems in a UI design Validation during
Design Heuristics and Evaluation Rapid Evaluation Selected material from The UX Book, Hartson & Pyla Heuristic Evaluation Another method for finding usability problems in a UI design Validation during
monolith to micro-services? event sourcing can help Doug
 monolith to micro-services? event sourcing can help Doug legacy Client Culture Amp (2012-2015) Rails App (Murmur) Read-write Query Server Read-only DB Our journey Our meandering path to CQRS & event sourcing
monolith to micro-services? event sourcing can help Doug legacy Client Culture Amp (2012-2015) Rails App (Murmur) Read-write Query Server Read-only DB Our journey Our meandering path to CQRS & event sourcing
PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between
 MITOCW Lecture 10A [MUSIC PLAYING] PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between all these high-level languages like Lisp and the query
MITOCW Lecture 10A [MUSIC PLAYING] PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between all these high-level languages like Lisp and the query
The Specification Phase
 The Specification Phase CS427: Elements of Software Engineering Lecture 4.1 10am, 30 Jan 2012 CS427 The Specification Phase 1/16 Outline 1 Recall... The Requirements Phase 2 Phase 2: Specifications 3 Requirements
The Specification Phase CS427: Elements of Software Engineering Lecture 4.1 10am, 30 Jan 2012 CS427 The Specification Phase 1/16 Outline 1 Recall... The Requirements Phase 2 Phase 2: Specifications 3 Requirements
CSE 440: Introduction to HCI User Interface Design, Prototyping, and Evaluation
 CSE 440: Introduction to HCI User Interface Design, Prototyping, and Evaluation Lecture 11: Inspection Tuesday / Thursday 12:00 to 1:20 James Fogarty Kailey Chan Dhruv Jain Nigini Oliveira Chris Seeds
CSE 440: Introduction to HCI User Interface Design, Prototyping, and Evaluation Lecture 11: Inspection Tuesday / Thursday 12:00 to 1:20 James Fogarty Kailey Chan Dhruv Jain Nigini Oliveira Chris Seeds
 1 of 5 3/28/2010 8:01 AM Unit Testing Notes Home Class Info Links Lectures Newsgroup Assignmen [Jump to Writing Clear Tests, What about Private Functions?] Testing The typical approach to testing code
1 of 5 3/28/2010 8:01 AM Unit Testing Notes Home Class Info Links Lectures Newsgroup Assignmen [Jump to Writing Clear Tests, What about Private Functions?] Testing The typical approach to testing code
Graph Theory. 26 March Graph Theory 26 March /29
 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
Graph Theory 26 March 2012 Graph Theory 26 March 2012 1/29 Graph theory was invented by a mathematician named Euler in the 18th century. We will see some of the problems which motivated its study. However,
(Refer Slide Time: 06:01)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 28 Applications of DFS Today we are going to be talking about
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 28 Applications of DFS Today we are going to be talking about
A function is a named piece of code that performs a specific task. Sometimes functions are called methods, procedures, or subroutines (like in LC-3).
 CIT Intro to Computer Systems Lecture # (//) Functions As you probably know from your other programming courses, a key part of any modern programming language is the ability to create separate functions
CIT Intro to Computer Systems Lecture # (//) Functions As you probably know from your other programming courses, a key part of any modern programming language is the ability to create separate functions
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java
 Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes Lecture 5 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes Lecture 5 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical
Overview of Sentence Order Reference Document Development Process
 Overview of Sentence Order Reference Document Development Process Scott Came Justice Integration Solutions, Inc. September 14, 2004 Purpose The purpose of this document is to outline the process/methodology
Overview of Sentence Order Reference Document Development Process Scott Came Justice Integration Solutions, Inc. September 14, 2004 Purpose The purpose of this document is to outline the process/methodology
3 Continuous Integration 3. Automated system finding bugs is better than people
 This presentation is based upon a 3 day course I took from Jared Richardson. The examples and most of the tools presented are Java-centric, but there are equivalent tools for other languages or you can
This presentation is based upon a 3 day course I took from Jared Richardson. The examples and most of the tools presented are Java-centric, but there are equivalent tools for other languages or you can
4.7 Approximate Integration
 4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
What You Don t Know Will Haunt You.
 Comprehensive Consulting Solutions, Inc. Business Savvy. IT Smart. Joint Application Design (JAD) A Case Study White Paper Published: June 2002 (with revisions) What You Don t Know Will Haunt You. Contents
Comprehensive Consulting Solutions, Inc. Business Savvy. IT Smart. Joint Application Design (JAD) A Case Study White Paper Published: June 2002 (with revisions) What You Don t Know Will Haunt You. Contents
Engineering Mechanics Prof. Siva Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Statics - 4.3
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. Siva Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Statics - 4.3 In this case let s say delta B and delta C are the kinematically consistent displacements.
Engineering Mechanics Prof. Siva Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Statics - 4.3 In this case let s say delta B and delta C are the kinematically consistent displacements.
CS519: Computer Networks
 : Computer Networks Lecture 2, part 2: Feb 4, 2004 IP (Internet Protocol) More ICMP messages These were added over time RFC1191: Path MTU Discovery Added the size of the limiting MTU to the ICMP Packet
: Computer Networks Lecture 2, part 2: Feb 4, 2004 IP (Internet Protocol) More ICMP messages These were added over time RFC1191: Path MTU Discovery Added the size of the limiting MTU to the ICMP Packet
CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic
 CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic John Magee 25 January 2017 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett Some slides credit Aaron Stevens 1 Overview/Questions What did
CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic John Magee 25 January 2017 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett Some slides credit Aaron Stevens 1 Overview/Questions What did
Cassandra Platform - A Case Study
 Cassandra Platform - A Case Study * Disclaimer: This is meant to be a short, high level overview of some of my contributions for the Cassandra project. ***This project is currently under development and
Cassandra Platform - A Case Study * Disclaimer: This is meant to be a short, high level overview of some of my contributions for the Cassandra project. ***This project is currently under development and
Participants. Results & Recommendations. Summary of Findings from User Study Round 3. Overall. Dashboard
 Summary of Findings from User Study Round 3 Participants 6 people total 4 Product users Jay Nicole Chris Nic 2 Non Product users Karine (QB ProAdvisor) Ellen (pilot test) Results & Recommendations Overall
Summary of Findings from User Study Round 3 Participants 6 people total 4 Product users Jay Nicole Chris Nic 2 Non Product users Karine (QB ProAdvisor) Ellen (pilot test) Results & Recommendations Overall
Foundations, Reasoning About Algorithms, and Design By Contract CMPSC 122
 Foundations, Reasoning About Algorithms, and Design By Contract CMPSC 122 I. Logic 101 In logic, a statement or proposition is a sentence that can either be true or false. A predicate is a sentence in
Foundations, Reasoning About Algorithms, and Design By Contract CMPSC 122 I. Logic 101 In logic, a statement or proposition is a sentence that can either be true or false. A predicate is a sentence in
Kuratowski Notes , Fall 2005, Prof. Peter Shor Revised Fall 2007
 Kuratowski Notes 8.30, Fall 005, Prof. Peter Shor Revised Fall 007 Unfortunately, the OCW notes on Kuratowski s theorem seem to have several things substantially wrong with the proof, and the notes from
Kuratowski Notes 8.30, Fall 005, Prof. Peter Shor Revised Fall 007 Unfortunately, the OCW notes on Kuratowski s theorem seem to have several things substantially wrong with the proof, and the notes from
Software Development Methodologies
 Software Development Methodologies Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 8 Agile Methodologies: XP 1 extreme Programming (XP) Developed by Beck in 1996. The first authentic XP book appeared in 1999, with a revised
Software Development Methodologies Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 8 Agile Methodologies: XP 1 extreme Programming (XP) Developed by Beck in 1996. The first authentic XP book appeared in 1999, with a revised
Domain Analysis. SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering. Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology.
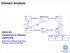 Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Extension Web Publishing 3 Lecture # 1. Chapter 6 Site Types and Architectures
 Chapter 6 Site Types and Architectures Site Types Definition: A public Web site, an Internet Web site, an external Web site or simply a Web site is one that is not explicitly restricted to a particular
Chapter 6 Site Types and Architectures Site Types Definition: A public Web site, an Internet Web site, an external Web site or simply a Web site is one that is not explicitly restricted to a particular
Professor Hausi A. Müller PhD PEng FCAE Department of Computer Science Faculty of Engineering University of Victoria
 Professor Hausi A. Müller PhD PEng FCAE Department of Computer Science Faculty of Engineering University of Victoria http://www.engr.uvic.ca/~seng321/ https://courses1.csc.uvic.ca/courses/201/spring/seng/321
Professor Hausi A. Müller PhD PEng FCAE Department of Computer Science Faculty of Engineering University of Victoria http://www.engr.uvic.ca/~seng321/ https://courses1.csc.uvic.ca/courses/201/spring/seng/321
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi.
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 18 Tries Today we are going to be talking about another data
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 18 Tries Today we are going to be talking about another data
SFU CMPT week 11
 SFU CMPT-363 2004-2 week 11 Manuel Zahariev E-mail: manuelz@cs.sfu.ca Based on course material from Arthur Kirkpatrick, Alissa Antle and Paul Hibbits July 21, 2004 1 Analytic Methods Advantages can be
SFU CMPT-363 2004-2 week 11 Manuel Zahariev E-mail: manuelz@cs.sfu.ca Based on course material from Arthur Kirkpatrick, Alissa Antle and Paul Hibbits July 21, 2004 1 Analytic Methods Advantages can be
XP: Planning, coding and testing. Practice Planning game. Release Planning. User stories. Annika Silvervarg
 XP: Planning, coding and testing Annika Silvervarg Practice Planning game Goal: schedule the most important tasks Which features to implement in what order Supports: simple design, acceptance testing,
XP: Planning, coding and testing Annika Silvervarg Practice Planning game Goal: schedule the most important tasks Which features to implement in what order Supports: simple design, acceptance testing,
Chapter 4 Objectives
 Chapter 4 Objectives Eliciting requirements from the customers Modeling requirements Reviewing requirements to ensure their quality Documenting requirements for use by the design and test teams 4.1 The
Chapter 4 Objectives Eliciting requirements from the customers Modeling requirements Reviewing requirements to ensure their quality Documenting requirements for use by the design and test teams 4.1 The
CO328- Human Computer Interaction Michael Kölling Caroline Li. Heuristic Evaluation
 CO328- Human Computer Interaction Michael Kölling Caroline Li Heuristic Evaluation Signage: What does this tells you? - History, what went earlier there before - Tells you more about a problematic situation
CO328- Human Computer Interaction Michael Kölling Caroline Li Heuristic Evaluation Signage: What does this tells you? - History, what went earlier there before - Tells you more about a problematic situation
Dealing with Bugs. Kenneth M. Anderson University of Colorado, Boulder CSCI 5828 Lecture 27 04/21/2009
 Dealing with Bugs Kenneth M. Anderson University of Colorado, Boulder CSCI 5828 Lecture 27 04/21/2009 University of Colorado, 2009 1 Goals 2 Review material from Chapter 11 of Pilone & Miles Dealing with
Dealing with Bugs Kenneth M. Anderson University of Colorado, Boulder CSCI 5828 Lecture 27 04/21/2009 University of Colorado, 2009 1 Goals 2 Review material from Chapter 11 of Pilone & Miles Dealing with
Introduction to Assurance
 Introduction to Assurance Overview Why assurance? Trust and assurance Life cycle and assurance April 1, 2015 Slide #1 Overview Trust Problems from lack of assurance Types of assurance Life cycle and assurance
Introduction to Assurance Overview Why assurance? Trust and assurance Life cycle and assurance April 1, 2015 Slide #1 Overview Trust Problems from lack of assurance Types of assurance Life cycle and assurance
Usability Testing Review
 Usability Testing Summary Usability Testing Review Alexis Anand, Katrina Ezis, Ma Shixuan, Cynthia Zhang CSE 440 Section AD All of our usability tests were conducted with students from Computer Science
Usability Testing Summary Usability Testing Review Alexis Anand, Katrina Ezis, Ma Shixuan, Cynthia Zhang CSE 440 Section AD All of our usability tests were conducted with students from Computer Science
WORKING IN TEAMS WITH CASECOMPLETE AND THE CASECOMPLETE PROJECT SHARING ADDIN. Contents
 WORKING IN TEAMS WITH CASECOMPLETE AND THE CASECOMPLETE PROJECT SHARING ADDIN Contents Working in Teams with CaseComplete... 2 Need an introduction to how version control works?... 2 Exclusive Checkout...
WORKING IN TEAMS WITH CASECOMPLETE AND THE CASECOMPLETE PROJECT SHARING ADDIN Contents Working in Teams with CaseComplete... 2 Need an introduction to how version control works?... 2 Exclusive Checkout...
EVALUATION ASSIGNMENT 2
 EVALUATION ASSIGNMENT 2 CS5760 Graduate Human-Computer Interaction Abstract An investigation of the user interface domain, heuristic principles, and critical usability concerns for the current design and
EVALUATION ASSIGNMENT 2 CS5760 Graduate Human-Computer Interaction Abstract An investigation of the user interface domain, heuristic principles, and critical usability concerns for the current design and
Automate Transform Analyze
 Competitive Intelligence 2.0 Turning the Web s Big Data into Big Insights Automate Transform Analyze Introduction Today, the web continues to grow at a dizzying pace. There are more than 1 billion websites
Competitive Intelligence 2.0 Turning the Web s Big Data into Big Insights Automate Transform Analyze Introduction Today, the web continues to grow at a dizzying pace. There are more than 1 billion websites
Credit where Credit is Due. Lecture 25: Refactoring. Goals for this lecture. Last Lecture
 Credit where Credit is Due Lecture 25: Refactoring Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI 6448 - Spring Semester, 2002 Some of the material for this lecture and lecture 26 is taken
Credit where Credit is Due Lecture 25: Refactoring Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI 6448 - Spring Semester, 2002 Some of the material for this lecture and lecture 26 is taken
Midterm Exam Solutions March 7, 2001 CS162 Operating Systems
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2001 Anthony D. Joseph Midterm Exam March 7, 2001 CS162 Operating Systems Your Name: SID AND 162 Login: TA:
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2001 Anthony D. Joseph Midterm Exam March 7, 2001 CS162 Operating Systems Your Name: SID AND 162 Login: TA:
Question #1: 1. The assigned readings use the phrase "Database Approach." In your own words, what is the essence of a database approach?
 Question #1: 1. The assigned readings use the phrase "Database Approach." In your own words, what is the essence of a database approach? Respondant: I understand the essence of "database approach" to be
Question #1: 1. The assigned readings use the phrase "Database Approach." In your own words, what is the essence of a database approach? Respondant: I understand the essence of "database approach" to be
3,500. The Developer Division at Microsoft
 3,500 The Developer Division at Microsoft 800 The VSTS team spread out across 40 feature teams Team Foundation Server (TFS) Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) Team Foundation Server (TFS) Visual Studio
3,500 The Developer Division at Microsoft 800 The VSTS team spread out across 40 feature teams Team Foundation Server (TFS) Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) Team Foundation Server (TFS) Visual Studio
The Crossed Swords wargame: Catching NATO red teams with cyber deception
 The Crossed Swords wargame: Catching NATO red teams with cyber deception 2015-2018 Cymmetria Inc. All rights reserved. 2 BACKSTORY Once a year, the pentesters* and red teams of the countries of NATO descend
The Crossed Swords wargame: Catching NATO red teams with cyber deception 2015-2018 Cymmetria Inc. All rights reserved. 2 BACKSTORY Once a year, the pentesters* and red teams of the countries of NATO descend
WHITE PAPER DATA DICATIONARY DEFINING AND USING A COMMON LANGUAGE
 DATA DICATIONARY DEFINING AND USING A COMMON LANGUAGE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 DEFINED 3 NEED FOR 3 USES OF 3 ANATOMY OF 4 BENEFITS OF USING 4 2 P a g e INTRODUCTION The success of any business
DATA DICATIONARY DEFINING AND USING A COMMON LANGUAGE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 DEFINED 3 NEED FOR 3 USES OF 3 ANATOMY OF 4 BENEFITS OF USING 4 2 P a g e INTRODUCTION The success of any business
DOWNLOAD PDF LEARN TO USE MICROSOFT ACCESS
 Chapter 1 : Microsoft Online IT Training Microsoft Learning Each video is between 15 to 20 minutes long. The first one covers the key concepts and principles that make Microsoft Access what it is, and
Chapter 1 : Microsoft Online IT Training Microsoft Learning Each video is between 15 to 20 minutes long. The first one covers the key concepts and principles that make Microsoft Access what it is, and
