CS-465 Computer Vision
|
|
|
- Karen Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS-465 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT 9. Optic Flow
2 Optic Flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 2 / 25
3 Optic Flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 3 / 25
4 Optic Flow Where does pixel (x, y) in frame z move to in frame z + 1? [ ] [ ] [ ] x x u y = + y v We want to find the displacement vector (u, v) T pixel. for every Input: image sequence I (x, y, z), where (x, y) specifies the location and z denotes time/frame number Goal: displacement vector field of the image structures: optic flow (u(x, y, z), v(x, y, z)) Such correspondence problems are key problems in computer vision. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 4 / 25
5 Grey Value Constancy Assumption Corresponding pixels should have the same grey value. Thus, the optic flow between frame z and z +1 should satisfy I (x + u, y + v, z + 1) = I (x, y, z) = I (x, y, z) + ui x (x, y, z) + vi y (x, y, z) + 1I z (x, y, z) I (x, y, z) = I x (x, y, z)u + I y (x, y, z)v + I z (x, y, z) 0 assuming (u, v) is a small displacement. Linearized optic flow constraint (OFC) I x u + I y v + I z = 0 where location (x, y, z) is implied. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 5 / 25
6 How good are the assumptions? We have made two assumptions 1. Gray value constancy 2. Small displacements (since we use first-order Taylor series approximation) Both assumptions are (almost) true in surprisingly many scenarios. 1. Gray values do not change much between consecutive 1 frames. 2. Objects do not move too much between consecutive frames. For large displacements, image pyramid can be used. 1 For a video recorded at 25 frames per second (fps), consecutive frames are only 1 seconds apart. 24 Nazar Khan Computer Vision 6 / 25
7 Aperture Problem Complete Flow Normal Flow No Flow When seen through an aperture, true movement cannot be determined. Only the component of movement normal to edge direction can be determined. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 7 / 25
8 Normal Flow The OFC is one equation in two unknowns (infinite solutions). Can be written as [ ] T u I + I v z = 0 Adding any flow component orthogonal to image gradient does not affect the OFC. ([ ] ) T [ ] T u +k I u I + I v z = I +k I T I v = = 0 [ ] T u I + I v z } {{ } + I z 0 Nazar Khan Computer Vision 8 / 25
9 Normal Flow I I (u, v) (u n, v n ) I I [ un v n ] ([ ] u = I ) I v I I = I z I ( [ u I I v] I + Iz = 0 ) = 1 [ ] Ix I z Ix 2 + Iy 2 I y I z Only the component of flow in the direction of the gradient I can be computed. Since gradient is normal to the edge direction, this flow vector is called the normal flow. To compute a better estimate of optic flow, we need to make some assumptions. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 9 / 25
10 Local Optic Flow Method of Lucas & Kanade Lucas & Kanade make the following assumption: Pixels around (i, j) all have the same displacement (u, v). For 3 3 neighbourhoods, this gives 9 OFCs all having the same 2 unknowns (u, v). The optimal unknown displacement minimizes the sum-squared-error E(u, v) = 1 2 N ij (I x u + I y v + I z ) 2 Nazar Khan Computer Vision 10 / 25
11 Local Optic Flow Method of Lucas & Kanade Setting E u E = 0 and v [ N ij I 2 x = 0 yields a linear system N ij I x I y N ij I x I y N ij I 2 y ] [u ] = v [ ] N ij I x I z N ij I y I z Replacing the sums by Gaussian averaging yields [ Gρ Ix 2 ] [ ] [ ] G ρ I x I y u Gρ I G ρ I x I y G ρ Iy 2 v = x I z G ρ I y I z }{{} A (1) Notice the re-appearance of the structure tensor which now serves as the system matrix. Previously, we used it for corner detection. Flow vector can be found if rank(a) = 2. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 11 / 25
12 Local Optic Flow Method of Lucas & Kanade If rank(a) = 0, no gradients exist in the neighbourhood. So no optic flow can be computed. If rank(a) = 1, gradient vectors over all pixels in the neighbourhood are identical. Only normal flow can be computed. [ ] un = 1 [ ] Ix I z v n Ix 2 + Iy 2 I y I z To save computations, avoid computing rank. trace(a) = A 11 + A 22 0 = rank(a) = 0 trace(a) 0 and det(a) = A 11 A 22 A = rank(a) = 1 Nazar Khan Computer Vision 12 / 25
13 Lucas & Kanade Algorithm Input: Frames I 1 and I 2. Parameters: 1) Noise smoothing scale σ, 2) Gradient smoothing scale ρ, 3) Thresholds τ trace and τ det. 1. Compute Gaussian derivatives at noise smoothing scale σ I x = Gσ x I 1 and I y = Gσ y I 1 2. Compute temporal derivative I z = I 2 I Compute the products I 2 x I 2 y I x I y I x I z and I y I z 4. Smooth the products at gradient smoothing scale ρ G ρ I 2 x G ρ I 2 y G ρ I x I y G ρ I x I z and G ρ I y I z and construct the linear system in (1) at every pixel. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 13 / 25
14 Lucas & Kanade Algorithm 5. For every pixel, solve the linear system conditioned on the rank. if A 11 + A 22 < τ trace rank(a)=0 so no flow else if A 11 A 22 A 2 12 < τ det rank(a)=1 so normal flow else rank(a)=2 so complete optic flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 14 / 25
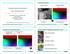
15 Visualising Displacement Vectors The HSV Color Space Each color is represented by 3 values 1. Hue or shade as an angle from 0 to Saturation or strength of the color 3. Value or brightness Figure: The HSV color space. Taken from /05/munsell-hue-circle.html. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 15 / 25
16 Visualising Displacement Vectors Figure: Vector angle represented by hue/shade of color and vector magnitude represented by the saturation/strength of color. HSV color space is useful for such a mapping. H(x, y) = θ(x, y), S(x, y) = u(x, y) 2 + v(x, y) 2 and V (x, y) = constant. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 16 / 25
17 Lucas & Kanade Figure: Left to right: frame 1, frame 2, flow classification and false color visualization of optic flow vectors. For flow classification: white = optic flow, gray = normal flow and black = no flow. Integration scale was ρ = 1. Author: N. Khan (2015) Nazar Khan Computer Vision 17 / 25
18 Lucas & Kanade Figure: Left to right: frame 1, frame 2, flow classification and false color visualization of optic flow vectors. For flow classification: white = optic flow, gray = normal flow and black = no flow. Increasing the integration scale ρ to 4 fills up pixels with no flow using values from neighbouring pixels having normal or complete optic flow. Author: N. Khan (2015) Nazar Khan Computer Vision 18 / 25
19 Lucas & Kanade Summary Advantages Simple and fast method. Requires only two frames (low memory requirements). Good value for money: results often superior to more complicated approaches. Disadvantages Problems at locations where the local constancy assumption is violated: flow discontinuities and non-translatory motion (e.g. rotation). Local method that does not compute the flow field at all locations. Next we study a global method that produces dense flow fields (i.e., at every pixel). Nazar Khan Computer Vision 19 / 25
20 Variational Method of Horn & Schunck At some given time z the optic flow field is determined as minimising the function (u(x, y), v(x, y)) T of the energy functional E(u, v) = 1 (I x u + I y v + I z ) 2 +α ( u 2 + v 2) 2 }{{}}{{} x,y data term smoothness term Has a unique solution that depends continuously on the image data. Global method since optic flow at (x, y) depends on all pixels in both frames. Notation Alert! u and v are 2D arrays of the same size as the frame but they are also used to refer to a pixel location. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 20 / 25
21 Variational Method of Horn & Schunck Regularisation parameter α > 0 determines smoothness of the flow field. α 0 yields the normal flow. The larger the value of α, the smoother the flow field. Dense flow fields due to filling-in effect: At locations, where no reliable flow estimation is possible (small I ), the smoothness term dominates over the data term. This propagates data from the neighbourhood. No additional threshold parameters necessary. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 21 / 25
22 Functionals and Calculus of Variations Since u is a function, E(u, v) is a function of a function. A function of a function is also called a functional. Normal calculus can optimize functions f (x) by requiring d dx f x = 0. Functionals are optimized via calculus of variations. Optimizer of an energy functional E(u, v) = x,y F (x, y, u, v, u x, u y, v x, v y ) must satisfy the so-called Euler-Lagrange equations x F ux + y F uy F u = 0 x F vx + y F vy F v = 0 with some boundary conditions. Nazar Khan Computer Vision 22 / 25
23 Functionals and Calculus of Variations For our energy functional E(u, v), F = 1 2 (I xu + I y v + I z ) 2 + α 2 with partial derivatives F u = I x (I x u + I y v + I z ) F v = I y (I x u + I y v + I z ) ( u 2 x + u 2 y + v 2 x + v 2 y ) F ux F uy F vx F vy = αu x = αu y = αv x = αv y Nazar Khan Computer Vision 23 / 25
24 Functionals and Calculus of Variations So the Euler-Lagrange equations can be written as α(u xx + u yy ) I x (I x u + I y v + I z ) = 0 α(v xx + v yy ) I y (I x u + I y v + I z ) = 0 After writing out the first and second order derivatives α h 2 (u j u i ) I xi (I xi u i + I yi v i + I zi ) = 0 j N i α h 2 (v j v i ) I yi (I xi u i + I yi v i + I zi ) = 0 j N i where h is the grid size (usually 1). Two equations for every pixel. Can be written as a sparse but very large linear system Bx = d. Size of B will be 69GB for a image! Nazar Khan Computer Vision 24 / 25
25 Functionals and Calculus of Variations All of the above boils down to a very simple iterative scheme α ( ) h 2 j N i u (k) j I xi I yi v (k) i + I zi u (k+1) i = v (k+1) i = α h 2 N i + I 2 xi α ( ) h 2 j N i v (k) j I yi I xi u (k) i + I zi α h 2 N i + I 2 xi with k = 0, 1, 2,... and an arbitrary initialisation (e.g. zero vector). Nazar Khan Computer Vision 25 / 25
CS 565 Computer Vision. Nazar Khan PUCIT Lectures 15 and 16: Optic Flow
 CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lectures 15 and 16: Optic Flow Introduction Basic Problem given: image sequence f(x, y, z), where (x, y) specifies the location and z denotes time wanted: displacement
CS 565 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT Lectures 15 and 16: Optic Flow Introduction Basic Problem given: image sequence f(x, y, z), where (x, y) specifies the location and z denotes time wanted: displacement
COMPUTER VISION > OPTICAL FLOW UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE
 COMPUTER VISION 2017-2018 > OPTICAL FLOW UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Optical flow Lucas-Kanade Horn-Schunck Applications of optical flow Optical flow tracking Histograms of oriented flow Assignment
COMPUTER VISION 2017-2018 > OPTICAL FLOW UTRECHT UNIVERSITY RONALD POPPE OUTLINE Optical flow Lucas-Kanade Horn-Schunck Applications of optical flow Optical flow tracking Histograms of oriented flow Assignment
Mariya Zhariy. Uttendorf Introduction to Optical Flow. Mariya Zhariy. Introduction. Determining. Optical Flow. Results. Motivation Definition
 to Constraint to Uttendorf 2005 Contents to Constraint 1 Contents to Constraint 1 2 Constraint Contents to Constraint 1 2 Constraint 3 Visual cranial reflex(vcr)(?) to Constraint Rapidly changing scene
to Constraint to Uttendorf 2005 Contents to Constraint 1 Contents to Constraint 1 2 Constraint Contents to Constraint 1 2 Constraint 3 Visual cranial reflex(vcr)(?) to Constraint Rapidly changing scene
Motion. 1 Introduction. 2 Optical Flow. Sohaib A Khan. 2.1 Brightness Constancy Equation
 Motion Sohaib A Khan 1 Introduction So far, we have dealing with single images of a static scene taken by a fixed camera. Here we will deal with sequence of images taken at different time intervals. Motion
Motion Sohaib A Khan 1 Introduction So far, we have dealing with single images of a static scene taken by a fixed camera. Here we will deal with sequence of images taken at different time intervals. Motion
CS 4495 Computer Vision Motion and Optic Flow
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS4 is out, due Sunday Oct 27 th. All relevant lectures posted Details about Problem Set: You may *not* use built in Harris
CS 4495 Computer Vision Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS4 is out, due Sunday Oct 27 th. All relevant lectures posted Details about Problem Set: You may *not* use built in Harris
Optic Flow and Basics Towards Horn-Schunck 1
 Optic Flow and Basics Towards Horn-Schunck 1 Lecture 7 See Section 4.1 and Beginning of 4.2 in Reinhard Klette: Concise Computer Vision Springer-Verlag, London, 2014 1 See last slide for copyright information.
Optic Flow and Basics Towards Horn-Schunck 1 Lecture 7 See Section 4.1 and Beginning of 4.2 in Reinhard Klette: Concise Computer Vision Springer-Verlag, London, 2014 1 See last slide for copyright information.
Dense Image-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow
 Dense mage-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow Video A video is a sequence of frames captured at different times The video data is a function of v time (t) v space (x,y) ntroduction to motion
Dense mage-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow Video A video is a sequence of frames captured at different times The video data is a function of v time (t) v space (x,y) ntroduction to motion
VC 11/12 T11 Optical Flow
 VC 11/12 T11 Optical Flow Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Optical Flow Constraint Equation Aperture
VC 11/12 T11 Optical Flow Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Optical Flow Constraint Equation Aperture
Leow Wee Kheng CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Motion Tracking. CS4243 Motion Tracking 1
 Leow Wee Kheng CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Motion Tracking CS4243 Motion Tracking 1 Changes are everywhere! CS4243 Motion Tracking 2 Illumination change CS4243 Motion Tracking 3 Shape
Leow Wee Kheng CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Motion Tracking CS4243 Motion Tracking 1 Changes are everywhere! CS4243 Motion Tracking 2 Illumination change CS4243 Motion Tracking 3 Shape
The 2D/3D Differential Optical Flow
 The 2D/3D Differential Optical Flow Prof. John Barron Dept. of Computer Science University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada, N6A 5B7 Email: barron@csd.uwo.ca Phone: 519-661-2111 x86896 Canadian
The 2D/3D Differential Optical Flow Prof. John Barron Dept. of Computer Science University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada, N6A 5B7 Email: barron@csd.uwo.ca Phone: 519-661-2111 x86896 Canadian
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 19: Optical flow http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/barberpole_illusion Readings Szeliski, Chapter 8.4-8.5 Announcements Project 2b due Tuesday, Nov 2 Please sign
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 19: Optical flow http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/barberpole_illusion Readings Szeliski, Chapter 8.4-8.5 Announcements Project 2b due Tuesday, Nov 2 Please sign
Lucas-Kanade Motion Estimation. Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides.
 Lucas-Kanade Motion Estimation Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides. 1 Why estimate motion? We live in a 4-D world Wide applications Object
Lucas-Kanade Motion Estimation Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides. 1 Why estimate motion? We live in a 4-D world Wide applications Object
Matching. Compare region of image to region of image. Today, simplest kind of matching. Intensities similar.
 Matching Compare region of image to region of image. We talked about this for stereo. Important for motion. Epipolar constraint unknown. But motion small. Recognition Find object in image. Recognize object.
Matching Compare region of image to region of image. We talked about this for stereo. Important for motion. Epipolar constraint unknown. But motion small. Recognition Find object in image. Recognize object.
Capturing, Modeling, Rendering 3D Structures
 Computer Vision Approach Capturing, Modeling, Rendering 3D Structures Calculate pixel correspondences and extract geometry Not robust Difficult to acquire illumination effects, e.g. specular highlights
Computer Vision Approach Capturing, Modeling, Rendering 3D Structures Calculate pixel correspondences and extract geometry Not robust Difficult to acquire illumination effects, e.g. specular highlights
Horn-Schunck and Lucas Kanade 1
 Horn-Schunck and Lucas Kanade 1 Lecture 8 See Sections 4.2 and 4.3 in Reinhard Klette: Concise Computer Vision Springer-Verlag, London, 2014 1 See last slide for copyright information. 1 / 40 Where We
Horn-Schunck and Lucas Kanade 1 Lecture 8 See Sections 4.2 and 4.3 in Reinhard Klette: Concise Computer Vision Springer-Verlag, London, 2014 1 See last slide for copyright information. 1 / 40 Where We
Line, edge, blob and corner detection
 Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Visual Tracking (1) Feature Point Tracking and Block Matching
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Feature Point Tracking and Block Matching Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Feature Point Tracking and Block Matching Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Peripheral drift illusion
 Peripheral drift illusion Does it work on other animals? Computer Vision Motion and Optical Flow Many slides adapted from J. Hays, S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, K. Grauman and others Video A video
Peripheral drift illusion Does it work on other animals? Computer Vision Motion and Optical Flow Many slides adapted from J. Hays, S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, K. Grauman and others Video A video
Motion Estimation. There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation:
 Members: D91922016 朱威達 R93922010 林聖凱 R93922044 謝俊瑋 Motion Estimation There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation: Parametric motion (image alignment) The main idea of parametric motion
Members: D91922016 朱威達 R93922010 林聖凱 R93922044 謝俊瑋 Motion Estimation There are three main types (or applications) of motion estimation: Parametric motion (image alignment) The main idea of parametric motion
Lecture 16: Computer Vision
 CS4442/9542b: Artificial Intelligence II Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field
CS4442/9542b: Artificial Intelligence II Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field
Feature Tracking and Optical Flow
 Feature Tracking and Optical Flow Prof. D. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Many slides adapted from James Hays, Derek Hoeim, Lana Lazebnik, Silvio Saverse, who 1 in turn adapted slides from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski,
Feature Tracking and Optical Flow Prof. D. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Many slides adapted from James Hays, Derek Hoeim, Lana Lazebnik, Silvio Saverse, who 1 in turn adapted slides from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski,
Optical Flow-Based Motion Estimation. Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides.
 Optical Flow-Based Motion Estimation Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides. 1 Why estimate motion? We live in a 4-D world Wide applications Object
Optical Flow-Based Motion Estimation Thanks to Steve Seitz, Simon Baker, Takeo Kanade, and anyone else who helped develop these slides. 1 Why estimate motion? We live in a 4-D world Wide applications Object
Feature Tracking and Optical Flow
 Feature Tracking and Optical Flow Prof. D. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Many slides adapted from James Hays, Derek Hoeim, Lana Lazebnik, Silvio Saverse, who in turn adapted slides from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski,
Feature Tracking and Optical Flow Prof. D. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Many slides adapted from James Hays, Derek Hoeim, Lana Lazebnik, Silvio Saverse, who in turn adapted slides from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski,
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
ELEC Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW
 ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Review of Motion Modelling and Estimation Introduction to Motion Modelling & Estimation Forward Motion Backward Motion Block Motion Estimation Motion
ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Review of Motion Modelling and Estimation Introduction to Motion Modelling & Estimation Forward Motion Backward Motion Block Motion Estimation Motion
Motion Estimation (II) Ce Liu Microsoft Research New England
 Motion Estimation (II) Ce Liu celiu@microsoft.com Microsoft Research New England Last time Motion perception Motion representation Parametric motion: Lucas-Kanade T I x du dv = I x I T x I y I x T I y
Motion Estimation (II) Ce Liu celiu@microsoft.com Microsoft Research New England Last time Motion perception Motion representation Parametric motion: Lucas-Kanade T I x du dv = I x I T x I y I x T I y
CS231A Section 6: Problem Set 3
 CS231A Section 6: Problem Set 3 Kevin Wong Review 6 -! 1 11/09/2012 Announcements PS3 Due 2:15pm Tuesday, Nov 13 Extra Office Hours: Friday 6 8pm Huang Common Area, Basement Level. Review 6 -! 2 Topics
CS231A Section 6: Problem Set 3 Kevin Wong Review 6 -! 1 11/09/2012 Announcements PS3 Due 2:15pm Tuesday, Nov 13 Extra Office Hours: Friday 6 8pm Huang Common Area, Basement Level. Review 6 -! 2 Topics
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Comparative
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 11, November -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Comparative
Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Tracking of Feature Points and Planar Rigid Objects Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
CS664 Lecture #18: Motion
 CS664 Lecture #18: Motion Announcements Most paper choices were fine Please be sure to email me for approval, if you haven t already This is intended to help you, especially with the final project Use
CS664 Lecture #18: Motion Announcements Most paper choices were fine Please be sure to email me for approval, if you haven t already This is intended to help you, especially with the final project Use
Finally: Motion and tracking. Motion 4/20/2011. CS 376 Lecture 24 Motion 1. Video. Uses of motion. Motion parallax. Motion field
 Finally: Motion and tracking Tracking objects, video analysis, low level motion Motion Wed, April 20 Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Many slides adapted from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, and S. Lazebnik
Finally: Motion and tracking Tracking objects, video analysis, low level motion Motion Wed, April 20 Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Many slides adapted from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, and S. Lazebnik
Real-Time Optic Flow Computation with Variational Methods
 Real-Time Optic Flow Computation with Variational Methods Andrés Bruhn 1, Joachim Weickert 1, Christian Feddern 1, Timo Kohlberger 2, and Christoph Schnörr 2 1 Mathematical Image Analysis Group Faculty
Real-Time Optic Flow Computation with Variational Methods Andrés Bruhn 1, Joachim Weickert 1, Christian Feddern 1, Timo Kohlberger 2, and Christoph Schnörr 2 1 Mathematical Image Analysis Group Faculty
Notes 9: Optical Flow
 Course 049064: Variational Methods in Image Processing Notes 9: Optical Flow Guy Gilboa 1 Basic Model 1.1 Background Optical flow is a fundamental problem in computer vision. The general goal is to find
Course 049064: Variational Methods in Image Processing Notes 9: Optical Flow Guy Gilboa 1 Basic Model 1.1 Background Optical flow is a fundamental problem in computer vision. The general goal is to find
Ninio, J. and Stevens, K. A. (2000) Variations on the Hermann grid: an extinction illusion. Perception, 29,
 Ninio, J. and Stevens, K. A. (2000) Variations on the Hermann grid: an extinction illusion. Perception, 29, 1209-1217. CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick Sparse to Dense Correspodence Building Rome in
Ninio, J. and Stevens, K. A. (2000) Variations on the Hermann grid: an extinction illusion. Perception, 29, 1209-1217. CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick Sparse to Dense Correspodence Building Rome in
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09
 EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Motion estimation Global vs. Local Motion Block Motion Estimation Optical Flow Estimation (normal equation) Man slides of this lecture are courtes of prof Milanfar (UCSC)
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Motion estimation Global vs. Local Motion Block Motion Estimation Optical Flow Estimation (normal equation) Man slides of this lecture are courtes of prof Milanfar (UCSC)
Augmented Reality VU. Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit
 Augmented Reality VU Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit Feature Point-Based 3D Tracking Feature Points for 3D Tracking Much less ambiguous than edges; Point-to-point reprojection
Augmented Reality VU Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit Feature Point-Based 3D Tracking Feature Points for 3D Tracking Much less ambiguous than edges; Point-to-point reprojection
CS4495 Fall 2014 Computer Vision Problem Set 5: Optic Flow
 CS4495 Fall 2014 Computer Vision Problem Set 5: Optic Flow DUE: Wednesday November 12-11:55pm In class we discussed optic flow as the problem of computing a dense flow field where a flow field is a vector
CS4495 Fall 2014 Computer Vision Problem Set 5: Optic Flow DUE: Wednesday November 12-11:55pm In class we discussed optic flow as the problem of computing a dense flow field where a flow field is a vector
Comparison Between The Optical Flow Computational Techniques
 Comparison Between The Optical Flow Computational Techniques Sri Devi Thota #1, Kanaka Sunanda Vemulapalli* 2, Kartheek Chintalapati* 3, Phanindra Sai Srinivas Gudipudi* 4 # Associate Professor, Dept.
Comparison Between The Optical Flow Computational Techniques Sri Devi Thota #1, Kanaka Sunanda Vemulapalli* 2, Kartheek Chintalapati* 3, Phanindra Sai Srinivas Gudipudi* 4 # Associate Professor, Dept.
Lecture 16: Computer Vision
 CS442/542b: Artificial ntelligence Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field Methods
CS442/542b: Artificial ntelligence Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field Methods
Ruch (Motion) Rozpoznawanie Obrazów Krzysztof Krawiec Instytut Informatyki, Politechnika Poznańska. Krzysztof Krawiec IDSS
 Ruch (Motion) Rozpoznawanie Obrazów Krzysztof Krawiec Instytut Informatyki, Politechnika Poznańska 1 Krzysztof Krawiec IDSS 2 The importance of visual motion Adds entirely new (temporal) dimension to visual
Ruch (Motion) Rozpoznawanie Obrazów Krzysztof Krawiec Instytut Informatyki, Politechnika Poznańska 1 Krzysztof Krawiec IDSS 2 The importance of visual motion Adds entirely new (temporal) dimension to visual
Motion and Optical Flow. Slides from Ce Liu, Steve Seitz, Larry Zitnick, Ali Farhadi
 Motion and Optical Flow Slides from Ce Liu, Steve Seitz, Larry Zitnick, Ali Farhadi We live in a moving world Perceiving, understanding and predicting motion is an important part of our daily lives Motion
Motion and Optical Flow Slides from Ce Liu, Steve Seitz, Larry Zitnick, Ali Farhadi We live in a moving world Perceiving, understanding and predicting motion is an important part of our daily lives Motion
Multiple Combined Constraints for Optical Flow Estimation
 Multiple Combined Constraints for Optical Flow Estimation Ahmed Fahad and Tim Morris School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester Manchester, M3 9PL, UK ahmed.fahad@postgrad.manchester.ac.uk,
Multiple Combined Constraints for Optical Flow Estimation Ahmed Fahad and Tim Morris School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester Manchester, M3 9PL, UK ahmed.fahad@postgrad.manchester.ac.uk,
MASTER THESIS. Optical Flow Features for Event Detection. Mohammad Afrooz Mehr, Maziar Haghpanah
 Master's Thesis in Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits MASTER THESIS Optical Flow Features for Event Detection Mohammad Afrooz Mehr, Maziar Haghpanah Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits
Master's Thesis in Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits MASTER THESIS Optical Flow Features for Event Detection Mohammad Afrooz Mehr, Maziar Haghpanah Embedded and Intelligent Systems, 120 credits
Overview. Video. Overview 4/7/2008. Optical flow. Why estimate motion? Motion estimation: Optical flow. Motion Magnification Colorization.
 Overview Video Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Lecture 9 Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Overview Optical flow Combination of slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Alyosha
Overview Video Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Lecture 9 Optical flow Motion Magnification Colorization Overview Optical flow Combination of slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Alyosha
Lecture 19: Motion. Effect of window size 11/20/2007. Sources of error in correspondences. Review Problem set 3. Tuesday, Nov 20
 Lecture 19: Motion Review Problem set 3 Dense stereo matching Sparse stereo matching Indexing scenes Tuesda, Nov 0 Effect of window size W = 3 W = 0 Want window large enough to have sufficient intensit
Lecture 19: Motion Review Problem set 3 Dense stereo matching Sparse stereo matching Indexing scenes Tuesda, Nov 0 Effect of window size W = 3 W = 0 Want window large enough to have sufficient intensit
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 11 140311 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Motion Analysis Motivation Differential Motion Optical
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 11 140311 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Motion Analysis Motivation Differential Motion Optical
Multi-stable Perception. Necker Cube
 Multi-stable Perception Necker Cube Spinning dancer illusion, Nobuyuki Kayahara Multiple view geometry Stereo vision Epipolar geometry Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Depth map extraction Essential matrix
Multi-stable Perception Necker Cube Spinning dancer illusion, Nobuyuki Kayahara Multiple view geometry Stereo vision Epipolar geometry Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Depth map extraction Essential matrix
CUDA GPGPU. Ivo Ihrke Tobias Ritschel Mario Fritz
 CUDA GPGPU Ivo Ihrke Tobias Ritschel Mario Fritz Today 3 Topics Intro to CUDA (NVIDIA slides) How is the GPU hardware organized? What is the programming model? Simple Kernels Hello World Gaussian Filtering
CUDA GPGPU Ivo Ihrke Tobias Ritschel Mario Fritz Today 3 Topics Intro to CUDA (NVIDIA slides) How is the GPU hardware organized? What is the programming model? Simple Kernels Hello World Gaussian Filtering
Visual Tracking. Image Processing Laboratory Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli studi di Catania.
 Image Processing Laboratory Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli studi di Catania 1 What is visual tracking? estimation of the target location over time 2 applications Six main areas:
Image Processing Laboratory Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli studi di Catania 1 What is visual tracking? estimation of the target location over time 2 applications Six main areas:
Hand-Eye Calibration from Image Derivatives
 Hand-Eye Calibration from Image Derivatives Abstract In this paper it is shown how to perform hand-eye calibration using only the normal flow field and knowledge about the motion of the hand. The proposed
Hand-Eye Calibration from Image Derivatives Abstract In this paper it is shown how to perform hand-eye calibration using only the normal flow field and knowledge about the motion of the hand. The proposed
Comparison between Optical Flow and Cross-Correlation Methods for Extraction of Velocity Fields from Particle Images
 Comparison between Optical Flow and Cross-Correlation Methods for Extraction of Velocity Fields from Particle Images (Optical Flow vs Cross-Correlation) Tianshu Liu, Ali Merat, M. H. M. Makhmalbaf Claudia
Comparison between Optical Flow and Cross-Correlation Methods for Extraction of Velocity Fields from Particle Images (Optical Flow vs Cross-Correlation) Tianshu Liu, Ali Merat, M. H. M. Makhmalbaf Claudia
SURVEY OF LOCAL AND GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW WITH COARSE TO FINE METHOD
 SURVEY OF LOCAL AND GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW WITH COARSE TO FINE METHOD M.E-II, Department of Computer Engineering, PICT, Pune ABSTRACT: Optical flow as an image processing technique finds its applications
SURVEY OF LOCAL AND GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW WITH COARSE TO FINE METHOD M.E-II, Department of Computer Engineering, PICT, Pune ABSTRACT: Optical flow as an image processing technique finds its applications
Image processing and features
 Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Visual Tracking. Antonino Furnari. Image Processing Lab Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli Studi di Catania
 Visual Tracking Antonino Furnari Image Processing Lab Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli Studi di Catania furnari@dmi.unict.it 11 giugno 2015 What is visual tracking? estimation
Visual Tracking Antonino Furnari Image Processing Lab Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università degli Studi di Catania furnari@dmi.unict.it 11 giugno 2015 What is visual tracking? estimation
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014
 SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
Chapter 10 Image Segmentation. Yinghua He
 Chapter 10 Image Segmentation Yinghua He The whole is equal to the sum of its parts. -Euclid The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. -Max Wertheimer The Whole is Not Equal to the Sum of Its Parts:
Chapter 10 Image Segmentation Yinghua He The whole is equal to the sum of its parts. -Euclid The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. -Max Wertheimer The Whole is Not Equal to the Sum of Its Parts:
Announcements. Edges. Last Lecture. Gradients: Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge Detection, Lines. Intro Computer Vision. CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Comparison of Feature Detection and Matching Approaches: SIFT and SURF
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 4 March 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 Comparison of Detection and Matching Approaches: SIFT and SURF Darshana Mistry PhD student
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 4 March 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 Comparison of Detection and Matching Approaches: SIFT and SURF Darshana Mistry PhD student
Part II: Modeling Aspects
 Yosemite test sequence Illumination changes Motion discontinuities Variational Optical Flow Estimation Part II: Modeling Aspects Discontinuity Di ti it preserving i smoothness th tterms Robust data terms
Yosemite test sequence Illumination changes Motion discontinuities Variational Optical Flow Estimation Part II: Modeling Aspects Discontinuity Di ti it preserving i smoothness th tterms Robust data terms
Event-based Computer Vision
 Event-based Computer Vision Charles Clercq Italian Institute of Technology Institut des Systemes Intelligents et de robotique November 30, 2011 Pinhole camera Principle light rays from an object pass through
Event-based Computer Vision Charles Clercq Italian Institute of Technology Institut des Systemes Intelligents et de robotique November 30, 2011 Pinhole camera Principle light rays from an object pass through
Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots
 Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots Lecture 7.1: 2D Motion Estimation in Images Jürgen Sturm Technische Universität München 3D to 2D Perspective Projections
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots Lecture 7.1: 2D Motion Estimation in Images Jürgen Sturm Technische Universität München 3D to 2D Perspective Projections
Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking
 Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Technion - Computer Science Department - Tehnical Report CIS
 Over-Parameterized Variational Optical Flow Tal Nir Alfred M. Bruckstein Ron Kimmel {taln, freddy, ron}@cs.technion.ac.il Department of Computer Science Technion Israel Institute of Technology Technion
Over-Parameterized Variational Optical Flow Tal Nir Alfred M. Bruckstein Ron Kimmel {taln, freddy, ron}@cs.technion.ac.il Department of Computer Science Technion Israel Institute of Technology Technion
Motion and Tracking. Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, Mestre (VE)
 Motion and Tracking Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Motion Segmentation Segment the video into multiple coherently moving objects Motion and Perceptual Organization
Motion and Tracking Andrea Torsello DAIS Università Ca Foscari via Torino 155, 30172 Mestre (VE) Motion Segmentation Segment the video into multiple coherently moving objects Motion and Perceptual Organization
Visual motion. Many slides adapted from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys
 Visual motion Man slides adapted from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefes Motion and perceptual organization Sometimes, motion is the onl cue Motion and perceptual organization Sometimes, motion is the
Visual motion Man slides adapted from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefes Motion and perceptual organization Sometimes, motion is the onl cue Motion and perceptual organization Sometimes, motion is the
Announcements. Edge Detection. An Isotropic Gaussian. Filters are templates. Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3.
 Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Marcel Worring Intelligent Sensory Information Systems
 Marcel Worring worring@science.uva.nl Intelligent Sensory Information Systems University of Amsterdam Information and Communication Technology archives of documentaries, film, or training material, video
Marcel Worring worring@science.uva.nl Intelligent Sensory Information Systems University of Amsterdam Information and Communication Technology archives of documentaries, film, or training material, video
Computer Vision Lecture 20
 Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/76 Augmented Computing Many slides adapted from K. Grauman, S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, S. Lazebnik Computer Vision Lecture 20 Motion and Optical Flow
Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/76 Augmented Computing Many slides adapted from K. Grauman, S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, S. Lazebnik Computer Vision Lecture 20 Motion and Optical Flow
Computer Vision for HCI. Topics of This Lecture
 Computer Vision for HCI Interest Points Topics of This Lecture Local Invariant Features Motivation Requirements, Invariances Keypoint Localization Features from Accelerated Segment Test (FAST) Harris Shi-Tomasi
Computer Vision for HCI Interest Points Topics of This Lecture Local Invariant Features Motivation Requirements, Invariances Keypoint Localization Features from Accelerated Segment Test (FAST) Harris Shi-Tomasi
Image Processing. BITS Pilani. Dr Jagadish Nayak. Dubai Campus
 Image Processing BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Dr Jagadish Nayak Image Segmentation BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Fundamentals Let R be the entire spatial region occupied by an image Process that partitions R into
Image Processing BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Dr Jagadish Nayak Image Segmentation BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Fundamentals Let R be the entire spatial region occupied by an image Process that partitions R into
LOCAL-GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW FOR IMAGE REGISTRATION
 LOCAL-GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW FOR IMAGE REGISTRATION Ammar Zayouna Richard Comley Daming Shi Middlesex University School of Engineering and Information Sciences Middlesex University, London NW4 4BT, UK A.Zayouna@mdx.ac.uk
LOCAL-GLOBAL OPTICAL FLOW FOR IMAGE REGISTRATION Ammar Zayouna Richard Comley Daming Shi Middlesex University School of Engineering and Information Sciences Middlesex University, London NW4 4BT, UK A.Zayouna@mdx.ac.uk
Corner Detection. Harvey Rhody Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology
 Corner Detection Harvey Rhody Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology rhody@cis.rit.edu April 11, 2006 Abstract Corners and edges are two of the most important geometrical
Corner Detection Harvey Rhody Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology rhody@cis.rit.edu April 11, 2006 Abstract Corners and edges are two of the most important geometrical
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
CSE 252A Computer Vision Homework 3 Instructor: Ben Ochoa Due : Monday, November 21, 2016, 11:59 PM
 CSE 252A Computer Vision Homework 3 Instructor: Ben Ochoa Due : Monday, November 21, 2016, 11:59 PM Instructions: Homework 3 has to be submitted in groups of 3. Review the academic integrity and collaboration
CSE 252A Computer Vision Homework 3 Instructor: Ben Ochoa Due : Monday, November 21, 2016, 11:59 PM Instructions: Homework 3 has to be submitted in groups of 3. Review the academic integrity and collaboration
extracted occurring from the spatial and temporal changes in an image sequence. An image sequence
 Motion: Introduction are interested in the visual information that can be We from the spatial and temporal changes extracted in an image sequence. An image sequence occurring of a series of images (frames)
Motion: Introduction are interested in the visual information that can be We from the spatial and temporal changes extracted in an image sequence. An image sequence occurring of a series of images (frames)
EE 264: Image Processing and Reconstruction. Image Motion Estimation I. EE 264: Image Processing and Reconstruction. Outline
 1 Image Motion Estimation I 2 Outline 1. Introduction to Motion 2. Why Estimate Motion? 3. Global vs. Local Motion 4. Block Motion Estimation 5. Optical Flow Estimation Basics 6. Optical Flow Estimation
1 Image Motion Estimation I 2 Outline 1. Introduction to Motion 2. Why Estimate Motion? 3. Global vs. Local Motion 4. Block Motion Estimation 5. Optical Flow Estimation Basics 6. Optical Flow Estimation
Optical Flow Estimation with CUDA. Mikhail Smirnov
 Optical Flow Estimation with CUDA Mikhail Smirnov msmirnov@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change Mikhail Smirnov Initial release Abstract Optical flow is the apparent
Optical Flow Estimation with CUDA Mikhail Smirnov msmirnov@nvidia.com Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change Mikhail Smirnov Initial release Abstract Optical flow is the apparent
Computer Vision Lecture 20
 Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/17 Augmented Computing Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/17 Augmented Computing Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/17 Augmented Computing
Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/17 Augmented Computing Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/17 Augmented Computing Computer Perceptual Vision and Sensory WS 16/17 Augmented Computing
Optical flow and tracking
 EECS 442 Computer vision Optical flow and tracking Intro Optical flow and feature tracking Lucas-Kanade algorithm Motion segmentation Segments of this lectures are courtesy of Profs S. Lazebnik S. Seitz,
EECS 442 Computer vision Optical flow and tracking Intro Optical flow and feature tracking Lucas-Kanade algorithm Motion segmentation Segments of this lectures are courtesy of Profs S. Lazebnik S. Seitz,
Visual Tracking (1) Pixel-intensity-based methods
 Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Pixel-intensity-based methods Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Intelligent Control Systems Visual Tracking (1) Pixel-intensity-based methods Shingo Kagami Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University swk(at)ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/ja/swk/
Automatic Image Alignment (direct) with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski
 Automatic Image Alignment (direct) with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Today Go over Midterm Go over Project #3
Automatic Image Alignment (direct) with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Today Go over Midterm Go over Project #3
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique. -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching --
 Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching -- Autumn 2015 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Reminder: Feature Detection and Matching
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching -- Autumn 2015 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Reminder: Feature Detection and Matching
Spatial track: motion modeling
 Spatial track: motion modeling Virginio Cantoni Computer Vision and Multimedia Lab Università di Pavia Via A. Ferrata 1, 27100 Pavia virginio.cantoni@unipv.it http://vision.unipv.it/va 1 Comparison between
Spatial track: motion modeling Virginio Cantoni Computer Vision and Multimedia Lab Università di Pavia Via A. Ferrata 1, 27100 Pavia virginio.cantoni@unipv.it http://vision.unipv.it/va 1 Comparison between
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Motion Analysis. Motion analysis. Now we will talk about. Differential Motion Analysis. Motion analysis. Difference Pictures
 Now we will talk about Motion Analysis Motion analysis Motion analysis is dealing with three main groups of motionrelated problems: Motion detection Moving object detection and location. Derivation of
Now we will talk about Motion Analysis Motion analysis Motion analysis is dealing with three main groups of motionrelated problems: Motion detection Moving object detection and location. Derivation of
Optical Flow. Adriana Bocoi and Elena Pelican. 1. Introduction
 Proceedings of the Fifth Workshop on Mathematical Modelling of Environmental and Life Sciences Problems Constanţa, Romania, September, 200, pp. 5 5 Optical Flow Adriana Bocoi and Elena Pelican This paper
Proceedings of the Fifth Workshop on Mathematical Modelling of Environmental and Life Sciences Problems Constanţa, Romania, September, 200, pp. 5 5 Optical Flow Adriana Bocoi and Elena Pelican This paper
High Accuracy Optical Flow Estimation Based on a Theory for Warping
 High Accuracy Optical Flow Estimation Based on a Theory for Warping Thomas Brox, Andrés Bruhn, Nils Papenberg, and Joachim Weickert Mathematical Image Analysis Group Faculty of Mathematics and Computer
High Accuracy Optical Flow Estimation Based on a Theory for Warping Thomas Brox, Andrés Bruhn, Nils Papenberg, and Joachim Weickert Mathematical Image Analysis Group Faculty of Mathematics and Computer
Particle Tracking. For Bulk Material Handling Systems Using DEM Models. By: Jordan Pease
 Particle Tracking For Bulk Material Handling Systems Using DEM Models By: Jordan Pease Introduction Motivation for project Particle Tracking Application to DEM models Experimental Results Future Work References
Particle Tracking For Bulk Material Handling Systems Using DEM Models By: Jordan Pease Introduction Motivation for project Particle Tracking Application to DEM models Experimental Results Future Work References
Towards the completion of assignment 1
 Towards the completion of assignment 1 What to do for calibration What to do for point matching What to do for tracking What to do for GUI COMPSCI 773 Feature Point Detection Why study feature point detection?
Towards the completion of assignment 1 What to do for calibration What to do for point matching What to do for tracking What to do for GUI COMPSCI 773 Feature Point Detection Why study feature point detection?
Lecture 20: Tracking. Tuesday, Nov 27
 Lecture 20: Tracking Tuesday, Nov 27 Paper reviews Thorough summary in your own words Main contribution Strengths? Weaknesses? How convincing are the experiments? Suggestions to improve them? Extensions?
Lecture 20: Tracking Tuesday, Nov 27 Paper reviews Thorough summary in your own words Main contribution Strengths? Weaknesses? How convincing are the experiments? Suggestions to improve them? Extensions?
Part 3: Image Processing
 Part 3: Image Processing Image Filtering and Segmentation Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 373 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 1 / 60 1 Image filtering 2 Median filtering 3 Mean filtering 4 Image segmentation
Part 3: Image Processing Image Filtering and Segmentation Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 373 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 1 / 60 1 Image filtering 2 Median filtering 3 Mean filtering 4 Image segmentation
Revisiting Lucas-Kanade and Horn-Schunck
 Revisiting Lucas-Kanade and Horn-Schunck Andry Maykol G. Pinto *1, A. Paulo Moreira 2, Paulo G. Costa 3, Miguel V. Correia 4 INESC TEC and Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Faculty of
Revisiting Lucas-Kanade and Horn-Schunck Andry Maykol G. Pinto *1, A. Paulo Moreira 2, Paulo G. Costa 3, Miguel V. Correia 4 INESC TEC and Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Faculty of
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING AT DIFFERENT ANGLES IN VIDEO USING OPTICAL FLOW
 FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING AT DIFFERENT ANGLES IN VIDEO USING OPTICAL FLOW Divya George and Arunkant A. Jose ECE Department SCET, Kodakara, India E-Mail: divyageorge2@gmail.com ABSTRACT Face detection
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING AT DIFFERENT ANGLES IN VIDEO USING OPTICAL FLOW Divya George and Arunkant A. Jose ECE Department SCET, Kodakara, India E-Mail: divyageorge2@gmail.com ABSTRACT Face detection
Chapter 3 Image Registration. Chapter 3 Image Registration
 Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
Chapter 3 Image Registration Distributed Algorithms for Introduction (1) Definition: Image Registration Input: 2 images of the same scene but taken from different perspectives Goal: Identify transformation
Tracking Weather Storms using 3D Doppler Radial Velocity Information
 Tracking Weather Storms using 3D Doppler Radial Velocity Information X. Tang 1 and J.L. Barron 1,R.E.Mercer 1,andP.Joe 2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Western Ontario London, Ontario,
Tracking Weather Storms using 3D Doppler Radial Velocity Information X. Tang 1 and J.L. Barron 1,R.E.Mercer 1,andP.Joe 2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Western Ontario London, Ontario,
Edge Detection. CS664 Computer Vision. 3. Edges. Several Causes of Edges. Detecting Edges. Finite Differences. The Gradient
 Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment
 Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Computer Vision for HCI. Motion. Motion
 Computer Vision for HCI Motion Motion Changing scene may be observed in a sequence of images Changing pixels in image sequence provide important features for object detection and activity recognition 2
Computer Vision for HCI Motion Motion Changing scene may be observed in a sequence of images Changing pixels in image sequence provide important features for object detection and activity recognition 2
The Lucas & Kanade Algorithm
 The Lucas & Kanade Algorithm Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Registration, Registration, Registration. Linearizing Registration. Lucas & Kanade Algorithm. 3 Biggest
The Lucas & Kanade Algorithm Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Registration, Registration, Registration. Linearizing Registration. Lucas & Kanade Algorithm. 3 Biggest
