Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure
|
|
|
- Barnard Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Introduction Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure One of the most powerful features of GeoStudio is the smooth integration that exists between all the individual programs. For simple pore-water pressure situations, there are several different options that can be used directly within SLOPE/W. However, if the pore-water pressures become more complex, it is sometimes necessary to use SEEP/W to conduct a finite element seepage analysis to compute the porewater pressure profile. This is achieved by solving the finite element equations for every node in a finite element mesh. Once the finite element equations have been solved, SLOPE/W can be used to determine the critical slip surface by using the pore-water pressures that exist within the finite element mesh at the base of each slice. The objective of this example is to highlight the use of SEEP/W total heads in a stability analysis. Other features of this analysis include: Use of SEEP/W total heads in SLOPE/W The use of φ b Slip surface grid with a single-point radius Stability on upstream and downstream slopes Multiple analyses 2 Configuration and setup A schematic picture of the earth dam being modeled is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Profile and material properties In order to reproduce this example, you must have both SEEP/W and SLOPE/W installed in your computer. It is possible to develop the profile in either the SEEP/W or SLOPE/W module; however, the SEEP/W finite element equations need to be solved first, before the pore-water pressure results are available for use within SLOPE/W. The material property parameters defined for the embankment material within SLOPE/W is shown in Table 1. SLOPE/W Example File: Stability with FE pore water pressure.doc (pdf) (gsz) Page 1 of 6
2 Table 1 Material property parameters used in SLOPE/W Parameter Embankment Frictional angle φ, (degrees) 30 Cohesion c, (kpa) 25 Unsaturated φ b, (degrees) 10 Unit weight γ, (kn/m 3 ) 20 3 SEEP/W steady state seepage result In SEEP/W, the presence of an upstream reservoir is reflected in the boundary condition assigned to the upstream face of the embankment. The presence of the upstream reservoir is reflected in SEEP/W by the total head boundary condition of 10 m. A potential seepage face is also included on the downstream face by defining a total flux boundary of Q=0 (potential seepage face). The conductivity function defined in SEEP/W for the embankment material is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 Conductivity function defined in SEEP/W for the embankment Figure 3 shows the steady state results of the seepage analysis, including the location of the phreatic surface and the development of a downstream seepage face; the velocity vectors and the pressure head contours. Note the presence of negative pore-water pressures above the phreatic surface (P=0 contour). Figure 3 Results obtained from the finite element simulation SLOPE/W Example File: Stability with FE pore water pressure.doc (pdf) (gsz) Page 2 of 6
3 4 SLOPE/W downstream stability Now that the total heads have been computed for every node within the profile, a stability analysis can be completed to determine the stability of the downstream face using the finite element computed pore-water pressure profile. Figure 4 shows the location of the search grid and the location of a single radius point for the stability analysis. Note that the water appears as a shaded zone with water force arrows acting on the ground surface line within the SLOPE/W module automatically. The vertical weight of the water and the horizontal hydrostatic force needs to be included in the SLOPE/W analysis as these forces affect the stability of the slope. There were not needed to solve the finite element seepage equations in SEEP/W. Internally, SLOPE/W develops the shaded water layer by referring to the positive pressures that exist on the ground surface line. Figure 4 Earth dam embankment as defined in SLOPE/W with the shaded water layer and water force vectors The finite element mesh still appears within the SLOPE/W module, but the finite element equations are not solved as part of the stability analysis. The pore-water pressures at the base of each slice will be determined from the heads computed at the finite element nodes. It is for this reason that a piezometric line is NOT drawn within SLOPE/W. The stabilizing weight of the water is modeled automatically from the finite element computed positive pore-water pressures that exist on the ground surface line. Figure 5 shows the location of the critical slip surface and the factor of safety for the downstream face. Note that a phreatic surface is drawn within the embankment, even though a piezometric line was not defined with SLOPE/W. The phreatic surface is part of the SEEP/W results, superimposed on the critical slip surface. Also note that the critical slip surface has passed through the single radius point at the bottom of the embankment. SLOPE/W Example File: Stability with FE pore water pressure.doc (pdf) (gsz) Page 3 of 6
4 Figure 5 Factor of safety and critical slip surface of downstream slope In assigning the material properties for the embankment material, an advanced parameter, φ b =10 was also defined. A graph of strength versus slice number (Figure 6) shows that for the slices that exist above the phreatic surface (slices 1 and 2), there are actually three strength components; cohesion, friction and suction. In this example, the additional strength due to suction is relatively small. Figure 6 Graph of strength versus slice number showing the presence of a strength component due to suction SLOPE/W Example File: Stability with FE pore water pressure.doc (pdf) (gsz) Page 4 of 6
5 5 SLOPE/W upstream stability In this analysis, the slip surface direction of movement has been changed to be from right to left and the search grid and radius has been moved to look at stability of the upstream embankment. Figures 7 shows the new location of the search grid and radius. The presence of the reservoir is still automatically included based on the computed SEEP/W pore water pressure on the upstream slope. Figure 7 Location of the grid and radius used to analyse upstream stability Figure 8 Factor of safety and critical slip surface of upstream slope SLOPE/W Example File: Stability with FE pore water pressure.doc (pdf) (gsz) Page 5 of 6
6 Figure 8 shows the computed factor of safety for the critical slip surface and Figure 9 shows the individual slice forces acting on Slice #8, which is located half-way up the submerged slope where the water is 6 m deep. Figure 9: Slice forces for slice #8 By hand calculation, the water force (F) acting on the top of the slice can be calculated as follows: where: FV = (γ x Hw) x bv x unit depth FH = (γ x Hw) x bh x unit depth γ = unit weight of water Hw = height of the water at the top, centre of the slice bv = width of the slice as given in the slice force information bh = bv* tan(α) α = angle of the slope For slice #8, with a water depth of 6 m, a slice width (bv) of m and a slope angle (α) of degrees, the vertical and horizontal water forces would be: Fv = (9.807 x 6) x m x 1 m = kn FH = (9.807 x 6) x [ m x tan(26.57)] = kn. The resultant force (F) is therefore computed as: F 2 = (FH 2 + FV 2 ) = ( ) = kn which corresponds exactly with the line load acting at the top of the slice as shown in Figure 9. SLOPE/W Example File: Stability with FE pore water pressure.doc (pdf) (gsz) Page 6 of 6
Stability with FE Stresses
 1 Introduction Stability with FE Stresses In the finite element stresses stability analysis method, the stresses in the ground can be computed using SIGMA/W, and then SLOPE/W uses the SIGMA/W stresses
1 Introduction Stability with FE Stresses In the finite element stresses stability analysis method, the stresses in the ground can be computed using SIGMA/W, and then SLOPE/W uses the SIGMA/W stresses
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Rapid drawdown
 Elevation Introduction Rapid drawdown The objective of this illustration is to show how to model the rapid drawdown of a reservoir. It presents two cases one with instantaneous drawdown and another with
Elevation Introduction Rapid drawdown The objective of this illustration is to show how to model the rapid drawdown of a reservoir. It presents two cases one with instantaneous drawdown and another with
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Sheet Pile Wall
 1 Introduction Sheet Pile Wall Deep excavation on a level group usually results in a very low factor of safety, unless it is properly reinforced. The purpose of this example is to illustrate how the stability
1 Introduction Sheet Pile Wall Deep excavation on a level group usually results in a very low factor of safety, unless it is properly reinforced. The purpose of this example is to illustrate how the stability
This is the script for the SEEP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, SEEP/W Getting Started.
 SEEP/W Tutorial This is the script for the SEEP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, SEEP/W Getting Started. Introduction Here are some results obtained by using SEEP/W to analyze unconfined
SEEP/W Tutorial This is the script for the SEEP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, SEEP/W Getting Started. Introduction Here are some results obtained by using SEEP/W to analyze unconfined
GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison
 GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element
GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Lysimeters
 1 Introduction Lysimeters This steady state SEEP/W example illustrates how to model a lysimeter from construction of the model to interpretation of the results. Lysimeters are used to measure flow through
1 Introduction Lysimeters This steady state SEEP/W example illustrates how to model a lysimeter from construction of the model to interpretation of the results. Lysimeters are used to measure flow through
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd , 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: Fax:
 Grid and Radius GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction In early limit equilibrium slope
Grid and Radius GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction In early limit equilibrium slope
Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage. Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis
 Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis Introduction Within the Slide program, Slide has the capability to carry out
Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis Introduction Within the Slide program, Slide has the capability to carry out
Developer s Tips. Groundwater analysis using Slide
 Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
Effects on an earth- and rockfill dam undergoing dam safety measures
 NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Effects on an earth- and rockfill dam undergoing dam safety measures J. Toromanović,
NGM 2016 Reykjavik Proceedings of the 17 th Nordic Geotechnical Meeting Challenges in Nordic Geotechnic 25 th 28 th of May Effects on an earth- and rockfill dam undergoing dam safety measures J. Toromanović,
RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS
 RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS 6 RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS This example concerns the stability of a reservoir dam under conditions of drawdown. Fast reduction of the reservoir level may lead to instability of the
RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS 6 RAPID DRAWDOWN ANALYSIS This example concerns the stability of a reservoir dam under conditions of drawdown. Fast reduction of the reservoir level may lead to instability of the
A Sliding Block Analysis
 1 Introduction A Sliding Block Analysis This example simulates the sliding of a block on a rigid surface. The primary purpose of this example is to check the behavior of the slip (interface) elements in
1 Introduction A Sliding Block Analysis This example simulates the sliding of a block on a rigid surface. The primary purpose of this example is to check the behavior of the slip (interface) elements in
2D & 3D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope
 D & D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASoft NY office Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform Finite Element
D & D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASoft NY office Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform Finite Element
Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown
 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown 17-1 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown When the water level at a dam drops, the stabilizing force due to the weight of the water is removed. If the dam material has a low permeability
Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown 17-1 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown When the water level at a dam drops, the stabilizing force due to the weight of the water is removed. If the dam material has a low permeability
Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes
 Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes Part 1: Planar Analysis A Deterministic Analysis This exercise will demonstrate the basics of a deterministic limit equilibrium planar analysis
Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes Part 1: Planar Analysis A Deterministic Analysis This exercise will demonstrate the basics of a deterministic limit equilibrium planar analysis
Three-Dimensional Slope Stability: Geometry Effects
 Three-Dimensional Slope Staility: Geometry Effects Krishna Bahadur Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, SK, Canada Vanessa Honorato Domingos Universidade Federal de Goias, Goiania, Brazil Gilson
Three-Dimensional Slope Staility: Geometry Effects Krishna Bahadur Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, SK, Canada Vanessa Honorato Domingos Universidade Federal de Goias, Goiania, Brazil Gilson
FLAC/Slope User s Guide Contents - 1
 FLAC/Slope User s Guide Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 FLAC/SLOPE 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 Guide to the FLAC/Slope Manual... 1-2 1.1.3 Summary of Features... 1-2 1.1.4 Analysis
FLAC/Slope User s Guide Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 FLAC/SLOPE 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.1.2 Guide to the FLAC/Slope Manual... 1-2 1.1.3 Summary of Features... 1-2 1.1.4 Analysis
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series
 MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D
 Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
GMS 8.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam Profile Analysis Use UTEXAS to find the critical failure surface for a complex earth dam
 v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Use UTEXAS to find the critical failure surface for a complex earth dam Objectives Import a CAD file and convert it to Feature Objects. Use the Feature Objects to create a UTEXAS
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial Use UTEXAS to find the critical failure surface for a complex earth dam Objectives Import a CAD file and convert it to Feature Objects. Use the Feature Objects to create a UTEXAS
Transient Groundwater Analysis
 Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
2016(v1.1) Release Notes
 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Ver 4.0.0. 개정내용 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Copyright c 1989~2014. MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 1 / 21 Release Note 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Pre-Processing
2016(v1.1) Release Notes Ver 4.0.0. 개정내용 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Copyright c 1989~2014. MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 1 / 21 Release Note 2016(v1.1) Release Notes Pre-Processing
Slope stability analysis
 Engineering manual No. 8 Updated: 04/2018 Slope stability analysis Program: Slope stability File: Demo_manual_08.gst This engineering manual shows how to verify the slope stability for a critical circular
Engineering manual No. 8 Updated: 04/2018 Slope stability analysis Program: Slope stability File: Demo_manual_08.gst This engineering manual shows how to verify the slope stability for a critical circular
Seepage Flow through Homogeneous Earth Dams
 Seepage Flow through Homogeneous Earth Dams In order to draw flow net to find quantity of seepage through the body of the earth dam it is essential to locate top line of seepage. This upper boundary is
Seepage Flow through Homogeneous Earth Dams In order to draw flow net to find quantity of seepage through the body of the earth dam it is essential to locate top line of seepage. This upper boundary is
CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT
 CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT 4 CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT The construction of an embankment on soft soil with a high groundwater level leads to an increase in pore pressure. As a result of
CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT 4 CONSTRUCTION OF A ROAD EMBANKMENT The construction of an embankment on soft soil with a high groundwater level leads to an increase in pore pressure. As a result of
Copyright by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd.
 Copyright 2004-2017 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
Copyright 2004-2017 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
Tutorial 2 Materials and Loading
 Tutorial 2 Materials and Loading Multiple material slope with weak layer Pore pressure defined by water table Uniformly distributed external load Circular slip surface search (Grid search) Introduction
Tutorial 2 Materials and Loading Multiple material slope with weak layer Pore pressure defined by water table Uniformly distributed external load Circular slip surface search (Grid search) Introduction
Seepage_CSM8. A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems.
 Seepage_CSM8 A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems. USER S MANUAL J. A. Knappett (2012) This user s manual
Seepage_CSM8 A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems. USER S MANUAL J. A. Knappett (2012) This user s manual
Slope Stability Problem Session
 Slope Stability Problem Session Stability Analysis of a Proposed Soil Slope Using Slide 5.0 Tuesday, February 28, 2006 10:00 am - 12:00 pm GeoCongress 2006 Atlanta, GA software tools for rock and soil
Slope Stability Problem Session Stability Analysis of a Proposed Soil Slope Using Slide 5.0 Tuesday, February 28, 2006 10:00 am - 12:00 pm GeoCongress 2006 Atlanta, GA software tools for rock and soil
Slip Surface Optimization
 Slip Surface Optimization GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Traditionally, trial slip
Slip Surface Optimization GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction Traditionally, trial slip
GeoStudio Product Details
 Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Vadose Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Methods Ordinary
Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Vadose Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Methods Ordinary
GeoStudio Product Details
 Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Ordinary Yes Yes Yes
Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Ordinary Yes Yes Yes
Stability Modeling with SLOPE/W
 Stability Modeling with SLOPE/W An Engineering Methodology John Krahn First Edition, Revision 1, August 2004 Copyright 2004 by GEO-SLOPE/W International, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this work
Stability Modeling with SLOPE/W An Engineering Methodology John Krahn First Edition, Revision 1, August 2004 Copyright 2004 by GEO-SLOPE/W International, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this work
THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK
 THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK 15 THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK A navigable lock is temporarily 'empty' due to maintenance. After some time there is significant increase of the air temperature,
THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK 15 THERMAL EXPANSION OF A NAVIGABLE LOCK A navigable lock is temporarily 'empty' due to maintenance. After some time there is significant increase of the air temperature,
GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE
 GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE Prof. J. N. Mandal Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Tel.022-25767328 email: cejnm@civil.iitb.ac.in Module-12 LECTURE-
GEOSYNTHETICS ENGINEERING: IN THEORY AND PRACTICE Prof. J. N. Mandal Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Tel.022-25767328 email: cejnm@civil.iitb.ac.in Module-12 LECTURE-
DRY EXCAVATION USING A TIE BACK WALL
 3 This example involves the dry construction of an excavation. The excavation is supported by concrete diaphragm walls. The walls are tied back by prestressed ground anchors. Silt Sand 10 m 2 m 20 m 10
3 This example involves the dry construction of an excavation. The excavation is supported by concrete diaphragm walls. The walls are tied back by prestressed ground anchors. Silt Sand 10 m 2 m 20 m 10
PLAXIS 2D. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 2D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 8601 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Settlement of a circular footing on sand 7 1.1 Geometry 7 1.2 Case A: Rigid footing 8 1.3 Case B: Flexible footing 23 2 Submerged
PLAXIS 2D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 8601 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Settlement of a circular footing on sand 7 1.1 Geometry 7 1.2 Case A: Rigid footing 8 1.3 Case B: Flexible footing 23 2 Submerged
An Introductory SIGMA/W Example
 1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
This is the script for the TEMP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, TEMP/W Getting Started.
 TEMP/W Tutorial This is the script for the TEMP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, TEMP/W Getting Started. Introduction Here is a schematic diagram of the problem to be solved. An ice
TEMP/W Tutorial This is the script for the TEMP/W tutorial movie. Please follow along with the movie, TEMP/W Getting Started. Introduction Here is a schematic diagram of the problem to be solved. An ice
UTEXAS4 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SLOPE STABILITY CALCULATIONS. Stephen G. Wright. May Revised September Shinoak Software Austin, Texas
 UTEXAS4 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SLOPE STABILITY CALCULATIONS By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 - Revised September 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights
UTEXAS4 A COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR SLOPE STABILITY CALCULATIONS By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 - Revised September 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights
PHASED EXCAVATION OF A SHIELD TUNNEL
 5 PHASED EXCAVATION OF A SHIELD TUNNEL The lining of a shield tunnel is often constructed using prefabricated concrete ring segments, which are bolted together within the tunnel boring machine to form
5 PHASED EXCAVATION OF A SHIELD TUNNEL The lining of a shield tunnel is often constructed using prefabricated concrete ring segments, which are bolted together within the tunnel boring machine to form
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
GTS. midas GTS Advanced Webinar. Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar
 midas GTS Advanced Webinar Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar Bridging Your Innovations to Realities GTS MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. [1/30] Contents:
midas GTS Advanced Webinar Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar Bridging Your Innovations to Realities GTS MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. [1/30] Contents:
SOIL PEMEABILITY AND SEEPAGE
 SOIL PEMEABILITY AND SEEPAGE The elevation head (z) is equal to the vertical distance of the point above the datum. The pressure head (p/γ w)is equal to the head indicated by a piezometer with its tip
SOIL PEMEABILITY AND SEEPAGE The elevation head (z) is equal to the vertical distance of the point above the datum. The pressure head (p/γ w)is equal to the head indicated by a piezometer with its tip
Critical acceleration versus static factor of safety in stability analysis of earth dams and embankments
 TECHNICAL NOTES Critical acceleration versus static factor of safety in stability analysis of earth dams and embankments S. K. SARMA, BTech, PhD, DIC* and M. V. BHAVE BSc, DIG* It has been shown (Sarma,
TECHNICAL NOTES Critical acceleration versus static factor of safety in stability analysis of earth dams and embankments S. K. SARMA, BTech, PhD, DIC* and M. V. BHAVE BSc, DIG* It has been shown (Sarma,
FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 14 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building consists
14 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building consists
Gabion analysis Input data
 Gabion analysis Input data Project Date :.0.0 Settings (input for current task) Wall analysis Active earth pressure calculation : Passive earth pressure calculation : Earthquake analysis : Shape of earth
Gabion analysis Input data Project Date :.0.0 Settings (input for current task) Wall analysis Active earth pressure calculation : Passive earth pressure calculation : Earthquake analysis : Shape of earth
Pseudo 3-D deposition and large-strain consolidation modeling of tailings deep deposits
 Pseudo 3-D deposition and large-strain consolidation modeling of tailings deep deposits Murray Fredlund, Matt Donaldson, Krishna Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd ABSTRACT The design of deep deposits requires
Pseudo 3-D deposition and large-strain consolidation modeling of tailings deep deposits Murray Fredlund, Matt Donaldson, Krishna Chaudhary SoilVision Systems Ltd ABSTRACT The design of deep deposits requires
Seepage Modeling. An Engineering Methodology. June 2015 Edition. GEO-SLOPE International Ltd.
 Seepage Modeling with SEEP/W An Engineering Methodology June 2015 Edition GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. Copyright 2004-2015 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this work may
Seepage Modeling with SEEP/W An Engineering Methodology June 2015 Edition GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. Copyright 2004-2015 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this work may
USER S MANUAL CLARA-W SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS IN TWO OR THREE DIMENSIONS FOR MICROCOMPUTERS
 USER S MANUAL CLARA-W SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS IN TWO OR THREE DIMENSIONS FOR MICROCOMPUTERS O.Hungr Geotechnical Research Inc. 4195 Almondel Road, West Vancouver B.C., Canada, V7V 3L6 Tel. (604) 926-9129
USER S MANUAL CLARA-W SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS IN TWO OR THREE DIMENSIONS FOR MICROCOMPUTERS O.Hungr Geotechnical Research Inc. 4195 Almondel Road, West Vancouver B.C., Canada, V7V 3L6 Tel. (604) 926-9129
OP-029. INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST
 INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page 1 of 7 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS KYW Compiled by : Checked by LCH : TYC Approved by : OP-09. INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page of 7 9. INTERPRETATION
INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page 1 of 7 WORK INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGINEERS KYW Compiled by : Checked by LCH : TYC Approved by : OP-09. INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST INTERPRETATION OF CIU TEST Page of 7 9. INTERPRETATION
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
v SEEP2D Sheet Pile Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
 v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) Figure 3.1 Geometry of a circular footing on a sand layer
 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
Stability Analysis of Cellular Retaining Structure by PLAXIS Finite Element Code
 The Iraqi Journal For Mechanical And Material Engineering, Special Issue (D) Stability Analysis of Cellular Retaining Structure by PLAXIS Finite Element Code By Kadhim Naief Al-Taee, Sarmad Hameed Al-Rammahi
The Iraqi Journal For Mechanical And Material Engineering, Special Issue (D) Stability Analysis of Cellular Retaining Structure by PLAXIS Finite Element Code By Kadhim Naief Al-Taee, Sarmad Hameed Al-Rammahi
PLAXIS 3D. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 9039 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 1.1 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 1.2 Case B: Raft foundation 20 1.3 Case C: Pile-Raft
PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2017 Build 9039 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 1.1 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 1.2 Case B: Raft foundation 20 1.3 Case C: Pile-Raft
CARL J. FRIMANN CLAUSEN CONSULTING CIVIL ENGINEER
 CARL J. FRIMANN CLAUSEN CONSULTING CIVIL ENGINEER BEAST A Computer Program for Limit Equilibrium Analysis by the Method of Slices Report 8302-2 Revision 0, 5 October 1988 Revision 1, 24 April 1990 Revision
CARL J. FRIMANN CLAUSEN CONSULTING CIVIL ENGINEER BEAST A Computer Program for Limit Equilibrium Analysis by the Method of Slices Report 8302-2 Revision 0, 5 October 1988 Revision 1, 24 April 1990 Revision
Verification Manual Written by: The SoilVision Systems Ltd. Team
 Verification Manual Written by: The SoilVision Systems Ltd. Team Last Updated: Thursday, September 06, 2018 SoilVision Systems Ltd. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada Software License The software described
Verification Manual Written by: The SoilVision Systems Ltd. Team Last Updated: Thursday, September 06, 2018 SoilVision Systems Ltd. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada Software License The software described
Copyright by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd
 Copyright 2004-2017 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
Copyright 2004-2017 by GEO-SLOPE International, Ltd All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
PLAXIS 3D Tunnel. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D Tunnel Tutorial Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 2 Getting started...2-1 2.1 Installation...2-1 2.2 General modelling aspects...2-1 2.3 Input procedures...2-3
PLAXIS 3D Tunnel Tutorial Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 2 Getting started...2-1 2.1 Installation...2-1 2.2 General modelling aspects...2-1 2.3 Input procedures...2-3
GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW
 CVE 341 Water Resources Lecture Notes 5: (Chapter 14) GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW FLOW CLASSIFICATION Uniform (normal) flow: Depth is constant at every section along length of channel Non-uniform (varied) flow:
CVE 341 Water Resources Lecture Notes 5: (Chapter 14) GRADUALLY VARIED FLOW FLOW CLASSIFICATION Uniform (normal) flow: Depth is constant at every section along length of channel Non-uniform (varied) flow:
Slope stability analysis software designed to solve geotechnical problems quickly and accurately using models that simulate geological conditions
 Slope stability analysis software designed to solve geotechnical problems quickly and accurately using models that simulate geological conditions GALENA is a powerful and easy to use slope stability analysis
Slope stability analysis software designed to solve geotechnical problems quickly and accurately using models that simulate geological conditions GALENA is a powerful and easy to use slope stability analysis
Modeling Foundations in RS
 Modeling Foundations in RS 3 Piled Raft Modeling in RS 3 Deep foundation piles are commonly used to increase foundation stability and to increase the bearing capacity of structural systems. The design
Modeling Foundations in RS 3 Piled Raft Modeling in RS 3 Deep foundation piles are commonly used to increase foundation stability and to increase the bearing capacity of structural systems. The design
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial SEEP2D Sheet Pile Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in
I/O format for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis
 I/O format for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis (f90 FEM SEEP.f90) December 2, 2012 1. Outline of a program f90 FEM SEEP.f90 This is a program for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis. This program can not treat
I/O format for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis (f90 FEM SEEP.f90) December 2, 2012 1. Outline of a program f90 FEM SEEP.f90 This is a program for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis. This program can not treat
Potential Applications of the new InfoWorks ICM Mesh level Zones
 Introduction Potential Applications of the new InfoWorks ICM Mesh level Zones Exciting new functionality has been added to InfoWorks ICM version 5.5 to allow improved editing of the 2D mesh. The new functionality
Introduction Potential Applications of the new InfoWorks ICM Mesh level Zones Exciting new functionality has been added to InfoWorks ICM version 5.5 to allow improved editing of the 2D mesh. The new functionality
Slope Stability (Sarma Method) Verification Manual
 Slide 2D limit equilibrium slope stability for soil and rock slopes Slope Stability (Sarma Method) Verification Manual 2016 Rocscience Inc. Table of Contents Introduction 1 Slide Verification Problem #1
Slide 2D limit equilibrium slope stability for soil and rock slopes Slope Stability (Sarma Method) Verification Manual 2016 Rocscience Inc. Table of Contents Introduction 1 Slide Verification Problem #1
Numerical Modeling Study for Fish Screen at River Intake Channel ; PH (505) ; FAX (505) ;
 Numerical Modeling Study for Fish Screen at River Intake Channel Jungseok Ho 1, Leslie Hanna 2, Brent Mefford 3, and Julie Coonrod 4 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque,
Numerical Modeling Study for Fish Screen at River Intake Channel Jungseok Ho 1, Leslie Hanna 2, Brent Mefford 3, and Julie Coonrod 4 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque,
Application Note - Gravity Wall Analysis
 LS-G-AN3 Software: LimitState:GEO 2.0f Date: February 2011 Application Note - Gravity Wall Analysis 1 Introduction This note describes the typical steps followed in setting up and analysing a gravity wall
LS-G-AN3 Software: LimitState:GEO 2.0f Date: February 2011 Application Note - Gravity Wall Analysis 1 Introduction This note describes the typical steps followed in setting up and analysing a gravity wall
PLAXIS 3D. Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2010 Build 2681 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction 5 2 Lesson 1: Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 2.1 Geometry 7 2.2 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 2.3 Case B:
PLAXIS 3D Tutorial Manual 2010 Build 2681 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction 5 2 Lesson 1: Foundation in overconsolidated clay 7 2.1 Geometry 7 2.2 Case A: Rigid foundation 8 2.3 Case B:
TOCHNOG PROFESSIONAL Tutorial manual
 1 TOCHNOG PROFESSIONAL Tutorial manual Dennis Roddeman March 7, 2018 2 Contents 1 Conditions 5 2 Basic information 6 3 Tutorial 1: slope safety factor analysis 7 3.1 Mesh generation with Gid................................
1 TOCHNOG PROFESSIONAL Tutorial manual Dennis Roddeman March 7, 2018 2 Contents 1 Conditions 5 2 Basic information 6 3 Tutorial 1: slope safety factor analysis 7 3.1 Mesh generation with Gid................................
Terrain settlement analysis
 Engineering manual No. 21 Updated: 02/2018 Terrain settlement analysis Program: File: FEM Demo_manual_21.gmk This example contains the solution to terrain settlement under surcharge loading using the Finite
Engineering manual No. 21 Updated: 02/2018 Terrain settlement analysis Program: File: FEM Demo_manual_21.gmk This example contains the solution to terrain settlement under surcharge loading using the Finite
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial SEEP2D Sheet Pile Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Prerequisite Tutorials None Time minutes
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in GMS.
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D to create a flow net around a sheet pile Objectives Learn how to set up and solve a seepage problem involving flow around a sheet pile using the SEEP2D interface in GMS.
Determination of Free Surface in Steady-State Seepage through a Dam with Toe Drain by the Boundary Element Method
 Determination of Free Surface in Steady-State Seepage through a Dam with Toe Drain by the Boundary Element Method Somchart Chantasiriwan Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University, Rangsit Campus, Pathum
Determination of Free Surface in Steady-State Seepage through a Dam with Toe Drain by the Boundary Element Method Somchart Chantasiriwan Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University, Rangsit Campus, Pathum
DESIGN OF PILES BASED ON THE 3-D SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS(LEM)
 ICCI2004, The First International Conference on Construction IT, Beijing, CHINA, August 12 th - 14 th DESIGN OF PILES BASED ON THE 3-D SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS(LEM) Atsushi Nakamura FORUM8 Co.,Ltd.,2-1-1,Nakameguro
ICCI2004, The First International Conference on Construction IT, Beijing, CHINA, August 12 th - 14 th DESIGN OF PILES BASED ON THE 3-D SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSIS(LEM) Atsushi Nakamura FORUM8 Co.,Ltd.,2-1-1,Nakameguro
Lab Practical - Boundary Element Stress Analysis
 Lab Practical - Boundary Element Stress Analysis Part A The Basics In this example we will model a simple set of excavations using the Rocscience program EXAMINE 2D. The first step is to define the geometry
Lab Practical - Boundary Element Stress Analysis Part A The Basics In this example we will model a simple set of excavations using the Rocscience program EXAMINE 2D. The first step is to define the geometry
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE
 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE Jungseok Ho 1, Hong Koo Yeo 2, Julie Coonrod 3, and Won-Sik Ahn 4 1 Research Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE Jungseok Ho 1, Hong Koo Yeo 2, Julie Coonrod 3, and Won-Sik Ahn 4 1 Research Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
UTEXAS Embankment on Soft Clay
 GMS TUTORIALS Figure 1. Sample slope stability problem from the Utexam1.dat file provided with the UTEXAS4 software. 1 Introduction UTEXAS4 is a slope stability software package created by Dr. Stephen
GMS TUTORIALS Figure 1. Sample slope stability problem from the Utexam1.dat file provided with the UTEXAS4 software. 1 Introduction UTEXAS4 is a slope stability software package created by Dr. Stephen
Bridge Software Institute 2
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report summarizes six API soil models that have been implemented into the FB- MultiPier computer program according to the American Petroleum Institute Recommended Practice 2A LRFD
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report summarizes six API soil models that have been implemented into the FB- MultiPier computer program according to the American Petroleum Institute Recommended Practice 2A LRFD
SSR Polygonal Search Area
 SSR Polygonal Search Area 22-1 SSR Polygonal Search Area In this tutorial, Phase2 is used to determine the factor of safety of a slope using the shear strength reduction (SSR) method. The SSR Polygon Search
SSR Polygonal Search Area 22-1 SSR Polygonal Search Area In this tutorial, Phase2 is used to determine the factor of safety of a slope using the shear strength reduction (SSR) method. The SSR Polygon Search
PLAXIS 3D TUNNEL Introductory Version Tutorial Manual
 PLAXIS 3D TUNNEL Introductory Version Tutorial Manual Disclaimer: PLAXIS is a finite element program for geotechnical applications in which soil models are used to simulate the soil behaviour. The PLAXIS
PLAXIS 3D TUNNEL Introductory Version Tutorial Manual Disclaimer: PLAXIS is a finite element program for geotechnical applications in which soil models are used to simulate the soil behaviour. The PLAXIS
1. Create a SEEP2D conceptual model. 3. Define conditions for both a saturated and unsaturated zone. 4. Convert the model to SEEP2D and run SEEP2D.
 GMS TUTORIALS SEEP 2D Unconfined SEEP2D can be used for both confined and unconfined problems. The steps involved in performing a SEEP2D simulation for the unconfined condition are described in this tutorial.
GMS TUTORIALS SEEP 2D Unconfined SEEP2D can be used for both confined and unconfined problems. The steps involved in performing a SEEP2D simulation for the unconfined condition are described in this tutorial.
Engineeringmanuals. Part3
 Engineeringmanuals Part3 Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs Part 3 Chapter 1-12, refer to Engineering Manual Part 1 Chapter 13-19, refer to Engineering Manual Part 2 Chapter 20. Finite Element Method
Engineeringmanuals Part3 Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs Part 3 Chapter 1-12, refer to Engineering Manual Part 1 Chapter 13-19, refer to Engineering Manual Part 2 Chapter 20. Finite Element Method
v GMS 10.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment on Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis
 v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials Feature Objects
lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir
TexGraf4 GRAPHICS PROGRAM FOR UTEXAS4. Stephen G. Wright. May Shinoak Software Austin, Texas
 TexGraf4 GRAPHICS PROGRAM FOR UTEXAS4 By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights Reserved i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page LIST OF TABLES...v
TexGraf4 GRAPHICS PROGRAM FOR UTEXAS4 By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights Reserved i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page LIST OF TABLES...v
( ) ( ) tutorial question 1. Given. γ soil := 21 kn m 3. x 2 = 3.3 m. at rest. k 0 = 0.5 lateral earth pressure co-eff. at 0.5 m below grade σ t u
 tutorial question 1 Given q := 4.8kPa γ soil := 1 kn ϕ := 30 x 1 := 0.5m x := x 1 +.8m k 0 := 1 sin( ϕ) at rest x = 3.3 m k 0 = 0.5 lateral earth pressure co-eff at 0.5 m below grade σ t u σ t := = x 1
tutorial question 1 Given q := 4.8kPa γ soil := 1 kn ϕ := 30 x 1 := 0.5m x := x 1 +.8m k 0 := 1 sin( ϕ) at rest x = 3.3 m k 0 = 0.5 lateral earth pressure co-eff at 0.5 m below grade σ t u σ t := = x 1
OPTUM COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS
 OPTUM COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS Version 2016 OptumG2: Analysis K Krabbenhoft, AV Lymain, J Krabbenhoft (Editors) c Optum Computational Engineering 2016 www.optumce.com CONTENTS Contents 1 GENERAL
OPTUM COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING ANALYSIS Version 2016 OptumG2: Analysis K Krabbenhoft, AV Lymain, J Krabbenhoft (Editors) c Optum Computational Engineering 2016 www.optumce.com CONTENTS Contents 1 GENERAL
v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment On Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis
 v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment On Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite
v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial UTEXAS Embankment On Soft Clay Introduction to the UTEXAS interface in GMS for a simple embankment analysis Objectives Learn how to build a simple UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite
A more general model for the analysis of the rock slope stability
 Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 4, August 2008, pp. 433 441. Printed in India A more general model for the analysis of the rock slope stability MEHDI ZAMANI Department of Technology and Engineering, Yasouj University,
Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 4, August 2008, pp. 433 441. Printed in India A more general model for the analysis of the rock slope stability MEHDI ZAMANI Department of Technology and Engineering, Yasouj University,
THE APPLICATION OF AN ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER TO EVALUATE TRUCK AERODYNAMICS IN CFD
 THE APPLICATION OF AN ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER TO EVALUATE TRUCK AERODYNAMICS IN CFD A SOLUTION FOR A REAL-WORLD ENGINEERING PROBLEM Ir. Niek van Dijk DAF Trucks N.V. CONTENTS Scope & Background Theory:
THE APPLICATION OF AN ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER TO EVALUATE TRUCK AERODYNAMICS IN CFD A SOLUTION FOR A REAL-WORLD ENGINEERING PROBLEM Ir. Niek van Dijk DAF Trucks N.V. CONTENTS Scope & Background Theory:
Introducing Slide 6.0
 Introducing Slide 6.0 It s been a long time since the release of Slide version 5 (seven years in fact!). In that time, Slide has been adopted by thousands of engineers around the world as their primary
Introducing Slide 6.0 It s been a long time since the release of Slide version 5 (seven years in fact!). In that time, Slide has been adopted by thousands of engineers around the world as their primary
Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle
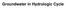 Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle Types of Terrestrial Water Surface Water Soil Moisture Ground water Pores Full of Combination of Air and Water Unsaturated Zone / Zone of Aeration / Vadose (Soil Water)
Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle Types of Terrestrial Water Surface Water Soil Moisture Ground water Pores Full of Combination of Air and Water Unsaturated Zone / Zone of Aeration / Vadose (Soil Water)
Chapter 20. Finite Element Method (FEM) Introduction
 Chapter 20. Finite Element Method (FEM) Introduction The objective of this chapter is to explain basic terms of the particular field of problems and practical application of GEO 5 FEM program to solve
Chapter 20. Finite Element Method (FEM) Introduction The objective of this chapter is to explain basic terms of the particular field of problems and practical application of GEO 5 FEM program to solve
General Applications
 Chapter General Applications The general analysis modules can be used to calculate section properties, wind pressures on buildings and evaluate drainage systems of building roofs. General Applications
Chapter General Applications The general analysis modules can be used to calculate section properties, wind pressures on buildings and evaluate drainage systems of building roofs. General Applications
9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 TUTORIAL MANUAL 9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading.
TUTORIAL MANUAL 9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading.
