Constraint Satisfaction Problems
|
|
|
- Phyllis Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Adrian Groza Department of Computer Science Technical University of Cluj-Napoca 12 Nov 2014
2 Outline 1 Constraint Reasoning 2 Systematic Search Methods Improving backtracking efficiency
3 Example Constraints programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has made to the Holy Grail of programming: the user states the problem, the computer solves it. Eugene C. Freuder, Inaugural issue of the Constraints Journal, Place numbers 1 through 8 on nodes 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers
4 Heuristic Search To succeed, try first where you are most likely to fail. Deal with hard cases first: they can only get more difficult if you put them off. Which nodes are hardest to number? Guess a value, but be prepared to backtrack Which are the least constraining values to use? Symmetry means we don t need to consider: 8 1
5 Inference & constraint propagation I 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers We can now eliminate many values for other nodes
6 Inference & constraint propagation II 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers We can now eliminate many values for other nodes
7 Inference & constraint propagation III 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers By simmetry
8 Inference & constraint propagation IV 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers
9 Inference & constraint propagation V 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers By symmetry
10 Inference & constraint propagation VI 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers
11 Inference & constraint propagation VII 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers
12 Inference & constraint propagation VIII 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers And propagate
13 Inference & constraint propagation IX 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers Guess a value, but be prepared to backtrack
14 Inference & constraint propagation X 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers And propagate
15 Inference & constraint propagation XI 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers More propagation?
16 Inference & constraint propagation XII 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers
17 Inference & constraint propagation XIII 1 each number appears exactly once 2 no connected nodes have consecutive numbers A solution
18 Constraint programming methodology 1 Model problem specify in terms of constraints on acceptable solutions: constraint satisfaction problem define/choose constraint model: variables, domains, constraints 2 Solve model define/choose algorithm define/choose heuristics 3 Verify and analyze solution
19 Constraints Properties A logical relation among several unknowns (variables) May specify partial information: X > 2, the circle is inside the square Non-directional: two variables X, Y can be used to infer a constraint on X given a constraint on Y and vice versa: X=Y+2 Declarative: specify what relationship must hold without specifying a computational procedure to enforce that relationship Additive: the order of imposition of constraints does not matter, all that matters, at the end is that the conjunction of constraints is in effect Rarely independent: typically constraints in the constraint store share variables.
20 Constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) A CSP is defined by a set of variables: X, Y, Z,... a domain of values for each variable: X :: {1, 2}, Y :: {1, 2}, Z :: {1, 2} a set of constraints between variables: X = Y, X Z, Y > Z A solution is an assignment of a value to each variable that satisfies the constraints: X = 2, Y = 2, Z = 1 Given a CSP Determine whether it has a solution or not (satisfiability) Find any solution Find all solutions Find an optimal solution, given some cost function
21 Give me some examples Puzzle Map coloring N-queen problem Sudoku Cryptarithmetic problem
22 Constraint Model For Puzzle variables v 1,..., v 8 domains {1,..., 8} constraints v 1 v 2 1 v 1 v 3 1. v 7 v 8 1 alldifferent(v 1,..., v 8 )
23 Constraint Model For Graph Coloring Given k colors, does there exist a coloring of the nodes such that adjacent nodes are assigned different colors variables v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4, v 5 domains {yellow, grey, blue} constraints v i v j if v i and v j are adjacent
24 Constraint Model For N-queens Place n-queens on an n x n board so that no pair of queens attacks each other variables x 1, x 2, x 3, x 4 domains {1, 2, 3, 4} constraints x i x j and x i x j i j a solution x 1 2, x 2 4, x 3 1, x 4 3
25 Modern Art Accident
26 Crypto-arithmetic problem Constraints [S,E,N,D,M,O,R,Y] in 0..9 alldifferent([s,e,n,d,m,o,r,y]) 1000*S + 100*E + 10*N + D+1000*M + 100*O + 10*R + E = 10000*M *O + 100*N + 10*E + Y More Constraints? S 0, M 0 M = 1, S = 9, O = 0, N + R > 10 N = E + 1, E in 2..7 N in 3..8, D, R, Y in 2..8 R in 3..8 N + R = 1E E < 7 R = 8 from N + R > 10, N = E + 1 E in 2..6, N in 3..7
27 Crypto-arithmetic problem E+D = Y+10*C1 C1+N+R = E+10*C2 C2+E+O = N+10*C3 C3+S+M = 10*M+O E,N,D,O,R,Y::{0,..,9} S,M::{1,..,9} C1,C2,C3::{0,1}
28 Send Most Money SEND+MOST=MONEY Money should be maximal
29 Example problem: Job-shop scheduling I Car assembly - 15 tasks: install axles (front and back), affix all four wheels (right and left, front and back), tighten nuts for each wheel, affix hubcaps, and inspect the final assembly, in maximum 30 minutes. Variables X = {Axle F, Axle B, Wheel RF, Wheel LF, Wheel RB, Wheel LB, Nuts RF, Nuts LF, Nuts RB, Nuts LB, Cap RF, Cap LF, Cap RB, Cap LB, Inspect} Precedence constraints: T 1 + d1 T 2 Axles have to be in place before the wheels are put on, and it takes 10 minutes to install an axle, Axle F + 10 WheelRF Axle B + 10 WheelRB Axle F + 10 WheelLF Axle B + 10 WheelLB
30 Example problem: Job-shop scheduling II For each wheel, we must affix the wheel (which takes 1 minute), then tighten the nuts (2 minutes) Wheel RF + 1 Nuts RF Nuts RF + 2 Cap RF Wheel LF + 1 Nuts LF Nuts LF + 2 Cap LF Wheel RB + 1 Nuts RB Nuts RB + 2 Cap RB Wheel LB + 1 Nuts LB Nuts LB + 2 Cap LB 4 our workers to install wheels, but they have to share one tool that helps put the axle in place. Disjunctive constraint to say that Axle F and Axle B must not overlap in time: (Axle F + 10 Axle B ) or (Axle B + 10 Axle F ) The inspection comes last and takes 3 minutes: X, X Inspect, X + d X Inspect All assembly done in 30 minute: D i = {1, 2, 3,..., 27}
31 Alldiff (A1,A2,A3,A4,A5,A6, A7, A8, A9) Alldiff (B1,B2,B3,B4,B5,B6,B7,B8,B9)... Alldiff (A1,B1,C1,D1,E1, F1,G1,H1, I1) Alldiff (A2,B2,C2,D2,E2, F2,G2,H2, I2)... Global constraints Involves an arbitrary number of constraints (but not necessarily all variables).
32 Global constraints At most contraint- resource contraints Let P1,..., P4 numbers of personnel assigned to each of four tasks. No more than 10 personnel are assigned in total: Atmost(10, P1, P2, P3, P4). Assume D = {3, 4, 5, 6} - detect inconsistency by checking the sum of the minimum values of the current domains; Assume D = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6} enforce consistency by deleting the maximum value of any domain if it is not consistent with the minimum values of the other domains Bounds propagation Example (Airline-scheduling problem) Two flights, F 1 and F 2, for which the planes have capacities 165 and 385, respectively: D 1 = [0, 165] and D 2 = [0, 385]. F 1 + F 2 = 420 D 1 = [35, 165] and D 2 = [255, 385]
33 Outline 1 Constraint Reasoning 2 Systematic Search Methods Improving backtracking efficiency
34 Systematic Search Methods Constraints, an Ultimate Anti NP-Hard weapon? Most problems that the constraint programming concerns belong to the group that conventional programming techniques find hardest Example Schedule the loading and unloading of 10 ships using only 5 berths (about 10 million) alternatives in the worst case: 3hours 10 berths and 20 ships: 300 million years No need to explore all alternatives: Some berths are too small for some ships Cannot load two ships in the same berth, at the same time You don t need an optimal schedule: break the problem in two parts - 6 hours
35 Systematic Search Methods Systematic Search Methods exploring the solution space complete and sound Complete- guarantees finding a solution or proving its non-existence Sound- guarantees finding only valid solutions efficiency issues Generate and Test (GT) Backtracking (BT)
36 Systematic Search Methods Systematic Search Methods Problem: X :: {1, 2}, Y :: {1, 2}, Z :: {1, 2}, X = Y, X Z, Y > Z Generate and Test Probably the most general problem solving method Algorithm: 1 generate labelling 2 test satisfaction Drawbacks: blind generator, late Backtracking The basic uninformed algorithm for CSP. Incrementally extends a partial solution towards a complete solution Algorithm: Build a partial solution: a partial consistent assignment Extend consistently the partial solution: one new assigned variable each time
37 Improving backtracking efficiency 1 Which variable should be assigned next? 2 In what order should its values be tried? 3 Can we detect inevitable failure early? 4 Can we take advantage of problem structure?
38 Improving backtracking efficiency Minimum remaining values Choose the variable with the fewest legal values (or most constrained variable or fail-first heuristic)
39 Improving backtracking efficiency Degree heuristic Choose the variable with the most constraints on remaining variables
40 Improving backtracking efficiency Least constraining value Given a variable, choose the least constraining value: the one that rules out the fewest values in the remaining variables Combining these heuristics makes 1000 queens feasible
41 Improving backtracking efficiency Constraint propagation Arc consistency : X Y is consistent iff for every value x of X there is some allowed y
42 Improving backtracking efficiency Constraint propagation Arc consistency : X Y is consistent iff for every value x of X there is some allowed y
43 Improving backtracking efficiency Weaknesses of Backtracking Thrashing: throws away the reason of the conflict Example: A, B, C, D, E :: 1..10, A > E: tries all the assignments for B,C,D before finding that A 1 The chronological backtracking backtracks to the Queen 5 and it finds another column for this queen (column H). However, it is still impossible to place the Queen 6 Solution: backjumping (jump to the source of the failure) The closest queen that can resolve the conflict is Queen 4 because then there is a chance that column D can be used for Queen 6.
44 Improving backtracking efficiency Weaknesses of Bactkracking Redundant Work Unnecessary constraint checks are repeated Even if the conflicting values of variables they are not remembered
45 Improving backtracking efficiency Weaknesses of Backtracking Late detection of conflict Constraint violation is discovered only when the values are known Example: A, B, C, D, E :: 1..10, A = 3 E The fact that A > 2 is discovered when labelling E Solution: forward checking - forward check of constraints
46 Improving backtracking efficiency Forward Checking
47 Improving backtracking efficiency Local Search for CSP
48 Improving backtracking efficiency 1 Which variable should be assigned next? 2 In what order should its values be tried? 3 Can we detect inevitable failure early? 4 Can we take advantage of problem structure?
49 Improving backtracking efficiency
Solving Problems by Searching: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Course 16 :198 :520 : Introduction To Artificial Intelligence Lecture 6 Solving Problems by Searching: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Abdeslam Boularias Wednesday, October 19, 2016 1 / 1 Outline We consider
Course 16 :198 :520 : Introduction To Artificial Intelligence Lecture 6 Solving Problems by Searching: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Abdeslam Boularias Wednesday, October 19, 2016 1 / 1 Outline We consider
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Constraint (Logic) Programming
 Constraint (Logic) Programming Roman Barták Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic bartak@ktiml.mff.cuni.cz Sudoku Combinatorial puzzle, whose goal is to enter
Constraint (Logic) Programming Roman Barták Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic bartak@ktiml.mff.cuni.cz Sudoku Combinatorial puzzle, whose goal is to enter
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CHAPTER 6 CSC 370 SPRING 2013 ALAN C. JAMIESN CSP Backtracking Search Problem Structure and Decomposition Local Search SME SLIDE CNTENT FRM RUSSELL & NRVIG PRVIDED SLIDES
Constraint Satisfaction Problems CHAPTER 6 CSC 370 SPRING 2013 ALAN C. JAMIESN CSP Backtracking Search Problem Structure and Decomposition Local Search SME SLIDE CNTENT FRM RUSSELL & NRVIG PRVIDED SLIDES
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Lecture 18. Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1
 Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Constraint Satisfaction
 Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
 9// CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Chapter 6 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search + Inference 9// 8-queens problem How would you go about deciding where to put
9// CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Chapter 6 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search + Inference 9// 8-queens problem How would you go about deciding where to put
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence. Peter Ljunglöf. 30 January, 2018
 DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
Comments about assign 1. Quick search recap. Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Search uninformed BFS, DFS, IDS. Adversarial search
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS5 David Kauchak Fall 00 http://www.xkcd.com/78/ Some material borrowed from: Sara Owsley Sood and others Comments about assign Grading actually out of 60 check
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS5 David Kauchak Fall 00 http://www.xkcd.com/78/ Some material borrowed from: Sara Owsley Sood and others Comments about assign Grading actually out of 60 check
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
 CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Read Chapter 6.1-6.3, Skim 6.4-6.5 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference (Search + Inference) 1 8-queens problem How would you go about
CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Read Chapter 6.1-6.3, Skim 6.4-6.5 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference (Search + Inference) 1 8-queens problem How would you go about
Admin. Quick search recap. Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)! Intro Example: 8-Queens. Where should I put the queens in columns 3 and 4?
 Admin Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)! CS David Kauchak Spring 0 Final project comments: Use preexisting code Get your data now! Use preexisting data sets Finding good references Google scholar
Admin Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)! CS David Kauchak Spring 0 Final project comments: Use preexisting code Get your data now! Use preexisting data sets Finding good references Google scholar
What is Search For? CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Announcements. Homework 4. Project 3. Due tonight at 11:59pm. Due 3/8 at 4:00pm
 Announcements Homework 4 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 3 Due 3/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Instructor: Stuart Russell & Sergey Levine, University of California,
Announcements Homework 4 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 3 Due 3/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Instructor: Stuart Russell & Sergey Levine, University of California,
What is Search For? CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence. Example: N-Queens. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring 4/7/17
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Dieter Fox What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning: sequences
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Dieter Fox What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning: sequences
Announcements. Homework 1: Search. Project 1: Search. Midterm date and time has been set:
 Announcements Homework 1: Search Has been released! Due Monday, 2/1, at 11:59pm. On edx online, instant grading, submit as often as you like. Project 1: Search Has been released! Due Friday 2/5 at 5pm.
Announcements Homework 1: Search Has been released! Due Monday, 2/1, at 11:59pm. On edx online, instant grading, submit as often as you like. Project 1: Search Has been released! Due Friday 2/5 at 5pm.
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A constraint satisfaction problem consists of three components, X, D, and C: X is a set of variables, {X 1,..., X n }. D is a
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A constraint satisfaction problem consists of three components, X, D, and C: X is a set of variables, {X 1,..., X n }. D is a
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Thursday: Chapter 8
 Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Space of Search Strategies. CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction. Recap: Search Problem. Example: Map-Coloring 11/30/2012
 /0/0 CSE 57: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Space of Search Strategies Blind Search DFS, BFS,
/0/0 CSE 57: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Space of Search Strategies Blind Search DFS, BFS,
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. What is Search For? Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
Example: Map-Coloring. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Australia. Example: Map-Coloring contd. Outline. Constraint graph
 Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Constraint Programming
 Constraint In Pursuit of The Holly Grail Roman Barták Charles University in Prague Constraint programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has yet made to the Holy Grail of programming:
Constraint In Pursuit of The Holly Grail Roman Barták Charles University in Prague Constraint programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has yet made to the Holy Grail of programming:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming
 Outline DM87 SCHEDULING, TIMETABLING AND ROUTING Lecture 3 Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming 1. Special Purpose Algorithms 2. Constraint Programming Marco Chiarandini DM87 Scheduling,
Outline DM87 SCHEDULING, TIMETABLING AND ROUTING Lecture 3 Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming 1. Special Purpose Algorithms 2. Constraint Programming Marco Chiarandini DM87 Scheduling,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
10/11/2017. Constraint Satisfaction Problems II. Review: CSP Representations. Heuristic 1: Most constrained variable
 //7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
//7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
Today. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP 3501 / COMP Lecture 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) CSP Definition
 Today COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 5 Finish up 2-player games Discuss homework Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. JGH 318 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) CSP s are our first work on factored
Today COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 5 Finish up 2-player games Discuss homework Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. JGH 318 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) CSP s are our first work on factored
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides)
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides) Constraint satisfaction problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables V, V 2,, V n Nonempty domain of possible values for
Constraint Satisfaction Problems A Quick Overview (based on AIMA book slides) Constraint satisfaction problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables V, V 2,, V n Nonempty domain of possible values for
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today. Example: Map-Coloring. Example: Cryptarithmetic.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 5: CSPs II 2/2/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 1 due Thursday Lecture videos reminder: don t count on
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 5: CSPs II 2/2/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 1 due Thursday Lecture videos reminder: don t count on
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Recap: Search
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4 and 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Recap: Search Search problem: States (configurations of the
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4 and 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Recap: Search Search problem: States (configurations of the
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
General Methods and Search Algorithms
 DM811 HEURISTICS AND LOCAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS FOR COMBINATORIAL OPTIMZATION Lecture 3 General Methods and Search Algorithms Marco Chiarandini 2 Methods and Algorithms A Method is a general framework for
DM811 HEURISTICS AND LOCAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS FOR COMBINATORIAL OPTIMZATION Lecture 3 General Methods and Search Algorithms Marco Chiarandini 2 Methods and Algorithms A Method is a general framework for
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problem
 CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problem Constraint Satisfaction Problems So far we have seen a problem can be solved by searching in space of states These states can be evaluated
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problem Constraint Satisfaction Problems So far we have seen a problem can be solved by searching in space of states These states can be evaluated
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
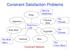 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Australia Western Australia Western Territory Northern Territory Northern Australia South Australia South Tasmania Queensland Tasmania Victoria
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Example: Map coloring
 Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
CS 4100/5100: Foundations of AI
 CS 4100/5100: Foundations of AI Constraint satisfaction problems 1 Instructor: Rob Platt r.platt@neu.edu College of Computer and information Science Northeastern University September 5, 2013 1 These notes
CS 4100/5100: Foundations of AI Constraint satisfaction problems 1 Instructor: Rob Platt r.platt@neu.edu College of Computer and information Science Northeastern University September 5, 2013 1 These notes
Constraint Satisfaction. AI Slides (5e) c Lin
 Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence
 CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2013 Chapter 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Jonathan Voris (based on slides by Sal Stolfo) Assignment 3 Go Encircling Game Ancient Chinese game Dates back At
CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2013 Chapter 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Jonathan Voris (based on slides by Sal Stolfo) Assignment 3 Go Encircling Game Ancient Chinese game Dates back At
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence
 CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Large Scale: Problems with A* What is Search For? Example: N-Queens
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 COMP3411/ 9414/ 9814: Artificial Intelligence Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems [Russell & Norvig: 6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,4.1] COMP3411/9414/9814 18s1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems 1 Outline Constraint
COMP3411/ 9414/ 9814: Artificial Intelligence Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems [Russell & Norvig: 6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,4.1] COMP3411/9414/9814 18s1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems 1 Outline Constraint
3rd CHR Summer School Topics: Introduction to Constraint Programming
 3rd CHR Summer School Topics: Introduction to Constraint Programming Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher 8.7.2013 c S.Abdennadher 1 Constraint Programming: Much Quoted Sentence Constraint Programming represents
3rd CHR Summer School Topics: Introduction to Constraint Programming Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher 8.7.2013 c S.Abdennadher 1 Constraint Programming: Much Quoted Sentence Constraint Programming represents
Recap: Search Problem. CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence. Space of Search Strategies. Constraint Satisfaction. Example: N-Queens 4/9/2012
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Recap: Search Problem States configurations of the world
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Recap: Search Problem States configurations of the world
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
 CONSRAI ISFACION oday Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search 1 8-queens problem Exploit the constraints Constraint Satisfaction Problems Advantages of CSPs Use general-purpose
CONSRAI ISFACION oday Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search 1 8-queens problem Exploit the constraints Constraint Satisfaction Problems Advantages of CSPs Use general-purpose
Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.3)
 Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.) Some slides adapted from Richard Lathrop, USC/ISI, CS 7 Review: The Minimax Rule Idea: Make the best move for MAX assuming that MIN always replies
Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.) Some slides adapted from Richard Lathrop, USC/ISI, CS 7 Review: The Minimax Rule Idea: Make the best move for MAX assuming that MIN always replies
Constraint Satisfaction. CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Constraint Satisfaction CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 1 Outline What are Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)? Standard Search and CSPs Improvements Backtracking Backtracking +
Constraint Satisfaction CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 1 Outline What are Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)? Standard Search and CSPs Improvements Backtracking Backtracking +
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
Constraint satisfaction problems. CS171, Winter 2018 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Richard Lathrop
 Constraint satisfaction problems CS171, Winter 2018 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Richard Lathrop Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables, X 1, X 2,, X n
Constraint satisfaction problems CS171, Winter 2018 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Richard Lathrop Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables, X 1, X 2,, X n
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/7/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Reminder: Project
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/7/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Reminder: Project
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Introduction and Backtracking Search
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Introduction and Backtracking Search This lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 6.1 6.4, except 6.3.3 Next lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 7.1 7.5 (Please read
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Introduction and Backtracking Search This lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 6.1 6.4, except 6.3.3 Next lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 7.1 7.5 (Please read
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Robert Platt Northeastern University Some images and slides are used from: 1. AIMA What is a CSP? The space of all search problems states and actions are atomic goals are
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Robert Platt Northeastern University Some images and slides are used from: 1. AIMA What is a CSP? The space of all search problems states and actions are atomic goals are
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] What is Search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] What is Search
Material. Thought Question. Outline For Today. Example: Map-Coloring EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS
 EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 6, 4/20/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Material Read all of chapter
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 6, 4/20/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Material Read all of chapter
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 4: A* wrap-up + Constraint Satisfaction 1/28/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 0 (Python tutorial) is due
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 4: A* wrap-up + Constraint Satisfaction 1/28/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 0 (Python tutorial) is due
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D)
 Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today. A* Review. Consistency. A* Graph Search Gone Wrong
 CS 88: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction /29/2009 John DeNero UC Berkeley Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements The Python tutorial
CS 88: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction /29/2009 John DeNero UC Berkeley Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements The Python tutorial
Artificial Intelligence
 Contents Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller What
Contents Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller What
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller SA-1 Contents
Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller SA-1 Contents
Constraint Satisfaction
 Constraint Satisfaction Reading: Russell & Norvig Chapter 5, Kumar, Algorithms for constraint satisfaction problems: A survey SEND + MORE = MONEY Assign distinct digits to the letters S, E, N, D, M, O,
Constraint Satisfaction Reading: Russell & Norvig Chapter 5, Kumar, Algorithms for constraint satisfaction problems: A survey SEND + MORE = MONEY Assign distinct digits to the letters S, E, N, D, M, O,
Announcements. Reminder: CSPs. Today. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
6.034 Notes: Section 3.1
 6.034 Notes: Section 3.1 Slide 3.1.1 In this presentation, we'll take a look at the class of problems called Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs). CSPs arise in many application areas: they can be used
6.034 Notes: Section 3.1 Slide 3.1.1 In this presentation, we'll take a look at the class of problems called Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs). CSPs arise in many application areas: they can be used
Map Colouring. Constraint Satisfaction. Map Colouring. Constraint Satisfaction
 Constraint Satisfaction Jacky Baltes Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Email: jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca WWW: http://www4.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky/teaching/cour ses/comp_4190- ArtificialIntelligence/current/index.php
Constraint Satisfaction Jacky Baltes Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Email: jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca WWW: http://www4.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky/teaching/cour ses/comp_4190- ArtificialIntelligence/current/index.php
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems. Maria Simi
 AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior
 PART III: Search Outline Depth-first Search Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior Best-First Search
PART III: Search Outline Depth-first Search Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior Best-First Search
CS 730/730W/830: Intro AI
 CS 730/730W/830: Intro AI 1 handout: slides asst 1 milestone was due Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 1 / 19 EOLQs Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 2 / 19 Comparison Heuristics Search Algorithms
CS 730/730W/830: Intro AI 1 handout: slides asst 1 milestone was due Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 1 / 19 EOLQs Wheeler Ruml (UNH) Lecture 4, CS 730 2 / 19 Comparison Heuristics Search Algorithms
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence. Peter Ljunglöf. 6 February, 2018
 DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapters 5, 7: Search part IV, and CSP, part II CHAPTERS 5, 7: SEARCH PART IV, AND CSP, PART II DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 6 February,
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapters 5, 7: Search part IV, and CSP, part II CHAPTERS 5, 7: SEARCH PART IV, AND CSP, PART II DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 6 February,
Lars Schmidt-Thieme, Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL), University of Hildesheim, Germany, Course on Artificial Intelligence,
 Course on Artificial Intelligence, winter term 2012/2013 0/35 Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence 3. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning
Course on Artificial Intelligence, winter term 2012/2013 0/35 Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence 3. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning
Set 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Set 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems ICS 271 Fall 2014 Kalev Kask ICS-271:Notes 5: 1 The constraint network model Outline Variables, domains, constraints, constraint graph, solutions Examples: graph-coloring,
Set 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems ICS 271 Fall 2014 Kalev Kask ICS-271:Notes 5: 1 The constraint network model Outline Variables, domains, constraints, constraint graph, solutions Examples: graph-coloring,
Constraint Programming
 Constraint Programming - An overview Examples, Satisfaction vs. Optimization Different Domains Constraint Propagation» Kinds of Consistencies Global Constraints Heuristics Symmetries 7 November 0 Advanced
Constraint Programming - An overview Examples, Satisfaction vs. Optimization Different Domains Constraint Propagation» Kinds of Consistencies Global Constraints Heuristics Symmetries 7 November 0 Advanced
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Inference The core topic of the following lectures
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Inference The core topic of the following lectures
What is Search For? CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Example: Map Coloring. Example: N-Queens. Example: N-Queens. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
Module 4. Constraint satisfaction problems. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Constraint satisfaction problems Lesson 10 Constraint satisfaction problems - II 4.5 Variable and Value Ordering A search algorithm for constraint satisfaction requires the order in which variables
Module 4 Constraint satisfaction problems Lesson 10 Constraint satisfaction problems - II 4.5 Variable and Value Ordering A search algorithm for constraint satisfaction requires the order in which variables
CMU-Q Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro AI PLANNING APPROACHES SO FAR Goal: Find the (best) sequence of actions that take
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro AI PLANNING APPROACHES SO FAR Goal: Find the (best) sequence of actions that take
What is Search For? CS 188: Ar)ficial Intelligence. Constraint Sa)sfac)on Problems Sep 14, 2015
 CS 188: Ar)ficial Intelligence Constraint Sa)sfac)on Problems Sep 14, 2015 What is Search For? Assump)ons about the world: a single agent, determinis)c ac)ons, fully observed state, discrete state space
CS 188: Ar)ficial Intelligence Constraint Sa)sfac)on Problems Sep 14, 2015 What is Search For? Assump)ons about the world: a single agent, determinis)c ac)ons, fully observed state, discrete state space
6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions
 6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions Open Book, Open Notes 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical
6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions Open Book, Open Notes 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical
Constraint satisfaction search
 CS 70 Foundations of AI Lecture 6 Constraint satisfaction search Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Search problem A search problem: Search space (or state space): a set of objects among
CS 70 Foundations of AI Lecture 6 Constraint satisfaction search Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Search problem A search problem: Search space (or state space): a set of objects among
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Tuomas Sandholm Carnegie Mellon University Computer Science Department [Read Chapter 6 of Russell & Norvig] Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search problem:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Tuomas Sandholm Carnegie Mellon University Computer Science Department [Read Chapter 6 of Russell & Norvig] Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) Standard search problem:
Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search.
 CS 1571 Introduction to AI Lecture 8 Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) Objective:
CS 1571 Introduction to AI Lecture 8 Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) Objective:
1 Tree Search (12 points)
 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical order when no other order is specified by the search,
1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical order when no other order is specified by the search,
Solving Minesweeper Using CSP
 Solving Minesweeper Using CSP AI Course Final Project Gil & Chai Usage (After using Makefile) java player/aiplayer
Solving Minesweeper Using CSP AI Course Final Project Gil & Chai Usage (After using Makefile) java player/aiplayer
