Nonlinear Manifold Learning for Visual Speech Recognition
|
|
|
- Angelica Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nonlinear Manifold Learning for Visual Speech Recognition Christoph Bregler and Stephen Omohundro University of California, Berkeley & NEC Research Institute, Inc. 1/25
2 Overview Manifold Learning: Applications to Lip Tracking, Image Interpolation, and Feature Extraction. Experiments with a full Speech Recognition System: A technique for representing and learning smooth nonlinear manifolds is presented and applied to several lip reading tasks. Given a set of points drawn from a smooth manifold in an abstract feature space, the technique is capable of determining the structure of the surface and of finding the closest manifold point to a given query point. We use this technique to learn the "space of lips" in a visual speech recognition task. The learned manifold is used for tracking and extracting the lips, for interpolating between frames in an image sequence and for providing features for recognition. We describe a system based on Hidden Markov Models and this learned lip manifold that significantly improves the performance of acoustic speech recognizers in degraded environments. We also present preliminary results on a purely visual lip reader. 2125
3 Problem 1. Boundary Tracking 2. Image Interpolation Acoustic Features - 3. Lip Features At A2A3 A4 A5 A6A7 Vt V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V Speech Recognition [ HMM ] 3/25
4 Full Reeo gnition System "Visual Speech" Acoustic Speech "Contour-Surfing" "Eigenlips" Lip-Interpolation MLPIHMM Hybrid Speech-Recognition System -- 'pi / -- I, ~' - ~ ",1 RASTA-PLP ~ Full Sentence Car-Noise Cross-Talk 4/25
5 Lip Tracking using Active Contour Models "Snake" Tracking Snake Model = "Controlled Continuity Spline" - 5/25
6 Space ofcontours as Constrained Manifold N Dimensional Features are Points in N Dimensional Space. K Dimensional Subspace N Dimensional Feature Space 6/25
7 Abstract Manifold Learning Task /' /_ '" / " \( J \ \ I I ) I I \ I \ i t \, ).. ""---..,._/ Samples Mixture of local adaptive Patches Learned Representation 7/25
8 Mixture ofpatches Architecture ~.L.L.L.Luence?'~, ction PI I,Gi (x) Pi (x) P(x) =.i I,Gi (x) i Linear Patch 8/25
9 Manifold Learning Initial Estimate - Cluster Feature Space (K-Means) - LocalPCA Minimize MSE between Training Set and Projection - EM Algorithm - Gradient Descent First Best Model Merging 9125
10 Synthetic Examples Learned surface Training Salllples 10/25
11 Comparison to Nearest Neighbor MSE 0.3 nearest point query 0.2 Surface Prior.,, I, 0.1 " 0.0 ;:
12 Manifold Dimension? Eigen Value st Eigenvalue... 2nd Eigenvalue ,,, ",, " , J,, " 80.00,,, ,,,.,, " " "."...".../ rd Eigenvalue o.oo...a...: "...""",..."...".' Samples per pea 12/25
13 Manifold-based Snake Tracking Jl - ~ Learned Manifold Directed Graylevel Gradients along Snake LIP-Space Manifold Snake Energy =Image Term+ Learned Manifold Term Use Manifold-Snakes to estimate position, scale, and rotation for gray level matrix extraction
14 Graylevel Manifolds Linear Lip-Space Real Lip-Space => Linear Dimension Reduction Nonlinear Dimension Reduction 14/25
15 Linear vs. Nonlinear Interpolation, / Leam nonlinear subspace of "legal" images... constrain interpolated images to subspace Graylevel Dimensions (16x16 pixel = 256 dim. space) 15/25
16 Nonlinear Interpolation Technique Y :,... /.-~--i~~> "Manifold-Snake" "- '\, ~ E = L IVi- 1 - i 2 2Vi + V i distance (Vi) - Begin with sequence of linear interpolated points - Iteratively move points toward manifold - Iterations are equal to gradient descent steps using the Manifold-Snake Energy.,,"'-.,., ", ;..".-... #"" - ",,.., -"\, '., l I '. I j i i j 'j,..."i.., ~~~... ~~ ~... "'f \ I \...._,,/....._wl'..._".. ~.~~" -"'11_...,,,, I alter. 1 Iter. 2 Iter. 5 Iter. loiter. 16/25
17
18 Linear Interpolation Natural Lip Images Nonlinear Interpolation 24x24 Images projected in a 32-D linear space and 8-D nonlinear manifold 18/25
19
20 Phone Probability Estimation -2 P(phone I acoustics, visual-input) Multi-Layer Perceptron Softmax Prob. Outputs Hidden Units t 19 frames - ~ ~~---""".,... ~ ~ 9 features 10 Eigen-Features (1 Energy, 8 RASTA-PLP) (+ 10 Delta-Eigen-Features) 20125
21 Viterbi Approximation Hidden Markov Models Mi (Word-Model) Likelihood: P(A, VIM i ) ele e e e e e P (phone la, V) e Ol~ III e~ Ol~... Time III P (A, Vlphone) oc P (phone) 21125
22 Reeo gnition Results Task Acoustic Eigenlips Delta-Lips Rel.Err.Red. clean 11.0 % 10.1 % 11.3 % - 20db SNR 33.5 % 28.9% 26.0% 22.4 % lodbsnr 56.1 % 51.7 % 48.0% 14.4 % 15dbSNR crosstalk 67.3 % 51.7% 46.0% 31.6 % Table 1: Spelling Task (6 Speakers) Word Error (wrong + insertion + deletion) Task Pure Lipreading-Error Bar-Tender 4.5% Table 2: Pure Lipreading (1 Speaker, "Bar-Thsk": 4 Cocktail-Names) 22/25
23 Related Linear Representations: Related Work Kirby et ai., Pentland et ai.: Linear Subspaces Simard: Tangent Distance Related Nonlinear Representation: Jacobs, Jordan, Nowlan, Hinton: Mixture of Experts Kambhatla, Leen: Local pea Related Interpolation Techniques: Poggio et ai.: RBFs for Image Interpolation 23/25
24 Computer Lipreading History - U.S.Patent (1965) E. Nassimbene (IBM) - E. Petajan (1984), Dissertation - B. Yuhas, M. Goldstein, T. Sejnowski (1989) - K. Mase, A. Pentland (1991) - O. Garcia, A. Goldschen, E. Petajan (1992) - D. Stork, G. Wolff, K. V. Prasad, M. Hennecke (1992) - P.L. Silsbee (1993), Dissertation - A.f. Goldschen (1993), Dissertation - f. Movellan (1994) 24125
25 Summary Lipreading: - Improves Speech Recognition Performance significantly - Full System Solution Manifold Learning: - New fundamental technique for learning in geometric domains - Applicable to variety of different tasks 25125
Nonlinear Image Interpolation using Manifold Learning
 Nonlinear Image Interpolation using Manifold Learning Christoph Bregler Computer Science Division University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 bregler@cs.berkeley.edu Stephen M. Omohundro'" Int. Computer
Nonlinear Image Interpolation using Manifold Learning Christoph Bregler Computer Science Division University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 bregler@cs.berkeley.edu Stephen M. Omohundro'" Int. Computer
Manifold Constrained Deep Neural Networks for ASR
 1 Manifold Constrained Deep Neural Networks for ASR Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McGill University Richard Rose and Vikrant Tomar Motivation Speech features can be characterized as
1 Manifold Constrained Deep Neural Networks for ASR Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McGill University Richard Rose and Vikrant Tomar Motivation Speech features can be characterized as
Why DNN Works for Speech and How to Make it More Efficient?
 Why DNN Works for Speech and How to Make it More Efficient? Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering, York University, CANADA Joint work with Y.
Why DNN Works for Speech and How to Make it More Efficient? Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering, York University, CANADA Joint work with Y.
Dimension Reduction CS534
 Dimension Reduction CS534 Why dimension reduction? High dimensionality large number of features E.g., documents represented by thousands of words, millions of bigrams Images represented by thousands of
Dimension Reduction CS534 Why dimension reduction? High dimensionality large number of features E.g., documents represented by thousands of words, millions of bigrams Images represented by thousands of
Acoustic to Articulatory Mapping using Memory Based Regression and Trajectory Smoothing
 Acoustic to Articulatory Mapping using Memory Based Regression and Trajectory Smoothing Samer Al Moubayed Center for Speech Technology, Department of Speech, Music, and Hearing, KTH, Sweden. sameram@kth.se
Acoustic to Articulatory Mapping using Memory Based Regression and Trajectory Smoothing Samer Al Moubayed Center for Speech Technology, Department of Speech, Music, and Hearing, KTH, Sweden. sameram@kth.se
AUDIOVISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION USING MULTISCALE NONLINEAR IMAGE DECOMPOSITION
 AUDIOVISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION USING MULTISCALE NONLINEAR IMAGE DECOMPOSITION Iain Matthews, J. Andrew Bangham and Stephen Cox School of Information Systems, University of East Anglia, Norwich, NR4 7TJ,
AUDIOVISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION USING MULTISCALE NONLINEAR IMAGE DECOMPOSITION Iain Matthews, J. Andrew Bangham and Stephen Cox School of Information Systems, University of East Anglia, Norwich, NR4 7TJ,
ICA mixture models for image processing
 I999 6th Joint Sy~nposiurn orz Neural Computation Proceedings ICA mixture models for image processing Te-Won Lee Michael S. Lewicki The Salk Institute, CNL Carnegie Mellon University, CS & CNBC 10010 N.
I999 6th Joint Sy~nposiurn orz Neural Computation Proceedings ICA mixture models for image processing Te-Won Lee Michael S. Lewicki The Salk Institute, CNL Carnegie Mellon University, CS & CNBC 10010 N.
Chapter 3. Speech segmentation. 3.1 Preprocessing
 , as done in this dissertation, refers to the process of determining the boundaries between phonemes in the speech signal. No higher-level lexical information is used to accomplish this. This chapter presents
, as done in this dissertation, refers to the process of determining the boundaries between phonemes in the speech signal. No higher-level lexical information is used to accomplish this. This chapter presents
A Comparison of Sequence-Trained Deep Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks Optical Modeling For Handwriting Recognition
 A Comparison of Sequence-Trained Deep Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks Optical Modeling For Handwriting Recognition Théodore Bluche, Hermann Ney, Christopher Kermorvant SLSP 14, Grenoble October
A Comparison of Sequence-Trained Deep Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks Optical Modeling For Handwriting Recognition Théodore Bluche, Hermann Ney, Christopher Kermorvant SLSP 14, Grenoble October
Example Based Image Synthesis of Articulated Figures
 Example Based Image Synthesis of Articulated Figures Trevor Darrell Interval Research. 1801C Page Mill Road. Palo Alto CA 94304 trevor@interval.com, http://www.interval.com/-trevor/ Abstract We present
Example Based Image Synthesis of Articulated Figures Trevor Darrell Interval Research. 1801C Page Mill Road. Palo Alto CA 94304 trevor@interval.com, http://www.interval.com/-trevor/ Abstract We present
Deep Learning. Volker Tresp Summer 2014
 Deep Learning Volker Tresp Summer 2014 1 Neural Network Winter and Revival While Machine Learning was flourishing, there was a Neural Network winter (late 1990 s until late 2000 s) Around 2010 there
Deep Learning Volker Tresp Summer 2014 1 Neural Network Winter and Revival While Machine Learning was flourishing, there was a Neural Network winter (late 1990 s until late 2000 s) Around 2010 there
Object Recognition Using Pictorial Structures. Daniel Huttenlocher Computer Science Department. In This Talk. Object recognition in computer vision
 Object Recognition Using Pictorial Structures Daniel Huttenlocher Computer Science Department Joint work with Pedro Felzenszwalb, MIT AI Lab In This Talk Object recognition in computer vision Brief definition
Object Recognition Using Pictorial Structures Daniel Huttenlocher Computer Science Department Joint work with Pedro Felzenszwalb, MIT AI Lab In This Talk Object recognition in computer vision Brief definition
A Comparison of Visual Features for Audio-Visual Automatic Speech Recognition
 A Comparison of Visual Features for Audio-Visual Automatic Speech Recognition N. Ahmad, S. Datta, D. Mulvaney and O. Farooq Loughborough Univ, LE11 3TU Leicestershire, UK n.ahmad@lboro.ac.uk 6445 Abstract
A Comparison of Visual Features for Audio-Visual Automatic Speech Recognition N. Ahmad, S. Datta, D. Mulvaney and O. Farooq Loughborough Univ, LE11 3TU Leicestershire, UK n.ahmad@lboro.ac.uk 6445 Abstract
( ) =cov X Y = W PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS. Eigenvectors of the covariance matrix are the principal components
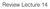 Review Lecture 14 ! PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS Eigenvectors of the covariance matrix are the principal components 1. =cov X Top K principal components are the eigenvectors with K largest eigenvalues
Review Lecture 14 ! PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS Eigenvectors of the covariance matrix are the principal components 1. =cov X Top K principal components are the eigenvectors with K largest eigenvalues
Introduction to SLAM Part II. Paul Robertson
 Introduction to SLAM Part II Paul Robertson Localization Review Tracking, Global Localization, Kidnapping Problem. Kalman Filter Quadratic Linear (unless EKF) SLAM Loop closing Scaling: Partition space
Introduction to SLAM Part II Paul Robertson Localization Review Tracking, Global Localization, Kidnapping Problem. Kalman Filter Quadratic Linear (unless EKF) SLAM Loop closing Scaling: Partition space
SCALE BASED FEATURES FOR AUDIOVISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION
 IEE Colloquium on Integrated Audio-Visual Processing for Recognition, Synthesis and Communication, pp 8/1 8/7, 1996 1 SCALE BASED FEATURES FOR AUDIOVISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION I A Matthews, J A Bangham and
IEE Colloquium on Integrated Audio-Visual Processing for Recognition, Synthesis and Communication, pp 8/1 8/7, 1996 1 SCALE BASED FEATURES FOR AUDIOVISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION I A Matthews, J A Bangham and
Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM
 Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 yingwu@northwestern.edu http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu
Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 yingwu@northwestern.edu http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu
Object Recognition. Lecture 11, April 21 st, Lexing Xie. EE4830 Digital Image Processing
 Object Recognition Lecture 11, April 21 st, 2008 Lexing Xie EE4830 Digital Image Processing http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~xlx/ee4830/ 1 Announcements 2 HW#5 due today HW#6 last HW of the semester Due May
Object Recognition Lecture 11, April 21 st, 2008 Lexing Xie EE4830 Digital Image Processing http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~xlx/ee4830/ 1 Announcements 2 HW#5 due today HW#6 last HW of the semester Due May
Image-Based Face Recognition using Global Features
 Image-Based Face Recognition using Global Features Xiaoyin xu Research Centre for Integrated Microsystems Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Windsor Supervisors: Dr. Ahmadi May 13, 2005
Image-Based Face Recognition using Global Features Xiaoyin xu Research Centre for Integrated Microsystems Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Windsor Supervisors: Dr. Ahmadi May 13, 2005
Neural Networks. CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 Neural Networks CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Biological and artificial neural networks Feed-forward neural networks Single layer
Neural Networks CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Biological and artificial neural networks Feed-forward neural networks Single layer
Automatic Alignment of Local Representations
 Automatic Alignment of Local Representations Yee Whye Teh and Sam Roweis Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto ywteh,roweis @cs.toronto.edu Abstract We present an automatic alignment procedure
Automatic Alignment of Local Representations Yee Whye Teh and Sam Roweis Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto ywteh,roweis @cs.toronto.edu Abstract We present an automatic alignment procedure
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein & Luke Zettlemoyer Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein & Luke Zettlemoyer Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning
Topological Mapping. Discrete Bayes Filter
 Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Assignment 2. Classification and Regression using Linear Networks, Multilayer Perceptron Networks, and Radial Basis Functions
 ENEE 739Q: STATISTICAL AND NEURAL PATTERN RECOGNITION Spring 2002 Assignment 2 Classification and Regression using Linear Networks, Multilayer Perceptron Networks, and Radial Basis Functions Aravind Sundaresan
ENEE 739Q: STATISTICAL AND NEURAL PATTERN RECOGNITION Spring 2002 Assignment 2 Classification and Regression using Linear Networks, Multilayer Perceptron Networks, and Radial Basis Functions Aravind Sundaresan
A New Manifold Representation for Visual Speech Recognition
 A New Manifold Representation for Visual Speech Recognition Dahai Yu, Ovidiu Ghita, Alistair Sutherland, Paul F. Whelan School of Computing & Electronic Engineering, Vision Systems Group Dublin City University,
A New Manifold Representation for Visual Speech Recognition Dahai Yu, Ovidiu Ghita, Alistair Sutherland, Paul F. Whelan School of Computing & Electronic Engineering, Vision Systems Group Dublin City University,
Announcements. Recognition I. Gradient Space (p,q) What is the reflectance map?
 Announcements I HW 3 due 12 noon, tomorrow. HW 4 to be posted soon recognition Lecture plan recognition for next two lectures, then video and motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 17
Announcements I HW 3 due 12 noon, tomorrow. HW 4 to be posted soon recognition Lecture plan recognition for next two lectures, then video and motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 17
Xing Fan, Carlos Busso and John H.L. Hansen
 Xing Fan, Carlos Busso and John H.L. Hansen Center for Robust Speech Systems (CRSS) Erik Jonsson School of Engineering & Computer Science Department of Electrical Engineering University of Texas at Dallas
Xing Fan, Carlos Busso and John H.L. Hansen Center for Robust Speech Systems (CRSS) Erik Jonsson School of Engineering & Computer Science Department of Electrical Engineering University of Texas at Dallas
10-701/15-781, Fall 2006, Final
 -7/-78, Fall 6, Final Dec, :pm-8:pm There are 9 questions in this exam ( pages including this cover sheet). If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly
-7/-78, Fall 6, Final Dec, :pm-8:pm There are 9 questions in this exam ( pages including this cover sheet). If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly
Classifier C-Net. 2D Projected Images of 3D Objects. 2D Projected Images of 3D Objects. Model I. Model II
 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 7. (99) The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. pp.949-96 Unsupervised Classication of 3D Objects from D Views Satoshi Suzuki Hiroshi Ando ATR Human Information
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 7. (99) The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. pp.949-96 Unsupervised Classication of 3D Objects from D Views Satoshi Suzuki Hiroshi Ando ATR Human Information
Three-Dimensional Computer Vision
 \bshiaki Shirai Three-Dimensional Computer Vision With 313 Figures ' Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Three-Dimensional Computer Vision
\bshiaki Shirai Three-Dimensional Computer Vision With 313 Figures ' Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Three-Dimensional Computer Vision
22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan. Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 1 22 October, 2012 MVA ENS Cachan Lecture 5: Introduction to generative models Iasonas Kokkinos Iasonas.kokkinos@ecp.fr Center for Visual Computing Ecole Centrale Paris
Clustering K-means. Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, Carlos Guestrin
 Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, 2014 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014
Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSEP546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington February 18, 2014 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] Carlos Guestrin 2005-2014
An Introduction to Pattern Recognition
 An Introduction to Pattern Recognition Speaker : Wei lun Chao Advisor : Prof. Jian-jiun Ding DISP Lab Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering 1 Abstract Not a new research field Wide range included
An Introduction to Pattern Recognition Speaker : Wei lun Chao Advisor : Prof. Jian-jiun Ding DISP Lab Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering 1 Abstract Not a new research field Wide range included
Face Recognition using Rectangular Feature
 Face Recognition using Rectangular Feature Sanjay Pagare, Dr. W. U. Khan Computer Engineering Department Shri G.S. Institute of Technology and Science Indore Abstract- Face recognition is the broad area
Face Recognition using Rectangular Feature Sanjay Pagare, Dr. W. U. Khan Computer Engineering Department Shri G.S. Institute of Technology and Science Indore Abstract- Face recognition is the broad area
Neural Networks. Single-layer neural network. CSE 446: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington March 10, /10/2017
 3/0/207 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/0/207 Perceptron as a neural
3/0/207 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/0/207 Perceptron as a neural
Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques
 Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques Sea Chen Department of Biomedical Engineering Advisors: Dr. Charles A. Bouman and Dr. Mark J. Lowe S. Chen Final Exam October
Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques Sea Chen Department of Biomedical Engineering Advisors: Dr. Charles A. Bouman and Dr. Mark J. Lowe S. Chen Final Exam October
ESTIMATING HEAD POSE WITH AN RGBD SENSOR: A COMPARISON OF APPEARANCE-BASED AND POSE-BASED LOCAL SUBSPACE METHODS
 ESTIMATING HEAD POSE WITH AN RGBD SENSOR: A COMPARISON OF APPEARANCE-BASED AND POSE-BASED LOCAL SUBSPACE METHODS Donghun Kim, Johnny Park, and Avinash C. Kak Robot Vision Lab, School of Electrical and
ESTIMATING HEAD POSE WITH AN RGBD SENSOR: A COMPARISON OF APPEARANCE-BASED AND POSE-BASED LOCAL SUBSPACE METHODS Donghun Kim, Johnny Park, and Avinash C. Kak Robot Vision Lab, School of Electrical and
LOW-DIMENSIONAL MOTION FEATURES FOR AUDIO-VISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION
 LOW-DIMENSIONAL MOTION FEATURES FOR AUDIO-VISUAL SPEECH Andrés Vallés Carboneras, Mihai Gurban +, and Jean-Philippe Thiran + + Signal Processing Institute, E.T.S.I. de Telecomunicación Ecole Polytechnique
LOW-DIMENSIONAL MOTION FEATURES FOR AUDIO-VISUAL SPEECH Andrés Vallés Carboneras, Mihai Gurban +, and Jean-Philippe Thiran + + Signal Processing Institute, E.T.S.I. de Telecomunicación Ecole Polytechnique
Segmentation by Clustering Reading: Chapter 14 (skip 14.5)
 Segmentation by Clustering Reading: Chapter 14 (skip 14.5) Data reduction - obtain a compact representation for interesting image data in terms of a set of components Find components that belong together
Segmentation by Clustering Reading: Chapter 14 (skip 14.5) Data reduction - obtain a compact representation for interesting image data in terms of a set of components Find components that belong together
Segmentation by Clustering. Segmentation by Clustering Reading: Chapter 14 (skip 14.5) General ideas
 Reading: Chapter 14 (skip 14.5) Data reduction - obtain a compact representation for interesting image data in terms of a set of components Find components that belong together (form clusters) Frame differencing
Reading: Chapter 14 (skip 14.5) Data reduction - obtain a compact representation for interesting image data in terms of a set of components Find components that belong together (form clusters) Frame differencing
COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION
 VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
Speech Recognition Lecture 8: Acoustic Models. Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Courant Institute Slide Credit: Mehryar Mohri
 Speech Recognition Lecture 8: Acoustic Models. Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Courant Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryar Mohri Speech Recognition Components Acoustic and pronunciation model:
Speech Recognition Lecture 8: Acoustic Models. Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Courant Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryar Mohri Speech Recognition Components Acoustic and pronunciation model:
More on Learning. Neural Nets Support Vectors Machines Unsupervised Learning (Clustering) K-Means Expectation-Maximization
 More on Learning Neural Nets Support Vectors Machines Unsupervised Learning (Clustering) K-Means Expectation-Maximization Neural Net Learning Motivated by studies of the brain. A network of artificial
More on Learning Neural Nets Support Vectors Machines Unsupervised Learning (Clustering) K-Means Expectation-Maximization Neural Net Learning Motivated by studies of the brain. A network of artificial
Digital Geometry Processing
 Digital Geometry Processing Spring 2011 physical model acquired point cloud reconstructed model 2 Digital Michelangelo Project Range Scanning Systems Passive: Stereo Matching Find and match features in
Digital Geometry Processing Spring 2011 physical model acquired point cloud reconstructed model 2 Digital Michelangelo Project Range Scanning Systems Passive: Stereo Matching Find and match features in
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Hierarchical Clustering
 INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Hierarchical Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 25, 2012 Agenda Topics we covered last week Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision, recall and F-score
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Hierarchical Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 25, 2012 Agenda Topics we covered last week Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision, recall and F-score
All lecture slides will be available at CSC2515_Winter15.html
 CSC2515 Fall 2015 Introduc3on to Machine Learning Lecture 9: Support Vector Machines All lecture slides will be available at http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/ CSC2515_Winter15.html Many
CSC2515 Fall 2015 Introduc3on to Machine Learning Lecture 9: Support Vector Machines All lecture slides will be available at http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/ CSC2515_Winter15.html Many
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong)
 Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
MACHINE LEARNING: CLUSTERING, AND CLASSIFICATION. Steve Tjoa June 25, 2014
 MACHINE LEARNING: CLUSTERING, AND CLASSIFICATION Steve Tjoa kiemyang@gmail.com June 25, 2014 Review from Day 2 Supervised vs. Unsupervised Unsupervised - clustering Supervised binary classifiers (2 classes)
MACHINE LEARNING: CLUSTERING, AND CLASSIFICATION Steve Tjoa kiemyang@gmail.com June 25, 2014 Review from Day 2 Supervised vs. Unsupervised Unsupervised - clustering Supervised binary classifiers (2 classes)
Deep Learning with Tensorflow AlexNet
 Machine Learning and Computer Vision Group Deep Learning with Tensorflow http://cvml.ist.ac.at/courses/dlwt_w17/ AlexNet Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton, "Imagenet classification
Machine Learning and Computer Vision Group Deep Learning with Tensorflow http://cvml.ist.ac.at/courses/dlwt_w17/ AlexNet Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton, "Imagenet classification
Manifold Learning for Video-to-Video Face Recognition
 Manifold Learning for Video-to-Video Face Recognition Abstract. We look in this work at the problem of video-based face recognition in which both training and test sets are video sequences, and propose
Manifold Learning for Video-to-Video Face Recognition Abstract. We look in this work at the problem of video-based face recognition in which both training and test sets are video sequences, and propose
Linear Discriminant Analysis in Ottoman Alphabet Character Recognition
 Linear Discriminant Analysis in Ottoman Alphabet Character Recognition ZEYNEB KURT, H. IREM TURKMEN, M. ELIF KARSLIGIL Department of Computer Engineering, Yildiz Technical University, 34349 Besiktas /
Linear Discriminant Analysis in Ottoman Alphabet Character Recognition ZEYNEB KURT, H. IREM TURKMEN, M. ELIF KARSLIGIL Department of Computer Engineering, Yildiz Technical University, 34349 Besiktas /
Pattern Recognition. Kjell Elenius. Speech, Music and Hearing KTH. March 29, 2007 Speech recognition
 Pattern Recognition Kjell Elenius Speech, Music and Hearing KTH March 29, 2007 Speech recognition 2007 1 Ch 4. Pattern Recognition 1(3) Bayes Decision Theory Minimum-Error-Rate Decision Rules Discriminant
Pattern Recognition Kjell Elenius Speech, Music and Hearing KTH March 29, 2007 Speech recognition 2007 1 Ch 4. Pattern Recognition 1(3) Bayes Decision Theory Minimum-Error-Rate Decision Rules Discriminant
Image Segmentation. Ross Whitaker SCI Institute, School of Computing University of Utah
 Image Segmentation Ross Whitaker SCI Institute, School of Computing University of Utah What is Segmentation? Partitioning images/volumes into meaningful pieces Partitioning problem Labels Isolating a specific
Image Segmentation Ross Whitaker SCI Institute, School of Computing University of Utah What is Segmentation? Partitioning images/volumes into meaningful pieces Partitioning problem Labels Isolating a specific
Computer Vision with MATLAB MATLAB Expo 2012 Steve Kuznicki
 Computer Vision with MATLAB MATLAB Expo 2012 Steve Kuznicki 2011 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Today s Topics Introduction Computer Vision Feature-based registration Automatic image registration Object recognition/rotation
Computer Vision with MATLAB MATLAB Expo 2012 Steve Kuznicki 2011 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Today s Topics Introduction Computer Vision Feature-based registration Automatic image registration Object recognition/rotation
Hidden Markov Models. Gabriela Tavares and Juri Minxha Mentor: Taehwan Kim CS159 04/25/2017
 Hidden Markov Models Gabriela Tavares and Juri Minxha Mentor: Taehwan Kim CS159 04/25/2017 1 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Brief review of HMMs Hidden Markov Support Vector Machines Large Margin Hidden Markov Models
Hidden Markov Models Gabriela Tavares and Juri Minxha Mentor: Taehwan Kim CS159 04/25/2017 1 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Brief review of HMMs Hidden Markov Support Vector Machines Large Margin Hidden Markov Models
Static Gesture Recognition with Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Static Gesture Recognition with Restricted Boltzmann Machines Peter O Donovan Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto 6 Kings College Rd, M5S 3G4, Canada odonovan@dgp.toronto.edu Abstract
Static Gesture Recognition with Restricted Boltzmann Machines Peter O Donovan Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto 6 Kings College Rd, M5S 3G4, Canada odonovan@dgp.toronto.edu Abstract
Last week. Multi-Frame Structure from Motion: Multi-View Stereo. Unknown camera viewpoints
 Last week Multi-Frame Structure from Motion: Multi-View Stereo Unknown camera viewpoints Last week PCA Today Recognition Today Recognition Recognition problems What is it? Object detection Who is it? Recognizing
Last week Multi-Frame Structure from Motion: Multi-View Stereo Unknown camera viewpoints Last week PCA Today Recognition Today Recognition Recognition problems What is it? Object detection Who is it? Recognizing
Motion Detection. Final project by. Neta Sokolovsky
 Motion Detection Final project by Neta Sokolovsky Introduction The goal of this project is to recognize a motion of objects found in the two given images. This functionality is useful in the video processing
Motion Detection Final project by Neta Sokolovsky Introduction The goal of this project is to recognize a motion of objects found in the two given images. This functionality is useful in the video processing
A Taxonomy of Semi-Supervised Learning Algorithms
 A Taxonomy of Semi-Supervised Learning Algorithms Olivier Chapelle Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics December 2005 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generative models 3 Low density separation 4 Graph
A Taxonomy of Semi-Supervised Learning Algorithms Olivier Chapelle Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics December 2005 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generative models 3 Low density separation 4 Graph
Adaptive Regularization. in Neural Network Filters
 Adaptive Regularization in Neural Network Filters Course 0455 Advanced Digital Signal Processing May 3 rd, 00 Fares El-Azm Michael Vinther d97058 s97397 Introduction The bulk of theoretical results and
Adaptive Regularization in Neural Network Filters Course 0455 Advanced Digital Signal Processing May 3 rd, 00 Fares El-Azm Michael Vinther d97058 s97397 Introduction The bulk of theoretical results and
From Raw Data to Meaningful Features
 From Raw Data to Meaningful Features Andreas Damianou University of Sheffield, UK Summer School on Machine Learning and Data Science 27 June, 2016 Makerere University, Uganda Working with data Data-science:
From Raw Data to Meaningful Features Andreas Damianou University of Sheffield, UK Summer School on Machine Learning and Data Science 27 June, 2016 Makerere University, Uganda Working with data Data-science:
Discriminative training and Feature combination
 Discriminative training and Feature combination Steve Renals Automatic Speech Recognition ASR Lecture 13 16 March 2009 Steve Renals Discriminative training and Feature combination 1 Overview Hot topics
Discriminative training and Feature combination Steve Renals Automatic Speech Recognition ASR Lecture 13 16 March 2009 Steve Renals Discriminative training and Feature combination 1 Overview Hot topics
Local Filter Selection Boosts Performance of Automatic Speechreading
 52 5th Joint Symposium on Neural Computation Proceedings, UCSD (1998) Local Filter Selection Boosts Performance of Automatic Speechreading Michael S. Gray, Terrence J. Sejnowski Computational Neurobiology
52 5th Joint Symposium on Neural Computation Proceedings, UCSD (1998) Local Filter Selection Boosts Performance of Automatic Speechreading Michael S. Gray, Terrence J. Sejnowski Computational Neurobiology
Computer Vision. Exercise Session 10 Image Categorization
 Computer Vision Exercise Session 10 Image Categorization Object Categorization Task Description Given a small number of training images of a category, recognize a-priori unknown instances of that category
Computer Vision Exercise Session 10 Image Categorization Object Categorization Task Description Given a small number of training images of a category, recognize a-priori unknown instances of that category
Structured Perceptron. Ye Qiu, Xinghui Lu, Yue Lu, Ruofei Shen
 Structured Perceptron Ye Qiu, Xinghui Lu, Yue Lu, Ruofei Shen 1 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Brief review of perceptron Structured Perceptron Discriminative Training Methods for Hidden Markov Models: Theory and
Structured Perceptron Ye Qiu, Xinghui Lu, Yue Lu, Ruofei Shen 1 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Brief review of perceptron Structured Perceptron Discriminative Training Methods for Hidden Markov Models: Theory and
INF 5860 Machine learning for image classification. Lecture 11: Visualization Anne Solberg April 4, 2018
 INF 5860 Machine learning for image classification Lecture 11: Visualization Anne Solberg April 4, 2018 Reading material The lecture is based on papers: Deep Dream: https://research.googleblog.com/2015/06/inceptionism-goingdeeper-into-neural.html
INF 5860 Machine learning for image classification Lecture 11: Visualization Anne Solberg April 4, 2018 Reading material The lecture is based on papers: Deep Dream: https://research.googleblog.com/2015/06/inceptionism-goingdeeper-into-neural.html
Large-Scale Face Manifold Learning
 Large-Scale Face Manifold Learning Sanjiv Kumar Google Research New York, NY * Joint work with A. Talwalkar, H. Rowley and M. Mohri 1 Face Manifold Learning 50 x 50 pixel faces R 2500 50 x 50 pixel random
Large-Scale Face Manifold Learning Sanjiv Kumar Google Research New York, NY * Joint work with A. Talwalkar, H. Rowley and M. Mohri 1 Face Manifold Learning 50 x 50 pixel faces R 2500 50 x 50 pixel random
03 - Reconstruction. Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung. CSCI-GA Geometric Modeling - Spring 17 - Daniele Panozzo
 3 - Reconstruction Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Geometry Acquisition Pipeline Scanning: results in range images Registration: bring all range images to one coordinate system Stitching/ reconstruction:
3 - Reconstruction Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Geometry Acquisition Pipeline Scanning: results in range images Registration: bring all range images to one coordinate system Stitching/ reconstruction:
9.913 Pattern Recognition for Vision. Class I - Overview. Instructors: B. Heisele, Y. Ivanov, T. Poggio
 9.913 Class I - Overview Instructors: B. Heisele, Y. Ivanov, T. Poggio TOC Administrivia Problems of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Overview of classes Quick review of Matlab Administrivia Instructors:
9.913 Class I - Overview Instructors: B. Heisele, Y. Ivanov, T. Poggio TOC Administrivia Problems of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Overview of classes Quick review of Matlab Administrivia Instructors:
Head Frontal-View Identification Using Extended LLE
 Head Frontal-View Identification Using Extended LLE Chao Wang Center for Spoken Language Understanding, Oregon Health and Science University Abstract Automatic head frontal-view identification is challenging
Head Frontal-View Identification Using Extended LLE Chao Wang Center for Spoken Language Understanding, Oregon Health and Science University Abstract Automatic head frontal-view identification is challenging
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, NOVEMBER Inverting Feedforward Neural Networks Using Linear and Nonlinear Programming
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, NOVEMBER 1999 1271 Inverting Feedforward Neural Networks Using Linear and Nonlinear Programming Bao-Liang Lu, Member, IEEE, Hajime Kita, and Yoshikazu
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, NOVEMBER 1999 1271 Inverting Feedforward Neural Networks Using Linear and Nonlinear Programming Bao-Liang Lu, Member, IEEE, Hajime Kita, and Yoshikazu
Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition. 1 Introduction 1
 Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition vii xi 1 Introduction 1 2 Overview of Supervised Learning 9 2.1 Introduction... 9 2.2 Variable Types and Terminology... 9 2.3 Two Simple Approaches
Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition vii xi 1 Introduction 1 2 Overview of Supervised Learning 9 2.1 Introduction... 9 2.2 Variable Types and Terminology... 9 2.3 Two Simple Approaches
Research Article Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using Lip Information Extracted from Side-Face Images
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing Volume 2007, Article ID 64506, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2007/64506 Research Article Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing Volume 2007, Article ID 64506, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2007/64506 Research Article Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using
Exercise: Training Simple MLP by Backpropagation. Using Netlab.
 Exercise: Training Simple MLP by Backpropagation. Using Netlab. Petr Pošík December, 27 File list This document is an explanation text to the following script: demomlpklin.m script implementing the beckpropagation
Exercise: Training Simple MLP by Backpropagation. Using Netlab. Petr Pošík December, 27 File list This document is an explanation text to the following script: demomlpklin.m script implementing the beckpropagation
Time Series Clustering Ensemble Algorithm Based on Locality Preserving Projection
 Based on Locality Preserving Projection 2 Information & Technology College, Hebei University of Economics & Business, 05006 Shijiazhuang, China E-mail: 92475577@qq.com Xiaoqing Weng Information & Technology
Based on Locality Preserving Projection 2 Information & Technology College, Hebei University of Economics & Business, 05006 Shijiazhuang, China E-mail: 92475577@qq.com Xiaoqing Weng Information & Technology
A Visualization Tool to Improve the Performance of a Classifier Based on Hidden Markov Models
 A Visualization Tool to Improve the Performance of a Classifier Based on Hidden Markov Models Gleidson Pegoretti da Silva, Masaki Nakagawa Department of Computer and Information Sciences Tokyo University
A Visualization Tool to Improve the Performance of a Classifier Based on Hidden Markov Models Gleidson Pegoretti da Silva, Masaki Nakagawa Department of Computer and Information Sciences Tokyo University
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS
 PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS RICHARD O. DUDA PETER E. HART Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS RICHARD O. DUDA PETER E. HART Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
Extensive research has been conducted, aimed at developing
 Chapter 4 Supervised Learning: Multilayer Networks II Extensive research has been conducted, aimed at developing improved supervised learning algorithms for feedforward networks. 4.1 Madalines A \Madaline"
Chapter 4 Supervised Learning: Multilayer Networks II Extensive research has been conducted, aimed at developing improved supervised learning algorithms for feedforward networks. 4.1 Madalines A \Madaline"
Multi-pose lipreading and audio-visual speech recognition
 RESEARCH Open Access Multi-pose lipreading and audio-visual speech recognition Virginia Estellers * and Jean-Philippe Thiran Abstract In this article, we study the adaptation of visual and audio-visual
RESEARCH Open Access Multi-pose lipreading and audio-visual speech recognition Virginia Estellers * and Jean-Philippe Thiran Abstract In this article, we study the adaptation of visual and audio-visual
Variable-Component Deep Neural Network for Robust Speech Recognition
 Variable-Component Deep Neural Network for Robust Speech Recognition Rui Zhao 1, Jinyu Li 2, and Yifan Gong 2 1 Microsoft Search Technology Center Asia, Beijing, China 2 Microsoft Corporation, One Microsoft
Variable-Component Deep Neural Network for Robust Speech Recognition Rui Zhao 1, Jinyu Li 2, and Yifan Gong 2 1 Microsoft Search Technology Center Asia, Beijing, China 2 Microsoft Corporation, One Microsoft
Juergen Luettin 1 and Stephane Dupont IDIAP Dalle Molle Institute for Perceptual Articial Intelligence, Rue du
 Continuous Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Juergen Luettin 1 and Stephane Dupont 2 1 1 IDIAP Dalle Molle Institute for Perceptual Articial Intelligence, Rue du Simplon 4, CH-1920 Martigny, Switzerland,
Continuous Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Juergen Luettin 1 and Stephane Dupont 2 1 1 IDIAP Dalle Molle Institute for Perceptual Articial Intelligence, Rue du Simplon 4, CH-1920 Martigny, Switzerland,
Semantic Word Embedding Neural Network Language Models for Automatic Speech Recognition
 Semantic Word Embedding Neural Network Language Models for Automatic Speech Recognition Kartik Audhkhasi, Abhinav Sethy Bhuvana Ramabhadran Watson Multimodal Group IBM T. J. Watson Research Center Motivation
Semantic Word Embedding Neural Network Language Models for Automatic Speech Recognition Kartik Audhkhasi, Abhinav Sethy Bhuvana Ramabhadran Watson Multimodal Group IBM T. J. Watson Research Center Motivation
IT Digital Image ProcessingVII Semester - Question Bank
 UNIT I DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS PART A Elements of Digital Image processing (DIP) systems 1. What is a pixel? 2. Define Digital Image 3. What are the steps involved in DIP? 4. List the categories of
UNIT I DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS PART A Elements of Digital Image processing (DIP) systems 1. What is a pixel? 2. Define Digital Image 3. What are the steps involved in DIP? 4. List the categories of
Homework 4: Clustering, Recommenders, Dim. Reduction, ML and Graph Mining (due November 19 th, 2014, 2:30pm, in class hard-copy please)
 Virginia Tech. Computer Science CS 5614 (Big) Data Management Systems Fall 2014, Prakash Homework 4: Clustering, Recommenders, Dim. Reduction, ML and Graph Mining (due November 19 th, 2014, 2:30pm, in
Virginia Tech. Computer Science CS 5614 (Big) Data Management Systems Fall 2014, Prakash Homework 4: Clustering, Recommenders, Dim. Reduction, ML and Graph Mining (due November 19 th, 2014, 2:30pm, in
Audio-visual speech recognition using deep bottleneck features and high-performance lipreading
 Proceedings of APSIPA Annual Summit and Conference 215 16-19 December 215 Audio-visual speech recognition using deep bottleneck features and high-performance lipreading Satoshi TAMURA, Hiroshi NINOMIYA,
Proceedings of APSIPA Annual Summit and Conference 215 16-19 December 215 Audio-visual speech recognition using deep bottleneck features and high-performance lipreading Satoshi TAMURA, Hiroshi NINOMIYA,
CS 195-5: Machine Learning Problem Set 5
 CS 195-5: Machine Learning Problem Set 5 Douglas Lanman dlanman@brown.edu 26 November 26 1 Clustering and Vector Quantization Problem 1 Part 1: In this problem we will apply Vector Quantization (VQ) to
CS 195-5: Machine Learning Problem Set 5 Douglas Lanman dlanman@brown.edu 26 November 26 1 Clustering and Vector Quantization Problem 1 Part 1: In this problem we will apply Vector Quantization (VQ) to
An Approach for Reduction of Rain Streaks from a Single Image
 An Approach for Reduction of Rain Streaks from a Single Image Vijayakumar Majjagi 1, Netravati U M 2 1 4 th Semester, M. Tech, Digital Electronics, Department of Electronics and Communication G M Institute
An Approach for Reduction of Rain Streaks from a Single Image Vijayakumar Majjagi 1, Netravati U M 2 1 4 th Semester, M. Tech, Digital Electronics, Department of Electronics and Communication G M Institute
Using Gradient Descent Optimization for Acoustics Training from Heterogeneous Data
 Using Gradient Descent Optimization for Acoustics Training from Heterogeneous Data Martin Karafiát Λ, Igor Szöke, and Jan Černocký Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology Department
Using Gradient Descent Optimization for Acoustics Training from Heterogeneous Data Martin Karafiát Λ, Igor Szöke, and Jan Černocký Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology Department
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Kernels and Clustering Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Kernels and Clustering Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
LOW-RANK MATRIX FACTORIZATION FOR DEEP NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING WITH HIGH-DIMENSIONAL OUTPUT TARGETS
 LOW-RANK MATRIX FACTORIZATION FOR DEEP NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING WITH HIGH-DIMENSIONAL OUTPUT TARGETS Tara N. Sainath, Brian Kingsbury, Vikas Sindhwani, Ebru Arisoy, Bhuvana Ramabhadran IBM T. J. Watson
LOW-RANK MATRIX FACTORIZATION FOR DEEP NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING WITH HIGH-DIMENSIONAL OUTPUT TARGETS Tara N. Sainath, Brian Kingsbury, Vikas Sindhwani, Ebru Arisoy, Bhuvana Ramabhadran IBM T. J. Watson
Neural Network Neurons
 Neural Networks Neural Network Neurons 1 Receives n inputs (plus a bias term) Multiplies each input by its weight Applies activation function to the sum of results Outputs result Activation Functions Given
Neural Networks Neural Network Neurons 1 Receives n inputs (plus a bias term) Multiplies each input by its weight Applies activation function to the sum of results Outputs result Activation Functions Given
Data fusion and multi-cue data matching using diffusion maps
 Data fusion and multi-cue data matching using diffusion maps Stéphane Lafon Collaborators: Raphy Coifman, Andreas Glaser, Yosi Keller, Steven Zucker (Yale University) Part of this work was supported by
Data fusion and multi-cue data matching using diffusion maps Stéphane Lafon Collaborators: Raphy Coifman, Andreas Glaser, Yosi Keller, Steven Zucker (Yale University) Part of this work was supported by
3D Models and Matching
 3D Models and Matching representations for 3D object models particular matching techniques alignment-based systems appearance-based systems GC model of a screwdriver 1 3D Models Many different representations
3D Models and Matching representations for 3D object models particular matching techniques alignment-based systems appearance-based systems GC model of a screwdriver 1 3D Models Many different representations
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Third Edition Rafael C. Gonzalez University of Tennessee Richard E. Woods MedData Interactive PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education International Contents Preface xv Acknowledgments
Digital Image Processing Third Edition Rafael C. Gonzalez University of Tennessee Richard E. Woods MedData Interactive PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education International Contents Preface xv Acknowledgments
Case-Based Reasoning. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Nearest-Neighbor Classification. Parametric / Non-parametric.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
Subdivision Curves and Surfaces
 Subdivision Surfaces or How to Generate a Smooth Mesh?? Subdivision Curves and Surfaces Subdivision given polyline(2d)/mesh(3d) recursively modify & add vertices to achieve smooth curve/surface Each iteration
Subdivision Surfaces or How to Generate a Smooth Mesh?? Subdivision Curves and Surfaces Subdivision given polyline(2d)/mesh(3d) recursively modify & add vertices to achieve smooth curve/surface Each iteration
Robust Lip Contour Extraction using Separability of Multi-Dimensional Distributions
 Robust Lip Contour Extraction using Separability of Multi-Dimensional Distributions Tomokazu Wakasugi, Masahide Nishiura and Kazuhiro Fukui Corporate Research and Development Center, Toshiba Corporation
Robust Lip Contour Extraction using Separability of Multi-Dimensional Distributions Tomokazu Wakasugi, Masahide Nishiura and Kazuhiro Fukui Corporate Research and Development Center, Toshiba Corporation
An Introduction to Hidden Markov Models
 An Introduction to Hidden Markov Models Max Heimel Fachgebiet Datenbanksysteme und Informationsmanagement Technische Universität Berlin http://www.dima.tu-berlin.de/ 07.10.2010 DIMA TU Berlin 1 Agenda
An Introduction to Hidden Markov Models Max Heimel Fachgebiet Datenbanksysteme und Informationsmanagement Technische Universität Berlin http://www.dima.tu-berlin.de/ 07.10.2010 DIMA TU Berlin 1 Agenda
Visual Learning and Recognition of 3D Objects from Appearance
 Visual Learning and Recognition of 3D Objects from Appearance (H. Murase and S. Nayar, "Visual Learning and Recognition of 3D Objects from Appearance", International Journal of Computer Vision, vol. 14,
Visual Learning and Recognition of 3D Objects from Appearance (H. Murase and S. Nayar, "Visual Learning and Recognition of 3D Objects from Appearance", International Journal of Computer Vision, vol. 14,
