(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
|
|
|
- Melvin Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
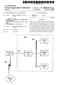
1 (19) United States US 2014O164892A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 NICKOLOV et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2014 (54) CONSUMING CONTENT INCREMENTALLY (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 17/2235 ( ); G06F 17/218 (71) Applicant: MICROSOFT CORPORATION, ( ) REDMOND, WA (US) USPC /205: 715/234 (72) Inventors: RADOSLAVNICKOLOV, SEATTLE, WA (US); MING LIU, BELLEVUE, (57) ABSTRACT WA (US); WEIZENG, SAMMAMISH, WA (US); RAMAN NARAYANAN, An e-reader application consumes content incrementally dur SEATTLE, WA (US) ing presentation. The application determines a location of another page in the content in response to a user action to load (73) Assignee: MICROSOFT CORPORATION, the other page in place of a currently displayed page. A user REDMOND, WA (US) initiates navigation to the other page by activating a naviga tion control to display an adjacent page or a random page of (21) Appl. No.: 13/711,098 the content. An increment of the content containing the other 1-1. page is retrieved from the determined location. An anchor (22) Filed: Dec. 11, 2012 associated with the other page can be used to find the location Publication Classification in the content. The increment is processed to extract the other page. Processing can include decoding the increment using a (51) Int. Cl. standard format used to store the increment. The extracted G06F 7/22 ( ) page is displayed by the application while unloading the G06F 7/2 ( ) previously displayed page from System memory. START DISPLAYAPAGE OFA CONTENT DETECT AUSERACTEON OOAD ANOTHERPAGE OF THE CONENT DETERMINEAOCAON OF THE OTHERPAGE IN THE CONTEN REREVEANINCREMENT OF THE CONTENT FROM THE LOCATON PROCESS THE INCREMENT TO EXTRACT THE OTHER PAGE SPLAY THE OTHERPAGE
2 Patent Application Publication Jun. 12, 2014 Sheet 1 of 6 US 2014/O A1 T\/_LNHWEB-HONË LNB LNO? LNB LNOO
3 Patent Application Publication Jun. 12, 2014 Sheet 2 of 6 US 2014/O A1 &.
4 Patent Application Publication Jun. 12, 2014 Sheet 3 of 6 US 2014/O A1 3. s
5 Patent Application Publication Jun. 12, 2014 Sheet 4 of 6 US 2014/O A1 FIG. 4
6 Patent Application Publication Jun. 12, 2014 Sheet 5 of 6 US 2014/O A1 COMPUTING DEVICE OPERATNG SYSTEM PROCESSENG UNT INPUT DEVICE(S) 514 OUTPUT DEVICE(S) E-READER APPLICATION NCREMENT MODUE 56 COMMUNCATION CONNECTION(S) OTHER COMPUTING DEVCES FIG. 5
7 Patent Application Publication Jun. 12, 2014 Sheet 6 of 6 US 2014/O A1 START OSPAYA PAGE OF A CONTENT DETECT A USER ACT ON TO OAD ANOTHER PAGE OF THE CONTENT DETERMNE AOCATION OF THE OTHER PAGE IN THE CONTENT RETREVE AN INCREMENT OF THE CONTENT FROM THE OCATION PROCESS THE INCREMENT TO EXTRACT THE OTHER PAGE OSPLAY THE OTHER PAGE END FIG. 6
8 US 2014/ A1 Jun. 12, 2014 CONSUMING CONTENT INCREMENTALLY BACKGROUND 0001 Mobile computing has transformed media con Sumption across markets. Miniaturization across product generations has enabled more functionality to be accom plished by Smaller devices. A modern Smartphone has more computing capacity thana desktop computer a few years ago. Mature product processes have also enabled advances in tech nology to be integrated to automated production of mobile devices seamlessly. Extensive automation has led to inexpen sive components. Inexpensive components have enabled manufacturing of inexpensive mobile devices providing functionality on the go Content presentation in mobile devices has signifi cant room for improvement. Navigation from a displayed portion to other areas in the content can be a uneven experi ence. Stutter during transition from one page to another while viewing the content can take away from the user experience. A malformed new page also can disrupt a user flow while consuming the content Variety of reasons can lead to a disruption of the user experience while consuming the content. Switching from content format to another usually leads to a pause for pro cessing the new format. Loading resource rich content can also tie up device resources in order to format and render the content. Buffering multiple content pages can exasperate the user experience by slowing down the device used to consume the content. Server based rendering can improve responsive ness. However, in spite of server based rendering, rapid con Sumption of rich content can still slow down a device unable to process complex media. SUMMARY This summary is provided to introduce a selection of concepts in a simplified form that are further described below in the Detailed Description. This summary is not intended to exclusively identify key features or essential features of the claimed Subject matter, nor is it intended as an aid in deter mining the scope of the claimed Subject matter Embodiments are directed to consuming content incrementally, for example, during a presentation. According to Some embodiments, an application of an e-reader device may display a page from hosted content. The content may include any media that is partitioned to pages or segments. A user action may be detected to load another page or segment of the content. Next, a location of the other page in the content may be determined by accessing the content at the content Source and traversing through the content to locate the other page. An increment of the content Such as a page or a portion of the content defined by a system setting (e.g., a chapter) may be retrieved from the location. The application may then process the increment to extract the other page, which may be displayed after processing These and other features and advantages will be apparent from a reading of the following detailed description and a review of the associated drawings. It is to be understood that both the foregoing general description and the following detailed description are explanatory and do not restrict aspects as claimed. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0007 FIG. 1 illustrates an example architectural diagram of consuming content incrementally during presentation in an e-reader according to some embodiments; 0008 FIG. 2 illustrates an example e-reader device con Suming content incrementally during presentation according to embodiments; 0009 FIG. 3 illustrates steps of consuming content incre mentally during presentation in an e-reader according to embodiments; 0010 FIG. 4 is a networked environment, where a system according to embodiments may be implemented; 0011 FIG. 5 is a block diagram of an example computing operating environment, where embodiments may be imple mented; and 0012 FIG. 6 illustrates a logic flow diagram for a process consuming content incrementally during presentation in an e-reader according to embodiments. DETAILED DESCRIPTION 0013 As briefly described above, content may be con Sumed incrementally during presentation in an e-reader device. An application of an e-reader device may determine a location of another page in content in response to detecting a user action to load the other page while displaying a page of the content. An increment of the content may be retrieved from the location and processed to extract and display the other page In the following detailed description, references are made to the accompanying drawings that form a part hereof, and in which are shown by way of illustrations specific embodiments or examples. These aspects may be combined, other aspects may be utilized, and structural changes may be made without departing from the spirit or scope of the present disclosure. The following detailed description is therefore not to be taken in a limiting sense, and the scope of the present disclosure is defined by the appended claims and their equiva lents While the embodiments will be described in the general context of program modules that execute in conjunc tion with an application program that runs on an operating system on a computing device, those skilled in the art will recognize that aspects may also be implemented in combina tion with other program modules Generally, program modules include routines, pro grams, components, data structures, and other types of struc tures that perform particular tasks or implement particular abstract data types. Moreover, those skilled in the art will appreciate that embodiments may be practiced with other computer system configurations, including hand-held devices, multiprocessor systems, microprocessor-based or programmable consumer electronics, minicomputers, main frame computers, and comparable computing devices. Embodiments may also be practiced in distributed computing environments where tasks are performed by remote process ing devices that are linked through a communications net work. In a distributed computing environment, program mod ules may be located in both local and remote memory storage devices Embodiments may be implemented as a computer implemented process (method), a computing system, or as an article of manufacture, such as a computer program product or computer readable media. The computer program product
9 US 2014/ A1 Jun. 12, 2014 may be a computer storage medium readable by a computer system and encoding a computer program that comprises instructions for causing a computer or computing system to perform example process(es). The computer-readable storage medium is a computer-readable memory device. The com puter-readable storage medium can for example be imple mented via one or more of a Volatile computer memory, a non-volatile memory, a hard drive, a flash drive, a floppy disk, or a compact disk, and comparable media Throughout this specification, the term platform may be a combination of software and hardware components for consuming content incrementally during presentation. Examples of platforms include, but are not limited to, a hosted service executed over a plurality of servers, an application executed on a single computing device, and comparable sys tems. The term server generally refers to a computing device executing one or more software programs typically in a networked environment. More detail on these technologies and example operations is provided below FIG. 1 illustrates an example architectural diagram of consuming content incrementally during presentation in an e-reader according to embodiments. The components and environments shown in diagram 100 are for illustration pur poses. Embodiments may be implemented in various local, networked, cloud-based and similar computing environments employing a variety of computing devices and systems, hard ware and Software An "e-reader device such as a tablet 110 may host an application providing incremental content 108 to a user. Such an application may be called an e-reader application, which may be a locally installed and executed application receiving content (e.g., e-books, documents, etc.) through wired or wireless networks. The e-reader application may also be a hosted service 106 provided by one or more servers and accessed by a user through the e-reader device (e.g., tablet 110). Content may be any type of consumable data including but not exclusive to text, audio, video, graphic, etc. Content may also include media combinations presented in a stan dardized format (e.g., a web page.) Content may be provided by a content server 102 hosting the content for consumption by services and devices An application according to embodiments may be a standalone application executed in a tablet device 110. A standalone application may retrieve incremental content directly from the content server 102. Alternatively, the appli cation may be a distributed application with multiple compo nents. In an example scenario, the application may have a client component executed in tablet 110. A reader service component 106 may be executed separately from the client component and manage content retrieval and processing Embodiments are not limited to implementation in a tablet 110. An application according to embodiments may process content incrementally during presentation in other platforms. A user may navigate through content incremen tally in any device capable of displaying the content. A touch enabled device (although preferable) is not necessary. A user may access incremental content using a standard mouse and keyboard interface FIG. 2 illustrates an example e-reader device con Suming content incrementally during presentation according to embodiments. Diagram 200 displays an application of an e-reader device presenting content incrementally A mobile device such as tablet 202 may display content through an e-reader application. The content may be partitioned to pages. Multiple pages 204 and 206 may be displayed through the tablet 202. In addition, navigation con trols 208 and 210 may provide navigation functionality. The navigation controls 208 and 210 are examples for illustration purposes. Additional navigation control may be provided through horizontal touch Swipes, keyboard strokes like arrow-left/page-up and arrow-right/page-down, a page loca tion slider, or similar techniques. A page as used herein refers to any predefined segment of content. Such segments may be of any size depending on application and/or device type, available display space, and similar parameters In response to detecting an activation of the naviga tion control 208, the application may contact the content resource to determine a location of an increment prior to page 204. The determined increment may be retrieved from the content source. If the increment encapsulates a single page, the increment may be processed for presentation in place of page 204. If the increment encapsulates multiple pages, the increment may be processed to extract the previous page. Next, the previous page may be displayed in place of page 204 and page 204 may be displayed in place of page 206. The page 206 may be unloaded from a local resource, including a memory segment, since it is no longer in active display In response to detecting an activation of the naviga tion control 210, the application may contact the content resource to determine a location of an increment next to page 206. The location may be determined by seeking an anchor to the other page in the content. The anchor may be stored within a link to the other page. The determined increment may be retrieved from the content resource. A Subsequent page in the increment may be displayed in place of page 206. Page 206 may be displayed in place of page 204. The page 204 may be unloaded from a local resource since it is no longer in active display Content may be formatted in a standard format such as hypertext markup language (html). The content may be partitioned into increments by the content resource. An incre ment may include a chapter. The increment may also be a single page The increment may be processed to retrieve a requested page for display. Processing may include decoding the increment using the format of the increment. Next, the requested page may be extracted from the decoded increment and prepared for display according to specifications of the display device. In addition, the prior page may be unloaded in response to displaying the requested page Content may be processed incrementally starting from the current reading position. The processing may be propagated forwards and backwards depending on the user action requesting the next page. Processed priority may be based on distance from the current location. The user action to navigate may include sequential request for a page Such as a previous and a next page. In addition, the user action may request to display a page out of sequence Such as a page available through a link in a table of contents. The user action may include an activation of a hyperlink to retrieve an incre ment containing the page FIG. 3 illustrates steps of consuming content incre mentally during presentation in an e-reader according to embodiments. Diagram 300 displays an e-reader device 306 displaying a page from an increment 304 retrieved from con tent An e-reader application executed in device 306 may respond to a user action to navigate to another page in the
10 US 2014/ A1 Jun. 12, 2014 content 302. The user action may be instigated by a user 308 by interacting with a navigation control of the e-reader appli cation. The application may determine a location of the requested page in the content 302. Upon determining the location, the application may retrieve the increment 304 from the content 302 from the location The increment may be processed to prepare the requested page for display by the e-reader application. An example process may include decoding a format of the incre ment. In an example scenario the increment may beformatted in extensible markup language (Xml) or html. The application may decode the Xml formatted increment and extract the requested page. The requested page may be formatted in a rendering format. The rendering format may include html. In addition, the requested page may be processed to match dis play characteristics of the currently displayed page. The dis play characteristics may include font size, font color, font type, etc If the increment includes multiple pages of the con tent, the processing may be prioritized based on proximity to the requested page. A page adjacent to the requested page may be assigned a high priority for processing. A page distant from the requested page may receive a low priority for pro cessing Each page may be processed using real page num bers. In an example scenario, a requested page may be pro vided an associated page number. If the requested page is adjacent to the currently presented page, the requested page may be provided with an incremented or decremented page number in relation to the page number of the currently pre sented page. If the user action requests a page away from the currently displayed page, the page number may be extracted from the increment retrieved from the content resource. In addition, the page number may be displayed according to a predetermined system specification. An example may include middle of a footer of the page The example scenarios and schemas in FIG. 2 through 3 are shown with specific components, data types, and configurations. Embodiments are not limited to systems according to these example configurations. Consuming con tent incrementally during presentation in an e-reader may be implemented in configurations employing fewer or additional components in applications and user interfaces. Furthermore, the example schema and components shown in FIG. 2 through 3 and their Subcomponents may be implemented in a similar manner with other values using the principles described herein FIG. 4 is a networked environment, where a system according to embodiments may be implemented. Local and remote resources may be provided by one or more servers 414 or a single server (e.g. web server) 416 Such as a hosted service. An application may execute on individual computing devices such as a smartphone 413, a tablet device 412, or a laptop computer 411 (client devices) and communicate with a content resource through network(s) As discussed above, an e-reader application may determine a location of another page within content in response to a detected user action to load the other page in place of a currently displayed page. The application may retrieve and process an increment from the location within the content to extract the other page. The processed page may be displayed in an e-reader device. Client devices may enable access to applications executed on remote server(s) (e.g. one of servers 414) as discussed previously. The server (s) may retrieve or store relevant data from/to data store(s) 419 directly or through database server Network(s) 410 may comprise any topology of serv ers, clients, Internet service providers, and communication media. A system according to embodiments may have a static or dynamic topology. Network(s) 410 may include secure networks such as an enterprise network, an unsecure network such as a wireless open network, or the Internet. Network(s) 410 may also coordinate communication over other networks such as Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) or cel lular networks. Furthermore, network(s) 410 may include short range wireless networks such as Bluetooth or similar ones. Network(s) 410 provide communication between the nodes described herein. By way of example, and not limita tion, network(s) 410 may include wireless media Such as acoustic, RF, infrared and other wireless media Many other configurations of computing devices, applications, data Sources, and data distribution systems may be employed to consume content incrementally during pre sentation in an e-reader. Furthermore, the networked environ ments discussed in FIG. 4 are for illustration purposes only. Embodiments are not limited to the example applications, modules, or processes FIG. 5 and the associated discussion are intended to provide a brief, general description of a Suitable computing environment in which embodiments may be implemented. With reference to FIG. 5, a block diagram of an example computing operating environment for an application accord ing to embodiments is illustrated, such as computing device 500. In a basic configuration, computing device 500 may include at least one processing unit 502 and system memory 504. Computing device 500 may also include a plurality of processing units that cooperate in executing programs. Depending on the exact configuration and type of computing device, the system memory 504 may be volatile (such as RAM), non-volatile (such as ROM, flash memory, etc.) or some combination of the two. System memory 504 typically includes an operating system 505 suitable for controlling the operation of the platform, such as the WINDOWS(R) and WINDOWS PHONE(R) operating systems from MICROSOFT CORPORATION of Redmond, Wash. The system memory 504 may also include one or more software applications such as program modules 506, an e-reader appli cation 522, and an increment module An e-reader application 522 may detecta user action to load another page of content to replace a currently dis played page of the content. The application 522 may deter mine a location of the other page and retrieve an increment from the location. The increment module 524 may process the increment to extract the other page. Processing may include decoding the format of the increment and preparing the extracted page for display. This basic configuration is illus trated in FIG. 5 by those components within dashed line Computing device 500 may have additional features or functionality. For example, the computing device 500 may also include additional data storage devices (removable and/ or non-removable) Such as, for example, magnetic disks, optical disks, or tape. Such additional storage is illustrated in FIG. 5 by removable storage 509 and non-removable storage 510. Computer readable storage media may include volatile and nonvolatile, removable and non-removable media imple mented in any method or technology for storage of informa tion, such as computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules, or other data. Computer readable storage
11 US 2014/ A1 Jun. 12, 2014 media is a computer readable memory device. System memory 504, removable storage 509 and non-removable stor age 510 are all examples of computer readable storage media. Computer readable storage media includes, but is not limited to, RAM, ROM, EEPROM, flash memory or other memory technology, CD-ROM, digital versatile disks (DVD) or other optical storage, magnetic cassettes, magnetic tape, magnetic disk storage or other magnetic storage devices, or any other medium which can be used to store the desired information and which can be accessed by computing device 500. Any Such computer readable storage media may be part of com puting device 500. Computing device 500 may also have input device(s)512 Such as keyboard, mouse, pen, Voice input device, touch input device, and comparable input devices. Output device(s) 514 Such as a display, speakers, printer, and other types of output devices may also be included. These devices are well known in the art and need not be discussed at length here Computing device 500 may also contain communi cation connections 516 that allow the device to communicate with other devices 518, such as over a wireless network in a distributed computing environment, a satellite link, a cellular link, and comparable mechanisms. Other devices 518 may include computer device(s) that execute communication applications, storage servers, and comparable devices. Com munication connection(s) 516 is one example of communi cation media. Communication media can include therein computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules, or other data in a modulated data signal, such as a carrier wave or other transport mechanism, and includes any information delivery media. The term modulated data sig nal means a signal that has one or more of its characteristics set or changed in Such a manner as to encode information in the signal. By way of example, and not limitation, communi cation media includes wired media Such as a wired network or direct-wired connection, and wireless media Such as acoustic, RF, infrared and other wireless media Example embodiments also include methods. These methods can be implemented in any number of ways, includ ing the structures described in this document. One Such way is by machine operations, of devices of the type described in this document Another optional way is for one or more of the individual operations of the methods to be performed in con junction with one or more human operators performing some. These human operators need not be co-located with each other, but each can be only with a machine that performs a portion of the program FIG. 6 illustrates a logic flow diagram for a process consuming content incrementally during presentation in an e-reader according to embodiments. Process 600 may be implemented by an e-reader application in Some examples Process 600 may begin with operation 610 where the e-reader application may display a page of content. The page may include any media or combination of media. The application may detect a user action to load another page of the content at operation 620. The user action may include activation of a navigation control to load the other page. At operation 630, the location of the other page in the content may be determined The location may be determined by tra versing the content to find the other page An increment of the content from the location may be retrieved at operation 640. The content may be partitioned to increments including one or more pages. An example increment may include a chapter. The increment may be processed to extract the other page at operation 650. The processing may include decoding the format of the increment and rendering the content to a display format. At operation 660, the other page may be displayed at the display device by the e-reader application Some embodiments may be implemented in a com puting device that includes a communication module, a memory, and a processor, where the processor executes a method as described above or comparable ones in conjunc tion with instructions stored in the memory. Other embodi ments may be implemented as a computer readable storage medium with instructions stored thereon for executing a method as described above or similar ones The operations included in process 600 is for illus tration purposes. Consuming content incrementally during presentation, according to embodiments, may be imple mented by similar processes with fewer or additional steps, as well as in different order of operations using the principles described herein The above specification, examples and data provide a complete description of the manufacture and use of the composition of the embodiments. Although the Subject mat ter has been described in language specific to structural fea tures and/or methodological acts, it is to be understood that the Subject matter defined in the appended claims is not nec essarily limited to the specific features or acts described above. Rather, the specific features and acts described above are disclosed as example forms of implementing the claims and embodiments. What is claimed is: 1. A method executed on a computing device for consum ing hosted content incrementally, the method comprising: displaying a page of the content; detecting an action to view another page of the content; determining a location of the other page in the content; retrieving an increment of the content from the location; processing the increment to extract the other page; and displaying the other page. 2. The method of claim 1, further comprising: detecting the action from an activation of a navigation control to load the other page. 3. The method of claim 1, further comprising: traversing the content at a content source to determine the location. 4. The method of claim 3, further comprising: retrieving an anchor from a link to the other page; seeking the anchor within the content at the content source to determine the location. 5. The method of claim 1, further comprising: in response to detecting an activation of a navigation con trol to load the other page, retrieving the increment from the location before a Subsequent location of the page. 6. The method of claim 1, further comprising: in response to detecting an activation of a navigation con trol to load the other page, retrieving the increment from the location after a previous location of the page. 7. The method of claim 1, further comprising: retrieving the increment including multiple pages; and decoding the increment using a format of the increment. 8. The method of claim 7, further comprising: extracting the other page from the decoded increment; and rendering the other page for display.
12 US 2014/ A1 Jun. 12, The method of claim 7, further comprising: decoding the increment using a standard format including at least one of extensible markup language (XML) and hypertext markup language (HTML). 10. The method of claim 1, further comprising: extracting the other page from the increment encompass ing a chapter. 11. The method of claim 1, further comprising: extracting the other page from the increment encompass ing a single page. 12. An e-reader device for consuming hosted content incre mentally, the e-reader device comprising: a memory configured to store instructions; and a processor coupled to the memory, the processor execut ing an application in conjunction with the instructions stored in the memory, wherein the application is config ured to: display a first page of the content; detect an action to load a second page of the content; determine a location of the second page in the content using a process to: retrieve an anchor from a link to the second page; seek the anchor within the content to determine the location; retrieve an increment of the content from the location; process the increment to extract the second page; and display the second page. 13. The e-reader device of claim 12, wherein the applica tion is further configured to: match at least one display characteristic of the second page to the first page including at least one of a font size, a font color, and a font type. 14. The e-reader device of claim 12, wherein the applica tion is further configured to: assign an adjacent page in relation the second page in the increment a high priority for processing. 15. The e-reader device of claim 12, wherein the applica tion is further configured to: assign a distant page in relation to the second page in the increment a low priority for processing. 16. The e-reader device of claim 15, wherein the applica tion is further configured to: remove the first page from a local resource including a memory segment in response to displaying the second page. 17. A computer-readable memory device with instructions stored thereon for consuming hosted content incrementally, the instructions comprising: displaying a first page of the content; detecting a user action to load a second page of the content; determining a location of the second page in the content by: retrieving an anchor from a link to the second page; seeking the anchor within the content to determine the location; retrieving an increment of the content from the location; processing the increment to extract the second page; matching at least one display characteristic of the second page to the first page including at least one of a fontsize, a font color, and a font type; and displaying the second page. 18. The computer-readable memory device of claim 17, wherein the instructions further comprise: presenting a page number while displaying the second page. 19. The computer-readable memory device of claim 18, wherein the instructions further comprise: retrieving the page number associated with the second page from the increment. 20. The computer-readable memory device of claim 18, wherein the instructions further comprise: incrementing a current page number of the first page to determine the page number if the first page is adjacent and prior in relation to the second page in the content; and decrementing a current page number of the first page to determine the page number if the first page is adjacent and next in relation to the second page in the content. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013
 (19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 00552O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0055202 A1 Heimendinger (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2011 (54) PREDICTIVE DATA CACHING (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/721:
(19) United States US 2011 00552O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0055202 A1 Heimendinger (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2011 (54) PREDICTIVE DATA CACHING (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/721:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O1591.22A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0159122 A1 Biswas et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) OPTIMIZER AS AN APPSTORE SERVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 705/26.1
(19) United States US 2013 O1591.22A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0159122 A1 Biswas et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) OPTIMIZER AS AN APPSTORE SERVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 705/26.1
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201402O1564A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0201564 A1 Jagtiani et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) HEALING CLOUD SERVICES DURING UPGRADES
(19) United States US 201402O1564A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0201564 A1 Jagtiani et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) HEALING CLOUD SERVICES DURING UPGRADES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 0347009 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0347009 A1 Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) API REDIRECTION FOR LIMITED (52) U.S. Cl. CAPABILITY
(19) United States US 2013 0347009 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0347009 A1 Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) API REDIRECTION FOR LIMITED (52) U.S. Cl. CAPABILITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PINNING Publication Classification. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060218500A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Sauve et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 28, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PINNING Publication Classification TABS IN A
(19) United States US 20060218500A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Sauve et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 28, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PINNING Publication Classification TABS IN A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(54) DISPLAY OF USER INTERFACE ELEMENTS (52) US. Cl. BASED ON TOUCH OR HARDWARE INPUT USPC /800; 715/764; 715/810; 715/788
 US 20130191779A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0191779 A1 Radakovitz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 25, 2013 (54) DISPLAY OF USER INTERFACE ELEMENTS (52) US.
US 20130191779A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0191779 A1 Radakovitz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 25, 2013 (54) DISPLAY OF USER INTERFACE ELEMENTS (52) US.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO941 1902B2 (12) United States Patent Rajabi et al. (54) RETRIEVING CONTENT FROMWEBSITE THROUGH SANDBOX (71) Applicant: Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC, Redmond, WA (US) (72) Inventors: Zeyad Rajabi,
USOO941 1902B2 (12) United States Patent Rajabi et al. (54) RETRIEVING CONTENT FROMWEBSITE THROUGH SANDBOX (71) Applicant: Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC, Redmond, WA (US) (72) Inventors: Zeyad Rajabi,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0352797 A1 Marusich et al. US 20160352797A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) COORONATING METADATA Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0352797 A1 Marusich et al. US 20160352797A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) COORONATING METADATA Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O103858A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0103858A1 Bracewell et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TEMPLATE ARCHITECTURE AND RENDERING ENGINE FOR WEB BROWSER
(19) United States US 2002O103858A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0103858A1 Bracewell et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TEMPLATE ARCHITECTURE AND RENDERING ENGINE FOR WEB BROWSER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O132798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0132798 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2008 (54) WIRELESS HEADSETS AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 2008O132798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0132798 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2008 (54) WIRELESS HEADSETS AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 (51) (52) (57) INFORMATION WORKER
 (19) United States US 20070299679A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0299679 A1 Sudan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) BUSINESS SYSTEM INTERFACE Inventors:
(19) United States US 20070299679A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0299679 A1 Sudan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) BUSINESS SYSTEM INTERFACE Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143881 A1 Smyers US 2009.0143881A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) DIGITAL MEDIA RECASTING Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O237046A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0237046A1 Burchall et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) UNICODE TRANSITIONAL CODE POINT DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl.... 71.5/531
US 2004O237046A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0237046A1 Burchall et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) UNICODE TRANSITIONAL CODE POINT DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl.... 71.5/531
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 200802601 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/02601 16 A1 Didcock (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 23, 2008 (54) FULLY REDUNDANT CALL RECORDING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 200802601 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/02601 16 A1 Didcock (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 23, 2008 (54) FULLY REDUNDANT CALL RECORDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction
 ( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 200801.72715A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0172715 A1 Geiger et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 17, 2008 (54) SCALABLE CONTEXT-BASED AUTHENTICATION (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 200801.72715A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0172715 A1 Geiger et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 17, 2008 (54) SCALABLE CONTEXT-BASED AUTHENTICATION (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,159,495 B2
 US0089495 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Carter-Schwendler et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012 (54) REMOTING SUB-PIXEL RESOLVED 6.2,671 B1* 6/2001 Peng et al.... 358,111 CHARACTERS 6,356,278
US0089495 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Carter-Schwendler et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012 (54) REMOTING SUB-PIXEL RESOLVED 6.2,671 B1* 6/2001 Peng et al.... 358,111 CHARACTERS 6,356,278
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/ A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr.
 US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140188977A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0188977 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPRATUS, METHOD FOR DEPLOYING (52) U.S. Cl. APPLICATIONS IN A
US 20140188977A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0188977 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPRATUS, METHOD FOR DEPLOYING (52) U.S. Cl. APPLICATIONS IN A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0215383 A1 PARK-EKECS et al. US 201402.15383A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) PARALLAX SCROLLING USER INTERFACE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0215383 A1 PARK-EKECS et al. US 201402.15383A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) PARALLAX SCROLLING USER INTERFACE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 9,588,741 B2. Liberant (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2017
 United States Patent USOO9588.741B2 (12) () Patent No.: Liberant (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2017 (54) METHODS, APPARATUSES AND 2006/0059464 A1 3/2006 Jameson... 717/120 COMPUTER PROGRAMI PRODUCTS FOR
United States Patent USOO9588.741B2 (12) () Patent No.: Liberant (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2017 (54) METHODS, APPARATUSES AND 2006/0059464 A1 3/2006 Jameson... 717/120 COMPUTER PROGRAMI PRODUCTS FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 200800284.06A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/00284.06 A1 JONNALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2008 (54) PROCESS REPLICATION METHOD AND (30) Foreign
US 200800284.06A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/00284.06 A1 JONNALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2008 (54) PROCESS REPLICATION METHOD AND (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015037.0644A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0370644 A1 Graefe et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOVERING PAGES OF A DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 11/1451
US 2015037.0644A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0370644 A1 Graefe et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOVERING PAGES OF A DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 11/1451
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070178909A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0178909 A1 Doyle (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification ENHANCED PRIVACY
US 20070178909A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0178909 A1 Doyle (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification ENHANCED PRIVACY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK
 SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014007 1473A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0071473 A1 Hohensee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) GENERIC SECONDARY
(19) United States US 2014007 1473A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0071473 A1 Hohensee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) GENERIC SECONDARY
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 20170046092A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0046092 A1 Srivilliputtur Mannarswamy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2017 (54) DATA DEDUPLICATION Publication Classification
US 20170046092A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0046092 A1 Srivilliputtur Mannarswamy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2017 (54) DATA DEDUPLICATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
Wireless devices supports in a simple environment
 USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 2014.0004952A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0004952 A1 Kern (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXCHANGINGVIRTUAL REWARDS FOR (52) U.S. Cl. COMPUTING RESOURCES USPC...
US 2014.0004952A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0004952 A1 Kern (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXCHANGINGVIRTUAL REWARDS FOR (52) U.S. Cl. COMPUTING RESOURCES USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0342470A1 (12) Patent Application Publication () Pub. No.: US 2016/0342470 A1 Cudak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) SEPARATING A HYBRIDASYMMETRIC (52) U.S. Cl. MX OF
(19) United States US 2016.0342470A1 (12) Patent Application Publication () Pub. No.: US 2016/0342470 A1 Cudak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) SEPARATING A HYBRIDASYMMETRIC (52) U.S. Cl. MX OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0097323A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097323 A1 Barsness et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) DYNAMIC PROCESSING UNIT RELOCATION IN A MULTI-NODAL
(19) United States US 2013 0097323A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0097323 A1 Barsness et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 18, 2013 (54) DYNAMIC PROCESSING UNIT RELOCATION IN A MULTI-NODAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application
 From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
