CS3500: Object-Oriented Design Fall 2013
|
|
|
- Noel O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS3500: Object-Oriented Design Fall 2013 Class
2 Assignment 8 Due Friday, November 15,
3 Software Process
4 Phases of the Software Requirements Process Design Implementation Testing Maintenance 4
5 Software Process Models 5
6 Waterfall Model Figure from [Braude & Bernstein] 6
7 Waterfall with Feedback figure 3.4 on page 37 Figure from [Braude & Bernstein] 7
8 Waterfall Pros - Simple & easy to use - Practiced for many years - Easy to manage - Facilitates allocation of resources - Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood Cons - Requirements must be known up front - Hard to estimate reliably - No stakeholder feedback until after testing - Major problems not discovered until late in process - Lack of parallelism - Inefficient use of resources 8
9 Iterative & Incremental 9
10 Iterative Figure from [Braude & Bernstein] 10
11 Spiral Figure from [Braude & Bernstein] 11
12 Incremental Figure from [Pressman] 12
13 Requirements
14 Why should we care about requirements?
15 There s no sense being exact about something if you don t even know what you re talking about. - John von Neumann 15
16 The hardest single part of building a software system is deciding precisely what to build. No other part of the conceptual work is so difficult as establishing the detailed technical requirements, including all the interfaces to people, to machines, and to other software systems. No other part of the work so cripples the resulting system if done wrong. No other part is more difficult to rectify later. - Fred Brooks 16
17 Cost of Defects Requirements 1 Design 5 Implementation 20 Test 50 Maintenance
18 Reasons for Project Failure Incomplete requirements 13.1% Lack of user involvement 12.4% Lack of resources 10.6% Unrealistic expectations 9.9% Lack of executive support 9.3% Changing requirements/specification 8.7% Lack of planning 8.1% Didn t need it any longer 7.5% Sources:Standish Group,1995 and 1996;Scientific American, September
19 Project Success Factors User involvement 15.9% Management support 13.9% Clear statement of requirements 13.0% Proper planning 9.6% Realistic expectations 8.2% Smaller milestones 7.7% Competent staff 7.2% Ownership 5.3% Sources:Standish Group,1995 and 1996;Scientific American, September
20 Sources of requirements Stakeholders Documents Books 20
21 Types of Requirements Functional - expresses a function that an application must perform Nonfunctional - does not involve specific functionality - qualifies services or functionalities - should be specific, quantifiable, and testable 21
22 Examples Functional - The application allows clerks to check out DVDs. Nonfunctional - The application shall display a customer s account status in less than two seconds. 22
23 Analysis & Specification Analysis: process of understanding the problem and the requirements for a solution Specification: process of describing what a system will do Analysis leads to Specification they are not the same [From NCSU CSC510 Slides] 23
24 Output Software Requirements Specification (SRS) All stakeholders can agree on set of requirements 24
25 User of a Requirements Document [Kotonya & Sommerville] System customers - Specify the requirements & read them to check that they meet their needs. - Specify changes to the requirements. Managers - Use the requirements document to plan a bid for the system & to plan the system development process System engineers - Use the requirements to understand what system is to be developed. System test engineers - Use the requirements to develop validation tests for the system. System maintenance engineers - Use the requirements to understand the system & the relationships between its parts 25
26 Requirements Document The official statement of what is required of the system developers should include both a definition and a specification of requirements It is NOT a design document As far as possible, it should set of WHAT the system should do rather than HOW it should do it [From NCSU CSC510 Slides] 26
27 Format of Requirements [Hull, Jackson, and Dick]
28 Functional Requirements The <stakeholder type> shall be able to <capability/function>. The system shall allow the <stakeholder type> to <capability/function>. The system shall <capability/function>. 28
29 Constraints [Hull, Jackson, and Dick] Performance/capability: The <system> shall be able to <function> <object> not less than <performance> times per <units>. Performance/capability: The <system> shall be able to <function> <object> of type <qualification> within <performance> <units> Performance/capacity: The <system> shall be able to <function> not less than <quantity> <object>. Performance/timeliness: The <system> shall be able to <function> <object> within <performance> <units> from <event>. Performance/periodicity: The <system> shall be able to <function> not less than <quantity> <object> within <performance> <units> Interoperability/capacity: The <system> shall be able to <function> <object> composed of not less than <performance> <units> with <external entity>. Sustainability/periodicity: The <system> shall be able to <function> <object> for <performance> <units> every <performance> <units>. Environmental/operability: The <system> shall be able to <function> <object> while <operational condition>. 29
30 Quality of Requirements - Comprehensiveness - How comprehensive is the SRS? - Does the SRS include all of the customer s wants and needs? - Consistency - How consistent is the SRS? - Are there contradictions in the SRS? - Self-Completeness - How self-complete is the SRS? - Does the SRS contain all of the necessary parts? - Understandability - How understandable is each requirement? - Unambiguity - How unambiguous is each requirement? - Can the requirement be interpreted in only one way? - Prioritization - How effectively prioritized are the requirements? - Is there an order for implementation? - Testability - How testable is each requirement? - Is it possible to validate the requirement in the finished product? - Traceability - How traceable is each requirement? - Is the requirement traceable forward? Backward? [Braude & Bernstein] 30
31 Traceability Track each requirement to design and code that implements it Track each part of code back to corresponding elements of design and requirements Critical in requirements engineering to link the requirements for the system and other important entities of the software 31
32 Traceability requirement accommodates design element implements relates to relates to implements test validates code verifies verifies verifies verifies inspection inspection inspection inspection Figure from [Braude & Bernstein] 32
33 Benefits of Traceability [Hull, Jackson, and Dick] Greater confidence in meeting objectives. Ability to assess the impact of change. Improved accountability of subordinate organizations. Ability to track progress. Ability to balance cost against benefit. 33
34 Stories 34
35 User Stories [Cohn] Describe software functionality that will be important for the users Allow software engineers to gain an understanding of what the software may include 35
36 Aspects in User Stories [Cohn] A written description of the story used for planning and as a reminder Conversations about the story that serve to flesh out the details of the story Tests that convey and document details and that can be used to determine when a story is complete 36
37 Use Cases Use case: sequence of actions taken by the actor and the application Actor (person or system) Scenario: list of numbered steps - Main success scenario - Extensions or error conditions 37
38 Use Case: Retrieve a File 1. User clicks File menu 2. System displays options New and Open 3. User clicks Open 4. System displays file window 5. User enters directory and file name 6. User hits Open button 7. System retrieves referenced file into word processor window Extensions 38
39 Use Case: Retrieve a File Main Success Scenario 1. User clicks File menu 2. System displays options New and Open 3. User clicks Open 4. System displays file window 5. User enters directory and file name 6. User hits Open button 7. System retrieves referenced file into word processor window Extensions Extension 7aSystem displays error indicating file could not be opened 39
40 Use Case Format Name: describes the task Associated requirement Actor: who is the user Priority Main success scenario Extensions 40
41 Use Case Exercise 41
42 Rent a Movie 1. User presses Rent a Movie 2. System displays movies that are for rent 3. User selects a movie 4. System displays selected movie information 5. User presses Rent 6. System prompts for credit card payment 7. User swipes credit card 8. System ejects movie 42
43 Rent a Movie 1. User presses Rent a Movie a. The user shall be able to press Rent a Movie from the Main screen when she wants to rent a movie. 2. System displays movies that are for rent a. The system shall display the list of possible movies to rent when the user presses Rent a Movie from the Main screen. 3. User selects a movie a. From the Movie Selection screen, the user shall be able to select a movie to rent. b. The system shall only display available movies on the Movie Selection screen. 4. System displays selected movie information a. The system shall display movie information on the selected movie when the user selects the movie from the Movie Selection screen. 43
44 Rent a Movie 5. User presses Rent a. The user shall be able to press Rent from the Movie screen when she wants to rent the selected movie. 6. System prompts for credit card payment a. The system shall prompt the user for credit card payment via the Payment screen when the user indicates she wants to rent the selected movie. 7. User swipes credit card a. The user shall be able to swipe her credit card to pay for the selected movie. 8. System ejects movie a. The system shall process the credit card payment when the user has selected a movie and swiped her credit card. b. The system shall eject the movie once the payment has been processed. 44
45 Stories for Online Bookstore Books can be searched by author, title, or ISBN. Books can be viewed detailed information by number of pages, publication date, and a brief description. Book can be placed in shopping cart and bought. Books can be rated and reviewed. 45
46 Requirements Engineering is difficult Despite the clear benefits of getting requirements complete, right, and errorfree early, they are the hardest part of the system development lifecycle to do right because: - we don t always understand everything about the real world that we need to know, - we may understand a lot, but we cannot express everything that we know - we may think we understand a lot, but our understanding may be wrong, - requirements change as client s needs change, - requirements change as clients and users think of new things they want, and - requirements of a system change as a direct result of deploying the system. [From NCSU CSC510 Slides] 46
47 47
48 48
49 49
50 Other Approaches to Balanced Trees AVL Trees 2-3 Trees 50
51 AVL Trees [Levitin] An AVL tree is a binary search tree in which the balance factor of every node, which is defined as the difference between the heights of the node s left and right subtrees, is either 0 or +1 or -1. (The height of the empty tree is defined as -1.) 51
52 AVL Tree Not AVL Tree Figures from Levitin 52
53 Figure from Levitin 53
54 2-3 Trees [Levitin] A 2-3 tree is a tree that can have nodes of two kinds: 2-nodes and 3-nodes. A 2-node contains a single key K and has two children. A 3-node contains two ordered keys K1 and K2 (K1 < K2) and has three children. A 2-3 tree is always height-balanced 54
55 Figure from Levitin 55
56 Inserting into 2-3 Trees [Levitin] Always insert a new key K at a leaf except for the empty tree. The appropriate leaf is found by performing a search of K. If the leaf in question is a 2-node, we insert K there as with the first or the second key, depending on whether K is smaller or larger than the node s old key. If the leaf is a 3-node, we split the leaf in two: the smallest of the three keys (two old ones and the new key) is put in the first leaf, the largest is put in the second leaf, while the middle key is promoted to the old leaf s parent. (If the leaf happens to be the tree s root, a new root is created to accept the middle key.) Note that promotion of a middle key to its parent can cause the parent s overflow (if it was a 3-node) and hence can lead to several node splits along the chain of the leaf s ancestors. 56
CIS 890: Safety Critical Systems
 CIS 890: Safety Critical Systems Lecture: Requirements Introduction Copyright 2011, John Hatcliff. The syllabus and all lectures for this course are copyrighted materials and may not be used in other course
CIS 890: Safety Critical Systems Lecture: Requirements Introduction Copyright 2011, John Hatcliff. The syllabus and all lectures for this course are copyrighted materials and may not be used in other course
User Stories Applied, Mike Cohn
 User Stories Applied, Mike Cohn Chapter 1: An Overview Composed of three aspects: 1. Written description of the story used for planning and as a reminder 2. Conversations about the story that serve to
User Stories Applied, Mike Cohn Chapter 1: An Overview Composed of three aspects: 1. Written description of the story used for planning and as a reminder 2. Conversations about the story that serve to
An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time
 B + -TREES MOTIVATION An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data structure for searching, indexing, etc. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time The theoretical conclusion
B + -TREES MOTIVATION An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data structure for searching, indexing, etc. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time The theoretical conclusion
Software specification and modelling. Requirements engineering
 Software specification and modelling Requirements engineering Requirements engineering (RE) Requirements engineering is the process of establishing the services that a customer requires from a system and
Software specification and modelling Requirements engineering Requirements engineering (RE) Requirements engineering is the process of establishing the services that a customer requires from a system and
Motivation for B-Trees
 1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
User Stories Applied, Mike Cohn
 User Stories Applied, Mike Cohn Chapter 1: An Overview Composed of three aspects: 1. Written description of the story used for planning and as a reminder 2. Conversations about the story that serve to
User Stories Applied, Mike Cohn Chapter 1: An Overview Composed of three aspects: 1. Written description of the story used for planning and as a reminder 2. Conversations about the story that serve to
Material You Need to Know
 Review Quiz 2 Material You Need to Know Normalization Storage and Disk File Layout Indexing B-trees and B+ Trees Extensible Hashing Linear Hashing Decomposition Goals: Lossless Joins, Dependency preservation
Review Quiz 2 Material You Need to Know Normalization Storage and Disk File Layout Indexing B-trees and B+ Trees Extensible Hashing Linear Hashing Decomposition Goals: Lossless Joins, Dependency preservation
2-3 and Trees. COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli
 2-3 and 2-3-4 Trees COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli Multi-Way Trees A binary search tree: One value in each node At most 2 children An M-way search tree: Between 1 to (M-1) values
2-3 and 2-3-4 Trees COL 106 Shweta Agrawal, Amit Kumar, Dr. Ilyas Cicekli Multi-Way Trees A binary search tree: One value in each node At most 2 children An M-way search tree: Between 1 to (M-1) values
Introduction to User Stories. CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014
 Introduction to User Stories CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014 1 Goals Present an introduction to the topic of user stories concepts and terminology benefits and limitations
Introduction to User Stories CSCI 5828: Foundations of Software Engineering Lecture 05 09/09/2014 1 Goals Present an introduction to the topic of user stories concepts and terminology benefits and limitations
Intro to Software Requirements
 Intro to Software Requirements What question do software requirements answer? Who, what, when, where, why, how What is the system to do? Who are the system user groups? Business case tells us why (and
Intro to Software Requirements What question do software requirements answer? Who, what, when, where, why, how What is the system to do? Who are the system user groups? Business case tells us why (and
Multi-way Search Trees! M-Way Search! M-Way Search Trees Representation!
 Lecture 10: Multi-way Search Trees: intro to B-trees 2-3 trees 2-3-4 trees Multi-way Search Trees A node on an M-way search tree with M 1 distinct and ordered keys: k 1 < k 2 < k 3
Lecture 10: Multi-way Search Trees: intro to B-trees 2-3 trees 2-3-4 trees Multi-way Search Trees A node on an M-way search tree with M 1 distinct and ordered keys: k 1 < k 2 < k 3
Administrivia. Wednesday: Requirements and Specification. CS169 Lecture 4. We assign teams and you start on Monday. Determining Stakeholders and Needs
 Administrivia Requirements and Specification CS169 Lecture 4 Wednesday: Groups and one-sentence idea(s) due at class One per group If you have a small group, still submit so that you will be kept together.
Administrivia Requirements and Specification CS169 Lecture 4 Wednesday: Groups and one-sentence idea(s) due at class One per group If you have a small group, still submit so that you will be kept together.
1. i. What are the 3 major components of a information system and show their relationship input output
 Higher National Diploma in Information Technology First Year, Second semesterexamination-2011 IT2005: System Analysis and Design Answer Script No. of pages: 11 1. i. What are the 3 major components of
Higher National Diploma in Information Technology First Year, Second semesterexamination-2011 IT2005: System Analysis and Design Answer Script No. of pages: 11 1. i. What are the 3 major components of
Lecture 7 (3-April-2013)
 SOFTWARE QUALITY ASSURANCE Lecture 7 (3-April-2013) Instructor: Mr. Natash Ali Mian Department of CS and IT Department of CS and IT The University of Lahore ` Switch off mobile phones during lectures,
SOFTWARE QUALITY ASSURANCE Lecture 7 (3-April-2013) Instructor: Mr. Natash Ali Mian Department of CS and IT Department of CS and IT The University of Lahore ` Switch off mobile phones during lectures,
Software Engineering - I
 Software Engineering - I An Introduction to Software Construction Techniques for Industrial Strength Software Chapter 3 Requirement Engineering Copy Rights Virtual University of Pakistan 1 Requirement
Software Engineering - I An Introduction to Software Construction Techniques for Industrial Strength Software Chapter 3 Requirement Engineering Copy Rights Virtual University of Pakistan 1 Requirement
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
User Stories for Agile Requirements. Mike Cohn - background. Copyright Mountain Goat Software, LLC
 User Stories for Agile Requirements 1 Mike Cohn - background 2 It s a communication problem Software requirements is a communication problem Those who want software must communicate with those who will
User Stories for Agile Requirements 1 Mike Cohn - background 2 It s a communication problem Software requirements is a communication problem Those who want software must communicate with those who will
Fundamentals: Software Engineering. Objectives. Last lectures. Unit 2: Light Introduction to Requirements Engineering
 Fundamentals: Software Engineering Dr. Rami Bahsoon School of Computer Science University of Birmingham r.bahsoon@cs.bham.ac.uk Unit 2: Light Introduction to Requirements Engineering Dr R Bahsoon 1 Objectives
Fundamentals: Software Engineering Dr. Rami Bahsoon School of Computer Science University of Birmingham r.bahsoon@cs.bham.ac.uk Unit 2: Light Introduction to Requirements Engineering Dr R Bahsoon 1 Objectives
M-ary Search Tree. B-Trees. B-Trees. Solution: B-Trees. B-Tree: Example. B-Tree Properties. Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height =
 M-ary Search Tree B-Trees Section 4.7 in Weiss Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary search trees Each
M-ary Search Tree B-Trees Section 4.7 in Weiss Maximum branching factor of M Complete tree has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary search trees Each
Requirement Analysis
 Requirement Analysis Requirements Analysis & Specification Objective: determine what the system must do to solve the problem (without describing how) Done by Analyst (also called Requirements Analyst)
Requirement Analysis Requirements Analysis & Specification Objective: determine what the system must do to solve the problem (without describing how) Done by Analyst (also called Requirements Analyst)
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees Dr. Chung- Wen Albert Tsao atsao@svuca.edu www.408codingschool.com/cs502_algorithm 1/12/16 Slide Source: http://www.slideshare.net/anujmodi555/b-trees-in-data-structure
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees Dr. Chung- Wen Albert Tsao atsao@svuca.edu www.408codingschool.com/cs502_algorithm 1/12/16 Slide Source: http://www.slideshare.net/anujmodi555/b-trees-in-data-structure
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II. Binary Search Trees
 CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees
 Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees 1. What 3 properties must an AVL tree have? a. Be a binary tree b. Have Binary Search Tree ordering property (left children < parent, right children > parent) c.
Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees 1. What 3 properties must an AVL tree have? a. Be a binary tree b. Have Binary Search Tree ordering property (left children < parent, right children > parent) c.
M-ary Search Tree. B-Trees. Solution: B-Trees. B-Tree: Example. B-Tree Properties. B-Trees (4.7 in Weiss)
 M-ary Search Tree B-Trees (4.7 in Weiss) Maximum branching factor of M Tree with N values has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 1/21/2011 1 1/21/2011 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary
M-ary Search Tree B-Trees (4.7 in Weiss) Maximum branching factor of M Tree with N values has height = # disk accesses for find: Runtime of find: 1/21/2011 1 1/21/2011 2 Solution: B-Trees specialized M-ary
Balanced Search Trees
 Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
CIS265/ Trees Red-Black Trees. Some of the following material is from:
 CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CMSC 341 Lecture 14: Priority Queues, Heaps
 CMSC 341 Lecture 14: Priority Queues, Heaps Prof. John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Priority Queues Abstract Data Type Implementations of Priority Queues:
CMSC 341 Lecture 14: Priority Queues, Heaps Prof. John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Priority Queues Abstract Data Type Implementations of Priority Queues:
Verification and Validation. Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1
 Verification and Validation Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1 Verification vs validation Verification: "Are we building the product right?. The software should
Verification and Validation Ian Sommerville 2004 Software Engineering, 7th edition. Chapter 22 Slide 1 Verification vs validation Verification: "Are we building the product right?. The software should
2014 Intelliware Development Inc.
 What You ll Learn in this Presentation: The basics of user stories. How user stories fit into the overall Agile planning process. How to write a user story. A story card example 2 Why is it so Difficult
What You ll Learn in this Presentation: The basics of user stories. How user stories fit into the overall Agile planning process. How to write a user story. A story card example 2 Why is it so Difficult
Requirements Engineering. Establishing what the customer requires from a software system. Requirements Engineering. What is a Requirement?
 Engineering Establishing what the customer requires from a software system Ian Sommerville 1995/2000 (Modified by Spiros Mancoridis 1999) Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapters 5 and 6 Slide 1 Engineering
Engineering Establishing what the customer requires from a software system Ian Sommerville 1995/2000 (Modified by Spiros Mancoridis 1999) Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapters 5 and 6 Slide 1 Engineering
CS Transform-and-Conquer
 CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
Ch 4: Requirements Engineering. What are requirements?
 Ch 4: Engineering What are? Functional and non-functional The software document specification engineering processes elicitation and analysis validation management The descriptions of what the system should
Ch 4: Engineering What are? Functional and non-functional The software document specification engineering processes elicitation and analysis validation management The descriptions of what the system should
Mathematics and Computing: Level 2 M253 Team working in distributed environments
 Mathematics and Computing: Level 2 M253 Team working in distributed environments SR M253 Resource Sheet Specifying requirements 1 Overview Having spent some time identifying the context and scope of our
Mathematics and Computing: Level 2 M253 Team working in distributed environments SR M253 Resource Sheet Specifying requirements 1 Overview Having spent some time identifying the context and scope of our
Dilbert Scott Adams. CSc 233 Spring 2012
 Dilbert Scott Adams CSc 233 Spring 2012 Dilbert Scott Adams CSc 233 Spring 2012 2 Dilbert Scott Adams CSc 233 Spring 2012 3 prerequisites CSc 233 Spring 2012 I thought we had agreed long ago that the Department
Dilbert Scott Adams CSc 233 Spring 2012 Dilbert Scott Adams CSc 233 Spring 2012 2 Dilbert Scott Adams CSc 233 Spring 2012 3 prerequisites CSc 233 Spring 2012 I thought we had agreed long ago that the Department
Trees. A tree is a directed graph with the property
 2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
2: Trees Trees A tree is a directed graph with the property There is one node (the root) from which all other nodes can be reached by exactly one path. Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees
AVL Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees 1
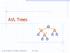 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
B-Trees. Disk Storage. What is a multiway tree? What is a B-tree? Why B-trees? Insertion in a B-tree. Deletion in a B-tree
 B-Trees Disk Storage What is a multiway tree? What is a B-tree? Why B-trees? Insertion in a B-tree Deletion in a B-tree Disk Storage Data is stored on disk (i.e., secondary memory) in blocks. A block is
B-Trees Disk Storage What is a multiway tree? What is a B-tree? Why B-trees? Insertion in a B-tree Deletion in a B-tree Disk Storage Data is stored on disk (i.e., secondary memory) in blocks. A block is
Quality Software Requirements By J. Chris Gibson
 Quality Software Requirements By J. Chris Gibson The information contained within this document has been gathered from a variety of sources and practices observed by the development team at Protera Software
Quality Software Requirements By J. Chris Gibson The information contained within this document has been gathered from a variety of sources and practices observed by the development team at Protera Software
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By
 CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CS301 - Data Structures Glossary By Abstract Data Type : A set of data values and associated operations that are precisely specified independent of any particular implementation. Also known as ADT Algorithm
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSC : Lecture 7 CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique CSC : Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a
CSC : Lecture 7 CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique CSC : Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a
Balanced Trees Part Two
 Balanced Trees Part Two Outline for Today Recap from Last Time Review of B-trees, 2-3-4 trees, and red/black trees. Order Statistic Trees BSTs with indexing. Augmented Binary Search Trees Building new
Balanced Trees Part Two Outline for Today Recap from Last Time Review of B-trees, 2-3-4 trees, and red/black trees. Order Statistic Trees BSTs with indexing. Augmented Binary Search Trees Building new
CS F-11 B-Trees 1
 CS673-2016F-11 B-Trees 1 11-0: Binary Search Trees Binary Tree data structure All values in left subtree< value stored in root All values in the right subtree>value stored in root 11-1: Generalizing BSTs
CS673-2016F-11 B-Trees 1 11-0: Binary Search Trees Binary Tree data structure All values in left subtree< value stored in root All values in the right subtree>value stored in root 11-1: Generalizing BSTs
CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees
 CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve
CS 350 : Data Structures B-Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction All of the data structures that we ve
Administrivia. Added 20 more so far. Software Process. Only one TA so far. CS169 Lecture 2. Start thinking about project proposal
 Administrivia Software Process CS169 Lecture 2 Added 20 more so far Will limit enrollment to ~65 students Only one TA so far Start thinking about project proposal Bonus points for proposals that will be
Administrivia Software Process CS169 Lecture 2 Added 20 more so far Will limit enrollment to ~65 students Only one TA so far Start thinking about project proposal Bonus points for proposals that will be
Lecture 32. No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions?
 Lecture 32 No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions? Friday, April 1 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 32 1 Outline Introduction
Lecture 32 No computer use today. Reminders: Homework 11 is due today. Project 6 is due next Friday. Questions? Friday, April 1 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II - Lecture 32 1 Outline Introduction
Software Engineering Fall 2015 (CSC 4350/6350) TR. 5:30 pm 7:15 pm. Rao Casturi 09/17/2015
 Software Engineering Fall 2015 (CSC 4350/6350) TR. 5:30 pm 7:15 pm Rao Casturi 09/17/2015 http://cs.gsu.edu/~ncasturi1 Requirement Elicitation 2 Requirement Engineering First step for understanding the
Software Engineering Fall 2015 (CSC 4350/6350) TR. 5:30 pm 7:15 pm Rao Casturi 09/17/2015 http://cs.gsu.edu/~ncasturi1 Requirement Elicitation 2 Requirement Engineering First step for understanding the
Homework 3. Theory (50 points) Data Structures and Algorithms in JAVA Shlomo Hershkop Department of Computer Science Columbia University Summer 2002
 Homework 3 Data Structures and Algorithms in JAVA Shlomo Hershkop Department of Computer Science Columbia University Summer 2002 Due Thursday, Aug 1 (at beginning of class) Theory (50 points) 1. (5 points)
Homework 3 Data Structures and Algorithms in JAVA Shlomo Hershkop Department of Computer Science Columbia University Summer 2002 Due Thursday, Aug 1 (at beginning of class) Theory (50 points) 1. (5 points)
Linked Structures Songs, Games, Movies Part III. Fall 2013 Carola Wenk
 Linked Structures Songs, Games, Movies Part III Fall 2013 Carola Wenk Biological Structures Nature has evolved vascular and nervous systems in a hierarchical manner so that nutrients and signals can quickly
Linked Structures Songs, Games, Movies Part III Fall 2013 Carola Wenk Biological Structures Nature has evolved vascular and nervous systems in a hierarchical manner so that nutrients and signals can quickly
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 7. Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique. Transform and Conquer
 // CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more
// CSC - Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 7 Transform and Conquer I Algorithm Design Technique Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more
Requirements Engineering
 Requirements Engineering An introduction to requirements engineering Gerald Kotonya and Ian Sommerville G. Kotonya and I. Sommerville 1998 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce the notion of system requirements
Requirements Engineering An introduction to requirements engineering Gerald Kotonya and Ian Sommerville G. Kotonya and I. Sommerville 1998 Slide 1 Objectives To introduce the notion of system requirements
Binary Search Trees Treesort
 Treesort CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, November 13, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009
Treesort CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, November 13, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009
CS 2150 (fall 2010) Midterm 2
 Name: Userid: CS 2150 (fall 2010) Midterm 2 You MUST write your name and e-mail ID on EACH page and bubble in your userid at the bottom of EACH page, including this page. If you are still writing when
Name: Userid: CS 2150 (fall 2010) Midterm 2 You MUST write your name and e-mail ID on EACH page and bubble in your userid at the bottom of EACH page, including this page. If you are still writing when
Binary Search Trees. Carlos Moreno uwaterloo.ca EIT https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250
 Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EIT-4103 https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250 Standard reminder to set phones to silent/vibrate mode, please! Previously, on ECE-250... We discussed trees (the
Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EIT-4103 https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece250 Standard reminder to set phones to silent/vibrate mode, please! Previously, on ECE-250... We discussed trees (the
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Binary Search Trees
 Computer Science 10 Data Structures Siena College Fall 018 Topic Notes: Binary Search Trees Possibly the most common usage of a binary tree is to store data for quick retrieval. Definition: A binary tree
Computer Science 10 Data Structures Siena College Fall 018 Topic Notes: Binary Search Trees Possibly the most common usage of a binary tree is to store data for quick retrieval. Definition: A binary tree
Agile Tester Foundation E-learning Course Outline
 Foundation E-learning Course Outline General Description This course provides testers and test managers with an understanding of the fundamentals of testing on agile projects. Attendees will learn how
Foundation E-learning Course Outline General Description This course provides testers and test managers with an understanding of the fundamentals of testing on agile projects. Attendees will learn how
Recall: Properties of B-Trees
 CSE 326 Lecture 10: B-Trees and Heaps It s lunch time what s cookin? B-Trees Insert/Delete Examples and Run Time Analysis Summary of Search Trees Introduction to Heaps and Priority Queues Covered in Chapters
CSE 326 Lecture 10: B-Trees and Heaps It s lunch time what s cookin? B-Trees Insert/Delete Examples and Run Time Analysis Summary of Search Trees Introduction to Heaps and Priority Queues Covered in Chapters
SOFTWARE LIFE-CYCLE PROCESSES From Waterfall to Extreme Programming
 SOFTWARE LIFE-CYCLE PROCESSES From Waterfall to Extreme Programming Slide 1 Lesson Objectives Understand major activities of software projects Understand the place of these in different lifecycle models
SOFTWARE LIFE-CYCLE PROCESSES From Waterfall to Extreme Programming Slide 1 Lesson Objectives Understand major activities of software projects Understand the place of these in different lifecycle models
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 B-Trees Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Motivation for B-Trees So far we have assumed that we can store an entire data structure in main memory.
B-Trees Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Motivation for B-Trees So far we have assumed that we can store an entire data structure in main memory.
Student WebAdvisor Training Manual
 Student WebAdvisor Training Manual Contents Logging into WebAdvisor..2 Registering for a Class Section..4 Paying on My Account. 9 Dropping a Class Section 12 1 Logging into WebAdvisor STEPS 1. Click the
Student WebAdvisor Training Manual Contents Logging into WebAdvisor..2 Registering for a Class Section..4 Paying on My Account. 9 Dropping a Class Section 12 1 Logging into WebAdvisor STEPS 1. Click the
Module 9: Binary trees
 Module 9: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Module 9: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
What is a Multi-way tree?
 B-Tree Motivation for studying Multi-way and B-trees A disk access is very expensive compared to a typical computer instruction (mechanical limitations) -One disk access is worth about 200,000 instructions.
B-Tree Motivation for studying Multi-way and B-trees A disk access is very expensive compared to a typical computer instruction (mechanical limitations) -One disk access is worth about 200,000 instructions.
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
Binary Heaps in Dynamic Arrays
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland We have already learned that the binary heap serves as an efficient implementation of a priority queue. Our previous discussion was based on pointers (for getting
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland We have already learned that the binary heap serves as an efficient implementation of a priority queue. Our previous discussion was based on pointers (for getting
Requirements engineering
 engineering Chapter 4 1 Engineering in the textbook 4.1 Functional and non-functional 4.2 The software document 4.4 engineering processes 4.5 elicitation and analysis 4.3 specification 4.6 validation 4.7
engineering Chapter 4 1 Engineering in the textbook 4.1 Functional and non-functional 4.2 The software document 4.4 engineering processes 4.5 elicitation and analysis 4.3 specification 4.6 validation 4.7
Sample Exam Syllabus
 ISTQB Foundation Level 2011 Syllabus Version 2.9 Release Date: December 16th, 2017. Version.2.9 Page 1 of 46 Dec 16th, 2017 Copyright 2017 (hereinafter called ISTQB ). All rights reserved. The authors
ISTQB Foundation Level 2011 Syllabus Version 2.9 Release Date: December 16th, 2017. Version.2.9 Page 1 of 46 Dec 16th, 2017 Copyright 2017 (hereinafter called ISTQB ). All rights reserved. The authors
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Physical Disk Structure. Physical Data Organization and Indexing. Pages and Blocks. Access Path. I/O Time to Access a Page. Disks.
 Physical Disk Structure Physical Data Organization and Indexing Chapter 11 1 4 Access Path Refers to the algorithm + data structure (e.g., an index) used for retrieving and storing data in a table The
Physical Disk Structure Physical Data Organization and Indexing Chapter 11 1 4 Access Path Refers to the algorithm + data structure (e.g., an index) used for retrieving and storing data in a table The
Chapter 5 Hashing. Introduction. Hashing. Hashing Functions. hashing performs basic operations, such as insertion,
 Introduction Chapter 5 Hashing hashing performs basic operations, such as insertion, deletion, and finds in average time 2 Hashing a hash table is merely an of some fixed size hashing converts into locations
Introduction Chapter 5 Hashing hashing performs basic operations, such as insertion, deletion, and finds in average time 2 Hashing a hash table is merely an of some fixed size hashing converts into locations
BST Deletion. First, we need to find the value which is easy because we can just use the method we developed for BST_Search.
 BST Deletion Deleting a value from a Binary Search Tree is a bit more complicated than inserting a value, but we will deal with the steps one at a time. First, we need to find the value which is easy because
BST Deletion Deleting a value from a Binary Search Tree is a bit more complicated than inserting a value, but we will deal with the steps one at a time. First, we need to find the value which is easy because
Tree Data Structures CSC 221
 Tree Data Structures CSC 221 BSTree Deletion - Merging template // LOOK AT THIS PARAMETER!!! void BST::deleteByMerging(BSTNode* & nodepointer) { BSTNode* temp= nodepointer;
Tree Data Structures CSC 221 BSTree Deletion - Merging template // LOOK AT THIS PARAMETER!!! void BST::deleteByMerging(BSTNode* & nodepointer) { BSTNode* temp= nodepointer;
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Problem. Indexing with B-trees. Indexing. Primary Key Indexing. B-trees: Example. B-trees. primary key indexing
 15-82 Advanced Topics in Database Systems Performance Problem Given a large collection of records, Indexing with B-trees find similar/interesting things, i.e., allow fast, approximate queries 2 Indexing
15-82 Advanced Topics in Database Systems Performance Problem Given a large collection of records, Indexing with B-trees find similar/interesting things, i.e., allow fast, approximate queries 2 Indexing
Basics : the Requirements Engineering Process
 SEG3101 (Fall 2010) Basics : the Requirements Engineering Process Gregor v. Bochmann, University of Ottawa Based on Powerpoint slides prepared by Gunter Mussbacher with material from: Sommerville & Kotonya
SEG3101 (Fall 2010) Basics : the Requirements Engineering Process Gregor v. Bochmann, University of Ottawa Based on Powerpoint slides prepared by Gunter Mussbacher with material from: Sommerville & Kotonya
CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 17. Fall 2017
 CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 17 Fall 2017 Announcement Quiz 6 Due: Tonight at 11:59 pm Project 1 Milepost 3 Due: Nov 10 Project 2 Part 2 (Optional) Due: Nov 15 The IO Model & External Sorting Today
CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 17 Fall 2017 Announcement Quiz 6 Due: Tonight at 11:59 pm Project 1 Milepost 3 Due: Nov 10 Project 2 Part 2 (Optional) Due: Nov 15 The IO Model & External Sorting Today
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/27/17
 01.433/33 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/2/1.1 Introduction In this lecture we ll talk about a useful abstraction, priority queues, which are
01.433/33 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/2/1.1 Introduction In this lecture we ll talk about a useful abstraction, priority queues, which are
Agile Accessibility. Presenters: Ensuring accessibility throughout the Agile development process
 Agile Accessibility Ensuring accessibility throughout the Agile development process Presenters: Andrew Nielson, CSM, PMP, MPA Ann Marie Davis, CSM, PMP, M. Ed. Cammie Truesdell, M. Ed. Overview What is
Agile Accessibility Ensuring accessibility throughout the Agile development process Presenters: Andrew Nielson, CSM, PMP, MPA Ann Marie Davis, CSM, PMP, M. Ed. Cammie Truesdell, M. Ed. Overview What is
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Process of Interaction Design and Design Languages
 Process of Interaction Design and Design Languages Process of Interaction Design This week, we will explore how we can design and build interactive products What is different in interaction design compared
Process of Interaction Design and Design Languages Process of Interaction Design This week, we will explore how we can design and build interactive products What is different in interaction design compared
Software testing. Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 23 Slide 1
 Software testing Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 23 Slide 1 Objectives To discuss the distinctions between validation testing and defect testing To describe the principles
Software testing Ian Sommerville 2006 Software Engineering, 8th edition. Chapter 23 Slide 1 Objectives To discuss the distinctions between validation testing and defect testing To describe the principles
CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps
 Based on slides from previous iterations of this course CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps Prof. John Park Review of Heaps Min Binary Heap A min binary heap is a Complete binary tree Neither child is smaller
Based on slides from previous iterations of this course CMSC 341 Lecture 15 Leftist Heaps Prof. John Park Review of Heaps Min Binary Heap A min binary heap is a Complete binary tree Neither child is smaller
Lecture 7. Transform-and-Conquer
 Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
Lecture 7 Transform-and-Conquer 6-1 Transform and Conquer This group of techniques solves a problem by a transformation to a simpler/more convenient instance of the same problem (instance simplification)
TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION RESOURCES. Test Scenario. Instructions. Version DEC 2006
 TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION RESOURCES Test Scenario Instructions Version 1.1 8 DEC 2006 Version History Current Framework documents, including a glossary, are available at www.dir.state.tx.us/pubs/framework/.
TEXAS DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION RESOURCES Test Scenario Instructions Version 1.1 8 DEC 2006 Version History Current Framework documents, including a glossary, are available at www.dir.state.tx.us/pubs/framework/.
Lecture 5: Requirements Specifications
 Lecture 5: Requirements Specifications Why we need to write specifications Purpose and audience Choosing an appropriate size and formality Desiderata for Specifications Properties of good specifications
Lecture 5: Requirements Specifications Why we need to write specifications Purpose and audience Choosing an appropriate size and formality Desiderata for Specifications Properties of good specifications
CSCI Trees. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
1: Specifying Requirements with Use Case Diagrams
 Outline UML Design Supplement 1: Specifying Requirements with Use Case Diagrams Introduction Use Case Diagrams Writing Use Cases Guidelines for Effective Use Cases Slide adapted from Eran Toch s lecture
Outline UML Design Supplement 1: Specifying Requirements with Use Case Diagrams Introduction Use Case Diagrams Writing Use Cases Guidelines for Effective Use Cases Slide adapted from Eran Toch s lecture
c) A perfect ternary tree of height h? (In a ternary tree, each node may have up to three children.)
 Spring 2007 C343 Final Name: Username: Question 1 (10 points): How many nodes can there be in: a) A complete binary tree of height h? b) A perfect binary tree of height h? c) A perfect ternary tree of
Spring 2007 C343 Final Name: Username: Question 1 (10 points): How many nodes can there be in: a) A complete binary tree of height h? b) A perfect binary tree of height h? c) A perfect ternary tree of
Black-box Testing Techniques
 T-76.5613 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Lecture 4, 20.9.2006 Black-box Testing Techniques SoberIT Black-box test case design techniques Basic techniques Equivalence partitioning Boundary value
T-76.5613 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Lecture 4, 20.9.2006 Black-box Testing Techniques SoberIT Black-box test case design techniques Basic techniques Equivalence partitioning Boundary value
CS 310 B-trees, Page 1. Motives. Large-scale databases are stored in disks/hard drives.
 CS 310 B-trees, Page 1 Motives Large-scale databases are stored in disks/hard drives. Disks are quite different from main memory. Data in a disk are accessed through a read-write head. To read a piece
CS 310 B-trees, Page 1 Motives Large-scale databases are stored in disks/hard drives. Disks are quite different from main memory. Data in a disk are accessed through a read-write head. To read a piece
Section 1: True / False (1 point each, 15 pts total)
 Section : True / False ( point each, pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
Section : True / False ( point each, pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
B2B Portal User Guide
 B2B Portal User Guide Table of Contents Introduction..3 Logging In.4 Changing your original password......6 Ordering Product....7 Product Waiting Lists......8 Payment Options.. 14 Finalizing your Order...
B2B Portal User Guide Table of Contents Introduction..3 Logging In.4 Changing your original password......6 Ordering Product....7 Product Waiting Lists......8 Payment Options.. 14 Finalizing your Order...
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Software Project Management, 9th Sep.
 Software Project Management, 9th Sep. Working hour reporting Preliminary analysis Project planning, development models Usability team co-operation Short project presentations on 16th September Course homepage:
Software Project Management, 9th Sep. Working hour reporting Preliminary analysis Project planning, development models Usability team co-operation Short project presentations on 16th September Course homepage:
The requirements engineering process
 3 rd Stage Lecture time: 8:30-12:30 AM Instructor: Ali Kadhum AL-Quraby Lecture No. : 5 Subject: Software Engineering Class room no.: Department of computer science Process activities The four basic process
3 rd Stage Lecture time: 8:30-12:30 AM Instructor: Ali Kadhum AL-Quraby Lecture No. : 5 Subject: Software Engineering Class room no.: Department of computer science Process activities The four basic process
Maps; Binary Search Trees
 Maps; Binary Search Trees PIC 10B Friday, May 20, 2016 PIC 10B Maps; Binary Search Trees Friday, May 20, 2016 1 / 24 Overview of Lecture 1 Maps 2 Binary Search Trees 3 Questions PIC 10B Maps; Binary Search
Maps; Binary Search Trees PIC 10B Friday, May 20, 2016 PIC 10B Maps; Binary Search Trees Friday, May 20, 2016 1 / 24 Overview of Lecture 1 Maps 2 Binary Search Trees 3 Questions PIC 10B Maps; Binary Search
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 25 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Balanced Binary Search trees AVL trees / Compression Uses binary trees Balanced
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 25 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Balanced Binary Search trees AVL trees / Compression Uses binary trees Balanced
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Software Design Models, Tools & Processes. Lecture 2: Inception Phase Cecilia Mascolo
 Software Design Models, Tools & Processes Lecture 2: Inception Phase Cecilia Mascolo Inception Phase This is the phase when most of the system requirements are identified. Discover and reach agreement
Software Design Models, Tools & Processes Lecture 2: Inception Phase Cecilia Mascolo Inception Phase This is the phase when most of the system requirements are identified. Discover and reach agreement
