Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry
|
|
|
- Magdalen Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry
2 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic Sections in Polar Coordinates
3 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic Sections in Polar Coordinates
4 Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Geometric Definitions of Conic Sections and Their Standard Equations Each conic secteach conic section (or simply conic) can be described as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. There are seven different possible intersections. Three Others When the intersecting plane passes through the vertex of the cone. Four Basic Conics For four basic conics, the intersecting plane does not pass through the vertex of the cone.
5 Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Geometric Definitions of Conic Sections and Their Standard Equations Parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas General second-degree equation Ax 2 + Bxy + Cy 2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 1. The paths of the planets around the sun (ellipses) 2. Parabolic mirrors are used to converge light beams at the focus of the parabola 3. Parabolic microphones perform a similar function with sound waves 4. Parabola is used in the design of car headlights and in spotlights 5. Trajectory of objects thrown or shot near the earth s surface will follow a parabolic path 6. Hyperbolas are used in a navigation system known as LORAN(long range navigation) 7. Hyperbolic as well as parabolic mirrors and lenses are used in systems of telescopes.
6 Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry In this section, we study their exact mathematical definition in which each of the conics is defined as a locus (collection) of points satisfying a certain geometric property. For example, a circle can be defined as the collection of all points (x, y) that are equidistant from a fixed point (h, k). This locus definition easily produces the standard equation of a circle x h 2 + y k 2 = r 2.
7 9.1 The Ellipse Objectives: Graph ellipses centered at the origin. Write equations of ellipses in standard form. Graph ellipses not centered at the origin. Solve applied problems involving ellipses.
8 9.1 The Ellipse Ellipse An ellipse is the set of points in a plane the sum of whose distances from two fixed points F 1 and F 2 is a constant. These two fixed points are called the foci (plural of focus). The midpoint of the line segment connecting the foci is called the center. The line passing through two foci is called the major axis. The perpendicular line to the major axis passing through the midpoint of two foci is called the minor axis. The two intersection points of the major axis and the ellipse are called vertices. minor axis vertex ( a, 0) (0, b) P(x, y) (0,0) F 1 F 2 ( c, 0) (c, 0) (0, b) vertex (a, 0) major axis Standard Equation Let the sum of the distances from a point on the ellipse to the foci be 2a. Then x 2 a 2 + y2 b 2 = 1 where c 2 = a 2 b 2 < a 2.
9 9.1 The Ellipse vertex ( a, 0) ( b, 0) (0, b) minor axis (0,0) P(x, y) F 1 F 2 ( c, 0) (c, 0) (0, b) vertex (0, a) (0, c) F 1 F (0, c) 2 major axis vertex (0,0) (0, a) vertex (a, 0) P(x, y) (b, 0) major axis minor axis Standard Equation Let the sum of the distances from a point on the ellipse to the foci be 2a. Then x 2 a 2 + y2 b 2 = 1 where b 2 = a 2 c 2 < a 2. Standard Equation Let the sum of the distances from a point on the ellipse to the foci be 2a. Then x 2 b 2 + y2 a 2 = 1 where b 2 = a 2 c 2 < a 2.
10 9.1 The Ellipse Standard Equation of an Ellipse with Translations The standard form of the equation of a parabola with center (h, k) and major and minor axes of lengths 2a and 2b, a > b, is x h 2 y k 2 a 2 + b 2 = 1 Major axis is horizontal or x h 2 2 y k b 2 + a 2 = 1 Major axis is vertical The foci lie on the major axis, c units from the center, with c 2 = a 2 b 2 The ration e = c/a is called the eccentricity of an ellipse.
11 9.1 The Ellipse Example 1. Graph and locate the foci: x2 9 + y2 4 = 1.
12 9.1 The Ellipse Example 2. Graph and locate the foci: 25x y 2 = 400.
13 9.1 The Ellipse Example 3. Find the strandard form of the equation of an ellipse with foci at ( 1, 0) and (1, 0) and vertices 2, 0 and 2, 0.
14 9.1 The Ellipse Example 4. Graph x y = 1. Where are the foci located?
15 9.1 The Ellipse Example 5. (Graphing an Ellipse Centered at (h, k) by Completing the Square Graph 4x y x 288y = 0. Where are the foci located?
16 9.1 The Ellipse Applications of Ellipse Movements of Planets in Our Solar System The planets in our solar system move in elliptical orbits, with the Sun at a focus. Earth satellites also travel in elliptic orbits, with Earth at a focus.
17 9.1 The Ellipse Applications of Ellipse Reflection Property of an Ellipse Let P be a point on an ellipse. The tangent line to the ellipse at point P makes equal angles with the lines through P and the foci.
18 9.1 The Ellipse Applications of Ellipse Constructive Design Example 6. A semielliptical archway over a one-way road has a height of 10 eet and a width of 40 feet. Your truck has a width of 10 feet and a height of 9 feet. Will your truck clear the opening of the archway? End of 9.1
19 9.2 The Hyperbola Objectives: Locate a hyperbola s vertices and foci. Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Graph hyperbolas centered at the origin. Graph hyperbolas not centered at the origin. Solve applied problems involving hyperbolas.
20 9.2 The Hyperbola Hyperbolas An hyperbola is the set of points in a plane the difference of whose distances from two fixed points F 1 and F 2 is a constant. These two fixed points are called the foci. The peaks are called the vertices of the hyperbola. An hyperbola has two slant asymptotes: y = b a x and y = b a x y = b a x P(x, y) (0,0) ( c, 0) (c, 0) F 1 F 2 vertices ( a, 0) and (a, 0) y = b a x Standard Equation Let the difference of the distances from a point on the ellipse to the foci be ±2a. Then x 2 a 2 y2 b 2 = 1 where c 2 = a 2 + b 2.
21 9.2 The Hyperbola P(x, y) (0,0) ( c, 0) (c, 0) F 1 F 2 vertices ( a, 0) and (a, 0) y = b a x y = b a x Standard Equation Let the difference of the distances from a point on the ellipse to the foci be ±2a. Then x 2 a 2 y2 b 2 = 1 where c 2 = a 2 + b 2. Asymptotes: y = ± b/a x. P(x, y) vertices (0, a) and (0, a) (0, c) F 2 (0,0) F 1 (0, c) y = a b x y = a b x Standard Equation Let the difference of the distances from a point on the ellipse to the foci be ±2a. Then y 2 a 2 x2 b 2 = 1 where c 2 = a 2 + b 2. Asymptotes: y = ± a/b x.
22 9.2 The Hyperbola Standard Equation of a Hyperbola The standard form of the equation of a parabola with center at (h, k) is x h 2 2 y k a 2 b 2 = 1 Transverse axis is horizontal or y k 2 a 2 x h 2 b 2 = 1 Transverse axis is vertical The vertices are a units from the center, and the foci are c units from the center, where c 2 = a 2 + b 2. The eccentricity e of a hyperbola is given by the ratio e = c/a (> 1). Asymptotes of a Hyperbola For a horizontal transverse axis, the equation of the asymptotes are y = k + b a x h and y = k b a x h. For a vertical transverse axis, the equation of the asymptotes are y = k + a b x h and y = k a b x h.
23 9.2 The Hyperbola Example 1. Find the vertices and locate the foci for each of the following hyperbolas with the given equation: a x2 16 y2 9 = 1 b y2 9 x2 16 = 1
24 9.2 The Hyperbola Example 2. Find the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with foci at (0, 3) and (0, 3) and vertices (0, 2) and (0, 2).
25 9.2 The Hyperbola Graphing Hyperbola 1. Locate the vertices Use DASHED lines to draw the rectangle centered at the origin with sides parallel to the axes, crossing one axis at ±a and the other at ±b. 3. Use dashed lines to draw the diagonals of this rectangle and extend them to obtain the asymptotes. 4. Draw the two branches of the hyperbola by starting at each vertex and approaching the asymptotes. Example 3. Graph and locate the foci: x2 y asymptotes. = 1. What are the equations of the
26 9.2 The Hyperbola Example 4. Graph and locate the foci: 9y 2 4x 2 = 36. What are the equations of the asymptotes?
27 9.2 The Hyperbola Example 5. Graph x y equations of the asymptotes? = 1. Where are the foci located? What are the
28 9.2 The Hyperbola Example 6. Graph 4x 2 24x 25y y 489 = 0. Where are the foci located? What are the equations of the asymptotes?
29 9.2 The Hyperbola Applications of the Hyperbola When a jet flies at a speed greater than the speed of sound, the shock wave that is created is heard as a sonic boom. The wave has the shape of a cone. The shape formed as the cone hits the ground is one branch of a hyperbola. Halley s Comet, a permanent part of our solar system, travels around the Sun in an elliptic orbit. Other comets pass through the solar system only once, following a hyperbolic path with the Sun as a focus.
30 9.2 The Hyperbola Example 7. (Application) An explosion is recorded by two microphones that are 2 miles apart. Microphone M 1 received the sound 4 seconds before microphone M 2. Assuming sound travels at 1100 feet per second, determine the possible locations of the explosion relative to the location of the microphones. End of 9.2
31 9.3 The Parabolas Objectives: Graph parabolas with vertices at the origin. Write equations of parabolas in standard form. Graph parabolas with vertices not at the origin. Solve applied problems involving parabolas. Identity conics without completing the square.
32 9.3 The Parabolas What we have learned about a parabola in Algebra class: y = a x h 2 + k or y = a x h 2 + k Note h = b b and k = f. 2a 2a Graphing Parabolas Graphing y = a x h 2 + k or y = a x h 2 + k If a > 0, the graph opens upward. If a < 0, the graph opens downward. The vertex of y = a x h 2 + k is (h, k). The x-coordinate of the vertex of y = ax 2 + bx + c is x = b 2a
33 9.3 The Parabolas Definition of Parabolas A parabola is a set of points in a plane that are equidistance from a fixed point F (called the focus) and a fixed line (called the directrix). The point halfway between the focus and the directrix lies on the parabola and it is called the vertex. The line through the focus perpendicular to the directrix is called the axis of the parabola. (0, p) F (focus) (0,0) vertex axis (x, y) directrix y = p Standard Equation An equation of the parabola with focus (0, p) and directrix y = p is x 2 = 4py (See Figure)
34 9.3 The Parabolas (0, p) F (focus) (0,0) vertex axis (x, y) directrix y = p Standard Equation An equation of the parabola with focus (0, p) and directrix y = p is x 2 = 4py (See Figure) vertex axis (0,0) (p, 0) F (focus) Standard Equation An equation of the parabola with focus (p, 0) and directrix x = p is y 2 = 4px directrix x = p (x, y)
35 9.3 The Parabolas Standard Equation of a Parabola The standard form of the equation of a parabola with vertex (h, k) and directrix y = k p is x h 2 = 4p y k Vertical axis For directrix x = h p, the equation is y k 2 = 4p x h Horizontal axis The focus lies on the axis p units (directed distance) from the vertex. The coordinates of the focus are as follows h, k + p Vertical axis h + p, k Horizontal axis
36 9.3 The Parabolas Example 1. Find the focus and directrix of the parabola given by y 2 = 12x. Then graph the parabola.
37 9.3 The Parabolas The Latus Rectum and Graphing Parabolas The latus rectum of a parabola is a line segment that passes through its focus, is parallel to its directrix, and has its endpoints on the parabola. The length of the latus rectum for the graphs of y 2 = 4px and x 2 = 4py is 4p. Example 2. Find the focus and directrix of the parabola given by x 2 = 8y. Then graph the parabola. Include the latus rectum on the graph.
38 9.3 The Parabolas Example 3. Find the standard form of the equation of a parabola with focus (5, 0) and directrix x = 5.
39 9.3 The Parabolas Example 4. Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola given by Then graph the parabola. x 3 2 = 8 y + 1.
40 9.3 The Parabolas Example 5. Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola given by Then graph the parabola. y 2 + 2y + 12x 23 = 0.
41 9.3 The Parabolas Applications of the Hyperbola Cables hung between structures to form suspension bridges form parabolas. Arches constructed of steel and concrete, whose main purpose is strength, are usually parabolic in shape Some comets follow parabolic paths. Only comets with elliptical orbits, such as Halley s Comet, return to our part of the galaxy Light originates at the focus. The refective properties of parabolic surfaces are used in the design of searchlights and automobile headlights.
42 9.3 The Parabolas Example 6. An engineer is designing a flashlight using a parabolic reflecting mirror and a light source. The casting has a diameter of 4 inches and a depth of 2 inches. What is the equation of the parabola used to shape the mirror? At what point should the light source be placed relative to the mirror s vertex?
43 Geometric Definitions of Conic Sections and Their Standard Equations Parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas General second-degree equation Ax 2 + Bxy + Cy 2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
44 Identifying a Conic Section without Completing the Square A nondegenerate conic section of the form Ax 2 + Cy 2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 in which A and C are not both zero, is a circle if A = C, a parabola if AC = 0. an ellipse if A C and AC > 0, and a hyperbola if AC < 0. Example 6. Identify the graph of each of the following nondegenerate conic sections: (a) 4x 2 25y 2 24x + 250y 489 = 0 (b) x 2 + y 2 + 6x 2y + 6 = 0 (c) y x + 2y 23 = 0 (d) 9x y 2 54x + 50y 119 = 0 End of 9.3
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds
 Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Pre-Calculus. 2) Find the equation of the circle having (2, 5) and (-2, -1) as endpoints of the diameter.
 Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
Conic Sections. College Algebra
 Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Unit 12 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork
 Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
13.1 2/20/2018. Conic Sections. Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
 13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
Mid-Chapter Quiz: Lessons 7-1 through 7-3
 Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Figures adapted from Mathworld.wolfram.com and vectosite.net.
 MTH 11 CONIC SECTIONS 1 The four basic types of conic sections we will discuss are: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. They were named conic by the Greeks who used them to describe the intersection
MTH 11 CONIC SECTIONS 1 The four basic types of conic sections we will discuss are: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. They were named conic by the Greeks who used them to describe the intersection
9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics
 9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Find asymptotes of and graph hyperbolas. Use
9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Find asymptotes of and graph hyperbolas. Use
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff. x h y k r
 NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas. Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School
 Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Chapter 10. Exploring Conic Sections
 Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Assignment Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment.1-.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way
Assignment.1-.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
 Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 181. Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Conic Sections Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet
 Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Practice Test - Chapter 7
 Write an equation for an ellipse with each set of characteristics. 1. vertices (7, 4), ( 3, 4); foci (6, 4), ( 2, 4) The distance between the vertices is 2a. 2a = 7 ( 3) a = 5; a 2 = 25 The distance between
Write an equation for an ellipse with each set of characteristics. 1. vertices (7, 4), ( 3, 4); foci (6, 4), ( 2, 4) The distance between the vertices is 2a. 2a = 7 ( 3) a = 5; a 2 = 25 The distance between
Name. Center axis. Introduction to Conic Sections
 Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct equation form as listed!! above, then determine the center and radius of each circle.
 Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
1.) Write the equation of a circle in standard form with radius 3 and center (-3,4). Then graph the circle.
 Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Chapter 3: The Parabola
 Chapter 3: The Parabola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 3: The Parabola Lecture 7: Introduction to Parabola Lecture 8: Converting
Chapter 3: The Parabola SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 3: The Parabola Lecture 7: Introduction to Parabola Lecture 8: Converting
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions
 Unit 5: Quadratic Functions LESSON #5: THE PARABOLA GEOMETRIC DEFINITION DIRECTRIX FOCUS LATUS RECTUM Geometric Definition of a Parabola Quadratic Functions Geometrically, a parabola is the set of all
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions LESSON #5: THE PARABOLA GEOMETRIC DEFINITION DIRECTRIX FOCUS LATUS RECTUM Geometric Definition of a Parabola Quadratic Functions Geometrically, a parabola is the set of all
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
Standard Equation of a Circle
 Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
Conic Sections: Parabolas
 Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Summary of Formulas: see
 To review the Conic Sections, Identify them and sketch them from the given equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering
To review the Conic Sections, Identify them and sketch them from the given equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering
Algebra II. Midpoint and Distance Formula. Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Slide 4 / 181. Slide 6 / 181. Slide 5 / 181.
 Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas
 TEKS 9.5 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Hperbolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas, circles, and ellipses. Now You will graph and write equations of hperbolas. Wh?
TEKS 9.5 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Hperbolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas, circles, and ellipses. Now You will graph and write equations of hperbolas. Wh?
Chapter 10 Test Review
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 10 Test Review Short Answer 1. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin and a focus at ( 2, 0). 2. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 10 Test Review Short Answer 1. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin and a focus at ( 2, 0). 2. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin
, minor axis of length 12. , asymptotes y 2x. 16y
 Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Conics. By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse
 Conics By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse Exploring Conics (This is basically the summary too) A conic section curve formed by intersection of a plane and double cone: by changing plane, one can create parabola,
Conics By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse Exploring Conics (This is basically the summary too) A conic section curve formed by intersection of a plane and double cone: by changing plane, one can create parabola,
Substituting a 2 b 2 for c 2 and using a little algebra, we can then derive the standard equation for an ellipse centred at the origin,
 Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 = 36. Then describe the
Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 = 36. Then describe the
Assignment 3/17/15. Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) (E)
 Section 10.2 Warm Up Assignment 3/17/15 Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) 24 40 (E) Objective We are going to find equations for parabolas identify the vertex, focus, and directrix of a parabola The parabola
Section 10.2 Warm Up Assignment 3/17/15 Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) 24 40 (E) Objective We are going to find equations for parabolas identify the vertex, focus, and directrix of a parabola The parabola
Flash Light Reflectors. Fountains and Projectiles. Algebraically, parabolas are usually defined in two different forms: Standard Form and Vertex Form
 Sec 6.1 Conic Sections Parabolas Name: What is a parabola? It is geometrically defined by a set of points or locus of points that are equidistant from a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). To
Sec 6.1 Conic Sections Parabolas Name: What is a parabola? It is geometrically defined by a set of points or locus of points that are equidistant from a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). To
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Precalculus Fall 204 Midterm Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find an equation in standard form for the hyperbola that
Precalculus Fall 204 Midterm Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find an equation in standard form for the hyperbola that
Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 2 4 x 0
 Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Study Guide and Review
 Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
Chapter. Implicit Function Graphs
 Chapter 14 Implicit Function Graphs You can graph any one of the following types of implicit functions using the calculator s built-in functions. Parabolic graph Circle graph Elliptical graph Hyperbolic
Chapter 14 Implicit Function Graphs You can graph any one of the following types of implicit functions using the calculator s built-in functions. Parabolic graph Circle graph Elliptical graph Hyperbolic
MATH 110 analytic geometry Conics. The Parabola
 1 MATH 11 analytic geometry Conics The graph of a second-degree equation in the coordinates x and y is called a conic section or, more simply, a conic. This designation derives from the fact that the curve
1 MATH 11 analytic geometry Conics The graph of a second-degree equation in the coordinates x and y is called a conic section or, more simply, a conic. This designation derives from the fact that the curve
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
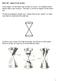 Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
x y 2 2 CONIC SECTIONS Problem 1
 CONIC SECTIONS Problem For the equations below, identify each conic section If it s a parabola, specify its vertex, focus and directrix If it s an ellipse, specify its center, vertices and foci If it s
CONIC SECTIONS Problem For the equations below, identify each conic section If it s a parabola, specify its vertex, focus and directrix If it s an ellipse, specify its center, vertices and foci If it s
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name
 Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x2 6 + y2 = 1 1) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. 2) (x + 2)2 + (y + 1)2 9 = 1 2) Objective:
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x2 6 + y2 = 1 1) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. 2) (x + 2)2 + (y + 1)2 9 = 1 2) Objective:
10.2: Parabolas. Chapter 10: Conic Sections. Conic sections are plane figures formed by the intersection of a double-napped cone and a plane.
 Conic sections are plane figures formed b the intersection of a double-napped cone and a plane. Chapter 10: Conic Sections Ellipse Hperbola The conic sections ma be defined as the sets of points in the
Conic sections are plane figures formed b the intersection of a double-napped cone and a plane. Chapter 10: Conic Sections Ellipse Hperbola The conic sections ma be defined as the sets of points in the
Geometry: Conic Sections
 Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
8.5 Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas p.518 What are the parts of a hyperbola? What are the standard form equations of a hyperbola?
 8.5 Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas p.518 What are the parts of a hyperbola? What are the standard form equations of a hyperbola? How do you know which way it opens? Given a & b, how do you find
8.5 Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas p.518 What are the parts of a hyperbola? What are the standard form equations of a hyperbola? How do you know which way it opens? Given a & b, how do you find
ATHS FC Math Department Al Ain Remedial Plan
 ATHS FC Math Department Al Ain Remedial Plan Section Name ID Date Lesson Marks 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3 Lesson 10.1 (Midpoint and Distance formula) Question: 1 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints
ATHS FC Math Department Al Ain Remedial Plan Section Name ID Date Lesson Marks 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3 Lesson 10.1 (Midpoint and Distance formula) Question: 1 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH. Dr Toh Pee Choon NIE 2 June 2016
 DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
CK 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 10.1 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Answers 1. up 2. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, 0.5), directrix: y = 0.5 5.focus: (0.0625, 0), directrix: x = 0.0625 6.focus: ( 1.25, 0), directrix: x = 1.25 7.focus:
10.1 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Answers 1. up 2. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, 0.5), directrix: y = 0.5 5.focus: (0.0625, 0), directrix: x = 0.0625 6.focus: ( 1.25, 0), directrix: x = 1.25 7.focus:
Today we will be exploring three-dimensional objects, those that possess length, width, and depth.
 Lesson 22 Lesson 22, page 1 of 13 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11.1 3-D figures & Polyhedra Today we will be exploring three-dimensional objects, those that possess length, width, and depth. In Euclidean,
Lesson 22 Lesson 22, page 1 of 13 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 11.1 3-D figures & Polyhedra Today we will be exploring three-dimensional objects, those that possess length, width, and depth. In Euclidean,
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. Page 1
 Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet PARABOLAS
 Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet Name Date Block 1) Complete these truths about parabolas: * Parabolas are - shaped. PARABOLAS * Parabolas have a line of. * Parabolas are the graphs of functions.
Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet Name Date Block 1) Complete these truths about parabolas: * Parabolas are - shaped. PARABOLAS * Parabolas have a line of. * Parabolas are the graphs of functions.
Analytic Geometry. Affine space. 3D y. Dimensions
 y x Analytic Geometry Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra The link between algebra and geometry was made
y x Analytic Geometry Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra The link between algebra and geometry was made
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
PreCalculus Chapter 9 Practice Test Name:
 This ellipse has foci 0,, and therefore has a vertical major axis. The standard form for an ellipse with a vertical major axis is: 1 Note: graphs of conic sections for problems 1 to 1 were made with the
This ellipse has foci 0,, and therefore has a vertical major axis. The standard form for an ellipse with a vertical major axis is: 1 Note: graphs of conic sections for problems 1 to 1 were made with the
Algebra II Chapter 10 Conics Notes Packet. Student Name Teacher Name
 Algebra II Chapter 10 Conics Notes Packet Student Name Teacher Name 1 Conic Sections 2 Identifying Conics Ave both variables squared?' No PARABOLA y = a(x- h)z + k x = a(y- k)z + h YEs Put l'h squared!'erms
Algebra II Chapter 10 Conics Notes Packet Student Name Teacher Name 1 Conic Sections 2 Identifying Conics Ave both variables squared?' No PARABOLA y = a(x- h)z + k x = a(y- k)z + h YEs Put l'h squared!'erms
Chapter 11. Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
OpenStax-CNX module: m The Ellipse. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49438 1 The Ellipse OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Write equations
OpenStax-CNX module: m49438 1 The Ellipse OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Write equations
7. r = r = r = r = r = 2 5
 Exercise a: I. Write the equation in standard form of each circle with its center at the origin and the given radius.. r = 4. r = 6 3. r = 7 r = 5 5. r = 6. r = 6 7. r = 0.3 8. r =.5 9. r = 4 0. r = 3.
Exercise a: I. Write the equation in standard form of each circle with its center at the origin and the given radius.. r = 4. r = 6 3. r = 7 r = 5 5. r = 6. r = 6 7. r = 0.3 8. r =.5 9. r = 4 0. r = 3.
Conic Sections. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Conic Sections MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department o Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction The conic sections include the parabola, the ellipse, and the hyperbola. y y y x x x Parabola A
Conic Sections MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department o Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction The conic sections include the parabola, the ellipse, and the hyperbola. y y y x x x Parabola A
2.) Write the standard form of the equation of a circle whose endpoints of diameter are (4, 7) and (2,3).
 Ch 10: Conic Sections Name: Objectives: Students will be able to: -graph parabolas, hyperbolas and ellipses and answer characteristic questions about these graphs. -write equations of conic sections Dec
Ch 10: Conic Sections Name: Objectives: Students will be able to: -graph parabolas, hyperbolas and ellipses and answer characteristic questions about these graphs. -write equations of conic sections Dec
Algebra II Lesson 10-5: Hyperbolas Mrs. Snow, Instructor
 Algebra II Lesson 10-5: Hyperbolas Mrs. Snow, Instructor In this section, we will look at the hyperbola. A hyperbola is a set of points P in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between
Algebra II Lesson 10-5: Hyperbolas Mrs. Snow, Instructor In this section, we will look at the hyperbola. A hyperbola is a set of points P in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between
3. Solve the following. Round to the nearest thousandth.
 This review does NOT cover everything! Be sure to go over all notes, homework, and tests that were given throughout the semester. 1. Given g ( x) i, h( x) x 4x x, f ( x) x, evaluate the following: a) f
This review does NOT cover everything! Be sure to go over all notes, homework, and tests that were given throughout the semester. 1. Given g ( x) i, h( x) x 4x x, f ( x) x, evaluate the following: a) f
Practice Test - Chapter 9
 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates 1 (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula Find the distance
Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates 1 (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula Find the distance
Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates. 1. (8, 3), ( 4, 9) SOLUTION: Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1
 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates. 1. (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula. 2. Substitute
Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates. 1. (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula. 2. Substitute
Chapter 10 Resource Masters
 Chapter 10 Resource Masters New York, New York Columbus, Ohio Woodland Hills, California Peoria, Illinois StudentWorks TM This CD-ROM includes the entire Student Edition along with the Study Guide, Practice,
Chapter 10 Resource Masters New York, New York Columbus, Ohio Woodland Hills, California Peoria, Illinois StudentWorks TM This CD-ROM includes the entire Student Edition along with the Study Guide, Practice,
Planes Intersecting Cones: Static Hypertext Version
 Page 1 of 12 Planes Intersecting Cones: Static Hypertext Version On this page, we develop some of the details of the plane-slicing-cone picture discussed in the introduction. The relationship between the
Page 1 of 12 Planes Intersecting Cones: Static Hypertext Version On this page, we develop some of the details of the plane-slicing-cone picture discussed in the introduction. The relationship between the
Montclair Public Schools Math Curriculum Unit Planning Template Unit # SLO # MC 2 MC 3
 Subject Geometry High Honors Grade Montclair Public Schools Math Curriculum Unit Planning Template Unit # Pacing 8-10 9 10 weeks Unit Circles, Conic Sections, Area & 3-D Measurements Name Overview Unit
Subject Geometry High Honors Grade Montclair Public Schools Math Curriculum Unit Planning Template Unit # Pacing 8-10 9 10 weeks Unit Circles, Conic Sections, Area & 3-D Measurements Name Overview Unit
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 14.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date The Origin of Parabolas Parabolas Centered at the Origin 1. Consider the parabola represented by the equation y 2 12x 0. a. Write the equation of the parabola
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date The Origin of Parabolas Parabolas Centered at the Origin 1. Consider the parabola represented by the equation y 2 12x 0. a. Write the equation of the parabola
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Chapter 9. Topics in Analytic Geometry. Selected Applications
 Chapter 9 Topics in Analtic Geometr 9. Circles and Parabolas 9. Ellipses 9. Hperbolas 9. Rotation and Sstems of Quadratic Equations 9.5 Parametric Equations 9. Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations
Chapter 9 Topics in Analtic Geometr 9. Circles and Parabolas 9. Ellipses 9. Hperbolas 9. Rotation and Sstems of Quadratic Equations 9.5 Parametric Equations 9. Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Buds Public School, Dubai
 Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Chapter 10: Parametric And Polar Curves; Conic Sections
 206 Chapter 10: Parametric And Polar Curves; Conic Sections Summary: This chapter begins by introducing the idea of representing curves using parameters. These parametric equations of the curves can then
206 Chapter 10: Parametric And Polar Curves; Conic Sections Summary: This chapter begins by introducing the idea of representing curves using parameters. These parametric equations of the curves can then
8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics
 8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics The diagram shows a double cone. The two cones have one point in common. The intersection of a double cone and a plane is called a conic section or a conic. The circle,
8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics The diagram shows a double cone. The two cones have one point in common. The intersection of a double cone and a plane is called a conic section or a conic. The circle,
12.6 Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces
 12 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 12.6 and Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and We have already looked at two special types of surfaces:
12 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 12.6 and Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and We have already looked at two special types of surfaces:
Final Exam Review Algebra Semester 1
 Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Final Exam Review Algebra 015-016 Semester 1 Name: Module 1 Find the inverse of each function. 1. f x 10 4x. g x 15x 10 Use compositions to check if the two functions are inverses. 3. s x 7 x and t(x)
Chapter 9. Topics in Analytic Geometry. Selected Applications
 Chapter 9 Topics in Analtic Geometr 9. Circles and Parabolas 9. Ellipses 9. Hperbolas 9. Rotation and Sstems of Quadratic Equations 9.5 Parametric Equations 9. Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations
Chapter 9 Topics in Analtic Geometr 9. Circles and Parabolas 9. Ellipses 9. Hperbolas 9. Rotation and Sstems of Quadratic Equations 9.5 Parametric Equations 9. Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations
Topics in Two-Dimensional Analytic Geometry
 Chapter Topics in Two-Dimensional Analytic Geometry In this chapter we look at topics in analytic geometry so we can use our calculus in many new settings. Most of the discussion will involve developing
Chapter Topics in Two-Dimensional Analytic Geometry In this chapter we look at topics in analytic geometry so we can use our calculus in many new settings. Most of the discussion will involve developing
Paper Folding and Conic Sections
 Scott G. Smith aper Folding and Conic Sections ne sign of a good problem is that it offers multiple revelations during its investigation. nother is that it can be approached mathematically in more than
Scott G. Smith aper Folding and Conic Sections ne sign of a good problem is that it offers multiple revelations during its investigation. nother is that it can be approached mathematically in more than
Precalculus. Cumulative Review Conics, Polar, Parametric, Sequences & Series, Rational Functions. Conics
 Name Precalculus Date Block Cumulative Review Conics, Polar, Parametric, Sequences & Series, Rational Functions Please do all work on a separate sheet of paper Conics Identify each equation If it is a
Name Precalculus Date Block Cumulative Review Conics, Polar, Parametric, Sequences & Series, Rational Functions Please do all work on a separate sheet of paper Conics Identify each equation If it is a
Parabolas Section 11.1
 Conic Sections Parabolas Section 11.1 Verte=(, ) Verte=(, ) Verte=(, ) 1 3 If the equation is =, then the graph opens in the direction. If the equation is =, then the graph opens in the direction. Parabola---
Conic Sections Parabolas Section 11.1 Verte=(, ) Verte=(, ) Verte=(, ) 1 3 If the equation is =, then the graph opens in the direction. If the equation is =, then the graph opens in the direction. Parabola---
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS. Apply Geometric Concepts in Modeling Situations
 UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Pre-Calculus Mid Term Review. January 2014 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use the graph of the function f, plotted with a solid
Pre-Calculus Mid Term Review. January 2014 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use the graph of the function f, plotted with a solid
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry
 NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
Geometry Common Core State Standard (CCSS) Math
 = ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
= ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended. Mathematics. Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas
 8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Where is the focus and directrix compared to the vertex? How do you know what direction a parabola opens? How do you write the equation of a parabola given the
8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Where is the focus and directrix compared to the vertex? How do you know what direction a parabola opens? How do you write the equation of a parabola given the
8.5. Quadratic Function A function f is a quadratic function if f(x) ax 2 bx c, where a, b, and c are real numbers, with a 0.
 8.5 Quadratic Functions, Applications, and Models In the previous section we discussed linear functions, those that are defined b firstdegree polnomials. In this section we will look at quadratic functions,
8.5 Quadratic Functions, Applications, and Models In the previous section we discussed linear functions, those that are defined b firstdegree polnomials. In this section we will look at quadratic functions,
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review
 Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
Math 8 EXAM #5 Name: Any work or answers completed on this test form, other than the problems that require you to graph, will not be graded.
 Math 8 EXAM #5 Name: Complete all problems in your blue book. Copy the problem into the bluebook then show all of the required work for that problem. Work problems out down the page, not across. Make only
Math 8 EXAM #5 Name: Complete all problems in your blue book. Copy the problem into the bluebook then show all of the required work for that problem. Work problems out down the page, not across. Make only
Make geometric constructions. (Formalize and explain processes)
 Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
