(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
|
|
|
- Prosper Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 Bartz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR DETERMINING SEMANTICALLY RELATED TERMS (75) Inventors: Kevin Bartz, Cambridge, MA (US); Vijay Murthi, Glendale, CA (US); Shaji Sebastian, Pasadens, CA (US) Correspondence Address: BRINKSHOFER GILSON & LONE FYAHOO OVERTURE P.O. BOX CHICAGO, IL (US) (73) Assignee: YAHOO. Inc. (21) Appl. No.: 11/731,396 (22) Filed: Mar. 30, 2007 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. G06F 7/27 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /9 (57) ABSTRACT Systems and methods for determining semantically related terms are disclosed. Generally, a semantically related term tool receives a seed set and identifies a plurality of terms that constitute the seed set. For each term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies concept terms asso ciated with terms of the seed set other than the term being processed, joins the term being processed with each of the identified concept terms, and adds the resulting terms to a plurality of semantically related terms. The semantically related term tool removes invalid terms from the plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model and ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the plurality of semantically related terms based on a metric indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the plu rality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the set seed. 200 N Search Engine Online Advertisement Service Provider Ad Campaign Management System Semantically Related Term Tool
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 7 US 2008/ A Advertiser Advertiser Advertiser to- Advertisement Campaign Management System Website Provider Advertisement Service Provider Search Engine Internet User Internet User internet User 112 FIG. 1
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 7 US 2008/ A1 200-N Search Engine Online Advertisement Service Provider Ad Campaign Management System Semantically Related Term Tool FIG. 2
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 7 US 2008/ A Receive Seed Set 30 ldentify terms of seed set 306 ldentify concept terms that do not include term being processed Jointerms and concept terms, and add 308 resulting terms to plurality of Semantically related terms 31 Are there remaining terms to be processed? No Remove duplicate terms 316 Remove invalid terms based on a language model 318 Rank terms of plurality of semantically related terms 320 Export semantically related terms to ad campaign management system and/or ad provider 32 Export semantically related terms to internet search engine FIG. 3
5 Patent Application Publication Sheet 4 of 7 US 2008/ A Identify terms of seed set 406 Identify concept terms that do not include term being processed 408 C Create plurality of concept terms based on combination and/or permutations of identified concept terms Determine Combinations and/or 410 permutations of term and plurality of concept terms 1. Add resulting terms to plurality of 4. semantically related terms 414 Are there remaining terms to be processed? Yes No Remove Duplicate Terms 420 Remove invalid terms based on a language model 42 Rank terms of plurality of semantically related terms Export semantically related terms to ad campaign management system and/or ad provider Export semantically related terms to Internet search engine FIG. 4
6 Patent Application Publication Sheet 5 of 7 US 2008/ A1 500 N Search Engine Online Advertisement Service Provider Ad Campaign Management System Semantically Related Term Tool Geographic Location Module FIG. 5
7 Patent Application Publication Sheet 6 of 7 US 2008/ A ldentify terms of seed set ldentify explicit geographic locations in Seed Set 608 Strip explicit geographic locations from Seed Set 610 ldentify concept terms that do not include term being processed Join term and concept terms and add 61 resulting terms to first plurality of semantically related terms Are there remaining terms 614 to be processed? No Remove duplicate terms 620 Create Second plurality of semantically related terms based on explicit geographic locations and first plurality of semantically related terms 622 Remove invalid terms based on a language model Remove terms identifying different explicit geographic location Rank terms of plurality of semantically related terms Export semantically related terms to ad Campaign management System and/or ad provider Export semantically related terms to Internet search engine FIG. 6
8 Patent Application Publication Sheet 7 of 7 US 2008/ A Identify terms of seed set 706 identify explicit geographic locations in seed set 708 Strip explicit geographic locations from seed set 710 Identify concept terms that do not include term being processed 712 u-n Create plurality of concept terms based on combinations and/or permutations of identified concept terms 714. Determine combinations and/or permutations of term and plurality of concept terms 716/N Add resulting terms to first plurality of semantically related terms Arethere remaining terms to be 718 processed? Yes Remove Duplicate Terms Create Second plurality of Semantically related terms based on explicit geographic locations and first plurality of semantically related terms 726 Remove invalid terms based on a language model 728 Remove terms identifying different explicit geographic location Rank terms of plurality of semantically related terms 732 Export semantically related terms to ad campaign management system and/or ad provider 734 Export semantically related terms to Internet search engine FIG. 7
9 SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR DETERMINING SEMANTICALLY RELATED TERMS BACKGROUND When advertising using an online advertisement service provider such as Yahoo! Search MarketingTM, or per forming a search using an Internet search engine Such as Yahoo!TM, users often wish to determine semantically related terms. Two terms, such as words or phrases, are semantically related if the terms are related in meaning in a language or in logic. Obtaining semantically related terms allows advertis ers to broaden or focus their online advertisements to relevant potential customers and allows searchers to broaden or focus their Internet searches in order to obtain more relevant search results Various systems and methods for determining semantically related terms are disclosed in U.S. patent appli cation Ser. Nos. 11/432,266 and 11/ , filed May 11, 2006 and assigned to Yahoo! Inc. For example, in some imple mentations in accordance with U.S. patent application Ser. Nos. 11/ and 11/ , a system determines semantically related terms based on web pages that advertis ers have associated with various terms during interaction with an advertisement campaign management system of an online advertisement service provider. In other implementations in accordance with U.S. patent application Ser. Nos. 11/ and 11/ , a system determines semantically related terms based on terms received at a search engine and a num ber of times one or more searchers clicked on particular universal resource locators ( URLs ) after searching for the received terms Yet other systems and methods for determining semantically related terms are disclosed in U.S. patent appli cation Ser. No. 1 1/600,698, filed Nov. 16, 2006, and assigned to Yahoo! Inc. For example, in some implementations in accordance with U.S. patent application Ser. No. 1 1/600,698, a system determines semantically related terms based on sequences of search queries received at an Internet search engine that are related to similar concepts It would be desirable to develop additional systems and methods for determining semantically related terms based on other sources of data. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0005 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of one embodiment of an environment in which a system for determining semantically related terms may operate; 0006 FIG. 2 is a block diagram of one embodiment of a system for determining semantically related terms; 0007 FIG. 3 is a flow chart of one embodiment of a method for determining semantically related terms; 0008 FIG. 4 is a flow chart of another embodiment of a method for determining semantically related terms; 0009 FIG. 5 is a block diagram of another embodiment of a system for determining semantically related terms; 0010 FIG. 6 is a flow chart of another embodiment of a method for determining semantically related terms; and 0011 FIG. 7 is a flow chart of another embodiment of a method for determining semantically related terms. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The present disclosure is directed to systems and methods for determining semantically related terms. An online advertisement service provider ( ad provider') may desire to determine semantically related terms to Suggest new terms to online advertisers so that the advertisers can better focus or expand delivery of advertisements to potential cus tomers. Similarly, a search engine may desire to determine semantically related terms to assist a searcher performing research at the search engine. Providing a searcher with semantically related terms allows the searcher to broaden or focus a search so that search engines provide more relevant search results to the searcher FIG. 1 is a block diagram of one embodiment of an environment in which a system for determining semantically related terms may operate. However, it should be appreciated that the systems and methods described below are not limited to use with a search engine or pay-for-placement online advertising The environment 100 may include a plurality of advertisers 102, an ad campaign management system 104, an ad provider 106, a search engine 108, a website provider 110. and a plurality of Internet users 112. Generally, an advertiser 102 bids on terms and creates one or more digital ads by interacting with the ad campaign management system 104 in communication with the ad provider 106. The advertisers 102 may purchase digital ads based on an auction model of buying ad space or a guaranteed delivery model by which an adver tiser pays a minimum cost-per-thousand impressions (i.e., CPM) to display the digital ad. Typically, the advertisers 102 may pay additional premiums for certain targeting options, Such as targeting by demographics, geography, technograph ics or context. The digital ad may be a graphical banner ad that appears on a website viewed by Internet users 112, a spon sored search listing that is served to an Internet user 112 in response to a search performed at a search engine, a video ad, a graphical banner ad based on a sponsored search listing, and/or any other type of online marketing media known in the art When an Internet user 112 performs a search at a search engine 108, thead provider 106 may serve one or more digital ads created using the ad campaign management sys tem 104 to the Internet user 112 based on search terms pro vided by the Internet user 112. Also, when an Internet user 112 views a website served by the website provider 110, the ad provider 106 may serve one or more digital ads to the Internet user 112 based onkeywords obtained from a website. When the digital ads are served, the ad campaign manage ment system 104 and the ad provider 106 may record and process information associated with the served digital ads for purposes such as billing, reporting, or ad campaign optimi Zation. For example, the ad campaign management system 104 and ad provider 106 may record the search terms that caused the ad provider 106 to serve the digital ads; whether the Internet user 112 clicked on a URL associated with the served digital ads; what additional digital ads the ad provider 106 served with the digital ad; a rank or position of a digital ad when the Internet user 112 clicked on the digital ad; and/or whether an Internet user 112 clicked on a URL associated with a different digital ad. One example of an ad campaign management system that may perform these types of actions is disclosed in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 1 1/413,514, filed Apr. 28, 2006, and assigned to Yahoo! Inc. It will be appreciated that the systems and methods for determining semantically related terms described below may operate in the environment of FIG. 1.
10 0016 FIG. 2 is a block diagram of one embodiment of a system for determining semantically related terms. The sys tem 200 may include a search engine 202, an ad provider 204, an advertisement campaign management system 206, and a semantically related term tool 208. In some implementations the semantically related term tool 208 may be part of the search engine 202, the ad provider 204, or the ad campaign management system 206, but in other implementations the semantically related term tool 208 is distinct from the search engine 202, the ad provider 204, and the ad campaign man agement system 206. The search engine 202, ad provider 204, ad campaign management system 206, and semantically related term tool 208 may communicate with each other over one or more external or internal networks. Further, the search engine 202, ad provider 204, ad campaign management sys tem 206, and semantically related term tool 208 may be implemented as Software code running in conjunction with a processor Such as a single server, a plurality of servers, or any other type of computing device known in the art As described in more detail below, the search engine 202, the ad provider 204, or the ad campaign management system 206 receives a seed set including two or more terms, each of which may include one or more words or phrases. Generally, the seed set represents the types of terms for which the user or system submitting the seed set would like to receive additional terms having a similar meaning in logic or in a language. The semantically related term tool 208 identi fies each term of the seed set. The semantically related term tool 208 then determines a plurality of semantically related terms based on concept terms within the seed set. A concept term refers to a term or phrase that when split apart loses its meaning. For example, with respect to the term New York Pizza, the concepts within the term are New York, "pizza and New York Pizza'. Breaking the term New York into New, or York. makes the term lose its meaning. The semantically related term tool 208 removes any invalid terms from the determined plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model. For example, the semantically related term tool 208 may remove each term from the plural ity of semantically related terms that is associated with a search volume below a predetermined threshold. The seman tically related term tool 208 then ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the plurality of semantically related terms to determine one or more terms that are closely related to one or more terms of the seed set. Two methods for determining terms semantically related to a seed set are described below with respect to FIGS. 3 and FIG.3 illustrates a flow chart for one embodiment of a method for determining terms semantically related to a seed set by joining terms of the seed set with concept terms within the seed set. The method 300 begins with a search engine, an ad provider, oranadcampaign management system receiving a seed set at step 302. The seed set may be a search query Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user, a series of search queries Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user that are related to similar concepts, a bidded phrase Submitted by an advertiser interacting with an advertisement campaign management system of an ad provider, a keyword received from a website provider with an ad request, or any other set of terms Submitted to a search engine, an ad provider, or an ad campaign management system. The seed set com prises two or more terms, each of which may include one or more words or phrases. For example, a search engine oranad provider may receive a seed set N.Y. pizza, fast delivery, cheap delivery including a first term N.Y. pizza, a second term fast delivery, and a third term cheap delivery The semantically related term tool identifies the terms that constitute the seed set at step 304. In some imple mentations, the semantically related term tool may identify terms of the seed set based on punctuation Such as commas within the seed set, where in other implementations the semantically related term tool may identify terms of the seed set based on spaces within the seed set. Examples of systems and methods for determining terms that constitute a seed set are described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/713,576 (now U.S. Pat. No. 7,051,023), filed Nov. 12, 2003 and assigned to Yahoo! Inc After identifying the terms that constitute the seed set, the semantically related term tool processes the terms of the seed set. Generally, for each term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies concept terms of the seed set not including the term being processed and joins the term being processed with the identified concept terms For a first term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies concept terms of the seed set that do not include the first term at step 306. Examples of systems and methods for identifying concept terms from a seed set are described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/713,576 (now U.S. Pat. No. 7,051,023), filed Nov. 12, 2003 and assigned to Yahoo! Inc For example, when processing the term N.Y. pizza of the seed set N.Y. pizza, fast delivery, cheap deliv ery, the semantically related term tool identifies the concept terms associated with the second term fast delivery and the concept terms associated with the third term cheap delivery. The semantically related term tool determines the second term fast delivery' includes the concept terms fast, deliv ery, and fast delivery. Similarly, the semantically related term tool determines the third term cheap delivery' includes the concept terms cheap. delivery, and cheap delivery. Thus, the semantically related term tool identifies the concept terms of the seed set not including the term N.Y. pizza' as fast, delivery, fast delivery, cheap, and cheap deliv ery It will be appreciated that in some implementations, as part of identifying concept terms, the semantically related term tool may remove any duplicate concept terms. For example, when identifying the concept terms associated with the second term fast delivery and the third term cheap delivery, the semantically related term tool will identify the concept term delivery' associated with both the second term and the third term. However, the duplicate of the term deliv ery' may be removed so that, as described below, the term N.Y. pizza' is only joined with the term delivery' once At step 308, the semantically related term tool joins the first term with each of the concept terms identified at step 306 to create a plurality of semantically related terms. Con tinuing with the example above, the semantically related term tool may join the term N.Y. pizza' with each of the above listed concept terms to create a plurality of semantically related terms including the terms fast N.Y. pizza. N.Y. pizza delivery, N.Y. pizza fast delivery, cheap N.Y. pizza, and cheap N.Y. pizza delivery The semantically related term tool determines if there are any remaining terms of the seed set to be processed at step 310. If the semantically related term tool determines there are remaining terms to be processed (312), the method 300 loops to step 306 where the above-described steps are
11 repeated for the next term of the seed set. It will be appreci ated that for each term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies concept terms of the seed set that do not include the term being processed, joins the term being pro cessed with each of the identified concept terms, and adds the resulting combined terms to the plurality of semantically related terms. For example, continuing with the example above, the above-described steps would be repeated for the terms fast delivery and cheap delivery' to add additional terms to the plurality of semantically related terms Once the semantically related term tool determines all the terms of the seed set have been processed (314), the method 300 proceeds to step 315. In some implementations, at step 315, the semantically related term tool may remove any duplicate terms of the plurality of semantically related terms before proceeding to step 316. At step 316, the seman tically related term tool may remove invalid terms from the plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model. For example, the semantically related term tool may remove each term of the plurality of semantically related terms associated with a search volume below a threshold. Typically a search Volume is a number of times users have Submitted a term to an Internet search engine in a defined period of time. By removing terms from the plurality of semantically related terms associated with a low search Vol ume, the semantically related term tool removes terms that are likely invalid or meaningless After removing invalid terms such as terms associ ated with a low search volume, the semantically related term tool ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the plurality of semantically related terms at step 318. The semantically related term tool may rank the remaining terms of the plurality of semantically related terms based on one or more factors such as lexical features of a semantically related term, Such as an edit distance or word edit distance between the semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; a degree of search overlap between a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; advertiser attributes associated with a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set, such as bid price or advertiser depth; or any other metric that indicates a degree of seman tical relationship between a semantically related termandone or more terms of the seed set Generally, an edit distance, also known as Levensh tein distance, is the Smallest number of inserts, deletions, and Substitutions of characters needed to change a semantically related term into one or more terms of the seed set, and word edit distance is the Smallest number of insertions, deletions, and Substitutions of words needed to change a semantically related term into one or more terms of the seed set. A degree of search overlap between a semantically related termandone or more terms of the seed set is a degree of similarity of search results resulting from a search at an Internet search engine for a semantically related term and a search at the Internet search engine for one or more terms of the seed set In one implementation, after ranking the plurality of semantically related terms at step 318, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the plurality of semantically related terms to an ad campaign management system and/or an ad provider at step 320 for use in a keyword suggestion tool or for use in keyword expansion. In another implementation, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the plurality of semantically related terms to a search engine at step 322 for use in broadening or focusing searches FIG. 4 illustrates a flow chart of another embodi ment of a method for determining semantically related terms. The method 400 beings with a search engine, an ad provider, oran ad campaign management system receiving a seed set at step 402. As discussed above, the seed set includes two or more terms, each of which may include one or more words or phrases. The seed set may be a search query Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user, a series of search queries Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user related to similar concepts, a bidded phrase Submitted by an advertiser interacting with an advertisement campaign management system of an ad provider, a keyword received from a website provider with an ad request, or any other set of terms Submit ted to a search engine, an ad provider, or an ad campaign management System The semantically related term tool identifies the terms that constitute the seed set at step 404. After identifying the seed set, the semantically related term tool processes each term of the seed set. Generally, for each term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies concept terms of the seed set not including the term being processed, deter mines a plurality of concept terms based on combinations and permutations of the identified concept terms, determines combinations and permutations of the term being processed and the plurality of concept terms, and adds the resulting terms to a plurality of semantically related terms For a first term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies the concept terms of the seed set that do not include the first term at step 406. The semantically related term tool then creates a plurality of concept terms at step 408 based on possible combinations and/or permutations of the concept terms identified at step Continuing with the example above regarding the seed set N.Y. pizza, fast delivery, cheap delivery, when processing the term N.Y. pizza, the semantically related term tool identifies the concept terms of the seed set not including the term N.Y. pizza as fast, delivery, fast delivery. cheap and cheap delivery. The semantically related term tool then determines possible combinations and permutations of the above-listed concept terms to create a plurality of concept terms including the terms fast, deliv ery, fast delivery, cheap, cheap delivery, and fast cheap delivery. Thus, by determining possible combinations and permutations of the above-listed concept terms, the semantically related term tool discovers additional concept terms such as fast cheap delivery that are not identified in methods such as those described above with respect to FIG.3 because the term fast cheap delivery is not a concept term of any term of the seed set. It will be appreciated that as seed sets include more terms, or the number of words or phrases that make up the terms of the seed set increases, the size of the created plurality of concept terms may grow at a great rate. Accordingly, in some implementations, the semantically related term tool may limit the size of the created plurality of concept terms The semantically related term tool then determines possible combinations and permutations of the first term and the plurality of concept terms at step 410, and adds the result ing terms to a plurality of semantically related terms at step 412. Continuing with the example above, the semantically related term tool determines possible combinations and per mutations of the term N.Y. pizza' and the above-listed terms
12 of the plurality of concept terms, and adds resulting terms such as fast N.Y. pizza. N.Y. pizza delivery, N.Y. pizza fast delivery. cheap N.Y. pizza. N.Y. pizza cheap deliv ery, and N.Y. pizza fast cheap delivery' to the plurality of semantically related terms The semantically related term tool determines if there are any remaining terms of the seed set to be processed at step 414. If the semantically related term tool determines there are remaining terms to be processed (416), the method 400 loops to step 406 where the above-described steps are repeated for the next term of the seed set. It will be appreci ated that for each term of the seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies the concept terms of the seed that do not include the term being processed, determines possible com binations and permutations of the concept terms to create a plurality of concept terms, determines possible combinations and permutations of the term being processed and the deter mined plurality of concept terms, and adds the resulting terms to the plurality of semantically related terms. For example, continuing with the example above, the above-described steps would be repeated for the terms fast delivery and cheap delivery' to add additional terms to the plurality of semantically related terms Once the semantically related term tool determines all the terms of seed set have been processed (418), the method 400 proceeds to step 419. At step 419, the semanti cally related term tool may remove any duplicate term from the plurality of semantically related terms before proceeding to step 420. At step 420, the semantically related term tool may remove invalid terms from the plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model. For example, the semantically related term tool may remove terms from the plurality of semantically related term tool based on whether a search volume associated with a term is below a threshold as described above. The semantically related term tool then ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the plurality of semantically related term at Step 422 based on one or more factors such as lexical features of a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; a degree of search overlap between a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; advertiser attributes associated with a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; or any other metric that indicates a degree of a semantical relationship between a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set In one implementation, after ranking the plurality of semantically related terms at step 422, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the plurality of semantically related terms to an ad campaign management system and/or an ad provider at step 424 for use in a keyword Suggestion tool or for use in keyword expansion. In another implementation, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the plurality of semantically related terms to a search engine at step 426 for use in broadening or focusing searches When a seed set received at a search engine oranad provider includes an explicit geographic location, a semanti cally related term tool may desire to implement systems and methods to better determine terms semantically related to the seed set based on the explicit geographic location within the seed set. FIGS. 5-7 disclose systems and methods for deter mining semantically related terms based on an explicit geo graphic location within a received seed set FIG. 5 is a block diagram of another embodiment of a system for determining semantically related terms based on an explicit geographic location within a seed set. Like the system of FIG. 2, the system 500 may include a search engine 502, an ad provider 504, an ad campaign management system 506, and a semantically related term tool 508. The system may additionally include a geographic location module 510 in communication with the search engine 502, thead provider 504, the ad campaign management system 508, and/or the semantically related term tool 508 for determining whether a term identifies a geographic location. The geographic loca tion module 510 may be implemented as software code run ning in conjunction with a processor Such as a single server, a plurality of servers, or any other type of computing device known in the art As described in more detail below, the search engine 502, the ad provider 504, or the ad campaign management system 506 receives a seed set. The semantically related term tool 508 identifies two or more terms that constitute the seed set and communicates with the geographic location module 510 to determine if any of the terms of the seed set identify an explicit geographic location. The semantically related term tool 508 removes any explicit geographic locations from the terms of the seed set to create a stripped seed set and deter mines a first plurality of semantically related terms using the terms of the stripped seed set and methods such as those described above with respect to FIGS. 3 and 4. The semanti cally related term tool 508 then combines each explicit geo graphic location determined above with each term of the first plurality of semantically related terms to create a second plurality of semantically related terms. Invalid or meaning less terms are removed from the second plurality of semanti cally related terms based on factors such as a search Volume associated with each term of the second plurality of seman tically related terms or a different explicit geographic location identified in a term of the second plurality of semantically related terms. The semantically related term tool then ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms based on metrics indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the sec ond plurality of semantically terms and one or terms of the seed set FIG. 6 illustrates a flow chart of one embodiment of a method for determining semantically related terms based on explicit geographic locations identified in a seed set. The method 600 begins with a search engine or an ad provider receiving a seed set at Step 602. As discussed above, the seed set includes two or more terms, each of which includes one or more words or phrases. The seed set may be a search query Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user, a series of search queries Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user related to similar concepts, a bidded phrase submitted by an advertiser interacting with an advertisement campaign management system of an ad provider, a keyword received from a website provider with an ad request, or any other type of term Submitted to a search engine, an ad provider, or an ad campaign management System The semantically related term tool identifies terms of the seed set at step 604 and communicates with a geo graphic location module to determine whether one or more of the terms of the seed set identify an explicit geographic loca tion at step 606. Examples of systems and methods for deter mining whether a term identifies an explicit geographic loca tion are disclosed in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/680,
13 495, filed Oct. 7, 2003 and assigned to Yahoo! Inc. Generally, as described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/680,495, to determine if a term identifies an explicit geographic loca tion, the term is parsed into text including a name of a geo graphic location and text that does not include a name of a geographic location. The geographic location module then determines whether the term identifies an explicit geographic location based on factors such as one or more names of geographic locations in the term; whether for any of the names of geographic locations in the term, multiple geo graphic locations exist with the same name; relationships between any of the geographic locations named in the term; and relationships between the geographic locations named in the term and the text of the term that does not include a name of a geographic location It will be appreciated that the geographic location module does not indicate that a seed set identifies an explicit location when a geographic location within the seed set is used to describe a type of product. For example, for a term N.Y. pizza delivery, the geographic location module would not indicate that the term identifies an explicit geographic location because N.Y. is being used to describe a type of pizza. Conversely, for a term Dayton pizza delivery, the geographic location module indicates that the term identifies an explicit geographic location of "Dayton' because the geo graphic location is not being used to describe a type of pizza. At step 608, the semantically related term tool removes any explicit geographic locations determined at Step 606 from the terms of the seed set to create a stripped seed set After removing the geographic locations from the seed set, the semantically related term tool processes terms of the stripped seed set. For each term of the stripped seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies the concept terms of the stripped seed set that do not include the term being processed, joins the term being processed with each of the concept terms, and adds the resulting combined terms to a first plurality of semantically related terms For a first term of the stripped seed set, the seman tically related term tool identifies concept terms within the stripped seed set that do not include the first term at step 610. At step 612, the semantically related term tool then joins the first term with each of the concept terms identified at step 610 to create a first plurality of semantically related terms The semantically related term tool determines if there are any remaining terms of the stripped seed set to be processed at step 614. If the semantically related term tool determines there are remaining terms to be processed (616), the method 600 loops to step 610 where the above-described steps are repeated for the next term of the stripped seed set. Once the semantically related term tool determines each term of stripped seed set has been processed (618), the method 600 proceeds to step At step 619, the semantically related term tool may remove any duplicate terms of the first plurality of semanti cally related terms before proceeding to step 620. At step 620, the semantically related term tool joins each explicit geo graphic location determined at step 606 with each remaining term of the first plurality of semantically related terms to create a second plurality of semantically related terms. In Some implementations, creating the second plurality of semantically related terms may include inserting prepositions Such as in or at to join the geographic locations deter mined at step 606 with each term of the first plurality of semantically related terms. For example, when joining the term hotels' with the explicit geographic location Los Angeles, the semantically related term tool may insert the preposition in so that the resulting term is hotels in Los Angeles The semantically related term tool removes invalid terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model at step 622. For example, the semantically related term tool may remove each term of the second plurality of semantically related term associated with a search volume below a threshold at step 622. Additionally, at step 624 the semantically related term tool removes each term of the second plurality of semantically related terms associated with an explicit geographic location other than the geographic locations determined at step 606. In one imple mentation, the semantically related term tool communicates with the geographic location module to determine whether a term of the second plurality of semantically related terms identifies an explicit geographic location. If the term identi fies an explicit geographic location, the explicit geographic location identified in the term is compared to the explicit geographic locations determined at step 608. If the explicit geographic location identified in the term is not related to one of the explicit geographic locations determined at step 606, the term is removed from the second plurality of semantically related term. For example the terms Arlington Tex. tooth doctor and dentist' can create a second plurality of seman tically related terms that includes terms such as "Arlington dentist. While the term Arlington dentist is a valid term, the term likely refers to a dentist in Arlington, Va. rather than an intended dentist in Arlington, Tex. Therefore, the term "Arlington dentist identifies an explicit geographic location other than one of the explicit geographic locations originally identified in the terms. Thus, the term Arlington dentist' is removed The semantically related term tool ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms at step 626. The semantically related term tool may rank at least a portion of the remaining terms based on one or more factors such as lexical features associated with a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; a degree of search overlap between a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; advertiser attributes associated with a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; or any other metric that indicates a degree of a semantical relation ship between a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set In one implementation, after ranking the terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms at step 628, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms to an ad campaign management system and/or an ad providerat step 626 for use in a keyword Suggestion tool or for use in keyword expansion. In another implementation, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms to a search engine at step 628 for use in broad ening or focusing searches FIG. 7 is a flow chart of another embodiment of a method for determining semantically related terms based on explicit geographic locations identified in a seed set. The method 700 beings with a search engine, an ad provider, oran ad campaign management system receiving a seed set at step 702. As discussed above, the seed set includes two or more
14 terms, each of which may include one or more words or phrases. The seed set may be a search query Submitted to a search engine by an Internet user, a sequence of search que ries Submitted by an Internet user related to similar concepts, a bidded phrase submitted by an advertiser interacting with an advertisement campaign management system of an ad pro vider, a keyword received from a website provider with an ad request, or any other type of term Submitted to a search engine, an ad provider, or an ad campaign management Sys tem The semantically related term tool identifies the terms that comprise the seed set at step 704 and communi cates with a geographic location module to determine whether one or more of the terms of the seed set identify an explicit geographic location at step 706. At step 708, the semantically related term tool removes any explicit geo graphic locations determined at step 706 from the terms com prising the seed set to create a stripped seed set After removing the geographic locations from the seed set, the semantically related term tool processes the remaining terms of the stripped seed set. For each term of the stripped seed set, the semantically related term tool identifies concept terms of the stripped seed set that do not include the term being processed, determines possible combinations and permutations of the identified concept terms to create a plu rality of concept terms, determines possible combinations and permutations of the term being processed and the plural ity of concept terms, and adds the resulting terms to a first plurality of semantically related term For a first term of the stripped seed set, the seman tically related term tool identifies concept terms in the stripped seed set that do not include the first term at step 710 and determines possible combinations and permutations of the concept terms to create a plurality of concept terms at Step 712. The semantically related term tool then determines pos sible combinations and permutations of the first term and the plurality of concept terms at 714, and adds the resulting terms to a first plurality of semantically related terms at step The semantically related term tool determines if there are any remaining terms of the stripped seed set to be processed at step 718. If the semantically related term tool determines there are terms to be processed (720), the method 700 loops to step 710 where the above-described steps are repeated for the next term of the stripped seed set. Once the semantically related term tool determines there are no remaining terms to be processed (722), the method 700 pro ceeds to step At step 723, the semantically related term tool may remove any duplicate terms of the first plurality of semanti cally related terms before proceeding to step 724. At step 724, the semantically related term tool determines possible com binations and permutations of the explicit geographic loca tion determined at step 706 and the terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms to create a second plurality of semantically related terms. In some implementations, creat ing the second plurality of semantically related terms may include inserting prepositions such as in or at to join the geographic locations determined at step 706 with each term of the first plurality of semantically related terms The semantically related term tool removes invalid terms from the second plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model at step 726. For example, the semantically related term tool may remove each term of the second plurality of semantically related terms associated with a search volume below a threshold at step 726. Additionally, at step 728 the semantically related term tool removes each term of the second plurality of semantically related terms that identifies an explicit geographic location that is not related to the explicit geographic locations determined at step The semantically related term tool ranks at least a portion of the remaining terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms at step 730. The semantically related term tool may rank the remaining terms based on one or more factors such as lexical features associated with a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; a degree of search overlap between a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; advertiser attributes associated with a semantically related term and one or more terms of the seed set; or any other metric that indi cates a degree of semantical relationship between a semanti cally related term and one or more terms of the seed set In one implementation, after ranking the second plurality of semantically related terms at step 732, the seman tically related term tool may export one or more of the top ranked terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms to an ad campaign management system and/or an ad provider at step 734 for use in a keyword suggestion tool or for use in keyword expansion. In another implementation, the semantically related term tool may export one or more of the top-ranked terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms to a search engine at step 736 for use in broad ening or focusing searches It should be appreciated that because in FIG. 7, a semantically related term tool determines a plurality of con cept terms, a first plurality of semantically related terms, and a second plurality of semantically related terms based on possible combinations and permutations of different terms rather than a semantically related term tool joining terms to determine a first plurality of semantically related terms and a second plurality of semantically related terms such as described above with respect to FIG. 6, a semantically related term tool implementing methods such as those described with respect to FIG.7 may determine terms semantically related to a seed set that a semantically related term tool implementing methods such as those described with respect to FIG. 6 would not identify FIGS. 1-7 disclose systems and methods for deter mining terms semantically related to a seed set. As described above, these systems and methods may be implemented for uses Such as discovering semantically related words for pur poses of bidding on online advertisements or to assist a searcher performing research at an Internet search engine With respect to assisting a searcher performing research at an Internet search engine, a searcher may send one or more terms, or one or more sequences ofterms, to a search engine. The search engine may use the received terms as seed terms and Suggest semantically related words related to the terms either with the search results generated in response to the received terms, or independent of any search results. Providing the searcher with semantically related terms allows the searcher to broaden or focus any further searches so that the search engine provides more relevant search results to the searcher With respect to online advertisements, in addition to providing terms to an advertiserina keyword Suggestion tool, an online advertisement service provider may use the dis closed systems and methods in a campaign optimizer com ponent to determine semantically related terms to match
15 advertisements to terms received from a search engine or terms extracted from the content of a webpage or news articles, also known as content match. Using semantically related terms allows an online advertisement service provider to serve an advertisement if the term that an advertiser bids on is semantically related to a term sent to a search engine rather than only serving an advertisement when a term sent to a search engine exactly matches a term that an advertiser has bid on. Providing the ability to serve an advertisement based on Semantically related terms when authorized by an adver tiser provides increased relevance and efficiency to an adver tiser so that an advertiser does not need to determine every possible word combination for which the advertiser's adver tisement is served to a potential customer. Further, using semantically related terms allows an online advertisement service provider to Suggest more precise terms to an adver tiser by clustering terms related to an advertiser, and then expanding each individual concept based on Semantically related terms An online advertisement service provider may addi tionally use semantically related terms to map advertisements or search listings directly to a sequence of search queries received at an online advertisement service provider or a search engine. For example, an online advertisement service provider may determine terms that are semantically related to a seed set including two or more search queries in a sequence of search queries. The online advertisement service provider then uses the determined semantically related terms to map an advertisement or search listing to the sequence of search queries It is therefore intended that the foregoing detailed description be regarded as illustrative rather than limiting, and that it be understood that it is the following claims, including all equivalents, that are intended to define the spirit and scope of this invention. 1. A method for determining semantically related terms, the method comprising: identifying two or more terms of a seed set; identifying concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than a first term of the seed set; and joining the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first term. 2. The method of claim 1, further comprising: adding resulting terms of the joining of the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first term to a plurality of seman tically related terms; and ranking at least a portion of the plurality of semantically related terms based on a metric indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the plurality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 3. The method of claim 2, further comprising: removing each term from the plurality of semantically related terms associated with a search volume below a threshold. 4. The method of claim 2, further comprising: identifying concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than a second term of the seed set; joining the second term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first set; and adding resulting terms of the joining of the second term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the second term to the plurality of semantically related terms. 5. The method of claim 2, further comprising: providing at least one of the plurality of semantically related terms to a user based on the ranking of the plu rality of semantically related terms. 6. The method of claim 2, further comprising: exporting at least one of the plurality of semantically related terms to an Internet search engine based on the ranking of the plurality of semantically related terms. 7. The method of claim 2, further comprising: exporting at least one of the plurality of semantically related terms to an online advertisement service pro vider based on the ranking of the plurality of semanti cally related terms. 8. The method of claim 2, wherein the plurality of seman tically related terms are ranked based on a lexical feature of each term of the plurality of semantically related termandone or more terms of the seed set. 9. The method of claim 8, wherein the lexical feature is an edit distance between a term of the plurality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 10. The method of claim 8, wherein the lexical feature is a word edit distance between a term of the plurality semanti cally related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 11. A computer-readable storage medium comprising a set of instructions for determining semantically related terms, the set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of identifying two or more terms of a seed set; identifying concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than a first term of the seed set; and joining the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first term. 12. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 11, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: adding resulting terms of the joining of the first term with the identified concept associated with terms of the seed set other than the first term to a plurality of semantically related terms; and ranking at least a portion of the plurality of semantically related terms based on a metric indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the plurality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 13. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 12, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: removing each term from the plurality of semantically related terms associated with a search volume below a threshold. 14. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 12, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: identifying concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than a second term of the seed set; joining the second term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first set; and adding resulting terms of the joining of the second term with the identified concept terms associated with terms
16 of the seed set other than the second term to the plurality of semantically related terms. 15. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 12, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: providing at least one of the plurality of semantically related terms to a user based on the ranking of the plu rality of semantically related terms. 16. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 12, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: exporting at least one of the plurality of semantically related terms to an Internet search engine based on the ranking of the plurality of semantically related terms. 17. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 12, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: exporting at least one of the plurality of semantically related terms to an online advertisement service pro vider based on the ranking of the plurality of semanti cally related terms. 18. A system for determining semantically related terms, the system comprising: a semantically related term tool operative to identify two or more terms of a seed set, to identify concept terms asso ciated with terms of the seed set other than a first term of the seed set; and to join the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first term. 19. The system of claim 18, wherein the semantically related term tool is further operative to add resulting terms of the joining of the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms of the seed set other than the first term to a plurality of semantically related terms, and to ranka least a portion of the plurality of semantically related terms based on a metric indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the plurality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 20. The system of claim 19, wherein the semantically related term tool is in communication with an Internet search engine, and the semantically related term tool is operative to receive the seed set from the Internet search engine and to export at least one term of the plurality of semantically related terms to the Internet search engine based on the ranking of the plurality of semantically related terms. 21. The system of claim 18, wherein the semantically related term tool is in communication with an online adver tisement service provider and the semantically related term tool is operative to receive the seed set from the online adver tisement service provider and to export at least one term of the plurality of semantically related terms to the online advertise ment service provider based on the ranking of the plurality of semantically related terms. 22. A method for determining semantically related terms, the method comprising: identifying two or more terms of a seed set; identifying one or more explicit geographic locations iden tified in the seed set; removing the identified explicit geographic locations from the terms of the seed set to create a stripped seed set; identifying concept terms associated with terms of the stripped seed set other than a first term of the stripped seed set; joining the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms in the stripped seed set other than the first term; adding resulting terms of the joining of the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms in the stripped seed set other than the first term to a first plu rality of semantically related terms; and joining a first explicit geographic location of the one or more identified geographic locations with terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms. 23. The method of claim 22, further comprising: adding resulting terms of the joining of the first explicit geographic location and terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms to a second plurality of semantically related terms; and ranking at least a portion of the second plurality of seman tically related terms based on a metric indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the second plurality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 24. The method of claim 23, further comprising: removing invalid terms from the second plurality of seman tically related terms based on language model. 25. The method of claim 23, further comprising: removing each term of the second plurality of semantically related terms identifying an explicit geographic location that is not associated with one of the identified geo graphic locations. 26. The method of claim 23, further comprising: joining a second explicit geographic location of the one or more identified geographic locations with terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms; and adding resulting terms of the joining of the second explicit geographic location with terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms to the second plurality of semantically related terms. 27. The method of claim 22, further comprising: identifying concept terms associated with terms of the stripped seed set other than a second term of the stripped seed set; joining the second term with the identified concept terms associated with terms in the stripped seed set other than the second term; and adding resulting terms of the joining of the second term with the identified concept terms associated with terms in the stripped seed set other than the second term to the first plurality of semantically related terms. 28. A computer-readable storage medium comprising a set of instructions for determining semantically related terms, the set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of identifying two or more terms of a seed set; identifying one or more explicit geographic locations iden tified in the seed set; removing the identified explicit geographic locations from the terms of the seed set to create a stripped seed set; identifying concept terms associated with terms of the stripped seed set other than a first term of the stripped seed set; joining the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms in the stripped seed set other than the first term; adding resulting terms of the joining of the first term with the identified concept terms associated with terms in the
17 stripped seed set other than the first term to a first plu rality of semantically related terms; and joining a first explicit geographic location of the one or more identified geographic locations with terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms. 29. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 28, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: adding resulting terms of the joining of the first explicit geographic location and terms of the first plurality of semantically related terms to a second plurality of semantically related terms; and ranking at least a portion of the second plurality of seman tically related terms based on a metric indicating a degree of semantical relationship between a term of the second plurality of semantically related terms and one or more terms of the seed set. 30. The computer-readable storage medium of claim 29, further comprising a set of instructions to direct a processor to perform acts of: removing each invalid terms of the second plurality of semantically related terms based on a language model; and removing each term of the second plurality of semantically related terms identifying an explicit geographic location that is not associated with one of the identified geo graphic locations.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2.19234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0219234 A1 Forbes (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2010 (54) MOBILE TICKET AUTHENTICATION Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2010O2.19234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0219234 A1 Forbes (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2010 (54) MOBILE TICKET AUTHENTICATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0095237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0095237 A1 Turakhia (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010.0095237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0095237 A1 Turakhia (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O123876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0123876A1 Sista et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOMMENDING AND PRESENTING ADVERTISEMENTS ON DISPLAY PAGES OVER
(19) United States US 2012O123876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0123876A1 Sista et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOMMENDING AND PRESENTING ADVERTISEMENTS ON DISPLAY PAGES OVER
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O281 008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0281008 A1 Braun Warth (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) UNIVERSAL TRACKINGAGENT SYSTEM Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2010O281 008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0281008 A1 Braun Warth (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) UNIVERSAL TRACKINGAGENT SYSTEM Publication Classification
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0005152A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0005152 A1 Singh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2005 (54) SECURITY VULNERABILITY MONITOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005.0005152A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0005152 A1 Singh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2005 (54) SECURITY VULNERABILITY MONITOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,418,453 B1
 USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 200600101.05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0010105 A1 Sarukkai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2006 (54) DATABASE SEARCH SYSTEMAND METHOD OF DETERMINING
(19) United States US 200600101.05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0010105 A1 Sarukkai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2006 (54) DATABASE SEARCH SYSTEMAND METHOD OF DETERMINING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012O117328A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0117328A1 McKean et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) MANAGING ASTORAGE CACHE UTILIZING Publication Classification
US 2012O117328A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0117328A1 McKean et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) MANAGING ASTORAGE CACHE UTILIZING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201603 00023A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0300023 A1 Leonard (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2016 (54) PROVIDER RATING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 19/327
US 201603 00023A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0300023 A1 Leonard (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2016 (54) PROVIDER RATING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 19/327
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009006.3169A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0063169 A1 Holloway (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) EXTENDING INDUSTRY CERTIFICATIONS TO AN UNCERTIFED
(19) United States US 2009006.3169A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0063169 A1 Holloway (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) EXTENDING INDUSTRY CERTIFICATIONS TO AN UNCERTIFED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0224641 A1 Elias et al. US 20160224641A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) OBTAINING INCREMENTALUPDATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0224641 A1 Elias et al. US 20160224641A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) OBTAINING INCREMENTALUPDATES
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
(12) United States Patent Cunningham et al.
 US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060O881 67A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0088167 A1 Bade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR BACKUP AND RESTORE OF A CONTEXT
(19) United States US 20060O881 67A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0088167 A1 Bade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR BACKUP AND RESTORE OF A CONTEXT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Di Mattia et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2011
 (19) United States US 2011 0314496A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0314496 A1 Di Mattia et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2011 (54) ENHANCED MEDIA CONTENT TRANSPORT STREAM FOR
(19) United States US 2011 0314496A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0314496 A1 Di Mattia et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2011 (54) ENHANCED MEDIA CONTENT TRANSPORT STREAM FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/ A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr.
 US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170070927A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0070927 A1 Olvera-Hernandez et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR STATION LOCATION BASED NEIGHBOR
(19) United States US 20170070927A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0070927 A1 Olvera-Hernandez et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR STATION LOCATION BASED NEIGHBOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140379466A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379466A1 Pisaris-Henderson (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF CURSOR-BASED (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 20140379466A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379466A1 Pisaris-Henderson (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF CURSOR-BASED (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(12) United States Patent
 USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2
 USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0083276 A1 Barsness et al. US 20090083276A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) INSERTING DATA INTO AN IN-MEMORY DISTRIBUTED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0083276 A1 Barsness et al. US 20090083276A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) INSERTING DATA INTO AN IN-MEMORY DISTRIBUTED
Fergusson (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006
 US 20060074897Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2006/0074897 A1 Fergusson (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DYNAMIC (52) US. Cl...... 707/4 DATA MASKING
US 20060074897Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2006/0074897 A1 Fergusson (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DYNAMIC (52) US. Cl...... 707/4 DATA MASKING
Printer. Data input/ Printout unit. processor) Control unit. (Raster image RIP. Display unit. Image
 (19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
Apr. 3, 2014 Sheet 1 0f2 14% PROCESS AUTOMATION. = SYSTEM l FIG. 1. MANAGE SHADOW REE/IggE ACTIVE CUSTOMER USERS SUPPORT INSTALLER CODE; XXXXXX
 Patent Application Publication Apr. 3, 2014 Sheet 1 0f2 US 2014/0096208 A1 OPERATIONS CONSOLE CONTROL PANEL 14% L10 PROCESS AUTOMATION = SYSTEM l CONSOLE SUPPORT REQUEST FIG. 1 r 11 MANAGE SHADOW REE/IggE
Patent Application Publication Apr. 3, 2014 Sheet 1 0f2 US 2014/0096208 A1 OPERATIONS CONSOLE CONTROL PANEL 14% L10 PROCESS AUTOMATION = SYSTEM l CONSOLE SUPPORT REQUEST FIG. 1 r 11 MANAGE SHADOW REE/IggE
101. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 26, Atkins et al.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0338854 A1 Atkins et al. US 2015.0338854A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 26, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) HIGH AUTHORITY STABILITY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0338854 A1 Atkins et al. US 2015.0338854A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 26, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) HIGH AUTHORITY STABILITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, (54) E-CARD Publication Classification
 (19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120284252A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0284252 A1 Drai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SEARCH Related U.S. Application
US 20120284252A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0284252 A1 Drai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SEARCH Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0307354A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0307354 A1 Erman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR G06O 50/00 (2006.01)
US 2011 0307354A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0307354 A1 Erman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR G06O 50/00 (2006.01)
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O33301 1A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0333011 A1 KOrnev et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2010 (54) TOUCH SCREEN INPUT RECOGNITION AND CHARACTER
(19) United States US 2010O33301 1A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0333011 A1 KOrnev et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2010 (54) TOUCH SCREEN INPUT RECOGNITION AND CHARACTER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: CHEN et al. US 20160366367A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) FALLBACK IN FRAME RATE CONVERSION SYSTEM Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: CHEN et al. US 20160366367A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) FALLBACK IN FRAME RATE CONVERSION SYSTEM Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
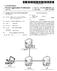 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(54) COLLECTING CONSUMER INFORMATION Publication Classi?cation. (75) Inventors: Robert A. SWirsky, Sunnyvale, CA (51) /00 (200601)
 US 20080114649Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114649 A1 Swirsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COLLECTING CONSUMER INFORMATION Publication Classi?cation (75)
US 20080114649Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114649 A1 Swirsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COLLECTING CONSUMER INFORMATION Publication Classi?cation (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Ennis (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2012
 US 201202840O8A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0284.008 A1 Ennis (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2012 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR MODELING Publication Classification
US 201202840O8A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0284.008 A1 Ennis (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2012 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR MODELING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0097323A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097323 A1 Barsness et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) DYNAMIC PROCESSING UNIT RELOCATION IN A MULTI-NODAL
(19) United States US 2013 0097323A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097323 A1 Barsness et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) DYNAMIC PROCESSING UNIT RELOCATION IN A MULTI-NODAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 USOO8301.496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,301.496 B2 Courchesne et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 30, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR INCREASING 38.6: A. 1939. I al.............. 23:
USOO8301.496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,301.496 B2 Courchesne et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 30, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR INCREASING 38.6: A. 1939. I al.............. 23:
