Graphs and Graph Algorithms. Slides by Larry Ruzzo
|
|
|
- Caroline Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Larry Ruzzo
2 Goals Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology Representation: input, internal Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search Three Algorithms: Connected components Bipartiteness Topological sort 2
3 Graphs An extremely important formalism for representing (binary) relationships Objects: "vertices," aka "nodes" Relationships between pairs: "edges," aka "arcs" Formally, a graph G = (V, E) is a pair of sets, V the vertices and E the edges
4 Meg Ryan was in "French Kiss" with Kevin Kline Meg Ryan was in "Sleepless in Seattle" with Tom Hanks Kevin Bacon was in "Apollo " with Tom Hanks
5 Objects & Relationships The Kevin Bacon Game: Obj: Actors Rel: Two are related if they've been in a movie together Exam Scheduling: Obj: Classes Rel: Two are related if they have students in common Traveling Salesperson Problem: Obj: Cities Rel: Two are related if can travel directly between them 5
6 Undirected Graph G = (V,E)
7 Undirected Graph G = (V,E)
8 Undirected Graph G = (V,E)
9 Undirected Graph G = (V,E) 2 0 "self- loop" "multiedge" 9
10 Undirected Graph G = (V,E) 2 0 "self- loop" "multiedge" 0
11 Graphs don't live in Flatland Geometrical drawing is mentally convenient, but mathematically irrelevant: drawings, graph. A A A A
12 Directed Graph G = (V,E)
13 Directed Graph G = (V,E)
14 Directed Graph G = (V,E)
15 Directed Graph G = (V,E) 2 0 "self- loop" "multiedge" 5
16 Directed Graph G = (V,E) 2 0 "self- loop" "multiedge" 6
17 Specifying undirected What are the vertices? Explicitly list them: {"A", "", "", ""} What are the edges? One possibility: (symmetric) adjacency matrix graphs as input A A A
18 Specifying directed What are the vertices? Explicitly list them: {"A", "", "", ""} What are the edges? graphs as input (Nonsymmetric) adjacency matrix: A 8 A A
19 # Vertices vs # Edges Let G be an undirected graph with n vertices and m edges. How are n and m related? 9
20 # Vertices vs # Edges Let G be an undirected graph with n vertices and m edges. How are n and m related? Since every edge connects two different vertices (no loops), and no two edges connect the same two vertices (no multi-edges), it must be true that: 0 m n(n-)/2 = O(n 2 ) 20
21 More Cool Graph Lingo A graph is called sparse if m n 2, otherwise it is dense Boundary is somewhat fuzzy; O(n) edges is certainly sparse, Ω(n 2 ) edges is dense. Sparse graphs are common in practice E.g., all planar graphs are sparse (m n-6, for n ) Q: which is a better run time, O(n+m) or O(n 2 )? 2
22 More Cool Graph Lingo A graph is called sparse if m n 2, otherwise it is dense Boundary is somewhat fuzzy; O(n) edges is certainly sparse, Ω(n 2 ) edges is dense. Sparse graphs are common in practice E.g., all planar graphs are sparse (m n-6, for n ) Q: which is a better run time, O(n+m) or O(n 2 )? A: O(n+m) = O(n 2 ), but n+m usually way better! 22
23 Representing Graph G = (V,E) internally, indp of input format Vertex set V = {v,, v n } A Adjacency Matrix A A[i,j] = iff (v i,v j ) E Space is n 2 bits Advantages? A A Disadvantages? 2
24 Representing Graph G = (V,E) internally, indp of input format Vertex set V = {v,, v n } Adjacency Matrix A A[i,j] = iff (v i,v j ) E Space is n 2 bits Advantages: O() test for presence or absence of edges. A A A Disadvantages: inefficient for sparse graphs, both in storage and access m n 2 2
25 Representing Graph G=(V,E) n vertices, m edges Adjacency List: O(n+m) words v v 2 2 Advantages? v Disadvantages? v n 25
26 Representing Graph G=(V,E) n vertices, m edges Adjacency List: O(n+m) words Advantages: Compact for sparse graphs v v 2 v Disadvantages More complex data structure no O() edge test v n 26
27 Representing Graph G=(V,E) n vertices, m edges Adjacency List: O(n+m) words v v 2 2 v Back- and cross pointers more work to build, but allow easier traversal and deletion of edges, if needed, (don't bother if not) v 2
28 Graph Traversal Learn the basic structure of a graph "Walk," via edges, from a fixed starting vertex s to all vertices reachable from s Being orderly helps. Two common ways: Breadth-First Search: order the nodes in successive layers based on distance from s Depth-First Search: more natural approach for exploring a maze; many efficient algs build on it. 28
29 Breadth-First Search Completely explore the vertices in order of their distance from s Naturally implemented using a queue 29
30 Graph Traversal: Implementation Learn the basic structure of a graph "Walk," via edges, from a fixed starting vertex s to all vertices reachable from s Three states of vertices undiscovered discovered fully-explored 0
31 BFS(s) Implementation Global initialization: mark all vertices "undiscovered" BFS(s) mark s "discovered" queue = { s } while queue not empty u = remove_first(queue) for each edge {u,x} if (x is undiscovered) mark x discovered append x on queue mark u fully explored
32 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
33 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
34 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
35 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
36 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
37 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
38 BFS(v) 2 Queue:
39 BFS(v) Queue:
40 BFS: Analysis, I O(n) + O() + O(n) x O(n) = O(n 2 ) Global initialization: mark all vertices "undiscovered" BFS(s) mark s "discovered" queue = { s } while queue not empty u = remove_first(queue) for each edge {u,x} if (x is undiscovered) mark x discovered append x on queue mark u fully explored Simple analysis: 2 nested loops. Get worst-case number of iterations of each; multiply. 0
41 BFS: Analysis, II Above analysis correct, but pessimistic (can't have Ω(n) edges incident to each of Ω(n) distinct "u" vertices if G is sparse). Alt, more global analysis: Each edge is explored once from each end-point, so total runtime of inner loop is O(m). Exercise: extend algorithm and analysis to nonconnected graphs Total O(n+m), n = # nodes, m = # edges
42 Properties of (Undirected) BFS(v) BFS(v) visits x if and only if there is a path in G from v to x. Edges into then-undiscovered vertices define a tree the "breadth first spanning tree" of G 2
43 Properties of (Undirected) BFS(v) BFS(v) visits x if and only if there is a path in G from v to x. Edges into then-undiscovered vertices define a tree the "breadth first spanning tree" of G Level i in this tree are exactly those vertices u such that the shortest path (in G, not just the tree) from the root v is of length i. All non-tree edges join vertices on the same or adjacent levels not true of every spanning tree!
44 BFS Application: Shortest Paths Tree (solid edges) gives shortest paths from start vertex can label by distances from start all edges connect same/adjacent levels 2
45 BFS Application: Shortest Paths Tree (solid edges) gives shortest paths from start vertex can label by distances from start all edges connect same/adjacent levels 2 5
46 BFS Application: Shortest Paths Tree (solid edges) gives shortest paths from start vertex can label by distances from start all edges connect same/adjacent levels 6
47 BFS Application: Shortest Paths Tree (solid edges) gives shortest paths from start vertex can label by distances from start all edges connect same/adjacent levels
48 Why fuss about trees? Trees are simpler than graphs Ditto for algorithms on trees vs algs on graphs So, this is often a good way to approach a graph problem: find a "nice" tree in the graph, i.e., one such that non-tree edges have some simplifying structure E.g., BFS finds a tree s.t. level-jumps are minimized DFS (below) finds a different tree, but it also has interesting structure 8
49 BFS(s) Implementation Global initialization: mark all vertices "undiscovered" BFS(s) mark s "discovered" queue = { s } while queue not empty u = remove_first(queue) for each edge {u,x} if (x is undiscovered) mark x discovered append x on queue mark u fully explored Exercise: modify code to compute level numbers Label edges as tree edges or non-tree edges (within/ between) Number of distinct shortest paths 9
50 Graph Search Application: Connected Components Want to answer questions of the form: given vertices u and v, is there a path from u to v? Set up one-time data structure to answer such questions efficiently. 50
51 Graph Search Application: Connected Components initial state: all v undiscovered for v = to n do if state(v)!= fully-explored then BFS(v) endif endfor Exercise: modify code to answer CC queries Total cost: O(n+m) each edge is touched a constant number of times (twice) works also with DFS 5
52 Graph Search Application: Connected Components Want to answer questions of the form: given vertices u and v, is there a path from u to v? Idea: create array A such that A[u] = smallest numbered vertex that is connected to u. Question reduces to whether A[u]=A[v]? Q: Why not create 2-d array Path[u,v]? 52
53 Graph Search Application: Connected Components Want to answer questions of the form: given vertices u and v, is there a path from u to v? Idea: create array A such that A[u] = smallest numbered vertex that is connected to u. Question reduces to whether A[u]=A[v]? Q: Why not create 2-d array Path[u,v]? 5
54 Graph Search Application: Connected Components initial state: all v undiscovered for v = to n do if state(v)!= fully-explored then BFS(v): setting A[u] v for each u found (and marking u discovered/fully-explored) endif endfor Total cost: O(n+m) each edge is touched a constant number of times (twice) works also with DFS 5
Goals! CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity!
 Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity. 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Goals. Chapter 3. Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
3.4 Testing Bipartiteness
 3.4 Testing Bipartiteness Bipartite Graphs Def. An undirected graph G = (V, E) is bipartite (2-colorable) if the nodes can be colored red or blue such that no edge has both ends the same color. Applications.
3.4 Testing Bipartiteness Bipartite Graphs Def. An undirected graph G = (V, E) is bipartite (2-colorable) if the nodes can be colored red or blue such that no edge has both ends the same color. Applications.
Algorithms: Lecture 10. Chalmers University of Technology
 Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search
 CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort
 Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications
 Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Graph Algorithms. Imran Rashid. Jan 16, University of Washington
 Graph Algorithms Imran Rashid University of Washington Jan 16, 2008 1 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs & Topological Ordering 3 DFS 2 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs
Graph Algorithms Imran Rashid University of Washington Jan 16, 2008 1 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs & Topological Ordering 3 DFS 2 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M.
 Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
Review: Graph Theory and Representation
 Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graph Algorithms: Chapters Part 1: Introductory graph concepts
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
Graph Theory. ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl
 Graph Theory ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl What can graphs model? Cost of wiring electronic components together. Shortest route between two cities. Finding the shortest distance
Graph Theory ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl What can graphs model? Cost of wiring electronic components together. Shortest route between two cities. Finding the shortest distance
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Introduction to Graphs. CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University
 Introduction to Graphs CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University A graph is a data structure for representing relationships. Each graph is a set of nodes connected by edges. Synonym Graph Hostile Slick Icy
Introduction to Graphs CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University A graph is a data structure for representing relationships. Each graph is a set of nodes connected by edges. Synonym Graph Hostile Slick Icy
CSE 421 DFS / Topological Ordering
 CSE 421 DFS / Topological Ordering Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Depth First Search Follow the first path you find as far as you can go; back up to last unexplored edge when you reach a dead end, then go as far
CSE 421 DFS / Topological Ordering Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Depth First Search Follow the first path you find as far as you can go; back up to last unexplored edge when you reach a dead end, then go as far
This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science.
 Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
Graphs: A graph is a data structure that has two types of elements, vertices and edges.
 Graphs: A graph is a data structure that has two types of elements, vertices and edges. An edge is a connection between two vetices If the connection is symmetric (in other words A is connected to B B
Graphs: A graph is a data structure that has two types of elements, vertices and edges. An edge is a connection between two vetices If the connection is symmetric (in other words A is connected to B B
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity
 CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity More Graph Algorithms Autumn 00 Paul Beame Given: a directed acyclic graph (DAG) G=(V,E) Output: numbering of the vertices of G with distinct numbers from
CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity More Graph Algorithms Autumn 00 Paul Beame Given: a directed acyclic graph (DAG) G=(V,E) Output: numbering of the vertices of G with distinct numbers from
Undirected Graphs. DSA - lecture 6 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1
 Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs. CMSC 420: Lecture 3
 Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Elements of Graph Theory
 Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms
 COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value
 The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
Lecture 10 Graph algorithms: testing graph properties
 Lecture 10 Graph algorithms: testing graph properties COMP 523: Advanced Algorithmic Techniques Lecturer: Dariusz Kowalski Lecture 10: Testing Graph Properties 1 Overview Previous lectures: Representation
Lecture 10 Graph algorithms: testing graph properties COMP 523: Advanced Algorithmic Techniques Lecturer: Dariusz Kowalski Lecture 10: Testing Graph Properties 1 Overview Previous lectures: Representation
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms
 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 15: Graph Data Structures, Topological Sort, and Traversals (DFS, BFS) Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017 Today: Announcements Graph data structures
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 15: Graph Data Structures, Topological Sort, and Traversals (DFS, BFS) Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017 Today: Announcements Graph data structures
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Information Science 2
 Information Science 2 - Applica(ons of Basic ata Structures- Week 03 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda l Week 02 review l Introduction to Graph Theory - Basic
Information Science 2 - Applica(ons of Basic ata Structures- Week 03 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda l Week 02 review l Introduction to Graph Theory - Basic
Graphs. Terminology. Graphs & Breadth First Search (BFS) Extremely useful tool in modeling problems. Consist of: Vertices Edges
 COMP Spring Graphs & BS / Slide Graphs Graphs & Breadth irst Search (BS) Extremely useful tool in modeling problems. Consist of: Vertices Edges Vertex A B D C E Edge Vertices can be considered sites or
COMP Spring Graphs & BS / Slide Graphs Graphs & Breadth irst Search (BS) Extremely useful tool in modeling problems. Consist of: Vertices Edges Vertex A B D C E Edge Vertices can be considered sites or
Algorithm Design (8) Graph Algorithms 1/2
 Graph Algorithm Design (8) Graph Algorithms / Graph:, : A finite set of vertices (or nodes) : A finite set of edges (or arcs or branches) each of which connect two vertices Takashi Chikayama School of
Graph Algorithm Design (8) Graph Algorithms / Graph:, : A finite set of vertices (or nodes) : A finite set of edges (or arcs or branches) each of which connect two vertices Takashi Chikayama School of
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.4-B.5, )
 Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.-B.,.-.) Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices V and a finite set of edges E. Directed graphs: E is a set of ordered pairs of vertices
Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.-B.,.-.) Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices V and a finite set of edges E. Directed graphs: E is a set of ordered pairs of vertices
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu
 Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Minimum spanning trees Definitions Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Minimum spanning trees Definitions Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees
 Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/84350835.jpg) Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
Theory of Computing. Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck
 Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
Graphs. Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1
 Graphs Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1 Warmup Discuss with your neighbors: Come up with as many kinds of relational data as you can (data that can be represented with a graph).
Graphs Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SU 18 BEN JONES 1 Warmup Discuss with your neighbors: Come up with as many kinds of relational data as you can (data that can be represented with a graph).
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Chapter 3. Graphs. Undirected Graphs. Some Graph Applications
 Chapter 3 31 Basic Definitions and Applications Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley All rights reserved 1 Undirected Graphs Some Graph Applications Undirected graph G = (V,
Chapter 3 31 Basic Definitions and Applications Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley All rights reserved 1 Undirected Graphs Some Graph Applications Undirected graph G = (V,
CS420/520 Algorithm Analysis Spring 2009 Lecture 14
 CS420/520 Algorithm Analysis Spring 2009 Lecture 14 "A Computational Analysis of Alternative Algorithms for Labeling Techniques for Finding Shortest Path Trees", Dial, Glover, Karney, and Klingman, Networks
CS420/520 Algorithm Analysis Spring 2009 Lecture 14 "A Computational Analysis of Alternative Algorithms for Labeling Techniques for Finding Shortest Path Trees", Dial, Glover, Karney, and Klingman, Networks
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13. Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico
 CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-5-2010 1 Last Time Spanning Trees BFS DFS Testing Bipartiteness 2 Today Inside BFS Running Time Implementation Degrees
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-5-2010 1 Last Time Spanning Trees BFS DFS Testing Bipartiteness 2 Today Inside BFS Running Time Implementation Degrees
22.1 Representations of graphs
 22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
Graphs. A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges. An edge is a connection between two nodes
 Graphs Graphs A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges An edge is a connection between two nodes A D B E C Nodes: A, B, C, D, E Edges: (A, B), (A, D), (D, E), (E, C) Nodes
Graphs Graphs A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges An edge is a connection between two nodes A D B E C Nodes: A, B, C, D, E Edges: (A, B), (A, D), (D, E), (E, C) Nodes
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals
 csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals Graph traversal (BFS and DFS) G can be undirected or directed We think about coloring each vertex WHITE before we start GRAY after we visit a vertex but before
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals Graph traversal (BFS and DFS) G can be undirected or directed We think about coloring each vertex WHITE before we start GRAY after we visit a vertex but before
Graphs Introduction and Depth first algorithm
 Graphs Introduction and Depth first algorithm Carol Zander Introduction to graphs Graphs are extremely common in computer science applications because graphs are common in the physical world. Everywhere
Graphs Introduction and Depth first algorithm Carol Zander Introduction to graphs Graphs are extremely common in computer science applications because graphs are common in the physical world. Everywhere
(Dijkstra s Algorithm) Consider the following positively weighted undirected graph for the problems below: 8 7 b c d h g f
 CS6: Algorithm Design and Analysis Recitation Section 8 Stanford University Week of 5 March, 08 Problem 8-. (Graph Representation) (a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using an adjacency matrix
CS6: Algorithm Design and Analysis Recitation Section 8 Stanford University Week of 5 March, 08 Problem 8-. (Graph Representation) (a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using an adjacency matrix
DS UNIT 4. Matoshri College of Engineering and Research Center Nasik Department of Computer Engineering Discrete Structutre UNIT - IV
 Sr.No. Question Option A Option B Option C Option D 1 2 3 4 5 6 Class : S.E.Comp Which one of the following is the example of non linear data structure Let A be an adjacency matrix of a graph G. The ij
Sr.No. Question Option A Option B Option C Option D 1 2 3 4 5 6 Class : S.E.Comp Which one of the following is the example of non linear data structure Let A be an adjacency matrix of a graph G. The ij
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS Topological Sort
 Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS Topological Sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (VG ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in G,
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS Topological Sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (VG ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in G,
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville. 3. Search (Part 1) CS 3030 Lecture Notes Yan Shi UW-Platteville
 Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Search (Part 1) CS 3030 Lecture Notes Yan Shi UW-Platteville Read: Textbook Chapter 3.7-3.9,3.12, 4. Problem Solving as
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Search (Part 1) CS 3030 Lecture Notes Yan Shi UW-Platteville Read: Textbook Chapter 3.7-3.9,3.12, 4. Problem Solving as
UNIT Name the different ways of representing a graph? a.adjacencymatrix b. Adjacency list
 UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
Chapter 3. Graphs. Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
Graph Theory. Part of Texas Counties.
 Graph Theory Part of Texas Counties. We would like to visit each of the above counties, crossing each county only once, starting from Harris county. Is this possible? This problem can be modeled as a graph.
Graph Theory Part of Texas Counties. We would like to visit each of the above counties, crossing each county only once, starting from Harris county. Is this possible? This problem can be modeled as a graph.
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Today s Outline. CSE 326: Data Structures. Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures. A Great Mathematician. The Bridges of Königsberg
 CSE 326: Data Structures Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures Ashish Sabharwal Autumn, 2003 Today s Outline Admin Project 3 in-progress checkin due tonight! Graph Algorithms Representation Applications
CSE 326: Data Structures Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures Ashish Sabharwal Autumn, 2003 Today s Outline Admin Project 3 in-progress checkin due tonight! Graph Algorithms Representation Applications
Announcements Problem Set 4 is out!
 CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
Theory of Computing. Lecture 10 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck
 Theory of Computing Lecture 10 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck Seven Bridges of Königsberg Can one take a walk that crosses each bridge exactly once? Seven Bridges of Königsberg Model as a graph Is there a path
Theory of Computing Lecture 10 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck Seven Bridges of Königsberg Can one take a walk that crosses each bridge exactly once? Seven Bridges of Königsberg Model as a graph Is there a path
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman
 CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
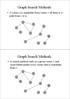 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
CSC263 Week 8. Larry Zhang.
 CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
EECS 203 Lecture 20. More Graphs
 EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 11. Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico
 CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 11 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 09-28-2010 1 Last Time Priority Queues & Heaps Heapify (up and down) 1: Preserve shape of tree 2: Swaps restore heap order
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 11 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 09-28-2010 1 Last Time Priority Queues & Heaps Heapify (up and down) 1: Preserve shape of tree 2: Swaps restore heap order
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
ECE 242. Data Structures
 ECE 242 Data Structures Lecture 28 Introduction to Graphs Overview Problem: How do we represent irregular connections between locations? Graphs Definition Directed and Undirected graph Simple path and
ECE 242 Data Structures Lecture 28 Introduction to Graphs Overview Problem: How do we represent irregular connections between locations? Graphs Definition Directed and Undirected graph Simple path and
Lecture 10. Graphs Vertices, edges, paths, cycles Sparse and dense graphs Representations: adjacency matrices and adjacency lists Implementation notes
 Lecture 10 Graphs Vertices, edges, paths, cycles Sparse and dense graphs Representations: adjacency matrices and adjacency lists Implementation notes Reading: Weiss, Chapter 9 Page 1 of 24 Midterm exam
Lecture 10 Graphs Vertices, edges, paths, cycles Sparse and dense graphs Representations: adjacency matrices and adjacency lists Implementation notes Reading: Weiss, Chapter 9 Page 1 of 24 Midterm exam
implementing the breadth-first search algorithm implementing the depth-first search algorithm
 Graph Traversals 1 Graph Traversals representing graphs adjacency matrices and adjacency lists 2 Implementing the Breadth-First and Depth-First Search Algorithms implementing the breadth-first search algorithm
Graph Traversals 1 Graph Traversals representing graphs adjacency matrices and adjacency lists 2 Implementing the Breadth-First and Depth-First Search Algorithms implementing the breadth-first search algorithm
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals
 csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals 1 Depth-first search (DFS) G can be directed or undirected DFS(v) mark v visited for all adjacent edges (v,w) of v do if w is not visited parent(w) = v (v,w)
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals 1 Depth-first search (DFS) G can be directed or undirected DFS(v) mark v visited for all adjacent edges (v,w) of v do if w is not visited parent(w) = v (v,w)
Algorithms: Graphs. Amotz Bar-Noy. Spring 2012 CUNY. Amotz Bar-Noy (CUNY) Graphs Spring / 95
 Algorithms: Graphs Amotz Bar-Noy CUNY Spring 2012 Amotz Bar-Noy (CUNY) Graphs Spring 2012 1 / 95 Graphs Definition: A graph is a collection of edges and vertices. Each edge connects two vertices. Amotz
Algorithms: Graphs Amotz Bar-Noy CUNY Spring 2012 Amotz Bar-Noy (CUNY) Graphs Spring 2012 1 / 95 Graphs Definition: A graph is a collection of edges and vertices. Each edge connects two vertices. Amotz
LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS
 Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Reference Sheet for CO142.2 Discrete Mathematics II
 Reference Sheet for CO14. Discrete Mathematics II Spring 017 1 Graphs Defintions 1. Graph: set of N nodes and A arcs such that each a A is associated with an unordered pair of nodes.. Simple graph: no
Reference Sheet for CO14. Discrete Mathematics II Spring 017 1 Graphs Defintions 1. Graph: set of N nodes and A arcs such that each a A is associated with an unordered pair of nodes.. Simple graph: no
