11 Behavioural Animation. Chapter 11. Behavioural Animation. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 11-1
|
|
|
- Stuart O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 11 Behavioural Animation 11-1
2 Behavioral Animation Knowing the environment Aggregate behavior Primitive behavior Intelligent behavior Crowd management 11-2
3 Behavioral Animation 11-3
4 Knowing the environment Vision what do you know about the present Memory what is recorded about the environment More about AI than graphics 11-4
5 Vision Geometric issue what s in sight? OR Can I see X? Computation v. accuracy Perceptual issue what do you see? Cognitive modeling necessary? At what level? 11-5
6 Omniscience Everything in database is known 11-6
7 FOV Vision Use surrogate bounding volumes, or sample points 11-7
8 Occluded Vision ray casting sample environment z-buffer use object IDs as color Use surrogate bounding volumes 11-8
9 Target-testing vision Can I see X? Cast ray Sample object Use surrogate bounding volumes 11-9
10 Object Recognition Cognitive modeling How much and what part is needed? Application need? Not yet addressed in literature More AI than graphics 11-10
11 Other senses? Hearing? Smell? Model sensors & signal propagation Spatial occupancy approach? Applications? 11-11
12 Memory What is recorded about the environment Spatial occupancy Transience of objects: time-stamps hierarchy: short-term, long-term 11-12
13 wall Spatial Occupancy transiency doorway doorway 11-13
14 Aggregate Behavior: E pluribus unum Emergent Behavior Typical qualities Type Elements Physics Intelligence Env/Others Particles Much/none None Flocking Some/some Limited Crowds Little/much Little-much 11-14
15 Primitive Behavior - Flocking Local control for realism, the flock member only reacts to locally accessible information Perception FOV vision angle can change with speed Interacting with other members stay with friends, avoid bumping into each other Interacting with the environment collision avoidance is primary 11-15
16 Primitive Behavior - Flocking Original work by Craig Reynolds Global control need control of flock script flock leader global migratory urge Negotiating the motion Collision avoidance steer to avoid Splitting and rejoining difficult to tune parameters Modeling flight e.g., banking into turns 11-16
17 Negotiating the Motion Forces Or Reasoning (e.g. rule-based) 11-17
18 Navigating Obstacles Problems with repulsive forces 11-18
19 Navigating using bounding sphere 11-19
20 Navigating Testing for being on a collision path with (bounding) sphere Given: P, V, C, r k ( C P ) V V s C P t s 2 k 2 t r 11-20
21 11-21 Finding closest non-colliding point sw U t P C P B U V U U V U W P C P C U t r s P C P C r k t t t P C P C t r k t P C s k t s r r P C k ) ( 2 2 ) ( Calculate s,t
22 Navigating finding a pass Vision Options: Render in z-buffer Sample environments with rays 11-22
23 Modeling Flight common in flocking 11-23
24 Modeling Flight 11-24
25 Modeling Flight 11-25
26 Modeling Flight 11-26
27 Primitive Behavior - Prey-Predator unbalanced abilities vision - distance, movement, fov maximum velocity maximum acceleration maximum angular velocity maximum angular acceleration 11-27
28 Prey-Predator - vision 11-28
29 Prey-Predator agility: speed and turning 11-29
30 Prey-Predator hidden by forces Using pure forces May not prevent object penetration Prey can be hidden by environmental repulsive forces 11-30
31 Intelligent Behavior Autonomous behavior Self-animated characters Perception & reasoning about environment Personality, emotions, dispositions Manifestations of Individuality Body Expressions and Gestures Facial expressions Speech 11-31
32 Internal State Models what the agent needs to do Suggested precedence classes of internal state variables Imperatives Desires Suggestions 11-32
33 Levels of Behavior Arbitration among competing intentions Hooks for the animator to impose control 11-33
34 Expressions and Gestures ToBI Tones and Break Indices LMA Laban Movement Analysis BEAT EMOTE RUTH Greta 11-34
35 EMOTE N. Badler at U.Penn Speech driven movement and gestures Torso & arms Laban Movement Analysis Effort Shape 11-35
36 BEAT J. Cassell at M.I.T. Input text marked up Generate non-verbal behavior in sync with speech Facial expressions, head & body motions gestures 11-36
37 Modeling Personality Personality long term qualities Emotions short term Mood third level Basic emotions: happy, sad, fear, disgust, surprise, anger 11-37
38 Personality Models Biology/evolutionary approaches brain & anatomy biochemistry & personality genetics & personality Psychoanalytic approach psychometrics Freud, Adler, Jung Adaptation Theory: traits: passive, aggressive, withdrawn Need theory: Freud + experiential learning Arousal Theory: absorb & discharge energy 11-38
39 Type & Trait Theory Type: individuals slotted into a type e.g. introvert v. extrovert Trait: lie on gradation combination defines behavior in situation e.g., Internal states: how perceptions dictate emotional experience 11-39
40 Trait Theory OCEAN: openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, neuroticism PEN: extraversion, neuroticism, psychoticism OCC: how perceptions dictate emotional experience 11-40
41 Modeling Individuality Improv AlphaWolf 11-41
42 Crowd Management Emergent behavior Statistical behavior v. believable individual behaviors Homogeneous activity v. Internal structure For evaluation Pedestrian traffic simulation Traffic flow Emergency response modeling For entertainment Background crowds 11-42
43 Crowds Emergent behavior: similar to flocking collision avoidance intelligent paths From a distance: statistical behavior nonsensical detailed motion reasonable visual effect Internal structure limited interaction among members group formation 11-43
44 Crowd Applications For evaluation Building evacuation, e.g. virtual fire drill Architecture evaluation, e.g. signage For training Military scenarios, e.g. sniper training Emergency response, e.g. disaster response For entertainment: e.g., background crowds games films, e.g., Titanic, Saving Private Ryan, Lord of the Ringss 11-44
45 Qualities of crowd Emergent behavior - similar to flocking, flocking system Uniform sameness of members Quantity & density - average distance between members Viewing distance aggregate behavior, inspect individuals Function simple traversal, background activity, main actions Individual processing amount of computation per member Physics simulated reaction to environment Intelligence - reasoning capability - agents 11-45
46 Uniformity, granularity Background noise: Activity without intention Statistical behavior: On average, intentional activity Individuality: Believable activity at level of individual 11-46
47 Execution environment Real-time v. Off-line computation simple computations avoid n-squared algorithms size limited 11-47
48 Spatial organization Cellular decomposition: Regular 2D grid Adjacency accessible Density limited Cells define obstructions Continuous space: Step in any direction Need to decipher obstructions Perception needed 11-48
49 Perception Modeling Vision Memory Knowledge of environment 11-49
50 Navigation Fluid flow: density fields, potential functions Particle systems: Individual navigation Flocking systems: individual perception, navigation Rule-based Cognitive modeling Cellular automata 11-50
51 Panic & Congestion handling Personal space Packing people during evacuation Stairwell traversal Exit awareness 11-51
52 Motion & Navigation Path planning Roadmaps Passing on pathways Potential fields Forming & maintaining subgroups 11-52
53 Structure in crowds Homogenous no individuality Subgroups Group by belief systems A collection of Individuals personality modeling 11-53
54 Penn Station See animations 11-54
55 Other topics Heterogeneous pedestrians and cars Data driven crowds image processing Comparison to real-world situations 11-55
56 Massive Commercial de facto standard See animation 11-56
Particle Systems. Typical Time Step. Particle Generation. Controlling Groups of Objects: Particle Systems. Flocks and Schools
 Particle Systems Controlling Groups of Objects: Particle Systems Flocks and Schools A complex, fuzzy system represented by a large collection of individual elements. Each element has simple behavior and
Particle Systems Controlling Groups of Objects: Particle Systems Flocks and Schools A complex, fuzzy system represented by a large collection of individual elements. Each element has simple behavior and
CS 231. Crowd Simulation. Outline. Introduction to Crowd Simulation. Flocking Social Forces 2D Cellular Automaton Continuum Crowds
 CS 231 Crowd Simulation Outline Introduction to Crowd Simulation Fields of Study & Applications Visualization vs. Realism Microscopic vs. Macroscopic Flocking Social Forces 2D Cellular Automaton Continuum
CS 231 Crowd Simulation Outline Introduction to Crowd Simulation Fields of Study & Applications Visualization vs. Realism Microscopic vs. Macroscopic Flocking Social Forces 2D Cellular Automaton Continuum
GPU-based Distributed Behavior Models with CUDA
 GPU-based Distributed Behavior Models with CUDA Courtesy: YouTube, ISIS Lab, Universita degli Studi di Salerno Bradly Alicea Introduction Flocking: Reynolds boids algorithm. * models simple local behaviors
GPU-based Distributed Behavior Models with CUDA Courtesy: YouTube, ISIS Lab, Universita degli Studi di Salerno Bradly Alicea Introduction Flocking: Reynolds boids algorithm. * models simple local behaviors
CS 378: Computer Game Technology
 CS 378: Computer Game Technology Dynamic Path Planning, Flocking Spring 2012 University of Texas at Austin CS 378 Game Technology Don Fussell Dynamic Path Planning! What happens when the environment changes
CS 378: Computer Game Technology Dynamic Path Planning, Flocking Spring 2012 University of Texas at Austin CS 378 Game Technology Don Fussell Dynamic Path Planning! What happens when the environment changes
Collision Avoidance with Unity3d
 Collision Avoidance with Unity3d Jassiem Ifill September 12, 2013 Abstract The primary goal of the research presented in this paper is to achieve natural crowd simulation and collision avoidance within
Collision Avoidance with Unity3d Jassiem Ifill September 12, 2013 Abstract The primary goal of the research presented in this paper is to achieve natural crowd simulation and collision avoidance within
Affective Embodied Conversational Agents. Summary of programme Affect and Personality in Interaction with Ubiquitous Systems.
 Summary of programme Affect and Personality in Interaction with Ubiquitous Systems speech, language, gesture, facial expressions, music, colour Professor Ruth Aylett Vision Interactive Systems & Graphical
Summary of programme Affect and Personality in Interaction with Ubiquitous Systems speech, language, gesture, facial expressions, music, colour Professor Ruth Aylett Vision Interactive Systems & Graphical
Traffic/Flocking/Crowd AI. Gregory Miranda
 Traffic/Flocking/Crowd AI Gregory Miranda Introduction What is Flocking? Coordinated animal motion such as bird flocks and fish schools Initially described by Craig Reynolds Created boids in 1986, generic
Traffic/Flocking/Crowd AI Gregory Miranda Introduction What is Flocking? Coordinated animal motion such as bird flocks and fish schools Initially described by Craig Reynolds Created boids in 1986, generic
Under the Guidance of
 Presented by Linga Venkatesh (10305085) Deepak Jayanth (10305913) Under the Guidance of Prof. Parag Chaudhuri Flocking/Swarming/Schooling Nature Phenomenon Collective Behaviour by animals of same size
Presented by Linga Venkatesh (10305085) Deepak Jayanth (10305913) Under the Guidance of Prof. Parag Chaudhuri Flocking/Swarming/Schooling Nature Phenomenon Collective Behaviour by animals of same size
Behavioral Animation in Crowd Simulation. Ying Wei
 Behavioral Animation in Crowd Simulation Ying Wei Goal Realistic movement: Emergence of crowd behaviors consistent with real-observed crowds Collision avoidance and response Perception, navigation, learning,
Behavioral Animation in Crowd Simulation Ying Wei Goal Realistic movement: Emergence of crowd behaviors consistent with real-observed crowds Collision avoidance and response Perception, navigation, learning,
12 - More Steering. from Milligan, "Artificial Intelligence for Games", Morgan Kaufman, 2006
 12 - More Steering from Milligan, "Artificial Intelligence for Games", Morgan Kaufman, 2006 Separation commonly used in crowds, when all characters moving in roughly the same direction (repulsion steering)
12 - More Steering from Milligan, "Artificial Intelligence for Games", Morgan Kaufman, 2006 Separation commonly used in crowds, when all characters moving in roughly the same direction (repulsion steering)
AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO F ^ k.^
 Computer a jap Animation Algorithms and Techniques Second Edition Rick Parent Ohio State University AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO
Computer a jap Animation Algorithms and Techniques Second Edition Rick Parent Ohio State University AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO
Crowd simulation influenced by agent s sociopsychological
 HTTPS://SITES.GOOGLE.COM/SITE/JOURNALOFCOMPUTING/ Crowd simulation influenced by agent s sociopsychological state F. Cherif, and R. Chighoub 48 Abstract The aim our work is to create virtual humans as
HTTPS://SITES.GOOGLE.COM/SITE/JOURNALOFCOMPUTING/ Crowd simulation influenced by agent s sociopsychological state F. Cherif, and R. Chighoub 48 Abstract The aim our work is to create virtual humans as
Autonomous Mobile Robots, Chapter 6 Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there? Localization. Cognition. Real World Environment
 Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there?? Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Perception Real World Environment Path Motion Control Competencies
Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there?? Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Perception Real World Environment Path Motion Control Competencies
AUTONOMOUS TAWAF CROWD SIMULATION. Ahmad Zakwan Azizul Fata, Mohd Shafry Mohd Rahim, Sarudin Kari
 BORNEO SCIENCE 36 (2): SEPTEMBER 2015 AUTONOMOUS TAWAF CROWD SIMULATION Ahmad Zakwan Azizul Fata, Mohd Shafry Mohd Rahim, Sarudin Kari MaGIC-X (Media and Games Innonovation Centre of Excellence UTM-IRDA
BORNEO SCIENCE 36 (2): SEPTEMBER 2015 AUTONOMOUS TAWAF CROWD SIMULATION Ahmad Zakwan Azizul Fata, Mohd Shafry Mohd Rahim, Sarudin Kari MaGIC-X (Media and Games Innonovation Centre of Excellence UTM-IRDA
Robot-Assisted Crowd Evacuation under Emergency Situations: A Survey
 robotics Article Robot-Assisted Crowd Evacuation under Emergency Situations: A Survey Ibraheem Sakour * and Huosheng Hu School of Computer and Electronic Engineering, University of Essex, Colchester CO4
robotics Article Robot-Assisted Crowd Evacuation under Emergency Situations: A Survey Ibraheem Sakour * and Huosheng Hu School of Computer and Electronic Engineering, University of Essex, Colchester CO4
PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED PLATFORM FOR PLUG-AND-PLAY AGENT-BASED SIMULATIONS. Wentong CAI
 PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED PLATFORM FOR PLUG-AND-PLAY AGENT-BASED SIMULATIONS Wentong CAI Parallel & Distributed Computing Centre School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore
PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED PLATFORM FOR PLUG-AND-PLAY AGENT-BASED SIMULATIONS Wentong CAI Parallel & Distributed Computing Centre School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore
Efficient Crowd Simulation for Mobile Games
 24 Efficient Crowd Simulation for Mobile Games Graham Pentheny 24.1 Introduction 24.2 Grid 24.3 Flow Field 24.4 Generating the Flow Field 24.5 Units 24.6 Adjusting Unit Movement Values 24.7 Mobile Limitations
24 Efficient Crowd Simulation for Mobile Games Graham Pentheny 24.1 Introduction 24.2 Grid 24.3 Flow Field 24.4 Generating the Flow Field 24.5 Units 24.6 Adjusting Unit Movement Values 24.7 Mobile Limitations
Crowd simulation. Taku Komura
 Crowd simulation Taku Komura Animating Crowds We have been going through methods to simulate individual characters What if we want to simulate the movement of crowds? Pedestrians in the streets Flock of
Crowd simulation Taku Komura Animating Crowds We have been going through methods to simulate individual characters What if we want to simulate the movement of crowds? Pedestrians in the streets Flock of
Crowd simulation of pedestrians in a virtual city
 Crowd simulation of pedestrians in a virtual city Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of the degree Bachelor of Science (Honours) of Rhodes University Flora Ponjou Tasse November 3, 2008
Crowd simulation of pedestrians in a virtual city Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of the degree Bachelor of Science (Honours) of Rhodes University Flora Ponjou Tasse November 3, 2008
Real-time Talking Head Driven by Voice and its Application to Communication and Entertainment
 ISCA Archive Real-time Talking Head Driven by Voice and its Application to Communication and Entertainment Shigeo MORISHIMA Seikei University ABSTRACT Recently computer can make cyberspace to walk through
ISCA Archive Real-time Talking Head Driven by Voice and its Application to Communication and Entertainment Shigeo MORISHIMA Seikei University ABSTRACT Recently computer can make cyberspace to walk through
Topics in Computer Animation
 Topics in Computer Animation Animation Techniques Artist Driven animation The artist draws some frames (keyframing) Usually in 2D The computer generates intermediate frames using interpolation The old
Topics in Computer Animation Animation Techniques Artist Driven animation The artist draws some frames (keyframing) Usually in 2D The computer generates intermediate frames using interpolation The old
Sketch-based Interface for Crowd Animation
 Sketch-based Interface for Crowd Animation Masaki Oshita 1, Yusuke Ogiwara 1 1 Kyushu Institute of Technology 680-4 Kawazu, Iizuka, Fukuoka, 820-8502, Japan oshita@ces.kyutech.ac.p ogiwara@cg.ces.kyutech.ac.p
Sketch-based Interface for Crowd Animation Masaki Oshita 1, Yusuke Ogiwara 1 1 Kyushu Institute of Technology 680-4 Kawazu, Iizuka, Fukuoka, 820-8502, Japan oshita@ces.kyutech.ac.p ogiwara@cg.ces.kyutech.ac.p
Real-time Crowd Movement On Large Scale Terrains
 Real-time Crowd Movement On Large Scale Terrains Wen Tang, Tao Ruan Wan* and Sanket Patel School of Computing and Mathematics, University of Teesside, Middlesbrough, United Kingdom E-mail: w.tang@tees.ac.uk
Real-time Crowd Movement On Large Scale Terrains Wen Tang, Tao Ruan Wan* and Sanket Patel School of Computing and Mathematics, University of Teesside, Middlesbrough, United Kingdom E-mail: w.tang@tees.ac.uk
Real-time Simulation and Rendering of Large-scale Crowd Motion
 Real-time Simulation and Rendering of Large-scale Crowd Motion A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Department of Computer Science by Bo Li
Real-time Simulation and Rendering of Large-scale Crowd Motion A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Department of Computer Science by Bo Li
Graphs, Search, Pathfinding (behavior involving where to go) Steering, Flocking, Formations (behavior involving how to go)
 Graphs, Search, Pathfinding (behavior involving where to go) Steering, Flocking, Formations (behavior involving how to go) Class N-2 1. What are some benefits of path networks? 2. Cons of path networks?
Graphs, Search, Pathfinding (behavior involving where to go) Steering, Flocking, Formations (behavior involving how to go) Class N-2 1. What are some benefits of path networks? 2. Cons of path networks?
STEERING BEHAVIORS MOTIVATION REQUIREMENTS FOR MOTION CONTROL MOTIVATION BOIDS & FLOCKING MODEL STEERING BEHAVIORS - BASICS
 Přednáška byla podpořena v rámci projektu OPPA CZ.2.17/3.1.00/33274 financovaného Evropským sociálním fondem a rozpočtem hlavního města Prahy. Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: investujeme do Vaší budoucnosti
Přednáška byla podpořena v rámci projektu OPPA CZ.2.17/3.1.00/33274 financovaného Evropským sociálním fondem a rozpočtem hlavního města Prahy. Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: investujeme do Vaší budoucnosti
Simulation: Particle Systems
 Simulation: Particle Systems Course web page: http://goo.gl/eb3aa February 28, 2012 Lecture 5 Particle Systems Definition: Simulation of a set of similar, moving agents in a larger environment Scale usually
Simulation: Particle Systems Course web page: http://goo.gl/eb3aa February 28, 2012 Lecture 5 Particle Systems Definition: Simulation of a set of similar, moving agents in a larger environment Scale usually
Agents and Avatars 2. Ruth Aylett
 Agents and Avatars 2 Ruth Aylett Overview- Crowds Speech and Expressive behaviour Embodied conversational characters Creating autonomy Scripting Architectures Crowds and flocking Interactions among members
Agents and Avatars 2 Ruth Aylett Overview- Crowds Speech and Expressive behaviour Embodied conversational characters Creating autonomy Scripting Architectures Crowds and flocking Interactions among members
STEERING BEHAVIORS. Markéta Popelová, marketa.popelova [zavináč] matfyz.cz. 2012, Umělé Bytosti, MFF UK
![STEERING BEHAVIORS. Markéta Popelová, marketa.popelova [zavináč] matfyz.cz. 2012, Umělé Bytosti, MFF UK STEERING BEHAVIORS. Markéta Popelová, marketa.popelova [zavináč] matfyz.cz. 2012, Umělé Bytosti, MFF UK](/thumbs/74/70541553.jpg) STEERING BEHAVIORS Markéta Popelová, marketa.popelova [zavináč] matfyz.cz 2012, Umělé Bytosti, MFF UK MOTIVATION MOTIVATION REQUIREMENTS FOR MOTION CONTROL Responding to dynamic environment Avoiding obstacles
STEERING BEHAVIORS Markéta Popelová, marketa.popelova [zavináč] matfyz.cz 2012, Umělé Bytosti, MFF UK MOTIVATION MOTIVATION REQUIREMENTS FOR MOTION CONTROL Responding to dynamic environment Avoiding obstacles
Agent Based Intersection Traffic Simulation
 Agent Based Intersection Traffic Simulation David Wilkie May 7, 2009 Abstract This project focuses on simulating the traffic at an intersection using agent-based planning and behavioral methods. The motivation
Agent Based Intersection Traffic Simulation David Wilkie May 7, 2009 Abstract This project focuses on simulating the traffic at an intersection using agent-based planning and behavioral methods. The motivation
MODELING REALISTIC HIGH DENSITY AUTONOMOUS AGENT CROWD MOVEMENT: SOCIAL FORCES, COMMUNICATION, ROLES AND PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES A DISSERTATION
 MODELING REALISTIC HIGH DENSITY AUTONOMOUS AGENT CROWD MOVEMENT: SOCIAL FORCES, COMMUNICATION, ROLES AND PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES NURIA PELECHANO GOMEZ A DISSERTATION in Computer and Information Science
MODELING REALISTIC HIGH DENSITY AUTONOMOUS AGENT CROWD MOVEMENT: SOCIAL FORCES, COMMUNICATION, ROLES AND PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES NURIA PELECHANO GOMEZ A DISSERTATION in Computer and Information Science
SWARMING PIXEL TRACKER
 SWARMING PIXEL TRACKER B.Tech Project submitted by Parth Kanungo Computers and Communication Engineering, The LNM Institute of Information Technology, Jaipur 2011 CERTIFICATE It is certified that the work
SWARMING PIXEL TRACKER B.Tech Project submitted by Parth Kanungo Computers and Communication Engineering, The LNM Institute of Information Technology, Jaipur 2011 CERTIFICATE It is certified that the work
Computer Animation. Algorithms and Techniques. z< MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS. Rick Parent Ohio State University AN IMPRINT OF ELSEVIER SCIENCE
 Computer Animation Algorithms and Techniques Rick Parent Ohio State University z< MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS AN IMPRINT OF ELSEVIER SCIENCE AMSTERDAM BOSTON LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO
Computer Animation Algorithms and Techniques Rick Parent Ohio State University z< MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS AN IMPRINT OF ELSEVIER SCIENCE AMSTERDAM BOSTON LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO
Mobile Robots: An Introduction.
 Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Real-time Path Planning and Navigation for Multi-Agent and Heterogeneous Crowd Simulation
 Real-time Path Planning and Navigation for Multi-Agent and Heterogeneous Crowd Simulation Ming C. Lin Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill lin@cs.unc.edu Joint work
Real-time Path Planning and Navigation for Multi-Agent and Heterogeneous Crowd Simulation Ming C. Lin Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill lin@cs.unc.edu Joint work
CS 354 R Game Technology
 CS 354 R Game Technology Particles and Flocking Behavior Fall 2017 Particle Effects 2 General Particle Systems Objects are considered point masses with orientation Simple rules control how the particles
CS 354 R Game Technology Particles and Flocking Behavior Fall 2017 Particle Effects 2 General Particle Systems Objects are considered point masses with orientation Simple rules control how the particles
Multi-Agent Simulation of Circular Pedestrian Movements Using Cellular Automata
 Second Asia International Conference on Modelling & Simulation Multi-Agent Simulation of Circular Pedestrian Movements Using Cellular Automata Siamak Sarmady, Fazilah Haron and Abdullah Zawawi Hj. Talib
Second Asia International Conference on Modelling & Simulation Multi-Agent Simulation of Circular Pedestrian Movements Using Cellular Automata Siamak Sarmady, Fazilah Haron and Abdullah Zawawi Hj. Talib
Implementing a Hybrid Space Discretisation Within An Agent Based Evacuation Model
 Paper presented at PED 2010, NIST, Maryland USA, March 8-10 2010 Implementing a Hybrid Space Discretisation Within An Agent Based Evacuation Model N. Chooramun, P.J. Lawrence and E.R.Galea Fire Safety
Paper presented at PED 2010, NIST, Maryland USA, March 8-10 2010 Implementing a Hybrid Space Discretisation Within An Agent Based Evacuation Model N. Chooramun, P.J. Lawrence and E.R.Galea Fire Safety
Swarm Intelligence Particle Swarm Optimization. Erick Luerken 13.Feb.2006 CS 790R, University of Nevada, Reno
 Swarm Intelligence Particle Swarm Optimization Erick Luerken 13.Feb.2006 CS 790R, University of Nevada, Reno Motivation Discuss assigned literature in terms of complexity leading to actual applications
Swarm Intelligence Particle Swarm Optimization Erick Luerken 13.Feb.2006 CS 790R, University of Nevada, Reno Motivation Discuss assigned literature in terms of complexity leading to actual applications
AUTOMATIC VIDEO INDEXING
 AUTOMATIC VIDEO INDEXING Itxaso Bustos Maite Frutos TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Methods Key-frame extraction Automatic visual indexing Shot boundary detection Video OCR Index in motion Image processing
AUTOMATIC VIDEO INDEXING Itxaso Bustos Maite Frutos TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Methods Key-frame extraction Automatic visual indexing Shot boundary detection Video OCR Index in motion Image processing
Rendering diffuse objects using particle systems inside voxelized surface geometry. Thorsten Juckel Steffi Beckhaus
 Rendering diffuse objects using particle systems inside voxelized surface geometry Thorsten Juckel Steffi Beckhaus University of Hamburg interactive media / virtual environments 1 Outline 1. Introduction
Rendering diffuse objects using particle systems inside voxelized surface geometry Thorsten Juckel Steffi Beckhaus University of Hamburg interactive media / virtual environments 1 Outline 1. Introduction
Advanced Algorithms. Particle Systems. Reading. What is a Particle System?
 Advanced Algorithms Particle Systems CMPT 466 Computer Animation Torsten Möller Hierarchical Kinematic Modeling Forward Kinematics Inverse Kinematics Rigid Body Constraints Basic Particle Forces Collision
Advanced Algorithms Particle Systems CMPT 466 Computer Animation Torsten Möller Hierarchical Kinematic Modeling Forward Kinematics Inverse Kinematics Rigid Body Constraints Basic Particle Forces Collision
Simulating Group Formations Using RVO
 Simulating Group Formations Using RVO Martin Funkquist martinfu@kth.se Supervisor: Christopher Peters Staffan Sandberg stsand@kth.se May 25, 2016 Figure 1: From left to right. First figure displays a real
Simulating Group Formations Using RVO Martin Funkquist martinfu@kth.se Supervisor: Christopher Peters Staffan Sandberg stsand@kth.se May 25, 2016 Figure 1: From left to right. First figure displays a real
NUMB3RS Activity: Follow the Flock. Episode: In Plain Sight
 Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Follow the Flock Topic: Introduction to Flock Behavior Grade Level: 8-12 Objective: Use a mathematical model to simulate an aspect of birds flying in a flock Time: 30 minutes
Teacher Page 1 NUMB3RS Activity: Follow the Flock Topic: Introduction to Flock Behavior Grade Level: 8-12 Objective: Use a mathematical model to simulate an aspect of birds flying in a flock Time: 30 minutes
Animation. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/23/07 1
 Animation Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/23/07 1 Today s Topics Interpolation Forward and inverse kinematics Rigid body simulation Fluids Particle systems Behavioral
Animation Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/23/07 1 Today s Topics Interpolation Forward and inverse kinematics Rigid body simulation Fluids Particle systems Behavioral
Chapter 3 Implementing Simulations as Individual-Based Models
 24 Chapter 3 Implementing Simulations as Individual-Based Models In order to develop models of such individual behavior and social interaction to understand the complex of an urban environment, we need
24 Chapter 3 Implementing Simulations as Individual-Based Models In order to develop models of such individual behavior and social interaction to understand the complex of an urban environment, we need
Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation. Revision Lecture
 Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation Revision Lecture Introduction Brief history; game genres Game structure A series of interesting choices Series of convexities Variable difficulty increase
Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation Revision Lecture Introduction Brief history; game genres Game structure A series of interesting choices Series of convexities Variable difficulty increase
When using Flocking with network rendering (LWSN, for instance) you must bake your Flocking results.
 Flocking About Flocking LightWave s flocking system is based on 3D computer models of coordinated animal motion, things like flocks of birds, herds of animals or schools of fish. It can be used with LightWave
Flocking About Flocking LightWave s flocking system is based on 3D computer models of coordinated animal motion, things like flocks of birds, herds of animals or schools of fish. It can be used with LightWave
Shape of Things to Come: Next-Gen Physics Deep Dive
 Shape of Things to Come: Next-Gen Physics Deep Dive Jean Pierre Bordes NVIDIA Corporation Free PhysX on CUDA PhysX by NVIDIA since March 2008 PhysX on CUDA available: August 2008 GPU PhysX in Games Physical
Shape of Things to Come: Next-Gen Physics Deep Dive Jean Pierre Bordes NVIDIA Corporation Free PhysX on CUDA PhysX by NVIDIA since March 2008 PhysX on CUDA available: August 2008 GPU PhysX in Games Physical
Complex behavior emergent from simpler ones
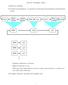 Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Simulation of Agent Movement with a Path Finding Feature Based on Modification of Physical Force Approach
 Simulation of Agent Movement with a Path Finding Feature Based on Modification of Physical Force Approach NURULAQILLA KHAMIS Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
Simulation of Agent Movement with a Path Finding Feature Based on Modification of Physical Force Approach NURULAQILLA KHAMIS Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia,
Multi Agent Navigation on GPU. Avi Bleiweiss
 Multi Agent Navigation on GPU Avi Bleiweiss Reasoning Explicit Implicit Script, storytelling State machine, serial Compute intensive Fits SIMT architecture well Navigation planning Collision avoidance
Multi Agent Navigation on GPU Avi Bleiweiss Reasoning Explicit Implicit Script, storytelling State machine, serial Compute intensive Fits SIMT architecture well Navigation planning Collision avoidance
Modeling the Virtual World
 Modeling the Virtual World Joaquim Madeira November, 2013 RVA - 2013/2014 1 A VR system architecture Modeling the Virtual World Geometry Physics Haptics VR Toolkits RVA - 2013/2014 2 VR object modeling
Modeling the Virtual World Joaquim Madeira November, 2013 RVA - 2013/2014 1 A VR system architecture Modeling the Virtual World Geometry Physics Haptics VR Toolkits RVA - 2013/2014 2 VR object modeling
Course Review. Computer Animation and Visualisation. Taku Komura
 Course Review Computer Animation and Visualisation Taku Komura Characters include Human models Virtual characters Animal models Representation of postures The body has a hierarchical structure Many types
Course Review Computer Animation and Visualisation Taku Komura Characters include Human models Virtual characters Animal models Representation of postures The body has a hierarchical structure Many types
Master s Thesis. Animal Stampede Simulation
 Master s Thesis Animal Stampede Simulation Akila Lakshminarayanan Brian Tran MSc Computer Animation and Visual Effects, NCCA 2011-2012 Abstract Large crowd scenes with humans and animals are abundant in
Master s Thesis Animal Stampede Simulation Akila Lakshminarayanan Brian Tran MSc Computer Animation and Visual Effects, NCCA 2011-2012 Abstract Large crowd scenes with humans and animals are abundant in
Human body animation. Computer Animation. Human Body Animation. Skeletal Animation
 Computer Animation Aitor Rovira March 2010 Human body animation Based on slides by Marco Gillies Human Body Animation Skeletal Animation Skeletal Animation (FK, IK) Motion Capture Motion Editing (retargeting,
Computer Animation Aitor Rovira March 2010 Human body animation Based on slides by Marco Gillies Human Body Animation Skeletal Animation Skeletal Animation (FK, IK) Motion Capture Motion Editing (retargeting,
A Memory Model for Autonomous Virtual Humans
 A Memory Model for Autonomous Virtual Humans Christopher Peters Carol O Sullivan Image Synthesis Group, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Republic of Ireland email: {christopher.peters, carol.osullivan}@cs.tcd.ie
A Memory Model for Autonomous Virtual Humans Christopher Peters Carol O Sullivan Image Synthesis Group, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Republic of Ireland email: {christopher.peters, carol.osullivan}@cs.tcd.ie
Robotic Behaviors. Potential Field Methods
 Robotic Behaviors Potential field techniques - trajectory generation - closed feedback-loop control Design of variety of behaviors - motivated by potential field based approach steering behaviors Closed
Robotic Behaviors Potential field techniques - trajectory generation - closed feedback-loop control Design of variety of behaviors - motivated by potential field based approach steering behaviors Closed
High-density Crowds. A masters student s journey to graphics and multi agent systems
 High-density Crowds A masters student s journey to graphics and multi agent systems Who am I and why am I here? Jack Shabo, student of CDATE, year 2012 Doing a degree project in Crowd Simulations with
High-density Crowds A masters student s journey to graphics and multi agent systems Who am I and why am I here? Jack Shabo, student of CDATE, year 2012 Doing a degree project in Crowd Simulations with
Announcements. Ray tracer is due in five days you should have started by now or you re going to have a bad week. Missing file posted on the web page
 Announcements Ray tracer is due in five days you should have started by now or you re going to have a bad week Missing file posted on the web page I m sorry for canceling class on Tuesday... 1 Animation
Announcements Ray tracer is due in five days you should have started by now or you re going to have a bad week Missing file posted on the web page I m sorry for canceling class on Tuesday... 1 Animation
Enhancing applications with Cognitive APIs IBM Corporation
 Enhancing applications with Cognitive APIs After you complete this section, you should understand: The Watson Developer Cloud offerings and APIs The benefits of commonly used Cognitive services 2 Watson
Enhancing applications with Cognitive APIs After you complete this section, you should understand: The Watson Developer Cloud offerings and APIs The benefits of commonly used Cognitive services 2 Watson
Computer Graphics and Visualization. What is computer graphics?
 CSCI 120 Computer Graphics and Visualization Shiaofen Fang Department of Computer and Information Science Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis What is computer graphics? Computer graphics
CSCI 120 Computer Graphics and Visualization Shiaofen Fang Department of Computer and Information Science Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis What is computer graphics? Computer graphics
Adding Virtual Characters to the Virtual Worlds. Yiorgos Chrysanthou Department of Computer Science University of Cyprus
 Adding Virtual Characters to the Virtual Worlds Yiorgos Chrysanthou Department of Computer Science University of Cyprus Cities need people However realistic the model is, without people it does not have
Adding Virtual Characters to the Virtual Worlds Yiorgos Chrysanthou Department of Computer Science University of Cyprus Cities need people However realistic the model is, without people it does not have
Scene Management. Video Game Technologies 11498: MSc in Computer Science and Engineering 11156: MSc in Game Design and Development
 Video Game Technologies 11498: MSc in Computer Science and Engineering 11156: MSc in Game Design and Development Chap. 5 Scene Management Overview Scene Management vs Rendering This chapter is about rendering
Video Game Technologies 11498: MSc in Computer Science and Engineering 11156: MSc in Game Design and Development Chap. 5 Scene Management Overview Scene Management vs Rendering This chapter is about rendering
Path Planning. Marcello Restelli. Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano tel:
 Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02 2399 3470 Path Planning Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
Marcello Restelli Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione Politecnico di Milano email: restelli@elet.polimi.it tel: 02 2399 3470 Path Planning Robotica for Computer Engineering students A.A. 2006/2007
CS 387/680: GAME AI MOVEMENT
 CS 387/680: GAME AI MOVEMENT 4/5/2016 Instructor: Santiago Ontañón santi@cs.drexel.edu Class website: https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~santi/teaching/2016/cs387/intro.html Reminders Check Blackboard site for
CS 387/680: GAME AI MOVEMENT 4/5/2016 Instructor: Santiago Ontañón santi@cs.drexel.edu Class website: https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~santi/teaching/2016/cs387/intro.html Reminders Check Blackboard site for
782 Schedule & Notes
 782 Schedule & Notes Tentative schedule - subject to change at a moment s notice. This is only a guide and not meant to be a strict schedule of how fast the material will be taught. The order of material
782 Schedule & Notes Tentative schedule - subject to change at a moment s notice. This is only a guide and not meant to be a strict schedule of how fast the material will be taught. The order of material
Spatial Data Structures
 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) [Angel 9.10] Outline Ray tracing review what rays matter? Ray tracing speedup faster
Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) [Angel 9.10] Outline Ray tracing review what rays matter? Ray tracing speedup faster
Motion Planning. Howie CHoset
 Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Large Scale Crowd Simulation Using A Hybrid Agent Model
 Large Scale Crowd Simulation Using A Hybrid Agent Model Seung In Park 1, Yong Cao 1, Francis Quek 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, Virginia,
Large Scale Crowd Simulation Using A Hybrid Agent Model Seung In Park 1, Yong Cao 1, Francis Quek 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, Virginia,
MODELING AND HIERARCHY
 MODELING AND HIERARCHY Introduction Models are abstractions of the world both of the real world in which we live and of virtual worlds that we create with computers. We are all familiar with mathematical
MODELING AND HIERARCHY Introduction Models are abstractions of the world both of the real world in which we live and of virtual worlds that we create with computers. We are all familiar with mathematical
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Introduction. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Introduction Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Contact Matthias Teschner Computer Graphics University of Freiburg Georges-Koehler-Allee
Simulation in Computer Graphics Introduction Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Contact Matthias Teschner Computer Graphics University of Freiburg Georges-Koehler-Allee
Formations in flow fields
 Formations in flow fields Rick van Meer June 11, 2015 1 Introduction Pathfinding and formations (i.e. an arrangement of agents) are both a part of artificial intelligence and can be used in games. However,
Formations in flow fields Rick van Meer June 11, 2015 1 Introduction Pathfinding and formations (i.e. an arrangement of agents) are both a part of artificial intelligence and can be used in games. However,
Graphics and Games. Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County
 Graphics and Games IS 101Y/CMSC 104Y First Year IT Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County Announcements Quizzes Project Questions Other questions Questions about Reading Asst Games with
Graphics and Games IS 101Y/CMSC 104Y First Year IT Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County Announcements Quizzes Project Questions Other questions Questions about Reading Asst Games with
Generating sparse navigation graphs for microscopic pedestrian simulation models
 Generating sparse navigation graphs for microscopic pedestrian simulation models Angelika Kneidl 1, André Borrmann 1, Dirk Hartmann 2 1 Computational Modeling and Simulation Group, TU München, Germany
Generating sparse navigation graphs for microscopic pedestrian simulation models Angelika Kneidl 1, André Borrmann 1, Dirk Hartmann 2 1 Computational Modeling and Simulation Group, TU München, Germany
Announcements. Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday
 Announcements Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday 1 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Grids Octrees BSP Trees 11/7/02 Speeding Up Computations
Announcements Written Assignment2 is out, due March 8 Graded Programming Assignment2 next Tuesday 1 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Grids Octrees BSP Trees 11/7/02 Speeding Up Computations
Last update: May 6, Robotics. CMSC 421: Chapter 25. CMSC 421: Chapter 25 1
 Last update: May 6, 2010 Robotics CMSC 421: Chapter 25 CMSC 421: Chapter 25 1 A machine to perform tasks What is a robot? Some level of autonomy and flexibility, in some type of environment Sensory-motor
Last update: May 6, 2010 Robotics CMSC 421: Chapter 25 CMSC 421: Chapter 25 1 A machine to perform tasks What is a robot? Some level of autonomy and flexibility, in some type of environment Sensory-motor
Enhancing Traditional Rasterization Graphics with Ray Tracing. October 2015
 Enhancing Traditional Rasterization Graphics with Ray Tracing October 2015 James Rumble Developer Technology Engineer, PowerVR Graphics Overview Ray Tracing Fundamentals PowerVR Ray Tracing Pipeline Using
Enhancing Traditional Rasterization Graphics with Ray Tracing October 2015 James Rumble Developer Technology Engineer, PowerVR Graphics Overview Ray Tracing Fundamentals PowerVR Ray Tracing Pipeline Using
Collision Detection. Pu Jiantao.
 Collision Detection Pu Jiantao. 12-09 Content Introduction CD with rays Dynamic CD using BSP Trees Hierarchical Method OBBTree Method Some Other Topics 12-1717 2 Introduction Collision Collision is a fundamental
Collision Detection Pu Jiantao. 12-09 Content Introduction CD with rays Dynamic CD using BSP Trees Hierarchical Method OBBTree Method Some Other Topics 12-1717 2 Introduction Collision Collision is a fundamental
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF REALISTIC PEDESTRIAN BEHAVIOURS
 MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF REALISTIC PEDESTRIAN BEHAVIOURS KOH WEE LIT School Of Computer Engineering A thesis submitted to the Nanyang Technological University in fulfillment of the requirement for the
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF REALISTIC PEDESTRIAN BEHAVIOURS KOH WEE LIT School Of Computer Engineering A thesis submitted to the Nanyang Technological University in fulfillment of the requirement for the
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
CrowdMixer: Multiple Agent Types in Situation-Based Crowd Simulations
 CrowdMixer: Multiple Agent Types in Situation-Based Crowd Simulations Shannon Blyth and Howard J. Hamilton Department of Computer Science University of Regina, Regina, SK, Canada S4S 0A2 {blyth1sh, hamilton}@cs.uregina.ca
CrowdMixer: Multiple Agent Types in Situation-Based Crowd Simulations Shannon Blyth and Howard J. Hamilton Department of Computer Science University of Regina, Regina, SK, Canada S4S 0A2 {blyth1sh, hamilton}@cs.uregina.ca
Study of Bluetooth Eyes Technology and Gesture Recognition Devices
 Study of Bluetooth Eyes Technology and Gesture Recognition Devices Mayank Kumar Gaur, Manjeet Kaur, *Upendra Kumar, Sakshi Sethi Amity University Gurgaon Haryana Priyanshu Gaur Meerut Institute of Engineering
Study of Bluetooth Eyes Technology and Gesture Recognition Devices Mayank Kumar Gaur, Manjeet Kaur, *Upendra Kumar, Sakshi Sethi Amity University Gurgaon Haryana Priyanshu Gaur Meerut Institute of Engineering
Crowd simulation. Summerschool Utrecht: Multidisciplinary Game Research. Dr. Roland Geraerts 23 August 2017
 Crowd simulation Summerschool Utrecht: Multidisciplinary Game Research Dr. Roland Geraerts 23 August 2017 1 Societal relevance of crowd simulation The number of environments with big crowds are growing
Crowd simulation Summerschool Utrecht: Multidisciplinary Game Research Dr. Roland Geraerts 23 August 2017 1 Societal relevance of crowd simulation The number of environments with big crowds are growing
Spring Localization II. Roland Siegwart, Margarita Chli, Martin Rufli. ASL Autonomous Systems Lab. Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Spring 2016 Localization II Localization I 25.04.2016 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Spring 2016 Localization II Localization I 25.04.2016 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Character AI: Sensing & Perception
 Lecture 22 Character AI: Take Away for Today Sensing as primary bottleneck Why is sensing so problematic? What types of things can we do to improve it? Optimized sense computation Can we improve sense
Lecture 22 Character AI: Take Away for Today Sensing as primary bottleneck Why is sensing so problematic? What types of things can we do to improve it? Optimized sense computation Can we improve sense
Personal style & NMF-based Exaggerative Expressions of Face. Seongah Chin, Chung-yeon Lee, Jaedong Lee Multimedia Department of Sungkyul University
 Personal style & NMF-based Exaggerative Expressions of Face Seongah Chin, Chung-yeon Lee, Jaedong Lee Multimedia Department of Sungkyul University Outline Introduction Related Works Methodology Personal
Personal style & NMF-based Exaggerative Expressions of Face Seongah Chin, Chung-yeon Lee, Jaedong Lee Multimedia Department of Sungkyul University Outline Introduction Related Works Methodology Personal
What is a Rigid Body?
 Physics on the GPU What is a Rigid Body? A rigid body is a non-deformable object that is a idealized solid Each rigid body is defined in space by its center of mass To make things simpler we assume the
Physics on the GPU What is a Rigid Body? A rigid body is a non-deformable object that is a idealized solid Each rigid body is defined in space by its center of mass To make things simpler we assume the
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Hierarchical Impostors for the Flocking Algorithm in 3D
 Volume 21 (2002), number 4 pp. 723 731 COMPUTER GRAPHICS forum Hierarchical Impostors for the Flocking Algorithm in 3D Noel O Hara Fruition Technologies Ltd, Dublin, Ireland Abstract The availability of
Volume 21 (2002), number 4 pp. 723 731 COMPUTER GRAPHICS forum Hierarchical Impostors for the Flocking Algorithm in 3D Noel O Hara Fruition Technologies Ltd, Dublin, Ireland Abstract The availability of
Algorithms. Algorithms GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS. 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search trees rectangle intersection
 Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search
Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search
Algorithms. Algorithms GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS. 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search trees rectangle intersection
 Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search
Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search
Topics. Ray Tracing II. Intersecting transformed objects. Transforming objects
 Topics Ray Tracing II CS 4620 Lecture 16 Transformations in ray tracing Transforming objects Transformation hierarchies Ray tracing acceleration structures Bounding volumes Bounding volume hierarchies
Topics Ray Tracing II CS 4620 Lecture 16 Transformations in ray tracing Transforming objects Transformation hierarchies Ray tracing acceleration structures Bounding volumes Bounding volume hierarchies
Integrating multiple representations of spatial knowledge for mapping, navigation, and communication
 Integrating multiple representations of spatial knowledge for mapping, navigation, and communication Patrick Beeson Matt MacMahon Joseph Modayil Aniket Murarka Benjamin Kuipers Department of Computer Sciences
Integrating multiple representations of spatial knowledge for mapping, navigation, and communication Patrick Beeson Matt MacMahon Joseph Modayil Aniket Murarka Benjamin Kuipers Department of Computer Sciences
Algorithms. Algorithms GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS. 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search trees rectangle intersection
 Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search
Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE GEOMETRIC APPLICATIONS OF BSTS Algorithms F O U R T H E D I T I O N ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 1d range search line segment intersection kd trees interval search
The 3D rendering pipeline (our version for this class)
 The 3D rendering pipeline (our version for this class) 3D models in model coordinates 3D models in world coordinates 2D Polygons in camera coordinates Pixels in image coordinates Scene graph Camera Rasterization
The 3D rendering pipeline (our version for this class) 3D models in model coordinates 3D models in world coordinates 2D Polygons in camera coordinates Pixels in image coordinates Scene graph Camera Rasterization
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
Animation. Itinerary. What is Animation? What is Animation? Animation Methods. Modeling vs. Animation Computer Graphics Lecture 22
 15-462 Computer Graphics Lecture 22 Animation April 22, 2003 M. Ian Graham Carnegie Mellon University What is Animation? Making things move What is Animation? Consider a model with n parameters Polygon
15-462 Computer Graphics Lecture 22 Animation April 22, 2003 M. Ian Graham Carnegie Mellon University What is Animation? Making things move What is Animation? Consider a model with n parameters Polygon
FGnet - Facial Expression and. Emotion Database
 Review Meeting 07. October 2004 FGnet - Facial Expression and Slide 1 Overview Assembly of a consistent Emotion and Facial Expressions database for dynamic algorithms using image sequences rather than
Review Meeting 07. October 2004 FGnet - Facial Expression and Slide 1 Overview Assembly of a consistent Emotion and Facial Expressions database for dynamic algorithms using image sequences rather than
Topological Navigation and Path Planning
 Topological Navigation and Path Planning Topological Navigation and Path Planning Based upon points of interest E.g., landmarks Navigation is relational between points of interest E.g., Go past the corner
Topological Navigation and Path Planning Topological Navigation and Path Planning Based upon points of interest E.g., landmarks Navigation is relational between points of interest E.g., Go past the corner
