If the center of the sphere is the origin the the equation is. x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0 -(2)
|
|
|
- Felix Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sphere Definition: A sphere is the locus of a point which remains at a constant distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre and the constant distance is the radius of the sphere. Let C(x 0, y 0,z 0) be the centre and r be the radius of a sphere S. Consider a point P(x, y,z) on the sphere. Then the equation of the sphere is given by (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) r - (1) If the center of the sphere is the origin the the equation is x y z r. General equation: Expanding (1), we get x y z 2x x 2y y 2z z x y z r This equation is of the form x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0 -(2) where u x, v y, w z, d x y z r Since C(x 0, y 0,z 0) is the centre and r is the radius of the sphere (2) represents the equation of the sphere whose center is ( u, v, w) and radius is u v w d. Example 1. Find the equation of the passes through the point (1,-2,0). Solution. Since (3,-1,4) is the centre, equation is The sphere passes through the point (1,-2,0), we have (1 3) ( 2 1) (0 4) r r 21 sphere whose centre is (3,-1,4) and which (x 3) (y 1) (z 4) r The required equation is (x 3) (y 1) (z 4) Obtain the equation of the sphere which passes through the points (1,0,0), (0,1,0), (0,0,1) and which has its centre on the plane x y z 6. Solution. Let x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0 be the required equation. Since it passes through the given points, we have
2 1 2u d 0 1 2v d 0 1 2w d 0 1 u v w (d 1). 2 Its centre lies on the plane x y z 6. u v w 6 d=3. Required equation is x y z 4x 4y 4z a) Find the equation of the sphere which has (x 1, y 1,z 1) and (x 2, y 2,z 2) as the extremities of a diameter. b) Find the equation of the sphere having the points (2,1,-3) and (1,-2,4) as the ends of a diameter Find its centre and radius. Solution. Consider a point P(x,y,z) on the sphere S having the points A (x 1, y 1,z 1 ) and B (x 2, y 2,z 2 ) as the extrimities of a diameter. Then AP and BP are at right angles. The direction ratios of AP are (x x 1, y y 1,z z 1) and those of BP are (x x 2, y y 2,z z 2). D A B C (x x 1)(x x 2) (y y 1)(y y 2) (z z 1)(z z 2) 0 is the required equation of the sphere. b) Given A=(2,1,-3), B= (1,-2,4) Equation is (x 2)(x 1) (y 1)(y 2) (z 3)(z 4) 0. x 2 y 2 z 2 3x y z 12 0
3 3 1 1 Centre= u, v, w,,. And radius= u v w d = Intersection of a plane and a sphere: Figure Section of a sphere by a plane is a base circle and the section of a sphere by a plane through its centre is called a great circle. The equations And x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0 Ax By Cz D 0 taken together represents a circle. Having center M and the radius 2 2 MA r p. Sphere through a circle of intersection The equation of a sphere that passes through the circle of intersection of the sphere and the plane is given by S+kT=0 where S=0 is the equation of the sphere and T=0 is the equation of the plane. Example 1. Find the centre, the radius and the area of the circle x y z 2y 4z 11, x 2y 2z 15. Solution. Centre of the sphere, C (0,1, 2)
4 And radius, r Let M(x 1, y 1,z 1) be the centre of the circle. Then the direction ratios of CM are (x 1, y1 1,z 1 2) Since CM is perpendicular to the plane x1 y1 1 z1 2 t M (x 1, y 1,z 1) (t,2t 1,2t 2) Since M lies on the given plane, we have x1 2y1 2z1 15 t 4t 2 4t 4 15 t=1 M (1,3,4) and p Radius of the circle= Area of the circle = 2 M Find the equation of the sphere that passes through the circle x y z 2x 3y 4z 8 0, x 2y z 8 0 and has its centre on the plane 4x 5y z 3 0. Solution. Equation of a sphere is x y z 2x 3y 4z 8 k(x 2y z 8) 0 Centre= k 3 k ( u, v, w) 1, k, 2 Since the centre lies on the plane 4x 5y z 3 0, we have k 3 k 41 5 k k 9 13 Required equation of a sphere is 13(x y z 2x 3y 4z 8) 9(x 2y z 8) 0.
5 3. Find the equation of the sphere having the circle x y z 10y 4z 8 0, x y z 3 as a great circle. Solution. The equation of the sphere passing through the given circle is x y z 10y 4z 8) k(x y z 3) 0 The given circle is a great circle of this sphere if the centre of the sphere and the centre of the circle coincide. This is possible if the centre of the sphere lies in the plane x y z 3 of the given circle. Center of the sphere is This centre lies on the plane if k 4 Equation of the sphere is x y z 4x 6y 8z 4 0 k k k, 5,2. k k k Exercise. 1.Show that the plane x 2y z 3 cuts the sphere x y z x z 2 0 in a circle of radius unity. Also find the equation of the sphere which has this circle as a great circle. 2. Find the spheres passing through the circle x y z 6x 2z 5 0, y 0 and touching the plane 3y 4z 5 0. Orthogonal spheres: Two spheres are said to be Orthogonal if the tangent planes at a point of intersection are at right angles. The radii of such spheres through their point of intersection P being perpendicular to the tangent planes at P are also at right angles.
6 Figure Thus the spheres cut orthogonally, if the square of the distance between their centers equal to the sum of the squares of their radii. C C r r Show that the condition for the spheres x y z 2u1x 2v1y 2w1z d1 0 and x y z 2u2x 2v2y 2w2z d2 0 to cut orthogonally is 2u1u 2 2v1v2 2w1w2 d1 d2. Solution : The centers of the sphere are C 1 ( u 1, v 1, w 1), C 2 ( u 2, v 2, w 2) and r u v w d, r u v w d 2 Spheres will cut orthogonally if C C r r (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) u v w d u v w d Simplifying, 2u1u 2 2v1v2 2w1w2 d1 d2 is the required condition.. Tangent plane to a sphere: A plane q touches a sphere S if the perpendicular distance of the centre C of S from q is equal to the radius r of S. Then q is called a tangent plane to S. Equation of the sphere S is x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d 0, C ( u, v, w). Let A (x 1, y 1,z 1) be the point of contact between S and q.
7 Then the direction ratios of CA= (x 1 u, y 1 v,z 1 w). Consider any point P(x,y,z) in the tangent plane. The the direction ratios of AP (x x 1, y y 1,z z 1). Since the radius CA is perpendicular to q, we have (x x 1)(x1 u) (y y 1)(y1 v) (z z 1)(z1 w) 0 xx yy zz u(x x ) v(y y ) w(z z ) x y z Since the point A lies on S, we have x y z 2ux 2vy 2wz d xx 1 yy 1 zz 1 u(x x 1 ) v(y y 1 ) w(z z 1 ) 2ux 1 2vy 1 2wz 1 d xx 1 yy 1 zz 1 u(x x 1 ) v(y y 1 ) w(z z 1 ) d 0 This is the equation of the tangent plane q to S at the point A (x 1, y 1,z 1). Example 1. Find the equation of the tangent plane at a point (1,2, 2) to the sphere x y z 2x 6y 0. Solution. (u, v, w) ( 1, 3,0), d=0 Equation of the tangent plane is x 2y 2z (x 1) 3(y 2) 0 y 2z Find the tangent planes to the sphere x y z 4x 2y 6z 5 0 which are parallel to the plane 2x 2y z 0. Solution. Any plane parallel to the given plane is 2x 2y z k 0 This plane is a tangent plane to the given sphere S if the perpendicular distance p of the centre C of S is equal to the radius r of S. C (2, 1,3), r p k k1 3 p r if k 1 =3 3 k 1 9, k 10 or -8.
8 Equation of the tangent plane are 2x 2y z 10 0 and 2x 2y z 8 0. Right Circular Cone : Definition : A right circular cone is a surface generated by a straight line which passes through a fixed point and makes a constant angle with a fixed line. The constant angle θ is called the semi vertical angle, a fixed point is called a vertex and the fixed line AP is called the axis. Figure: A(vertex) Generator Axis C p B Equation of a right circular cone: Let (x 0, y 0, z 0) be the co-ordinates of the vertex A and (a, b, c) be the direction ratios of the axis. Consider any point P(x, y, z) on the cone. Then the direction ratios of the generator AP are (x x 0, y y 0, z z 0) and cos a(x x ) b(y y ) c(z z ) a (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) Or a(x x ) b(y y ) c(z z ) (a b c ) (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) cos This equation holds for any point P on the cone and hence is the equation of the right circular cone.
9 Example 1: Find the equation of the right circular cone whose vertex is the origin, whose axis is the line x y z and which has semi vertical angle of Solution. Given (x 0, y 0,z 0) (0,0,0). Direction ratios of the axis are (1,2,3) and Then the required equation is (x 2y 3z) (1 2 3 ) x y z cos x 4y 9z 4xy 12yz 6xz 14(x y z ) 4 19x 13y 3z 8xy 24yz 12xz 0. Example 2: Find the equation of the right circular cone generated when the straight line 2y 3z 6, x 0 revolves about z- axis. Solution. Let P(x, y,z) be any point on the cone. The vertex is the point of intersection of the line 2y 3z 6, x 0 and the z- axis. Therefore the vertex A is (0,0,2). A generator of the cone is x y z 2. Direction ratios of the generator are (0,3,2) and the axis are (0,0,1). The semi vertical angle θ is given by cos 2 13 Let P(x,y,z) be any point on the cone so that the direction ratios of AP are (x,y,z-2). Since AP makes an angle θ with AZ, we have x.0 y.0 (z 2).1 cos x y (z 2) 2 4 (z 2) 13 x y (z 2) 4x 2 4y 2 9z 2 36z 36 0, which is the required equation of the cone.
10 Right circular cylinder: Definition: A right circular cylinder is a surface generated by a straight line which is parallel to a straight line and is at a constant distance from it. The constant distance is called the radius of the cylinder. Equation of a right circular cylinder: P L R A Q Let (l,m,n) be the direction cosines of the axis and A(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) be a point on L. Consider an arbitrary point P(x,y,z) on the cylinder. If Q is the foot of the perpendicular from P onto L, then PQ=R, the radius of the cylinder. Also AQ is the projection of AP on L. AQ l(x x 0) m(y y 0) n(z z 0) Also AP (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) Then AP AQ PQ is the required equation of the cylinder. Example 1. The radius of a normal section of a right circular cylinder is 2 units. x 1 y 3 z 2 The axis lies along the straight line. Find its equation Solution.
11 Figure Z R P O A Q Let P(x,y,z) be any point on the cylinder. Draw PN perpendicular to the axis AN. Then PN=2. AN is the projection of AP on AN. Directio ratios of AN are (2,-1,5). Direction cosines of AN= Then the required equation is 2 1 5,, (x 1) (y 3) (z 2) (x 1) (y 3) (z 2) Example 2: Find the equation of the right circular cylinder having the circle x y z 9, x y z 3 as base circle. Solution. The axis of the cylinder is the line through the centre of S and perpendicular to the plane q. We note that O(0,0,0) is the center of S and (1,-1,1) are the direction ratios of the normal to q. The direction cosines of the axis are 1 1 1,,. The perpendicular distance from O on to the plane q is 3 OA If Q is a point common to S and q, then OQ= radius of the sphere= AQ OQ OA 9 3 6
12 Let P(x,y,z) be any point on the cylinder. Then ZP= 6 The equation of the cylinder is (x 0) (y 0) (z 0) (x 0) (y 0) (z 0) x 2 y 2 z 2 xy yz zx 9. 2
CHAPTER 3. Cylinder. ) be any point on the cylinder. The equation of the generator through the point P and parallel to equation (2) are
 CAPTER 3 Cylinder 3.. DENTON A cylinder is a surface generated by a straight line which is parallel to a fixed line and intersects a given curve or touches a given surface. The fixed line is called the
CAPTER 3 Cylinder 3.. DENTON A cylinder is a surface generated by a straight line which is parallel to a fixed line and intersects a given curve or touches a given surface. The fixed line is called the
12 - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions ) = 2. ( d ) - 3. ^i - 2. ^j c 3. ( d )
 - THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page ( ) If the angle θ between the line x - y + x + y - z - and the plane λ x + 4 0 is such that sin θ, then the value of λ is - 4-4 [ AIEEE 00 ] ( ) If the plane ax - ay
- THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Page ( ) If the angle θ between the line x - y + x + y - z - and the plane λ x + 4 0 is such that sin θ, then the value of λ is - 4-4 [ AIEEE 00 ] ( ) If the plane ax - ay
Design and Communication Graphics
 An approach to teaching and learning Design and Communication Graphics Solids in Contact Syllabus Learning Outcomes: Construct views of up to three solids having curved surfaces and/or plane surfaces in
An approach to teaching and learning Design and Communication Graphics Solids in Contact Syllabus Learning Outcomes: Construct views of up to three solids having curved surfaces and/or plane surfaces in
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS 1.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP
 PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
CIRCLE. Circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point.
 CIRCLE Circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point. The fixed point is called as the centre and the constant distance is called as the radius. Parts of a Circle
CIRCLE Circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point. The fixed point is called as the centre and the constant distance is called as the radius. Parts of a Circle
volume & surface area of a right circular cone cut by a plane parallel to symmetrical axis (Hyperbolic section)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter December 25, 2016 volume & surface area of a right circular cone cut by a plane parallel to symmetrical axis (Hyperbolic section) Harish
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter December 25, 2016 volume & surface area of a right circular cone cut by a plane parallel to symmetrical axis (Hyperbolic section) Harish
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
For more important questions visit : www4onocom CHAPTER 11 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY POINTS TO REMEMBER Distance between points P(x 1 ) and Q(x, y, z ) is PQ x x y y z z 1 1 1 (i) The coordinates of point
Elements of three dimensional geometry
 Lecture No-3 Elements of three dimensional geometr Distance formula in three dimension Let P( x1, 1, z1) and Q( x2, 2, z 2) be two points such that PQ is not parallel to one of the 2 2 2 coordinate axis
Lecture No-3 Elements of three dimensional geometr Distance formula in three dimension Let P( x1, 1, z1) and Q( x2, 2, z 2) be two points such that PQ is not parallel to one of the 2 2 2 coordinate axis
Rectangular Coordinates in Space
 Rectangular Coordinates in Space Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Rectangular Coordinates in Space Today 1 / 11 Introduction We quickly review one and two-dimensional spaces and then
Rectangular Coordinates in Space Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Rectangular Coordinates in Space Today 1 / 11 Introduction We quickly review one and two-dimensional spaces and then
Int 2 Checklist (Unit 1) Int 2 Checklist (Unit 1) Percentages
 Percentages Know that appreciation means an increase in value and depreciation means a decrease in value Calculate simple interest over 1 year Calculate simple interest over a certain number of months
Percentages Know that appreciation means an increase in value and depreciation means a decrease in value Calculate simple interest over 1 year Calculate simple interest over a certain number of months
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
Analytical Solid Geometry
 Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics by B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics by B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
4. The following diagram shows the triangle AOP, where OP = 2 cm, AP = 4 cm and AO = 3 cm.
 Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) 1. In the triangle PQR, PR = 5 cm, QR = 4 cm and PQ = 6 cm. Calculate (a) the size of ; (b) the area of triangle PQR. 2. The following diagram shows
CBSE CLASS X MATHS , 1 2p
 CBSE CLASS X MATHS -2013 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. (iii) Sections A contains 8 questions
CBSE CLASS X MATHS -2013 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A,B,C and D. (iii) Sections A contains 8 questions
12 m. 30 m. The Volume of a sphere is 36 cubic units. Find the length of the radius.
 NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2
 1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-2 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
PART A (5x5M =25M) dx +2xy 4x2 = 0 and passing through the origin. using the method of multipliers. PART B (5x10M = 50M)
 FIRST YEAR B.SC. MATHEMATICS PAPER I SEMESTER I DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS MODEL QUESTION PAPER (THEORY) Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 *This Paper Csists of Two parts. Follow the Instructis Carefully PART A
FIRST YEAR B.SC. MATHEMATICS PAPER I SEMESTER I DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS MODEL QUESTION PAPER (THEORY) Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 *This Paper Csists of Two parts. Follow the Instructis Carefully PART A
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
BOARD PAPER - MARCH 2014
 BOARD PAPER - MARCH 2014 Time : 2 Hours Marks : 40 Notes : (i) Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. Use of calculator is not allowed. Figures to the right indicate full marks. Marks of
BOARD PAPER - MARCH 2014 Time : 2 Hours Marks : 40 Notes : (i) Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. Use of calculator is not allowed. Figures to the right indicate full marks. Marks of
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral
 1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
Review Exercise. 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the
 Review Exercise 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the points A11, 2, 12, B12, 1, 12, and C13, 1, 42. 2. In question 1, there are a variety of different answers possible,
Review Exercise 1. Determine vector and parametric equations of the plane that contains the points A11, 2, 12, B12, 1, 12, and C13, 1, 42. 2. In question 1, there are a variety of different answers possible,
Q-1 The first three terms of an AP respectively are 3y 1, 3y +5 and 5y +1. Then y equals
 CBSE CLASS X Math Paper-2014 Q-1 The first three terms of an AP respectively are 3y 1, 3y +5 and 5y +1. Then y equals (A) -3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 2 Q-2 In Fig. 1, QR is a common tangent to the given circles,
CBSE CLASS X Math Paper-2014 Q-1 The first three terms of an AP respectively are 3y 1, 3y +5 and 5y +1. Then y equals (A) -3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 2 Q-2 In Fig. 1, QR is a common tangent to the given circles,
Activity 21 OBJECTIVE. MATERIAL REQUIRED Cardboard, white paper, adhesive, pens, geometry box, eraser, wires, paper arrow heads.
 Activity 21 OBJECTIVE To verify that angle in a semi-circle is a right angle, using vector method. MATERIAL REQUIRED Cardboard, white paper, adhesive, pens, geometry box, eraser, wires, paper arrow heads.
Activity 21 OBJECTIVE To verify that angle in a semi-circle is a right angle, using vector method. MATERIAL REQUIRED Cardboard, white paper, adhesive, pens, geometry box, eraser, wires, paper arrow heads.
You may know these...
 You may know these... Chapter 1: Multivariables Functions 1.1 Functions of Two Variables 1.1.1 Function representations 1.1. 3-D Coordinate System 1.1.3 Graph of two variable functions 1.1.4 Sketching
You may know these... Chapter 1: Multivariables Functions 1.1 Functions of Two Variables 1.1.1 Function representations 1.1. 3-D Coordinate System 1.1.3 Graph of two variable functions 1.1.4 Sketching
Mathematics (www.tiwariacademy.com)
 () Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 10 Question 1: Find the values of k for which the line is (a) Parallel to the x-axis, (b) Parallel to the y-axis, (c) Passing through the origin. Answer 1: The given
() Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 10 Question 1: Find the values of k for which the line is (a) Parallel to the x-axis, (b) Parallel to the y-axis, (c) Passing through the origin. Answer 1: The given
Coordinate Geometry. Topic 1. DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS. Point 2. The distance of the point P(.x, y)from the origin O(0,0) is given by
 Topic 1. DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS Point 1.The distance between two points A(x,, y,) and B(x 2, y 2) is given by the formula Point 2. The distance of the point P(.x, y)from the origin O(0,0) is given
Topic 1. DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS Point 1.The distance between two points A(x,, y,) and B(x 2, y 2) is given by the formula Point 2. The distance of the point P(.x, y)from the origin O(0,0) is given
Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron (solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
Objective Mathematics
 6. In angle etween the pair of tangents drawn from a 1. If straight line y = mx + c is tangential to paraola y 16( x 4), then exhaustive set of values of 'c' is given y (a) R /( 4, 4) () R /(, ) (c) R
6. In angle etween the pair of tangents drawn from a 1. If straight line y = mx + c is tangential to paraola y 16( x 4), then exhaustive set of values of 'c' is given y (a) R /( 4, 4) () R /(, ) (c) R
Analytical Solid Geometry
 Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics By B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Analytical Solid Geometry Distance formula(without proof) Division Formula Direction cosines Direction ratios Planes Straight lines Books Higher Engineering Mathematics By B S Grewal Higher Engineering
Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths
 1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
Mathematics. Geometry Revision Notes for Higher Tier
 Mathematics Geometry Revision Notes for Higher Tier Thomas Whitham Sixth Form S J Cooper Pythagoras Theorem Right-angled trigonometry Trigonometry for the general triangle rea & Perimeter Volume of Prisms,
Mathematics Geometry Revision Notes for Higher Tier Thomas Whitham Sixth Form S J Cooper Pythagoras Theorem Right-angled trigonometry Trigonometry for the general triangle rea & Perimeter Volume of Prisms,
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes. 1 Objectives. 2 Assignments. 3 Lecture Notes
 Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes 1 Objectives 1. Find vector, symmetric, or parametric equations for a line in space given two points on the line, given a point on the line and a vector parallel
Section 13.5: Equations of Lines and Planes 1 Objectives 1. Find vector, symmetric, or parametric equations for a line in space given two points on the line, given a point on the line and a vector parallel
1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D
 1.5. EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES IN 3-D 55 Figure 1.16: Line through P 0 parallel to v 1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D Recall that given a point P = (a, b, c), one can draw a vector from the
1.5. EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES IN 3-D 55 Figure 1.16: Line through P 0 parallel to v 1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D Recall that given a point P = (a, b, c), one can draw a vector from the
INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Mathematics is both the queen and the hand-maiden of all sciences E.T. BELL 1.1 Introduction You may recall that to locate the position of a point in
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY Mathematics is both the queen and the hand-maiden of all sciences E.T. BELL 1.1 Introduction You may recall that to locate the position of a point in
Co-ordinate Geometry
 Co-ordinate Geometry 1. Find the value of P for which the points (1, -), (2, -6) and (p, -1) are collinear 2. If the point P (x, y) is equidistant from the points A (1,) and B(4, 1). Prove that 2x+y =
Co-ordinate Geometry 1. Find the value of P for which the points (1, -), (2, -6) and (p, -1) are collinear 2. If the point P (x, y) is equidistant from the points A (1,) and B(4, 1). Prove that 2x+y =
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Stereographic Projections
 C6H3 PART IIA and PART IIB C6H3 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND METALLURGY Course C6: Crystallography Stereographic Projections Representation of directions and plane orientations In studying crystallographic and
C6H3 PART IIA and PART IIB C6H3 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND METALLURGY Course C6: Crystallography Stereographic Projections Representation of directions and plane orientations In studying crystallographic and
CBSE X Mathematics 2012 Solution (SET 1) Section C
 CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Q19. Solve for x : 4x 4ax + (a b ) = 0 Section C The given quadratic equation is x ax a b 4x 4ax a b 0 4x 4ax a b a b 0 4 4 0. 4 x [ a a b b] x ( a b)( a b) 0 4x
CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Q19. Solve for x : 4x 4ax + (a b ) = 0 Section C The given quadratic equation is x ax a b 4x 4ax a b 0 4x 4ax a b a b 0 4 4 0. 4 x [ a a b b] x ( a b)( a b) 0 4x
2009 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2 This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles 3 bearings 8 triangle similarity 9 triangle congruency 11 Pythagoras
2 This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles 3 bearings 8 triangle similarity 9 triangle congruency 11 Pythagoras
MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry
 Chapter I THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry INTRODUCTION The word trigonometry literally means triangle measurement. It is concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides,
Chapter I THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry INTRODUCTION The word trigonometry literally means triangle measurement. It is concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides,
Three Dimensional Geometry. Linear Programming
 Three Dimensional Geometry Linear Programming A plane is determined uniquely if any one of the following is known: The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given, i.e. equation of a
Three Dimensional Geometry Linear Programming A plane is determined uniquely if any one of the following is known: The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given, i.e. equation of a
Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90
 Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A, B, C, and D. 3. Section A contains of 8
Time: 3 hour Total Marks: 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 34 questions divided into four sections A, B, C, and D. 3. Section A contains of 8
If (x, y, z) are the coordinates of a point P in space, then the position vector of the point P w.r.t. the same origin is.
 7. 3D GEOMETRY. COORDINATE OF A POINT IN SPACE Let P be a point in the space. If a perpendicular from that point is dropped to the xyplane, then the algebraic length of this perpendicular is considered
7. 3D GEOMETRY. COORDINATE OF A POINT IN SPACE Let P be a point in the space. If a perpendicular from that point is dropped to the xyplane, then the algebraic length of this perpendicular is considered
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
14.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector 1. Directional Derivatives. Recall z = f (x, y) and the partial derivatives f x and f y are defined as f (x 0 + h, y 0 ) f (x 0, y 0 ) f x (x 0, y 0
not to be republished NCERT CONSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 10 (A) Main Concepts and Results (B) Multiple Choice Questions
 CONSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 10 (A) Main Concepts and Results Division of a line segment internally in a given ratio. Construction of a triangle similar to a given triangle as per given scale factor which may
CONSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 10 (A) Main Concepts and Results Division of a line segment internally in a given ratio. Construction of a triangle similar to a given triangle as per given scale factor which may
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
Notes on Spherical Geometry
 Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
Notes on Spherical Geometry Abhijit Champanerkar College of Staten Island & The Graduate Center, CUNY Spring 2018 1. Vectors and planes in R 3 To review vector, dot and cross products, lines and planes
P is the centre of the circle and its radius is 10 cm. Distance of a chord AB from the
 Sample uestion aper No. 1 Std 10 th Maths art II Time : 2 Hrs. Marks : 40 Note : ll questions are compulsory. Use of calculator is not allowed. (3) Total marks are shown on the right side of the question.
Sample uestion aper No. 1 Std 10 th Maths art II Time : 2 Hrs. Marks : 40 Note : ll questions are compulsory. Use of calculator is not allowed. (3) Total marks are shown on the right side of the question.
SECTION A / 1. Any point where graph of linear equation in two variables cuts x-axis is of the form. (a) (x, y) (b) (0, y) (c) (x, 0) (d) (y, x)
 SECTION A / Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. For each question, four alternative choices have been provided, of which only one is correct. You have to select the correct choice. 1 8 1 1. Any
SECTION A / Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. For each question, four alternative choices have been provided, of which only one is correct. You have to select the correct choice. 1 8 1 1. Any
Revision Problems for Examination 2 in Algebra 1
 Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Intersecting Simple Surfaces. Dr. Scott Schaefer
 Intersecting Simple Surfaces Dr. Scott Schaefer 1 Types of Surfaces Infinite Planes Polygons Convex Ray Shooting Winding Number Spheres Cylinders 2/66 Infinite Planes Defined by a unit normal n and a point
Intersecting Simple Surfaces Dr. Scott Schaefer 1 Types of Surfaces Infinite Planes Polygons Convex Ray Shooting Winding Number Spheres Cylinders 2/66 Infinite Planes Defined by a unit normal n and a point
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions. 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
Answers to Geometry Unit 5 Practice
 Lesson 0- Answers to Geometry Unit 5 Practice. a. Rectangle; Sample answer: It has four right angles. b. length: units; width: 9 units A 5 bh 7 units. 96 units. a. Parallelogram; Sample answer: Opposite
Lesson 0- Answers to Geometry Unit 5 Practice. a. Rectangle; Sample answer: It has four right angles. b. length: units; width: 9 units A 5 bh 7 units. 96 units. a. Parallelogram; Sample answer: Opposite
Mathematics. Geometry. Stage 6. S J Cooper
 Mathematics Geometry Stage 6 S J Cooper Geometry (1) Pythagoras Theorem nswer all the following questions, showing your working. 1. Find x 2. Find the length of PR P 6cm x 5cm 8cm R 12cm Q 3. Find EF correct
Mathematics Geometry Stage 6 S J Cooper Geometry (1) Pythagoras Theorem nswer all the following questions, showing your working. 1. Find x 2. Find the length of PR P 6cm x 5cm 8cm R 12cm Q 3. Find EF correct
FURTHER MATHS. WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL
 FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
6. Find the equation of the plane that passes through the point (-1,2,1) and contains the line x = y = z.
 Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE
 ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE It is given that the straight line L passes through A(5, 5) and is perpendicular to the straight line L : x+ y 5= 0 (a) Find the equation of L (b) Find
ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE It is given that the straight line L passes through A(5, 5) and is perpendicular to the straight line L : x+ y 5= 0 (a) Find the equation of L (b) Find
Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1
 Phone: (0) 8007 684 Email: info@dc.edu.au Web: dc.edu.au 018 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE MATERIALS Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1 Parametric Equations Term 1 Week 1 Name. Class day and time Teacher
Phone: (0) 8007 684 Email: info@dc.edu.au Web: dc.edu.au 018 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE MATERIALS Preliminary Mathematics Extension 1 Parametric Equations Term 1 Week 1 Name. Class day and time Teacher
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas
 AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER)
 BY PROF. RAHUL MISHRA VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CONSTRUCTIONS Class :- X Subject :- Maths Total Time :- SET A Total Marks :- 240 QNo. General Instructions Questions 1 Divide
BY PROF. RAHUL MISHRA VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CONSTRUCTIONS Class :- X Subject :- Maths Total Time :- SET A Total Marks :- 240 QNo. General Instructions Questions 1 Divide
cbsemath.com: Bathinda based website since Feb 2006.
 Attempt option 1 for challenging questions and 2 for easy-moderate questions Section A 1 Mark Each 1. If a + b + c = 0, a 0 and a, b, c are real numbers then roots of equation ax 2 +bx + c = 0 are (A)
Attempt option 1 for challenging questions and 2 for easy-moderate questions Section A 1 Mark Each 1. If a + b + c = 0, a 0 and a, b, c are real numbers then roots of equation ax 2 +bx + c = 0 are (A)
Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
True/False. MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY
 MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
ME 111: Engineering Drawing. Geometric Constructions
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
K.S.E.E.B., Malleshwaram, Bangalore SSLC Model Question Paper-2 (2015) MATHEMATICS
 Max Marks: 80 No. of Questions: 40 K.S.E.E.B., Malleshwaram, Bangalore SSLC Model Question Paper- (015) MATHEMATICS 81E Time: Hours 45 minutes Code No. : 81E Four alternatives are given for the each question.
Max Marks: 80 No. of Questions: 40 K.S.E.E.B., Malleshwaram, Bangalore SSLC Model Question Paper- (015) MATHEMATICS 81E Time: Hours 45 minutes Code No. : 81E Four alternatives are given for the each question.
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 11.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Conics? Conics as Cross Sections Determine the conic section that results from the intersection of the double-napped cone shown and each plane described. 1.
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Conics? Conics as Cross Sections Determine the conic section that results from the intersection of the double-napped cone shown and each plane described. 1.
Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form
 Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Get Ready. Solving Equations 1. Solve each equation. a) 4x + 3 = 11 b) 8y 5 = 6y + 7
 Get Ready BLM... Solving Equations. Solve each equation. a) 4x + = 8y 5 = 6y + 7 c) z+ = z+ 5 d) d = 5 5 4. Write each equation in the form y = mx + b. a) x y + = 0 5x + y 7 = 0 c) x + 6y 8 = 0 d) 5 0
Get Ready BLM... Solving Equations. Solve each equation. a) 4x + = 8y 5 = 6y + 7 c) z+ = z+ 5 d) d = 5 5 4. Write each equation in the form y = mx + b. a) x y + = 0 5x + y 7 = 0 c) x + 6y 8 = 0 d) 5 0
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
Mathematics
 Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
11 cm. A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm.
 Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
Diagram NOT accurately drawn 10 cm 11 cm 12 cm 3.5 cm A rectangular container is 12 cm long, 11 cm wide and 10 cm high. The container is filled with water to a depth of 8 cm. A metal sphere of radius 3.5
5200/7200 Fall 2007 Concurrence theorems for triangles
 5200/7200 Fall 2007 Concurrence theorems for triangles There are two basic concurrence theorems for triangles that hold in neutral geometry, that of medians and of angle bisectors, but it seems hard to
5200/7200 Fall 2007 Concurrence theorems for triangles There are two basic concurrence theorems for triangles that hold in neutral geometry, that of medians and of angle bisectors, but it seems hard to
4 = 1 which is an ellipse of major axis 2 and minor axis 2. Try the plane z = y2
 12.6 Quadrics and Cylinder Surfaces: Example: What is y = x? More correctly what is {(x,y,z) R 3 : y = x}? It s a plane. What about y =? Its a cylinder surface. What about y z = Again a cylinder surface
12.6 Quadrics and Cylinder Surfaces: Example: What is y = x? More correctly what is {(x,y,z) R 3 : y = x}? It s a plane. What about y =? Its a cylinder surface. What about y z = Again a cylinder surface
Geometry 2 Final Review
 Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Mathematics. Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum : The question paper consists of 31 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D.
 Sample Paper (CBSE) Series SC/SP Code No. SP-16 Mathematics Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum : 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 31 questions divided
Sample Paper (CBSE) Series SC/SP Code No. SP-16 Mathematics Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum : 90 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. The question paper consists of 31 questions divided
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Sarvaakarshak classes
 Sarvaakarshak classes Revision_Test_2 The best way to learn SECTION-A Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 2 marks each. 1. If the equation kx 2-2kx + 6 = 0 has equal roots, then find the value of k. 2. Which
Sarvaakarshak classes Revision_Test_2 The best way to learn SECTION-A Question numbers 1 to 8 carry 2 marks each. 1. If the equation kx 2-2kx + 6 = 0 has equal roots, then find the value of k. 2. Which
Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate
 1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
Circumference of a Circle
 Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Mathematical derivations of inscribed & circumscribed radii for three externally touching circles (Geometry of Circles by HCR)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter February 15, 2015 Mathematical derivations of inscribed & circumscribed radii for three externally touching circles Geometry of Circles
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter February 15, 2015 Mathematical derivations of inscribed & circumscribed radii for three externally touching circles Geometry of Circles
SAMPLE PAPER 2 (SA II) Mathematics CLASS : X. Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90
 SAMPLE PAPER 2 (SA II) Mathematics MR SANDESH KUMAR BHAT KV 1 JAMMU CLASS : X Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90 General Instruction:- 1. All questions are Compulsory. 1. The question paper consists of 34 questions
SAMPLE PAPER 2 (SA II) Mathematics MR SANDESH KUMAR BHAT KV 1 JAMMU CLASS : X Time: 3hrs Max. Marks: 90 General Instruction:- 1. All questions are Compulsory. 1. The question paper consists of 34 questions
Analytic Spherical Geometry:
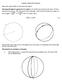 Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Analytic Spherical Geometry: Begin with a sphere of radius R, with center at the origin O. Measuring the length of a segment (arc) on a sphere. Let A and B be any two points on the sphere. We know that
Parallel projection Special type of mapping of 3D object on a 2D medium (technical drawing, display)
 Parallel projection Special type of mapping of 3D object on a 2D medium (technical drawing, display) Parallel projection 1. Direction of projection s, plane of projection p 1 Parallel projection (parallel
Parallel projection Special type of mapping of 3D object on a 2D medium (technical drawing, display) Parallel projection 1. Direction of projection s, plane of projection p 1 Parallel projection (parallel
Quadric Surfaces. Philippe B. Laval. Today KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24
 Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables. The general
Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables. The general
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS. Apply Geometric Concepts in Modeling Situations
 UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
Quadric Surfaces. Philippe B. Laval. Spring 2012 KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring /
 .... Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables.
.... Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables.
Geometry Diagnostic Test
 Geometry Diagnostic Test 1. A pentagonal-based prism is sliced horizontally by a plane parallel to the base. Which figure best represents the shape of the cross-section parallel to the slice? rectangle
Geometry Diagnostic Test 1. A pentagonal-based prism is sliced horizontally by a plane parallel to the base. Which figure best represents the shape of the cross-section parallel to the slice? rectangle
Quadric surface. Ellipsoid
 Quadric surface Quadric surfaces are the graphs of any equation that can be put into the general form 11 = a x + a y + a 33z + a1xy + a13xz + a 3yz + a10x + a 0y + a 30z + a 00 where a ij R,i, j = 0,1,,
Quadric surface Quadric surfaces are the graphs of any equation that can be put into the general form 11 = a x + a y + a 33z + a1xy + a13xz + a 3yz + a10x + a 0y + a 30z + a 00 where a ij R,i, j = 0,1,,
Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-1
 1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-1 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
1 Mathematics Class 10 Board Sample paper-1 Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 80 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists of 30 questions divided into four
Conic Sections. College Algebra
 Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
Conic Sections College Algebra Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines
