WELCOME TO THE NAE US FRONTIERS OF ENGINEERING SYMPOSIUM 2005
|
|
|
- Linette Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WELCOME TO THE NAE US FRONTIERS OF ENGINEERING SYMPOSIUM 2005
2 Ongoing Challenges in Face Recognition Peter Belhumeur Columbia University New York City
3 How are people identified? People are identified by three basic means: Something they have (identity document or token) Something they know (password, PIN) Something they are (human body)
4 Iris
5 Retina Every eye has its own totally unique pattern of blood vessels.
6 Hand
7 Fingerprint
8 Ear
9 Face
10 Who are these people? [Sinha and Poggio 1996]
11 Who are these people? [Sinha and Poggio 2002]
12 Images as Points in Euclidean Space x 2 x 1 x n Let an n-pixel image to be a point in an n-d space, x R n. Each pixel value is a coordinate of x.
13 Face Recognition: Euclidean Distances D 1 > 0 D 2 > 0 ~ D 3 = 0
14 Face Recognition: Euclidean Distances D 1 > 0 D 2 > 0 D 3 > D 1 or 2 [Hallinan 1994] [Adini, Moses, and Ullman 1994]
15 Same Person or Different People
16
17 Same Person or Different People
18
19 Why is Face Recognition Hard?
20 Challenges: Image Variability Expression Short Term Pose Illumination Facial Hair Makeup Eyewear Long Term Hairstyle Piercings Aging
21 Illumination Invariants? Does there exist a function f s.t. f ( ) = f ( ) = f ( ) = a and f ( ) = f ( ) = f ( ) = b?
22 Can Any Two Images Arise from a Single Surface? s n I(x,y) a I(x,y) = a(x,y) n(x,y) s n l Same Albedo Different and Lighting Surface J(x,y) a J(x,y) = a(x,y) n(x,y) l
23 The Surface PDE I(x,y) = a(x,y) n(x,y) s J(x,y) = a(x,y) n(x,y) l ( I l J s ) n = 0 Nonlinear PDE Linear PDE
24 Non-Existence Theorem for Illumination Invariants Illumination invariants for 3-D objects do not exist. This result does not ignore attached and cast shadows, as well as surface interreflection. [Chen, Belhumeur, and Jacobs 2000]
25 Geometric Invariants? Does there exist a function f s.t. f ( ) = f ( ) = f ( ) = a and f ( ) = f ( ) = f ( ) = b?
26 Non-Existence Theorem for Geometric Invariants Geometric invariants for rigid transformations of 3-D objects viewed under perspective projective projection do not exist. [Burns, Weiss, and Riseman 1992]
27 Image Variability: Appearance Manifolds x 2 x n x 1 Lighting x Pose [Murase and Nayar 1993]
28 Modeling Image Variability Can we model illumination and pose variability in images of a face? Yes, if we can determine the shape and texture of the face. But how?
29 Modeling Image Variability: 3-D Faces Laser Range Scanners Stereo Cameras Structured Light Photometric Stereo [Atick, Griffin, Redlich 1996] [Georghiades, Belhumeur, Kriegman 1996] [Blanz and Vetter 1999] [Zhao and Chellepa 1999] [Kimmel and Sapiro 2003] [Geometrix 2001] [MERL 2005]
30 Illumination Variation Reveals Object Shape s 1 n a s 2 s 3 I 1 I 2 I 3 [Woodham1984]
31 Illumination Movie Illumination Movie
32 Shape Movie Shape Movie
33 Image Variability: From Few to Many Lighting x Pose x 2 x n Real Synthetic x 1 [Georghiades, Belhumeur, and Kriegman 1999]
34 Illumination Dome
35 Real vs. Synthetic Real Synthetic
36 Real vs. Synthetic Real Synthetic
37 A Step Back in Time
38 Albrecht Dürer, Four Books on Human Proportion (1528)
39 D arcy Thompson, On Growth and Form (1917)
40 D arcy Thompson, On Growth and Form (1917)
41 D arcy Thompson, On Growth and Form (1917)
42 But what if we could.? [Blanz and Vetter 1999, 2003]
43 Building a Morphable Face Model [Blanz and Vetter 1999, 2003]
44 3-D Morphaple Models: Semi-Automatic [Blanz and Vetter 1999, 2003]
45 Building Morphable Face Models [Blanz and Vetter 1999, 2003]
46 Fitting Morphable Face Models [Blanz and Vetter 1999, 2003]
47 National Geographic 1984 and
48 Identity Confirmed by IRIS = [Daugman 2002]
Photometric stereo. Recovering the surface f(x,y) Three Source Photometric stereo: Step1. Reflectance Map of Lambertian Surface
 Photometric stereo Illumination Cones and Uncalibrated Photometric Stereo Single viewpoint, multiple images under different lighting. 1. Arbitrary known BRDF, known lighting 2. Lambertian BRDF, known lighting
Photometric stereo Illumination Cones and Uncalibrated Photometric Stereo Single viewpoint, multiple images under different lighting. 1. Arbitrary known BRDF, known lighting 2. Lambertian BRDF, known lighting
Announcements. Introduction. Why is this hard? What is Computer Vision? We all make mistakes. What do you see? Class Web Page is up:
 Announcements Introduction Computer Vision I CSE 252A Lecture 1 Class Web Page is up: http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/classes/wi05/cse252a/ Assignment 0: Getting Started with Matlab is posted to web page, due 1/13/04
Announcements Introduction Computer Vision I CSE 252A Lecture 1 Class Web Page is up: http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/classes/wi05/cse252a/ Assignment 0: Getting Started with Matlab is posted to web page, due 1/13/04
Three-Dimensional Face Recognition: A Fishersurface Approach
 Three-Dimensional Face Recognition: A Fishersurface Approach Thomas Heseltine, Nick Pears, Jim Austin Department of Computer Science, The University of York, United Kingdom Abstract. Previous work has
Three-Dimensional Face Recognition: A Fishersurface Approach Thomas Heseltine, Nick Pears, Jim Austin Department of Computer Science, The University of York, United Kingdom Abstract. Previous work has
Face Recognition Under Varying Illumination Based on MAP Estimation Incorporating Correlation Between Surface Points
 Face Recognition Under Varying Illumination Based on MAP Estimation Incorporating Correlation Between Surface Points Mihoko Shimano 1, Kenji Nagao 1, Takahiro Okabe 2,ImariSato 3, and Yoichi Sato 2 1 Panasonic
Face Recognition Under Varying Illumination Based on MAP Estimation Incorporating Correlation Between Surface Points Mihoko Shimano 1, Kenji Nagao 1, Takahiro Okabe 2,ImariSato 3, and Yoichi Sato 2 1 Panasonic
What is Computer Vision? Introduction. We all make mistakes. Why is this hard? What was happening. What do you see? Intro Computer Vision
 What is Computer Vision? Trucco and Verri (Text): Computing properties of the 3-D world from one or more digital images Introduction Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 1 Sockman and Shapiro:
What is Computer Vision? Trucco and Verri (Text): Computing properties of the 3-D world from one or more digital images Introduction Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 1 Sockman and Shapiro:
Face Recognition Markus Storer, 2007
 Face Recognition Markus Storer, 2007 Agenda Face recognition by humans 3D morphable models pose and illumination model creation model fitting results Face recognition vendor test 2006 Face Recognition
Face Recognition Markus Storer, 2007 Agenda Face recognition by humans 3D morphable models pose and illumination model creation model fitting results Face recognition vendor test 2006 Face Recognition
Recovering 3D Facial Shape via Coupled 2D/3D Space Learning
 Recovering 3D Facial hape via Coupled 2D/3D pace Learning Annan Li 1,2, higuang han 1, ilin Chen 1, iujuan Chai 3, and Wen Gao 4,1 1 Key Lab of Intelligent Information Processing of CA, Institute of Computing
Recovering 3D Facial hape via Coupled 2D/3D pace Learning Annan Li 1,2, higuang han 1, ilin Chen 1, iujuan Chai 3, and Wen Gao 4,1 1 Key Lab of Intelligent Information Processing of CA, Institute of Computing
Image Morphing. Application: Movie Special Effects. Application: Registration /Alignment. Image Cross-Dissolve
 Image Morphing Application: Movie Special Effects Morphing is turning one image into another (through a seamless transition) First movies with morphing Willow, 1988 Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade,
Image Morphing Application: Movie Special Effects Morphing is turning one image into another (through a seamless transition) First movies with morphing Willow, 1988 Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade,
Component-based Face Recognition with 3D Morphable Models
 Component-based Face Recognition with 3D Morphable Models B. Weyrauch J. Huang benjamin.weyrauch@vitronic.com jenniferhuang@alum.mit.edu Center for Biological and Center for Biological and Computational
Component-based Face Recognition with 3D Morphable Models B. Weyrauch J. Huang benjamin.weyrauch@vitronic.com jenniferhuang@alum.mit.edu Center for Biological and Center for Biological and Computational
The Quotient Image: Class Based Recognition and Synthesis Under Varying Illumination Conditions
 The Quotient Image: Class Based Recognition and Synthesis Under Varying Illumination Conditions Tammy Riklin-Raviv and Amnon Shashua Institute of Computer Science, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904,
The Quotient Image: Class Based Recognition and Synthesis Under Varying Illumination Conditions Tammy Riklin-Raviv and Amnon Shashua Institute of Computer Science, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem 91904,
Lambertian model of reflectance I: shape from shading and photometric stereo. Ronen Basri Weizmann Institute of Science
 Lambertian model of reflectance I: shape from shading and photometric stereo Ronen Basri Weizmann Institute of Science Variations due to lighting (and pose) Relief Dumitru Verdianu Flying Pregnant Woman
Lambertian model of reflectance I: shape from shading and photometric stereo Ronen Basri Weizmann Institute of Science Variations due to lighting (and pose) Relief Dumitru Verdianu Flying Pregnant Woman
Face Matching between Near Infrared and Visible Light Images
 Face Matching between Near Infrared and Visible Light Images Dong Yi, Rong Liu, RuFeng Chu, Zhen Lei, and Stan Z. Li Center for Biometrics Security Research & National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition
Face Matching between Near Infrared and Visible Light Images Dong Yi, Rong Liu, RuFeng Chu, Zhen Lei, and Stan Z. Li Center for Biometrics Security Research & National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition
Statistical Symmetric Shape from Shading for 3D Structure Recovery of Faces
 Statistical Symmetric Shape from Shading for 3D Structure Recovery of Faces Roman Dovgard and Ronen Basri Dept. of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100,
Statistical Symmetric Shape from Shading for 3D Structure Recovery of Faces Roman Dovgard and Ronen Basri Dept. of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100,
Face Recognition Based on Frontal Views Generated from Non-Frontal Images
 Face Recognition Based on Frontal Views Generated from Non-Frontal Images Volker Blanz 1, Patrick Grother 2, P. Jonathon Phillips 2 and Thomas Vetter 3 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik, Saarbrücken,
Face Recognition Based on Frontal Views Generated from Non-Frontal Images Volker Blanz 1, Patrick Grother 2, P. Jonathon Phillips 2 and Thomas Vetter 3 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik, Saarbrücken,
Model-based Enhancement of Lighting Conditions in Image Sequences
 Model-based Enhancement of Lighting Conditions in Image Sequences Peter Eisert and Bernd Girod Information Systems Laboratory Stanford University {eisert,bgirod}@stanford.edu http://www.stanford.edu/ eisert
Model-based Enhancement of Lighting Conditions in Image Sequences Peter Eisert and Bernd Girod Information Systems Laboratory Stanford University {eisert,bgirod}@stanford.edu http://www.stanford.edu/ eisert
Parametric Manifold of an Object under Different Viewing Directions
 Parametric Manifold of an Object under Different Viewing Directions Xiaozheng Zhang 1,2, Yongsheng Gao 1,2, and Terry Caelli 3 1 Biosecurity Group, Queensland Research Laboratory, National ICT Australia
Parametric Manifold of an Object under Different Viewing Directions Xiaozheng Zhang 1,2, Yongsheng Gao 1,2, and Terry Caelli 3 1 Biosecurity Group, Queensland Research Laboratory, National ICT Australia
A Bilinear Illumination Model for Robust Face Recognition
 A Bilinear Illumination Model for Robust Face Recognition Jinho Lee Baback Moghaddam Hanspeter Pfister Raghu Machiraju Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) 201 Broadway, Cambridge MA 02139,
A Bilinear Illumination Model for Robust Face Recognition Jinho Lee Baback Moghaddam Hanspeter Pfister Raghu Machiraju Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) 201 Broadway, Cambridge MA 02139,
Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model
 Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model TAE IN SEOL*, SUN-TAE CHUNG*, SUNHO KI**, SEONGWON CHO**, YUN-KWANG HONG*** *School of Electronic Engineering
Illumination-Robust Face Recognition based on Gabor Feature Face Intrinsic Identity PCA Model TAE IN SEOL*, SUN-TAE CHUNG*, SUNHO KI**, SEONGWON CHO**, YUN-KWANG HONG*** *School of Electronic Engineering
Multi-View Stereo for Community Photo Collections Michael Goesele, et al, ICCV Venus de Milo
 Vision Sensing Multi-View Stereo for Community Photo Collections Michael Goesele, et al, ICCV 2007 Venus de Milo The Digital Michelangelo Project, Stanford How to sense 3D very accurately? How to sense
Vision Sensing Multi-View Stereo for Community Photo Collections Michael Goesele, et al, ICCV 2007 Venus de Milo The Digital Michelangelo Project, Stanford How to sense 3D very accurately? How to sense
Component-based Face Recognition with 3D Morphable Models
 Component-based Face Recognition with 3D Morphable Models Jennifer Huang 1, Bernd Heisele 1,2, and Volker Blanz 3 1 Center for Biological and Computational Learning, M.I.T., Cambridge, MA, USA 2 Honda
Component-based Face Recognition with 3D Morphable Models Jennifer Huang 1, Bernd Heisele 1,2, and Volker Blanz 3 1 Center for Biological and Computational Learning, M.I.T., Cambridge, MA, USA 2 Honda
22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan. Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Illumination Compensation and Enhancement for Face Recognition
 APSIPA ASC 2011 Xi an Illumination Compensation and Enhancement for Face Recognition Muwei Jian, * Kin-Man Lam * and Junyu Dong * The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Department of Electronic and Information
APSIPA ASC 2011 Xi an Illumination Compensation and Enhancement for Face Recognition Muwei Jian, * Kin-Man Lam * and Junyu Dong * The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Department of Electronic and Information
A Morphable Model for the Synthesis of 3D Faces
 A Morphable Model for the Synthesis of 3D Faces Marco Nef Volker Blanz, Thomas Vetter SIGGRAPH 99, Los Angeles Presentation overview Motivation Introduction Database Morphable 3D Face Model Matching a
A Morphable Model for the Synthesis of 3D Faces Marco Nef Volker Blanz, Thomas Vetter SIGGRAPH 99, Los Angeles Presentation overview Motivation Introduction Database Morphable 3D Face Model Matching a
Lambertian model of reflectance II: harmonic analysis. Ronen Basri Weizmann Institute of Science
 Lambertian model of reflectance II: harmonic analysis Ronen Basri Weizmann Institute of Science Illumination cone What is the set of images of an object under different lighting, with any number of sources?
Lambertian model of reflectance II: harmonic analysis Ronen Basri Weizmann Institute of Science Illumination cone What is the set of images of an object under different lighting, with any number of sources?
Age Group Estimation using Face Features Ranjan Jana, Debaleena Datta, Rituparna Saha
 Estimation using Face Features Ranjan Jana, Debaleena Datta, Rituparna Saha Abstract Recognition of the most facial variations, such as identity, expression and gender has been extensively studied. Automatic
Estimation using Face Features Ranjan Jana, Debaleena Datta, Rituparna Saha Abstract Recognition of the most facial variations, such as identity, expression and gender has been extensively studied. Automatic
Faces. Face Modeling. Topics in Image-Based Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 17
 Face Modeling Topics in Image-Based Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 17 Faces CS291-J00, Winter 2003 From David Romdhani Kriegman, slides 2003 1 Approaches 2-D Models morphing, indexing, etc.
Face Modeling Topics in Image-Based Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 17 Faces CS291-J00, Winter 2003 From David Romdhani Kriegman, slides 2003 1 Approaches 2-D Models morphing, indexing, etc.
Face Recognition using Segmentation Method and Measurement based Approach under Varying Poses and Illumination
 Face Recognition using Segmentation Method and Measurement based Approach under Varying Poses and Illumination Bakul Pandhre Computer Engineering Department PVPIT Bavdhan,Pune-21,Maharashtra,India Abstract-
Face Recognition using Segmentation Method and Measurement based Approach under Varying Poses and Illumination Bakul Pandhre Computer Engineering Department PVPIT Bavdhan,Pune-21,Maharashtra,India Abstract-
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST /$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 2008 1331 A Subspace Model-Based Approach to Face Relighting Under Unknown Lighting and Poses Hyunjung Shim, Student Member, IEEE, Jiebo Luo,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 2008 1331 A Subspace Model-Based Approach to Face Relighting Under Unknown Lighting and Poses Hyunjung Shim, Student Member, IEEE, Jiebo Luo,
REAL-TIME FACE SWAPPING IN VIDEO SEQUENCES: MAGIC MIRROR
 REAL-TIME FACE SWAPPING IN VIDEO SEQUENCES: MAGIC MIRROR Nuri Murat Arar1, Fatma Gu ney1, Nasuh Kaan Bekmezci1, Hua Gao2 and Hazım Kemal Ekenel1,2,3 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Bogazici University,
REAL-TIME FACE SWAPPING IN VIDEO SEQUENCES: MAGIC MIRROR Nuri Murat Arar1, Fatma Gu ney1, Nasuh Kaan Bekmezci1, Hua Gao2 and Hazım Kemal Ekenel1,2,3 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Bogazici University,
Other Reconstruction Techniques
 Other Reconstruction Techniques Ruigang Yang CS 684 CS 684 Spring 2004 1 Taxonomy of Range Sensing From Brain Curless, SIGGRAPH 00 Lecture notes CS 684 Spring 2004 2 Taxonomy of Range Scanning (cont.)
Other Reconstruction Techniques Ruigang Yang CS 684 CS 684 Spring 2004 1 Taxonomy of Range Sensing From Brain Curless, SIGGRAPH 00 Lecture notes CS 684 Spring 2004 2 Taxonomy of Range Scanning (cont.)
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 46 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 46 (2015 ) 1754 1761 International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies (ICICT 2014) Age Estimation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 46 (2015 ) 1754 1761 International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies (ICICT 2014) Age Estimation
Object. Radiance. Viewpoint v
 Fisher Light-Fields for Face Recognition Across Pose and Illumination Ralph Gross, Iain Matthews, and Simon Baker The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213
Fisher Light-Fields for Face Recognition Across Pose and Illumination Ralph Gross, Iain Matthews, and Simon Baker The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213
Unified Stereo-Based 3D Head Tracking Using Online Illumination Modeling
 AN, CHUNG: UNIFIED STEREO-BASED 3D HEAD TRACKING USING OIM Unified Stereo-Based 3D Head Tracking Using Online Illumination Modeling Kwang Ho An akh@cheonjikaistackr Myung Jin Chung mjchung@eekaistackr
AN, CHUNG: UNIFIED STEREO-BASED 3D HEAD TRACKING USING OIM Unified Stereo-Based 3D Head Tracking Using Online Illumination Modeling Kwang Ho An akh@cheonjikaistackr Myung Jin Chung mjchung@eekaistackr
FACE RECOGNITION UNDER GENERIC ILLUMINATION BASED ON HARMONIC RELIGHTING
 International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence Vol. 19, No. 4 (2005) 513 531 c World Scientific Publishing Company FACE RECOGNITION UNDER GENERIC ILLUMINATION BASED ON HARMONIC
International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence Vol. 19, No. 4 (2005) 513 531 c World Scientific Publishing Company FACE RECOGNITION UNDER GENERIC ILLUMINATION BASED ON HARMONIC
Efficient detection under varying illumination conditions and image plane rotations q
 Computer Vision and Image Understanding xxx (2003) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/cviu Efficient detection under varying illumination conditions and image plane rotations q Margarita Osadchy and Daniel
Computer Vision and Image Understanding xxx (2003) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/cviu Efficient detection under varying illumination conditions and image plane rotations q Margarita Osadchy and Daniel
In Between 3D Active Appearance Models and 3D Morphable Models
 In Between 3D Active Appearance Models and 3D Morphable Models Jingu Heo and Marios Savvides Biometrics Lab, CyLab Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 jheo@cmu.edu, msavvid@ri.cmu.edu Abstract
In Between 3D Active Appearance Models and 3D Morphable Models Jingu Heo and Marios Savvides Biometrics Lab, CyLab Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 jheo@cmu.edu, msavvid@ri.cmu.edu Abstract
Clustering Appearances of Objects Under Varying Illumination Conditions
 Clustering Appearances of Objects Under Varying Illumination Conditions Jeffrey Ho Ming-Hsuan Yang Jongwoo Lim Kuang-Chih Lee David Kriegman jho@cs.ucsd.edu myang@honda-ri.com jlim1@uiuc.edu klee10@uiuc.edu
Clustering Appearances of Objects Under Varying Illumination Conditions Jeffrey Ho Ming-Hsuan Yang Jongwoo Lim Kuang-Chih Lee David Kriegman jho@cs.ucsd.edu myang@honda-ri.com jlim1@uiuc.edu klee10@uiuc.edu
depict shading and attached shadows under extreme lighting; in [10] the cone representation was extended to include cast shadows for objects with non-
![depict shading and attached shadows under extreme lighting; in [10] the cone representation was extended to include cast shadows for objects with non- depict shading and attached shadows under extreme lighting; in [10] the cone representation was extended to include cast shadows for objects with non-](/thumbs/80/80766483.jpg) To appear in IEEE Workshop on Multi-View Modeling and Analysis of Visual Scenes, 1999. Illumination-Based Image Synthesis: Creating Novel Images of Human Faces Under Diering Pose and Lighting A. S. Georghiades
To appear in IEEE Workshop on Multi-View Modeling and Analysis of Visual Scenes, 1999. Illumination-Based Image Synthesis: Creating Novel Images of Human Faces Under Diering Pose and Lighting A. S. Georghiades
From Few to Many: Illumination Cone Models for Face Recognition under Variable Lighting and Pose
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2001 643 From Few to Many: Illumination Cone Models for Face Recognition under Variable Lighting and Pose Athinodoros
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2001 643 From Few to Many: Illumination Cone Models for Face Recognition under Variable Lighting and Pose Athinodoros
We recommend you cite the published version. The publisher s URL is:
 Atkinson, G., Hansen, M. F., Smith, M. and Smith, L. (2010) An efficient and practical 3D face scanner using near infrared and visible photometric stereo. In: Proceedings of the International Conference
Atkinson, G., Hansen, M. F., Smith, M. and Smith, L. (2010) An efficient and practical 3D face scanner using near infrared and visible photometric stereo. In: Proceedings of the International Conference
Nine Points of Light: Acquiring Subspaces for Face Recognition under Variable Lighting
 To Appear in CVPR 2001 Nine Points of Light: Acquiring Subspaces for Face Recognition under Variable Lighting Kuang-Chih Lee Jeffrey Ho David Kriegman Beckman Institute and Computer Science Department
To Appear in CVPR 2001 Nine Points of Light: Acquiring Subspaces for Face Recognition under Variable Lighting Kuang-Chih Lee Jeffrey Ho David Kriegman Beckman Institute and Computer Science Department
A 3D Face Model for Pose and Illumination Invariant Face Recognition
 A 3D Face Model for Pose and Illumination Invariant Face Recognition Pascal Paysan Reinhard Knothe Brian Amberg pascal.paysan@unibas.ch reinhard.knothe@unibas.ch brian.amberg@unibas.ch Sami Romdhani Thomas
A 3D Face Model for Pose and Illumination Invariant Face Recognition Pascal Paysan Reinhard Knothe Brian Amberg pascal.paysan@unibas.ch reinhard.knothe@unibas.ch brian.amberg@unibas.ch Sami Romdhani Thomas
Face Recognition under Varying Illumination
 Face Recognition under Varying Illumination Erald VUÇINI Vienna University of echnology Inst. of Computer Graphics and Algorithms Vienna, Austria vucini@cg.tuwien.ac.at Muhittin GÖKMEN Istanbul echnical
Face Recognition under Varying Illumination Erald VUÇINI Vienna University of echnology Inst. of Computer Graphics and Algorithms Vienna, Austria vucini@cg.tuwien.ac.at Muhittin GÖKMEN Istanbul echnical
Course Administration
 Course Administration Project 2 results are online Project 3 is out today The first quiz is a week from today (don t panic!) Covers all material up to the quiz Emphasizes lecture material NOT project topics
Course Administration Project 2 results are online Project 3 is out today The first quiz is a week from today (don t panic!) Covers all material up to the quiz Emphasizes lecture material NOT project topics
Pose 1 (Frontal) Pose 4 Pose 8. Pose 6. Pose 5 Pose 9. Subset 1 Subset 2. Subset 3 Subset 4
 From Few to Many: Generative Models for Recognition Under Variable Pose and Illumination Athinodoros S. Georghiades Peter N. Belhumeur David J. Kriegman Departments of Electrical Engineering Beckman Institute
From Few to Many: Generative Models for Recognition Under Variable Pose and Illumination Athinodoros S. Georghiades Peter N. Belhumeur David J. Kriegman Departments of Electrical Engineering Beckman Institute
Recognition of Non-symmetric Faces Using Principal Component Analysis
 Recognition of Non-symmetric Faces Using Principal Component Analysis N. Krishnan Centre for Information Technology & Engineering Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli-627012, India Krishnan17563@yahoo.com
Recognition of Non-symmetric Faces Using Principal Component Analysis N. Krishnan Centre for Information Technology & Engineering Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli-627012, India Krishnan17563@yahoo.com
3D Face Modelling Under Unconstrained Pose & Illumination
 David Bryan Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Biomedical Engineering Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University January 12, 2009 Agenda Problem Overview 3D Morphable Model Fitting Model
David Bryan Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Biomedical Engineering Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University January 12, 2009 Agenda Problem Overview 3D Morphable Model Fitting Model
Recognition: Face Recognition. Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576
 Recognition: Face Recognition Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 1 Face recognition: once you ve detected and cropped a face, try to recognize it Detection Recognition Sally 2 Face recognition: overview Typical
Recognition: Face Recognition Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 1 Face recognition: once you ve detected and cropped a face, try to recognize it Detection Recognition Sally 2 Face recognition: overview Typical
Haresh D. Chande #, Zankhana H. Shah *
 Illumination Invariant Face Recognition System Haresh D. Chande #, Zankhana H. Shah * # Computer Engineering Department, Birla Vishvakarma Mahavidyalaya, Gujarat Technological University, India * Information
Illumination Invariant Face Recognition System Haresh D. Chande #, Zankhana H. Shah * # Computer Engineering Department, Birla Vishvakarma Mahavidyalaya, Gujarat Technological University, India * Information
Illumination invariant face recognition and impostor rejection using different MINACE filter algorithms
 Illumination invariant face recognition and impostor rejection using different MINACE filter algorithms Rohit Patnaik and David Casasent Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University,
Illumination invariant face recognition and impostor rejection using different MINACE filter algorithms Rohit Patnaik and David Casasent Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University,
Roger Woodman [ ]
![Roger Woodman [ ] Roger Woodman [ ]](/thumbs/89/98215564.jpg) A Photometric Stereo Approach to Face Recognition Roger Woodman [ www.razorrobotics.com/roger-woodman ] A dissertation submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of the University of the West
A Photometric Stereo Approach to Face Recognition Roger Woodman [ www.razorrobotics.com/roger-woodman ] A dissertation submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of the University of the West
An Automatic Face Recognition System in the Near Infrared Spectrum
 An Automatic Face Recognition System in the Near Infrared Spectrum Shuyan Zhao and Rolf-Rainer Grigat Technical University Hamburg Harburg Vision Systems, 4-08/1 Harburger Schloßstr 20 21079 Hamburg, Germany
An Automatic Face Recognition System in the Near Infrared Spectrum Shuyan Zhao and Rolf-Rainer Grigat Technical University Hamburg Harburg Vision Systems, 4-08/1 Harburger Schloßstr 20 21079 Hamburg, Germany
Face Recognition from Video using the Generic Shape-Illumination Manifold
 Face Recognition from Video using the Generic Shape-Illumination Manifold Ognjen Arandjelović and Roberto Cipolla Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK {oa214,cipolla}@eng.cam.ac.uk
Face Recognition from Video using the Generic Shape-Illumination Manifold Ognjen Arandjelović and Roberto Cipolla Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Cambridge, CB2 1PZ, UK {oa214,cipolla}@eng.cam.ac.uk
Illumination Compensation and Normalization for Robust Face Recognition Using Discrete Cosine Transform in Logarithm Domain
 458 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MAN, AND CYBERNETICS PART B: CYBERNETICS, VOL. 36, NO. 2, APRIL 2006 Illumination Compensation and Normalization for Robust Face Recognition Using Discrete Cosine Transform
458 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MAN, AND CYBERNETICS PART B: CYBERNETICS, VOL. 36, NO. 2, APRIL 2006 Illumination Compensation and Normalization for Robust Face Recognition Using Discrete Cosine Transform
Using Stereo Matching for 2-D Face Recognition Across Pose
 Using Stereo Matching for 2-D Face Recognition Across Pose Carlos D. Castillo Computer Science Department University of Maryland, College Park carlos@cs.umd.edu November 28, 2007 Abstract We propose using
Using Stereo Matching for 2-D Face Recognition Across Pose Carlos D. Castillo Computer Science Department University of Maryland, College Park carlos@cs.umd.edu November 28, 2007 Abstract We propose using
Face Tracking. Synonyms. Definition. Main Body Text. Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury and Yilei Xu. Facial Motion Estimation
 Face Tracking Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury and Yilei Xu Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Riverside, CA 92521, USA {amitrc,yxu}@ee.ucr.edu Synonyms Facial Motion Estimation Definition
Face Tracking Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury and Yilei Xu Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Riverside, CA 92521, USA {amitrc,yxu}@ee.ucr.edu Synonyms Facial Motion Estimation Definition
Face Recognition Based on Face-Specific Subspace
 Face Recognition Based on Face-Specific Subspace Shiguang Shan, 1 Wen Gao, 1,2 Debin Zhao 2 1 JDL, Institute of Computing Technology, CAS, P.O. Box 2704, Beijing, China, 100080 2 Department of Computer
Face Recognition Based on Face-Specific Subspace Shiguang Shan, 1 Wen Gao, 1,2 Debin Zhao 2 1 JDL, Institute of Computing Technology, CAS, P.O. Box 2704, Beijing, China, 100080 2 Department of Computer
Pose Normalization for Robust Face Recognition Based on Statistical Affine Transformation
 Pose Normalization for Robust Face Recognition Based on Statistical Affine Transformation Xiujuan Chai 1, 2, Shiguang Shan 2, Wen Gao 1, 2 1 Vilab, Computer College, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin,
Pose Normalization for Robust Face Recognition Based on Statistical Affine Transformation Xiujuan Chai 1, 2, Shiguang Shan 2, Wen Gao 1, 2 1 Vilab, Computer College, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin,
Self-similarity Based Editing of 3D Surface Textures
 J. Dong et al.: Self-similarity based editing of 3D surface textures. In Texture 2005: Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Texture Analysis and Synthesis, pp. 71 76, 2005. Self-similarity
J. Dong et al.: Self-similarity based editing of 3D surface textures. In Texture 2005: Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Texture Analysis and Synthesis, pp. 71 76, 2005. Self-similarity
Announcement. Photometric Stereo. Computer Vision I. Shading reveals 3-D surface geometry. Shape-from-X. CSE252A Lecture 8
 Announcement Photometric Stereo Lecture 8 Read Chapter 2 of Forsyth & Ponce Office hours tomorrow: 3-5, CSE 4127 5-6, CSE B260A Piazza Next lecture Shape-from-X Shading reveals 3-D surface geometry Where
Announcement Photometric Stereo Lecture 8 Read Chapter 2 of Forsyth & Ponce Office hours tomorrow: 3-5, CSE 4127 5-6, CSE B260A Piazza Next lecture Shape-from-X Shading reveals 3-D surface geometry Where
CS4670/5760: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Scott Wehrwein. Lecture 23: Photometric Stereo
 CS4670/5760: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Scott Wehrwein Lecture 23: Photometric Stereo Announcements PA3 Artifact due tonight PA3 Demos Thursday Signups close at 4:30 today No lecture on Friday Last Time:
CS4670/5760: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Scott Wehrwein Lecture 23: Photometric Stereo Announcements PA3 Artifact due tonight PA3 Demos Thursday Signups close at 4:30 today No lecture on Friday Last Time:
Shading and Recognition OR The first Mrs Rochester. D.A. Forsyth, UIUC
 Shading and Recognition OR The first Mrs Rochester D.A. Forsyth, UIUC Structure Argument: History why shading why shading analysis died reasons for hope Classical SFS+Critiques Primitives Reconstructions
Shading and Recognition OR The first Mrs Rochester D.A. Forsyth, UIUC Structure Argument: History why shading why shading analysis died reasons for hope Classical SFS+Critiques Primitives Reconstructions
Analysis of photometric factors based on photometric linearization
 3326 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 24, No. 10/ October 2007 Mukaigawa et al. Analysis of photometric factors based on photometric linearization Yasuhiro Mukaigawa, 1, * Yasunori Ishii, 2 and Takeshi Shakunaga
3326 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 24, No. 10/ October 2007 Mukaigawa et al. Analysis of photometric factors based on photometric linearization Yasuhiro Mukaigawa, 1, * Yasunori Ishii, 2 and Takeshi Shakunaga
Shading Models for Illumination and Reflectance Invariant Shape Detectors
 Shading Models for Illumination and Reflectance Invariant Shape Detectors Peter Nillius Department of Physics Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) SE-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden nillius@mi.physics.kth.se Josephine
Shading Models for Illumination and Reflectance Invariant Shape Detectors Peter Nillius Department of Physics Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) SE-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden nillius@mi.physics.kth.se Josephine
Automatic 3D Face Recognition Combining Global Geometric Features with Local Shape Variation Information
 Automatic 3D Face Recognition Combining Global Geometric Features with Local Shape Variation Information Chenghua Xu 1, Yunhong Wang 1, Tieniu Tan 1, Long Quan 2 1 Center for Biometric Authentication and
Automatic 3D Face Recognition Combining Global Geometric Features with Local Shape Variation Information Chenghua Xu 1, Yunhong Wang 1, Tieniu Tan 1, Long Quan 2 1 Center for Biometric Authentication and
Estimation of Face Depth Maps from Color Textures using Canonical Correlation Analysis
 Computer Vision Winter Workshop 006, Ondřej Chum, Vojtěch Franc (eds.) Telč, Czech Republic, February 6 8 Czech Pattern Recognition Society Estimation of Face Depth Maps from Color Textures using Canonical
Computer Vision Winter Workshop 006, Ondřej Chum, Vojtěch Franc (eds.) Telč, Czech Republic, February 6 8 Czech Pattern Recognition Society Estimation of Face Depth Maps from Color Textures using Canonical
Announcements. Recognition I. Gradient Space (p,q) What is the reflectance map?
 Announcements I HW 3 due 12 noon, tomorrow. HW 4 to be posted soon recognition Lecture plan recognition for next two lectures, then video and motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 17
Announcements I HW 3 due 12 noon, tomorrow. HW 4 to be posted soon recognition Lecture plan recognition for next two lectures, then video and motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 17
Photometric Stereo.
 Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo v.s.. Structure from Shading [1] Photometric stereo is a technique in computer vision for estimating the surface normals of objects by observing that object under
Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo v.s.. Structure from Shading [1] Photometric stereo is a technique in computer vision for estimating the surface normals of objects by observing that object under
What Is the Set of Images of an Object under All Possible Illumination Conditions?
 International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. no. 28, Issue No. 3, 1 16 (1998) c 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston. Manufactured in The Netherlands. What Is the Set of Images of an Object under
International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. no. 28, Issue No. 3, 1 16 (1998) c 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston. Manufactured in The Netherlands. What Is the Set of Images of an Object under
Learning Face Appearance under Different Lighting Conditions
 Learning Face Appearance under Different Lighting Conditions Brendan Moore, Marshall Tappen, Hassan Foroosh Computational Imaging Laboratory, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL 32816 Abstract-
Learning Face Appearance under Different Lighting Conditions Brendan Moore, Marshall Tappen, Hassan Foroosh Computational Imaging Laboratory, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL 32816 Abstract-
Realistic Texture Extraction for 3D Face Models Robust to Self-Occlusion
 Realistic Texture Extraction for 3D Face Models Robust to Self-Occlusion Chengchao Qu 1,2 Eduardo Monari 2 Tobias Schuchert 2 Jürgen Beyerer 2,1 1 Vision and Fusion Laboratory, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Realistic Texture Extraction for 3D Face Models Robust to Self-Occlusion Chengchao Qu 1,2 Eduardo Monari 2 Tobias Schuchert 2 Jürgen Beyerer 2,1 1 Vision and Fusion Laboratory, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
A Study on Similarity Computations in Template Matching Technique for Identity Verification
 A Study on Similarity Computations in Template Matching Technique for Identity Verification Lam, S. K., Yeong, C. Y., Yew, C. T., Chai, W. S., Suandi, S. A. Intelligent Biometric Group, School of Electrical
A Study on Similarity Computations in Template Matching Technique for Identity Verification Lam, S. K., Yeong, C. Y., Yew, C. T., Chai, W. S., Suandi, S. A. Intelligent Biometric Group, School of Electrical
Object and Class Recognition I:
 Object and Class Recognition I: Object Recognition Lectures 10 Sources ICCV 2005 short courses Li Fei-Fei (UIUC), Rob Fergus (Oxford-MIT), Antonio Torralba (MIT) http://people.csail.mit.edu/torralba/iccv2005
Object and Class Recognition I: Object Recognition Lectures 10 Sources ICCV 2005 short courses Li Fei-Fei (UIUC), Rob Fergus (Oxford-MIT), Antonio Torralba (MIT) http://people.csail.mit.edu/torralba/iccv2005
Depth. Common Classification Tasks. Example: AlexNet. Another Example: Inception. Another Example: Inception. Depth
 Common Classification Tasks Recognition of individual objects/faces Analyze object-specific features (e.g., key points) Train with images from different viewing angles Recognition of object classes Analyze
Common Classification Tasks Recognition of individual objects/faces Analyze object-specific features (e.g., key points) Train with images from different viewing angles Recognition of object classes Analyze
Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture David Eigen, Rob Fergus
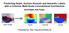 Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture David Eigen, Rob Fergus Presented by: Rex Ying and Charles Qi Input: A Single RGB Image Estimate
Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture David Eigen, Rob Fergus Presented by: Rex Ying and Charles Qi Input: A Single RGB Image Estimate
Shape Reconstruction Based on Similarity in Radiance Changes under Varying Illumination
 Shape Reconstruction Based on Similarity in Radiance Changes under Varying Illumination Imari Sato National Institute of Informatics imarik@nii.ac.jp Takahiro Okabe Qiong Yu Yoichi Sato The University
Shape Reconstruction Based on Similarity in Radiance Changes under Varying Illumination Imari Sato National Institute of Informatics imarik@nii.ac.jp Takahiro Okabe Qiong Yu Yoichi Sato The University
Covariates of Face Recognition
 COMPREHENSIVE REPORT 1 Covariates of Face Recognition Submitted by: Himanshu Sharad Bhatt Advisors: Dr. Richa Singh and Dr. Mayank Vatsa Abstract Face recognition has found several applications ranging
COMPREHENSIVE REPORT 1 Covariates of Face Recognition Submitted by: Himanshu Sharad Bhatt Advisors: Dr. Richa Singh and Dr. Mayank Vatsa Abstract Face recognition has found several applications ranging
Construction of Frontal Face from Side-view Images using Face Mosaicing
 Construction of Frontal Face from Side-view Images using Face Mosaicing Hiranmoy Roy 1, Debotosh Bhattacherjee 2, Mita Nasipuri 2, Dipak Kumar Basu 2* and Mahantapas Kundu 2 1 Department of Information
Construction of Frontal Face from Side-view Images using Face Mosaicing Hiranmoy Roy 1, Debotosh Bhattacherjee 2, Mita Nasipuri 2, Dipak Kumar Basu 2* and Mahantapas Kundu 2 1 Department of Information
Using Stereo Matching for 2-D Face Recognition Across Pose
 Using Stereo Matching for 2-D Face Recognition Across Pose Carlos D. Castillo David W. Jacobs Computer Science Department, University of Maryland, College Park {carlos, djacobs}@cs.umd.edu Abstract We
Using Stereo Matching for 2-D Face Recognition Across Pose Carlos D. Castillo David W. Jacobs Computer Science Department, University of Maryland, College Park {carlos, djacobs}@cs.umd.edu Abstract We
Why study Computer Vision?
 Computer Vision Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance
Computer Vision Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance
And if that 120MP Camera was cool
 Reflectance, Lights and on to photometric stereo CSE 252A Lecture 7 And if that 120MP Camera was cool Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 3.2Gigapixel camera 189 CCD s, each with 16 megapixels Pixels are 10µm
Reflectance, Lights and on to photometric stereo CSE 252A Lecture 7 And if that 120MP Camera was cool Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 3.2Gigapixel camera 189 CCD s, each with 16 megapixels Pixels are 10µm
arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 4 Aug 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 4 Aug 2011 arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 4 Aug 2011](/thumbs/78/76896474.jpg) arxiv:1108.1122v1 [cs.cv] 4 Aug 2011 Leveraging Billions of Faces to Overcome Performance Barriers in Unconstrained Face Recognition Yaniv Taigman and Lior Wolf face.com {yaniv, wolf}@face.com Abstract
arxiv:1108.1122v1 [cs.cv] 4 Aug 2011 Leveraging Billions of Faces to Overcome Performance Barriers in Unconstrained Face Recognition Yaniv Taigman and Lior Wolf face.com {yaniv, wolf}@face.com Abstract
Ligh%ng and Reflectance
 Ligh%ng and Reflectance 2 3 4 Ligh%ng Ligh%ng can have a big effect on how an object looks. Modeling the effect of ligh%ng can be used for: Recogni%on par%cularly face recogni%on Shape reconstruc%on Mo%on
Ligh%ng and Reflectance 2 3 4 Ligh%ng Ligh%ng can have a big effect on how an object looks. Modeling the effect of ligh%ng can be used for: Recogni%on par%cularly face recogni%on Shape reconstruc%on Mo%on
TIED FACTOR ANALYSIS FOR FACE RECOGNITION ACROSS LARGE POSE DIFFERENCES
 TIED FACTOR ANALYSIS FOR FACE RECOGNITION ACROSS LARGE POSE DIFFERENCES SIMON J.D. PRINCE, JAMES H. ELDER, JONATHAN WARRELL, FATIMA M. FELISBERTI IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE,
TIED FACTOR ANALYSIS FOR FACE RECOGNITION ACROSS LARGE POSE DIFFERENCES SIMON J.D. PRINCE, JAMES H. ELDER, JONATHAN WARRELL, FATIMA M. FELISBERTI IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE,
Large-Scale 3D Point Cloud Processing Tutorial 2013
 Large-Scale 3D Point Cloud Processing Tutorial 2013 Features The image depicts how our robot Irma3D sees itself in a mirror. The laser looking into itself creates distortions as well as changes in Prof.
Large-Scale 3D Point Cloud Processing Tutorial 2013 Features The image depicts how our robot Irma3D sees itself in a mirror. The laser looking into itself creates distortions as well as changes in Prof.
Exploitation of 3D Images for Face Authentication Under Pose and Illumination Variations
 Exploitation of 3D Images for Face Authentication Under Pose and Illumination Variations Filareti Tsalakanidou 1,2, Sotiris Malassiotis 2, and Michael G. Strintzis 1,2 1 Information Processing Laboratory,
Exploitation of 3D Images for Face Authentication Under Pose and Illumination Variations Filareti Tsalakanidou 1,2, Sotiris Malassiotis 2, and Michael G. Strintzis 1,2 1 Information Processing Laboratory,
Photometric*Stereo* October*8,*2013* Dr.*Grant*Schindler* *
 Photometric*Stereo* October*8,*2013* Dr.*Grant*Schindler* * schindler@gatech.edu* Mul@ple*Images:*Different*Ligh@ng* Mul@ple*Images:*Different*Ligh@ng* Mul@ple*Images:*Different*Ligh@ng* Religh@ng*the*Scene*
Photometric*Stereo* October*8,*2013* Dr.*Grant*Schindler* * schindler@gatech.edu* Mul@ple*Images:*Different*Ligh@ng* Mul@ple*Images:*Different*Ligh@ng* Mul@ple*Images:*Different*Ligh@ng* Religh@ng*the*Scene*
FACE RECOGNITION USING 2D MEASUREMENT BASED APPROACH AND 3D FEATURE EXTRACTION METHODS UNDER VARYING POSES AND ILLUMINATION
 FACE RECOGNITION USING 2D MEASUREMENT BASED APPROACH AND 3D FEATURE EXTRACTION METHODS UNDER VARYING POSES AND ILLUMINATION Bakul Pandhre 1, S.U.Kadam 2 1 2 Computer Engineering Department. 1 PVPIT, Bavdhan,Pune-21.
FACE RECOGNITION USING 2D MEASUREMENT BASED APPROACH AND 3D FEATURE EXTRACTION METHODS UNDER VARYING POSES AND ILLUMINATION Bakul Pandhre 1, S.U.Kadam 2 1 2 Computer Engineering Department. 1 PVPIT, Bavdhan,Pune-21.
Face Re-Lighting from a Single Image under Harsh Lighting Conditions
 Face Re-Lighting from a Single Image under Harsh Lighting Conditions Yang Wang 1, Zicheng Liu 2, Gang Hua 3, Zhen Wen 4, Zhengyou Zhang 2, Dimitris Samaras 5 1 The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University,
Face Re-Lighting from a Single Image under Harsh Lighting Conditions Yang Wang 1, Zicheng Liu 2, Gang Hua 3, Zhen Wen 4, Zhengyou Zhang 2, Dimitris Samaras 5 1 The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University,
Applications Video Surveillance (On-line or off-line)
 Face Face Recognition: Dimensionality Reduction Biometrics CSE 190-a Lecture 12 CSE190a Fall 06 CSE190a Fall 06 Face Recognition Face is the most common biometric used by humans Applications range from
Face Face Recognition: Dimensionality Reduction Biometrics CSE 190-a Lecture 12 CSE190a Fall 06 CSE190a Fall 06 Face Recognition Face is the most common biometric used by humans Applications range from
3D Face Reconstruction from a Single Image using a Single Reference Face Shape
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE 1 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single Image using a Single Reference Face Shape Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, Ronen Basri, Member, IEEE Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE 1 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single Image using a Single Reference Face Shape Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, Ronen Basri, Member, IEEE Abstract
Waleed Pervaiz CSE 352
 Waleed Pervaiz CSE 352 Computer Vision is the technology that enables machines to see and obtain information from digital images. It is seen as an integral part of AI in fields such as pattern recognition
Waleed Pervaiz CSE 352 Computer Vision is the technology that enables machines to see and obtain information from digital images. It is seen as an integral part of AI in fields such as pattern recognition
Synthesizing Realistic Facial Expressions from Photographs
 Synthesizing Realistic Facial Expressions from Photographs 1998 F. Pighin, J Hecker, D. Lischinskiy, R. Szeliskiz and D. H. Salesin University of Washington, The Hebrew University Microsoft Research 1
Synthesizing Realistic Facial Expressions from Photographs 1998 F. Pighin, J Hecker, D. Lischinskiy, R. Szeliskiz and D. H. Salesin University of Washington, The Hebrew University Microsoft Research 1
Pattern Recognition Letters
 Pattern Recognition Letters 32 (2011) 561 571 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Pattern Recognition Letters journal homepage: wwwelseviercom/locate/patrec Face recognition based on 2D images under
Pattern Recognition Letters 32 (2011) 561 571 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Pattern Recognition Letters journal homepage: wwwelseviercom/locate/patrec Face recognition based on 2D images under
3D Photography: Stereo
 3D Photography: Stereo Marc Pollefeys, Torsten Sattler Spring 2016 http://www.cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/3dvision/ 3D Modeling with Depth Sensors Today s class Obtaining depth maps / range images unstructured
3D Photography: Stereo Marc Pollefeys, Torsten Sattler Spring 2016 http://www.cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/3dvision/ 3D Modeling with Depth Sensors Today s class Obtaining depth maps / range images unstructured
Model-based 3D Shape Recovery from Single Images of Unknown Pose and Illumination using a Small Number of Feature Points
 Model-based 3D Shape Recovery from Single Images of Unknown Pose and Illumination using a Small Number of Feature Points Ham M. Rara and Aly A. Farag CVIP Laboratory, University of Louisville {hmrara01,
Model-based 3D Shape Recovery from Single Images of Unknown Pose and Illumination using a Small Number of Feature Points Ham M. Rara and Aly A. Farag CVIP Laboratory, University of Louisville {hmrara01,
Hybrid Textons: Modeling Surfaces with Reflectance and Geometry
 Hybrid Textons: Modeling Surfaces with Reflectance and Geometry Jing Wang and Kristin J. Dana Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Rutgers University Piscataway, NJ, USA {jingwang,kdana}@caip.rutgers.edu
Hybrid Textons: Modeling Surfaces with Reflectance and Geometry Jing Wang and Kristin J. Dana Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Rutgers University Piscataway, NJ, USA {jingwang,kdana}@caip.rutgers.edu
12/3/2009. What is Computer Vision? Applications. Application: Assisted driving Pedestrian and car detection. Application: Improving online search
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence V22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 26: Computer Vision Rob Fergus Dept of Computer Science, Courant Institute, NYU Slides from Andrew Zisserman What is Computer Vision?
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence V22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 26: Computer Vision Rob Fergus Dept of Computer Science, Courant Institute, NYU Slides from Andrew Zisserman What is Computer Vision?
Faces and Image-Based Lighting
 Announcements Faces and Image-Based Lighting Project #3 artifacts voting Final project: Demo on 6/25 (Wednesday) 13:30pm in this room Reports and videos due on 6/26 (Thursday) 11:59pm Digital Visual Effects,
Announcements Faces and Image-Based Lighting Project #3 artifacts voting Final project: Demo on 6/25 (Wednesday) 13:30pm in this room Reports and videos due on 6/26 (Thursday) 11:59pm Digital Visual Effects,
Face Recognition under Severe Shadow Effects Using Gradient Field Transformation
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013 1 Face Recognition under Severe Shadow Effects Using Gradient Field Transformation Parisa Beham M *, Bala Bhattachariar
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013 1 Face Recognition under Severe Shadow Effects Using Gradient Field Transformation Parisa Beham M *, Bala Bhattachariar
