Construction: Draw a ray with its endpoint on the left. Label this point B.
|
|
|
- Vivien Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Ms. Ayinde Date: Geometry CC 1.13: Constructing Angles Objective: To copy angles and construct angle bisectors using a compass and straightedge. To construct an equilateral triangle. Copy an Angle: For this construction, you are learning how to copy the degree measurement of an angle. Step 1: Construction: Draw a ray with its endpoint on the left. Label this point B. Step 2: Place the center of the compass on Point B and slide your slider holes to the right so that you are able to create an arc that intersects with both sides of the angle. Step 3: Move your compass onto point B. Without altering the positioning of the slider, place you pencil in the slider hole and create a long arc starting above the ray and intersecting then with ray. Step 4: Place you compass on one of the intersection points between the arc and the original angle. Place the hole of the slider over the second intersection. You are using the compass to measure the distance between these two intersection points. Step 5: Without altering the compass settings. Slide the center of the clear circle over the point of intersection between the ray you drew and the arc intersecting it. Create an arc that intersects with the arc already drawn. What is the relationship between these two angles? Step 6: Draw a line from point B to the point of intersection for those arcs. Do not erase any of your construction marks!
2 Bisect an angle: For this construction, you are learning how to bisect an angle by constructing an angle bisector. Construction: Step 1: Place the compass point on the vertex of the angle. Create an arc that intersects both sides of the angle. Step 2: Without changing the settings of the compass, place the compass point on one of the intersections between the arc and the angle. Draw a nice big arc within the interior of the angle. Step 3: Without changing the settings of the compass, place the compass point on the second intersection between the arc and the angle. Draw a nice big arc within the interior of the angle. Step 4: Your two arcs should intersect. Using your straightedge, you are going to draw a ray starting from the vertex B going through the intersection point between the two arcs. Label this point of intersection D What is the relationship between these two small angles? What is the relationship between the three angles?
3 Construct an Equilateral Triangle: For this construction, we will create an equilateral triangle. Step 1: Place the center of the clear circle on point A and slide your slider on point B. Create a large arc. Construction: Step 2: Without changing the settings, place your clear circle on Point B and create a large arc. Step 3: The two arcs will intersect. This intersection is the third vertex of the triangle. Label it C. Step 4: Using your straightedge, connect A with C. Then connect B with C. Do not erase any of your construction marks! What is the relationship between the three sides of the triangle.
4 Practice: Leave all your construction marks. 1. Construct an obtuse angle below. Label this PHD. Using your straightedge and compass copy the angle and label the new angle P H D. 2. Construct an acute angle without using your protractor. Label the acute angle HOP. Using a compass and straightedge, construct angle bisector OG. Write a congruence statement about the two angles. 3. Construct an equilateral triangle whose side is equal in length (congruent to) the segment AB. Write a congruence statement about the three sides of the triangle.
5 4. Construct an acute angle. Label this SIP. Using a compass and straightedge, construct angle bisector IT. a. Write a congruence statement about the two small angles and an addition statement about the three angles. b. If m SIT = 5x + 4 and m TIP = 3(x 4), what is the m SIP? Justify every step you take when solving.
6 5. Create and equilateral triangle with sides that are each 5 cm long. Label the triangle ABC. a. Write a congruence statement about the three sides of the triangle. b. If AB = x+2, BC = 3x-4, and CA = 11-2x, determine the value of x.
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS
 MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
Mth 97 Winter 2013 Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
Construction Instructions. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment.
 Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
CONSTRUCTING CONGRUENT LINE SEGMENTS
 NME: 1. Given: Task: Construct a segment congruent to. CONSTRUCTING CONGRUENT LINE SEGMENTS B a) Draw a new, longer segment with your straightedge. b) Place an endpoint on the left side of the new segment
NME: 1. Given: Task: Construct a segment congruent to. CONSTRUCTING CONGRUENT LINE SEGMENTS B a) Draw a new, longer segment with your straightedge. b) Place an endpoint on the left side of the new segment
Geometric Constructions
 Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task
 90 Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task For each of the following straightedge and compass constructions, illustrate or list the steps for completing the construction and give an eplanation
90 Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task For each of the following straightedge and compass constructions, illustrate or list the steps for completing the construction and give an eplanation
2. A straightedge can create straight line, but can't measure. A ruler can create straight lines and measure distances.
 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
no triangle can have more than one right angle or obtuse angle.
 Congruence Theorems in Action Isosceles Triangle Theorems.3 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Prove the Isosceles Triangle Base Theorem. Prove the Isosceles Triangle Vertex Angle Theorem. Prove
Congruence Theorems in Action Isosceles Triangle Theorems.3 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Prove the Isosceles Triangle Base Theorem. Prove the Isosceles Triangle Vertex Angle Theorem. Prove
Constructions Quiz Review November 29, 2017
 Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
2 Partial Solution of Homework
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_fall12h2.tex Use the back pages for extra space, attach blank pages if necessary You may submit the solution in groups up to four students due September 21
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_fall12h2.tex Use the back pages for extra space, attach blank pages if necessary You may submit the solution in groups up to four students due September 21
Mth 97 Fall 2013 Chapter 4
 4.1 Reasoning and Proof in Geometry Direct reasoning or reasoning is used to draw a conclusion from a series of statements. Conditional statements, if p, then q, play a central role in deductive reasoning.
4.1 Reasoning and Proof in Geometry Direct reasoning or reasoning is used to draw a conclusion from a series of statements. Conditional statements, if p, then q, play a central role in deductive reasoning.
Type of Triangle Definition Drawing. Name the triangles below, and list the # of congruent sides and angles:
 Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Warm-Up. Find the domain and range:
 Warm-Up Find the domain and range: Geometry Vocabulary & Notation Point Name: Use only the capital letter, without any symbol. Line Name: Use any two points on the line with a line symbol above. AB Line
Warm-Up Find the domain and range: Geometry Vocabulary & Notation Point Name: Use only the capital letter, without any symbol. Line Name: Use any two points on the line with a line symbol above. AB Line
Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task
 90 Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task For each of the following straightedge and compass constructions, illustrate or list the steps for completing the construction and give an eplanation
90 Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task For each of the following straightedge and compass constructions, illustrate or list the steps for completing the construction and give an eplanation
Geometry: Traditional Pathway
 GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
Geometry Notes Chapter 4: Triangles
 Geometry Notes Chapter 4: Triangles Name Date Assignment Questions I have Day 1 Section 4.1: Triangle Sum, Exterior Angles, and Classifying Triangles Day 2 Assign: Finish Ch. 3 Review Sheet, WS 4.1 Section
Geometry Notes Chapter 4: Triangles Name Date Assignment Questions I have Day 1 Section 4.1: Triangle Sum, Exterior Angles, and Classifying Triangles Day 2 Assign: Finish Ch. 3 Review Sheet, WS 4.1 Section
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Unit 2. Properties of Triangles. Unit Bundle
 Unit 2 Properties of Triangles Unit Bundle Math 2 Spring 2017 1 Day Topic Homework Monday 2/6 Triangle Angle Sum Tuesday 2/7 Wednesday 2/8 Thursday 2/9 Friday 2/10 (Early Release) Monday 2/13 Tuesday 2/14
Unit 2 Properties of Triangles Unit Bundle Math 2 Spring 2017 1 Day Topic Homework Monday 2/6 Triangle Angle Sum Tuesday 2/7 Wednesday 2/8 Thursday 2/9 Friday 2/10 (Early Release) Monday 2/13 Tuesday 2/14
Problem 2.1. Complete the following proof of Euclid III.20, referring to the figure on page 1.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe October 30, 2015 All3181\3181_fall15t2.tex 2 Solution of Test Name: Figure 1: Central and circumference angle of a circular arc, both obtained as differences Problem 2.1. Complete
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe October 30, 2015 All3181\3181_fall15t2.tex 2 Solution of Test Name: Figure 1: Central and circumference angle of a circular arc, both obtained as differences Problem 2.1. Complete
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
You try: What is the definition of an angle bisector? You try: You try: is the bisector of ABC. BD is the bisector of ABC. = /4.MD.
 US Geometry 1 What is the definition of a midpoint? midpoint of a line segment is the point that bisects the line segment. That is, M is the midpoint of if M M. 1 What is the definition of an angle bisector?
US Geometry 1 What is the definition of a midpoint? midpoint of a line segment is the point that bisects the line segment. That is, M is the midpoint of if M M. 1 What is the definition of an angle bisector?
Classify Triangles. by the Angle Measure &The Side Lengths. Properties a SCALENE Triangle angles 1.Sum of the interior
 Classify s by the Angle Measure &The Side Lengths Foldable Resource & Reference Properties a SCALENE angles 1.Sum of the interior equals. 180 2. The measure of each is side length is. different Note: If
Classify s by the Angle Measure &The Side Lengths Foldable Resource & Reference Properties a SCALENE angles 1.Sum of the interior equals. 180 2. The measure of each is side length is. different Note: If
Term Definition Figure
 Geometry Unit 1 Packet - Language of Geometry Name: #: Video Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruent, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term
Geometry Unit 1 Packet - Language of Geometry Name: #: Video Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruent, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term
Lesson 3: Rectangles Inscribed in Circles
 Classwork Opening Exercise Using only a compass and straightedge, find the location of the center of the circle below. Follow the steps provided. Draw chord. AAAA Construct a chord perpendicular to AAAA
Classwork Opening Exercise Using only a compass and straightedge, find the location of the center of the circle below. Follow the steps provided. Draw chord. AAAA Construct a chord perpendicular to AAAA
Module 1 Topic C Lesson 14 Reflections
 Geometry Module 1 Topic C Lesson 14 Reflections The purpose of lesson 14 is for students to identify the properties of reflection, to use constructions to find line of reflection, get familiar with notations
Geometry Module 1 Topic C Lesson 14 Reflections The purpose of lesson 14 is for students to identify the properties of reflection, to use constructions to find line of reflection, get familiar with notations
CONSTRUCTION SOL PROBLEMS
 Modified and Animated By Chris Headlee Dec 2011 CONSTRUCTION SOL PROBLEMS Super Second-grader Methods SOL Problems; not Dynamic Variable Problems Use scratch paper to measure AB See which line segment
Modified and Animated By Chris Headlee Dec 2011 CONSTRUCTION SOL PROBLEMS Super Second-grader Methods SOL Problems; not Dynamic Variable Problems Use scratch paper to measure AB See which line segment
Term Definition Figure
 Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruency, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term Definition Figure collinear on the same line (note: you do
Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruency, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term Definition Figure collinear on the same line (note: you do
Lesson 11: Conditions on Measurements that Determine a Triangle
 Lesson 11: Conditions on Measurements that Determine a Triangle Classwork Exploratory Challenge 1 a. Can any three side lengths form a triangle? Why or why not? b. Draw a triangle according to these instructions:
Lesson 11: Conditions on Measurements that Determine a Triangle Classwork Exploratory Challenge 1 a. Can any three side lengths form a triangle? Why or why not? b. Draw a triangle according to these instructions:
Extra Practice 1A. Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines. Name Date. 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b)
 Extra Practice 1A Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Draw line segment MN of length 8 cm. a) Use a ruler to draw a line segment parallel to
Extra Practice 1A Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Draw line segment MN of length 8 cm. a) Use a ruler to draw a line segment parallel to
Introduction to Geometry
 Introduction to Geometry Objective A: Problems involving lines and angles Three basic concepts of Geometry are: Points are a single place represented by a dot A Lines are a collection of points that continue
Introduction to Geometry Objective A: Problems involving lines and angles Three basic concepts of Geometry are: Points are a single place represented by a dot A Lines are a collection of points that continue
Geometry Final Review
 Name: ate: 1. In the accompanying diagram, lines a and b are parallel, and lines c and d are transversals. Which angle is congruent to angle 8? 2. Which geometric principle is used to justify the construction
Name: ate: 1. In the accompanying diagram, lines a and b are parallel, and lines c and d are transversals. Which angle is congruent to angle 8? 2. Which geometric principle is used to justify the construction
Special Lines and Constructions of Regular Polygons
 Special Lines and Constructions of Regular Polygons A regular polygon with a center A is made up of congruent isosceles triangles with a principal angle A. The red line in the regular pentagon below is
Special Lines and Constructions of Regular Polygons A regular polygon with a center A is made up of congruent isosceles triangles with a principal angle A. The red line in the regular pentagon below is
Elementary Planar Geometry
 Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Lab Area of Other Quadrilaterals
 Name: Date: Period: Area of a Trapezoid: Compass Lab Area of Other Quadrilaterals Part 1: Constructing the Trapezoid Isosceles a. Using your straightedge, construct 2 intersecting lines in the space provided
Name: Date: Period: Area of a Trapezoid: Compass Lab Area of Other Quadrilaterals Part 1: Constructing the Trapezoid Isosceles a. Using your straightedge, construct 2 intersecting lines in the space provided
GEOMETRY MIDTERM REVIEW
 Name: GEOMETRY MIDTERM REVIEW DATE: Thursday, January 25 th, 2018 at 8:00am ROOM: Please bring in the following: Pens, pencils, compass, ruler & graphing calculator with working batteries (Calhoun will
Name: GEOMETRY MIDTERM REVIEW DATE: Thursday, January 25 th, 2018 at 8:00am ROOM: Please bring in the following: Pens, pencils, compass, ruler & graphing calculator with working batteries (Calhoun will
A ray is a part of a line that starts at an endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction.
 Angles A ray is a part of a line that starts at an endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction. A ray is named by its endpoint and any other point on the ray. For example, the ray in the diagram is
Angles A ray is a part of a line that starts at an endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction. A ray is named by its endpoint and any other point on the ray. For example, the ray in the diagram is
Unit 6. Patterns in Shape PRACTICE PROBLEMS. /36 points. Lesson 1: 2-Dimensional Shapes #6, 7, 8, 9, 10. #11, 12, 13 8 points
 Name: Unit 6 Patterns in Shape Lesson 1: 2-Dimensional Shapes PRACTICE PROBLEMS I can discover properties of triangles and quadrilaterals, and apply congruence conditions to reason about shapes. Investigation
Name: Unit 6 Patterns in Shape Lesson 1: 2-Dimensional Shapes PRACTICE PROBLEMS I can discover properties of triangles and quadrilaterals, and apply congruence conditions to reason about shapes. Investigation
Definitions. You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
 Definitions Name Block Term Definition Notes Sketch Notation Point A location in space that is represented by a dot and has no dimension You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
Definitions Name Block Term Definition Notes Sketch Notation Point A location in space that is represented by a dot and has no dimension You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1
 Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
AJ has been constructed as the angle bisector of BAD. B. AJ is the of BD.
 im #9: How do we construct a perpendicular bisector? Do Now: Using the angle below: 1. isect the angle. Label the bisector D. 2. Construct a copy of DC using vertex '. CC Geometry H C ' Relevant Vocabulary
im #9: How do we construct a perpendicular bisector? Do Now: Using the angle below: 1. isect the angle. Label the bisector D. 2. Construct a copy of DC using vertex '. CC Geometry H C ' Relevant Vocabulary
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
7. 2 More Things Under. Construction. A Develop Understanding Task
 7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
Study Guide - Geometry
 Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
HONORS GEOMETRY CHAPTER 1 WORKBOOK
 HONORS GEOMETRY CHAPTER 1 WORKBOOK FALL 2016 0 Honors Geometry Skills Review Worksheet For numbers 1 3, solve each equation. 1. 8x 2 = 9 + 7x 2. 12 = 4( 6x 3) 3. 5(1 5x) + 5( 8x 2) = 4x 8x For numbers
HONORS GEOMETRY CHAPTER 1 WORKBOOK FALL 2016 0 Honors Geometry Skills Review Worksheet For numbers 1 3, solve each equation. 1. 8x 2 = 9 + 7x 2. 12 = 4( 6x 3) 3. 5(1 5x) + 5( 8x 2) = 4x 8x For numbers
Geometry 1-1. Non-collinear Points not on the same line. Need at least 3 points to be non-collinear since two points are always collinear
 Name Geometry 1-1 Undefined terms terms which cannot be defined only described. Point, line, plane Point a location in space Line a series of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. It
Name Geometry 1-1 Undefined terms terms which cannot be defined only described. Point, line, plane Point a location in space Line a series of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. It
Section Congruence Through Constructions
 Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended. Mathematics. Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Lesson 3.6 Overlapping Triangles
 Lesson 3.6 Overlapping Triangles Getting Ready: Each division in the given triangle is 1 unit long. Hence, the side of the largest triangle is 4- unit long. Figure 3.6.1. Something to think about How many
Lesson 3.6 Overlapping Triangles Getting Ready: Each division in the given triangle is 1 unit long. Hence, the side of the largest triangle is 4- unit long. Figure 3.6.1. Something to think about How many
Chapter 1. Essentials of Geometry
 Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Objective: Name and sketch geometric figures so you can use geometry terms in the real world. Essential Question: How do you name
Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Objective: Name and sketch geometric figures so you can use geometry terms in the real world. Essential Question: How do you name
1-1. Points, Lines, and Planes. Lesson 1-1. What You ll Learn. Active Vocabulary
 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes What You ll Learn Scan the text in Lesson 1-1. Write two facts you learned about points, lines, and planes as you scanned the text. 1. Active Vocabulary 2. New Vocabulary
1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes What You ll Learn Scan the text in Lesson 1-1. Write two facts you learned about points, lines, and planes as you scanned the text. 1. Active Vocabulary 2. New Vocabulary
How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.)
 Geometric Constructions How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.) Construct a perpendicular line to each side of this triangle. Find the intersection of the three perpendicular lines. This point
Geometric Constructions How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.) Construct a perpendicular line to each side of this triangle. Find the intersection of the three perpendicular lines. This point
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM
 M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM #1-11: True or false? If false, replace the underlined word or phrase to make a true sentence. 1. Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form a right angle.
M2 GEOMETRY REVIEW FOR MIDTERM EXAM #1-11: True or false? If false, replace the underlined word or phrase to make a true sentence. 1. Two lines are perpendicular if they intersect to form a right angle.
Geometry Midterm Review 2019
 Geometry Midterm Review 2019 Name To prepare for the midterm: Look over past work, including HW, Quizzes, tests, etc Do this packet Unit 0 Pre Requisite Skills I Can: Solve equations including equations
Geometry Midterm Review 2019 Name To prepare for the midterm: Look over past work, including HW, Quizzes, tests, etc Do this packet Unit 0 Pre Requisite Skills I Can: Solve equations including equations
Chapter 8. Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals. 02/2017 LSowatsky
 Chapter 8 Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 02/2017 LSowatsky 1 8-1A: Points, Lines, and Planes I can Identify and label basic geometric figures. LSowatsky 2 Vocabulary: Point: a point has no
Chapter 8 Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 02/2017 LSowatsky 1 8-1A: Points, Lines, and Planes I can Identify and label basic geometric figures. LSowatsky 2 Vocabulary: Point: a point has no
Activity 8. Midsegment of a Triangle. Name. Date
 . Name Date Activity 8 Midsegment of a Triangle Construct the geometric object by following the instructions below, and then answer the questions about the object. 1. From the Lines Toolbar, select Triangle.
. Name Date Activity 8 Midsegment of a Triangle Construct the geometric object by following the instructions below, and then answer the questions about the object. 1. From the Lines Toolbar, select Triangle.
Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines
 Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines Tangent lines are useful in calculating distances as well as diagramming in the professions of construction, architecture, and landscaping. Geometry construction
Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines Tangent lines are useful in calculating distances as well as diagramming in the professions of construction, architecture, and landscaping. Geometry construction
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Date Name of Lesson Assignments & Due Dates
 Date Name of Lesson Assignments & Due Dates Basic Terms Points, Lines and Planes Constructions (Copy Angle and Segment) Distance Formula Activity for Distance Formula Midpoint Formula Quiz Angle Measure
Date Name of Lesson Assignments & Due Dates Basic Terms Points, Lines and Planes Constructions (Copy Angle and Segment) Distance Formula Activity for Distance Formula Midpoint Formula Quiz Angle Measure
Geometry. 1.5 Measuring and Constructing Angles Day 1
 Geometry Day 1 1.5 warm up 1. Identify two planes that intersect at EF. 2. The cities on the map lie approximately in a straight line. Find the distance from Ann Arbor to Nashville. 3. Sketch DR in plane
Geometry Day 1 1.5 warm up 1. Identify two planes that intersect at EF. 2. The cities on the map lie approximately in a straight line. Find the distance from Ann Arbor to Nashville. 3. Sketch DR in plane
Morley s Theorem and Triangle within Triangle Lesson Plan
 Morley s Theorem and Triangle within Triangle Lesson Plan By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 10/8/2003 Class: Geometry Grades: 9/10 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: This is a two part lesson designed to be given over
Morley s Theorem and Triangle within Triangle Lesson Plan By: Douglas A. Ruby Date: 10/8/2003 Class: Geometry Grades: 9/10 INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES: This is a two part lesson designed to be given over
Geometry: Semester 1 Midterm
 Class: Date: Geometry: Semester 1 Midterm Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The first two steps for constructing MNO that is congruent to
Class: Date: Geometry: Semester 1 Midterm Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The first two steps for constructing MNO that is congruent to
Name: Extra Midterm Review January 2018
 Name: Extra Midterm Review January 2018 1. Which drawing best illustrates the construction of an equilateral triangle? A) B) C) D) 2. Construct an equilateral triangle in which A is one vertex. A 3. Construct
Name: Extra Midterm Review January 2018 1. Which drawing best illustrates the construction of an equilateral triangle? A) B) C) D) 2. Construct an equilateral triangle in which A is one vertex. A 3. Construct
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
Chapter. Triangles. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.3 Isosceles Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of equal length are
Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.3 Isosceles Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. In an isosceles triangle, the two sides of equal length are
not to be republished NCERT CONSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 10 (A) Main Concepts and Results (B) Multiple Choice Questions
 CONSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 10 (A) Main Concepts and Results Division of a line segment internally in a given ratio. Construction of a triangle similar to a given triangle as per given scale factor which may
CONSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 10 (A) Main Concepts and Results Division of a line segment internally in a given ratio. Construction of a triangle similar to a given triangle as per given scale factor which may
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Common Core State Standards High School Geometry Constructions
 ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Name. 6b, Triangles. 1. A bridge contains beams that form triangles, as shown below.
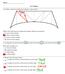 Name 6b, Triangles 1. A bridge contains beams that form triangles, as shown below. Which of the following best describes the triangle with the given measures? acute scalene triangle obtuse scalene triangle
Name 6b, Triangles 1. A bridge contains beams that form triangles, as shown below. Which of the following best describes the triangle with the given measures? acute scalene triangle obtuse scalene triangle
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Constructing a square with given side length. -Extend a side perpendicular Bisector Measure lengths.
 Name Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral triangle-
Name Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral triangle-
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures
 Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY ( ) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A
 APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY (2017 18) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 CLASS: VII LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A MATHEMATICS 1. The supplement of 0 is. 2. The common end point where two rays meet to form an angle
APEX PON VIDYASHRAM, VELACHERY (2017 18) HALF-YEARLY WORKSHEET 1 CLASS: VII LINES AND ANGLES SECTION A MATHEMATICS 1. The supplement of 0 is. 2. The common end point where two rays meet to form an angle
Geometry ~ Chapter 1 Capacity Matrix
 Geometry ~ Chapter 1 Capacity Matrix Learning Targets 1. Drawing and labeling the Geometry Vocabulary 2. Using the distance and midpoint formula 3. Classifying triangles and polygons Section Required Assignments
Geometry ~ Chapter 1 Capacity Matrix Learning Targets 1. Drawing and labeling the Geometry Vocabulary 2. Using the distance and midpoint formula 3. Classifying triangles and polygons Section Required Assignments
7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
 Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
Name lass Date 7.2 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Essential Question: What are the special relationships among angles and sides in isosceles and equilateral triangles? Resource Locker Explore G.6.D
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
Geometry IB Date: 2/18/2013 ID Check Objective: Students will identify and use medians and altitudes in triangles. Bell Ringer: Complete Constructions
 Geometry IB Date: 2/18/2013 ID Check Objective: Students will identify and use medians and altitudes in triangles. Bell Ringer: Complete Constructions HW Requests: pg 327 #17-25 odds 45, 46, pg 338 #11,
Geometry IB Date: 2/18/2013 ID Check Objective: Students will identify and use medians and altitudes in triangles. Bell Ringer: Complete Constructions HW Requests: pg 327 #17-25 odds 45, 46, pg 338 #11,
Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26)
 Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26) Learning Target: At the end of today s lesson we will be able to successfully name and sketch geometric figures.
Geometry Lesson 1-1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Name Hr Pg. 5 (1, 3-22, 25, 26) Learning Target: At the end of today s lesson we will be able to successfully name and sketch geometric figures.
Downloaded from
 Lines and Angles 1.If two supplementary angles are in the ratio 2:7, then the angles are (A) 40, 140 (B) 85, 95 (C) 40, 50 (D) 60, 120. 2.Supplementary angle of 103.5 is (A) 70.5 (B) 76.5 (C) 70 (D)
Lines and Angles 1.If two supplementary angles are in the ratio 2:7, then the angles are (A) 40, 140 (B) 85, 95 (C) 40, 50 (D) 60, 120. 2.Supplementary angle of 103.5 is (A) 70.5 (B) 76.5 (C) 70 (D)
Chapter 1: Essentials of Geometry
 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Chapter 1: Essentials of Geometry Point: Line: Collinear points: Coplanar points: Segment: Ray: Opposite rays: Example 1: Use the diagram at the right to answer the
1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes Chapter 1: Essentials of Geometry Point: Line: Collinear points: Coplanar points: Segment: Ray: Opposite rays: Example 1: Use the diagram at the right to answer the
Geometry Angles
 1 Geometry Angles 2016-03-22 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Angles Congruent Angles Angles & Angle Addition Postulate Protractors Special Angle Pairs Proofs
1 Geometry Angles 2016-03-22 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Angles Congruent Angles Angles & Angle Addition Postulate Protractors Special Angle Pairs Proofs
Mathematics For Class IX Lines and Angles
 Mathematics For Class IX Lines and Angles (Q.1) In Fig, lines PQ and RS intersect each other at point O. If, find angle POR and angle ROQ (1 Marks) (Q.2) An exterior angle of a triangle is 110 and one
Mathematics For Class IX Lines and Angles (Q.1) In Fig, lines PQ and RS intersect each other at point O. If, find angle POR and angle ROQ (1 Marks) (Q.2) An exterior angle of a triangle is 110 and one
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review
 Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Geometry Unit 6 Properties of Quadrilaterals Classifying Polygons Review Polygon a closed plane figure with at least 3 sides that are segments -the sides do not intersect except at the vertices N-gon -
Day 1: Geometry Terms & Diagrams CC Geometry Module 1
 Name ate ay 1: Geometry Terms & iagrams Geometry Module 1 For #1-3: Identify each of the following diagrams with the correct geometry term. #1-3 Vocab. ank Line Segment Line Ray 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain why
Name ate ay 1: Geometry Terms & iagrams Geometry Module 1 For #1-3: Identify each of the following diagrams with the correct geometry term. #1-3 Vocab. ank Line Segment Line Ray 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain why
Activity 1. Simple Constructions. Introduction. Construction. Objective. Cabri Jr. Tools. Part I: Construct a parallelogram.
 Objective To use Cabri Jr. tools to perform simple constructions Activity 1 Cabri Jr. Tools Introduction Construction Simple Constructions The Constructions Tools Menu in Cabri Jr. contains tools for operating
Objective To use Cabri Jr. tools to perform simple constructions Activity 1 Cabri Jr. Tools Introduction Construction Simple Constructions The Constructions Tools Menu in Cabri Jr. contains tools for operating
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
1 In the diagram below, lines, m, n, and p intersect line r. Which statement is true? 1) 2) 3) 4)
 1 In the diagram below, lines, m, n, and p intersect line r. Which statement is true? 2 Which transformation would not always produce an image that would be congruent to the original figure? translation
1 In the diagram below, lines, m, n, and p intersect line r. Which statement is true? 2 Which transformation would not always produce an image that would be congruent to the original figure? translation
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions. ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations REFLECT
 2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions Essential question: How do you identify transformations that are rigid motions? ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations A transformation is a function that changes
2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions Essential question: How do you identify transformations that are rigid motions? ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations A transformation is a function that changes
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS. Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line.
 GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Postulate 2: The measure of any line segment is a unique positive number. The measure (or length) of AB
GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Postulate 2: The measure of any line segment is a unique positive number. The measure (or length) of AB
Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths
 1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
Math-2. Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms And Isosceles Triangles
 Math-2 Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms nd Isosceles Triangles What sequence of angles would you link to prove m4 m9 3 1 4 2 13 14 16 15 lternate Interior Corresponding 8 5 7 6 9 10 12 11 What sequence
Math-2 Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms nd Isosceles Triangles What sequence of angles would you link to prove m4 m9 3 1 4 2 13 14 16 15 lternate Interior Corresponding 8 5 7 6 9 10 12 11 What sequence
Mid-point & Perpendicular Bisector of a line segment AB
 Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
