5th Grade Geometry
|
|
|
- Posy Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slide 1 / 112
2 Slide 2 / 112 5th Grade Geometry
3 Slide 3 / 112 Geometry Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Polygons Classifying Triangles & Quadrilaterals Coordinate Plane First Quadrant
4 Slide 4 / 112 Polygons Click to return to the table of contents
5 Slide 5 / 112 Polygons Examples of polygons and figures that are not polygons These are polygons These are not polygons
6 Slide 6 / 112 Shapes That Are Not Polygons This is not a polygon. It is open, click to reveal not closed. This is not a polygon. The sides cross over. click to reveal This is not a polygon Not all sides click are to reveal straight.
7 Slide 7 / 112 Polygons A polygon is a simple, closed plane figure made up of 3 or more line segments. Simple - line segments do not intersect (remember, line segments are straight, not curved) Closed - When you trace the figure, it ends at the starting point. Plane figure - a two-dimensional (flat) shape
8 Slide 8 / 112
9 Slide 9 / Is this figure a polygon? Yes No
10 Slide 10 / Is this figure a polygon? Yes No
11 Slide 11 / Is this figure a polygon? Yes No
12 Slide 12 / Is this figure a polygon? Yes No
13 Slide 13 / Is this figure a polygon? Yes No
14 Slide 14 / 112 Polygons Polygons are named by their number of sides. Name Triangle 3 Quadrilateral 4 Number of Sides Pentagon 5 Hexagon 6 Heptagon 7 Octagon 8 Nonagon 9 Decagon 10
15 Slide 15 / 112 Polygons Interesting fact: A polygon's number of sides and number of angles are always the same. 3 sides 3 angles 10 sides 10 angles
16 Slide 16 / How many sides does a heptagon have?
17 Slide 17 / How many angles does a nonagon have?
18 Slide 18 / Name the figure. A B C D Quadrilateral Hexagon Decagon Octagon
19 Slide 19 / Name the figure. A B C D Decagon Hexagon Nonagon Octagon
20 Slide 20 / 112 Regular vs. Irregular Polygons If the figure's sides and angles are congruent, it is called a regular polygon.
21 Slide 21 / 112 Regular vs. Irregular Polygons If either the figure's sides or angles are not congruent, it is called an irregular polygon.
22 Slide 22 / 112
23 Slide 23 / What kind of polygon is this? A B C regular irregular not a polygon
24 Slide 24 / What kind of polygon is this? A B C regular irregular not a polygon
25 Slide 25 / What kind of polygon is this? A B C regular irregular not a polygon
26 Slide 26 / What kind of polygon is this? A B C regular irregular not a polygon
27 Slide 27 / What kind of polygon is this? A B C regular irregular not a polygon
28 Slide 28 / What kind of polygon is this? A B C regular irregular not a polygon
29 Slide 29 / 112 Classifying Triangles & Quadrilaterals Click to return to the table of contents
30 By Sides Equilateral Triangle All sides are congruent. Slide 30 / 112 Triangles Classifying Triangles- Triangles can be classified by their angles or their sides. Isosceles Triangle At least two sides are congruent. Match the picture to the definition Scalene Triangle No sides are congruent.
31 Slide 31 / Classify the triangle by its sides A B C equilateral scalene isosceles
32 Slide 32 / Classify the triangle by its sides A B C equilateral scalene isosceles
33 Slide 33 / 112 Triangles By Angles Match the picture to the definition Acute Triangle All three angles are less than 90 degrees. Right Triangle One angle is 90 degrees. Obtuse Triangle One angle is more than 90 degrees.
34 Slide 34 / Classify the triangle by its angles A B C acute obtuse right
35 Slide 35 / Classify the triangle by its angles A B C acute obtuse right
36 Slide 36 / Classify the triangle by its angles A B C acute obtuse right
37 Slide 37 / 112 Click to go to web site then choose Triangle Sort.
38 Slide 38 / Classify the triangle. A equilateral B isosceles C scalene D acute E F right obtuse Remember: Classify by sides and angles (put in two answers)
39 Slide 39 / Classify the triangle. A B C D E F equilateral isosceles scalene acute right obtuse Remember: Classify by sides and angles (put in two answers)
40 Slide 40 / If each of the angles in a triangle measures 60 º, what is the triangle? A B C D E F equilateral isosceles scalene acute right obtuse Remember: Classify by sides and angles (put in two answers)
41 Slide 41 / Classify the triangle. A B C D E F equilateral isosceles scalene acute right obtuse Remember: Classify by sides and angles (put in two answers)
42 Slide 42 / Classify the triangle in the yield sign. A B C D E F equilateral isosceles scalene acute right obtuse Remember: Classify by sides and angles (put in two answers)
43 Slide 43 / Classify the triangle this bridge makes. A B C D E F equilateral isosceles scalene acute right obtuse Remember: Classify by sides and angles (put in two answers)
44 Slide 44 / 112 Quadrilaterals Classifying Quadrilaterals You must use the properties of quadrilaterals to identify and classify them. Trapezoids - Exactly one pair of parallel sides.
45 Slide 45 / 112 Quadrilaterals Classifying Quadrilaterals You must use the properties of quadrilaterals to identify and classify them. Parallelogram - Opposite sides are congruent & parallel. Interesting fact: The opposite angles of a parallelogram are also congruent.
46 Slide 46 / 112 Quadrilaterals Classifying Quadrilaterals You must use the properties of quadrilaterals to identify and classify them. Similar to triangles, quadrilaterals are classified by the relationships between their sides and angles. Rectangle - Special parallelogram with four right angles
47 Slide 47 / 112 Quadrilaterals Classifying Quadrilaterals You must use the properties of quadrilaterals to identify and classify them. Rhombus - Parallelogram with four congruent sides and opposite angles congruent
48 Slide 48 / 112 Quadrilaterals Classifying Quadrilaterals You must use the properties of quadrilaterals to identify and classify them. Square - Rhombus with four right angles or a Rectangle with four congruent sides.
49 Slide 49 / 112 Match the shape with the description.
50 Slide 50 / 112 Quadrilaterals Quadrilateral 4-sided polygon Parallelogram 4-sided polygon two pairs of // sides Trapezoid 4-sided polygon one pair of // sides Rectangle Square Rhombus 4-sided polygon 4-sided polygon two pairs of // sides two pairs of // sides all sides ~ all angles ~ = = 4-sided polygon two pairs of // sides all angles ~ = all sides ~ =
51 Slide 51 / 112 Polygon Quadilateral
52 Slide 52 / 112 Polygon Quadilateral Trapezoid
53 Slide 53 / 112 Polygon Quadilateral Parallelogram Trapezoid
54 Slide 54 / 112 Polygon Quadilateral Parallelogram Trapezoid Rectangle
55 Slide 55 / 112 Polygon Trapezoid Quadilateral Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus
56 Slide 56 / 112 Polygon Quadilateral Parallelogram Trapezoid Rectangle Square Rhombus
57 Slide 57 / 112 Click for web site and then choose polygon sort.
58 Slide 58 / 112 Drag and drop the names to complete the diagram that shows the relationship among the figures listed. Each category will be used only once. rhombuses parallelograms rectangles quadrilaterals From PARCC EOY sample test #13
59 Slide 59 / Which of the following shapes is a trapezoid? A B C D
60 Slide 60 / Which of statement(s) do NOT describe the figure? A trapezoid B parallelogram C rectangle D rhombus E square
61 Slide 61 / Which of the statements does NOT describe the figure? A B C D E trapezoid parallelogram rectangle rhombus square
62 Slide 62 / Which of the statement(s) does NOT describe the figure? A trapezoid B parallelogram C rectangle D rhombus E square
63 Slide 63 / Which of the following statements is true? A B C D A square is not a rectangle. A rectangle is a square. A square is not a parallelogram. A square is a rectangle.
64 Slide 64 / Which shape has exactly one pair of // sides? A square B rhombus C triangle D trapezoid
65 Slide 65 / Which shape has two sets of congruent angles and adjacent sides congruent? A square B rectangle C rhombus D kite
66 Slide 66 / Describe the figure. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
67 Slide 67 / Describe the figure. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
68 Slide 68 / Describe the figure. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
69 Slide 69 / Describe the figure. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
70 Slide 70 / Describe the shape of the top of the desk. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
71 Slide 71 / Describe the shape for the face of the clock. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
72 Slide 72 / Describe the shape of the mouth of the shark. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
73 Slide 73 / Describe the shape of this marker. Choose all answers that apply. A B C D E F G Quadrilateral Trapezoid Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square None of the Above
74 Slide 74 / Which of the following shapes could never have perpendicular sides? A rectangle B triangle C circle D square
75 Slide 75 / Which of these shapes could never have parallel opposite sides? A trapezoid B triangle C rectangle D rhombus
76 Slide 76 / Which explanation about figures is correct? A All rhombuses are parallelograms. Parallelograms have 2 pair of parallel sides. Therefore, all rhombuses have 2 pairs of parallel sides. B All rhombuses are parallelograms. Parallelograms have exactly 1 pair of parallel sides. Therefore, all rhombuses have exactly 1 pair of parallel sides. C Only some rhombuses are parallelograms. Parallelograms have 2 pairs of parallel sides. Therefore, only some rhombuses have 2 pair of parallel sides. D Only some rhombuses are parallelograms. Parallelograms have exactly 1 pair of parallel sides. Therefore, only some rhombuses have exactly 1 pair of parallel sides. From PARCC EOY sample test #7
77 Slide 77 / Select an answer for each blank. Because a is a, it must have 4 A square D square B rectangle E rectangle C trapezoid F rhombus opposite angles and all four sides.
78 Slide 78 / 112 Coordinate Plane Click to return to the table of contents
79 Slide 79 / 112 Coordinate Plane The coordinate plane is formed by two intersecting number lines called axes. The horizontal line is the x-axis. The vertical line is the y-axis.
80 Slide 80 / 112 Coordinate Plane Origin (0, 0) The point at which the x and y axes intersect is called the origin. The coordinates of the origin are (0, 0).
81 Slide 81 / 112 Coordinate Plane y x Points can be plotted on the plane using one coordinate from each of the axes. These sets are called ordered pairs. The x coordinate always appears first in these pairs. The y coordinate appears second. (x,y)
82 Slide 82 / 112 Coordinate Plane To graph an ordered pair, such as(4,3): Start at the origin (0,0). Move right on the x-axis, since the first number is positive. Then, move up since the second number is positive. Plot the point. (4,3)
83 Slide 83 / 112 Coordinate Plane y x (x,y) This point is (3,2). To plot the point, go over 3, then up 2.
84 Slide 84 / 112 Coordinate Plane y x (x,y) This point is (1,4). To plot the point, go over 1, then up 4.
85 Slide 85 / 112 Coordinate Plane y x (x,y) This point is (5,0). To plot the point, go over 5, then up 0.
86 46 Which point is at the origin? y Slide 86 / 112 A B D C x
87 47 Which point is at (1,3)? Slide 87 / 112 y A B D C x
88 48 Which point is at (3,3)? Slide 88 / 112 y A B D C x
89 49 Which point is at (0,5)? A Slide 89 / 112 y B D C x
90 Slide 90 / Which ordered pair is the origin? A (4,0) B (0,0) C (0,4) D (4,4)
91 Slide 91 / Which number in the ordered pair (7,3) is the x-coordinate? A 7 B 3 C 0 D x
92 Slide 92 / Which number in the ordered pair (5,9) is the y-coordinate? A 0 B 5 C 9 D y
93 Slide 93 / Which number in the ordered pair (7,12) is the y-coordinate? A 7 B 12 C 0 D y
94 Slide 94 / Which number in the ordered pair (7,12) is the x-coordinate? A 7 B 12 C 0 D x
95 Slide 95 / Select three statements that correctly describe the coordinate system. A The x- and y-axes intersect at 10. B The x- and y-axes intersect at the origin. C The x- and y-axes are parallel number lines. D The x- and y-axes are perpendicular number lines. E The x- and y-axes are used to locate points on a coordinate plane. From PARCC EOY sample test #32
96 Slide 96 / 112 Mia is playing several rounds of a word game. Each coordinate pair shows the number of the round and Mia's score fore that round. She is keeping track of these coordinate pairs on a graph. Round 1: (1, 3) Round 2: (2, 6) Round 3: (3, 3) Part A Graph Mia's scores for the first three rounds of play. Move the 3 points to their location on the graph. A B C From PARCC EOY sample test #26
97 Slide 97 / Part B In round 4, Mia scores the same number of points as in rounds 2 and 3 combined. What is the coordinate pair that represents Mia's score for round 4? A (4, 5) B (9, 4) C (5, 4) D (4, 9) From PARCC EOY sample test #26
98 Slide 98 / The following points were graphed on the coordinate plane. Select the correct letter that corresponds with each point on the graph. 1. (4,6) (A or B) A 2. (6,4) (B or C) B C A C B 3. (3,0) (D or E) D D E F E From PARCC EOY sample test #2
99 Slide 99 / 112 First Quadrant Click to return to the table of contents
100 Slide 100 / 112 First Quadrant First Quadrant When the x and y coordinates are both positive, points are plotted in the first quadrant.
101 Slide 101 / 112 Play Billy Bug and His Quest for Grub Game Click for web site.
102 Slide 102 / 112 First Quadrant Sometimes we are asked to create a shape in the first Quadrant by finding the missing point... Try these examples.
103 Slide 103 / Which point will create a square? A (3,2) B (5,1) C (2,1) D (1,2)
104 Slide 104 / Which point will create a right triangle? A (1,4) B (4,1) C (3,4) D (2,1)
105 Slide 105 / Which point will create a parallelogram? A (4, 8) B (8, 4) C (9, 5) D (7, 4)
106 Slide 106 / Which point will create a trapezoid? A (1, 3) B (1, 1) C (3, 3) D (3, 1)
107 Slide 107 / Emily drew a figure on a coordinate grid. The figure has one pair of opposite sides that are parallel, but not equal. Which of the following figures could Emily have drawn? A C B D
108 Slide 108 / Chose an answer to fill in each blank. Point A is units to the x-axis A 2 D closer to B 5 E further from C 7 and units to the y-axis than point C. F 2 I closer to 10 G 5 E 9 J further from H A B C D
109 Slide 109 / Chose an answer to fill in each blank. Point D is units to the x-axis A 2 D closer to B 3 E further from C 4 and units to the y-axis than point B. F 2 I closer to 10 G 3 E 9 J further from H A B C D
110 Slide 110 / The coordinate plane shows the number of customers the Ice Cream Shoppe had in the first 3 weeks of June. If the pattern continues, how many customers will they have during the 4th week of June? A 5 B 6 C 55 D 60 # of customers (in tens.)
111 Slide 111 / The coordinate plane shows the number of customers the Ice Cream Shoppe had in the first 3 weeks of September. If the pattern continues, how many customers will they have during the 5th week of September? A 15 B 20 C 25 D 30 # of customers (in tens.)
112 Slide 112 / 112 Coordinate Grid Geoboards Activity Work in partners. One partner creates a polygon on the geoboard and writes down the vertices. Other partner plots the points, and connects them with line segments. Compare the polygons, then switch roles. This example, the vertices are: (1,3) (4,1) (4,3) Click above to practice using the National Library of Virtual Manipulatives web site.
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever.
 Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Math Polygons
 Math 310 9.2 Polygons Curve & Connected Idea The idea of a curve is something you could draw on paper without lifting your pencil. The idea of connected is that a set can t be split into two disjoint sets.
Math 310 9.2 Polygons Curve & Connected Idea The idea of a curve is something you could draw on paper without lifting your pencil. The idea of connected is that a set can t be split into two disjoint sets.
An angle that has a measure less than a right angle.
 Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Polygon. Note: Each segment is called a side. Each endpoint is called a vertex.
 Polygons Polygon A closed plane figure formed by 3 or more segments. Each segment intersects exactly 2 other segments at their endpoints. No 2 segments with a common endpoint are collinear. Note: Each
Polygons Polygon A closed plane figure formed by 3 or more segments. Each segment intersects exactly 2 other segments at their endpoints. No 2 segments with a common endpoint are collinear. Note: Each
Skill: Polygons. Vocabulary: Polygon a closed two-dimensional figure with straight edges
 Skill: Polygons Standard: 5.13.a ~ The student, using plane figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezoid), will develop definitions of these plane figures; 5.13.b ~ The student,
Skill: Polygons Standard: 5.13.a ~ The student, using plane figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezoid), will develop definitions of these plane figures; 5.13.b ~ The student,
Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation.
 10 8: Polygons and Tesselations Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation. Vocabulary: polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments
10 8: Polygons and Tesselations Main Idea: classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellation. Vocabulary: polygon A simple closed figure in a plane formed by three or more line segments
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures
 Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 1 Slide 1 AND
 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 1 Slide 1 AND Chapter 9 Geometry Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 1 Slide 2 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Points, lines, planes, and
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 1 Slide 1 AND Chapter 9 Geometry Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 9 Section 1 Slide 2 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Points, lines, planes, and
1. Write three things you already know about angles. Share your work with a classmate. Does your classmate understand what you wrote?
 LESSON : PAPER FOLDING. Write three things you already know about angles. Share your work with a classmate. Does your classmate understand what you wrote? 2. Write your wonderings about angles. Share your
LESSON : PAPER FOLDING. Write three things you already know about angles. Share your work with a classmate. Does your classmate understand what you wrote? 2. Write your wonderings about angles. Share your
M05.C-G Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
 M05.C-G.2.1.1 Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on 1. Mr. Diaz is building a fence around his yard. He drew a sketch of the fence line. Which best describes the fence line? A. pentagon;
M05.C-G.2.1.1 Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on 1. Mr. Diaz is building a fence around his yard. He drew a sketch of the fence line. Which best describes the fence line? A. pentagon;
Contents. Lines, angles and polygons: Parallel lines and angles. Triangles. Quadrilaterals. Angles in polygons. Congruence.
 Colegio Herma. Maths Bilingual Departament Isabel Martos Martínez. 2015 Contents Lines, angles and polygons: Parallel lines and angles Triangles Quadrilaterals Angles in polygons Congruence Similarity
Colegio Herma. Maths Bilingual Departament Isabel Martos Martínez. 2015 Contents Lines, angles and polygons: Parallel lines and angles Triangles Quadrilaterals Angles in polygons Congruence Similarity
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Constructing Symmetrical Shapes
 1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
Polygons - Part 1. Triangles
 Polygons - Part 1 Triangles Introduction Complementary Angles: are two angles that add up to 90 Example: degrees A ADB = 65 degrees Therefore B + ADB BDC 65 deg 25 deg D BDC = 25 degrees C 90 Degrees Introduction
Polygons - Part 1 Triangles Introduction Complementary Angles: are two angles that add up to 90 Example: degrees A ADB = 65 degrees Therefore B + ADB BDC 65 deg 25 deg D BDC = 25 degrees C 90 Degrees Introduction
UNIT 6: Connecting Algebra & Geometry through Coordinates
 TASK: Vocabulary UNIT 6: Connecting Algebra & Geometry through Coordinates Learning Target: I can identify, define and sketch all the vocabulary for UNIT 6. Materials Needed: 4 pieces of white computer
TASK: Vocabulary UNIT 6: Connecting Algebra & Geometry through Coordinates Learning Target: I can identify, define and sketch all the vocabulary for UNIT 6. Materials Needed: 4 pieces of white computer
Grade Common Core Math
 th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
Closed shapes with straight sides
 41 Unit 6 and 7 Properties of 2D shapes Activity 1 Closed shapes with straight sides (polygons). Let s revise the 2D shapes you learnt about in Grade 5 Closed shapes with straight sides triangle quadrilateral
41 Unit 6 and 7 Properties of 2D shapes Activity 1 Closed shapes with straight sides (polygons). Let s revise the 2D shapes you learnt about in Grade 5 Closed shapes with straight sides triangle quadrilateral
SHAPE AND STRUCTURE. Shape and Structure. An explanation of Mathematical terminology
 Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Describe Plane Shapes
 Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
1.6 Classifying Polygons
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Basics of Geometry 1.6 Classifying Polygons Learning Objectives Define triangle and polygon. Classify triangles by their sides and angles. Understand the difference between convex
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Basics of Geometry 1.6 Classifying Polygons Learning Objectives Define triangle and polygon. Classify triangles by their sides and angles. Understand the difference between convex
Geometry Vocabulary. acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees
 Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Yimin Math Centre. 6.1 Properties of geometrical figures Recognising plane shapes... 1
 Yimin Math Centre Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of Contents 6 Year 7 Term 3 Week 6 Homework 1 6.1 Properties of geometrical figures............................ 1 6.1.1 Recognising plane shapes...........................
Yimin Math Centre Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of Contents 6 Year 7 Term 3 Week 6 Homework 1 6.1 Properties of geometrical figures............................ 1 6.1.1 Recognising plane shapes...........................
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES. Grade 6 Mathematics 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES Grade 6 Mathematics 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 2 Content Review: Standards of Learning in Detail Grade 6 Mathematics: Third Nine Weeks 2016-2017 This resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES Grade 6 Mathematics 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 2 Content Review: Standards of Learning in Detail Grade 6 Mathematics: Third Nine Weeks 2016-2017 This resource
Section 9.1. Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 9.1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles What You Will Learn Points Lines Planes Angles 9.1-2 Basic Terms A point, line, and plane are three basic terms in geometry that are NOT given a formal definition,
Section 9.1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles What You Will Learn Points Lines Planes Angles 9.1-2 Basic Terms A point, line, and plane are three basic terms in geometry that are NOT given a formal definition,
3rd Grade. Shapes and Perimeter.
 1 3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter 2015 11 10 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Area Perimeter Lines, Rays and Line Segments Angles Click on a topic to go to that section Parallel and Intersecting Lines
1 3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter 2015 11 10 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Area Perimeter Lines, Rays and Line Segments Angles Click on a topic to go to that section Parallel and Intersecting Lines
Chapter 8. Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals. 02/2017 LSowatsky
 Chapter 8 Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 02/2017 LSowatsky 1 8-1A: Points, Lines, and Planes I can Identify and label basic geometric figures. LSowatsky 2 Vocabulary: Point: a point has no
Chapter 8 Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 02/2017 LSowatsky 1 8-1A: Points, Lines, and Planes I can Identify and label basic geometric figures. LSowatsky 2 Vocabulary: Point: a point has no
Contents. Lines, angles and polygons: Parallel lines and angles. Triangles. Quadrilaterals. Angles in polygons. Congruence.
 Colegio Herma. Maths Bilingual Departament Isabel Martos Martínez. 2015 Contents Lines, angles and polygons: Parallel lines and angles Triangles Quadrilaterals Angles in polygons Congruence Similarity
Colegio Herma. Maths Bilingual Departament Isabel Martos Martínez. 2015 Contents Lines, angles and polygons: Parallel lines and angles Triangles Quadrilaterals Angles in polygons Congruence Similarity
Show all work on a separate sheet of paper.
 Sixth Grade Review 15: Geometric Shapes & Angles Name: Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. Geometry Word Bank Obtuse Angle Right Angle Acute Angle Straight Angle Pentagon Octagon Decagon Scalene
Sixth Grade Review 15: Geometric Shapes & Angles Name: Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. Geometry Word Bank Obtuse Angle Right Angle Acute Angle Straight Angle Pentagon Octagon Decagon Scalene
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Points, lines, angles
 Points, lines, angles Point Line Line segment Parallel Lines Perpendicular lines Vertex Angle Full Turn An exact location. A point does not have any parts. A straight length that extends infinitely in
Points, lines, angles Point Line Line segment Parallel Lines Perpendicular lines Vertex Angle Full Turn An exact location. A point does not have any parts. A straight length that extends infinitely in
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. no no R89. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Digits. Value The numbers a digit. Standard Form. Expanded Form. The symbols used to show numbers: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
 Digits The symbols used to show numbers: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Value The numbers a digit represents, which is determined by the position of the digits Standard Form Expanded Form A common way of the writing
Digits The symbols used to show numbers: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Value The numbers a digit represents, which is determined by the position of the digits Standard Form Expanded Form A common way of the writing
Geometry. Geometry is the study of shapes and sizes. The next few pages will review some basic geometry facts. Enjoy the short lesson on geometry.
 Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Lesson 1 Introduction to Geometry (Grades 9-12) Instruction 1-5 Definitions of Figures
 efinitions of igures Quadrilaterals Quadrilaterals are closed four-sided figures. The interior angles of a quadrilateral always total 360. Quadrilaterals classified in two groups: Trapeziums and Trapezoids.
efinitions of igures Quadrilaterals Quadrilaterals are closed four-sided figures. The interior angles of a quadrilateral always total 360. Quadrilaterals classified in two groups: Trapeziums and Trapezoids.
POSITION, DIRECTION AND MOVEMENT Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Use mathematical
 POSITION, DIRECTION AND MOVEMENT Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Use mathematical Use mathematical Describe positions on a Identify, describe and vocabulary to describe vocabulary to describe
POSITION, DIRECTION AND MOVEMENT Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Use mathematical Use mathematical Describe positions on a Identify, describe and vocabulary to describe vocabulary to describe
MPM1D Page 1 of 6. length, width, thickness, area, volume, flatness, infinite extent, contains infinite number of points. A part of a with endpoints.
 MPM1D Page 1 of 6 Unit 5 Lesson 1 (Review) Date: Review of Polygons Activity 1: Watch: http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/dimensions.html OBJECT Point # of DIMENSIONS CHARACTERISTICS location, length,
MPM1D Page 1 of 6 Unit 5 Lesson 1 (Review) Date: Review of Polygons Activity 1: Watch: http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/dimensions.html OBJECT Point # of DIMENSIONS CHARACTERISTICS location, length,
Consolidation of Grade 6 EQAO Questions Geometry and Spatial Sense
 Consolidation of Grade 6 EQAO Questions Geometry and Spatial Sense SE2 Families of Schools Year GV1 GV2 GV3 Spring 2006 Spring 2007 Spring 2008 MC14 MC24 MC13 OR9 MC17 OR30 OR9 MC21 MC18 MC3 MC23 OR30
Consolidation of Grade 6 EQAO Questions Geometry and Spatial Sense SE2 Families of Schools Year GV1 GV2 GV3 Spring 2006 Spring 2007 Spring 2008 MC14 MC24 MC13 OR9 MC17 OR30 OR9 MC21 MC18 MC3 MC23 OR30
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Year 10 Topic Practice Papers: Polygons Polygons 1 Grade 4 Look at the shapes below A B C Shape A, B and C are polygons Write down the mathematical name for each of the polygons
PLC Papers Created For: Year 10 Topic Practice Papers: Polygons Polygons 1 Grade 4 Look at the shapes below A B C Shape A, B and C are polygons Write down the mathematical name for each of the polygons
Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template
 Lesson Development Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template Lesson Title: Basic Geometric Concepts Lesson # Author(s): Phone Number(s): E-mail Address(es): Juan Carlos Martínez jcmartinez@dadeschoolsnet Bergman
Lesson Development Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template Lesson Title: Basic Geometric Concepts Lesson # Author(s): Phone Number(s): E-mail Address(es): Juan Carlos Martínez jcmartinez@dadeschoolsnet Bergman
Spiral Back: Evaluate the following when x = -2 and y = 3 1) -4y x + (3+ x 2 ) Solve the following equations: 2) x 6 = -20 3) 2x 2 = -16 4)
 Name: Date: / / Spiral Back: Evaluate the following when x = -2 and y = 3 1) -4y x + (3+ x 2 ) Let s see what you remember! Sticker Challenge! Solve the following equations: 2) x 6 = -20 3) 2x 2 = -16
Name: Date: / / Spiral Back: Evaluate the following when x = -2 and y = 3 1) -4y x + (3+ x 2 ) Let s see what you remember! Sticker Challenge! Solve the following equations: 2) x 6 = -20 3) 2x 2 = -16
ame Date Class Practice A 11. What is another name for a regular quadrilateral with four right angles?
 ame Date Class Practice A Polygons Name each polygon. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Tell whether each polygon appears to be regular or not regular. 7. 8. 9. 10. What is another name for a regular triangle? 11. What
ame Date Class Practice A Polygons Name each polygon. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Tell whether each polygon appears to be regular or not regular. 7. 8. 9. 10. What is another name for a regular triangle? 11. What
Unit 3: Triangles and Polygons
 Unit 3: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about triangles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Example 1: Trapezoid on the coordinate plane below has the following
Unit 3: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about triangles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Example 1: Trapezoid on the coordinate plane below has the following
Answer Key. 1.1 The Three Dimensions. Chapter 1 Basics of Geometry. CK-12 Geometry Honors Concepts 1. Answers
 1.1 The Three Dimensions 1. Possible answer: You need only one number to describe the location of a point on a line. You need two numbers to describe the location of a point on a plane. 2. vary. Possible
1.1 The Three Dimensions 1. Possible answer: You need only one number to describe the location of a point on a line. You need two numbers to describe the location of a point on a plane. 2. vary. Possible
Mathematics Success Level E
 T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises?
 Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises? Here is a question for you. In the diagram on the board, DE is parallel to AC, DB = 4, AB = 9 and BE = 8. What is the length EC? Polygons Definitions:
Any questions about the material so far? About the exercises? Here is a question for you. In the diagram on the board, DE is parallel to AC, DB = 4, AB = 9 and BE = 8. What is the length EC? Polygons Definitions:
Unit 3 Geometry. Chapter 7 Geometric Relationships Chapter 8 Measurement Relationships Chapter 9 Optimizing Measurements MPM1D
 Unit 3 Geometry Chapter 7 Geometric Relationships Chapter 8 Measurement Relationships Chapter 9 Optimizing Measurements MPM1D Chapter 7 Outline Section Subject Homework Notes Lesson and Homework Complete
Unit 3 Geometry Chapter 7 Geometric Relationships Chapter 8 Measurement Relationships Chapter 9 Optimizing Measurements MPM1D Chapter 7 Outline Section Subject Homework Notes Lesson and Homework Complete
Right Angle Triangle. Square. Opposite sides are parallel
 Triangles 3 sides ngles add up to 18⁰ Right ngle Triangle Equilateral Triangle ll sides are the same length ll angles are 6⁰ Scalene Triangle ll sides are different lengths ll angles are different Isosceles
Triangles 3 sides ngles add up to 18⁰ Right ngle Triangle Equilateral Triangle ll sides are the same length ll angles are 6⁰ Scalene Triangle ll sides are different lengths ll angles are different Isosceles
Area. Angle where two rays. Acute angle. Addend. a number to be added. an angle measuring less than 90 degrees. or line segments share an endpoint
 Acute angle Addend an angle measuring less than 90 degrees a number to be added Angle where two rays or line segments share an endpoint Area the measure of space inside a figure. Area is measured in square
Acute angle Addend an angle measuring less than 90 degrees a number to be added Angle where two rays or line segments share an endpoint Area the measure of space inside a figure. Area is measured in square
M8WSB-C07.qxd 4/4/08 7:00 PM Page NEL
 8 NEL GOAL Chapter 7 Tessellations You will be able to use angle measurements to identify regular and irregular polygons that might tessellate identify and describe translations, reflections, or rotations
8 NEL GOAL Chapter 7 Tessellations You will be able to use angle measurements to identify regular and irregular polygons that might tessellate identify and describe translations, reflections, or rotations
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Geometry !!!!! Tri-Folds 3.G.1 - # 1. 4 Mystery Shape 5 Compare & Contrast. 3rd Grade Math. Compare. Name: Date: Contrast
 4 Mystery Shape 5 Compare & Contrast 1. Draw and label a shape that has one more side than a triangle. Draw it. 2. Draw and label a shape that has three more sides than a triangle. 3. Draw and label a
4 Mystery Shape 5 Compare & Contrast 1. Draw and label a shape that has one more side than a triangle. Draw it. 2. Draw and label a shape that has three more sides than a triangle. 3. Draw and label a
Examples: Identify the following as equilateral, equiangular or regular. Using Variables: S = 180(n 2)
 Ch. 6 Notes 6.1: Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems Examples: Identify the following as equilateral, equiangular or regular. 1) 2) 3) S = 180(n 2) Using Variables: and Examples: Find the sum of the interior angles
Ch. 6 Notes 6.1: Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems Examples: Identify the following as equilateral, equiangular or regular. 1) 2) 3) S = 180(n 2) Using Variables: and Examples: Find the sum of the interior angles
Polygons, Congruence, Similarity Long-Term Memory Review Grade 8 Review 1
 Review 1 1. In the diagram below, XYZ is congruent to CDE XYZ CDE. Y D E X Z C Complete the following statements: a) C b) XZ c) CDE d) YZ e) Z f) DC 2. In the diagram below, ABC is similar to DEF ABC DEF.
Review 1 1. In the diagram below, XYZ is congruent to CDE XYZ CDE. Y D E X Z C Complete the following statements: a) C b) XZ c) CDE d) YZ e) Z f) DC 2. In the diagram below, ABC is similar to DEF ABC DEF.
Geometry Basics of Geometry Precise Definitions Unit CO.1 OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.1
 OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.1 OBJECTIVE Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.1 OBJECTIVE Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Vocabulary for Geometry. Line (linea) a straight collection of points extending in opposite directions without end.
 Vocabulary for Geometry Line (linea) a straight collection of points extending in opposite directions without end. A line AB or line BA B Symbol for a line is AB Jan 27 2:56 PM Line Segment (linea segmento)
Vocabulary for Geometry Line (linea) a straight collection of points extending in opposite directions without end. A line AB or line BA B Symbol for a line is AB Jan 27 2:56 PM Line Segment (linea segmento)
Definition: Convex polygon A convex polygon is a polygon in which the measure of each interior angle is less than 180º.
 Definition: Convex polygon A convex polygon is a polygon in which the measure of each interior angle is less than 180º. Definition: Convex polygon A convex polygon is a polygon in which the measure of
Definition: Convex polygon A convex polygon is a polygon in which the measure of each interior angle is less than 180º. Definition: Convex polygon A convex polygon is a polygon in which the measure of
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Core 9 GM1.1 Answers. 1 a
 GM1.1 Answers 1 a b 2 Shape Name Regular Irregular Convex Concave A Decagon B Octagon C Pentagon D Quadrilateral E Heptagon F Hexagon G Quadrilateral H Triangle I Triangle J Hexagon Original Material Cambridge
GM1.1 Answers 1 a b 2 Shape Name Regular Irregular Convex Concave A Decagon B Octagon C Pentagon D Quadrilateral E Heptagon F Hexagon G Quadrilateral H Triangle I Triangle J Hexagon Original Material Cambridge
Does a group of parallel line segments need to be the same length?
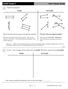 1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
15. First make a parallelogram by rotating the original triangle. Then tile with the Parallelogram.
 Shapes and Designs: Homework Examples from ACE Investigation 1: Question 15 Investigation 2: Questions 4, 20, 24 Investigation 3: Questions 2, 12 Investigation 4: Questions 9 12, 22. ACE Question ACE Investigation
Shapes and Designs: Homework Examples from ACE Investigation 1: Question 15 Investigation 2: Questions 4, 20, 24 Investigation 3: Questions 2, 12 Investigation 4: Questions 9 12, 22. ACE Question ACE Investigation
Mathematics Concepts 2 Exam 1 Version 4 21 September 2018
 Mathematics Concepts 2 Exam 1 Version 4 21 September 2018 Name: Permissible Aides: The small ruler distributed by the proctor Prohibited: Class Notes Class Handouts Study Guides and Materials The Book
Mathematics Concepts 2 Exam 1 Version 4 21 September 2018 Name: Permissible Aides: The small ruler distributed by the proctor Prohibited: Class Notes Class Handouts Study Guides and Materials The Book
The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9
 Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
MATH-6 Unit 5 Study Guide Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MTH-6 Unit 5 Study Guide Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam I:1TF6 1 Which ordered pair describes the point located on this coordinate plane? (0, 5) (0, -5) (5, 0) (-5, 0) 2 On a regular
MTH-6 Unit 5 Study Guide Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam I:1TF6 1 Which ordered pair describes the point located on this coordinate plane? (0, 5) (0, -5) (5, 0) (-5, 0) 2 On a regular
4.G.1. Name Date. Geometry. Use the figure below to answer questions Draw an intersecting line through the line below. E H
 Name Date ssessment 1 4.G.1 questions 1-3. 5. Draw an intersecting line through the line below. E H B C D G F 6. Draw a perpendicular line through the set of lines below. 1. Name a pair of parallel lines.
Name Date ssessment 1 4.G.1 questions 1-3. 5. Draw an intersecting line through the line below. E H B C D G F 6. Draw a perpendicular line through the set of lines below. 1. Name a pair of parallel lines.
HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS FCAT ITEM SPECIFICATION
 Benchmark Support Task Cards MA.3.A.1.1 BENCHMARK: MA.3.A.1.1 Model multiplication and division, including problems presented in context: repeated addition, multiplicative comparison, array, how many combinations,
Benchmark Support Task Cards MA.3.A.1.1 BENCHMARK: MA.3.A.1.1 Model multiplication and division, including problems presented in context: repeated addition, multiplicative comparison, array, how many combinations,
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review
 Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Skill. 69 Graph Ordered Pairs. (First Quadrant) Using Skill 69 COMMON ERRORS. 285 Holt Mathematics. OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant)
 Skill Graph Ordered Pairs (First Quadrant) Using Skill OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant) Minutes Direct students attention to the definition at the top of the page. Work through the example
Skill Graph Ordered Pairs (First Quadrant) Using Skill OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant) Minutes Direct students attention to the definition at the top of the page. Work through the example
16. [Shapes] Q. What shape is this object? A. sphere. a) Circle the cube. b) Circle the cone. c) Circle the cylinder. d) Circle the sphere.
![16. [Shapes] Q. What shape is this object? A. sphere. a) Circle the cube. b) Circle the cone. c) Circle the cylinder. d) Circle the sphere. 16. [Shapes] Q. What shape is this object? A. sphere. a) Circle the cube. b) Circle the cone. c) Circle the cylinder. d) Circle the sphere.](/thumbs/87/95210254.jpg) 16. [Shapes] Skill 16.1 Recognising 3D shapes (1). Observe whether the 3D shape has a curved surface. If so, the shape will be either a cone, cylinder or sphere. Observe whether the curved surface formes
16. [Shapes] Skill 16.1 Recognising 3D shapes (1). Observe whether the 3D shape has a curved surface. If so, the shape will be either a cone, cylinder or sphere. Observe whether the curved surface formes
Geometry Foundations Planning Document
 Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Activity 1 Look at the pattern on the number line and find the missing numbers. Model. (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (d)
 Lesson Look at the pattern on the number line and find the missing numbers. Model (a) (b) (c) 9 Answers: (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) 00 00. (a) (b) 00. (c) 0 0 (a) (b) (c) Use the number
Lesson Look at the pattern on the number line and find the missing numbers. Model (a) (b) (c) 9 Answers: (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) 00 00. (a) (b) 00. (c) 0 0 (a) (b) (c) Use the number
Use the space on the page to do your work. Then mark the answer you have chosen. If you change your answer, be sure to erase completely.
 Form B Use the space on the page to do your work. Then mark the answer you have chosen. f you change your answer, be sure to erase completely. 1 Leo drew the shape below. How many sides does the shape
Form B Use the space on the page to do your work. Then mark the answer you have chosen. f you change your answer, be sure to erase completely. 1 Leo drew the shape below. How many sides does the shape
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
8.1 Find Angle Measures in Polygons
 VOCABULARY 8.1 Find Angle Measures in Polygons DIAGONAL Review: EQUILATERAL EQUIANGULAR REGULAR CLASSIFYING POLYGONS Polygon Interior Angle Theorem: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a
VOCABULARY 8.1 Find Angle Measures in Polygons DIAGONAL Review: EQUILATERAL EQUIANGULAR REGULAR CLASSIFYING POLYGONS Polygon Interior Angle Theorem: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a
MAT104: Fundamentals of Mathematics II Introductory Geometry Terminology Summary. Section 11-1: Basic Notions
 MAT104: Fundamentals of Mathematics II Introductory Geometry Terminology Summary Section 11-1: Basic Notions Undefined Terms: Point; Line; Plane Collinear Points: points that lie on the same line Between[-ness]:
MAT104: Fundamentals of Mathematics II Introductory Geometry Terminology Summary Section 11-1: Basic Notions Undefined Terms: Point; Line; Plane Collinear Points: points that lie on the same line Between[-ness]:
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes.
 1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes. A book, a birthday cap and a dice are some examples of 3-D shapes. 1) Write two examples of 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes. A book, a birthday cap and a dice are some examples of 3-D shapes. 1) Write two examples of 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes
Unit 2: Triangles and Polygons
 Unit 2: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about lines and angles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Using the diagram below, answer the following questions. Line
Unit 2: Triangles and Polygons Background for Standard G.CO.9: Prove theorems about lines and angles. Objective: By the end of class, I should Using the diagram below, answer the following questions. Line
The Ultimate Maths Vocabulary List
 The Ultimate Maths Vocabulary List The 96 Words Every Pupil Needs to Know by the End of Year 6 KS1 & KS2 How to Use This Resource An essential building block in pupil s understanding of maths is their
The Ultimate Maths Vocabulary List The 96 Words Every Pupil Needs to Know by the End of Year 6 KS1 & KS2 How to Use This Resource An essential building block in pupil s understanding of maths is their
Reteaching Transversals and Angle Relationships
 Name Date Class Transversals and Angle Relationships INV Transversals A transversal is a line that intersects two or more coplanar lines at different points. Line a is the transversal in the picture to
Name Date Class Transversals and Angle Relationships INV Transversals A transversal is a line that intersects two or more coplanar lines at different points. Line a is the transversal in the picture to
Polygons. Name each polygon Find the sum of the angle measures in each figure
 Practice A Polygons Name each polygon. 1. 2. 3. Find the sum of the angle measures in each figure. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Find the angle measures in each regular polygon. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Give all the
Practice A Polygons Name each polygon. 1. 2. 3. Find the sum of the angle measures in each figure. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Find the angle measures in each regular polygon. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Give all the
MATH GRADE 6. Assessment Anchors & Eligible Content. Pennsylvania Department of Education 2007
 MATH GRADE 6 Assessment Anchors & Eligible Content Pennsylvania Department of Education 2007 M6.A Numbers and Operations M6.A.1 Demonstrate an understanding of numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships
MATH GRADE 6 Assessment Anchors & Eligible Content Pennsylvania Department of Education 2007 M6.A Numbers and Operations M6.A.1 Demonstrate an understanding of numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships
Lesson Polygons
 Lesson 4.1 - Polygons Obj.: classify polygons by their sides. classify quadrilaterals by their attributes. find the sum of the angle measures in a polygon. Decagon - A polygon with ten sides. Dodecagon
Lesson 4.1 - Polygons Obj.: classify polygons by their sides. classify quadrilaterals by their attributes. find the sum of the angle measures in a polygon. Decagon - A polygon with ten sides. Dodecagon
Standard 2.0 Knowledge of Geometry: Students will apply the properties of one-,
 VSC - Mathematics Print pages on legal paper, landscape mode. Grade PK Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Geometry: Students will apply the properties of one-, two-,
VSC - Mathematics Print pages on legal paper, landscape mode. Grade PK Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Geometry: Students will apply the properties of one-, two-,
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
Reporting Category 3. Geometry and Measurement BINGO
 Reporting Category 3 Geometry and Measurement BINGO names an exact location in space, named by a capital letter Has NO width, length, or depth. 2 a straight path with 2 endpoints, has a definite beginning
Reporting Category 3 Geometry and Measurement BINGO names an exact location in space, named by a capital letter Has NO width, length, or depth. 2 a straight path with 2 endpoints, has a definite beginning
For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet.
 Accelerated Review 9: Geometric Relationships Name: For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet. Caleb drew a quadrilateral on his paper. Which of the following
Accelerated Review 9: Geometric Relationships Name: For full credit, show all work. Study all geometry vocabulary words from your chapter packet. Caleb drew a quadrilateral on his paper. Which of the following
Number and Operations - Fractions
 NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
Secondary Math II Honors. Unit 4 Notes. Polygons. Name: Per:
 Secondary Math II Honors Unit 4 Notes Polygons Name: Per: Day 1: Interior and Exterior Angles of a Polygon Unit 4 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors Vocabulary: Polygon: Regular Polygon: Example(s): Discover the
Secondary Math II Honors Unit 4 Notes Polygons Name: Per: Day 1: Interior and Exterior Angles of a Polygon Unit 4 Notes / Secondary 2 Honors Vocabulary: Polygon: Regular Polygon: Example(s): Discover the
AngLegs Activity Cards Written by Laura O Connor & Debra Stoll
 LER 4340/4341/4342 AngLegs Activity Cards Written by Laura O Connor & Debra Stoll Early Elementary (K-2) Polygons Activity 1 Copy Cat Students will identify and create shapes. AngLegs Pencil Paper 1. Use
LER 4340/4341/4342 AngLegs Activity Cards Written by Laura O Connor & Debra Stoll Early Elementary (K-2) Polygons Activity 1 Copy Cat Students will identify and create shapes. AngLegs Pencil Paper 1. Use
3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter Table of Contents Area Area Exploring Area
 Slide 1 / 102 Slide 2 / 102 3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 102 Slide 4 / 102 Table of ontents rea Perimeter lick on a topic to go to that section Lines, Rays and Line
Slide 1 / 102 Slide 2 / 102 3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 102 Slide 4 / 102 Table of ontents rea Perimeter lick on a topic to go to that section Lines, Rays and Line
Go to Grade 5 Everyday Mathematics Sample Lesson
 McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
Geometry. Standardized Practice Have students try the following problem.
 1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
PCTI Geometry. Summer Packet
 PCTI Geometry Summer Packet 2017 1 This packet has been designed to help you review various mathematical topics that will be necessary for your success in Geometry. INSTRUCTIONS: Do all problems without
PCTI Geometry Summer Packet 2017 1 This packet has been designed to help you review various mathematical topics that will be necessary for your success in Geometry. INSTRUCTIONS: Do all problems without
Mathematics Assessment Anchor Glossary Grades 3 & 4
 Mathematics Assessment Anchor Glossary Grades 3 & 4 The definitions for this glossary were taken from one or more of the following sources: Webster s Dictionary, various mathematics dictionaries, the PA
Mathematics Assessment Anchor Glossary Grades 3 & 4 The definitions for this glossary were taken from one or more of the following sources: Webster s Dictionary, various mathematics dictionaries, the PA
Transformations. Working backwards is performing the inverse operation. + - and x 3. Given coordinate rule
 Transformations In geometry we use input/output process when we determine how shapes are altered or moved. Geometric objects can be moved in the coordinate plane using a coordinate rule. These rules can
Transformations In geometry we use input/output process when we determine how shapes are altered or moved. Geometric objects can be moved in the coordinate plane using a coordinate rule. These rules can
UNIT 6 Nets and Surface Area Overhead Slides
 UNIT 6 Nets and Surface Area Overhead Slides Overhead Slides 6.1 Polygons 6.2 Triangles 6.3 Quadrilaterals 6.4 Name that Shape! 6.5 Drawing Parallelograms 6.6 3-D Shapes 6.7 Cuboid 6.8 Prism 6.9 Plan and
UNIT 6 Nets and Surface Area Overhead Slides Overhead Slides 6.1 Polygons 6.2 Triangles 6.3 Quadrilaterals 6.4 Name that Shape! 6.5 Drawing Parallelograms 6.6 3-D Shapes 6.7 Cuboid 6.8 Prism 6.9 Plan and
Choose the correct answer. For 1 3, use the diagram. Which triangle is right and isosceles? Which angle is an acute angle? J L K
 Choose the correct answer. For, use the diagram. Page Which triangle is right and isosceles? Which angle is an acute angle? J L K N Which is a right angle? J L K M Which is an obtuse angle? J L Which triangle
Choose the correct answer. For, use the diagram. Page Which triangle is right and isosceles? Which angle is an acute angle? J L K N Which is a right angle? J L K M Which is an obtuse angle? J L Which triangle
