P = NP; P NP. Intuition of the reduction idea:
|
|
|
- Camron Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Polynomial Time Reducibility The question of whether P = NP is one of the greatest unsolved problems in the theoretical computer science. Two possibilities of relationship between P and N P P = NP; P NP. Intuition of the reduction idea: If a problem A is reducible to a problem B, an algorithm forsolvingb canbeusedtoconstructanalgorithmfora. If A is polynomially reducible to B, then a polynomial algorithm for B can be used to construct a polynomial algorithm for A. 1
2 Definition 1 Language A is polynomial time (mapping) reducible to language B, written A P B, if a polynomial time computable function exists, where for every w, f : Σ Σ w A iff f(w) B. A f B A f B 2
3 Theorem 1 If A P B and B P C, then A P C. Definition 2 A language L is called NP-complete iff 1. L NP; 2. for every language L NP, there is a polynomialtime mapping from L to L. Proposition 1 Let L be an NP-complete language. Then P = NP iff L P. Theorem 2 SAT P 3SAT. Theorem 3 3SAT p CLIQUE. Corollary 1 SAT P CLIQUE. 3
4 2 More Computational Classes Class P of problems that can be decided in polynomial time on a deterministic Turing machine. Class NP of problems that can be decided in polynomial time on a non-deterministic Turing machine. Class CNP of NP-complete problems; a language A NP is called NP-complete if B NP B P A. Class co-np of problems {L} such that L NP. 4
5 Definition 3 Two graphs G 1 (V 1,E 1 ) and G 2 (V 2,E 2 ) are called isomorphic if there is a one-to-one mapping f from V 1 onto V 2 such that (x,y) E 1 iff (f(x),f(y)) E 2. Graph Isomorphism Problem: Given two graphs G and H, is it true that they are isomorphic? This is a decision problem with a polynomial verifier. A polynomial verifier is known to check if graphs are isomorphic. 5
6 Graph Non-isomorphism Problem: Given two graphs G and H, is it true that they are not isomorphic? This is a decision problem for which no polynomial verifier was found. The complement to this problem belongs to NP; thus, the problem is in co-np. No polynomial verifier is known to check if two graphs are non-isomorphic. 6
7 3 Decision problems vs Optimization Problems Example: Clique (decision version): Given a graph G(V, E) and an integer k > 0, is there a clique of size k in G? L = { G(V,E),k : G contains a clique of size k}. Clique (optimization version): Given a graph G(V, E), find a clique in G of the maximal size. Proposition 2 If A is an algorithm for the decision version of the Clique-problem, then O(log n) applications of A solves the optimization version of the Clique-problem. 7
8 Problem 1 If A is an algorithm for the decision version of the Clique-problem, and A accepted G(V, E), k, how to find a clique of size k in G? Solution idea: Repeat 1. for every vertex v of G, apply A to H,k where H is the subgraph induced on the set containing v and its neighbors; 2. include into the clique the first v for which the application of A above yielded acceptance; Reset G to be the subgraph induced on the neighbors of v and k = k 1. 8
9 Problem 2 If A is an algorithm for the decision version of the Partitioning-problem, and A accepted S, C, how to find a subset T S for which a i = C? a i T Solution idea: Let S = {a 1,a 2,...,a n }. Repeat 1. find a i S for which A accepts S {a i },C a i ; include a i into T. 2. resets andc bys = S {a i }andc = C a i. 9
10 4 Vertex Coloring A k-vertex-coloring of a graph G(V,E) is a functioon f : V [1,k], such that for any edge xy E, f(x) f(y). Vertex Color (decision version): Given a graph G(V, E) and an integer k > 0, is there a vertex coloring of G which uses k colors? L = { G(V,E),k : G : there exists k vertex coloring.} Vertex Color (optimization version): Given a graph G(V,E), find a vertex-coloring of G which uses the smallest number of colors. Proposition 3 If A is an algorithm for the decision version of Vertex Color, then O(log n) applications of A are sufficient to determine the smallest number k for which there exists a k-vertex- coloring of G. Question: How to discover an optimal vertex-coloring? 10
11 Given an algorithm A for the decision version of Vertex_Color, we design a coloring algorithm Construct (G) which for every graph G outputs a k coloring, where k is such that A accepted <G,k> <G(V,E); k> is G complete? yes color G no select non adjacent pair xy. Form graph G[x,y] by fusing x and y apply A is G k colorable? yes Construct (G[x,y]) no Form graph H by adding xy to G Use k coloring of G[x,y] to create k coloring of G Construct (H) Use k coloring of H to create k coloring of G 11
12 Proposition 4 Let G be k-colorable and complete(any two vertiices are adjacent). Then, a k-coloring is obtained by the following rule: every vertex gets its own color. Proposition 5 Let G be k-colorable and not complete, and let x and y be two non-adjacent vertices in G. Form two graphs G[x,y] and H as follows: G[x,y]: remove x and y and add a new vertex [x,y] making it adjacent to all vertices in G that were adjacent to x or to y; H: add edge xy to G. Then there exists a k-coloring f of G iff at least one of the two options is correct: f(x) = f(y), in which case there is a k-coloring g of G[x,y] which preserves all colors and uses color f(x) for vertex [x,y]; f(x) f(y), in which case there is a k-coloring h on H which preserves all colors of f on G. Theorem 4 Assume that every application of procedure A is executed in one time unit. Prove that under this assumption, there is a polynomial algorithm for k-vertex-coloring. 12
P and NP (Millenium problem)
 CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 P and NP (Millenium problem) Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Piotr Indyk with additions by Carola Wenk CMPS 2200 Introduction to Algorithms 1 We have seen so far Algorithms for various
CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 P and NP (Millenium problem) Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Piotr Indyk with additions by Carola Wenk CMPS 2200 Introduction to Algorithms 1 We have seen so far Algorithms for various
NP-Completeness. Algorithms
 NP-Completeness Algorithms The NP-Completeness Theory Objective: Identify a class of problems that are hard to solve. Exponential time is hard. Polynomial time is easy. Why: Do not try to find efficient
NP-Completeness Algorithms The NP-Completeness Theory Objective: Identify a class of problems that are hard to solve. Exponential time is hard. Polynomial time is easy. Why: Do not try to find efficient
Introduction to Algorithms. Lecture 24. Prof. Patrick Jaillet
 6.006- Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 24 Prof. Patrick Jaillet Outline Decision vs optimization problems P, NP, co-np Reductions between problems NP-complete problems Beyond NP-completeness Readings
6.006- Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 24 Prof. Patrick Jaillet Outline Decision vs optimization problems P, NP, co-np Reductions between problems NP-complete problems Beyond NP-completeness Readings
Graph Theory S 1 I 2 I 1 S 2 I 1 I 2
 Graph Theory S I I S S I I S Graphs Definition A graph G is a pair consisting of a vertex set V (G), and an edge set E(G) ( ) V (G). x and y are the endpoints of edge e = {x, y}. They are called adjacent
Graph Theory S I I S S I I S Graphs Definition A graph G is a pair consisting of a vertex set V (G), and an edge set E(G) ( ) V (G). x and y are the endpoints of edge e = {x, y}. They are called adjacent
NP Completeness. Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch]
![NP Completeness. Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch] NP Completeness. Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch]](/thumbs/76/73396698.jpg) NP Completeness Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch] Overview We already know the following examples of NPC problems: SAT 3SAT We are going to show that the following are
NP Completeness Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch] Overview We already know the following examples of NPC problems: SAT 3SAT We are going to show that the following are
CS154, Lecture 18: PCPs, Hardness of Approximation, Approximation-Preserving Reductions, Interactive Proofs, Zero-Knowledge, Cold Fusion, Peace in
 CS154, Lecture 18: PCPs, Hardness of Approximation, Approximation-Preserving Reductions, Interactive Proofs, Zero-Knowledge, Cold Fusion, Peace in the Middle East There are thousands of NP-complete problems
CS154, Lecture 18: PCPs, Hardness of Approximation, Approximation-Preserving Reductions, Interactive Proofs, Zero-Knowledge, Cold Fusion, Peace in the Middle East There are thousands of NP-complete problems
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Other NP-Complete Problems Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 7 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Sections 7.4 and 7.5. The 3SAT
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Other NP-Complete Problems Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 7 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Sections 7.4 and 7.5. The 3SAT
NP-Hardness. We start by defining types of problem, and then move on to defining the polynomial-time reductions.
 CS 787: Advanced Algorithms NP-Hardness Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek We review the concept of polynomial-time reductions, define various classes of problems including NP-complete, and show that 3-SAT
CS 787: Advanced Algorithms NP-Hardness Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek We review the concept of polynomial-time reductions, define various classes of problems including NP-complete, and show that 3-SAT
Introduction to Graph Theory
 Introduction to Graph Theory Tandy Warnow January 20, 2017 Graphs Tandy Warnow Graphs A graph G = (V, E) is an object that contains a vertex set V and an edge set E. We also write V (G) to denote the vertex
Introduction to Graph Theory Tandy Warnow January 20, 2017 Graphs Tandy Warnow Graphs A graph G = (V, E) is an object that contains a vertex set V and an edge set E. We also write V (G) to denote the vertex
NP-Complete Problems
 NP-omplete Problems P and NP Polynomial time reductions Satisfiability Problem, lique Problem, Vertex over, and ominating Set 10/19/2009 SE 5311 FLL 2009 KUMR 1 Polynomial lgorithms Problems encountered
NP-omplete Problems P and NP Polynomial time reductions Satisfiability Problem, lique Problem, Vertex over, and ominating Set 10/19/2009 SE 5311 FLL 2009 KUMR 1 Polynomial lgorithms Problems encountered
1 Matchings in Graphs
 Matchings in Graphs J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 Definition Two edges are called independent if they are not adjacent
Matchings in Graphs J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 Definition Two edges are called independent if they are not adjacent
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401 Lecture 21 Prof. Piotr Indyk P vs NP (interconnectedness of all things) A whole course by itself We ll do just two lectures More in 6.045, 6.840J, etc. Introduction
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401 Lecture 21 Prof. Piotr Indyk P vs NP (interconnectedness of all things) A whole course by itself We ll do just two lectures More in 6.045, 6.840J, etc. Introduction
Fast-Mixed Searching and Related Problems on Graphs
 Fast-Mixed Searching and Related Problems on Graphs Boting Yang Department of Computer Science University of Regina May 27, 2012 GRASCan 2012, Ryerson University 1 Outline Fast searching and mixed searching
Fast-Mixed Searching and Related Problems on Graphs Boting Yang Department of Computer Science University of Regina May 27, 2012 GRASCan 2012, Ryerson University 1 Outline Fast searching and mixed searching
W[1]-hardness. Dániel Marx. Recent Advances in Parameterized Complexity Tel Aviv, Israel, December 3, 2017
![W[1]-hardness. Dániel Marx. Recent Advances in Parameterized Complexity Tel Aviv, Israel, December 3, 2017 W[1]-hardness. Dániel Marx. Recent Advances in Parameterized Complexity Tel Aviv, Israel, December 3, 2017](/thumbs/92/108052593.jpg) 1 W[1]-hardness Dániel Marx Recent Advances in Parameterized Complexity Tel Aviv, Israel, December 3, 2017 2 Lower bounds So far we have seen positive results: basic algorithmic techniques for fixed-parameter
1 W[1]-hardness Dániel Marx Recent Advances in Parameterized Complexity Tel Aviv, Israel, December 3, 2017 2 Lower bounds So far we have seen positive results: basic algorithmic techniques for fixed-parameter
Complexity of clique coloring and related problems
 Complexity of clique coloring and related problems Dániel Marx Institut für Informatik Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany dmarx@cs.bme.hu 23rd February 2011 Abstract A k-clique-coloring of a graph
Complexity of clique coloring and related problems Dániel Marx Institut für Informatik Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany dmarx@cs.bme.hu 23rd February 2011 Abstract A k-clique-coloring of a graph
Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In
 Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In Hans L. Bodlaender Pinar Heggernes Yngve Villanger Abstract We present two parameterized algorithms for the Minimum Fill-In problem, also known as Chordal
Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In Hans L. Bodlaender Pinar Heggernes Yngve Villanger Abstract We present two parameterized algorithms for the Minimum Fill-In problem, also known as Chordal
Vertex Cover is Fixed-Parameter Tractable
 Vertex Cover is Fixed-Parameter Tractable CS 511 Iowa State University November 28, 2010 CS 511 (Iowa State University) Vertex Cover is Fixed-Parameter Tractable November 28, 2010 1 / 18 The Vertex Cover
Vertex Cover is Fixed-Parameter Tractable CS 511 Iowa State University November 28, 2010 CS 511 (Iowa State University) Vertex Cover is Fixed-Parameter Tractable November 28, 2010 1 / 18 The Vertex Cover
Bayesian Networks, Winter Yoav Haimovitch & Ariel Raviv
 Bayesian Networks, Winter 2009-2010 Yoav Haimovitch & Ariel Raviv 1 Chordal Graph Warm up Theorem 7 Perfect Vertex Elimination Scheme Maximal cliques Tree Bibliography M.C.Golumbic Algorithmic Graph Theory
Bayesian Networks, Winter 2009-2010 Yoav Haimovitch & Ariel Raviv 1 Chordal Graph Warm up Theorem 7 Perfect Vertex Elimination Scheme Maximal cliques Tree Bibliography M.C.Golumbic Algorithmic Graph Theory
Bipartite Roots of Graphs
 Bipartite Roots of Graphs Lap Chi Lau Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Graph H is a root of graph G if there exists a positive integer k such that x and y are adjacent in G if and only
Bipartite Roots of Graphs Lap Chi Lau Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Graph H is a root of graph G if there exists a positive integer k such that x and y are adjacent in G if and only
Characterizing Graphs (3) Characterizing Graphs (1) Characterizing Graphs (2) Characterizing Graphs (4)
 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 1 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 3 Characterizing Graphs (1) Characterizing Graphs (3) Characterizing a class G by a condition P means proving the equivalence G G
S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 1 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 3 Characterizing Graphs (1) Characterizing Graphs (3) Characterizing a class G by a condition P means proving the equivalence G G
Domination, Independence and Other Numbers Associated With the Intersection Graph of a Set of Half-planes
 Domination, Independence and Other Numbers Associated With the Intersection Graph of a Set of Half-planes Leonor Aquino-Ruivivar Mathematics Department, De La Salle University Leonorruivivar@dlsueduph
Domination, Independence and Other Numbers Associated With the Intersection Graph of a Set of Half-planes Leonor Aquino-Ruivivar Mathematics Department, De La Salle University Leonorruivivar@dlsueduph
The Maximum Clique Problem
 November, 2012 Motivation How to put as much left-over stuff as possible in a tasty meal before everything will go off? Motivation Find the largest collection of food where everything goes together! Here,
November, 2012 Motivation How to put as much left-over stuff as possible in a tasty meal before everything will go off? Motivation Find the largest collection of food where everything goes together! Here,
Preimages of Small Geometric Cycles
 Preimages of Small Geometric Cycles Sally Cockburn Department of Mathematics Hamilton College, Clinton, NY scockbur@hamilton.edu Abstract A graph G is a homomorphic preimage of another graph H, or equivalently
Preimages of Small Geometric Cycles Sally Cockburn Department of Mathematics Hamilton College, Clinton, NY scockbur@hamilton.edu Abstract A graph G is a homomorphic preimage of another graph H, or equivalently
Unit 8: Coping with NP-Completeness. Complexity classes Reducibility and NP-completeness proofs Coping with NP-complete problems. Y.-W.
 : Coping with NP-Completeness Course contents: Complexity classes Reducibility and NP-completeness proofs Coping with NP-complete problems Reading: Chapter 34 Chapter 35.1, 35.2 Y.-W. Chang 1 Complexity
: Coping with NP-Completeness Course contents: Complexity classes Reducibility and NP-completeness proofs Coping with NP-complete problems Reading: Chapter 34 Chapter 35.1, 35.2 Y.-W. Chang 1 Complexity
Adjacent: Two distinct vertices u, v are adjacent if there is an edge with ends u, v. In this case we let uv denote such an edge.
 1 Graph Basics What is a graph? Graph: a graph G consists of a set of vertices, denoted V (G), a set of edges, denoted E(G), and a relation called incidence so that each edge is incident with either one
1 Graph Basics What is a graph? Graph: a graph G consists of a set of vertices, denoted V (G), a set of edges, denoted E(G), and a relation called incidence so that each edge is incident with either one
Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u, v V, then u is adjacent to v if {u, v} E. We also use the notation u v to denote that u is adjacent to v.
 Graph Adjacent Endpoint of an edge Incident Neighbors of a vertex Degree of a vertex Theorem Graph relation Order of a graph Size of a graph Maximum and minimum degree Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u,
Graph Adjacent Endpoint of an edge Incident Neighbors of a vertex Degree of a vertex Theorem Graph relation Order of a graph Size of a graph Maximum and minimum degree Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u,
Theorem 3.1 (Berge) A matching M in G is maximum if and only if there is no M- augmenting path.
 3 Matchings Hall s Theorem Matching: A matching in G is a subset M E(G) so that no edge in M is a loop, and no two edges in M are incident with a common vertex. A matching M is maximal if there is no matching
3 Matchings Hall s Theorem Matching: A matching in G is a subset M E(G) so that no edge in M is a loop, and no two edges in M are incident with a common vertex. A matching M is maximal if there is no matching
with Dana Richards December 1, 2017 George Mason University New Results On Routing Via Matchings Indranil Banerjee The Routing Model
 New New with Dana Richards George Mason University richards@gmu.edu December 1, 2017 GMU December 1, 2017 1 / 40 New Definitions G(V, E) is an undirected graph. V = {1, 2, 3,..., n}. A pebble at vertex
New New with Dana Richards George Mason University richards@gmu.edu December 1, 2017 GMU December 1, 2017 1 / 40 New Definitions G(V, E) is an undirected graph. V = {1, 2, 3,..., n}. A pebble at vertex
NP-Complete Reductions 2
 x 1 x 1 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 4 x 4 12 22 32 CS 447 11 13 21 23 31 33 Algorithms NP-Complete Reductions 2 Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Lecture Outline NP-Complete
x 1 x 1 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 4 x 4 12 22 32 CS 447 11 13 21 23 31 33 Algorithms NP-Complete Reductions 2 Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Lecture Outline NP-Complete
Graph theory - solutions to problem set 1
 Graph theory - solutions to problem set 1 1. (a) Is C n a subgraph of K n? Exercises (b) For what values of n and m is K n,n a subgraph of K m? (c) For what n is C n a subgraph of K n,n? (a) Yes! (you
Graph theory - solutions to problem set 1 1. (a) Is C n a subgraph of K n? Exercises (b) For what values of n and m is K n,n a subgraph of K m? (c) For what n is C n a subgraph of K n,n? (a) Yes! (you
Where Can We Draw The Line?
 Where Can We Draw The Line? On the Hardness of Satisfiability Problems Complexity 1 Introduction Objectives: To show variants of SAT and check if they are NP-hard Overview: Known results 2SAT Max2SAT Complexity
Where Can We Draw The Line? On the Hardness of Satisfiability Problems Complexity 1 Introduction Objectives: To show variants of SAT and check if they are NP-hard Overview: Known results 2SAT Max2SAT Complexity
Infinite locally random graphs
 Infinite locally random graphs Pierre Charbit and Alex D. Scott Abstract Motivated by copying models of the web graph, Bonato and Janssen [3] introduced the following simple construction: given a graph
Infinite locally random graphs Pierre Charbit and Alex D. Scott Abstract Motivated by copying models of the web graph, Bonato and Janssen [3] introduced the following simple construction: given a graph
8 NP-complete problem Hard problems: demo
 Ch8 NPC Millennium Prize Problems http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/millennium_prize_problems 8 NP-complete problem Hard problems: demo NP-hard (Non-deterministic Polynomial-time hard), in computational complexity
Ch8 NPC Millennium Prize Problems http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/millennium_prize_problems 8 NP-complete problem Hard problems: demo NP-hard (Non-deterministic Polynomial-time hard), in computational complexity
PCP and Hardness of Approximation
 PCP and Hardness of Approximation January 30, 2009 Our goal herein is to define and prove basic concepts regarding hardness of approximation. We will state but obviously not prove a PCP theorem as a starting
PCP and Hardness of Approximation January 30, 2009 Our goal herein is to define and prove basic concepts regarding hardness of approximation. We will state but obviously not prove a PCP theorem as a starting
GRAPH THEORY and APPLICATIONS. Factorization Domination Indepence Clique
 GRAPH THEORY and APPLICATIONS Factorization Domination Indepence Clique Factorization Factor A factor of a graph G is a spanning subgraph of G, not necessarily connected. G is the sum of factors G i, if:
GRAPH THEORY and APPLICATIONS Factorization Domination Indepence Clique Factorization Factor A factor of a graph G is a spanning subgraph of G, not necessarily connected. G is the sum of factors G i, if:
A graph is finite if its vertex set and edge set are finite. We call a graph with just one vertex trivial and all other graphs nontrivial.
 2301-670 Graph theory 1.1 What is a graph? 1 st semester 2550 1 1.1. What is a graph? 1.1.2. Definition. A graph G is a triple (V(G), E(G), ψ G ) consisting of V(G) of vertices, a set E(G), disjoint from
2301-670 Graph theory 1.1 What is a graph? 1 st semester 2550 1 1.1. What is a graph? 1.1.2. Definition. A graph G is a triple (V(G), E(G), ψ G ) consisting of V(G) of vertices, a set E(G), disjoint from
arxiv: v3 [cs.ds] 26 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v3 [cs.ds] 26 Sep 2013 arxiv: v3 [cs.ds] 26 Sep 2013](/thumbs/96/129281842.jpg) Preprocessing Subgraph and Minor Problems: When Does a Small Vertex Cover Help?, Fedor V. Fomin a, Bart M. P. Jansen a,, Micha l Pilipczuk a a Department of Informatics, University of Bergen. PO Box 7803,
Preprocessing Subgraph and Minor Problems: When Does a Small Vertex Cover Help?, Fedor V. Fomin a, Bart M. P. Jansen a,, Micha l Pilipczuk a a Department of Informatics, University of Bergen. PO Box 7803,
Chordal Graphs: Theory and Algorithms
 Chordal Graphs: Theory and Algorithms 1 Chordal graphs Chordal graph : Every cycle of four or more vertices has a chord in it, i.e. there is an edge between two non consecutive vertices of the cycle. Also
Chordal Graphs: Theory and Algorithms 1 Chordal graphs Chordal graph : Every cycle of four or more vertices has a chord in it, i.e. there is an edge between two non consecutive vertices of the cycle. Also
5 Graph Theory Basics
 November 14, 2017 5 Graph Theory Basics William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Basic Definitions Definition A graph G is a pair (V, E) where V is a finite set and E is a set of 2-element subsets of
November 14, 2017 5 Graph Theory Basics William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Basic Definitions Definition A graph G is a pair (V, E) where V is a finite set and E is a set of 2-element subsets of
Small Survey on Perfect Graphs
 Small Survey on Perfect Graphs Michele Alberti ENS Lyon December 8, 2010 Abstract This is a small survey on the exciting world of Perfect Graphs. We will see when a graph is perfect and which are families
Small Survey on Perfect Graphs Michele Alberti ENS Lyon December 8, 2010 Abstract This is a small survey on the exciting world of Perfect Graphs. We will see when a graph is perfect and which are families
Coloring edges and vertices of graphs without short or long cycles
 Coloring edges and vertices of graphs without short or long cycles Marcin Kamiński and Vadim Lozin Abstract Vertex and edge colorability are two graph problems that are NPhard in general. We show that
Coloring edges and vertices of graphs without short or long cycles Marcin Kamiński and Vadim Lozin Abstract Vertex and edge colorability are two graph problems that are NPhard in general. We show that
NP-complete Reductions
 NP-complete Reductions 1. Prove that 3SAT P DOUBLE-SAT, i.e., show DOUBLE-SAT is NP-complete by reduction from 3SAT. The 3-SAT problem consists of a conjunction of clauses over n Boolean variables, where
NP-complete Reductions 1. Prove that 3SAT P DOUBLE-SAT, i.e., show DOUBLE-SAT is NP-complete by reduction from 3SAT. The 3-SAT problem consists of a conjunction of clauses over n Boolean variables, where
The k-center problem Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas
 Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas 1 Definition: Let G=(V,E) be a complete undirected graph with edge costs satisfying the triangle inequality and k be an integer, 0 < k V. For any S V and vertex
Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas 1 Definition: Let G=(V,E) be a complete undirected graph with edge costs satisfying the triangle inequality and k be an integer, 0 < k V. For any S V and vertex
Approximation slides 1. An optimal polynomial algorithm for the Vertex Cover and matching in Bipartite graphs
 Approximation slides 1 An optimal polynomial algorithm for the Vertex Cover and matching in Bipartite graphs Approximation slides 2 Linear independence A collection of row vectors {v T i } are independent
Approximation slides 1 An optimal polynomial algorithm for the Vertex Cover and matching in Bipartite graphs Approximation slides 2 Linear independence A collection of row vectors {v T i } are independent
The Six Color Theorem
 The Six Color Theorem The Six Color Theorem Theorem. Let G be a planar graph. There exists a proper -coloring of G. Proof. Let G be a the smallest planar graph (by number of vertices) that has no proper
The Six Color Theorem The Six Color Theorem Theorem. Let G be a planar graph. There exists a proper -coloring of G. Proof. Let G be a the smallest planar graph (by number of vertices) that has no proper
Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In
 Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In Hans L. Bodlaender Pinar Heggernes Yngve Villanger Technical Report UU-CS-2008-042 December 2008 Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht
Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In Hans L. Bodlaender Pinar Heggernes Yngve Villanger Technical Report UU-CS-2008-042 December 2008 Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht
EE512 Graphical Models Fall 2009
 EE512 Graphical Models Fall 2009 Prof. Jeff Bilmes University of Washington, Seattle Department of Electrical Engineering Fall Quarter, 2009 http://ssli.ee.washington.edu/~bilmes/ee512fa09 Lecture 11 -
EE512 Graphical Models Fall 2009 Prof. Jeff Bilmes University of Washington, Seattle Department of Electrical Engineering Fall Quarter, 2009 http://ssli.ee.washington.edu/~bilmes/ee512fa09 Lecture 11 -
Section 3.1: Nonseparable Graphs Cut vertex of a connected graph G: A vertex x G such that G x is not connected. Theorem 3.1, p. 57: Every connected
 Section 3.1: Nonseparable Graphs Cut vertex of a connected graph G: A vertex x G such that G x is not connected. Theorem 3.1, p. 57: Every connected graph G with at least 2 vertices contains at least 2
Section 3.1: Nonseparable Graphs Cut vertex of a connected graph G: A vertex x G such that G x is not connected. Theorem 3.1, p. 57: Every connected graph G with at least 2 vertices contains at least 2
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R + Goal: find a tour (Hamiltonian cycle) of minimum cost
 Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R + Goal: find a tour (Hamiltonian cycle) of minimum cost Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R + Goal: find a tour (Hamiltonian cycle) of minimum cost Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity
 Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
Lecture 7: Counting classes
 princeton university cos 522: computational complexity Lecture 7: Counting classes Lecturer: Sanjeev Arora Scribe:Manoj First we define a few interesting problems: Given a boolean function φ, #SAT is the
princeton university cos 522: computational complexity Lecture 7: Counting classes Lecturer: Sanjeev Arora Scribe:Manoj First we define a few interesting problems: Given a boolean function φ, #SAT is the
Vertex 3-colorability of claw-free graphs
 Algorithmic Operations Research Vol.2 (27) 5 2 Vertex 3-colorability of claw-free graphs Marcin Kamiński a Vadim Lozin a a RUTCOR - Rutgers University Center for Operations Research, 64 Bartholomew Road,
Algorithmic Operations Research Vol.2 (27) 5 2 Vertex 3-colorability of claw-free graphs Marcin Kamiński a Vadim Lozin a a RUTCOR - Rutgers University Center for Operations Research, 64 Bartholomew Road,
V :non-empty vertex ornode set E V V :edge set G (V, E) :directed graph on V, or digraph on V
 -93-11. Graph Theory Example: V :non-empty vertex ornode set E V V :edge set G (V, E) :directed graph on V, or digraph on V b e f V={a, b, c, d, e, f, g} a c d f E={(a,b), (b,c), (c,a),... } Note: (a,
-93-11. Graph Theory Example: V :non-empty vertex ornode set E V V :edge set G (V, E) :directed graph on V, or digraph on V b e f V={a, b, c, d, e, f, g} a c d f E={(a,b), (b,c), (c,a),... } Note: (a,
Tree Spanners of Simple Graphs
 Tree Spanners of Simple Graphs by Ioannis E. Papoutsakis A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate Department of Computer Science University
Tree Spanners of Simple Graphs by Ioannis E. Papoutsakis A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate Department of Computer Science University
arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 8 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 8 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 8 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/113547113.jpg) Subset Feedback Vertex Set in Chordal and Split Graphs Geevarghese Philip 1, Varun Rajan 2, Saket Saurabh 3,4, and Prafullkumar Tale 5 arxiv:1901.02209v1 [cs.ds] 8 Jan 2019 1 Chennai Mathematical Institute,
Subset Feedback Vertex Set in Chordal and Split Graphs Geevarghese Philip 1, Varun Rajan 2, Saket Saurabh 3,4, and Prafullkumar Tale 5 arxiv:1901.02209v1 [cs.ds] 8 Jan 2019 1 Chennai Mathematical Institute,
Chordal deletion is fixed-parameter tractable
 Chordal deletion is fixed-parameter tractable Dániel Marx Institut für Informatik, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Unter den Linden 6, 10099 Berlin, Germany. dmarx@informatik.hu-berlin.de Abstract. It
Chordal deletion is fixed-parameter tractable Dániel Marx Institut für Informatik, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Unter den Linden 6, 10099 Berlin, Germany. dmarx@informatik.hu-berlin.de Abstract. It
The NP-completeness of some edge-partitioning. problems
 The NP-completeness of some edge-partitioning problems by Sebastian M. Cioabă A thesis submitted to the Department of Mathematics and Statistics in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master
The NP-completeness of some edge-partitioning problems by Sebastian M. Cioabă A thesis submitted to the Department of Mathematics and Statistics in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master
Prove, where is known to be NP-complete. The following problems are NP-Complete:
 CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 21 To prove is NP-complete: Prove NP. Prove, where is known to be NP-complete. The following problems are NP-Complete: SAT (Cook-Levin Theorem) 3-SAT 3-COLOR CLIQUE
CMPSCI 601: Recall From Last Time Lecture 21 To prove is NP-complete: Prove NP. Prove, where is known to be NP-complete. The following problems are NP-Complete: SAT (Cook-Levin Theorem) 3-SAT 3-COLOR CLIQUE
Lecture 10 October 7, 2014
 6.890: Algorithmic Lower Bounds: Fun With Hardness Proofs Fall 2014 Lecture 10 October 7, 2014 Prof. Erik Demaine Scribes: Fermi Ma, Asa Oines, Mikhail Rudoy, Erik Waingarten Overview This lecture begins
6.890: Algorithmic Lower Bounds: Fun With Hardness Proofs Fall 2014 Lecture 10 October 7, 2014 Prof. Erik Demaine Scribes: Fermi Ma, Asa Oines, Mikhail Rudoy, Erik Waingarten Overview This lecture begins
Math 170- Graph Theory Notes
 1 Math 170- Graph Theory Notes Michael Levet December 3, 2018 Notation: Let n be a positive integer. Denote [n] to be the set {1, 2,..., n}. So for example, [3] = {1, 2, 3}. To quote Bud Brown, Graph theory
1 Math 170- Graph Theory Notes Michael Levet December 3, 2018 Notation: Let n be a positive integer. Denote [n] to be the set {1, 2,..., n}. So for example, [3] = {1, 2, 3}. To quote Bud Brown, Graph theory
Reductions of Graph Isomorphism Problems. Margareta Ackerman. Technical Report 08
 CS-2008-08 Reductions of Graph Isomorphism Problems Margareta Ackerman Technical Report 08 David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science, University of Waterloo. 1 REDUCTIONS OF GRAPH ISOMORPHISM PROBLEMS
CS-2008-08 Reductions of Graph Isomorphism Problems Margareta Ackerman Technical Report 08 David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science, University of Waterloo. 1 REDUCTIONS OF GRAPH ISOMORPHISM PROBLEMS
Lecture 21: Other Reductions Steven Skiena. Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY
 Lecture 21: Other Reductions Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena Problem of the Day Show that the Dense
Lecture 21: Other Reductions Steven Skiena Department of Computer Science State University of New York Stony Brook, NY 11794 4400 http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/ skiena Problem of the Day Show that the Dense
CS 125 Section #10 Midterm 2 Review 11/5/14
 CS 125 Section #10 Midterm 2 Review 11/5/14 1 Topics Covered This midterm covers up through NP-completeness; countability, decidability, and recognizability will not appear on this midterm. Disclaimer:
CS 125 Section #10 Midterm 2 Review 11/5/14 1 Topics Covered This midterm covers up through NP-completeness; countability, decidability, and recognizability will not appear on this midterm. Disclaimer:
Treewidth and graph minors
 Treewidth and graph minors Lectures 9 and 10, December 29, 2011, January 5, 2012 We shall touch upon the theory of Graph Minors by Robertson and Seymour. This theory gives a very general condition under
Treewidth and graph minors Lectures 9 and 10, December 29, 2011, January 5, 2012 We shall touch upon the theory of Graph Minors by Robertson and Seymour. This theory gives a very general condition under
by conservation of flow, hence the cancelation. Similarly, we have
 Chapter 13: Network Flows and Applications Network: directed graph with source S and target T. Non-negative edge weights represent capacities. Assume no edges into S or out of T. (If necessary, we can
Chapter 13: Network Flows and Applications Network: directed graph with source S and target T. Non-negative edge weights represent capacities. Assume no edges into S or out of T. (If necessary, we can
Math 776 Graph Theory Lecture Note 1 Basic concepts
 Math 776 Graph Theory Lecture Note 1 Basic concepts Lectured by Lincoln Lu Transcribed by Lincoln Lu Graph theory was founded by the great Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707-178) after he solved
Math 776 Graph Theory Lecture Note 1 Basic concepts Lectured by Lincoln Lu Transcribed by Lincoln Lu Graph theory was founded by the great Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707-178) after he solved
Proposition 1. The edges of an even graph can be split (partitioned) into cycles, no two of which have an edge in common.
 Math 3116 Dr. Franz Rothe June 5, 2012 08SUM\3116_2012t1.tex Name: Use the back pages for extra space 1 Solution of Test 1.1 Eulerian graphs Proposition 1. The edges of an even graph can be split (partitioned)
Math 3116 Dr. Franz Rothe June 5, 2012 08SUM\3116_2012t1.tex Name: Use the back pages for extra space 1 Solution of Test 1.1 Eulerian graphs Proposition 1. The edges of an even graph can be split (partitioned)
Lecture and notes by: Nate Chenette, Brent Myers, Hari Prasad November 8, Property Testing
 Property Testing 1 Introduction Broadly, property testing is the study of the following class of problems: Given the ability to perform (local) queries concerning a particular object (e.g., a function,
Property Testing 1 Introduction Broadly, property testing is the study of the following class of problems: Given the ability to perform (local) queries concerning a particular object (e.g., a function,
UML CS Algorithms Qualifying Exam Spring, 2004 ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM
 NAME: This exam is open: - books - notes and closed: - neighbors - calculators ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM The upper bound on exam time is 3 hours. Please put all your work on the exam paper. (Partial credit
NAME: This exam is open: - books - notes and closed: - neighbors - calculators ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM The upper bound on exam time is 3 hours. Please put all your work on the exam paper. (Partial credit
Best known solution time is Ω(V!) Check every permutation of vertices to see if there is a graph edge between adjacent vertices
 Hard Problems Euler-Tour Problem Undirected graph G=(V,E) An Euler Tour is a path where every edge appears exactly once. The Euler-Tour Problem: does graph G have an Euler Path? Answerable in O(E) time.
Hard Problems Euler-Tour Problem Undirected graph G=(V,E) An Euler Tour is a path where every edge appears exactly once. The Euler-Tour Problem: does graph G have an Euler Path? Answerable in O(E) time.
1 Introduction The concept of graph spanners has been studied in several recent papers in the context of communication networks, distributed computing
 On the Hardness of Approximating Spanners Guy Kortsarz June 1, 1999 Abstract A k spanner of a connected graph G = (V; E) is a subgraph G 0 consisting of all the vertices of V and a subset of the edges,
On the Hardness of Approximating Spanners Guy Kortsarz June 1, 1999 Abstract A k spanner of a connected graph G = (V; E) is a subgraph G 0 consisting of all the vertices of V and a subset of the edges,
COLORING EDGES AND VERTICES OF GRAPHS WITHOUT SHORT OR LONG CYCLES
 Volume 2, Number 1, Pages 61 66 ISSN 1715-0868 COLORING EDGES AND VERTICES OF GRAPHS WITHOUT SHORT OR LONG CYCLES MARCIN KAMIŃSKI AND VADIM LOZIN Abstract. Vertex and edge colorability are two graph problems
Volume 2, Number 1, Pages 61 66 ISSN 1715-0868 COLORING EDGES AND VERTICES OF GRAPHS WITHOUT SHORT OR LONG CYCLES MARCIN KAMIŃSKI AND VADIM LOZIN Abstract. Vertex and edge colorability are two graph problems
HW Graph Theory SOLUTIONS (hbovik) - Q
 1, Diestel 9.3: An arithmetic progression is an increasing sequence of numbers of the form a, a+d, a+ d, a + 3d.... Van der Waerden s theorem says that no matter how we partition the natural numbers into
1, Diestel 9.3: An arithmetic progression is an increasing sequence of numbers of the form a, a+d, a+ d, a + 3d.... Van der Waerden s theorem says that no matter how we partition the natural numbers into
THE RAINBOW DOMINATION SUBDIVISION NUMBERS OF GRAPHS. N. Dehgardi, S. M. Sheikholeslami and L. Volkmann. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 67, 2 (2015), 102 114 June 2015 originalni nauqni rad research paper THE RAINBOW DOMINATION SUBDIVISION NUMBERS OF GRAPHS N. Dehgardi, S. M. Sheikholeslami and L. Volkmann Abstract.
MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 67, 2 (2015), 102 114 June 2015 originalni nauqni rad research paper THE RAINBOW DOMINATION SUBDIVISION NUMBERS OF GRAPHS N. Dehgardi, S. M. Sheikholeslami and L. Volkmann Abstract.
Kernelization Upper Bounds for Parameterized Graph Coloring Problems
 Kernelization Upper Bounds for Parameterized Graph Coloring Problems Pim de Weijer Master Thesis: ICA-3137910 Supervisor: Hans L. Bodlaender Computing Science, Utrecht University 1 Abstract This thesis
Kernelization Upper Bounds for Parameterized Graph Coloring Problems Pim de Weijer Master Thesis: ICA-3137910 Supervisor: Hans L. Bodlaender Computing Science, Utrecht University 1 Abstract This thesis
Chordal graphs MPRI
 Chordal graphs MPRI 2017 2018 Michel Habib habib@irif.fr http://www.irif.fr/~habib Sophie Germain, septembre 2017 Schedule Chordal graphs Representation of chordal graphs LBFS and chordal graphs More structural
Chordal graphs MPRI 2017 2018 Michel Habib habib@irif.fr http://www.irif.fr/~habib Sophie Germain, septembre 2017 Schedule Chordal graphs Representation of chordal graphs LBFS and chordal graphs More structural
Computing minimum distortion embeddings into a path for bipartite permutation graphs and threshold graphs
 Computing minimum distortion embeddings into a path for bipartite permutation graphs and threshold graphs Pinar Heggernes Daniel Meister Andrzej Proskurowski Abstract The problem of computing minimum distortion
Computing minimum distortion embeddings into a path for bipartite permutation graphs and threshold graphs Pinar Heggernes Daniel Meister Andrzej Proskurowski Abstract The problem of computing minimum distortion
Principles of AI Planning. Principles of AI Planning. 7.1 How to obtain a heuristic. 7.2 Relaxed planning tasks. 7.1 How to obtain a heuristic
 Principles of AI Planning June 8th, 2010 7. Planning as search: relaxed planning tasks Principles of AI Planning 7. Planning as search: relaxed planning tasks Malte Helmert and Bernhard Nebel 7.1 How to
Principles of AI Planning June 8th, 2010 7. Planning as search: relaxed planning tasks Principles of AI Planning 7. Planning as search: relaxed planning tasks Malte Helmert and Bernhard Nebel 7.1 How to
ECS 20 Lecture 17b = Discussion D8 Fall Nov 2013 Phil Rogaway
 1 ECS 20 Lecture 17b = Discussion D8 Fall 2013 25 Nov 2013 Phil Rogaway Today: Using discussion section to finish up graph theory. Much of these notes the same as those prepared for last lecture and the
1 ECS 20 Lecture 17b = Discussion D8 Fall 2013 25 Nov 2013 Phil Rogaway Today: Using discussion section to finish up graph theory. Much of these notes the same as those prepared for last lecture and the
Genus Characterizes the Complexity of Certain Graph Problems: Some Tight Results
 Genus Characterizes the Complexity of Certain Graph Problems: Some Tight Results Jianer Chen Iyad A. Kanj Ljubomir Perković Eric Sedgwick Ge Xia Abstract We study the fixed-parameter tractability, subexponential
Genus Characterizes the Complexity of Certain Graph Problems: Some Tight Results Jianer Chen Iyad A. Kanj Ljubomir Perković Eric Sedgwick Ge Xia Abstract We study the fixed-parameter tractability, subexponential
Graph Editing to a Given Degree Sequence,
 Graph Editing to a Given Degree Sequence, Petr A. Golovach a, George B. Mertzios b, a Department of Informatics, University of Bergen, N-5020 Bergen, Norway b School of Engineering and Computing Sciences,
Graph Editing to a Given Degree Sequence, Petr A. Golovach a, George B. Mertzios b, a Department of Informatics, University of Bergen, N-5020 Bergen, Norway b School of Engineering and Computing Sciences,
Vertex coloring, chromatic number
 Vertex coloring, chromatic number A k-coloring of a graph G is a labeling f : V (G) S, where S = k. The labels are called colors; the vertices of one color form a color class. A k-coloring is proper if
Vertex coloring, chromatic number A k-coloring of a graph G is a labeling f : V (G) S, where S = k. The labels are called colors; the vertices of one color form a color class. A k-coloring is proper if
Introduction to Parameterized Complexity
 Introduction to Parameterized Complexity M. Pouly Department of Informatics University of Fribourg, Switzerland Internal Seminar June 2006 Outline Introduction & Motivation The Misery of Dr. O The Perspective
Introduction to Parameterized Complexity M. Pouly Department of Informatics University of Fribourg, Switzerland Internal Seminar June 2006 Outline Introduction & Motivation The Misery of Dr. O The Perspective
arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 30 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 30 Jan 2018 arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 30 Jan 2018](/thumbs/83/87511369.jpg) The complexity of tropical graph homomorphisms Florent Foucaud Ararat Harutyunyan Pavol Hell Sylvain Legay annis Manoussakis Reza Naserasr January 31, 2018 Note to readers. A shorter version of this article
The complexity of tropical graph homomorphisms Florent Foucaud Ararat Harutyunyan Pavol Hell Sylvain Legay annis Manoussakis Reza Naserasr January 31, 2018 Note to readers. A shorter version of this article
Modules. 6 Hamilton Graphs (4-8 lectures) Introduction Necessary conditions and sufficient conditions Exercises...
 Modules 6 Hamilton Graphs (4-8 lectures) 135 6.1 Introduction................................ 136 6.2 Necessary conditions and sufficient conditions............. 137 Exercises..................................
Modules 6 Hamilton Graphs (4-8 lectures) 135 6.1 Introduction................................ 136 6.2 Necessary conditions and sufficient conditions............. 137 Exercises..................................
9 About Intersection Graphs
 9 About Intersection Graphs Since this lecture we focus on selected detailed topics in Graph theory that are close to your teacher s heart... The first selected topic is that of intersection graphs, i.e.
9 About Intersection Graphs Since this lecture we focus on selected detailed topics in Graph theory that are close to your teacher s heart... The first selected topic is that of intersection graphs, i.e.
The Structure of Bull-Free Perfect Graphs
 The Structure of Bull-Free Perfect Graphs Maria Chudnovsky and Irena Penev Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 USA May 18, 2012 Abstract The bull is a graph consisting of a triangle and two vertex-disjoint
The Structure of Bull-Free Perfect Graphs Maria Chudnovsky and Irena Penev Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 USA May 18, 2012 Abstract The bull is a graph consisting of a triangle and two vertex-disjoint
Decision Problems. Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not.
 Decision Problems Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not. Definition: The class of problems that can be solved by polynomial-time
Decision Problems Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not. Definition: The class of problems that can be solved by polynomial-time
Computational problems. Lecture 2: Combinatorial search and optimisation problems. Computational problems. Examples. Example
 Lecture 2: Combinatorial search and optimisation problems Different types of computational problems Examples of computational problems Relationships between problems Computational properties of different
Lecture 2: Combinatorial search and optimisation problems Different types of computational problems Examples of computational problems Relationships between problems Computational properties of different
The NP-Completeness of Some Edge-Partition Problems
 The NP-Completeness of Some Edge-Partition Problems Ian Holyer y SIAM J. COMPUT, Vol. 10, No. 4, November 1981 (pp. 713-717) c1981 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics 0097-5397/81/1004-0006
The NP-Completeness of Some Edge-Partition Problems Ian Holyer y SIAM J. COMPUT, Vol. 10, No. 4, November 1981 (pp. 713-717) c1981 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics 0097-5397/81/1004-0006
The Restrained Edge Geodetic Number of a Graph
 International Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 11, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9 19 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcam.htm The Restrained Edge
International Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 11, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9 19 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcam.htm The Restrained Edge
1 Matchings with Tutte s Theorem
 1 Matchings with Tutte s Theorem Last week we saw a fairly strong necessary criterion for a graph to have a perfect matching. Today we see that this condition is in fact sufficient. Theorem 1 (Tutte, 47).
1 Matchings with Tutte s Theorem Last week we saw a fairly strong necessary criterion for a graph to have a perfect matching. Today we see that this condition is in fact sufficient. Theorem 1 (Tutte, 47).
Definition: A graph G = (V, E) is called a tree if G is connected and acyclic. The following theorem captures many important facts about trees.
 Tree 1. Trees and their Properties. Spanning trees 3. Minimum Spanning Trees 4. Applications of Minimum Spanning Trees 5. Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms 1.1 Properties of Trees: Definition: A graph G
Tree 1. Trees and their Properties. Spanning trees 3. Minimum Spanning Trees 4. Applications of Minimum Spanning Trees 5. Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms 1.1 Properties of Trees: Definition: A graph G
How many colors are needed to color a map?
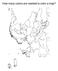 How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
EE512 Graphical Models Fall 2009
 EE512 Graphical Models Fall 2009 Prof. Jeff Bilmes University of Washington, Seattle Department of Electrical Engineering Fall Quarter, 2009 http://ssli.ee.washington.edu/~bilmes/ee512fa09 Lecture 13 -
EE512 Graphical Models Fall 2009 Prof. Jeff Bilmes University of Washington, Seattle Department of Electrical Engineering Fall Quarter, 2009 http://ssli.ee.washington.edu/~bilmes/ee512fa09 Lecture 13 -
arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 30 Apr 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 30 Apr 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 30 Apr 2014](/thumbs/84/90655931.jpg) The stable set polytope of (P 6,triangle)-free graphs and new facet-inducing graphs Raffaele Mosca arxiv:1404.7623v1 [cs.dm] 30 Apr 2014 May 1, 2014 Abstract The stable set polytope of a graph G, denoted
The stable set polytope of (P 6,triangle)-free graphs and new facet-inducing graphs Raffaele Mosca arxiv:1404.7623v1 [cs.dm] 30 Apr 2014 May 1, 2014 Abstract The stable set polytope of a graph G, denoted
Vertex coloring, chromatic number
 Vertex coloring, chromatic number A k-coloring of a graph G is a labeling f : V (G) S, where S = k. The labels are called colors; the vertices of one color form a color class. A k-coloring is proper if
Vertex coloring, chromatic number A k-coloring of a graph G is a labeling f : V (G) S, where S = k. The labels are called colors; the vertices of one color form a color class. A k-coloring is proper if
On Approximating Minimum Vertex Cover for Graphs with Perfect Matching
 On Approximating Minimum Vertex Cover for Graphs with Perfect Matching Jianer Chen and Iyad A. Kanj Abstract It has been a challenging open problem whether there is a polynomial time approximation algorithm
On Approximating Minimum Vertex Cover for Graphs with Perfect Matching Jianer Chen and Iyad A. Kanj Abstract It has been a challenging open problem whether there is a polynomial time approximation algorithm
v 2 v 3 v 1 v 0 K 3 K 1
 It is Hard to Know when Greedy is Good for Finding Independent Sets Hans L. Bodlaender, Dimitrios M. Thilikos, Koichi Yamazaki Department of Computer Science, Utrecht University, P.O. Box 80.089, 3508
It is Hard to Know when Greedy is Good for Finding Independent Sets Hans L. Bodlaender, Dimitrios M. Thilikos, Koichi Yamazaki Department of Computer Science, Utrecht University, P.O. Box 80.089, 3508
arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 19 Feb 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 19 Feb 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 19 Feb 2014](/thumbs/72/67418946.jpg) Turing Kernelization for Finding Long Paths and Cycles in Restricted Graph Classes Bart M. P. Jansen 1 University of Bergen, Norway. Bart.Jansen@ii.uib.no arxiv:1402.4718v1 [cs.ds] 19 Feb 2014 Abstract.
Turing Kernelization for Finding Long Paths and Cycles in Restricted Graph Classes Bart M. P. Jansen 1 University of Bergen, Norway. Bart.Jansen@ii.uib.no arxiv:1402.4718v1 [cs.ds] 19 Feb 2014 Abstract.
