Finding the Equation of a Straight Line
|
|
|
- Juliet Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Finding the Equation of a Straight Line You should have, before now, ome aross the equation of a straight line, perhaps at shool. Engineers use this equation to help determine how one quantity is related to another this an be for many reasons as you will find out throughout this ourse. Mathematially the equation of a straight line is given as Where: y mx or y axb x is the x o-ordinate (x, y) y is the y o-ordinate (x, y) m or a is the slope of the line [rise run ] or b is where the line rosses the y axes [also known as the y interept] Chek these out on the graph in Figure 1. Figure 1: Simple Plot If we know all of the above information we an use this to find the atual mathematial relationship between the x and y values. That is, ultimately, if we know the value of x we an alulate y. Why would we want to do this? Well, in many modern omputer ontrolled systems a sensors output is used to determine a value for example the position of a printer head the output of the position sensor is a voltage and the omputer uses this to determine the displaement of the printhead in mm. Let s see how it works. MjD Aug of 7
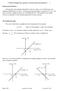
2 Chek out Figure 2. Here we an see two plots, one whih appears to slope up the way, plot height inreases as the x value inreases and the other appears to slope down, plot height dereases as the x value inreases. We will hek out the straight line equation for both of these plots and see how the straight line equation desribes eah. The straight line equation: for the rest of this hand-out we will use y mx First we identify and selet two o-ordinate pairs from one of the plots that best desribes the plot. Let s hoose values from the line that slopes upwards first. Looking at the plot from the origin (0,0) we an see that the left hand end of the line is sitting at the point x1 = 1 and y1 = 2 also written (1,2) while the other end of the line is at x2 = 8 and y2 = 8 or (8,8). We will use these as our two sets of o-ordinates. Figure 2: Two different plots. x1 = 1 x2 = 8 y1 = 2 y2 = 8 We an now use the o-ordinate pair to find the slope of the line m. The slope of the line is a measure of how steep it is and is alulated by finding out how high [the rise] it moves over what distane [the run]. To find m we arry out the following alulation: rise m = run We an determine the rise from the o-ordinates; it is the differene in the y oordinates or y2 y1 = 8 2 MjD Aug of 7
3 Whilst for the run; it is the differene in the x o-ordinates or x 2 x 1 ; in this ase 8 1 Plaing this in the equation for m: 8 2 m = = 7 = This allows us to re-write our partially ompleted straight line equation as: y = x We now have to determine the (y interept) or. In order to find we first have to re-arrange the straight line equation so that is on the left of the equals sign. y mx First we need to move the mx term over to the left of the equation in order to do this we subtrat mx from both sides [we have to subtrat from both sides in order to keep the equation balaned]. y mx = mx mx+ We an re-write this as: y mx = + but this ould also be written as y mx = or = y mx We an now use this equation and our previous o-ordinate pairs to find. We know the values of some of the points on the line that makes up our plot; let s use the first o-ordinate pair x1 and y1 by substituting these values into our new equation we an alulate. [N.B remember m has a value of ] x = x1 = 1 y = y1 = 2 m = = y mx = = = We an now write out the full equation for the straight line graph: y = x How do we know that the equation is orret? We use the other o-ordinate pair to hek it. We substitute x2 in for x and alulate through the answer should be y2. MjD Aug of 7
4 x2 = 8 y2 = 8 y = x As expeted. y = = = 8 MjD Aug of 7
5 The equation: y = mx+ For the seond plot. Again we identify and selet two o-ordinate pairs from the plot. Looking at the plot from the origin (0,0) we an see that the left hand end of the line is sitting at the point x1 = 1 and y1 = 6 also written (1,6) while the other end of the line is at x2 = 5 and y2 = 1 or (5,1). We will use these as our two sets of o-ordinates. Figure 3: Two different plots. x1 = 1 x2 = 5 y1 = 6 y2 = 1 We an now use the o-ordinate pair to find the slope of the line m. The slope of the line is a measure of how steep it is and is alulated by finding out how high [rise] it moves in what distane [run]. To find m we arry out the following alulation: rise m run We an determine the rise from the o-ordinates it is the differene in the y oordinates or y2 y1 = 1 6 Whilst the run is the differene in the x o-ordinates or x2 x1 in this ase 5 1 Plaing this in the equation for m: 1 6 m = = 4 = 1.25 This allows us to re-write our partially ompleted straight line equation as: y = x We now have to determine the (y interept) or. NB a negative sign in front of m just shows us that the plot is sloping downwards. MjD Aug of 7
6 In order to find we first have to re-arrange the straight line equation so that is on the left of the equals sign. y = mx+ First we need to move the mx term over to the left of the equation in order to do this we subtrat mx from both sides [we have to subtrat from both sides in order to keep the equation balaned]. y mx = mx mx+ We an re-write this as: y mx = + but this ould also be written as y mx = or = y mx We an now use this equation and our previous o-ordinate pairs to find. We know the values of some of the points on the line that makes up our plot; let s use the first o-ordinate pair x1 and y1 by substituting these values into our new equation we an alulate. [N.B remember m has a value of ] x = x1 = 6 y = y1 = 1 m = = y mx = 6 ( 1.251) = = We an now write out the full equation for the straight line graph: y = x How do we know that the equation is orret? We use the other o-ordinate pair to hek it. We substitute x2 in for x and alulate through the answer y should be y2. x2 = 5 y2 = 1 As expeted. y = x 1= = = 1 NB a negative sign in front of m just shows us that the plot is sloping downwards. MjD Aug of 7
7 Knowing the equation for the straight line allows us to alulate the y value for any given x value. We an also extend our equation manipulation to let us find where the line rosses the x axis or the x interept. If we are looking to find where the graph line rosses the x axis then at that point the y value must be equal to zero y=0: If we now arry this knowledge bak to our equation of a straight line we an see: x 1.25 x 5.80 y = x = x x( 1.25) If we now examine the graph we an see this is what would be expeted. MjD Aug of 7
The Mathematics of Simple Ultrasonic 2-Dimensional Sensing
 The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing President, Bitstream Tehnology The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing Introdution Our ompany, Bitstream Tehnology, has been developing
The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing President, Bitstream Tehnology The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing Introdution Our ompany, Bitstream Tehnology, has been developing
And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequency domain by
 Problem Set no.3.a) The ideal low-pass filter is given in the frequeny domain by B ideal ( f ), f f; =, f > f. () And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequeny domain by B
Problem Set no.3.a) The ideal low-pass filter is given in the frequeny domain by B ideal ( f ), f f; =, f > f. () And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequeny domain by B
Intro. To Graphing Linear Equations
 Intro. To Graphing Linear Equations The Coordinate Plane A. The coordinate plane has 4 quadrants. B. Each point in the coordinate plain has an x-coordinate (the abscissa) and a y-coordinate (the ordinate).
Intro. To Graphing Linear Equations The Coordinate Plane A. The coordinate plane has 4 quadrants. B. Each point in the coordinate plain has an x-coordinate (the abscissa) and a y-coordinate (the ordinate).
GRAPHING WORKSHOP. A graph of an equation is an illustration of a set of points whose coordinates satisfy the equation.
 GRAPHING WORKSHOP A graph of an equation is an illustration of a set of points whose coordinates satisfy the equation. The figure below shows a straight line drawn through the three points (2, 3), (-3,-2),
GRAPHING WORKSHOP A graph of an equation is an illustration of a set of points whose coordinates satisfy the equation. The figure below shows a straight line drawn through the three points (2, 3), (-3,-2),
Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots. Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle.
 Algebra I Chapter 4 Notes Name Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle. X-axis: The horizontal axis Y-axis: The vertical
Algebra I Chapter 4 Notes Name Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle. X-axis: The horizontal axis Y-axis: The vertical
SNAP Centre Workshop. Graphing Lines
 SNAP Centre Workshop Graphing Lines 45 Graphing a Line Using Test Values A simple way to linear equation involves finding test values, plotting the points on a coordinate plane, and connecting the points.
SNAP Centre Workshop Graphing Lines 45 Graphing a Line Using Test Values A simple way to linear equation involves finding test values, plotting the points on a coordinate plane, and connecting the points.
Graphing Linear Equations
 Graphing Linear Equations Question 1: What is a rectangular coordinate system? Answer 1: The rectangular coordinate system is used to graph points and equations. To create the rectangular coordinate system,
Graphing Linear Equations Question 1: What is a rectangular coordinate system? Answer 1: The rectangular coordinate system is used to graph points and equations. To create the rectangular coordinate system,
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions
 Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Section Graphs and Lines
 Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
CHAPTER. Graphs of Linear Equations. 3.1 Introduction to Graphing 3.2 Graphing Linear Equations 3.3 More with Graphing 3.4 Slope and Applications
 Graphs of Linear Equations CHAPTER 3 3.1 Introduction to Graphing 3.2 Graphing Linear Equations 3.3 More with Graphing 3.4 Slope and Applications Slide 2 3.1 Introduction to Graphing OBJECTIVES a Plot
Graphs of Linear Equations CHAPTER 3 3.1 Introduction to Graphing 3.2 Graphing Linear Equations 3.3 More with Graphing 3.4 Slope and Applications Slide 2 3.1 Introduction to Graphing OBJECTIVES a Plot
Writing and Graphing Linear Equations. Linear equations can be used to represent relationships.
 Writing and Graphing Linear Equations Linear equations can be used to represent relationships. Linear equation An equation whose solutions form a straight line on a coordinate plane. Collinear Points that
Writing and Graphing Linear Equations Linear equations can be used to represent relationships. Linear equation An equation whose solutions form a straight line on a coordinate plane. Collinear Points that
represent = as a finite deimal" either in base 0 or in base. We an imagine that the omputer first omputes the mathematial = then rounds the result to
 Sientifi Computing Chapter I Computer Arithmeti Jonathan Goodman Courant Institute of Mathemaial Sienes Last revised January, 00 Introdution One of the many soures of error in sientifi omputing is inexat
Sientifi Computing Chapter I Computer Arithmeti Jonathan Goodman Courant Institute of Mathemaial Sienes Last revised January, 00 Introdution One of the many soures of error in sientifi omputing is inexat
Math-2. Lesson 3-1. Equations of Lines
 Math-2 Lesson 3-1 Equations of Lines How can an equation make a line? y = x + 1 x -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 Fill in the rest of the table rule x + 1 f(x) -4 + 1-3 -3 + 1-2 -2 + 1-1 -1 + 1 0 0 + 1 1 1 + 1 2 2 +
Math-2 Lesson 3-1 Equations of Lines How can an equation make a line? y = x + 1 x -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 Fill in the rest of the table rule x + 1 f(x) -4 + 1-3 -3 + 1-2 -2 + 1-1 -1 + 1 0 0 + 1 1 1 + 1 2 2 +
Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work
 Week beginning 6 th 13 th 20 th HALF TERM 27th Topis for revision Fators, multiples and primes Indies Frations, Perentages, Deimals Rounding 6 th Marh Ratio Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work Understand
Week beginning 6 th 13 th 20 th HALF TERM 27th Topis for revision Fators, multiples and primes Indies Frations, Perentages, Deimals Rounding 6 th Marh Ratio Year 11 GCSE Revision - Re-visit work Understand
Background/Review on Numbers and Computers (lecture)
 Bakground/Review on Numbers and Computers (leture) ICS312 Mahine-Level and Systems Programming Henri Casanova (henri@hawaii.edu) Numbers and Computers Throughout this ourse we will use binary and hexadeimal
Bakground/Review on Numbers and Computers (leture) ICS312 Mahine-Level and Systems Programming Henri Casanova (henri@hawaii.edu) Numbers and Computers Throughout this ourse we will use binary and hexadeimal
Relevance for Computer Vision
 The Geometry of ROC Spae: Understanding Mahine Learning Metris through ROC Isometris, by Peter A. Flah International Conferene on Mahine Learning (ICML-23) http://www.s.bris.a.uk/publiations/papers/74.pdf
The Geometry of ROC Spae: Understanding Mahine Learning Metris through ROC Isometris, by Peter A. Flah International Conferene on Mahine Learning (ICML-23) http://www.s.bris.a.uk/publiations/papers/74.pdf
Grade 6. Mathematics. Student Booklet SPRING 2009 RELEASED ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS. Assessment of Reading, Writing and Mathematics, Junior Division
 Grade 6 Assessment of Reading, Writing and Mathematis, Junior Division Student Booklet Mathematis SPRING 2009 RELEASED ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS Please note: The format of these booklets is slightly different
Grade 6 Assessment of Reading, Writing and Mathematis, Junior Division Student Booklet Mathematis SPRING 2009 RELEASED ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS Please note: The format of these booklets is slightly different
.(3, 2) Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinates. Every point has two co-ordinates. Plot the following points on the plane. A (4, 1) D (2, 5) G (6, 3)
 Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinates Every point has two co-ordinates. (3, 2) x co-ordinate y co-ordinate Plot the following points on the plane..(3, 2) A (4, 1) D (2, 5) G (6, 3) B (3, 3) E ( 4, 4) H (6,
Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinates Every point has two co-ordinates. (3, 2) x co-ordinate y co-ordinate Plot the following points on the plane..(3, 2) A (4, 1) D (2, 5) G (6, 3) B (3, 3) E ( 4, 4) H (6,
STRAIGHT LINE GRAPHS THE COORDINATES OF A POINT. The coordinates of any point are written as an ordered pair (x, y)
 THE COORDINATES OF A POINT STRAIGHT LINE GRAPHS The coordinates of any point are written as an ordered pair (x, y) Point P in the diagram has coordinates (2, 3). Its horizontal distance along the x axis
THE COORDINATES OF A POINT STRAIGHT LINE GRAPHS The coordinates of any point are written as an ordered pair (x, y) Point P in the diagram has coordinates (2, 3). Its horizontal distance along the x axis
Algebra Unit 2: Linear Functions Notes. Slope Notes. 4 Types of Slope. Slope from a Formula
 Undefined Slope Notes Types of Slope Zero Slope Slope can be described in several ways: Steepness of a line Rate of change rate of increase or decrease Rise Run Change (difference) in y over change (difference)
Undefined Slope Notes Types of Slope Zero Slope Slope can be described in several ways: Steepness of a line Rate of change rate of increase or decrease Rise Run Change (difference) in y over change (difference)
slope rise run Definition of Slope
 The Slope of a Line Mathematicians have developed a useful measure of the steepness of a line, called the slope of the line. Slope compares the vertical change (the rise) to the horizontal change (the
The Slope of a Line Mathematicians have developed a useful measure of the steepness of a line, called the slope of the line. Slope compares the vertical change (the rise) to the horizontal change (the
Supplementary Material: Geometric Calibration of Micro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features
 Supplementary Material: Geometri Calibration of Miro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features Yunsu Bok, Hae-Gon Jeon and In So Kweon KAIST, Korea As the supplementary material, we provide detailed
Supplementary Material: Geometri Calibration of Miro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features Yunsu Bok, Hae-Gon Jeon and In So Kweon KAIST, Korea As the supplementary material, we provide detailed
Sketching graphs of polynomials
 Sketching graphs of polynomials We want to draw the graphs of polynomial functions y = f(x). The degree of a polynomial in one variable x is the highest power of x that remains after terms have been collected.
Sketching graphs of polynomials We want to draw the graphs of polynomial functions y = f(x). The degree of a polynomial in one variable x is the highest power of x that remains after terms have been collected.
Forms of Linear Equations
 6. 1-6.3 Forms of Linear Equations Name Sec 6.1 Writing Linear Equations in Slope-Intercept Form *Recall that slope intercept form looks like y = mx + b, where m = slope and b = y=intercept 1) Writing
6. 1-6.3 Forms of Linear Equations Name Sec 6.1 Writing Linear Equations in Slope-Intercept Form *Recall that slope intercept form looks like y = mx + b, where m = slope and b = y=intercept 1) Writing
9.4 Exponential Growth and Decay Functions
 Setion 9. Eponential Growth and Dea Funtions 56 9. Eponential Growth and Dea Funtions S Model Eponential Growth. Model Eponential Dea. Now that we an graph eponential funtions, let s learn about eponential
Setion 9. Eponential Growth and Dea Funtions 56 9. Eponential Growth and Dea Funtions S Model Eponential Growth. Model Eponential Dea. Now that we an graph eponential funtions, let s learn about eponential
Motion Graphs. Plotting position against time can tell you a lot about motion. Let's look at the axes:
 Motion Graphs 1 Name Motion Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion
Motion Graphs 1 Name Motion Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion
Practice Test (page 391) 1. For each line, count squares on the grid to determine the rise and the run. Use slope = rise
 Practice Test (page 91) 1. For each line, count squares on the grid to determine the rise and the. Use slope = rise 4 Slope of AB =, or 6 Slope of CD = 6 9, or Slope of EF = 6, or 4 Slope of GH = 6 4,
Practice Test (page 91) 1. For each line, count squares on the grid to determine the rise and the. Use slope = rise 4 Slope of AB =, or 6 Slope of CD = 6 9, or Slope of EF = 6, or 4 Slope of GH = 6 4,
Section 4.4: Parabolas
 Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials
 Math 3201 5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials In Math 1201/2201, we examined three types of polynomial functions: Constant Function - horizontal line such as y = 2 Linear Function - sloped line,
Math 3201 5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials In Math 1201/2201, we examined three types of polynomial functions: Constant Function - horizontal line such as y = 2 Linear Function - sloped line,
UCSB Math TI-85 Tutorials: Basics
 3 UCSB Math TI-85 Tutorials: Basis If your alulator sreen doesn t show anything, try adjusting the ontrast aording to the instrutions on page 3, or page I-3, of the alulator manual You should read the
3 UCSB Math TI-85 Tutorials: Basis If your alulator sreen doesn t show anything, try adjusting the ontrast aording to the instrutions on page 3, or page I-3, of the alulator manual You should read the
graphing_9.1.notebook March 15, 2019
 1 2 3 Writing the equation of a line in slope intercept form. In order to write an equation in y = mx + b form you will need the slope "m" and the y intercept "b". We will subsitute the values for m and
1 2 3 Writing the equation of a line in slope intercept form. In order to write an equation in y = mx + b form you will need the slope "m" and the y intercept "b". We will subsitute the values for m and
Calculation of typical running time of a branch-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-cover problem
 Calulation of typial running time of a branh-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-over problem Joni Pajarinen, Joni.Pajarinen@iki.fi Otober 21, 2007 1 Introdution The vertex-over problem is one of a olletion
Calulation of typial running time of a branh-and-bound algorithm for the vertex-over problem Joni Pajarinen, Joni.Pajarinen@iki.fi Otober 21, 2007 1 Introdution The vertex-over problem is one of a olletion
Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Straight Lines. 2 of 71. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
FLC Ch 3. Ex 1 Plot the points Ex 2 Give the coordinates of each point shown. Sec 3.2: Solutions and Graphs of Linear Equations
 Math 100 Elementary Algebra Sec 3.1: The Rectangular Coordinate System x-axis and y-axis origin ordered pair x-coordinate y-coordinate quadrants (I, II, III, and IV) Rectangular/Cartesian Coordinate System
Math 100 Elementary Algebra Sec 3.1: The Rectangular Coordinate System x-axis and y-axis origin ordered pair x-coordinate y-coordinate quadrants (I, II, III, and IV) Rectangular/Cartesian Coordinate System
Section 9.3 Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Section 9.3 Graphing Quadratic Functions A Quadratic Function is an equation that can be written in the following Standard Form., where a 0. Every quadratic function has a U-shaped graph called a. If the
Section 9.3 Graphing Quadratic Functions A Quadratic Function is an equation that can be written in the following Standard Form., where a 0. Every quadratic function has a U-shaped graph called a. If the
Four Types of Slope Positive Slope Negative Slope Zero Slope Undefined Slope Slope Dude will help us understand the 4 types of slope
 Four Types of Slope Positive Slope Negative Slope Zero Slope Undefined Slope Slope Dude will help us understand the 4 types of slope https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=avs6c6_kvxm Direct Variation
Four Types of Slope Positive Slope Negative Slope Zero Slope Undefined Slope Slope Dude will help us understand the 4 types of slope https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=avs6c6_kvxm Direct Variation
2 Unit Bridging Course Day 2 Linear functions I: Gradients
 1 / 33 2 Unit Bridging Course Day 2 Linear functions I: Gradients Clinton Boys 2 / 33 Linear functions Linear functions are a particularly simple and special type of functions. They are widely used in
1 / 33 2 Unit Bridging Course Day 2 Linear functions I: Gradients Clinton Boys 2 / 33 Linear functions Linear functions are a particularly simple and special type of functions. They are widely used in
Math 1313 Prerequisites/Test 1 Review
 Math 1313 Prerequisites/Test 1 Review Test 1 (Prerequisite Test) is the only exam that can be done from ANYWHERE online. Two attempts. See Online Assignments in your CASA account. Note the deadline too.
Math 1313 Prerequisites/Test 1 Review Test 1 (Prerequisite Test) is the only exam that can be done from ANYWHERE online. Two attempts. See Online Assignments in your CASA account. Note the deadline too.
«From straight line graph to polynomial inequalities»
 «Fro straight line graph to polynoial inequalities» Bakground inforation: Solving linear and quadrati inequalities are the two topis over in Eleentary and Additional Matheatis at level. Solving polynoial
«Fro straight line graph to polynoial inequalities» Bakground inforation: Solving linear and quadrati inequalities are the two topis over in Eleentary and Additional Matheatis at level. Solving polynoial
 Algebra Lab Investigating Trigonometri Ratios You an use paper triangles to investigate the ratios of the lengths of sides of right triangles. Virginia SOL Preparation for G.8 The student will solve realworld
Algebra Lab Investigating Trigonometri Ratios You an use paper triangles to investigate the ratios of the lengths of sides of right triangles. Virginia SOL Preparation for G.8 The student will solve realworld
with respect to the normal in each medium, respectively. The question is: How are θ
 Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
Coordinate Geometry. Coordinate geometry is the study of the relationships between points on the Cartesian plane
 Coordinate Geometry Coordinate geometry is the study of the relationships between points on the Cartesian plane What we will explore in this tutorial (a) Explore gradient I. Identify the gradient of a
Coordinate Geometry Coordinate geometry is the study of the relationships between points on the Cartesian plane What we will explore in this tutorial (a) Explore gradient I. Identify the gradient of a
An Event Display for ATLAS H8 Pixel Test Beam Data
 An Event Display for ATLAS H8 Pixel Test Beam Data George Gollin Centre de Physique des Partiules de Marseille and University of Illinois April 17, 1999 g-gollin@uiu.edu An event display program is now
An Event Display for ATLAS H8 Pixel Test Beam Data George Gollin Centre de Physique des Partiules de Marseille and University of Illinois April 17, 1999 g-gollin@uiu.edu An event display program is now
Algebra II Quadratic Functions
 1 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org 2 Ta b le o f C o n te n t Key Terms click on the topic to go to that section Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations
1 Algebra II Quadratic Functions 2014-10-14 www.njctl.org 2 Ta b le o f C o n te n t Key Terms click on the topic to go to that section Explain Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Combining Transformations
Lecture 4. If P1(x1,y1) and P2(x2,y2) are points on a non-vertical line, then the slope m of the line is defined by
 Lines Lecture 4 In this section we shall discuss ways to measure the "steepness" or "slope" of a line in the plane. The ideas we develop here will be important when we discuss equations and graphs of straight
Lines Lecture 4 In this section we shall discuss ways to measure the "steepness" or "slope" of a line in the plane. The ideas we develop here will be important when we discuss equations and graphs of straight
PR3 & PR4 CBR Activities Using EasyData for CBL/CBR Apps
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Process Page 23. PR3 & PR4 CBR Activities Using EasyData for CBL/CBR Apps The TI Exploration Series for CBR or CBL/CBR books, are all written for the old CBL/CBR Application. Now we can
Summer 2006 I2T2 Process Page 23. PR3 & PR4 CBR Activities Using EasyData for CBL/CBR Apps The TI Exploration Series for CBR or CBL/CBR books, are all written for the old CBL/CBR Application. Now we can
Notes Lesson 3 4. Positive. Coordinate. lines in the plane can be written in standard form. Horizontal
 A, B, C are Notes Lesson 3 4 Standard Form of an Equation: Integers Ax + By = C Sometimes it is preferred that A is Positive All lines in the plane can be written in standard form. Oblique Coordinate Horizontal
A, B, C are Notes Lesson 3 4 Standard Form of an Equation: Integers Ax + By = C Sometimes it is preferred that A is Positive All lines in the plane can be written in standard form. Oblique Coordinate Horizontal
Chapter 2: Introduction to Maple V
 Chapter 2: Introdution to Maple V 2-1 Working with Maple Worksheets Try It! (p. 15) Start a Maple session with an empty worksheet. The name of the worksheet should be Untitled (1). Use one of the standard
Chapter 2: Introdution to Maple V 2-1 Working with Maple Worksheets Try It! (p. 15) Start a Maple session with an empty worksheet. The name of the worksheet should be Untitled (1). Use one of the standard
Smooth Trajectory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Velocity Constraints
 Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
Triangles. Learning Objectives. Pre-Activity
 Setion 3.2 Pre-tivity Preparation Triangles Geena needs to make sure that the dek she is building is perfetly square to the brae holding the dek in plae. How an she use geometry to ensure that the boards
Setion 3.2 Pre-tivity Preparation Triangles Geena needs to make sure that the dek she is building is perfetly square to the brae holding the dek in plae. How an she use geometry to ensure that the boards
UNIT 4 NOTES. 4-1 and 4-2 Coordinate Plane
 UNIT 4 NOTES 4-1 and 4-2 Coordinate Plane y Ordered pairs on a graph have several names. (X coordinate, Y coordinate) (Domain, Range) (Input,Output) Plot these points and label them: a. (3,-4) b. (-5,2)
UNIT 4 NOTES 4-1 and 4-2 Coordinate Plane y Ordered pairs on a graph have several names. (X coordinate, Y coordinate) (Domain, Range) (Input,Output) Plot these points and label them: a. (3,-4) b. (-5,2)
Measurement of the stereoscopic rangefinder beam angular velocity using the digital image processing method
 Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs
 Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs Section 12.1 Quadratic Graphs x 2 + 2 a 2 + 2a - 6 r r 2 x 2 5x + 8 2y 2 + 9y + 2 All the above equations contain a squared number. They are therefore called quadratic
Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs Section 12.1 Quadratic Graphs x 2 + 2 a 2 + 2a - 6 r r 2 x 2 5x + 8 2y 2 + 9y + 2 All the above equations contain a squared number. They are therefore called quadratic
You should be able to plot points on the coordinate axis. You should know that the the midpoint of the line segment joining (x, y 1 1
 Name GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA: You should be able to plot points on the coordinate axis. You should know that the the midpoint of the line segment joining (x, y 1 1 ) and (x, y ) is x1 x y1 y,.
Name GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA: You should be able to plot points on the coordinate axis. You should know that the the midpoint of the line segment joining (x, y 1 1 ) and (x, y ) is x1 x y1 y,.
0.4 Family of Functions/Equations
 0.4 Family of Functions/Equations By a family of functions, we are referring to a function definition such as f(x) = mx + 2 for m = 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2. 2 2 This says, work with all the functions obtained
0.4 Family of Functions/Equations By a family of functions, we are referring to a function definition such as f(x) = mx + 2 for m = 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2. 2 2 This says, work with all the functions obtained
Bell Ringer Write each phrase as a mathematical expression. Thinking with Mathematical Models
 Bell Ringer Write each phrase as a mathematical expression. 1. the sum of nine and eight 2. the sum of nine and a number 3. nine increased by a number x 4. fourteen decreased by a number p 5. the product
Bell Ringer Write each phrase as a mathematical expression. 1. the sum of nine and eight 2. the sum of nine and a number 3. nine increased by a number x 4. fourteen decreased by a number p 5. the product
About Graphing Lines
 About Graphing Lines TABLE OF CONTENTS About Graphing Lines... 1 What is a LINE SEGMENT?... 1 Ordered Pairs... 1 Cartesian Co-ordinate System... 1 Ordered Pairs... 2 Line Segments... 2 Slope of a Line
About Graphing Lines TABLE OF CONTENTS About Graphing Lines... 1 What is a LINE SEGMENT?... 1 Ordered Pairs... 1 Cartesian Co-ordinate System... 1 Ordered Pairs... 2 Line Segments... 2 Slope of a Line
Example 1: Give the coordinates of the points on the graph.
 Ordered Pairs Often, to get an idea of the behavior of an equation, we will make a picture that represents the solutions to the equation. A graph gives us that picture. The rectangular coordinate plane,
Ordered Pairs Often, to get an idea of the behavior of an equation, we will make a picture that represents the solutions to the equation. A graph gives us that picture. The rectangular coordinate plane,
Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas
 Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas 1 y axis origin x axis 2 Plot the points: ( 3, 5), (0,7), ( 6,0), (6,4) 3 Distance Formula y x 4 Finding the Distance Between Two Points Find the distance
Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas 1 y axis origin x axis 2 Plot the points: ( 3, 5), (0,7), ( 6,0), (6,4) 3 Distance Formula y x 4 Finding the Distance Between Two Points Find the distance
The x-intercept can be found by setting y = 0 and solving for x: 16 3, 0
 y=-3/4x+4 and y=2 x I need to graph the functions so I can clearly describe the graphs Specifically mention any key points on the graphs, including intercepts, vertex, or start/end points. What is the
y=-3/4x+4 and y=2 x I need to graph the functions so I can clearly describe the graphs Specifically mention any key points on the graphs, including intercepts, vertex, or start/end points. What is the
An Alternative Approach to the Fuzzifier in Fuzzy Clustering to Obtain Better Clustering Results
 An Alternative Approah to the Fuzziier in Fuzzy Clustering to Obtain Better Clustering Results Frank Klawonn Department o Computer Siene University o Applied Sienes BS/WF Salzdahlumer Str. 46/48 D-38302
An Alternative Approah to the Fuzziier in Fuzzy Clustering to Obtain Better Clustering Results Frank Klawonn Department o Computer Siene University o Applied Sienes BS/WF Salzdahlumer Str. 46/48 D-38302
A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR
 Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Graphing Linear Equations
 Graphing Linear Equations A.REI.10 Understand that the graph of an equation in two variables is the set of all its solutions plotted in the coordinate plane. What am I learning today? How to graph a linear
Graphing Linear Equations A.REI.10 Understand that the graph of an equation in two variables is the set of all its solutions plotted in the coordinate plane. What am I learning today? How to graph a linear
12 Rational Functions
 Funtions Conepts: The Definition of a Funtion Identifing Funtions Finding the Domain of a Funtion The Big-Little Priniple Vertial and Horizontal Asmptotes The Graphs of Funtions (Setion.) Definition. A
Funtions Conepts: The Definition of a Funtion Identifing Funtions Finding the Domain of a Funtion The Big-Little Priniple Vertial and Horizontal Asmptotes The Graphs of Funtions (Setion.) Definition. A
Type of document: Usebility Checklist
 Projet: JEGraph Type of doument: Usebility Cheklist Author: Max Bryan Version: 1.30 2011 Envidate GmbH Type of Doumet Developer guidelines User guidelines Dutybook Speifiation Programming and testing Test
Projet: JEGraph Type of doument: Usebility Cheklist Author: Max Bryan Version: 1.30 2011 Envidate GmbH Type of Doumet Developer guidelines User guidelines Dutybook Speifiation Programming and testing Test
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 6
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
Definitions Homework. Quine McCluskey Optimal solutions are possible for some large functions Espresso heuristic. Definitions Homework
 EECS 33 There be Dragons here http://ziyang.ees.northwestern.edu/ees33/ Teaher: Offie: Email: Phone: L477 Teh dikrp@northwestern.edu 847 467 2298 Today s material might at first appear diffiult Perhaps
EECS 33 There be Dragons here http://ziyang.ees.northwestern.edu/ees33/ Teaher: Offie: Email: Phone: L477 Teh dikrp@northwestern.edu 847 467 2298 Today s material might at first appear diffiult Perhaps
AP PHYSICS B 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP PHYSICS B 009 SCORING GUIDELINES General Notes About 009 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines 1. The solutions contain the most common method of solving the free-response questions and the allocation of points
AP PHYSICS B 009 SCORING GUIDELINES General Notes About 009 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines 1. The solutions contain the most common method of solving the free-response questions and the allocation of points
In math, the rate of change is called the slope and is often described by the ratio rise
 Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
1. Introduction. 2. The Probable Stope Algorithm
 1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
Introductory Programming, IMM, DTU Systematic Software Test. Software test (afprøvning) Motivation. Structural test and functional test
 Introdutory Programming, IMM, DTU Systemati Software Test Peter Sestoft a Programs often ontain unintended errors how do you find them? Strutural test Funtional test Notes: Systemati Software Test, http://www.dina.kvl.dk/
Introdutory Programming, IMM, DTU Systemati Software Test Peter Sestoft a Programs often ontain unintended errors how do you find them? Strutural test Funtional test Notes: Systemati Software Test, http://www.dina.kvl.dk/
How do you roll? Fig. 1 - Capstone screen showing graph areas and menus
 How do you roll? Purpose: Observe and compare the motion of a cart rolling down hill versus a cart rolling up hill. Develop a mathematical model of the position versus time and velocity versus time for
How do you roll? Purpose: Observe and compare the motion of a cart rolling down hill versus a cart rolling up hill. Develop a mathematical model of the position versus time and velocity versus time for
Multiple Assignments
 Two Outputs Conneted Together Multiple Assignments Two Outputs Conneted Together if (En1) Q
Two Outputs Conneted Together Multiple Assignments Two Outputs Conneted Together if (En1) Q
A Load-Balanced Clustering Protocol for Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Networks
 International Journal of Advanes in Computer Networks and Its Seurity IJCNS A Load-Balaned Clustering Protool for Hierarhial Wireless Sensor Networks Mehdi Tarhani, Yousef S. Kavian, Saman Siavoshi, Ali
International Journal of Advanes in Computer Networks and Its Seurity IJCNS A Load-Balaned Clustering Protool for Hierarhial Wireless Sensor Networks Mehdi Tarhani, Yousef S. Kavian, Saman Siavoshi, Ali
Sketching Straight Lines (Linear Relationships)
 Sketching Straight Lines (Linear Relationships) The slope of the line is m = y x = y 2 y 1 = rise run. Horizontal lines have the form y = b and have slope m = 0. Vertical lines have the form x = a and
Sketching Straight Lines (Linear Relationships) The slope of the line is m = y x = y 2 y 1 = rise run. Horizontal lines have the form y = b and have slope m = 0. Vertical lines have the form x = a and
Plot-to-track correlation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surface Movement Radar
 Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Motion Graphs. Plotting distance against time can tell you a lot about motion. Let's look at the axes:
 Motion Graphs 1 _ Motion Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion
Motion Graphs 1 _ Motion Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion
Name Class Date. Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities
 4-1 Reteaching Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities An important life skill is to be able to a read graph. When looking at a graph, you should check the title, the labels on the axes, and the general
4-1 Reteaching Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities An important life skill is to be able to a read graph. When looking at a graph, you should check the title, the labels on the axes, and the general
3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane
 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Substitute the given values of m, x, and y into the equation y = mx + b and solve for b. 1. m = 2, x = 3, and
3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Substitute the given values of m, x, and y into the equation y = mx + b and solve for b. 1. m = 2, x = 3, and
特集 Road Border Recognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Processing
 デンソーテクニカルレビュー Vol. 15 2010 特集 Road Border Reognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Proessing 高木聖和 バーゼル ファルディ Kiyokazu TAKAGI Basel Fardi ヘンドリック ヴァイゲル Hendrik Weigel ゲルド ヴァニーリック Gerd Wanielik This paper
デンソーテクニカルレビュー Vol. 15 2010 特集 Road Border Reognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Proessing 高木聖和 バーゼル ファルディ Kiyokazu TAKAGI Basel Fardi ヘンドリック ヴァイゲル Hendrik Weigel ゲルド ヴァニーリック Gerd Wanielik This paper
3.5 Day 1 Warm Up. Graph each line. 3.4 Proofs with Perpendicular Lines
 3.5 Day 1 Warm Up Graph each line. 1. y = 4x 2. y = 3x + 2 3. y = x 3 4. y = 4 x + 3 3 November 2, 2015 3.4 Proofs with Perpendicular Lines Geometry 3.5 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Day
3.5 Day 1 Warm Up Graph each line. 1. y = 4x 2. y = 3x + 2 3. y = x 3 4. y = 4 x + 3 3 November 2, 2015 3.4 Proofs with Perpendicular Lines Geometry 3.5 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Day
This is called the vertex form of the quadratic equation. To graph the equation
 Name Period Date: Topic: 7-5 Graphing ( ) Essential Question: What is the vertex of a parabola, and what is its axis of symmetry? Standard: F-IF.7a Objective: Graph linear and quadratic functions and show
Name Period Date: Topic: 7-5 Graphing ( ) Essential Question: What is the vertex of a parabola, and what is its axis of symmetry? Standard: F-IF.7a Objective: Graph linear and quadratic functions and show
Algorithms for External Memory Lecture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking
 Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes
 CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example
 14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
Re-programming a many-to-many merge with Hash Objects
 Re-programming a many-to-many merge with Hash Objets CS05 PhUSE 2012 Budapest D. J. Garbutt 17 Otober 2012 Why? 1 In this talk I will demonstrate how you an re-program a many-to-many merge using hash objets
Re-programming a many-to-many merge with Hash Objets CS05 PhUSE 2012 Budapest D. J. Garbutt 17 Otober 2012 Why? 1 In this talk I will demonstrate how you an re-program a many-to-many merge using hash objets
Adapting K-Medians to Generate Normalized Cluster Centers
 Adapting -Medians to Generate Normalized Cluster Centers Benamin J. Anderson, Deborah S. Gross, David R. Musiant Anna M. Ritz, Thomas G. Smith, Leah E. Steinberg Carleton College andersbe@gmail.om, {dgross,
Adapting -Medians to Generate Normalized Cluster Centers Benamin J. Anderson, Deborah S. Gross, David R. Musiant Anna M. Ritz, Thomas G. Smith, Leah E. Steinberg Carleton College andersbe@gmail.om, {dgross,
1 The Knuth-Morris-Pratt Algorithm
 5-45/65: Design & Analysis of Algorithms September 26, 26 Leture #9: String Mathing last hanged: September 26, 27 There s an entire field dediated to solving problems on strings. The book Algorithms on
5-45/65: Design & Analysis of Algorithms September 26, 26 Leture #9: String Mathing last hanged: September 26, 27 There s an entire field dediated to solving problems on strings. The book Algorithms on
Revision Topic 11: Straight Line Graphs
 Revision Topic : Straight Line Graphs The simplest way to draw a straight line graph is to produce a table of values. Example: Draw the lines y = x and y = 6 x. Table of values for y = x x y - - - - =
Revision Topic : Straight Line Graphs The simplest way to draw a straight line graph is to produce a table of values. Example: Draw the lines y = x and y = 6 x. Table of values for y = x x y - - - - =
Sequential Incremental-Value Auctions
 Sequential Inremental-Value Autions Xiaoming Zheng and Sven Koenig Department of Computer Siene University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781 {xiaominz,skoenig}@us.edu Abstrat We study the
Sequential Inremental-Value Autions Xiaoming Zheng and Sven Koenig Department of Computer Siene University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781 {xiaominz,skoenig}@us.edu Abstrat We study the
Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables is a Line
 Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables is a Line Classwork Exercises Theorem: The graph of a linear equation y = mx + b is a non-vertical line with slope m and passing through (0, b),
Lesson 19: The Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables is a Line Classwork Exercises Theorem: The graph of a linear equation y = mx + b is a non-vertical line with slope m and passing through (0, b),
arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017](/thumbs/96/126543346.jpg) An effiient lustering algorithm from the measure of loal Gaussian distribution Yuan-Yen Tai (Dated: May 27, 2018) In this paper, I will introdue a fast and novel lustering algorithm based on Gaussian distribution
An effiient lustering algorithm from the measure of loal Gaussian distribution Yuan-Yen Tai (Dated: May 27, 2018) In this paper, I will introdue a fast and novel lustering algorithm based on Gaussian distribution
Let us start with a quick revision of algebra and how to work with variables. Now let us look at the simpler topic, namely Substitution.
 Section F Algebra & Equations Objective In this section, we will be dealing with solving equations for the variable involved, manipulating formulae to get one variable as the subject of the formula and
Section F Algebra & Equations Objective In this section, we will be dealing with solving equations for the variable involved, manipulating formulae to get one variable as the subject of the formula and
Exploring Quadratic Graphs
 Exploring Quadratic Graphs The general quadratic function is y=ax 2 +bx+c It has one of two basic graphs shapes, as shown below: It is a symmetrical "U"-shape or "hump"-shape, depending on the sign of
Exploring Quadratic Graphs The general quadratic function is y=ax 2 +bx+c It has one of two basic graphs shapes, as shown below: It is a symmetrical "U"-shape or "hump"-shape, depending on the sign of
Outline: Software Design
 Outline: Software Design. Goals History of software design ideas Design priniples Design methods Life belt or leg iron? (Budgen) Copyright Nany Leveson, Sept. 1999 A Little History... At first, struggling
Outline: Software Design. Goals History of software design ideas Design priniples Design methods Life belt or leg iron? (Budgen) Copyright Nany Leveson, Sept. 1999 A Little History... At first, struggling
13.1 Numerical Evaluation of Integrals Over One Dimension
 13.1 Numerial Evaluation of Integrals Over One Dimension A. Purpose This olletion of subprograms estimates the value of the integral b a f(x) dx where the integrand f(x) and the limits a and b are supplied
13.1 Numerial Evaluation of Integrals Over One Dimension A. Purpose This olletion of subprograms estimates the value of the integral b a f(x) dx where the integrand f(x) and the limits a and b are supplied
Advanced Algebra. Equation of a Circle
 Advanced Algebra Equation of a Circle Task on Entry Plotting Equations Using the table and axis below, plot the graph for - x 2 + y 2 = 25 x -5-4 -3 0 3 4 5 y 1 4 y 2-4 3 2 + y 2 = 25 9 + y 2 = 25 y 2
Advanced Algebra Equation of a Circle Task on Entry Plotting Equations Using the table and axis below, plot the graph for - x 2 + y 2 = 25 x -5-4 -3 0 3 4 5 y 1 4 y 2-4 3 2 + y 2 = 25 9 + y 2 = 25 y 2
MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED
 FOM 11 T9 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS REVIEW - 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) -INTERCEPT = the point where the graph touches or crosses the -ais. It occurs when = 0. ) -INTERCEPT = the
FOM 11 T9 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS REVIEW - 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) -INTERCEPT = the point where the graph touches or crosses the -ais. It occurs when = 0. ) -INTERCEPT = the
